Microseismic monitoring is a valuable
|
|
|
- Roy Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SPECIAL SECTION: M i c r o s e i s m i c moment tensors: A path to understanding frac growth ADAM BAIG and TED URBANCIC, Engineering Seismology Group Canada monitoring is a valuable tool in understanding the efficacy of hydraulic fracture treatments. Determination of event locations and magnitudes leads to estimations of the geometry of the fracture zone and certain dynamics of the fracturing process. With sufficient resolution, the hypocenters may even reveal failure planes or other underlying structures controlling the distribution of events and of interest to petroleum engineers to test various hypotheses on fracture growth. However, inverting for the moment tensor distribution opens up new dimensions in understanding the processes underlying the fracturing as it is a direct representation of the strain in the immediate vicinity of the source. The properties of the seismic moment tensor allow the orthogonal strain axes to be estimated for each event, and we can use that deformation information to identify the state of stress in the vicinity of the treatment and the potential failure planes. From there, we can examine a canonical problem in earthquake seismology: that of determining the orientation of the fault plane from a moment tensor. The fault-plane solution is an approximation of the moment tensor that assumes that deformation follows a double-couple shear model, but the symmetry of the solution admits two orthogonal solutions for the fault plane orientation. Using the strain axes of an ensemble of events with constraints to the stress field can help to resolve this ambiguity in fault orientation as one possible fault plane will be more consistent with the overall state of stress than the other. Therefore, we can determine the underlying fracture geometries independent of event locations contributing additional constraints to the resolution of the fracture network. The full moment tensor, especially for microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing or other injection treatments, can be used to identify the volumetric failure mechanisms of events. One decomposition of these mechanisms partitions the moment tensor in three components: a double-couple component; an isotropic component that describes the volumetric strain (i.e., explosive or implosive); and a compensated linear vector dipole that describes strain in one sense along one axis and strain in the other sense along the other two (crack opening or crack closure). If we assume that the volumetric strain is in response to fluids, then we can begin to think about tracking the flow of proppant through the system by determining the volumetric deformation through the isotropic component of the moment tensor. Moment tensors The seismic moment tensor (SMT) is a symmetric, rank The Leading Edge March 2010 Figure 1. Different modes of failure produce different moment tensors visualized though the beach ball diagrams, which are stereographic projections of the P-wave radiation patterns over the focal sphere. Figure 2. The moment tensors for 147 events plotted with the condition number that determines how well one can invert for the mechanism of the event. The moment tensors are shown as beach balls colored by the proportion of double-couple, compensated linear vector dipole, and isotropic components according to the color triangle. Also shown is the treatment well (gray), the observation wells (red), and the triaxial sensors (the triads of gray cylinders). tensor, which therefore has six independent components. The SMT is responsible for the observed radiation pattern from the event; mapping the total amplitudes (especially including the sense, positive or negative, of the first motion) of the P, SV, and SH phases to the focal sphere surrounding the source should determine this tensor, provided the sensor geometry is sufficiently well-distributed and the seismic data are high quality and properly modeled. For monitoring hydraulic fractures, full resolution of all six independent components requires that these total amplitudes be identified on at least two linear borehole arrays that are not coplanar with the event.
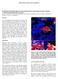
2 Figure 3. Stereographic density plots of P axes (left) and T axes (right) for over 147 events recorded from a hydraulic fracture treatment. The principal stress axes determined from the algorithm of Gephart and Forsyth from this data set are overlain on both plots. Each SMT can be decomposed into six independent parameters: the three geometric parameters are controlled by the orientation of the fracture and the sense of slip thereon; one parameter is the total seismic moment (i.e., the strength of the event); and the other two control the relative strengths of the double-couple, compensated linear vector dipole and isotropic components. The non-double-couple modes of failure play an important role in elucidating the underlying failure mechanisms as they impart information about how the volume of the medium is changing in response to the treatment. Examples of the radiation patterns from various failure mechanisms are shown in Figure 1, and are related to various crack modes. Determination of principal stress axes and fracture planes As the SMT is a representation of strain at the source, with an ensemble of events each giving a measure of strain in the treatment zone, we can invert these strain axes for the stress regime that best fits these events. Gephart and Forsyth (1984) proposed an algorithm for realizing such an inversion for earthquake data in California. We can apply this method to microseismic data, by considering the double-couple approximations of the SMTs. The concept of this approach is not new for induced microseismicity. Urbancic et al. (1993) for example, applied this technique to mining-induced seismicity. The strain encoded in a moment tensor is frequently described by the P (pressure) and T (tension) axis of the event, which are simply the eigenvectors corresponding to the smallest and largest eigenvalues, respectively. With an ensemble of events, we can test various states of stress by determining the total rotations necessary to make the P and T axes of every event conform to the uniform test stress state; thus, the problem of determining the in-situ stress amounts to finding the state of stress that minimizes the total rotation of the strain axes from the ensemble of SMTs. In Figure 2, we show the locations and moment tensor solutions for 147 events recorded utilizing three borehole arrays during a hydraulic fracture. The color scale of the events is controlled by the proportion of double-couple, compensated linear vector dipole, and isotropic components to the full source mechanism as prescribed with the color triangle. The events shown in the figure span an unusual vertical range of 500 m. Plotted behind the events is the condition number for the inversion to show the confidence that we have in the inversion of these moment tensors: the closer this number is to unity, the better constrained the inversion. In general, the observed low-condition numbers indicate that the obtained solutions are well-defined. The events themselves fall along a vertical plane trending N 40 E and feature a variety of mechanisms, suggesting that the events cannot be considered as simple shear failures but include volumetric components of failure. In Figure 3, we show stereographic projections of the strain axes densities (pressure on the left, tension on the right) for a group of events recorded during the hydraulic fracture. Overlain as white crosses are the stress axes determined from the algorithm of Gephart and Forsyth. The trend of σ 1 is in agreement with the maximum horizontal shear stress observed from borehole strain measurements as well as being in agreement with the general trend of the events. Double-couple moment tensors admit two orthogonal solutions for the fracture plane orientation. However, now that we can invert for the state of stress, for each event we can test these two candidate solutions: the plane that is most consistent with the state of stress is chosen for each event. Figure 4, on the left, shows a stereographic density plot for the poles of the best-fitting fracture planes determined from March 2010 The Leading Edge 321
