FW 1 CDR 1 FW 2 CDR 2
|
|
|
- Rachel Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Interface of the E9:Fas structure. The two interfaces formed by V H and V L of E9 with Fas are shown in stereo. The Fas receptor is represented as a surface with the epitope residues displayed as blue and light blue sticks for CRD1 and CRD2, respectively. The paratope residues of CDRs 1, 2 and 3 of V H and V L are represented as sticks and colored violet, orange and red, respectively. In the V H epitope the position of the V L epitope is indicated by the dashed circle. Supplementary Figure 2 Heavy chain sequence alignment FW 1 CDR 1 FW 2 CDR 2 Kabat numbering a 35b a 52b 52c 52d 52e E9 Q L Q L Q E S G P G L V K P S E T L S L T C T V S G A S I S A N S Y Y G V W V R Q S P G K G L E W V G S I A Y R G N S N S G S T Y Y N P S L K S EP12r_E1 Q L Q L Q E S G P G L V K P S E T L S L T C T V S G A S I S A N S Y Y G V W V R Q S P G K G L E W V G S I A Y R E N S N S G S T Y Y N P S F K S EP4b_E3 Q L Q L Q E S G P G L V K P S E T L S L T C T V S G A P I S A N S Y Y G V W V R Q S P G K G L E W V G S I A Y R G N S N S G S T Y Y N P S L K S EP5b_E5 Q L Q L Q E S G P G L V K P S E T L Y L T C T V S G A S I G A N S Y Y G V W V R Q S P G K G L E W V G S I A Y R G S S N S G S T Y Y N P S L K S EP6b_B1 Q L Q L Q E S G P G L V K P S E T L S L T C T V S G A S I S A N S Y Y G V W V R Q S P G K G L E W V G S I A Y R G N S N S G S T Y Y N P S L K S FW 3 CDR 3 FW 4 Kabat numbering a 82b 82c a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f 1g 1h 1i E9 R A T V S V D T S K N Q V S L R L T S V T A A D T A L Y Y C A R R Q L L D D G T G Y Q W A A F D V W G Q G T M V T V S S EP12r_E1 R A T V S V D T S K N Q V S L R L T S V T A A D T A L Y Y C A R R Q L L D D G T G Y Q W A A F D V W G Q G T M V T V S S EP4b_E3 R A T V S V D T S K N Q V S L R L T S V T A A D T A L Y Y C A R R Q L L D D G T G Y Q W A A F D V W G Q G T M V T I S S EP5b_E5 R A T V S V D T S K N Q V S L R L T S V T A A D T A L Y Y C A R R Q L L D D G T G Y Q W A A F D V W G Q G T M V T V S S EP6b_B1 R A T V S V D S S K N Q V S L R L T S V T A A D T A L Y Y C A R R Q L L D D G T G Y Q W A A F D V W G Q G T M V T V S S Light chain sequence alignment * FW 1 CDR 1 FW 2 CDR 2 Kabat numbering a 27b E9 Q S V L T Q P P S V S E A P R Q T V T I S C S G N S F N I G R Y P V N W Y Q Q L P G K A P K L L I Y Y N N L R F S EP12r_E1 Q S V L T Q P P S V S E A P R Q T V T I S C S G N S F N I G R Y P V N W Y Q Q L P G K A P K L L I Y Y N N L R F S EP4b_E3 Q S V L T Q P P S V S E A P R Q T V T I S C S G N S F N I G R Y P V N W Y Q Q L P G K A P K L L I Y N N N L R F S EP5b_E5 Q S V L T Q P P S V S E A P R Q T V T I S C S G N S F N T G R Y P V N W Y Q Q L P G K A P K L L I Y S N N L R L S EP6b_B1 Q S V L T Q P P S V S E A P R Q T V T I S C S G N S S N I G R Y P V N W Y Q Q L P G K A P K L L I Y S D N L R F S FW 3 CDR 3 FW Kabat numbering a 95b E9 G V S D R F S G S K S G T S A S L A I R D L L S E D E A D Y Y C S T W D D T L K G W V F G G G T K V T V L EP12r_E1 G V S D R F S G S K S G T S A S L A I R D L L S E D E A D Y Y C S T W D D T L K G W V F G G G T K V T V L EP4b_E3 G V S D R F S G S K S G T S A S L A I R D L L S E D E A D Y Y C S T W D D T L K G W V F G G G T K V T V L EP5b_E5 G V S D R F S G S K S G T S A S L A I R D L L S E D E A D Y Y C S T W D D T L E G W V F G G G T K V T V L EP6b_B1 G V P D R F S G S K S G T T A S L A I R D L L S E D E A D Y Y C S T W D D T L E G W V F G G G T K V T V L Supplementary Figure 2: Amino acid sequence alignment for E9 and variant antibodies. Heavy (top) and light (bottom) variable domain sequences are aligned versus the parental E9 antibody and differences are shown in pink. Hotspot mutations found in the round 6 population are highlighted in boxes.
