SEG/San Antonio 2007 Annual Meeting. γ Q in terms of complex-valued weaknesses that relates
|
|
|
- Ambrose Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chichinina* G Ronquillo-Jarillo abinin nstituto Mexicano del etróleo; Obolentseva L Gik and B Bobrov nstitute of etroleum Geology and Geophysics of iberian Branch of Russian Academy of ciences ummary We perform an ultrasonic experiment on anisotropy of wave propagation in the model constructed from plexiglas plates with oil saturation and without any saturation We determine the directional dependencies of - and -waves attenuations and velocities and estimate homsen-style parameters for attenuation ε and γ as well as homsen s velocity parameters We develop a theory that predicts certain relationship between anisotropies of - H- and -wave attenuation and velocity in transversely isotropic () media due to aligned fracture set aking into account the interplay of the velocity and attenuation anisotropies we develop the effective model of the attenuative fractured medium fitted to the experimental data We derive formulas for the parameters ε and γ in terms of complex-valued weaknesses that relates these parameters to fractured medium parameters We found out that the ratio of the symmetry-axis - and -wave attenuations / and the parameter are interlinked and strongly dependent of the fluid type in cracks that is confirmed by the experiment he value of is much greater for dry-crack medium than for wet-crack medium that is correlated with the / -ratio which is on the contrary larger in wet-crack medium and smaller in drycrack medium his is in accordance with laboratory measurements at ultrasonic frequencies of - and -wave quality factors ntroduction owadays reliable seismic data on -anisotropy is in very short supply; there are only few recent works eg asconselos & Jenner (005) Maultzsch et al (005) and arela et al (006) As for ultrasonic laboratory data there are some petrophysical experiments on -anisotropy where attenuation of - and -waves is measured at two orthogonal directions (eg Yin and ur 99; rasad and ur 003; Best 994) n order to obtain the reliable estimates of -anisotropy for attenuative medium one needs to know the values of - - and H-wave attenuations in the full interval of incidence angles i e from 0 to 90 with the symmetry axis here are few ultrasonic experiments with artificial plate models on - wave attenuation anisotropy for wide range of propagation angles (eg Hosten et al 987; Zhu et al 007) Ultrasonic experiments on -anisotropy for all three types of waves and H in the full interval of wave incidence angles in medium are close to be absent n the presented experiment we get attenuations and velocities for - and H-waves Joint analysis of the data for - - and H-wave attenuations and velocities provides the information for the proper reconstruction of the attenuation-anisotropy properties of the model Joint inversion of all the attenuations and velocities enables estimating homsen-style (homsen 986) parameters for attenuation ε and γ which were introduced by Zhu & svankin (006) We derive formulas for the directionally dependent attenuation and the attenuation parameters in terms of complex-valued weaknesses that relate these parameters to fractured-medium properties (Chichinina et al 004; 005; 006a; 006b) We are going to reveal the new sense of the parameter which is close to be meaningful for fracture characterization in seismic exploration heoretical background o describe anisotropy in attenuative medium (due to a single set of fractures) we introduce complex-valued stiffness matrix We rewrite the elastic stiffness matrix { C ij } given in the form of choenberg and ayers (995 p 07) and get the following complex-valued stiffness matrix { C ij } for medium with vertical symmetry axis (): L K ( ); ( ); K λ ξ λ K L J C ij L M ( ξ ); µ ( ); J M ( ); R µ R where () are complex-valued weaknesses which and were generated from the real-valued weaknesses in the following manner: and i i () see also (MacBeth 999) n equation () λ µ are the Lame s constants in the background rock M λ + µ ξ λ M g and g is defined as g µ /( λ + µ ) ( / ) where and are -wave and -wave velocities in the background rock n equation () and are the normal and tangential weaknesses (Bakulin et al 000) which weaken the isotropic background rock due to the presence of fractures ( 0 < < 0 < < ) EG/an Antonio 007 Annual Meeting 49
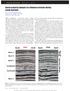
2 We describe the anisotropy of attenuation by the matrix of the inverse quality factor that is { ij } which can be expressed (Carcione 000) as mc ij ij (3) ReCij where { C ij } is the complex-valued stiffness matrix given by equation () hen the matrix { ij } for the attenuative medium can be written as ξ L K J K ; ξ K L J ξ L ; J J J ξ ij J ; ; (4) Following choenberg and Douma (988) we express the -wave velocity (α ) as ( ) ( [ sin ] sin α g α g α ) (5) the -wave velocity (α ) as ( ( g )sin α ) (6) and the H-wave velocity H (α ) as H ( cos α) (7) where α is measured relatively the symmetry axis z We define attenuation (Carcione 000) as m( ) Re( ) (8) where is complex-valued phase velocity and then can be written as Re( ) + i m( ) Within equations (5)-(7) we replace the weaknesses and with the complex-valued weaknesses and following equation () o we get complex-valued ( α ) H and ( ) hen we separate the imaginary and real parts m( ) and Re( ) and derive the attenuation following equation (8) By this manner we get the - - and H-wave attenuation as ( [ g sin α ] + g sin α α ) [ g sin α ] g sin α (9) + ( g )sin α ( g )sin α (0) cos α ( α ) () cos α H Experiment versus theory he model is constructed from rectangular plexiglas plates each mm thick which were held on together by compressing uniaxial pressure Ma here is periodic variability of plate thickness (from 00 to 03 mm) with the spatial period of 0 mmt is assumed that attenuation is due to linear slip interfaces between the plates he ultrasonic experiment was performed for two models with oil saturation and without any saturation ( dry model ) he experimental data on the - - and H-wave velocity and attenuation is presented in Figure (marked by symbols) for the dry model (a c) and the oil-saturated model (b d) he angle α is measured relatively the symmetry axis z ote that only the restricted α -angle range from 45 to 90 is available in the experiment (see details in Gik & Bobrov (996)) heory-predicted attenuation and velocity Figure (a-b) shows phase velocities (α ) (α ) and H (α ) calculated from equations (5)-(7) with the model-input parameters ( and ) from able Figure (c-d) shows the corresponding curves for attenuation ( α ) ( α ) and ( α ) calculated from equations (9)-() H with the model-input parameters ( and ) given in ables - homsen-style approximation curves are shown by dotted line o describe the shear-wave attenuation and ( α H ) observed in the experiment we have to introduce the O isotropic attenuation ( ) hen equations (0) and () for and ( α H ) should be corrected as O ( α ) ( α ) + ( ) () O H ( α ) H + ( ) (3) O where ( ) in the oil-saturated model and ( ) O 003 in the dry model able Model-input parameters for velocity ε γ We found out certain theory-predicted interrelationships between the - and -wave velocities and attenuations in terms of the weaknesses that enabled us Oil Dry n Oil-saturated and Dry models the host-rock velocities 680 m/s 340 m/s and g ( ) 0 5 able Model-input parameters for attenuation γ ε Oil Dry EG/an Antonio 007 Annual Meeting 50