3 the events from Figure 3. This plot reveals that these orientations fall into two groupings that are suborthogonal to each other. One explanation for this distribution is that the events are occurring along an en-echelon fracture network as shown on the right of Figure 4. Non-double-couple components Because of the injection of fluids and proppant, the assumption that the moment tensors are purely doublecouple is too confining. Relaxing this restriction, there are generally two other modes of failure: a pure isotropic mechanism that corresponds to an implosion or explosion where all deformation is accommodated by a volumetric change, and a compensated linear vector dipole where strain along one axis is compensated by contraction or expansion along the other axes. In reality, we 147 events in Figure 1. The red crosses mark the centers of the two main clusters in the density Figure 4. (left) A stereographic density plot of the poles of the best-fi tting fault planes from the expect most moment tensors to be a plot and are the poles to the red planes. The white planes give an indication of the amount of scatter in these best-fi t planes. (right) An en-echelon model (in plan view) for the fracture hybrid of these three modes. propagation inferred from the stress distribution and the fracture planes. To parametrize the source type from the moment tensor, we note that the tensor has three real eigenvalues: m 1, m 2, and m 3. These eigenvalues determine the proportion of isotropic, compensated linear vector dipole, and double-couple contributions to the full moment tensor. The isotropic component is described by the trace of the tensor (3m = m 1 + m 2 + m 3 ) and the deviatoric moments are defined as: m 1 = m 1 m m 2 = m 2 m m 3 = m 3 m. Following Hudson et al. (1989), we then order these deviatoric moments such that m 1 < m 2 < m 3. This separation of the isotropic strain from the deviatoric allows the source type to be parameterized in terms of the quantities k and T, respectively: and Both quantities vary between 1 and 1. A source with k = 1 corresponds to a purely explosive event, while one with k = 1 corresponds to a pure implosion. The T ± 1 extremes are perhaps less easily envisioned, but correspond to sources where one strain axis is shortening while the other two are lengthening, or vice versa. All pure double-couple sources are uniquely described by k = T = 0. We note that all orientation information is not contained in this decomposition, because it relies only on the eigenvalues of the moment tensor. The variety of source mechanisms can be discriminated in the source-type diagram (Figure 5) introduced by Hudson et al. In these plots, k, is on the vertical axis and the axis parallel to the top-right edge is T. The peculiar shape of this diagram is to ensure the even probability distribution of all source Figure 5. A source-type diagram. In these plots, a mechanism will plot to different regions depending on the proportion of double-couple, compensated linear vector dipole, and isotropic contributions to the moment tensor. The sign of the compensated linear vector dipole and isotropic components is also distinguished here. types. Double-couple mechanisms map to the center; purely explosive and implosive events are at the top and bottom of the diamond, respectively; and mechanisms corresponding to opening and closing of cracks translate to the top-right and bottom-left edges of the diagram. In Figure 6, three such data sets from different treatments from separate wells in the same field are plotted. In the top left (red), there are a wide variety of mechanisms showing that the fracture is behaving in a very complex manner. To the top right (blue), the data are sparser, but there seems to be a small cluster of events representing crack openings and a larger cluster near the region of the diagram representing crack closures. 322 The Leading Edge March 2010
4 Figure 6. Source-type diagrams for three treatments in different wells from the same field. In the lower right is a histogram of the proportion of events with a given amount of double-couple component for the three data sets; the color of the bars corresponds to the color of the point in the source-type plots. This type of pattern is seen in the lower-left source-type plot (green): events cluster on the poles of the axis between crack opening and closure. The difference in behavior of these data sets can be further illustrated in the histogram in the lower right. The higher proportion of double-couple events in the red data set would indicate that the events here are generated by a very different mechanism than the events in the other two data sets, possibly the re-activation of a pre-existing fault-fracture set resulting in a large amount of shear events. As these events were all recorded on multiple linear receiver arrays, moment tensor inversion condition numbers are similar to those shown in Figure 2. Because of the wealth of events in the lower-left (green) data set, we can analyze it further and try to see if some coherent pattern emerges when plotted against the wellhead pressure and the total proppant pumped downhole. In Figure 7, we show four different windows of the treatment, roughly corresponding to different parts of the proppant volume curve. The first window (upper left) corresponds to the first injection of proppant (before this, not many events were observed); here the events concentrate to the crack opening axis of the source-type plots. The color scale of the events in the scatter plots shows that most events here are close to the well. After this first injection phase, most events still cluster to the crack opening axis with some events occurring farther away from the well. However, a significant number of events are starting to cluster around the crack closure axis, close to the well. The third interval corresponds to the start of a second phase of proppant injection. Events are still clustering to the poles of the crack opening/closure axis, but now the majority are closure-type failures. However, the same trend is observed in the locations of the events: the events are distributed even farther away from the well, with the farthest opening events still outpacing the closure events. Finally, at the end of the treatment, closure-type events are dominant. The farthest-out events in each phase of the treatment are progressing the fracture further away from the well and are uniformly crack-opening type mechanisms. Behind this fracture front, the region in the vicinity of the well shows a transition: initially fractures are expanded generating opening-type events and then relax back with closure-type mechanisms. There is also a closure front, defined by the maximum offset of the crack-closure events, behind the breakout front that progresses more slowly. These openings and closures tend to occur along similar fracture plane orientations Thoughts Monitoring microseismicity related to hydraulic fracture stimulations typically focuses on deriving event locations and the relative magnitude of events. As we have shown, a wealth of additional information can be obtained about the events themselves, and the conditions under which the events March 2010 The Leading Edge 323
5 Figure 7. For each quadrant, data from a different window of the treatment are plotted: (upper left) the scatter plot source-type diagram where each event is colored according to the horizontal distance from the treatment well (see color bar at far left); (upper right) a density contour plot of the same scatter plots, where red = an area of high density and blue = regions of few or no events; and (bottom) the time series of pressure and proppant volume with the time window, in yellow, of the data. The different quadrants correspond to (upper left) the beginning of the proppant injection; (upper right) a pause in the proppant injection; (lower left) the beginning of the next injection of proppant; and (lower right) the end of the treatment. are generated during the stimulation process, under appropriate monitoring conditions. Determining the stress-strain state and fracture orientations allows resolution of progressive fracture growth, such as we suggested by invoking an enechelon fracture distribution along the maximum horizontal stress orientation. Further investigation of the individual strain components reveals the complexity of the individual failures but more importantly, by looking at the spatial and temporal variations of these failure components, a more definitive image of fracture development can be realized. The effective relation of pressure, proppant volume and rates, as seen, can be examined in the context of the observed seismic response, suggesting a direction for future assessment of the effectiveness of a treatment program. Further, it provides the opportunity to develop numerical models that can be used to predict the behaviour of the stimulation program. Of course, microseismic monitoring may then provide an approach to both validate and calibrate numerical models to enhance production. References