Seeing is Believing Direct Observation of the Wavefunction Jeff Lundeen. CAP Lecture Tour 2014 Nature, 474, 188 (2011)
|
|
|
- Alisha Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seeing is Believing Direct Observation of the Wavefunction Jeff Lundeen CAP Lecture Tour 2014 Nature, 474, 188 (2011)
2 Outline 1. The wavefunction revisited and reviewed. 2. Progress in understanding the wavefunction 3. How we directly measure the wavefunction.
3 The Wavefunction Ψ(r,t) In classical physics, a particle has a single position r and momentum p. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle x p ħ/2 implies that this is not the case for a quantum particle. In quantum physics, a particle is associated a distribution of positions and momenta the wavefunction, Ψ(r). e.g. the Hydrogen Electron Orbitals
4 The Schrödinger Equation The wavefunction Ψ(r) is used to make probabilistic predictions. e.g. Probability of finding a particle at r is Ψ(r) 2 The probability of anything measurable can be predicted from the Ψ(r) by the Born Rule (e.g. energy, momentum, etc.)
5 The Schrodinger Equation Ψ(x,t) x(t), p(t) Along with the wavefunction, the Schrodinger Equation allows us to predict how a system changes in time.
6 The Schrodinger Equation Barrier Some predicted phenomena (e.g. tunneling) don t happen in classical physics
7 Weird things about the wavefunction: 1. Wave and Particle-like Behaviour Ψ(x) = Ψ(x) e iφ(x) or Ψ = slit 1 + e iφ slit 2 The wavefunction interferes just as though it were a real wave (e.g. a water wave) Even a single particle has wave-like behaviour!
8 Weird things about the wavefunction: 2. Measurement Consider an atom that decays and can emit in all directions Ψ click Ψ new Ψ Collapses instantaneously to Ψ new Faster than light? Non-deterministic, Probabilistic, not in the Schrodinger Eq.
9 Great minds argue about Quantum Physics
10 Einstein Einstein: an Quantum inner voice Physics tells me is not that complete [quantum physics] is We not are yet ignorant the real of thing the underlying I, at any rate, system(s) am and physics convinced that God does not throw dice. Photo by Canadian Yousuf Karsh
11 Probability of Sum, Prob(S) Is Ψ a statistical probability distribution? 1.0 Consider rolling two dice: Probability Distribution of Sum 0.5 Dice Sum, S A roll results in a particular sum S, e.g. S=5, and distribution collapses to Prob(5)=100%. Collapse is no longer weird, nonlocal, or unphysical
12 Is Ψ a statistical probability distribution? Consider rolling two dice: Position, x Angular Momentum Momentum, p Force In any given dice roll, one can predict the dice sum. The underlying physics is deterministic Ψ is the result of ignorance of the exact state of the dice
13 Einstein, stop telling God what to do! ~ Niels Bohr Bohr: The wavefunction is an abstract object simply an element of a theory used to make predictions about observations
14
15 Weird things about the wavefunction 3. Entanglement Bell s theorem is the most profound discovery of science ~ Henry Stapp (Particle Physicist, Berkeley) John Stewart Bell ( )
16 Bell s Theorem Violation of the Bell inequality shows that nature is either (or both) Nonlocal: things can instantaneously affect other far away things. Not real: No fixed pre-existing properties that determine the results of measurements.
17 Bell s Theorem Violation of the Bell inequality shows that nature is either (or both) Nonlocal: things can instantaneously affect other far away things. Not real: No fixed pre-existing properties that determine the results of measurements. Quantum entangled systems can violate the inequality: The spins are perfectly opposite in all directions: Ψ = - = - = -? 1? 2 Entangled: No wavefunction for one particle by itself
18 Bell s Theorem Detectors are set to detect particles of certain direction Consider four cases:?? 1. Randomly set the detector directions 2. Do this outside the other detector s light cone
19 Bell s Theorem Detectors are set to detect particles of certain direction Consider four cases:?? 1. Randomly set the detector directions 2. Do this outside the other detector s light cone
20 Bell s Theorem Detectors are set to detect particles of certain direction Consider four cases:?? 1. Randomly set the detector directions 2. Do this outside the other detector s light cone? Perfect correlations: e.g. even/odd digits of Perfect randomness: e.g. flip a second coin for or
21 Bell s Theorem Detectors are set to detect particles of certain direction Consider four cases:?? 1. Randomly set the detector directions 2. Do this outside the other detector s light cone? C(a,b)-C(a,c) 1+C(b,c) Local realistic theories can produce either perfect correlations or perfect randomness but not both. The wavefunction is not locally real
22 Recent Progress in understanding Ψ Quantum State Cannot be Interpreted Statistically Pusey, Barrett & Rudolph, Nature Physics, Marginally different wavefunctions correspond to completely distinct underlying statistical states. if Ψ Ψ 1 then No extension of quantum theory can have improved predictive power, Colbeck & Renner, Nature Comm Assuming the Born Rule is correct, nature is sufficiently constrained by it to not leave room for new or better experimental predictions.
23 What is the wavefunction? The wave function does not describe a single system; it relates rather to many systems, to an ensemble of systems. The wave function represents an observer's knowledge of the system. Heisenberg The state function is purely symbolic. Einstein Bohr Shut up and measure! Shut up and calculate! Mermin Lundeen No-Cloning Theorem: one cannot copy a particle s wavefunction Corollary: It is impossible to determine an arbitrary wavefunction of a single particle.
24 Photon Position Momentum Simultaneous Measurement of x and p x f f p (x) (p) Lens, focal length = f Can easily measure Prob(x)= (x) 2 and then Prob(p)= (p) 2 We don t see the phase, i.e. the in = e i Measure x and we cause p Heisenberg Uncertainty Relation Can not know x and p perfectly at the same time Why not gently measure x and then strongly measure p?
25 Quantum Measurement Gas Tank Strong Measurement Fuel Meter: E ¼ ½ ¾ F gt H int =gpâ Pointer (P) Model both the measured system and the measurement apparatus as quantum systems. System+Pointer= c System= c i a i P i e.g. The pointer needle on a fuel gauge has a wavefunction and so does the gas tank.
26 Quantum Measurement Gas Tank Strong Measurement Fuel Meter: E ¼ ½ ¾ F gt H int =gpâ Pointer Model both the measured system and the measurement apparatus as quantum systems. System+Pointer= c System= ¾ System= ¼ i a i P i Average Value of A: ψ Â ψ e.g. The pointer needle on a fuel gauge has a wavefunction and so does the gas tank. Born Rule!