2 Supplementary Figure Framework VH CDRs Vernier residues V H73 Heavy chain % re si du e m ut at ed Framework VL CDRs Vernier residues V L27a V L5 VL51 V L AA numbering in V chains Light chain V L95a Supplementary Figure 3: Analysis of mutations after the directed evolution process. The percentage of residues mutated following 6 rounds of directed evolution selection is shown for both the heavy (top) and light (bottom) chains. Amino acids are numbered numerically. Positions mutated above 2% were defined as hotspots. Residues in the framework regions, the CDR loops and at Vernier positions are shown in grey, blue and orange bars, respectively. Supplementary Figure 4 A V H R52b B V H A52 V H S56 V H Y52a V H G55 E9 Heavy chain FasR V H Y58 V H CDR2 Supplementary Figure 4: Fas receptor affinity modulation by single point mutagenesis. A) Close-up view of the E9 heavy chain (cyan) in complex with the cysteine-rich repeat domain (CRD)- 1 of Fas (green). Heavy chain CDR2 loop is shown in yellow and the 6 residues chosen for sitedirected mutagenesis are shown in orange. B) Affinity of single point-mutants for Fas receptor as determined by SPR. Point mutants were purified as scfv and run as analyte on Fas ECD in fusion with Fc fragment previously immobilised on Protein G-immobilised CM5 chip. Points, each one representing a different sidechain replacement, were grouped by the residue mutated and sorted by K d value on the Y-axis. Affinity of the parent E9 is shown as a grey line.
3 Supplementary Figure 5 B A Supplementary Figure 5: Influence of cross-linking IgGs on cell viability. Dose-dependent in vitro cell killing of Jurkat cells by anti-fas E9 and variant antibodies without (A) or with (B) protein A crosslinking prior to the assay. Supplementary Table 1 A. Diffraction data Space group Unit cell constants [Å]/ [ ] Resolution [Å] Rsym [%] I/σ No. of reflections No. of unique reflections Completeness [%] sfasr:e9 C2221 a= 89.49, b= 166.4, c= 11.72; α=β=γ= ( ) a 4.5 (43.9) (4.73) (99.6) EP6b_B1:sFasR P3121 a=b= 94.51, c= α=β= 9, γ= ( ) 1.4 (63.7) 16.4 (4.13) (1) A. Refinement No. of reflections work / test / / / (incl. H).182 / (incl. H) NAG, 1 FUC, 5 EDO, 1 Na Rwork/Rfree Number of atoms Number of residues Number of heteromolecules 2 Cd, 1 Cl, 6 EDO Number of waters Rmsd (bonds) [Å].8.6 Rmsd (angles) [ ] DPI Biso [Å2] Wilson B [Å2] Ramachandran plot (Molprobity) Residues in most favored region [%] Outliers [%].2 Molprobity score a Numbers in parentheses refer to the highest resolution shell
4 Supplementary Table 2 Fas Residue ASA BSA % ig Interaction 39 Asp Gly H-bond 41 Gln H-bond 42 Phe Cys H-bond 44 His H-bond 45 Lys Pro Cys Pro Pro Thr Val Asn Gly Tyr Thr Asp H-bond 78 Lys Ala His Phe Cation-Pi 86 Arg H-bond / Cation-Pi Supplementary Table 2 (continued) Supplementary Table 2: Interface residues in the E9:Fas complex determined by PISA. The antibody residues are numbered with the Kabat system. The accessible surface area (ASA) and the buried surface area (BSA) in Å2 of the indicated interface residues are indicated with the change in percent upon complex formation. The solvation energy effect is shown as ig in kcal/mol. Interaction types are also listed. E9 V L Residue ASA BSA % ig 29 Gly Arg Tyr Pro Tyr Asn Trp Asp A Lys Trp Interaction Interaction E9 V H Residue ASA BSA % ig 33 Ser Tyr Tyr H-bond 5 Ser Ile Ala A Tyr B Arg E Ser Ser Gly Ser H-bond 57 Thr Tyr Arg H-bond / Cation-Pi 96 Gln Leu B Thr H-bond 1C Gly D Tyr H-bond/Cation-Pi 1E Gln F Trp H Ala
5 Supplementary Table 3 E9 mutants (scfv) # scfv Mutation kd (1/s) ka (1/Ms) KD (M) Change KD/parent 1 E9_WT / 2.4E-3 2.8E+5 8.6E E9_H73S H73_T>S 1.3E-3 3.6E+5 3.5E E9_L27aS L27a_F>S 2.E-3 2.5E+5 7.9E E9_L5S L5_Y>S 2.9E-4 3.3E+5 8.7E E9_L51D L51_N>D 5.E-4 4.5E+5 1.1E E9_L59P L59_S>P 2.6E-3 3.3E+5 8.E E9_L7T L7_S>T 2.6E-3 3.E+5 8.5E E9_L95aE L95aE_K>E 1.9E-3 2.9E+5 6.7E EP6bB1 revertants (scfv) # scfv Mutation kd (1/s) ka (1/Ms) KD (M) Change KD/parent 1 EP6B_WT / 7.8E-5 4.2E+5 1.8E EP6B_H73S H73_S>T 9.3E-5 4.8E+5 2.E EP6B_L27aS L27a_S>F 1.E-4 5.6E+5 1.8E EP6B_L5S L5_S>Y 1.4E-4 3.9E+5 3.7E EP6B_L51D L51_D>N 1.1E-4 3.2E+5 3.3E EP6B_L59P L59_P>S 1.3E-4 4.1E+5 3.1E EP6B_L7T L7_T>S 8.4E-5 5.2E+5 1.6E EP6B_L95aE L95aE_E>K 1.E-4 5.E+5 2.E Supplementary Table 3: Affinity data for E9 point mutants and EP6b_B1 revertants. The seven mutations found in the high affinity antibody EP6b_B1 were individually introduced in the parent E9 backbone or removed from EP6b_B1 to measure their impact on affinity improvement. Kinetic parameters and affinity for recombinant Fas of the mutants, revertants, parent E9 and EP6b_B1 were determined by BIAcore. KA values (1/KD in M-1) were used to calculate free energy of binding compared to the parent E9 ( G(mut.