Ayers, W., T. I. Urbancic, and S. C. Maxwell, 2001, Passive microseismic monitoring to optimize well stimulation designs, SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, LA. Gephart, J. and D. Forsyth, 1984, An improved method for determining the regional stress tensor using earthquake focal mechanism data: An application to the San Fernando earthquake sequence, Journal of Geophysical Research, 89, Hudson, J., R. Pearce, and R. Rogers, 1989, Source type plot for inversion of the moment tensor, Journal of Geophysical Research, 94, Jost, M. and R. Hermann, 1989, A student s guide to and review of moment tensors, Seismological Research Letters, 60, Trifu, C-I., D. Angus, and V. Shumila, 2000, A fast evaluation of the seismic moment tensor for induced seismicity, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90, Urbancic, T. I., C-I. Trifu and R. P. Young, 1993, ity derived fault-planes and their relationship to focal mechanism, stress inversion, and geologic data, Geophysical Research Letters, 20, Acknowledgments: The authors thank their colleagues at ESG for their support and contribution to the studies. In particular, we thank Vladimir Shumila for his valuable discussions, and Sheri Bowman, Marc Prince, Lawrence Wamboldt, Keni Mallinen, Tiberius Trifu, Katherine Buckingham, Stephanie Alexander, Scott Valberg, and Christopher Orr for their invaluable input to the data analysis. Finally, the original manuscript was improved by comments from the guest editor and an anonymous reviewer. Corresponding author: adam.baig@esg.ca 324 The Leading Edge March 2010
Resolving sill pillar stress behaviour associated with blasts and rockbursts
 Deep Mining 2017: Eighth International Conference on Deep and High Stress Mining J Wesseloo (ed.) 2017 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Perth, ISBN 978-0-9924810-6-3 https://papers.acg.uwa.edu.au/p/1704_17_smith/
Deep Mining 2017: Eighth International Conference on Deep and High Stress Mining J Wesseloo (ed.) 2017 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Perth, ISBN 978-0-9924810-6-3 https://papers.acg.uwa.edu.au/p/1704_17_smith/
Abstracts ESG Solutions
 Abstracts ESG Solutions 2015-2016 For more information, please contact Melissa Hoy, Technical Marketing Coordinator at melissa.hoy@esgsolutions.com Visit us online at www.esgsolutions.com Abstract #1 Fracture
Abstracts ESG Solutions 2015-2016 For more information, please contact Melissa Hoy, Technical Marketing Coordinator at melissa.hoy@esgsolutions.com Visit us online at www.esgsolutions.com Abstract #1 Fracture
Focal Mechanism Analysis of a Multi-lateral Completion in the Horn River Basin
 Focal Mechanism Analysis of a Multi-lateral Completion in the Horn River Basin Paige Snelling*, Cameron Wilson, MicroSeismic Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada psnelling@microseismic.com Neil Taylor, Michael de
Focal Mechanism Analysis of a Multi-lateral Completion in the Horn River Basin Paige Snelling*, Cameron Wilson, MicroSeismic Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada psnelling@microseismic.com Neil Taylor, Michael de
F021 Detetection of Mechanical Failure During Hyraulic Fracturing Through Passive Seismic Microseismic Monitoring
 F021 Detetection of Mechanical Failure During Hyraulic Fracturing Through Passive Seismic Microseismic Monitoring A. De La Pena* (Microseismic Inc.), L. Eisner (Microseismic Inc.), M.P. Thornton (Microseismic
F021 Detetection of Mechanical Failure During Hyraulic Fracturing Through Passive Seismic Microseismic Monitoring A. De La Pena* (Microseismic Inc.), L. Eisner (Microseismic Inc.), M.P. Thornton (Microseismic
Overview of moment-tensor inversion of microseismic events
 Overview of moment-tensor inversion of microseismic events Thomas S. Eyre 1 and Mirko van der Baan 1 Downloaded 08/11/15 to 142.244.191.52. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms
Overview of moment-tensor inversion of microseismic events Thomas S. Eyre 1 and Mirko van der Baan 1 Downloaded 08/11/15 to 142.244.191.52. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms
Comparison of Microseismic Results in Complex Geologies Reveals the Effect of Local Stresses on Fracture Propagation
 Comparison of Microseismic Results in Complex Geologies Reveals the Effect of Local Stresses on Fracture Propagation Mike Preiksaitis, Sheri Bowman, Ted Urbancic ESG Canada Inc. Summary Understanding the
Comparison of Microseismic Results in Complex Geologies Reveals the Effect of Local Stresses on Fracture Propagation Mike Preiksaitis, Sheri Bowman, Ted Urbancic ESG Canada Inc. Summary Understanding the
Theory. Summary. Introduction
 Waveform similarity for quality control of event locations, time picking and moment tensor solutions Fernando Castellanos, University of Alberta. Edmonton, AB. Mirko van der Baan, University of Alberta.
Waveform similarity for quality control of event locations, time picking and moment tensor solutions Fernando Castellanos, University of Alberta. Edmonton, AB. Mirko van der Baan, University of Alberta.
Seismic Monitoring of Mine Environments
 Mapping and Monitoring the Mine Environment Paper 123 Explor97 Master Page Explor97 Contents Previous Paper G O T O Author Index Section Contents Next Paper Seismic Monitoring of Mine Environments Urbancic,
Mapping and Monitoring the Mine Environment Paper 123 Explor97 Master Page Explor97 Contents Previous Paper G O T O Author Index Section Contents Next Paper Seismic Monitoring of Mine Environments Urbancic,
3D velocity model with complex geology and voids for microseismic location and mechanism
 Deep Mining 2014 A.A. Editor and B. Editor (eds) 2014 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Sudbury, ISBN 978-0-9870937-9-0 3D velocity model with complex geology and voids for microseismic location and
Deep Mining 2014 A.A. Editor and B. Editor (eds) 2014 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Sudbury, ISBN 978-0-9870937-9-0 3D velocity model with complex geology and voids for microseismic location and
Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms
 Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary The spatial dimensions and rupture characteristics of microseismic
Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary The spatial dimensions and rupture characteristics of microseismic
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN
 Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
Failure Mechanism and Evolution Law of Fractured-Rocks based on Moment Tensor Inversion
 Failure Mechanism and Evolution Law of Fractured-Rocks based on Moment Tensor Inversion Jinfei Chai 1), Yongtao Gao 1), Shunchuan Wu 1), Langqiu Sun 2), Yu Zhou 1) 1) School of Civil and Environmental
Failure Mechanism and Evolution Law of Fractured-Rocks based on Moment Tensor Inversion Jinfei Chai 1), Yongtao Gao 1), Shunchuan Wu 1), Langqiu Sun 2), Yu Zhou 1) 1) School of Civil and Environmental
Microearthquake Focal Mechanisms
 Microearthquake Focal Mechanisms A Tool for Monitoring Geothermal Systems By Bruce R. Julian (U. S. Geological Survey - Menlo Park, CA) and Gillian R. Foulger (University of Durham - Durham, United Kingdom)
Microearthquake Focal Mechanisms A Tool for Monitoring Geothermal Systems By Bruce R. Julian (U. S. Geological Survey - Menlo Park, CA) and Gillian R. Foulger (University of Durham - Durham, United Kingdom)
Extending the magnitude range of seismic reservoir monitoring by Utilizing Hybrid Surface Downhole Seismic Networks
 Extending the magnitude range of seismic reservoir monitoring by Utilizing Hybrid Surface Downhole Seismic Networks Gisela Viegas*, ESG, Kingston, Ontario, Canada Gisela.Fernandes@esgsolutions.com and
Extending the magnitude range of seismic reservoir monitoring by Utilizing Hybrid Surface Downhole Seismic Networks Gisela Viegas*, ESG, Kingston, Ontario, Canada Gisela.Fernandes@esgsolutions.com and
Recent advances in seismic monitoring technology at Canadian mines
 Ž. Journal of Applied Geophysics 45 2000 225 237 www.elsevier.nlrlocaterjappgeo Recent advances in seismic monitoring technology at Canadian mines Theodore I. Urbancic ), Cezar-Ioan Trifu Engineering Seismology
Ž. Journal of Applied Geophysics 45 2000 225 237 www.elsevier.nlrlocaterjappgeo Recent advances in seismic monitoring technology at Canadian mines Theodore I. Urbancic ), Cezar-Ioan Trifu Engineering Seismology
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation.
 Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
Microseismic Monitoring: Insights from Moment Tensor Inversion
 Microseismic Monitoring: Insights from Moment Tensor Inversion Farshid Forouhideh and David W. Eaton ABSTRACT This paper reviews the mathematical tools used for describing microseismic source mechanisms.