27 Gas Tank Quantum Measurement Strong Measurement Fuel Meter: E ¼ ½ ¾ F gt Pointer Weak Measurement E ¼ ½ ¾ F gt H int =gpâ g<<1 System= ¾ Average Value of A: ψ Â ψ System, ψ = c i a i Average Value of A: ψ Â ψ
28 Gas Tank Quantum Measurement Strong Measurement Fuel Meter: E ¼ ½ ¾ F gt Pointer Weak Measurement E ¼ ½ ¾ F A W H int =gpâ g<<1 ψ Strong B System= ¾ In the cases where result of B is b Average Value of A: Average Value of A: < b A y > ψ Â ψ A W = < b y > Real part of A W is the position shift of the pointer Imaginary part of A w is the momentum shift of the pointer
29 Photon Strong Measurement Example Position Lens Consider a strong measurement of position, e.g. x x π x Rotates polarization by θ = 90 The photon was at x (x) x Polarizing beamsplitter The photon was not at x The average result of a strong measurement: π = ψ x x ψ = ψ(x) 2 = Prob(x) = the probability of finding the photon at position x
30 Photon Lens Position Weak Measurement Example For a weak measurement we reduce the rotation of the polarization x Rotates polarization by θ << 1 The photon was at x (x) x Polarizing beamsplitter The photon was not at x
31 Photon Lens Position Weak Measurement Example For a weak measurement we reduce the rotation of the polarization x Rotates polarization by θ << 1 The photon was at x (x) x Polarizing beamsplitter The photon was not at x From a single run, we get little information the result is random
32 Photon Lens Position Weak Measurement Example The average result of the weak measurement is the final rotation of our pointer: the linear polarization. x Rotates polarization by θ << 1 (x) x Rotation of linear polarization ( - ) Re(A w ) = ψ(x) 2 The average result of the weak measurement is the same as a standard ( strong ) one: A W = Re(A W )= ψ x x ψ = ψ(x) 2 = Prob(x)
33 Weak then Strong Measurement What if we do a weak measurement of x, and then make a strong measurement of p? Imbalance in circular polarizations ( - ) Im(A W ) x f f p LHC (p) RHC (x) half-waveplate θ = 20 Lens, focal length=f + Pinhole Beam Splitter ( - ) Re(A w ) Rotation of linear polarization Real and Imaginary parts of the weak measurement average appear in the linear and circular polarization rotations.
34 The idea What if we do a weak measurement of X, and then make a strong measurement of P? i.e. A = x x =π, Initial state= ψ, Strong measurement result P=p Average shift of the pointer: < b A y > A W = < b y > And if p=0, π w = π w = p x x ψ p ψ 1/ 2π x ψ Prob(p=0) = k ψ(x) The average shift of the pointer (i.e. rotation of the polarization) is proportional to the wavefunction
35 Direct Measurement of the Wavefunction Weakly measure x x then strongly measure p, and keep only the photons found with p=0. x f Imbalance in circular polarizations f p ( - ) Im (x) LHC (p) RHC (x) half-waveplate θ = 20 Lens, focal length=f + Pinhole Beam Splitter ( - ) Re (x) Rotation of linear polarization The average result of the weak measurement is the real and imaginary components of the wavefunction
36 Our Source of Single Photons A pump photon is spontaneously converted into two lower frequency photons in a nonlinear optical material Photons are produced rarely but always in pairs Detection of one photon Heralds the presence of its twin
37
38 Direct Measurement of the Wavefunction Phase ψ ψ(x) 2 Prob(x) Re[ψ] Im[ψ]
39 Testing another wavefunction shape Created new transverse wavefunction with a reverse bullseye filter ψ Phase Discontinuity: Placed a glass square across half the wavefunction ψ ψ(x) 2 Prob(x) ψ(x) 2 Phase Im[ψ] Re[ψ]
40 Testing other wavefunctions phase profiles Phase Gradient Phase Curvature ψ
41 Why it is Direct 1. It is local - measures ψ(x) at x 2. No complicated mathematical reconstruction 3. The value of ψ(x) appears right on our measurement apparatus 4. The procedure is simple and general - measure x and then p
42 Test Particles (i.e. m 0, C 0) helped establish the existence of Electric and Magnetic Fields. Test measurement (i.e. weak measurement) might be similarly useful.
43 An operational definition of the wavefunction Currently there is no definition of the wavefunction. Clarity can come from Operational definitions of physical concepts. i.e. the set of operations used in the lab to observe something. Bridgman, P. The Logic of Modern Physics (1927). The wavefunction is the average result of a weak measurement of a variable followed by a strong measurement of the complementary variable
44 Students and Collaborators Rick Gerson (NRC) Charles Bamber (NRC) Aabid Patel (PhD Photonics, Southhampton, UK) Corey Stewart (Phd Photonics with Harry Ruda, UofT) Brandon Sutherland (PhD Photonics, Ted Sargent, UofT)
45 Conclusion Even though it may seem like a philosophical question, there has been progress (and more can be made!) The math is simple undergraduates are probably asking the right questions (remember them!) Idea behind direct wavefunction measurement is universal e.g. frequency-time photon wavefunction, electron spin state, entangled multiparticle states, etc. Willis Lamb (Nobel Laureate). After writing Ψ on the blackboard, said to his class at Columbia: Don t worry about what this means, you ll get used to it.
46 Recruiting undergrads, graduate students, and post-docs for more info Bob Boyd Jacob Krich Anne Broadbent Ksenia Dolgaleva Jeff Lundeen At least one more
Direct Measurement of the Photon Wavefunction Single Photon Workshop: Boulder Nov 3, 2009
 Direct Measurement of the Photon Wavefunction Single Photon Workshop: Boulder Nov 3, 2009 Charles Bamber, Jeff Lundeen, Joanne Zwinkels, Rick Gerson, Aabid Patel, Corey Stewart, Brandon Sutherland Presentation
Direct Measurement of the Photon Wavefunction Single Photon Workshop: Boulder Nov 3, 2009 Charles Bamber, Jeff Lundeen, Joanne Zwinkels, Rick Gerson, Aabid Patel, Corey Stewart, Brandon Sutherland Presentation
How does it work? QM describes the microscopic world in a way analogous to how classical mechanics (CM) describes the macroscopic world.