3 Figure Experimental data (marked by symbols) and theoretical curves for the - - and H-wave velocity (α ) (a b) and attenuation (c d); for the dry model (a c) and the oil-saturated model (b d) he angle α is measured relatively the symmetry axis For - and H-wave attenuation is calculated from equations (9) () and (3) elocity (α ) is calculated from equations (5) (6) and (7) (solid line) Model-input parameters are given in ables homsen-style approximation for and (α ) is marked by dotted line with the anisotropy parameters given in ables to get the corrected (mutually compatible) values of the - and -wave symmetry-axis velocities and attenuations from the experimental data (Because of the lack of data at the angles α from 0 to 45 the straightforward estimation of the symmetry-axis velocities was unavailable) Following the theory we have substantially corrected the velocities especially the H-wave velocity H (α ) in the case of the dry-crack model; that is why it occurred to be not wellsuited to the experimental data as it is shown in Figure (a) for the dry model he same takes place in the case of the attenuation curves shown in Figure (d) for the oilsaturated models homsen-style parameters for attenuation Following Zhu & svankin (006) we write homsenstyle anisotropy parameters for attenuation as ε γ H 05 d ( α ) dα α 0 where the symbol marks the direction of wave propagation normal to fracture planes (that is the symmetry-axis direction) and the symbol marks the direction parallel to fracture planes (that is the isotropyplane direction) n terms of the matrix { ij } and H 66 For the -wave attenuation homsen-style approximation can be written (Zhu and svankin 006) as 4 [ + sin α + ( ε )sin α] (4) We found out that ε is independent of the attenuation: ε ( ) ) (5) On the contrary the parameter does depend on the attenuation: EG/an Antonio 007 Annual Meeting 5
4 4 (6) Following approximations of Zhu and svankin (006) we define the H-wave attenuation as ( + γ sin α) (7) H where the γ -value is given in able he -wave attenuation is ( + σ sin α ) (8) 4 where the parameter σ was estimated as 55 for the dry model and σ -6 for the oil-saturated model Following the sign of σ (plus or minus) the -wave attenuation curve shown in Figure (c) turns its pattern from the convex (for the dry model) to the concave (for the oil-saturated model) Figure (d)) Unfortunately to corroborate this we have not got any reliable experimental data for -wave attenuation in the case of the dry model ote that in equations (7) and (8) the -value given in able should be corrected for the isotropic attenuation O ( ) following equations () (3) -anisotropy in the oil-saturated and dry models We found out that neither ε no γ can serve for distinguishing dry cracks from oil-saturated Moreover the velocity parameter ε is much more sensitive to the fluidfill type in cracks than the attenuation parameter ε Besides we found out the essential difference in the symmetry-axis - and -wave attenuations and in the oil-saturated and dry models Actually after oil saturation the -wave attenuation increases: OL ( ) ( ) 4 6 but at the same time the -wave attenuation decreases: OL ( ) ( ) 0 34 his resulted in the essential contrast in -values for the oil-saturated and dry models that is OL 7 Actually it follows from equation (6) that can be defined by the relative difference between - and -wave attenuations and : ( ) (9) if assumed / 0 5 in equation (6) hus the essential difference in -values for the oilsaturated and dry models is caused by the great change in the / -value for the oil-saturated and dry models ( ) OL ( ) 4 hus we found out that the symmetry-axis- -ratio is much larger in a wet-crack medium than in a dry-crack medium ( ) WE ( ) >> his is in accordance to laboratory measurements at ultrasonic frequencies of - and -wave quality factors (oksöz et al 979) as well as attenuation data from sonic logs (Klimentos 995) that WE show ( ) ( ) / > / (ote that / / ) n particular they have observed / > for wet rocks (with water or brine) and / < for dry (or gassaturated) rocks Conclusions he experimental data was used as an illustration material for the theory application We managed with the lack of data at the angles from 0 to 45 to the symmetry axis this situation is similar to that which takes place in the case of seismic reflection data in frames of H model he behavior of - - and H-wave attenuation as a function of the wave-propagation direction is similar in common to the well known directional dependences for the velocities in medium he attenuation curves are alike the velocity curves according to the principle the maximum of velocity curve corresponds to the minimum of attenuation curve and vice versa Attenuation anisotropy is much stronger than velocity anisotropy For example in the oil-saturated model the - wave velocity anisotropy is 4% but the anisotropy of attenuation is much greater 5% n real seismic data the -wave velocity anisotropy caused by liquid-saturated cracks is very small and hardly can be used for seismic exploration However the -wave attenuation anisotropy is rather strong and can be used in fracture characterization for estimation of fracture direction in reservoir rocks from azimuthally varying Examples are in asconselos & Jenner (005) Maultzsch et al (005) arela et al (006) and Chichinina et al ( a 006b) We found out that the ratio of the symmetry-axis - and - wave attenuations / and the parameter are interlinked and strongly dependent of the fluid type in cracks that is confirmed by our ultrasonic experiment herefore we believe that analysis of -anisotropy may get potential use for seismic exploration for example the analysis of versus offset (O) in seismic reflection data he value of estimated by means of the O analysis may serve as an indicator of the crack-fill fluid due to its link to the parameter / An estimate of / ( / < or / >) may provide an additional information for fracture-reservoir characterization (oksöz et al (979) Klimentos (995) Winkler (979) iwari and McMechan (003) and Batzle et al (005)) EG/an Antonio 007 Annual Meeting 5
5 EDED REFERECE ote: his reference list is a copy-edited version of the reference list submitted by the author Reference lists for the 007 EG echnical rogram Expanded Abstracts have been copy edited so that references provided with the online metadata for each paper will achieve a high degree of linking to cited sources that appear on the Web REFERECE Bakulin A Grechka and svankin 000 Estimation of fracture parameters from reflection seismic data art : H model due to a single fracture set: Geophysics Batzle M R Hofmann M rasad G Kumar L Duranti and H De-Hua 005 eismic attenuation: Observations and mechanisms: 75th Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts Best A 994 eismic attenuation anisotropy in reservoir sedimentary rocks: 64th Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts 8 85 Carcione J M 000 A model for seismic velocity and attenuation in petroleum source rocks: Geophysics Chichinina abinin and G Ronquillo-Jarillo 004 -wave attenuation anisotropy in fracture characterization: umerical modeling for reflection data: 74th Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts OA analysis as an instrument for fracture characterization: 75th Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts a OA analysis: -wave attenuation anisotropy for fracture characterization: Geophysics 7 no 3 C37 C48 Chichinina abinin G Ronquillo-Jarillo R Obolentseva 006b Azimuthal O analysis applied to oil and gas exploration: Russian Geology and Geophysics Gik L D and B A Bobrov 996 Experimental laboratory study of anisotropy for thin-layered media: Russian Geology and Geophysics Hosten B M Deschamps and B R ittmann 987 nhomogeneous wave generation and propagation in lossy anisotropic solids: Application to the characterization of viscoelastic composite materials: Journal of the Acoustical ociety of America Klimentos 995 Attenuation of - and -waves as a method of distinguishing gas and condensate from oil and water: Geophysics Macbeth C 999 Azimuthal variation in -wave signatures due to fluid flow: Geophysics Maultzsch M Chapman E Liu and X Y Li 005 Observation and modeling of anisotropic attenuation in data: 75th Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts 3 34 rasad M and A ur 003 elocity and attenuation anisotropy in reservoir rocks: 73rd Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts choenberg M and J Douma 988 Elastic wave propagation in media with parallel fractures and aligned cracks: Geophysical rospecting choenberg M and C M ayers 995 eismic anisotropy of fractured rock: Geophysics homsen L 986 Weak elastic anisotropy: Geophysics iwari U K and G A McMechan 003 Estimation of water/gas saturation and effective pressure from seismic velocities and quality factors as function of frequency: redictions of an empirical model: Journal of eismic Exploration oksöz M D H Jounston and A imur 979 Attenuation of seismic waves in dry and saturated rocks: Laboratory and measurements: Geophysics arela M asser M Chapman and E Liu 006 Anisotropic azimuthal attenuation as an indicator of fracture properties a case study on time-lapse walkaround data: 68th Annual Conference and Exhibition EAGE 46 asconcelos and E Jenner 005 Estimation of azimuthally varying attenuation from wide-azimuth -wave data: 75th Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts 3 6 Winkler K W 979 he effects of pore fluids and frictional sliding on seismic attenuation: hd thesis tanford University Yin H and A ur 99 tress-induced ultrasonic velocity and attenuation anisotropy of rocks: 6nd Annual nternational Meeting EG Expanded Abstracts Zhu Y and svankin 006 lane-wave propagation in attenuative transversely isotropic media: Geophysics 7 no 7 30 Zhu Y svankin Dewangan and K van Wijk 007 hysical modeling and analysis of -wave attenuation anisotropy in transversely isotropic media: Geophysics 7 no D D7 EG/an Antonio 007 Annual Meeting 53