Microseismic Monitoring: Insights from Moment Tensor Inversion Farshid Forouhideh and David W. Eaton ABSTRACT This paper reviews the mathematical tools used for describing microseismic source mechanisms.
DETAILED IMAGE OF FRACTURES ACTIVATED BY A FLUID INJECTION IN A PRODUCING INDONESIAN GEOTHERMAL FIELD
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 9-11, 2009 SGP-TR-187 DETAILED IMAGE OF FRACTURES ACTIVATED BY A FLUID INJECTION
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Fourth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 9-11, 2009 SGP-TR-187 DETAILED IMAGE OF FRACTURES ACTIVATED BY A FLUID INJECTION
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Waveform modelling P-wave first-motions
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Waveform modelling P-wave first-motions
Stress Shadows Explained: What It Is, What It Isn t, And Why You Should Care
 Stress Shadows Explained: What It Is, What It Isn t, And Why You Should Care Introduction Much is now made about Stress Shadows (SSs) and its impact on hydraulic fracturing. In fact, many (most?) of the
Stress Shadows Explained: What It Is, What It Isn t, And Why You Should Care Introduction Much is now made about Stress Shadows (SSs) and its impact on hydraulic fracturing. In fact, many (most?) of the
Laboratory Shear Stimulation and Hydraulic Fracture Characterization Using Acoustic Emission
 31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Th.2.A.1 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17553 Laboratory Shear Stimulation and Hydraulic Fracture Characterization
31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Th.2.A.1 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17553 Laboratory Shear Stimulation and Hydraulic Fracture Characterization
The effect of location error on microseismic mechanism estimation: synthetic and real field data examples
 The effect of location error on microseismic mechanism estimation: synthetic and real field data examples Michael Kratz 1 and Michael Thornton 1 present an issue that is of primary concern for all basins
The effect of location error on microseismic mechanism estimation: synthetic and real field data examples Michael Kratz 1 and Michael Thornton 1 present an issue that is of primary concern for all basins
A new methodology for estimating field horizontal stress from microseismic focal mechanisms
 A new methodology for estimating field horizontal stress from microseismic focal mechanisms Alireza Agharazi 1*, Peter Duncan 1 and Michael Thornton 1 introduce a new methodology for the estimation of
A new methodology for estimating field horizontal stress from microseismic focal mechanisms Alireza Agharazi 1*, Peter Duncan 1 and Michael Thornton 1 introduce a new methodology for the estimation of
Microseismic Aids In Fracturing Shale By Adam Baig, Sheri Bowman and Katie Jeziorski
 AUGUST 2014 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Microseismic Aids In Fracturing Shale By Adam Baig, Sheri Bowman and Katie Jeziorski KINGSTON, ONTARIO
AUGUST 2014 The Better Business Publication Serving the Exploration / Drilling / Production Industry Microseismic Aids In Fracturing Shale By Adam Baig, Sheri Bowman and Katie Jeziorski KINGSTON, ONTARIO
Monitoring induced microseismic events usually
 SPECIAL M i c r SECTION: o s e i s m M i ci c r o s e i s m i c Beyond the dots in the box: microseismicity-constrained fracture models for reservoir simulation Leo Eisner, Sherilyn Williams-Stroud, Andrew
SPECIAL M i c r SECTION: o s e i s m M i ci c r o s e i s m i c Beyond the dots in the box: microseismicity-constrained fracture models for reservoir simulation Leo Eisner, Sherilyn Williams-Stroud, Andrew
of other regional earthquakes (e.g. Zoback and Zoback, 1980). I also want to find out
 4. Focal Mechanism Solutions A way to investigate source properties of the 2001 sequence is to attempt finding well-constrained focal mechanism solutions to determine if they are consistent with those
4. Focal Mechanism Solutions A way to investigate source properties of the 2001 sequence is to attempt finding well-constrained focal mechanism solutions to determine if they are consistent with those
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs
 Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Characterization of Induced Seismicity in a Petroleum Reservoir: A Case Study
 Characterization of Induced Seismicity in a Petroleum Reservoir: A Case Study Edmond Sze, M. Nafi Toksöz, and Daniel R. Burns Earth Resources Laboratory Dept. of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences
Characterization of Induced Seismicity in a Petroleum Reservoir: A Case Study Edmond Sze, M. Nafi Toksöz, and Daniel R. Burns Earth Resources Laboratory Dept. of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences
Microseismic monitoring of borehole fluid injections: Data modeling and inversion for hydraulic properties of rocks
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 68, NO. 2 (MARCH-APRIL 2003); P. 685 689, 5 FIGS. 10.1190/1.1567239 Short Note Microseismic monitoring of borehole fluid injections: Data modeling and inversion for hydraulic properties
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 68, NO. 2 (MARCH-APRIL 2003); P. 685 689, 5 FIGS. 10.1190/1.1567239 Short Note Microseismic monitoring of borehole fluid injections: Data modeling and inversion for hydraulic properties
BEYOND TRAVELTIMES AND EARTHQUAKE LOCATION What else can seismograms tell us about the nature of earthquakes on faults?
 BEYOND TRAVELTIMES AND EARTHQUAKE LOCATION What else can seismograms tell us about the nature of earthquakes on faults? What are some of the key parameters which we describe faults? GEOMETRICAL PROPERTIES
BEYOND TRAVELTIMES AND EARTHQUAKE LOCATION What else can seismograms tell us about the nature of earthquakes on faults? What are some of the key parameters which we describe faults? GEOMETRICAL PROPERTIES
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference held in San Antonio, Texas, USA, 1-3 August 2016.
 URTeC: 2461621 Determining Maximum Horizontal Stress With Microseismic Focal Mechanisms Case Studies in the Marcellus, Eagle Ford, Wolfcamp Alireza Agharazi*, MicroSeismic Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
URTeC: 2461621 Determining Maximum Horizontal Stress With Microseismic Focal Mechanisms Case Studies in the Marcellus, Eagle Ford, Wolfcamp Alireza Agharazi*, MicroSeismic Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
Use of S-wave attenuation from perforation shots to map the growth of the stimulated reservoir volume in the Marcellus gas shale
 Use of S-wave attenuation from perforation shots to map the growth of the stimulated reservoir volume in the Marcellus gas shale Yunhui Tan 1, Chengping Chai 1, and Terry Engelder 1 Downloaded 10/07/14
Use of S-wave attenuation from perforation shots to map the growth of the stimulated reservoir volume in the Marcellus gas shale Yunhui Tan 1, Chengping Chai 1, and Terry Engelder 1 Downloaded 10/07/14
Calculation of Focal mechanism for Composite Microseismic Events
 Calculation of Focal mechanism for Composite Microseismic Events Hongliang Zhang, David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary It is often difficult to obtain a reliable single-event
Calculation of Focal mechanism for Composite Microseismic Events Hongliang Zhang, David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary It is often difficult to obtain a reliable single-event
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5
 Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Microdeformation: combining direct fracture height measurement with microseismic response Natalia Verkhovtseva, Greg Stanley
 Microdeformation: combining direct fracture height measurement with microseismic response Natalia Verkhovtseva, Greg Stanley Principal Geophysicist Pinnacle a Halliburton service Outline Introduction Microseismic
Microdeformation: combining direct fracture height measurement with microseismic response Natalia Verkhovtseva, Greg Stanley Principal Geophysicist Pinnacle a Halliburton service Outline Introduction Microseismic
What Can Microseismic Tell Us About Hydraulic Fracturing?