 Today Quantum Mechanics (QM) is used in the university and beyond on a regular basis: Chemical bonds NMR spectroscopy The laser (blue beam in Blue-ray player; red beam in a DVD player for example) The
Today Quantum Mechanics (QM) is used in the university and beyond on a regular basis: Chemical bonds NMR spectroscopy The laser (blue beam in Blue-ray player; red beam in a DVD player for example) The
The Weak Measurement in Quantum Mechanics
 University of Ljubljana Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Seminar The Weak Measurement in Quantum Mechanics Tilen Knaflič Mentor: prof. dr. Anton Ramšak November 16, 2012 Abstract The topic of this seminar
University of Ljubljana Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Seminar The Weak Measurement in Quantum Mechanics Tilen Knaflič Mentor: prof. dr. Anton Ramšak November 16, 2012 Abstract The topic of this seminar
226 My God, He Plays Dice! Entanglement. Chapter This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/entanglement
 226 My God, He Plays Dice! Entanglement Chapter 29 20 This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/entanglement Entanglement 227 Entanglement Entanglement is a mysterious quantum phenomenon
226 My God, He Plays Dice! Entanglement Chapter 29 20 This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/entanglement Entanglement 227 Entanglement Entanglement is a mysterious quantum phenomenon
2 Quantum Mechanics. 2.1 The Strange Lives of Electrons
 2 Quantum Mechanics A philosopher once said, It is necessary for the very existence of science that the same conditions always produce the same results. Well, they don t! Richard Feynman Today, we re going
2 Quantum Mechanics A philosopher once said, It is necessary for the very existence of science that the same conditions always produce the same results. Well, they don t! Richard Feynman Today, we re going
1.1.1 Bell Inequality - Spin correlation
 January 8, 015 Lecture IV 1.1.1 Bell Inequality - Spin correlation Consider the final spin singlet state of the decay η 0 µ + µ We suppose that the η 0 decays and the muon and µ + travel in opposite directions,
January 8, 015 Lecture IV 1.1.1 Bell Inequality - Spin correlation Consider the final spin singlet state of the decay η 0 µ + µ We suppose that the η 0 decays and the muon and µ + travel in opposite directions,
Beginning Modern Quantum
 Beginning Modern Quantum Born s probability interpretation The indeterminacy ( uncertainty ) principle The Schroedinger equation The Copenhagen interpretation 419 Term Paper Abstract due today Homework
Beginning Modern Quantum Born s probability interpretation The indeterminacy ( uncertainty ) principle The Schroedinger equation The Copenhagen interpretation 419 Term Paper Abstract due today Homework
The Relativistic Quantum World
 The Relativistic Quantum World A lecture series on Relativity Theory and Quantum Mechanics Marcel Merk University of Maastricht, Sept 24 Oct 15, 2014 Relativity Quantum Mechanics The Relativistic Quantum
The Relativistic Quantum World A lecture series on Relativity Theory and Quantum Mechanics Marcel Merk University of Maastricht, Sept 24 Oct 15, 2014 Relativity Quantum Mechanics The Relativistic Quantum
Bell s Theorem 1964 Local realism is in conflict with quantum mechanics
 Bell s Theorem 1964 Local realism is in conflict with quantum mechanics the most profound discovery in science in the last half of the twentieth century. For a technical presentation search Youtube.com
Bell s Theorem 1964 Local realism is in conflict with quantum mechanics the most profound discovery in science in the last half of the twentieth century. For a technical presentation search Youtube.com
Cosmology Lecture 2 Mr. Kiledjian
 Cosmology Lecture 2 Mr. Kiledjian Lecture 2: Quantum Mechanics & Its Different Views and Interpretations a) The story of quantum mechanics begins in the 19 th century as the physicists of that day were
Cosmology Lecture 2 Mr. Kiledjian Lecture 2: Quantum Mechanics & Its Different Views and Interpretations a) The story of quantum mechanics begins in the 19 th century as the physicists of that day were
Physics-I. Dr. Anurag Srivastava. Web address: Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus
 Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
Physics-I Dr. Anurag Srivastava Web address: http://tiiciiitm.com/profanurag Email: profanurag@gmail.com Visit me: Room-110, Block-E, IIITM Campus Syllabus Electrodynamics: Maxwell s equations: differential
If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it.
 Quantum Mechanics If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it. Niels Bohr Today, I will tell you more about quantum mechanics what weird thing it is and why it is so weird.
Quantum Mechanics If quantum mechanics hasn t profoundly shocked you, you haven t understood it. Niels Bohr Today, I will tell you more about quantum mechanics what weird thing it is and why it is so weird.
Theory and Experiment
 Theory and Experiment Mark Beck OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Table of Symbols Preface xiii xix 1 MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1 Probability and Statistics 3 1.2 LinearAlgebra 9 1.3 References 17
Theory and Experiment Mark Beck OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Table of Symbols Preface xiii xix 1 MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1 Probability and Statistics 3 1.2 LinearAlgebra 9 1.3 References 17
Lecture 21 Matter acts like waves!
 Particles Act Like Waves! De Broglie s Matter Waves λ = h / p Schrodinger s Equation Announcements Schedule: Today: de Broglie and matter waves, Schrodinger s Equation March Ch. 16, Lightman Ch. 4 Net
Particles Act Like Waves! De Broglie s Matter Waves λ = h / p Schrodinger s Equation Announcements Schedule: Today: de Broglie and matter waves, Schrodinger s Equation March Ch. 16, Lightman Ch. 4 Net
Problems with/failures of QM
 CM fails to describe macroscopic quantum phenomena. Phenomena where microscopic properties carry over into macroscopic world: superfluidity Helium flows without friction at sufficiently low temperature.
CM fails to describe macroscopic quantum phenomena. Phenomena where microscopic properties carry over into macroscopic world: superfluidity Helium flows without friction at sufficiently low temperature.
Introduction to Bell s theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics
 Introduction to Bells theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics Jia Wang Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, 930 N. University Ave., Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (Received November 30,
Introduction to Bells theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics Jia Wang Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, 930 N. University Ave., Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (Received November 30,
David Bohm s Hidden Variables
 ccxxii My God, He Plays Dice! David Bohm s Hidden Variables Hidden Variablesccxxiii David Bohm s Hidden Variables David Bohm is perhaps best known for new experimental methods to test Einstein s supposed
ccxxii My God, He Plays Dice! David Bohm s Hidden Variables Hidden Variablesccxxiii David Bohm s Hidden Variables David Bohm is perhaps best known for new experimental methods to test Einstein s supposed
Odd Things about Quantum Mechanics: Abandoning Determinism In Newtonian physics, Maxwell theory, Einstein's special or general relativity, if an initi
 Odd Things about Quantum Mechanics: Abandoning Determinism In Newtonian physics, Maxwell theory, Einstein's special or general relativity, if an initial state is completely known, the future can be predicted.