Estimation of fractured weaknesses and attenuation factors from azimuthal seismic data
 Estimation of fractured weaknesses and attenuation factors from azimuthal seismic data Huaizhen Chen and Kris Innanen CREWES project Department of Geoscience University of Calgary Summary Seismic wave
Estimation of fractured weaknesses and attenuation factors from azimuthal seismic data Huaizhen Chen and Kris Innanen CREWES project Department of Geoscience University of Calgary Summary Seismic wave
QVOA analysis: P-wave attenuation anisotropy for fracture characterization
 GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 7, NO. 3 MAY-JUNE 2006 ; P. C37 C48, FGS., 2 TABLES. 0.90/.29453 QVOA analysis: P-wave attenuation anisotropy for fracture characterization Tatiana Chichinina, Vladimir Sabinin, and Gerardo
GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 7, NO. 3 MAY-JUNE 2006 ; P. C37 C48, FGS., 2 TABLES. 0.90/.29453 QVOA analysis: P-wave attenuation anisotropy for fracture characterization Tatiana Chichinina, Vladimir Sabinin, and Gerardo
Anisotropy of Seismic Attenuation in Fractured Media: Theory and Ultrasonic Experiment
 Transp orous Med (2009) 79:1 14 DOI 10.1007/s11242-008-9233-9 Anisotropy of Seismic Attenuation in Fractured Media: Theory and Ultrasonic Experiment T. I. Chichinina I. R. Oolentseva G. Ronquillo-Jarillo
Transp orous Med (2009) 79:1 14 DOI 10.1007/s11242-008-9233-9 Anisotropy of Seismic Attenuation in Fractured Media: Theory and Ultrasonic Experiment T. I. Chichinina I. R. Oolentseva G. Ronquillo-Jarillo
Downloaded 08/30/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Modeling the effect of pores and cracks interactions on the effective elastic properties of fractured porous rocks Luanxiao Zhao*, De-hua Han, Qiuliang Yao and Fuyong Yan, University of Houston; Mosab
Modeling the effect of pores and cracks interactions on the effective elastic properties of fractured porous rocks Luanxiao Zhao*, De-hua Han, Qiuliang Yao and Fuyong Yan, University of Houston; Mosab
Effects of Fracture Parameters in an Anisotropy Model on P-Wave Azimuthal Amplitude Responses
 PROC. ITB Eng. Science Vol. 38 B, No. 2, 2006, 159-170 159 Effects of Fracture Parameters in an Anisotropy Model on P-Wave Azimuthal Amplitude Responses Fatkhan Program Studi Teknik Geofisika FIKTM-ITB
PROC. ITB Eng. Science Vol. 38 B, No. 2, 2006, 159-170 159 Effects of Fracture Parameters in an Anisotropy Model on P-Wave Azimuthal Amplitude Responses Fatkhan Program Studi Teknik Geofisika FIKTM-ITB
CHARACTERIZATION OF SATURATED POROUS ROCKS WITH OBLIQUELY DIPPING FRACTURES. Jiao Xue and Robert H. Tatham
 CHARACTERIZATION OF SATURATED POROUS ROCS WITH OBLIQUELY DIPPING FRACTURES Jiao Xue and Robert H. Tatham Department of Geological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin ABSTRACT Elastic properties,
CHARACTERIZATION OF SATURATED POROUS ROCS WITH OBLIQUELY DIPPING FRACTURES Jiao Xue and Robert H. Tatham Department of Geological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin ABSTRACT Elastic properties,
P191 Bayesian Linearized AVAZ Inversion in HTI Fractured Media
 P9 Bayesian Linearized AAZ Inversion in HI Fractured Media L. Zhao* (University of Houston), J. Geng (ongji University), D. Han (University of Houston) & M. Nasser (Maersk Oil Houston Inc.) SUMMARY A new
P9 Bayesian Linearized AAZ Inversion in HI Fractured Media L. Zhao* (University of Houston), J. Geng (ongji University), D. Han (University of Houston) & M. Nasser (Maersk Oil Houston Inc.) SUMMARY A new
6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling
 6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling M. Brajanovski* (Curtin University of Technology), B. Gurevich (Curtin University of Technology), D. Nadri (CSIRO) & M. Urosevic (Curtin
6298 Stress induced azimuthally anisotropic reservoir - AVO modeling M. Brajanovski* (Curtin University of Technology), B. Gurevich (Curtin University of Technology), D. Nadri (CSIRO) & M. Urosevic (Curtin
Estimation of interval anisotropic attenuation from reflection data
 GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 74, NO. 6 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 9 ; P. A69 A74, 7 FGS..9/.39733 Estimation of interval anisotropic attenuation from reflection data Jyoti Behura and lya Tsvankin ABSTRACT Knowledge of interval
GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 74, NO. 6 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 9 ; P. A69 A74, 7 FGS..9/.39733 Estimation of interval anisotropic attenuation from reflection data Jyoti Behura and lya Tsvankin ABSTRACT Knowledge of interval
Attenuation anisotropy in the linear-slip model: Interpretation of physical modeling data
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 74, NO. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2009 ; P. WB165 WB176, 12 FIGS., 2 TABLES. 10.1190/1.3173806 Attenuation anisotropy in the linear-slip model: Interpretation of physical modeling data Tatiana
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 74, NO. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2009 ; P. WB165 WB176, 12 FIGS., 2 TABLES. 10.1190/1.3173806 Attenuation anisotropy in the linear-slip model: Interpretation of physical modeling data Tatiana
Waveform inversion for attenuation estimation in anisotropic media Tong Bai & Ilya Tsvankin Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines
 Waveform inversion for attenuation estimation in anisotropic media Tong Bai & Ilya Tsvankin Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Robust estimation of attenuation coefficients remains
Waveform inversion for attenuation estimation in anisotropic media Tong Bai & Ilya Tsvankin Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Robust estimation of attenuation coefficients remains
Summary. Simple model for kerogen maturity (Carcione, 2000)
 Malleswar Yenugu* and De-hua Han, University of Houston, USA Summary The conversion of kerogen to oil/gas will build up overpressure. Overpressure is caused by conversion of solid kerogen to fluid hydrocarbons
Malleswar Yenugu* and De-hua Han, University of Houston, USA Summary The conversion of kerogen to oil/gas will build up overpressure. Overpressure is caused by conversion of solid kerogen to fluid hydrocarbons
Azimuthal AVO and Curvature. Jesse Kolb* David Cho Kris Innanen
 Azimuthal AVO and Curvature Jesse Kolb* David Cho Kris Innanen Azimuthal AVO What is azimuthal AVO?: Analysis of incidence angle and azimuthal amplitude variations of reflection coefficients; Measures
Azimuthal AVO and Curvature Jesse Kolb* David Cho Kris Innanen Azimuthal AVO What is azimuthal AVO?: Analysis of incidence angle and azimuthal amplitude variations of reflection coefficients; Measures
Physical modeling and analysis of P-wave attenuation anisotropy in transversely isotropic media
 GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 72, NO. 1 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 27 ; P. D1 D7, 8 FGS. 1.119/1.2374797 Physical modeling and analysis of P-wave attenuation anisotropy in transversely isotropic media Yaping Zhu 1, lya Tsvankin
GEOPHYSCS, VOL. 72, NO. 1 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 27 ; P. D1 D7, 8 FGS. 1.119/1.2374797 Physical modeling and analysis of P-wave attenuation anisotropy in transversely isotropic media Yaping Zhu 1, lya Tsvankin
Seismic inversion for the parameters of two orthogonal fracture sets in a VTI background medium