 What Can Microseismic Tell Us About Hydraulic Fracturing? Shawn Maxwell May 2015 Microseismic Geomechanics: Increased understanding; reduced risk 1 Outline Microseismic Introduction Microseismic in Unconventional
What Can Microseismic Tell Us About Hydraulic Fracturing? Shawn Maxwell May 2015 Microseismic Geomechanics: Increased understanding; reduced risk 1 Outline Microseismic Introduction Microseismic in Unconventional
Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source
 Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Microseismic Geomechanical Modelling of Asymmetric Upper Montney Hydraulic Fractures
 Microseismic Geomechanical Modelling of Asymmetric Upper Montney Hydraulic Fractures Drew Chorney, Byungtark Lee, Shawn Maxwell (IMaGE) Summary Geomechanical modelling is a powerful tool to quantitatively
Microseismic Geomechanical Modelling of Asymmetric Upper Montney Hydraulic Fractures Drew Chorney, Byungtark Lee, Shawn Maxwell (IMaGE) Summary Geomechanical modelling is a powerful tool to quantitatively
Yusuke Mukuhira. Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics
 Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics Yusuke Mukuhira Postdoctoral Fellow (JSPS research fellow) Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics Yusuke Mukuhira Postdoctoral Fellow (JSPS research fellow) Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Analytical Stress Modeling for Mine related Microseismicity
 Analytical Stress Modeling for Mine related Microseismicity Himanshu Barthwal and Mirko van der Baan University of Alberta Summary Microseismicity is recorded in an underground mine by a network of 7 boreholes
Analytical Stress Modeling for Mine related Microseismicity Himanshu Barthwal and Mirko van der Baan University of Alberta Summary Microseismicity is recorded in an underground mine by a network of 7 boreholes
Passive seismic monitoring in unconventional oil and gas
 Passive seismic monitoring in unconventional oil and gas Michael Kendall, James Verdon, Alan Baird, Anna Stork and Philip Usher Bristol University Microseismicity Projects (BUMPS) Microseismicity and
Passive seismic monitoring in unconventional oil and gas Michael Kendall, James Verdon, Alan Baird, Anna Stork and Philip Usher Bristol University Microseismicity Projects (BUMPS) Microseismicity and
! EN! EU! NE! EE.! ij! NN! NU! UE! UN! UU
 A-1 Appendix A. Equations for Translating Between Stress Matrices, Fault Parameters, and P-T Axes Coordinate Systems and Rotations We use the same right-handed coordinate system as Andy Michael s program,
A-1 Appendix A. Equations for Translating Between Stress Matrices, Fault Parameters, and P-T Axes Coordinate Systems and Rotations We use the same right-handed coordinate system as Andy Michael s program,
High Resolution Imaging of Fault Zone Properties
 Annual Report on 1998-99 Studies, Southern California Earthquake Center High Resolution Imaging of Fault Zone Properties Yehuda Ben-Zion Department of Earth Sciences, University of Southern California
Annual Report on 1998-99 Studies, Southern California Earthquake Center High Resolution Imaging of Fault Zone Properties Yehuda Ben-Zion Department of Earth Sciences, University of Southern California
Discrimination of blasts in mine seismology
 Deep Mining 2012 Y. otvin (ed) 2012 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, erth, IBN 978-0-9806154-8-7 https://papers.acg.uwa.edu.au/p/1201_11_malovichko/ Discrimination of blasts in mine seismology D. Malovichko
Deep Mining 2012 Y. otvin (ed) 2012 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, erth, IBN 978-0-9806154-8-7 https://papers.acg.uwa.edu.au/p/1201_11_malovichko/ Discrimination of blasts in mine seismology D. Malovichko
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story
 Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel
 Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca and Neda Boroumand,
Estimating energy balance for hydraulic fracture stimulations: Lessons Learned from Basel David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca and Neda Boroumand,
Chapter 6. Conclusions. 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives
 Chapter 6 Conclusions 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives In this thesis an approach is presented for the in-situ characterization of rocks in terms of the distribution of hydraulic parameters (called SBRC
Chapter 6 Conclusions 6.1 Conclusions and perspectives In this thesis an approach is presented for the in-situ characterization of rocks in terms of the distribution of hydraulic parameters (called SBRC
Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b
 Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b values, and energy release analyses of microseismicity Scott Wessels*, Michael Kratz, Alejandro De La
Identifying fault activation during hydraulic stimulation in the Barnett shale: source mechanisms, b values, and energy release analyses of microseismicity Scott Wessels*, Michael Kratz, Alejandro De La
Location uncertainty for a microearhquake cluster
 Analysis of location uncertainty for a microearhquake cluster: A case study Gabriela Melo, Alison Malcolm, Oleg Poliannikov, and Michael Fehler Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Analysis of location uncertainty for a microearhquake cluster: A case study Gabriela Melo, Alison Malcolm, Oleg Poliannikov, and Michael Fehler Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Constraining of Focal Mechanisms of Induced Seismicity Using Borehole Logging Information
 PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 2018 SGP-TR-213 Constraining of Focal Mechanisms of Induced Seismicity Using Borehole
PROCEEDINGS, 43rd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 12-14, 2018 SGP-TR-213 Constraining of Focal Mechanisms of Induced Seismicity Using Borehole
Exercise: concepts from chapter 6
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Chapter 6 1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Chapter 6 1) The definition of the traction vector (6.7) relies upon the approximation of rock as a continuum, so the ratio of resultant force to surface area
FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING
 SPE Workshop OILFIELD GEOMECHANICS Slide 1 FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING A. Pimenov, R. Kanevskaya Ltd. BashNIPIneft March 27-28, 2017 Moscow, Russia Slide
SPE Workshop OILFIELD GEOMECHANICS Slide 1 FRACTURE REORIENTATION IN HORIZONTAL WELL WITH MULTISTAGE HYDRAULIC FRACTURING A. Pimenov, R. Kanevskaya Ltd. BashNIPIneft March 27-28, 2017 Moscow, Russia Slide
4((F'~) 2) = ~ = (2)
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 74, No. 5, pp. 1615-1621, October 1984 AVERAGE BODY-WAVE RADIATION COEFFICIENTS BY DAVID M. BOORE AND JOHN BOATWRIGHT ABSTRACT Averages of P- and
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 74, No. 5, pp. 1615-1621, October 1984 AVERAGE BODY-WAVE RADIATION COEFFICIENTS BY DAVID M. BOORE AND JOHN BOATWRIGHT ABSTRACT Averages of P- and
Checking up on the neighbors: Quantifying uncertainty in relative event location
 Checking up on the neighbors: Quantifying uncertainty in relative event location The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Checking up on the neighbors: Quantifying uncertainty in relative event location The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