Odd Things about Quantum Mechanics: Abandoning Determinism In Newtonian physics, Maxwell theory, Einstein's special or general relativity, if an initial state is completely known, the future can be predicted.
Closing the Debates on Quantum Locality and Reality: EPR Theorem, Bell's Theorem, and Quantum Information from the Brown-Twiss Vantage
 Closing the Debates on Quantum Locality and Reality: EPR Theorem, Bell's Theorem, and Quantum Information from the Brown-Twiss Vantage C. S. Unnikrishnan Fundamental Interactions Laboratory Tata Institute
Closing the Debates on Quantum Locality and Reality: EPR Theorem, Bell's Theorem, and Quantum Information from the Brown-Twiss Vantage C. S. Unnikrishnan Fundamental Interactions Laboratory Tata Institute
Chapter 4 Section 2 Notes
 Chapter 4 Section 2 Notes Vocabulary Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. Quantum
Chapter 4 Section 2 Notes Vocabulary Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. Quantum
A more comprehensive theory was needed. 1925, Schrödinger and Heisenberg separately worked out a new theory Quantum Mechanics.
 Ch28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms Bohr s model was very successful to explain line spectra and the ionization energy for hydrogen. However, it also had many limitations: It was not able to predict the line
Ch28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms Bohr s model was very successful to explain line spectra and the ionization energy for hydrogen. However, it also had many limitations: It was not able to predict the line
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 1-1B: THE INTERACTION OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Introductory Video Quantum Mechanics Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 1-1B: THE INTERACTION OF MATTER WITH RADIATION Introductory Video Quantum Mechanics Essential Idea: The microscopic quantum world offers
Quantum Entanglement. Chapter Introduction. 8.2 Entangled Two-Particle States
 Chapter 8 Quantum Entanglement 8.1 Introduction In our final chapter on quantum mechanics we introduce the concept of entanglement. This is a feature of two-particle states (or multi-particle states) in
Chapter 8 Quantum Entanglement 8.1 Introduction In our final chapter on quantum mechanics we introduce the concept of entanglement. This is a feature of two-particle states (or multi-particle states) in
Week 11: April 9, The Enigma of Measurement: Detecting the Quantum World
 Week 11: April 9, 2018 Quantum Measurement The Enigma of Measurement: Detecting the Quantum World Two examples: (2) Measuring the state of electron in H-atom Electron can be in n = 1, 2, 3... state. In
Week 11: April 9, 2018 Quantum Measurement The Enigma of Measurement: Detecting the Quantum World Two examples: (2) Measuring the state of electron in H-atom Electron can be in n = 1, 2, 3... state. In
Quantum Measurements: some technical background
 Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box
 1 OF 5 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider a particle of mass m confined to an infinite one-dimensional well of width L. The potential is given by V (x) = V 0 x L/2, V (x) =
1 OF 5 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider a particle of mass m confined to an infinite one-dimensional well of width L. The potential is given by V (x) = V 0 x L/2, V (x) =
J = L + S. to this ket and normalize it. In this way we get expressions for all the kets
 Lecture 3 Relevant sections in text: 3.7, 3.9 Total Angular Momentum Eigenvectors How are the total angular momentum eigenvectors related to the original product eigenvectors (eigenvectors of L z and S
Lecture 3 Relevant sections in text: 3.7, 3.9 Total Angular Momentum Eigenvectors How are the total angular momentum eigenvectors related to the original product eigenvectors (eigenvectors of L z and S
Physics. Light Quanta
 Physics Light Quanta Quantum Theory Is light a WAVE or a PARTICLE? Particle tiny object like a bullet, has mass and travels in straight lines unless a force acts upon it Waves phenomena that extend in
Physics Light Quanta Quantum Theory Is light a WAVE or a PARTICLE? Particle tiny object like a bullet, has mass and travels in straight lines unless a force acts upon it Waves phenomena that extend in
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5. De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Many experimental
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5. De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Many experimental
1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box
 1 OF 5 NOTE: This problem set is to be handed in to my mail slot (SMITH) located in the Clarendon Laboratory by 5:00 PM (noon) Tuesday, 24 May. 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider
1 OF 5 NOTE: This problem set is to be handed in to my mail slot (SMITH) located in the Clarendon Laboratory by 5:00 PM (noon) Tuesday, 24 May. 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider
We can't solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them.!
 PuNng Local Realism to the Test We can't solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them.! - Albert Einstein! Day 39: Ques1ons? Revisit EPR-Argument Tes1ng Local Realism
PuNng Local Realism to the Test We can't solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them.! - Albert Einstein! Day 39: Ques1ons? Revisit EPR-Argument Tes1ng Local Realism
Collapse versus correlations, EPR, Bell Inequalities, Cloning
 Collapse versus correlations, EPR, Bell Inequalities, Cloning The Quantum Eraser, continued Equivalence of the collapse picture and just blithely/blindly calculating correlations EPR & Bell No cloning
Collapse versus correlations, EPR, Bell Inequalities, Cloning The Quantum Eraser, continued Equivalence of the collapse picture and just blithely/blindly calculating correlations EPR & Bell No cloning
The Uncertainty Principle The Limits of Measurement
 Quantum Weirdness Part 5 The Uncertainty Principle The Laser Quantum Zeno Effect Quantum Entanglement The Uncertainty Principle The Limits of Measurement 14:28 1 14:28 2 Accuracy and Precision If I aim
Quantum Weirdness Part 5 The Uncertainty Principle The Laser Quantum Zeno Effect Quantum Entanglement The Uncertainty Principle The Limits of Measurement 14:28 1 14:28 2 Accuracy and Precision If I aim
Singlet State Correlations
 Chapter 23 Singlet State Correlations 23.1 Introduction This and the following chapter can be thought of as a single unit devoted to discussing various issues raised by a famous paper published by Einstein,
Chapter 23 Singlet State Correlations 23.1 Introduction This and the following chapter can be thought of as a single unit devoted to discussing various issues raised by a famous paper published by Einstein,
UNIT 4 Electrons in Atoms. Advanced Chemistry 235 Lanphier High School Mr. David Peeler
 UNIT 4 Electrons in Atoms Advanced Chemistry 235 Lanphier High School Mr. David Peeler Section 4.1 Models of the Atom OBJECTIVES: Identify the inadequacies in the Rutherford atomic model. Section 4.1 Models
UNIT 4 Electrons in Atoms Advanced Chemistry 235 Lanphier High School Mr. David Peeler Section 4.1 Models of the Atom OBJECTIVES: Identify the inadequacies in the Rutherford atomic model. Section 4.1 Models