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 67, NO. 1 (JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2002); P. 292 299, 3 FIGS. 10.1190/1.1451801 Seismic inversion for the parameters of two orthogonal fracture sets in a VTI background medium Andrey Bakulin,
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 67, NO. 1 (JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2002); P. 292 299, 3 FIGS. 10.1190/1.1451801 Seismic inversion for the parameters of two orthogonal fracture sets in a VTI background medium Andrey Bakulin,
Numerical Modeling for Different Types of Fractures
 umerical Modeling for Different Types of Fractures Xiaoqin Cui* CREWES Department of Geoscience University of Calgary Canada xicui@ucalgary.ca and Laurence R. Lines Edward S. Krebes Department of Geoscience
umerical Modeling for Different Types of Fractures Xiaoqin Cui* CREWES Department of Geoscience University of Calgary Canada xicui@ucalgary.ca and Laurence R. Lines Edward S. Krebes Department of Geoscience
Stress induced seismic velocity anisotropy study Bin Qiu, Mita Sengupta, Jorg Herwanger, WesternGeco/Schlumberger
 anisotropy study Bin Qiu, Mita Sengupta, Jorg Herwanger, WesternGeco/Schlumberger Summary A method of calculating stress induced seismic velocity anisotropy is presented and studied. In a first step an
anisotropy study Bin Qiu, Mita Sengupta, Jorg Herwanger, WesternGeco/Schlumberger Summary A method of calculating stress induced seismic velocity anisotropy is presented and studied. In a first step an
SEG/New Orleans 2006 Annual Meeting
 On the applicability of Gassmann model in carbonates Ravi Sharma*, Manika Prasad and Ganpat Surve (Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay), G C Katiyar (Third Eye Centre, Oil and Natural Gas Corporation
On the applicability of Gassmann model in carbonates Ravi Sharma*, Manika Prasad and Ganpat Surve (Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay), G C Katiyar (Third Eye Centre, Oil and Natural Gas Corporation
The title of my presentation is Constraints on C13 for shales. -2-
 1-1- 1. The title of my presentation is Constraints on C13 for shales. -2-2. Outline: C13 in shales and physical models. Different Poisson's ratios in VTI rock. Compliance tensor for VTI shale. 2-3- 3.It
1-1- 1. The title of my presentation is Constraints on C13 for shales. -2-2. Outline: C13 in shales and physical models. Different Poisson's ratios in VTI rock. Compliance tensor for VTI shale. 2-3- 3.It
GEOPHYSICAL PROSPECTING: DYNAMIC RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION AND TIME-LAPSE MULTICOMPONENT SEISMOLOGY FOR RESERVOIR MONITORING UNESCO EOLSS
 GEOPHYSICAL PROSPECTING: DYNAMIC RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION AND TIME-LAPSE MULTICOMPONENT SEISMOLOGY FOR RESERVOIR MONITORING Steven L. Roche CGGVeritas, Multicomponent Processing & Technology Group Thomas
GEOPHYSICAL PROSPECTING: DYNAMIC RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION AND TIME-LAPSE MULTICOMPONENT SEISMOLOGY FOR RESERVOIR MONITORING Steven L. Roche CGGVeritas, Multicomponent Processing & Technology Group Thomas
Laboratory Measurements of P-wave and S-wave Anisotropy in Synthetic Sandstones with Controlled Fracture Density
 Laboratory Measurements of P-wave and S-wave Anisotropy in Synthetic Sandstones with Controlled Fracture Density P.B. Ding* (China University of Petroleum), B.R. Di (China University of Petroleum), J.X.
Laboratory Measurements of P-wave and S-wave Anisotropy in Synthetic Sandstones with Controlled Fracture Density P.B. Ding* (China University of Petroleum), B.R. Di (China University of Petroleum), J.X.
ATTENUATION CHARACTERISTICS OF SAUDI ARABIAN RESERVOIR SANDSTONE AND LIMESTONE CORES
 ATTENUATION CHARACTERISTICS OF SAUDI ARABIAN RESERVOIR SANDSTONE AND LIMESTONE CORES M. A. Mohiuddin 1, G. Korvin 2, A. Abdulraheem 1, and K. Khan 1 1 Center for Petroleum & Minerals, The Research Institute.
ATTENUATION CHARACTERISTICS OF SAUDI ARABIAN RESERVOIR SANDSTONE AND LIMESTONE CORES M. A. Mohiuddin 1, G. Korvin 2, A. Abdulraheem 1, and K. Khan 1 1 Center for Petroleum & Minerals, The Research Institute.
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study
 AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian*, Gary F. Margrave, and Joe Wong, University of Calgary. CREWES fmahmoud@ucalgary.ca Summary We present
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian*, Gary F. Margrave, and Joe Wong, University of Calgary. CREWES fmahmoud@ucalgary.ca Summary We present
Anisotropic velocity changes in seismic time-lapse data Jorg Herwanger*, Ed Palmer (WesternGeco), Christian Rau Schiøtt (Hess)
 Anisotropic velocity changes in seismic time-lapse data Jorg Herwanger*, Ed Palmer (WesternGeco), Christian Rau Schiøtt (Hess) Summary Reservoir production causes subsurface deformations and changes in
Anisotropic velocity changes in seismic time-lapse data Jorg Herwanger*, Ed Palmer (WesternGeco), Christian Rau Schiøtt (Hess) Summary Reservoir production causes subsurface deformations and changes in
Stress-induced transverse isotropy in rocks
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 318 Stress-induced transverse isotropy in rocks Lawrence M. Schwartz, 1 William F. Murphy, III, 1 and James G. Berryman 1 ABSTRACT The application
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 318 Stress-induced transverse isotropy in rocks Lawrence M. Schwartz, 1 William F. Murphy, III, 1 and James G. Berryman 1 ABSTRACT The application
Effects of VTI Anisotropy in Shale-Gas Reservoir Characterization
 P-014 Summary Effects of VTI Anisotropy in Shale-Gas Reservoir Characterization Niranjan Banik* and Mark Egan, WesternGeco Shale reservoirs are one of the hottest plays in the oil industry today. Our understanding
P-014 Summary Effects of VTI Anisotropy in Shale-Gas Reservoir Characterization Niranjan Banik* and Mark Egan, WesternGeco Shale reservoirs are one of the hottest plays in the oil industry today. Our understanding
Some consideration about fluid substitution without shear wave velocity Fuyong Yan*, De-Hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston
 ain enu Some consideration about fluid substitution without shear wave velocity Fuyong Yan*, De-Hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary When S-wave velocity is absent, approximate Gassmann
ain enu Some consideration about fluid substitution without shear wave velocity Fuyong Yan*, De-Hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary When S-wave velocity is absent, approximate Gassmann
2011 SEG SEG San Antonio 2011 Annual Meeting 771. Summary. Method
 Geological Parameters Effecting Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Feasibility: A North Sea Sand Reservoir Example Michelle Ellis and Robert Keirstead, RSI Summary Seismic and electromagnetic data measure
Geological Parameters Effecting Controlled-Source Electromagnetic Feasibility: A North Sea Sand Reservoir Example Michelle Ellis and Robert Keirstead, RSI Summary Seismic and electromagnetic data measure
Shear Wave Velocity Estimation Utilizing Wireline Logs for a Carbonate Reservoir, South-West Iran
 Iranian Int. J. Sci. 4(2), 2003, p. 209-221 Shear Wave Velocity Estimation Utilizing Wireline Logs for a Carbonate Reservoir, South-West Iran Eskandari, H. 1, Rezaee, M.R., 2 Javaherian, A., 3 and Mohammadnia,
Iranian Int. J. Sci. 4(2), 2003, p. 209-221 Shear Wave Velocity Estimation Utilizing Wireline Logs for a Carbonate Reservoir, South-West Iran Eskandari, H. 1, Rezaee, M.R., 2 Javaherian, A., 3 and Mohammadnia,
Fracture-porosity inversion from P-wave AVOA data along 2D seismic lines: An example from the Austin Chalk of southeast Texas
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 72, NO. 1 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2007 ; P. B1 B7, 7 FIGS., 3 TABLES. 10.1190/1.2399444 Fracture-porosity inversion from P-wave AVOA data along 2D seismic lines: An example from the Austin Chalk
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 72, NO. 1 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2007 ; P. B1 B7, 7 FIGS., 3 TABLES. 10.1190/1.2399444 Fracture-porosity inversion from P-wave AVOA data along 2D seismic lines: An example from the Austin Chalk
RESEARCH PROPOSAL. Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q. Yi Shen
 RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