The Stability Of Fault Systems In The South Shore Of The. St. Lawrence Lowlands Of Québec Implications For Shale Gas Development
 The Stability Of Fault Systems In The South Shore Of The St. Lawrence Lowlands Of Québec Implications For Shale Gas Development John Brodylo, Jean-Yves Chatellier,Guillaume Matton & Michel Rheault Copyright
The Stability Of Fault Systems In The South Shore Of The St. Lawrence Lowlands Of Québec Implications For Shale Gas Development John Brodylo, Jean-Yves Chatellier,Guillaume Matton & Michel Rheault Copyright
Title: Application and use of near-wellbore mechanical rock property information to model stimulation and completion operations
 SPE OKC Oil and Gas Symposium March 27-31, 2017 Best of OKC Session Chairperson: Matthew Mower, Chaparral Energy Title: Application and use of near-wellbore mechanical rock property information to model
SPE OKC Oil and Gas Symposium March 27-31, 2017 Best of OKC Session Chairperson: Matthew Mower, Chaparral Energy Title: Application and use of near-wellbore mechanical rock property information to model
URTeC: Abstract
 URTeC: 2902950 Can Seismic Inversion Be Used for Geomechanics? A Casing Deformation Example Jeremy J. Meyer 1*, Jeremy Gallop 1, Alvin Chen 1, Scott Reynolds 1, Scott Mildren 1 ; 1. Ikon Science Copyright
URTeC: 2902950 Can Seismic Inversion Be Used for Geomechanics? A Casing Deformation Example Jeremy J. Meyer 1*, Jeremy Gallop 1, Alvin Chen 1, Scott Reynolds 1, Scott Mildren 1 ; 1. Ikon Science Copyright
Determination of Maximum Horizontal Field Stress from Microseismic Focal Mechanisms A Deterministic Approach
 ARMA 16-691 Determination of Maximum Horizontal Field Stress from Microseismic Focal Mechanisms A Deterministic Approach Agharazi, A MicroSeismic Inc., Houston, Texas, USA Copyright 2016 ARMA, American
ARMA 16-691 Determination of Maximum Horizontal Field Stress from Microseismic Focal Mechanisms A Deterministic Approach Agharazi, A MicroSeismic Inc., Houston, Texas, USA Copyright 2016 ARMA, American
Understanding hydraulic fracture variability through a penny shaped crack model for pre-rupture faults
 Penny shaped crack model for pre-rupture faults Understanding hydraulic fracture variability through a penny shaped crack model for pre-rupture faults David Cho, Gary F. Margrave, Shawn Maxwell and Mark
Penny shaped crack model for pre-rupture faults Understanding hydraulic fracture variability through a penny shaped crack model for pre-rupture faults David Cho, Gary F. Margrave, Shawn Maxwell and Mark
Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth. Michael Kendall
 Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth Michael Kendall Issues and Challanges Geometry (aspect ratio, size, orientation, density) Non-uniqueness (e.g., single set of aligned
Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth Michael Kendall Issues and Challanges Geometry (aspect ratio, size, orientation, density) Non-uniqueness (e.g., single set of aligned
Focal mechanisms produced by shear faulting in weakly transversely isotropic crustal rocks
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 71, NO. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2006 ; P. D145 D151, 6 FIGS., 2 TABLES. 10.1190/1.2236378 Focal mechanisms produced by shear faulting in weakly transversely isotropic crustal rocks Václav
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 71, NO. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2006 ; P. D145 D151, 6 FIGS., 2 TABLES. 10.1190/1.2236378 Focal mechanisms produced by shear faulting in weakly transversely isotropic crustal rocks Václav
Radiation pattern in homogeneous and transversely isotropic attenuating media
 Radiation pattern in homogeneous and transversely isotropic attenuating media Satish Sinha*, Sergey Abaseyev** and Evgeni Chesnokov** *Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology, Rae Bareli, UP 229010
Radiation pattern in homogeneous and transversely isotropic attenuating media Satish Sinha*, Sergey Abaseyev** and Evgeni Chesnokov** *Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology, Rae Bareli, UP 229010
7.2.1 Seismic waves. Waves in a mass- spring system
 7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock
 Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
1. Background. is usually significantly lower than it is in uniaxial tension
 NOTES ON QUANTIFYING MODES OF A SECOND- ORDER TENSOR. The mechanical behavior of rocks and rock-like materials (concrete, ceramics, etc.) strongly depends on the loading mode, defined by the values and
NOTES ON QUANTIFYING MODES OF A SECOND- ORDER TENSOR. The mechanical behavior of rocks and rock-like materials (concrete, ceramics, etc.) strongly depends on the loading mode, defined by the values and
SHALE GAS AND HYDRAULIC FRACTURING
 SHALE GAS AND HYDRAULIC FRACTURING JAMES VERDON FRONTIERS IN EARTH SCIENCES (EASC M0016) WEDNESDAY 29.11.2011 Tight gas reservoirs have permeability of 0.1mD or less difficult to produce at economic rates.
SHALE GAS AND HYDRAULIC FRACTURING JAMES VERDON FRONTIERS IN EARTH SCIENCES (EASC M0016) WEDNESDAY 29.11.2011 Tight gas reservoirs have permeability of 0.1mD or less difficult to produce at economic rates.
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Unconventional Resources Technology Conference held in San Antonio, Texas, USA, 1-3 August 2016.
 URTeC: 2444366 Using Depletion-Zone Microseismicity to Understand Producing Volumes Jonathan P. McKenna*, Michael H. Grealy, Michael S. Blaz and Nathan M. Toohey, MicroSeismic, Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
URTeC: 2444366 Using Depletion-Zone Microseismicity to Understand Producing Volumes Jonathan P. McKenna*, Michael H. Grealy, Michael S. Blaz and Nathan M. Toohey, MicroSeismic, Inc. Copyright 2016, Unconventional
Low-frequency tremor signals from a hydraulic fracture treatment in northeast British Columbia, Canada
 Low-frequency tremor signals from a hydraulic fracture treatment in northeast British Columbia, Canada David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca
Low-frequency tremor signals from a hydraulic fracture treatment in northeast British Columbia, Canada David W. Eaton*, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada eatond@ucalgary.ca
2010 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 DEVELOPING AND EXPLOITING A UNIQUE DATASET FROM SOUTH AFRICAN GOLD MINES FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION AND WAVE PROPAGATION Jordi Julià 1, Andrew A. Nyblade 1, Rengin Gök 2, William R. Walter 2, Lindsay
DEVELOPING AND EXPLOITING A UNIQUE DATASET FROM SOUTH AFRICAN GOLD MINES FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION AND WAVE PROPAGATION Jordi Julià 1, Andrew A. Nyblade 1, Rengin Gök 2, William R. Walter 2, Lindsay
Gain information on the development of Engineered Geothermal Systems (EGS) and enhance our understanding of long-term reservoir behaviour.
 1 GEOTHERMAL ICL was involved in the first commercial Enhanced Geothermal System (EGS) project in the EU and for over 15 years has undertaken international research programs for the monitoring of rock
1 GEOTHERMAL ICL was involved in the first commercial Enhanced Geothermal System (EGS) project in the EU and for over 15 years has undertaken international research programs for the monitoring of rock
Summary so far. Geological structures Earthquakes and their mechanisms Continuous versus block-like behavior Link with dynamics?