1. Griffiths Suppose two spin-1/2 particles are known to be in the singlet configuration.
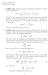 Physics 443 HW #7 Due March 12, 2008 1. Griffiths 4.50. Suppose two spin-1/2 particles are known to be in the singlet configuration. ( 00 = 1 2 ( + 1 2 1 2 1 2 +1 2 ) Let S a (1) be the component of the
Physics 443 HW #7 Due March 12, 2008 1. Griffiths 4.50. Suppose two spin-1/2 particles are known to be in the singlet configuration. ( 00 = 1 2 ( + 1 2 1 2 1 2 +1 2 ) Let S a (1) be the component of the
EPR Paradox and Bell s Inequality
 EPR Paradox and Bell s Inequality James Cross 2018-08-18 1 Introduction The field of quantum mechanics is practically synonymous with modern physics. The basics of quantum theory are taught in every introductory
EPR Paradox and Bell s Inequality James Cross 2018-08-18 1 Introduction The field of quantum mechanics is practically synonymous with modern physics. The basics of quantum theory are taught in every introductory
Announcements. Please check for errors now
 Announcements Print worksheet #10 prior to your Thursday discussion section LON-CAPA assignment #6 due Tuesday, Oct. 5 at 9am Next week s quiz will be on Tuesday atomic history and electron configurations
Announcements Print worksheet #10 prior to your Thursday discussion section LON-CAPA assignment #6 due Tuesday, Oct. 5 at 9am Next week s quiz will be on Tuesday atomic history and electron configurations
Lecture 15: Time-Dependent QM & Tunneling Review and Examples, Ammonia Maser
 ecture 15: Time-Dependent QM & Tunneling Review and Examples, Ammonia Maser ψ(x,t=0) 2 U(x) 0 x ψ(x,t 0 ) 2 x U 0 0 E x 0 x ecture 15, p.1 Special (Optional) ecture Quantum Information One of the most
ecture 15: Time-Dependent QM & Tunneling Review and Examples, Ammonia Maser ψ(x,t=0) 2 U(x) 0 x ψ(x,t 0 ) 2 x U 0 0 E x 0 x ecture 15, p.1 Special (Optional) ecture Quantum Information One of the most
Final Exam. Tuesday, May 8, Starting at 8:30 a.m., Hoyt Hall.
 Final Exam Tuesday, May 8, 2012 Starting at 8:30 a.m., Hoyt Hall. Summary of Chapter 38 In Quantum Mechanics particles are represented by wave functions Ψ. The absolute square of the wave function Ψ 2
Final Exam Tuesday, May 8, 2012 Starting at 8:30 a.m., Hoyt Hall. Summary of Chapter 38 In Quantum Mechanics particles are represented by wave functions Ψ. The absolute square of the wave function Ψ 2
Lecture PowerPoint. Chapter 28 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 28 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 28 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Quantum Weirdness. Part 5 The Uncertainty Principle The Laser Quantum Zeno Effect Quantum Entanglement 14:28 1
 Quantum Weirdness Part 5 The Uncertainty Principle The Laser Quantum Zeno Effect Quantum Entanglement 14:28 1 The Uncertainty Principle The Limits of Measurement 14:28 2 Accuracy and Precision Accuracy
Quantum Weirdness Part 5 The Uncertainty Principle The Laser Quantum Zeno Effect Quantum Entanglement 14:28 1 The Uncertainty Principle The Limits of Measurement 14:28 2 Accuracy and Precision Accuracy
PHY202 Quantum Mechanics. Topic 1. Introduction to Quantum Physics
 PHY202 Quantum Mechanics Topic 1 Introduction to Quantum Physics Outline of Topic 1 1. Dark clouds over classical physics 2. Brief chronology of quantum mechanics 3. Black body radiation 4. The photoelectric
PHY202 Quantum Mechanics Topic 1 Introduction to Quantum Physics Outline of Topic 1 1. Dark clouds over classical physics 2. Brief chronology of quantum mechanics 3. Black body radiation 4. The photoelectric
about Quantum Physics Bill Poirier MVJS Mini-Conference Lawrence Hall of Science July 9, 2015
 about Quantum Physics Bill Poirier MVJS Mini-Conference Lawrence Hall of Science July 9, 2015 Some Notable Quotes If we knew what we were doing, it wouldn't be called 'research Albert Einstein The paradox
about Quantum Physics Bill Poirier MVJS Mini-Conference Lawrence Hall of Science July 9, 2015 Some Notable Quotes If we knew what we were doing, it wouldn't be called 'research Albert Einstein The paradox
A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels
 JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY 57 VOLUME NUMBER DECEMBER 8 005 A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels Miri Shlomi
JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY 57 VOLUME NUMBER DECEMBER 8 005 A review on quantum teleportation based on: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen channels Miri Shlomi
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214
 All the fifty years of conscious brooding have brought me no closer to answer the question, What are light quanta? Of course today every rascal thinks he knows the answer, but he is deluding himself. -Albert
All the fifty years of conscious brooding have brought me no closer to answer the question, What are light quanta? Of course today every rascal thinks he knows the answer, but he is deluding himself. -Albert
COLLEGE PHYSICS. Chapter 30 ATOMIC PHYSICS
 COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 30 ATOMIC PHYSICS Matter Waves: The de Broglie Hypothesis The momentum of a photon is given by: The de Broglie hypothesis is that particles also have wavelengths, given by: Matter
COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 30 ATOMIC PHYSICS Matter Waves: The de Broglie Hypothesis The momentum of a photon is given by: The de Broglie hypothesis is that particles also have wavelengths, given by: Matter
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (Prelude to Nuclear Shell Model) Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle In the microscopic world,
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (Prelude to Nuclear Shell Model) Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle In the microscopic world, x p h π If you try to specify/measure the exact position of a particle you
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (Prelude to Nuclear Shell Model) Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle In the microscopic world, x p h π If you try to specify/measure the exact position of a particle you
5.111 Lecture Summary #6
 5.111 Lecture Summary #6 Readings for today: Section 1.9 (1.8 in 3 rd ed) Atomic Orbitals. Read for Lecture #7: Section 1.10 (1.9 in 3 rd ed) Electron Spin, Section 1.11 (1.10 in 3 rd ed) The Electronic
5.111 Lecture Summary #6 Readings for today: Section 1.9 (1.8 in 3 rd ed) Atomic Orbitals. Read for Lecture #7: Section 1.10 (1.9 in 3 rd ed) Electron Spin, Section 1.11 (1.10 in 3 rd ed) The Electronic
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer Choose the better choice of all choices given.
 PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case
 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
3/10/11. Which interpreta/on sounds most reasonable to you? PH300 Modern Physics SP11
 3// PH3 Modern Physics SP The problems of language here are really serious. We wish to speak in some way about the structure of the atoms. But we cannot speak about atoms in ordinary language. Recently:.
3// PH3 Modern Physics SP The problems of language here are really serious. We wish to speak in some way about the structure of the atoms. But we cannot speak about atoms in ordinary language. Recently:.
Honors 225 Physics Study Guide/Chapter Summaries for Final Exam; Roots Chapters 15-18
 Honors 225 Physics Study Guide/Chapter Summaries for Final Exam; Roots Chapters 15-18 Chapter 15 Collapsing the Wave If a particle is in a quantum superposition state (that is, a superposition of eigenfunctions
Honors 225 Physics Study Guide/Chapter Summaries for Final Exam; Roots Chapters 15-18 Chapter 15 Collapsing the Wave If a particle is in a quantum superposition state (that is, a superposition of eigenfunctions
Outline Chapter 9 The Atom Photons Photons The Photoelectron Effect Photons Photons
 Outline Chapter 9 The Atom 9-1. Photoelectric Effect 9-3. What Is Light? 9-4. X-rays 9-5. De Broglie Waves 9-6. Waves of What? 9-7. Uncertainty Principle 9-8. Atomic Spectra 9-9. The Bohr Model 9-10. Electron
Outline Chapter 9 The Atom 9-1. Photoelectric Effect 9-3. What Is Light? 9-4. X-rays 9-5. De Broglie Waves 9-6. Waves of What? 9-7. Uncertainty Principle 9-8. Atomic Spectra 9-9. The Bohr Model 9-10. Electron
Quantum Mechanics. Reading: Gray: (1 8) to (1 12) OGN: (15.5)
 Quantum Mechanics Reading: Gray: (1 8) to (1 12) OGN: (15.5) A Timeline of the Atom...... 400 BC 0 1800 1850 1900 1950 400 B.C. Democritus: idea of an atom 1808 John Dalton introduces his atomic theory.
Quantum Mechanics Reading: Gray: (1 8) to (1 12) OGN: (15.5) A Timeline of the Atom...... 400 BC 0 1800 1850 1900 1950 400 B.C. Democritus: idea of an atom 1808 John Dalton introduces his atomic theory.
Introduction. Introductory Remarks
 Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Alan Mortimer PhD. Ideas of Modern Physics
 Alan Mortimer PhD Ideas of Modern Physics Electromagnetic Waves Last Week Special Relativity General Relativity The Quantum World Index Planck s Law Atomic Structure and emission lines Matter waves Uncertainty
Alan Mortimer PhD Ideas of Modern Physics Electromagnetic Waves Last Week Special Relativity General Relativity The Quantum World Index Planck s Law Atomic Structure and emission lines Matter waves Uncertainty
84 My God, He Plays Dice! Chapter 12. Irreversibility. This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/reversibility
 84 My God, He Plays Dice! This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/reversibility Microscopic In the 1870 s, Ludwig Boltzmann developed his transport equation and his dynamical H-theorem
84 My God, He Plays Dice! This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/reversibility Microscopic In the 1870 s, Ludwig Boltzmann developed his transport equation and his dynamical H-theorem
WEAK-VALUES AMPLIFICATION: WHEN PRECISION MEASUREMENTS BECOME EASY
 WEAK-VALUES AMPLIFICATION: WHEN PRECISION MEASUREMENTS BECOME EASY Julián Martínez-Rincón Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester 03/05/14 OUTLINE A quick review on QM: Strong/projective
WEAK-VALUES AMPLIFICATION: WHEN PRECISION MEASUREMENTS BECOME EASY Julián Martínez-Rincón Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Rochester 03/05/14 OUTLINE A quick review on QM: Strong/projective
Erwin Schrödinger and his cat
 Erwin Schrödinger and his cat How to relate discrete energy levels with Hamiltonian described in terms of continгous coordinate x and momentum p? Erwin Schrödinger (887-96) Acoustics: set of frequencies
Erwin Schrödinger and his cat How to relate discrete energy levels with Hamiltonian described in terms of continгous coordinate x and momentum p? Erwin Schrödinger (887-96) Acoustics: set of frequencies
228 My God - He Plays Dice! Schrödinger s Cat. Chapter 28. This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/scrodingerscat
 228 My God - He Plays Dice! Schrödinger s Cat This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/scrodingerscat Schrödinger s Cat Schrödinger s Cat Erwin Schrödinger s goal for his infamous cat-killing
228 My God - He Plays Dice! Schrödinger s Cat This chapter on the web informationphilosopher.com/problems/scrodingerscat Schrödinger s Cat Schrödinger s Cat Erwin Schrödinger s goal for his infamous cat-killing
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 15: QUANTUM THEORY This lecture will help you understand: The Photoelectric Effect Absorption Spectra Fluorescence Incandescence Lasers Wave-Particle Duality Particles
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 15: QUANTUM THEORY This lecture will help you understand: The Photoelectric Effect Absorption Spectra Fluorescence Incandescence Lasers Wave-Particle Duality Particles
Atomic Theory. Atomic Theory. Atomic Theory. The Bohr Model 2/29/16
 Atomic Theory A tested explanation of the atom. Review: From Thomson s experiment with CRTs we know that atoms have electrons that have a negative charge. From the gold foil experiment we know that atoms
Atomic Theory A tested explanation of the atom. Review: From Thomson s experiment with CRTs we know that atoms have electrons that have a negative charge. From the gold foil experiment we know that atoms
3 Bananaworld. 3.1 Einstein Podolsky Rosen bananas
 3 Bananaworld The really remarkable thing about our quantum world is the existence of nonlocal correlations correlations between events at separate locations that can t be explained by either of the two
3 Bananaworld The really remarkable thing about our quantum world is the existence of nonlocal correlations correlations between events at separate locations that can t be explained by either of the two
Card Appendix Quantum Concepts
 1 Physics 310 Card Appendix Quantum Concepts Table of Contents 0. Blackbody Radiation 2 3. Normalize 2 4. Angular Momentum 3 4. Hydrogen 4 5. Wavefunction 4 6. Photoelectric Effect 5 7. Lowering Operator
1 Physics 310 Card Appendix Quantum Concepts Table of Contents 0. Blackbody Radiation 2 3. Normalize 2 4. Angular Momentum 3 4. Hydrogen 4 5. Wavefunction 4 6. Photoelectric Effect 5 7. Lowering Operator
1 Photoelectric effect - Classical treatment. 2 Photoelectric effect - Quantum treatment
 1 OF 5 NOTE: This problem set is to be handed in to my mail slot (SMITH) located in the Clarendon Laboratory by 5:00 PM Tuesday, 10 May. 1 Photoelectric effect - Classical treatment A laser beam with an
1 OF 5 NOTE: This problem set is to be handed in to my mail slot (SMITH) located in the Clarendon Laboratory by 5:00 PM Tuesday, 10 May. 1 Photoelectric effect - Classical treatment A laser beam with an