RESEARCH PROPOSAL Effects of scales and extracting methods on quantifying quality factor Q Yi Shen 2:30 P.M., Wednesday, November 28th, 2012 Shen 2 Ph.D. Proposal ABSTRACT The attenuation values obtained
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales
 P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
P314 Anisotropic Elastic Modelling for Organic Shales X. Wu* (British Geological Survey), M. Chapman (British Geological Survey), X.Y. Li (British Geological Survey) & H. Dai (British Geological Survey)
Main Menu. Summary (1)
 Elastic roerty changes of bitumen reservoir during steam injection Ayato Kato*, University of Houston, higenobu Onozuka, JOGMEC, and Toru Nakayama, JAPEX ummary Elastic roerty changes of bitumen reservoir
Elastic roerty changes of bitumen reservoir during steam injection Ayato Kato*, University of Houston, higenobu Onozuka, JOGMEC, and Toru Nakayama, JAPEX ummary Elastic roerty changes of bitumen reservoir
Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs
 Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Worldwide interest
Workflows for Sweet Spots Identification in Shale Plays Using Seismic Inversion and Well Logs Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Worldwide interest
Recent advances in application of AVO to carbonate reservoirs: case histories
 Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
Recent advances in application of AVO to reservoirs: case histories Yongyi Li, Bill Goodway*, and Jonathan Downton Core Lab Reservoir Technologies Division *EnCana Corporation Summary The application of
A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC
 A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock hysics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC Summary Eaton s equation is the most popularly used
A new model for pore pressure prediction Fuyong Yan* and De-hua Han, Rock hysics Lab, University of Houston Keyin Ren, Nanhai West Corporation, CNOOC Summary Eaton s equation is the most popularly used
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study
 AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian and Gary F Margrave ABSTRACT AVAZ inversion We present a pre-stack amplitude inversion of P-wave data
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian and Gary F Margrave ABSTRACT AVAZ inversion We present a pre-stack amplitude inversion of P-wave data
LINK BETWEEN ATTENUATION AND VELOCITY DISPERSION
 LINK BETWEEN ATTENUATION AND VELOCITY DISPERSION Jack Dvorkin Stanford University and Rock Solid Images April 25, 2005 SUMMARY In a viscoelastic sample, the causality principle links the attenuation of
LINK BETWEEN ATTENUATION AND VELOCITY DISPERSION Jack Dvorkin Stanford University and Rock Solid Images April 25, 2005 SUMMARY In a viscoelastic sample, the causality principle links the attenuation of
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes
 Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
Reservoir properties inversion from AVO attributes Xin-gang Chi* and De-hua Han, University of Houston Summary A new rock physics model based inversion method is put forward where the shaly-sand mixture
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
 Frequency dependent elastic properties and attenuation in heavy-oil sands: comparison between measured and modeled data Agnibha Das, and Michael Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We have measured
Frequency dependent elastic properties and attenuation in heavy-oil sands: comparison between measured and modeled data Agnibha Das, and Michael Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We have measured
RP 2.6. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1521
 Ludmila Adam 1, Michael Batzle 1, and Ivar Brevik 2 1 Colorado School of Mines, 2 Statoil R&D Summary A set of carbonate plugs of different porosity, permeability, mineralogy and texture are measured at
Ludmila Adam 1, Michael Batzle 1, and Ivar Brevik 2 1 Colorado School of Mines, 2 Statoil R&D Summary A set of carbonate plugs of different porosity, permeability, mineralogy and texture are measured at
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AMPLITUDE VARIATION WITH OFFSET (AVO) IN FRACTURED MEDIA
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AMPLITUDE VARIATION WITH OFFSET AVO) IN FRACTURED MEDIA Mary L. Krasovec, William L. Rodi, and M. Nafi Toksoz Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AMPLITUDE VARIATION WITH OFFSET AVO) IN FRACTURED MEDIA Mary L. Krasovec, William L. Rodi, and M. Nafi Toksoz Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Measurement of elastic properties of kerogen Fuyong Yan, De-hua Han*, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston
 Measurement of elastic properties of kerogen Fuyong Yan, De-hua Han*, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary To have good understanding of elastic properties of organic shale, it is fundamental
Measurement of elastic properties of kerogen Fuyong Yan, De-hua Han*, Rock Physics Lab, University of Houston Summary To have good understanding of elastic properties of organic shale, it is fundamental
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE PETROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES VARIATIONS ON THE SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A CO2 STORAGE SITE. Juan E. Santos
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE PETROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES VARIATIONS ON THE SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A CO2 STORAGE SITE Juan E. Santos Instituto del Gas y del Petróleo, Facultad de Ingeniería UBA and Department
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF THE PETROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES VARIATIONS ON THE SEISMIC RESPONSE OF A CO2 STORAGE SITE Juan E. Santos Instituto del Gas y del Petróleo, Facultad de Ingeniería UBA and Department
SEG/San Antonio 2007 Annual Meeting SUMMARY DATA
 An experimental study of the dilation factor in sandstone under anisotropic stress conditions Arpita Pal-Bathija and Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Dilation factor (R) is defined as the
An experimental study of the dilation factor in sandstone under anisotropic stress conditions Arpita Pal-Bathija and Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Dilation factor (R) is defined as the
Temperature Dependence of Acoustic Velocities in Gas-Saturated Sandstones
 Temperature Dependence of Acoustic Velocities in Gas-Saturated Sandstones Andreas Bauer, Christian Lehr, Frans Korndorffer, Arjan van der Linden Shell Global Solutions International, Rijswijk. Netherlands
Temperature Dependence of Acoustic Velocities in Gas-Saturated Sandstones Andreas Bauer, Christian Lehr, Frans Korndorffer, Arjan van der Linden Shell Global Solutions International, Rijswijk. Netherlands
3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie Zhang, Wei Zhang, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC)
 Downloaded 01/03/14 to 16.01.198.34. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ 3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie
Downloaded 01/03/14 to 16.01.198.34. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ 3D VTI traveltime tomography for near-surface imaging Lina Zhang*, Jie
SUMMARY NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF BRINE-CO 2 FLOW AND WAVE PROPAGATION
 Sensitivity analysis of the petrophysical properties variations on the seismic response of a CO 2 storage site Juan E. Santos, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Facultad Ingeniería, Instituto del Gas y del
Sensitivity analysis of the petrophysical properties variations on the seismic response of a CO 2 storage site Juan E. Santos, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Facultad Ingeniería, Instituto del Gas y del
P235 Modelling Anisotropy for Improved Velocities, Synthetics and Well Ties
 P235 Modelling Anisotropy for Improved Velocities, Synthetics and Well Ties P.W. Wild* (Ikon Science Ltd), M. Kemper (Ikon Science Ltd), L. Lu (Ikon Science Ltd) & C.D. MacBeth (Heriot Watt University)
P235 Modelling Anisotropy for Improved Velocities, Synthetics and Well Ties P.W. Wild* (Ikon Science Ltd), M. Kemper (Ikon Science Ltd), L. Lu (Ikon Science Ltd) & C.D. MacBeth (Heriot Watt University)
Estimation of density from seismic data without long offsets a novel approach.