 Summary so far Geodetic measurements velocities velocity gradient tensor (spatial derivatives of velocity) Velocity gradient tensor = strain rate (sym.) + rotation rate (antisym.) Strain rate tensor can
Summary so far Geodetic measurements velocities velocity gradient tensor (spatial derivatives of velocity) Velocity gradient tensor = strain rate (sym.) + rotation rate (antisym.) Strain rate tensor can
Anisotropic moment tensor inversion and visualization applied to a dual well monitoring survey
 Anisotropic moment tensor inversion and visualization applied to a dual well monitoring survey Scott Leaney, Xin Yu, Chris Chapman, Les Bennett, Shawn Maxwell, Jim Rutledge, Schlumberger Microseismic Services;
Anisotropic moment tensor inversion and visualization applied to a dual well monitoring survey Scott Leaney, Xin Yu, Chris Chapman, Les Bennett, Shawn Maxwell, Jim Rutledge, Schlumberger Microseismic Services;
Induced microseismic fracture prediction
 Predicting hydraulically-induced microseismic fractures from seismic inversion volumes: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol*, University of Oklahoma, Joël Le Calvez, Schlumberger,
Predicting hydraulically-induced microseismic fractures from seismic inversion volumes: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol*, University of Oklahoma, Joël Le Calvez, Schlumberger,
Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale
 ARMA 15-189 Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale Xu, Shaochuan and Zoback, M.D. Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA Copyright 2015 ARMA,
ARMA 15-189 Analysis of stress variations with depth in the Permian Basin Spraberry/Dean/Wolfcamp Shale Xu, Shaochuan and Zoback, M.D. Stanford University, Stanford, California, USA Copyright 2015 ARMA,
Modeling pressure response into a fractured zone of Precambrian basement to understand deep induced-earthquake hypocenters from shallow injection
 Modeling pressure response into a fractured zone of Precambrian basement to understand deep induced-earthquake hypocenters from shallow injection S. Raziperchikolaee 1 and J. F. Miller 1 Abstract Analysis
Modeling pressure response into a fractured zone of Precambrian basement to understand deep induced-earthquake hypocenters from shallow injection S. Raziperchikolaee 1 and J. F. Miller 1 Abstract Analysis
Identifying faults and fractures in unconventional reservoirs through microseismic monitoring
 first break volume 29, July 2011 special topic Identifying faults and fractures in unconventional reservoirs through microseismic monitoring Scott A. Wessels, * Alejandro De La Peña, Michael Kratz, Sherilyn
first break volume 29, July 2011 special topic Identifying faults and fractures in unconventional reservoirs through microseismic monitoring Scott A. Wessels, * Alejandro De La Peña, Michael Kratz, Sherilyn
Duvernay Fracturing: From Microseismic Monitoring to Unconventional Fracture Model Construction
 Duvernay Fracturing: From Microseismic Monitoring to Unconventional Fracture Model Construction Martin Haege, Alexey Zhmodik, Drazenko Boskovic, Venkateshwaran Ramanathan, Tina Hoffart, Qiuguo Li, and
Duvernay Fracturing: From Microseismic Monitoring to Unconventional Fracture Model Construction Martin Haege, Alexey Zhmodik, Drazenko Boskovic, Venkateshwaran Ramanathan, Tina Hoffart, Qiuguo Li, and
Summary. Introduction
 1540160 Using Microseismicity to Understand Subsurface Fracture Systems and Increase the Effectiveness of Completions: Eagle Ford Shale, TX John P. Detring 1 and Sherilyn Williams-Stroud 2 1. Analysis,
1540160 Using Microseismicity to Understand Subsurface Fracture Systems and Increase the Effectiveness of Completions: Eagle Ford Shale, TX John P. Detring 1 and Sherilyn Williams-Stroud 2 1. Analysis,
DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELLING OF HYDRAULIC FRACTURING IN A STRUCTURALLY CONTROLLED AREA OF THE MONTNEY FORMATION, BC
 DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELLING OF HYDRAULIC FRACTURING IN A STRUCTURALLY CONTROLLED AREA OF THE MONTNEY FORMATION, BC Steve Rogers Golder Associates Ltd Pat McLellan McLellan Energy Advisors Inc Gordon
DISCRETE FRACTURE NETWORK MODELLING OF HYDRAULIC FRACTURING IN A STRUCTURALLY CONTROLLED AREA OF THE MONTNEY FORMATION, BC Steve Rogers Golder Associates Ltd Pat McLellan McLellan Energy Advisors Inc Gordon
Geomechanics, Anisotropy and LMR
 Geomechanics, Anisotropy and LMR Marco Perez *, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada marco.perez@apachecorp.com Bill Goodway, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada bill.goodway@apachecorp.com David
Geomechanics, Anisotropy and LMR Marco Perez *, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada marco.perez@apachecorp.com Bill Goodway, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada bill.goodway@apachecorp.com David
In situ stress estimation using acoustic televiewer data
 Underground Mining Technology 2017 M Hudyma & Y Potvin (eds) 2017 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Perth, ISBN 978-0-9924810-7-0 https://papers.acg.uwa.edu.au/p/1710_39_goodfellow/ SD Goodfellow KORE
Underground Mining Technology 2017 M Hudyma & Y Potvin (eds) 2017 Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Perth, ISBN 978-0-9924810-7-0 https://papers.acg.uwa.edu.au/p/1710_39_goodfellow/ SD Goodfellow KORE
**********************************************************************
 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering School of Mining and Petroleum Engineering 3-33 Markin/CNRL Natural Resources Engineering Facility www.engineering.ualberta.ca/civil Tel: 780.492.4235
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering School of Mining and Petroleum Engineering 3-33 Markin/CNRL Natural Resources Engineering Facility www.engineering.ualberta.ca/civil Tel: 780.492.4235
Locating Events using Borehole Microseismic Monitoring by Inclusion of Particle Motion Analysis
 Locating Events using Borehole Microseismic Monitoring by Inclusion of Particle Motion Analysis Balikpapan, October 5th-8th, 2015 REXHA VERDHORA RY Geophysical Engineering Institut Teknologi Bandung ANDRI
Locating Events using Borehole Microseismic Monitoring by Inclusion of Particle Motion Analysis Balikpapan, October 5th-8th, 2015 REXHA VERDHORA RY Geophysical Engineering Institut Teknologi Bandung ANDRI
Main Menu. Summary. Introduction
 Kyosuke Okamoto *, JSPS Research Fellow, Kyoto University; Ru-shan Wu, University of California, Santa Cruz; Hitoshi Mikada, Tada-nori Goto, Junichi Takekawa, Kyoto University Summary Coda-Q is a stochastic
Kyosuke Okamoto *, JSPS Research Fellow, Kyoto University; Ru-shan Wu, University of California, Santa Cruz; Hitoshi Mikada, Tada-nori Goto, Junichi Takekawa, Kyoto University Summary Coda-Q is a stochastic
FULL MOMENT TENSOR ANALYSIS USING FIRST MOTION DATA AT THE GEYSERS GEOTHERMAL FIELD
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 2013 SGP-TR-198 FULL MOMENT TENSOR ANALYSIS USING FIRST MOTION DATA AT
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Eighth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 11-13, 2013 SGP-TR-198 FULL MOMENT TENSOR ANALYSIS USING FIRST MOTION DATA AT
An Open Air Museum. Success breeds Success. Depth Imaging; Microseismics; Dip analysis. The King of Giant Fields WESTERN NEWFOUNDLAND:
 VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 GEOSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINED GEO EXPRO VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 Success breeds Success geoexpro.com Country Profile: Senegal Ocean Bottom Node Seismic WESTERN NEWFOUNDLAND: An Open Air
VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 GEOSCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINED GEO EXPRO VOL. 7, NO. 4 2010 Success breeds Success geoexpro.com Country Profile: Senegal Ocean Bottom Node Seismic WESTERN NEWFOUNDLAND: An Open Air
The Unique Source Mechanism of an Explosively Induced Mine Collapse
 The Unique Source Mechanism of an Explosively Induced Mine Collapse Xiaoning Yang, Brian W. Stump, W. Scott Phillips Geophysics Group - EES-3, Los Alamos National Laboratory Contract No. W-7405-ENG-36
The Unique Source Mechanism of an Explosively Induced Mine Collapse Xiaoning Yang, Brian W. Stump, W. Scott Phillips Geophysics Group - EES-3, Los Alamos National Laboratory Contract No. W-7405-ENG-36
Oil and natural gas production from shale formations
 SPECIAL Passive SECTION: seismic Pand a s s ive microseismic Part and microseismic Part 2 2 Source characteristics of seismicity associated with underground wastewater disposal: A case study from the 2008
SPECIAL Passive SECTION: seismic Pand a s s ive microseismic Part and microseismic Part 2 2 Source characteristics of seismicity associated with underground wastewater disposal: A case study from the 2008
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013310 A.M. Thomas et al. MOMENT TENSOR SOLUTIONS SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Earthquake records were acquired from the Northern California Earthquake Data Center. Waveforms are corrected
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013310 A.M. Thomas et al. MOMENT TENSOR SOLUTIONS SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Earthquake records were acquired from the Northern California Earthquake Data Center. Waveforms are corrected
Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting , Birmensdorf, Switzerland
 Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting 14 15.09.2017, Birmensdorf, Switzerland J. Doetsch, F. Amann, V. Gischig, M. Jalali, H. Krietsch, B. Valley, C.
Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting 14 15.09.2017, Birmensdorf, Switzerland J. Doetsch, F. Amann, V. Gischig, M. Jalali, H. Krietsch, B. Valley, C.
Identifying faults and fractures using source mechanism inversion, b values, and energy release rates
 Identifying faults and fractures using source mechanism inversion, b values, and energy release rates Abstract: Identifying and differentiating between fracture stimulation and fault activation is critical
Identifying faults and fractures using source mechanism inversion, b values, and energy release rates Abstract: Identifying and differentiating between fracture stimulation and fault activation is critical
Characterisation of Acoustic Emission Sources in a Rock Salt Specimen under Triaxial Load
 Characterisation of Acoustic Emission Sources in a Rock Salt Specimen under Triaxial Load Gerd Manthei Gesellschaft für Materialprüfung und Geophysik Dieselstraße 6a, D-61239 Ober-Mörlen, Germany Phone.-
Characterisation of Acoustic Emission Sources in a Rock Salt Specimen under Triaxial Load Gerd Manthei Gesellschaft für Materialprüfung und Geophysik Dieselstraße 6a, D-61239 Ober-Mörlen, Germany Phone.-
Stress Orientations Obtained from Earthquake Focal Mechanisms: What Are Appropriate Uncertainty Estimates?
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91, 2, pp. 250 262, April 2001 Stress Orientations Obtained from Earthquake Focal Mechanisms: What Are Appropriate Uncertainty Estimates? by Jeanne L.
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91, 2, pp. 250 262, April 2001 Stress Orientations Obtained from Earthquake Focal Mechanisms: What Are Appropriate Uncertainty Estimates? by Jeanne L.
Stress Damage in Borehole and Rock Cores; Developing New Tools to Update the Stress Map of Alberta
 Stress Damage in Borehole and Rock Cores; Developing New Tools to Update the Stress Map of Alberta Qing Jia, University of Alberta, Edmonton qjia@ualberta.ca and Randy Kofman, University of Alberta, Edmonton
Stress Damage in Borehole and Rock Cores; Developing New Tools to Update the Stress Map of Alberta Qing Jia, University of Alberta, Edmonton qjia@ualberta.ca and Randy Kofman, University of Alberta, Edmonton
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is currently one of
 SPECIAL 2 SECTION: C O 2 Passive seismic monitoring of carbon dioxide storage at Weyburn JAMES P. VERDON and J-MICHAEL KENDALL, University of Bristol DON J. WHITE, Geological Survey of Canada DOUG A. ANGUS
SPECIAL 2 SECTION: C O 2 Passive seismic monitoring of carbon dioxide storage at Weyburn JAMES P. VERDON and J-MICHAEL KENDALL, University of Bristol DON J. WHITE, Geological Survey of Canada DOUG A. ANGUS
Stimulated Fractured Reservoir DFN Models Calibrated with Microseismic Source Mechanisms
 ARMA 10-520 Stimulated Fractured Reservoir DFN Models Calibrated with Microseismic Source Mechanisms Williams-Stroud, S. C. and Eisner, L. MicroSeismic, Inc., Houston, TX, USA Copyright 2010 ARMA, American
ARMA 10-520 Stimulated Fractured Reservoir DFN Models Calibrated with Microseismic Source Mechanisms Williams-Stroud, S. C. and Eisner, L. MicroSeismic, Inc., Houston, TX, USA Copyright 2010 ARMA, American
EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE MECHANISMS SHOW MOTION
 6-1 6: EARTHQUAKE FOCAL MECHANISMS AND PLATE MOTIONS Hebgen Lake, Montana 1959 Ms 7.5 1 Stein & Wysession, 2003 Owens Valley, California 1872 Mw ~7.5 EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE
6-1 6: EARTHQUAKE FOCAL MECHANISMS AND PLATE MOTIONS Hebgen Lake, Montana 1959 Ms 7.5 1 Stein & Wysession, 2003 Owens Valley, California 1872 Mw ~7.5 EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE
Geo736: Seismicity along mid-ocean ridges
 Geo736: Seismicity along mid-ocean ridges Course Notes: S. G. Wesnousky Spring 2018 Bathymetric maps show the ocean basins of the world are characteristically divided by a bathymetric ridge. The bathymetric
Geo736: Seismicity along mid-ocean ridges Course Notes: S. G. Wesnousky Spring 2018 Bathymetric maps show the ocean basins of the world are characteristically divided by a bathymetric ridge. The bathymetric
Force and Stress. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/ :35 PM
 Force and Stress Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/2017 12:35 PM We Discuss Force and Stress Force and Units (Trigonometry) Newtonian
Force and Stress Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/9/2017 12:35 PM We Discuss Force and Stress Force and Units (Trigonometry) Newtonian
Call for Papers. Hydraulic Fracturing Special Issue
 Call for Papers Hydraulic Fracturing Special Issue Hydraulic fracturing of ultra-low and low permeability reservoirs has become the hottest energy-related topic within the oil and gas community as well
Call for Papers Hydraulic Fracturing Special Issue Hydraulic fracturing of ultra-low and low permeability reservoirs has become the hottest energy-related topic within the oil and gas community as well