Chapter 28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms
 Chapter 28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms 28.1 Quantum Mechanics The Theory Quantum mechanics incorporates wave-particle duality, and successfully explains energy states in complex atoms and molecules, the
Chapter 28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms 28.1 Quantum Mechanics The Theory Quantum mechanics incorporates wave-particle duality, and successfully explains energy states in complex atoms and molecules, the
Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox and Bell s inequalities
 Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox and Bell s inequalities Jan Schütz November 27, 2005 Abstract Considering the Gedankenexperiment of Einstein, Podolsky, and Rosen as example the nonlocal character of quantum
Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox and Bell s inequalities Jan Schütz November 27, 2005 Abstract Considering the Gedankenexperiment of Einstein, Podolsky, and Rosen as example the nonlocal character of quantum
Experiment 6 - Tests of Bell s Inequality
 Exp.6-Bell-Page 1 Experiment 6 - Tests of Bell s Inequality References: Entangled photon apparatus for the undergraduate laboratory, and Entangled photons, nonlocality, and Bell inequalities in the undergraduate
Exp.6-Bell-Page 1 Experiment 6 - Tests of Bell s Inequality References: Entangled photon apparatus for the undergraduate laboratory, and Entangled photons, nonlocality, and Bell inequalities in the undergraduate
Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics Units of Chapter 38 38-1 Quantum Mechanics A New Theory 37-2 The Wave Function and Its Interpretation; the Double-Slit Experiment 38-3 The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics Units of Chapter 38 38-1 Quantum Mechanics A New Theory 37-2 The Wave Function and Its Interpretation; the Double-Slit Experiment 38-3 The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Playing Games with Quantum Information: Experiments with Photons and Laser-Cooled Atoms
 Playing Games with Quantum Information: Experiments with Photons and Laser-Cooled Atoms Interns: Grad Students: Postdocs: Supervisor: Jeff Lundeen Univ. of Toronto Dept. of Physics CAP 2003 Rockson Chang,
Playing Games with Quantum Information: Experiments with Photons and Laser-Cooled Atoms Interns: Grad Students: Postdocs: Supervisor: Jeff Lundeen Univ. of Toronto Dept. of Physics CAP 2003 Rockson Chang,
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer Choose the better choice of all choices given.
 PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
The Bohr model describes definite electron energy levels within atoms Bohr s model only applied to hydrogen it has been replaced by more
 The Bohr model describes definite electron energy levels within atoms Bohr s model only applied to hydrogen it has been replaced by more sophisticated models. Quantum Mechanics is the present model it
The Bohr model describes definite electron energy levels within atoms Bohr s model only applied to hydrogen it has been replaced by more sophisticated models. Quantum Mechanics is the present model it
PHY 571: Quantum Physics
 PHY 571: Quantum Physics John Venables 5-1675, john.venables@asu.edu Spring 2008 The Transition to Quantum Mechanics Module 1, Lecture 6, 7 and 8 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Describe waves/particles
PHY 571: Quantum Physics John Venables 5-1675, john.venables@asu.edu Spring 2008 The Transition to Quantum Mechanics Module 1, Lecture 6, 7 and 8 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Describe waves/particles
Causality and Local Determinism versus Quantum Nonlocality.
 Contribution to EMQ13 in Vienna, October 2013 Causality and Local Determinism versus Quantum Nonlocality. UQO marian.kupczynski@uqo.ca Intro It was shown by many authors that the violation of Bell Inequalities
Contribution to EMQ13 in Vienna, October 2013 Causality and Local Determinism versus Quantum Nonlocality. UQO marian.kupczynski@uqo.ca Intro It was shown by many authors that the violation of Bell Inequalities
Lecture 9: Introduction to QM: Review and Examples
 Lecture 9: Introduction to QM: Review and Examples S 1 S 2 Lecture 9, p 1 Photoelectric Effect V stop (v) KE e V hf F max stop Binding energy F The work function: F is the minimum energy needed to strip
Lecture 9: Introduction to QM: Review and Examples S 1 S 2 Lecture 9, p 1 Photoelectric Effect V stop (v) KE e V hf F max stop Binding energy F The work function: F is the minimum energy needed to strip
Introduction. Introductory Remarks
 Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra. Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016
 Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Problem Set: TT Quantum Information
 Problem Set: TT Quantum Information Basics of Information Theory 1. Alice can send four messages A, B, C, and D over a classical channel. She chooses A with probability 1/, B with probability 1/4 and C
Problem Set: TT Quantum Information Basics of Information Theory 1. Alice can send four messages A, B, C, and D over a classical channel. She chooses A with probability 1/, B with probability 1/4 and C
Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 1 Quantum Mechanics - An Introduction (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) I will
Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 1 Quantum Mechanics - An Introduction (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) I will
EPR Paradox Solved by Special Theory of Relativity
 EPR Paradox Solved by Special Theory of Relativity Justin Lee June 20 th, 2013 Abstract This paper uses the special theory of relativity (SR) to introduce a novel solution to Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen (EPR)
EPR Paradox Solved by Special Theory of Relativity Justin Lee June 20 th, 2013 Abstract This paper uses the special theory of relativity (SR) to introduce a novel solution to Einstein- Podolsky-Rosen (EPR)
CHM The Basics of Quantum Mechanics (r14) Charles Taylor 1/6
 CHM 110 - The Basics of Quantum Mechanics (r14) - 2014 Charles Taylor 1/6 Introduction We've discussed how Bohr's model predicted the behavior of the hydrogen atom. To describe the other atoms (and get
CHM 110 - The Basics of Quantum Mechanics (r14) - 2014 Charles Taylor 1/6 Introduction We've discussed how Bohr's model predicted the behavior of the hydrogen atom. To describe the other atoms (and get
 Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
The controlled-not (CNOT) gate exors the first qubit into the second qubit ( a,b. a,a + b mod 2 ). Thus it permutes the four basis states as follows:
 C/CS/Phys C9 Qubit gates, EPR, ell s inequality 9/8/05 Fall 005 Lecture 4 Two-qubit gate: COT The controlled-not (COT) gate exors the first qubit into the second qubit ( a,b a,a b = a,a + b mod ). Thus