 Estimation of density from seismic data without long offsets a novel approach. Ritesh Kumar Sharma* and Satinder Chopra Arcis seismic solutions, TGS, Calgary Summary Estimation of density plays an important
Estimation of density from seismic data without long offsets a novel approach. Ritesh Kumar Sharma* and Satinder Chopra Arcis seismic solutions, TGS, Calgary Summary Estimation of density plays an important
Modeling seismic wave propagation during fluid injection in a fractured network: Effects of pore fluid pressure on time-lapse seismic signatures
 Modeling seismic wave propagation during fluid injection in a fractured network: Effects of pore fluid pressure on time-lapse seismic signatures ENRU LIU, SERAFEIM VLASTOS, and XIANG-YANG LI, Edinburgh
Modeling seismic wave propagation during fluid injection in a fractured network: Effects of pore fluid pressure on time-lapse seismic signatures ENRU LIU, SERAFEIM VLASTOS, and XIANG-YANG LI, Edinburgh
An efficient wave extrapolation method for tilted orthorhombic media using effective ellipsoidal models
 An efficient wave extrapolation method for tilted orthorhombic media using effective ellipsoidal models Item Type Conference Paper Authors Waheed Umair bin; Alkhalifah Tariq Ali Eprint version Pre-print
An efficient wave extrapolation method for tilted orthorhombic media using effective ellipsoidal models Item Type Conference Paper Authors Waheed Umair bin; Alkhalifah Tariq Ali Eprint version Pre-print
Geomechanics, Anisotropy and LMR
 Geomechanics, Anisotropy and LMR Marco Perez *, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada marco.perez@apachecorp.com Bill Goodway, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada bill.goodway@apachecorp.com David
Geomechanics, Anisotropy and LMR Marco Perez *, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada marco.perez@apachecorp.com Bill Goodway, Apache Canada Ltd, Calgary, AB, Canada bill.goodway@apachecorp.com David
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach
 Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Seismic characterization of Montney shale formation using Passey s approach Ritesh Kumar Sharma*, Satinder Chopra and Amit Kumar Ray Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary Summary Seismic characterization of
Seismic wave propagation in Kelvin visco-elastic VTI media*
 APPLIED GEOPHYSICS, Vol.7, No.4 (December 21), P. 368-375, 5 Figures. DOI: 1.17/s1177-1-256-y Seismic wave propagation in Kelvin visco-elastic VTI media* Lu Jun 1 and Wang Yun 2 Abstract: In this article,
APPLIED GEOPHYSICS, Vol.7, No.4 (December 21), P. 368-375, 5 Figures. DOI: 1.17/s1177-1-256-y Seismic wave propagation in Kelvin visco-elastic VTI media* Lu Jun 1 and Wang Yun 2 Abstract: In this article,
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc.
 Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Integrating rock physics and full elastic modeling for reservoir characterization Mosab Nasser and John B. Sinton*, Maersk Oil Houston Inc. Summary Rock physics establishes the link between reservoir properties,
Downloaded 02/05/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Relationship among porosity, permeability, electrical and elastic properties Zair Hossain Alan J Cohen RSI, 2600 South Gessner Road, Houston, TX 77063, USA Summary Electrical resisivity is usually easier
Relationship among porosity, permeability, electrical and elastic properties Zair Hossain Alan J Cohen RSI, 2600 South Gessner Road, Houston, TX 77063, USA Summary Electrical resisivity is usually easier
Effective attenuation anisotropy of thin-layered media
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 72, O. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 27; P. D93 D6, 3 FIGS., TABLE..9/.275485 Effective attenuation anisotropy of thin-layered media Yaping Zhu, Ilya Tsvankin 2, Ivan Vasconcelos 3 ABSTRACT One
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 72, O. 5 SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 27; P. D93 D6, 3 FIGS., TABLE..9/.275485 Effective attenuation anisotropy of thin-layered media Yaping Zhu, Ilya Tsvankin 2, Ivan Vasconcelos 3 ABSTRACT One
SEG/San Antonio 2007 Annual Meeting. Summary. Fracture identification in boreholes. Introduction. Dipole sonic anisotropy in boreholes
 Forward modeling of fracture-induced sonic anisotropy using a combination of borehole image and sonic logs Romain Prioul, Adam Donald, Randy Koepsell, om Bratton, Claude Signer, and Austin Boyd, Schlumberger
Forward modeling of fracture-induced sonic anisotropy using a combination of borehole image and sonic logs Romain Prioul, Adam Donald, Randy Koepsell, om Bratton, Claude Signer, and Austin Boyd, Schlumberger
Anisotropic dispersion and attenuation due to wave induced fluid flow: Quasi static finite element modeling in poroelastic solids
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006644, 2010 Anisotropic dispersion and attenuation due to wave induced fluid flow: Quasi static finite element
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006644, 2010 Anisotropic dispersion and attenuation due to wave induced fluid flow: Quasi static finite element
An acoustic wave equation for orthorhombic anisotropy
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 98, August 1, 1998, pages 6?? An acoustic wave equation for orthorhombic anisotropy Tariq Alkhalifah 1 keywords: Anisotropy, finite difference, modeling ABSTRACT Using
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 98, August 1, 1998, pages 6?? An acoustic wave equation for orthorhombic anisotropy Tariq Alkhalifah 1 keywords: Anisotropy, finite difference, modeling ABSTRACT Using
Downloaded 09/04/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Channel wave propagation analysis of the 3D tunnel model in isotropic viscoelastic medium Hui Li*, University of Houston, Peimin Zhu, China University of Geoscieces, Guangzhong Ji, Xi an Branch of China
Channel wave propagation analysis of the 3D tunnel model in isotropic viscoelastic medium Hui Li*, University of Houston, Peimin Zhu, China University of Geoscieces, Guangzhong Ji, Xi an Branch of China
Correspondence between the low- and high-frequency limits for anisotropic parameters in a layered medium
 GEOPHYSICS VOL. 74 NO. MARCH-APRIL 009 ; P. WA5 WA33 7 FIGS. 10.1190/1.3075143 Correspondence between the low- and high-frequency limits for anisotropic parameters in a layered medium Mercia Betania Costa
GEOPHYSICS VOL. 74 NO. MARCH-APRIL 009 ; P. WA5 WA33 7 FIGS. 10.1190/1.3075143 Correspondence between the low- and high-frequency limits for anisotropic parameters in a layered medium Mercia Betania Costa
Th LHR2 08 Towards an Effective Petroelastic Model for Simulator to Seismic Studies
 Th LHR2 08 Towards an Effective Petroelastic Model for Simulator to Seismic Studies A. Briceno* (Heriot-Watt University), C. MacBeth (Heriot-Watt University) & M.D. Mangriotis (Heriot-Watt University)
Th LHR2 08 Towards an Effective Petroelastic Model for Simulator to Seismic Studies A. Briceno* (Heriot-Watt University), C. MacBeth (Heriot-Watt University) & M.D. Mangriotis (Heriot-Watt University)
Velocity Measurements of Pore Fluids at Pressure and Temperature: Application to bitumen
 Velocity Measurements of Pore Fluids at Pressure and Temperature: Application to bitumen Arif Rabbani 1*, Douglas R Schmitt 1, Jason Nycz 2, and Ken Gray 3 1 Institute for Geophysical Research, Department
Velocity Measurements of Pore Fluids at Pressure and Temperature: Application to bitumen Arif Rabbani 1*, Douglas R Schmitt 1, Jason Nycz 2, and Ken Gray 3 1 Institute for Geophysical Research, Department
Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS
 Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS SUMMARY Anelastic properties of the earth cause frequency dependent energy
Compensating visco-acoustic effects in anisotropic resverse-time migration Sang Suh, Kwangjin Yoon, James Cai, and Bin Wang, TGS SUMMARY Anelastic properties of the earth cause frequency dependent energy
Wave Propagation in Fractured Poroelastic Media
 Wave Propagation in Fractured Poroelastic Media WCCM, MS170: Advanced Computational Techniques in Geophysical Sciences, Barcelona, Spain, July 2014 Juan E. Santos Instituto del Gas y del Petróleo (IGPUBA),
Wave Propagation in Fractured Poroelastic Media WCCM, MS170: Advanced Computational Techniques in Geophysical Sciences, Barcelona, Spain, July 2014 Juan E. Santos Instituto del Gas y del Petróleo (IGPUBA),
We Challenges in shale-reservoir characterization by means of AVA and AVAZ
 We-06-15 Challenges in shale-reservoir characterization by means of AVA and AVAZ N.C. Banik* (WesternGeco), M. Egan (WesternGeco), A. Koesoemadinata (WesternGeco) & A. Padhi (WesternGeco) SUMMARY In most
We-06-15 Challenges in shale-reservoir characterization by means of AVA and AVAZ N.C. Banik* (WesternGeco), M. Egan (WesternGeco), A. Koesoemadinata (WesternGeco) & A. Padhi (WesternGeco) SUMMARY In most
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study
 The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
Exact Seismic Velocities for VTI and HTI Media and Extended Thomsen Formulas for Stronger Anisotropies. Abstract
 Submitted to : Geophysics Exact Seismic Velocities for VTI and HTI Media and Extended Thomsen Formulas for Stronger Anisotropies James G. Berryman 1, 1 University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National
Submitted to : Geophysics Exact Seismic Velocities for VTI and HTI Media and Extended Thomsen Formulas for Stronger Anisotropies James G. Berryman 1, 1 University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National
Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play
 Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play Ayato Kato 1, Kunio Akihisa 1, Carl Wang 2 and Reona Masui 3 1 JOGMEC-TRC, Chiba, Japan, kato-ayato@jogmec.go.jp 2 Encana, Calgary, Alberta 3 Mitsubishi
Rock Physics Modeling in Montney Tight Gas Play Ayato Kato 1, Kunio Akihisa 1, Carl Wang 2 and Reona Masui 3 1 JOGMEC-TRC, Chiba, Japan, kato-ayato@jogmec.go.jp 2 Encana, Calgary, Alberta 3 Mitsubishi
Acoustic Anisotropy Measurements and Interpretation in Deviated Wells
 Acoustic Anisotropy Measurements and Interpretation in Deviated Wells X. M. Tang, and D. Patterson, Houston Technology Center, Baker Atlas, Houston, Texas, USA ABSTRACT Many acoustic anisotropy measurements
Acoustic Anisotropy Measurements and Interpretation in Deviated Wells X. M. Tang, and D. Patterson, Houston Technology Center, Baker Atlas, Houston, Texas, USA ABSTRACT Many acoustic anisotropy measurements
Laboratory experiments and numerical simulation on Bitumen Saturated Carbonates: A Rock Physics Study for 4D Seismology
 Laboratory experiments and numerical simulation on Bitumen Saturated Carbonates: A Rock Physics Study for 4D Seismology Arif Rabbani Jason Nycz* Zizhen Wong Doug Schmitt Ken Gray Department of Physics
Laboratory experiments and numerical simulation on Bitumen Saturated Carbonates: A Rock Physics Study for 4D Seismology Arif Rabbani Jason Nycz* Zizhen Wong Doug Schmitt Ken Gray Department of Physics
Downloaded 12/20/17 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Downloaded 12/2/17 to 129.241.191.29. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Overburden geomechanical effects on 4D seismic response influences
Downloaded 12/2/17 to 129.241.191.29. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Overburden geomechanical effects on 4D seismic response influences
Downloaded 10/02/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Downloaded 10/02/13 to 129.7.247.135. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Physical constraints on c 13 and Thomsen parameter delta for VTI rocks
Downloaded 10/02/13 to 129.7.247.135. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Physical constraints on c 13 and Thomsen parameter delta for VTI rocks
Radiation pattern in homogeneous and transversely isotropic attenuating media
 Radiation pattern in homogeneous and transversely isotropic attenuating media Satish Sinha*, Sergey Abaseyev** and Evgeni Chesnokov** *Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology, Rae Bareli, UP 229010
Radiation pattern in homogeneous and transversely isotropic attenuating media Satish Sinha*, Sergey Abaseyev** and Evgeni Chesnokov** *Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Petroleum Technology, Rae Bareli, UP 229010
Characterization of Heterogeneities in Carbonates Ravi Sharma* and Manika Prasad, Colorado School of Mines
 Characterization of Heterogeneities in Carbonates Ravi Sharma* and Manika Prasad, Colorado School of Mines Summary Heterogeneity in carbonate rock is the principal reason for its improper characterization
Characterization of Heterogeneities in Carbonates Ravi Sharma* and Manika Prasad, Colorado School of Mines Summary Heterogeneity in carbonate rock is the principal reason for its improper characterization
AVAZ and VVAZ practical analysis to estimate anisotropic properties
 AVAZ and VVAZ practical analysis to estimate anisotropic properties Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Seismic anisotropic properties, such as orientation
AVAZ and VVAZ practical analysis to estimate anisotropic properties Yexin Liu*, SoftMirrors Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada yexinliu@softmirrors.com Summary Seismic anisotropic properties, such as orientation
Angular and Frequency-Dependent Wave Velocity and Attenuation in Fractured Porous Media
 Pure Appl. Geophys. 170 (2013), 1673 1683 Ó 2013 Springer Basel DOI 10.1007/s00024-012-0636-8 Pure and Applied Geophysics Angular and Frequency-Dependent Wave Velocity and Attenuation in Fractured Porous
Pure Appl. Geophys. 170 (2013), 1673 1683 Ó 2013 Springer Basel DOI 10.1007/s00024-012-0636-8 Pure and Applied Geophysics Angular and Frequency-Dependent Wave Velocity and Attenuation in Fractured Porous
A look into Gassmann s Equation
 A look into Gassmann s Equation Nawras Al-Khateb, CHORUS Heavy Oil Consortium, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary nawras.alkhateb@ucalgary.ca Summary By describing the influence of the pore
A look into Gassmann s Equation Nawras Al-Khateb, CHORUS Heavy Oil Consortium, Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary nawras.alkhateb@ucalgary.ca Summary By describing the influence of the pore
Seismic characterization of naturally fractured reservoirs using amplitude versus offset and azimuth analysis
 Geophysical Prospecting doi: 10.1111/1365-478.1011 Seismic characterization of naturally fractured reservoirs using amplitude versus offset and azimuth analysis ehdi E. Far 1, Colin. Sayers 1,, Leon Thomsen
Geophysical Prospecting doi: 10.1111/1365-478.1011 Seismic characterization of naturally fractured reservoirs using amplitude versus offset and azimuth analysis ehdi E. Far 1, Colin. Sayers 1,, Leon Thomsen
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story
 Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Comparison of two physical modeling studies of 3D P-wave fracture detection
 Comparison of two physical modeling studies of 3D P-wave fracture detection ZHONGPING QIAN 1,2, XIANG-YANG LI 1 AND SHANGXU WANG 3 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Comparison of two physical modeling studies of 3D P-wave fracture detection ZHONGPING QIAN 1,2, XIANG-YANG LI 1 AND SHANGXU WANG 3 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Seismic fracture detection in the Second White Speckled Shale: Anisotropic perspectives on an isotropic workflow
 Fracture detection in the SWS Seismic fracture detection in the Second White Speckled Shale: Anisotropic perspectives on an isotropic workflow David Cho, Craig Coulombe, Scott McLaren, Kevin Johnson and