C/CS/Phys C9 Qubit gates, EPR, ell s inequality 9/8/05 Fall 005 Lecture 4 Two-qubit gate: COT The controlled-not (COT) gate exors the first qubit into the second qubit ( a,b a,a b = a,a + b mod ). Thus
Lecture 14: Superposition & Time-Dependent Quantum States
 Lecture 14: Superposition & Time-Dependent Quantum States U= y(x,t=0) 2 U= U= y(x,t 0 ) 2 U= x 0 x L 0 x L Lecture 14, p 1 Last Week Time-independent Schrodinger s Equation (SEQ): 2 2m d y ( x) U ( x)
Lecture 14: Superposition & Time-Dependent Quantum States U= y(x,t=0) 2 U= U= y(x,t 0 ) 2 U= x 0 x L 0 x L Lecture 14, p 1 Last Week Time-independent Schrodinger s Equation (SEQ): 2 2m d y ( x) U ( x)
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/02/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
Quantum Physics & From Ideas to Implementation. Underlying concepts in the syllabus
 Quantum Physics & From Ideas to Implementation Underlying concepts in the syllabus 1 1 What is Quantum Physics? Wave-particle duality Tells us that energy comes in packets, particles are wave-like. Systems
Quantum Physics & From Ideas to Implementation Underlying concepts in the syllabus 1 1 What is Quantum Physics? Wave-particle duality Tells us that energy comes in packets, particles are wave-like. Systems
Interference, vector spaces
 Interference, vector spaces Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Quantum Mechanics 1 August 6, 2008 Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 1 / 16 Outline 1 The double-slit
Interference, vector spaces Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Quantum Mechanics 1 August 6, 2008 Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 1 / 16 Outline 1 The double-slit
Rutherford s Gold Foil Experiment. Quantum Theory Max Planck (1910)
 Neils Bohr Niels Bohr (1913) developed the planetary model of the atom based upon the following: Rutherford s Gold Foil Experiment E = mc 2 Albert Einstein (1905) Quantum Theory Max Planck (1910) He postulated
Neils Bohr Niels Bohr (1913) developed the planetary model of the atom based upon the following: Rutherford s Gold Foil Experiment E = mc 2 Albert Einstein (1905) Quantum Theory Max Planck (1910) He postulated
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
 CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Kozet YAPSAKLI Who are these men? Ancient Philosophy Who: Aristotle, Democritus When: More than 2000 years ago Where:
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms Kozet YAPSAKLI Who are these men? Ancient Philosophy Who: Aristotle, Democritus When: More than 2000 years ago Where:
Bell s Theorem. Ben Dribus. June 8, Louisiana State University
 Bell s Theorem Ben Dribus Louisiana State University June 8, 2012 Introduction. Quantum Theory makes predictions that challenge intuitive notions of physical reality. Einstein and others were sufficiently
Bell s Theorem Ben Dribus Louisiana State University June 8, 2012 Introduction. Quantum Theory makes predictions that challenge intuitive notions of physical reality. Einstein and others were sufficiently
On the origin of probability in quantum mechanics
 On the origin of probability in quantum mechanics Steve Hsu Benasque, September 2010 Outline 1. No Collapse quantum mechanics 2. Does the Born rule (probabilities) emerge? 3. Possible resolutions R. Buniy,
On the origin of probability in quantum mechanics Steve Hsu Benasque, September 2010 Outline 1. No Collapse quantum mechanics 2. Does the Born rule (probabilities) emerge? 3. Possible resolutions R. Buniy,
The Mysteries of Quantum Mechanics
 The Mysteries of Quantum Mechanics Class 5: Quantum Behavior and Interpreta=ons Steve Bryson www.stevepur.com/quantum Ques=ons? The Quantum Wave Quantum Mechanics says: A par=cle s behavior is described
The Mysteries of Quantum Mechanics Class 5: Quantum Behavior and Interpreta=ons Steve Bryson www.stevepur.com/quantum Ques=ons? The Quantum Wave Quantum Mechanics says: A par=cle s behavior is described
Lecture 4. QUANTUM MECHANICS FOR MULTIPLE QUBIT SYSTEMS
 Lecture 4. QUANTUM MECHANICS FOR MULTIPLE QUBIT SYSTEMS 4.1 Multiple Qubits Next we consider a system of two qubits. If these were two classical bits, then there would be four possible states,, 1, 1, and
Lecture 4. QUANTUM MECHANICS FOR MULTIPLE QUBIT SYSTEMS 4.1 Multiple Qubits Next we consider a system of two qubits. If these were two classical bits, then there would be four possible states,, 1, 1, and
We also find the development of famous Schrodinger equation to describe the quantization of energy levels of atoms.
 Lecture 4 TITLE: Quantization of radiation and matter: Wave-Particle duality Objectives In this lecture, we will discuss the development of quantization of matter and light. We will understand the need
Lecture 4 TITLE: Quantization of radiation and matter: Wave-Particle duality Objectives In this lecture, we will discuss the development of quantization of matter and light. We will understand the need
The Future. Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers.
 Quantum Computing Moore s Law The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. When gate lengths
Quantum Computing Moore s Law The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. The Future Currently state of the art chips have gates of length 35 nanometers. When gate lengths
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY
 Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
Quantum Mechanics: Interpretation and Philosophy
 Quantum Mechanics: Interpretation and Philosophy Significant content from: Quantum Mechanics and Experience by David Z. Albert, Harvard University Press (1992). Main Concepts: -- complementarity -- the
Quantum Mechanics: Interpretation and Philosophy Significant content from: Quantum Mechanics and Experience by David Z. Albert, Harvard University Press (1992). Main Concepts: -- complementarity -- the
The wavefunction and quantum jumps
 ydrogen atom in 3D Today From ast Time Electron has a particle and wave nature and is spread out over space Wave nature must interfere constructively to exist Satisfies 3 conditions for constructive interference
ydrogen atom in 3D Today From ast Time Electron has a particle and wave nature and is spread out over space Wave nature must interfere constructively to exist Satisfies 3 conditions for constructive interference
Interference, Complementarity, Entanglement and all that Jazz
 nterference, Complementarity, Entanglement and all that Jazz Mark Beck Dept. of Physics, Whitman College With lots of help from: Faculty: obert Davies (Seattle U) Students: Ashifi ogo, William Snyder,
nterference, Complementarity, Entanglement and all that Jazz Mark Beck Dept. of Physics, Whitman College With lots of help from: Faculty: obert Davies (Seattle U) Students: Ashifi ogo, William Snyder,