Fracture detection in the SWS Seismic fracture detection in the Second White Speckled Shale: Anisotropic perspectives on an isotropic workflow David Cho, Craig Coulombe, Scott McLaren, Kevin Johnson and
Introduction to Seismology Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 1.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Introduction to
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 1.510 Introduction to Seismology Spring 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 1.510 Introduction to
Seismic wavepropagation concepts applied to the interpretation of marine controlled-source electromagnetics
 Seismic wavepropagation concepts applied to the interpretation of marine controlled-source electromagnetics Rune Mittet, EMGS SUMMARY are very useful for the interpretation of seismic data. Moreover, these
Seismic wavepropagation concepts applied to the interpretation of marine controlled-source electromagnetics Rune Mittet, EMGS SUMMARY are very useful for the interpretation of seismic data. Moreover, these
Evaluation Of The Fracture Sizes By Using The Frequency Dependence Of Anisotropy
 Evaluation Of The Fracture Sizes By Using The Frequency Dependence Of Anisotropy Vahid Mahmoudian Ataabadi Arvandan Oil and Gas Company Saeed Sajjadian Hafizollah Kashani Birgani Abstract: Frequency-dependent
Evaluation Of The Fracture Sizes By Using The Frequency Dependence Of Anisotropy Vahid Mahmoudian Ataabadi Arvandan Oil and Gas Company Saeed Sajjadian Hafizollah Kashani Birgani Abstract: Frequency-dependent
A Fast Method For Estimating Shear Wave Velocity By Using Neural Network
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(11): 1429-1434, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 A Fast Method For Estimating Shear Wave Velocity By Using Neural Network 1 Khashayar Tabari, 1 Orod Tabari, 2 Mahsa
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(11): 1429-1434, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 A Fast Method For Estimating Shear Wave Velocity By Using Neural Network 1 Khashayar Tabari, 1 Orod Tabari, 2 Mahsa
RP 2.7. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1525
 Manika Prasad, Ronny Hofmann, Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines; M. Kopycinska-Müller, U. Rabe, and W. Arnold, Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing, IZFP, Saarbrücken Summary Seismic wave
Manika Prasad, Ronny Hofmann, Mike Batzle, Colorado School of Mines; M. Kopycinska-Müller, U. Rabe, and W. Arnold, Fraunhofer Institute for Nondestructive Testing, IZFP, Saarbrücken Summary Seismic wave
Estimation of fracture parameters from reflection seismic data Part II: Fractured models with orthorhombic symmetry
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 65, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 2000); P. 1803 1817, 5 FIGS., 1 TABLE. Estimation of fracture parameters from reflection seismic data Part II: Fractured models with orthorhomic symmetry Andrey
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 65, NO. 6 (NOVEMBER-DECEMBER 2000); P. 1803 1817, 5 FIGS., 1 TABLE. Estimation of fracture parameters from reflection seismic data Part II: Fractured models with orthorhomic symmetry Andrey
TIV Contrast Source Inversion of mcsem data
 TIV Contrast ource Inversion of mcem data T. Wiik ( ), L. O. Løseth ( ), B. Ursin ( ), K. Hokstad (, ) ( )epartment for Petroleum Technology and Applied Geophysics, Norwegian University of cience and Technology
TIV Contrast ource Inversion of mcem data T. Wiik ( ), L. O. Løseth ( ), B. Ursin ( ), K. Hokstad (, ) ( )epartment for Petroleum Technology and Applied Geophysics, Norwegian University of cience and Technology
The Hangingstone steam-assisted gravity drainage
 SPECIAL Heavy SECTION: oil H e a v y o i l Elastic property changes in a bitumen reservoir during steam injection AYATO KATO, University of Houston, USA SHIGENOBU ONOZUKA, JOGMEC, Chiba, Japan TORU NAKAYAMA,
SPECIAL Heavy SECTION: oil H e a v y o i l Elastic property changes in a bitumen reservoir during steam injection AYATO KATO, University of Houston, USA SHIGENOBU ONOZUKA, JOGMEC, Chiba, Japan TORU NAKAYAMA,
Borehole Acoustics and Logging Consortium. Annual Report
 Borehole Acoustics and Logging Consortium Annual Report 1994 EARTH RESOURCES LABORATORY Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Mass. 02139
Borehole Acoustics and Logging Consortium Annual Report 1994 EARTH RESOURCES LABORATORY Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Mass. 02139
SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting
 Improving seismic calibration and geomechanical models through characterization of anisotropy using single and multi well data: Case Study in Forties Field, UK Adam Donald*, Andrea Paxton (Schlumberger),
Improving seismic calibration and geomechanical models through characterization of anisotropy using single and multi well data: Case Study in Forties Field, UK Adam Donald*, Andrea Paxton (Schlumberger),
Characterizing the effect of elastic interactions on the effective elastic properties of porous, cracked rocks
 Geophysical Prospecting, 2015 doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12243 Characterizing the effect of elastic interactions on the effective elastic properties of porous, cracked rocks Luanxiao Zhao 1,2, Qiuliang Yao
Geophysical Prospecting, 2015 doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12243 Characterizing the effect of elastic interactions on the effective elastic properties of porous, cracked rocks Luanxiao Zhao 1,2, Qiuliang Yao
P- and S-Wave Velocity Measurements and Pressure Sensitivity Analysis of AVA Response
 P- and S-Wave Velocity Measurements and Pressure Sensitivity Analysis of AVA Response Tiewei He* University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada tieweihe@phys.ualberta.ca and Douglas Schmitt University
P- and S-Wave Velocity Measurements and Pressure Sensitivity Analysis of AVA Response Tiewei He* University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada tieweihe@phys.ualberta.ca and Douglas Schmitt University
Phase-shift modelling for HTI media
 HTI-Modelling Phase-shift modelling for HTI media R. K. Sharma and R. J. Ferguson ABSTRACT Fractures play an important role in hydrocarbon production as they determine the pathways and volume of crustal
HTI-Modelling Phase-shift modelling for HTI media R. K. Sharma and R. J. Ferguson ABSTRACT Fractures play an important role in hydrocarbon production as they determine the pathways and volume of crustal
Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth. Michael Kendall
 Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth Michael Kendall Issues and Challanges Geometry (aspect ratio, size, orientation, density) Non-uniqueness (e.g., single set of aligned
Seismic techniques for imaging fractures, cracks and faults in the Earth Michael Kendall Issues and Challanges Geometry (aspect ratio, size, orientation, density) Non-uniqueness (e.g., single set of aligned
Acoustics in Porous Media.
 Acoustics in Porous Media. JUAN E. SANTOS work in collaboration with J. M. Carcione, S. Picotti, P. M. Gauzellino and R. Martinez Corredor. Department of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, Indiana,
Acoustics in Porous Media. JUAN E. SANTOS work in collaboration with J. M. Carcione, S. Picotti, P. M. Gauzellino and R. Martinez Corredor. Department of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, Indiana,
Downloaded 03/14/14 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Downloae 3/14/14 to 19.1.18.19. eistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see ers of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Fracture-nuce Q-Anisotropy: nversion for Fracture Paraeters atiana Chichinina*
Downloae 3/14/14 to 19.1.18.19. eistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see ers of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Fracture-nuce Q-Anisotropy: nversion for Fracture Paraeters atiana Chichinina*