-WT) ) presented in Figure 4B. Supplementary Table 4 Antibody Cell killing efficiency (%) Cell killing EC5 (nm) E EP12r_E EP4b_E EP5b_E EP6b_B1 Non Functional Non Functional E9_Y58W E9_Y52aR E9_R52bS Supplementary Table 4: Cell killing data for E9 and variant antibodies. Cell killing efficiency and EC 5 were determined from in vitro viability assays using Jurkat cells and a titration of the anti-fas antibodies without cross-linking.
Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase Cwc27
 Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound ogm-csf and ogm-csf as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine
 Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Supplementary figure 1. Comparison of unbound and as captured in the GIF:GM-CSF complex. Alignment of two copies of unbound ovine GM-CSF (slate) with bound GM-CSF in the GIF:GM-CSF complex (GIF: green,
Supplementary Figure 3 a. Structural comparison between the two determined structures for the IL 23:MA12 complex. The overall RMSD between the two
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biopanningg and clone enrichment of Alphabody binders against human IL 23. Positive clones in i phage ELISA with optical density (OD) 3 times higher than background are shown for
Supplementary Figure 1. Biopanningg and clone enrichment of Alphabody binders against human IL 23. Positive clones in i phage ELISA with optical density (OD) 3 times higher than background are shown for
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
doi:1.138/nature1737 Supplementary Table 1 variant Description FSEC - 2B12 a FSEC - 6A1 a K d (leucine) c Leucine uptake e K (wild-type like) K (Y18F) K (TS) K (TSY) K288A mutant, lipid facing side chain
Stabilizing the CH2 domain of an Antibody by Engineering in an Enhanced Aromatic Sequon
 Stabilizing the CH2 domain of an Antibody by Engineering in an Enhanced Aromatic Sequon Wentao Chen,, Leopold Kong, Stephen Connelly, Julia M. Dendle,, Yu Liu,, Ian A. Wilson,#, Evan T. Powers, *, Jeffery
Stabilizing the CH2 domain of an Antibody by Engineering in an Enhanced Aromatic Sequon Wentao Chen,, Leopold Kong, Stephen Connelly, Julia M. Dendle,, Yu Liu,, Ian A. Wilson,#, Evan T. Powers, *, Jeffery
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 14, 2018 02:00 pm GMT PDB ID : 3RRQ Title : Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human PD-1 Authors : Lazar-Molnar, E.; Ramagopal, U.A.; Nathenson,
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 14, 2018 02:00 pm GMT PDB ID : 3RRQ Title : Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human PD-1 Authors : Lazar-Molnar, E.; Ramagopal, U.A.; Nathenson,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
Sensitive NMR Approach for Determining the Binding Mode of Tightly Binding Ligand Molecules to Protein Targets
 Supporting information Sensitive NMR Approach for Determining the Binding Mode of Tightly Binding Ligand Molecules to Protein Targets Wan-Na Chen, Christoph Nitsche, Kala Bharath Pilla, Bim Graham, Thomas
Supporting information Sensitive NMR Approach for Determining the Binding Mode of Tightly Binding Ligand Molecules to Protein Targets Wan-Na Chen, Christoph Nitsche, Kala Bharath Pilla, Bim Graham, Thomas
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Jan 17, 2019 09:42 AM EST PDB ID : 6D3Z Title : Protease SFTI complex Authors : Law, R.H.P.; Wu, G. Deposited on : 2018-04-17 Resolution : 2.00 Å(reported)
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Jan 17, 2019 09:42 AM EST PDB ID : 6D3Z Title : Protease SFTI complex Authors : Law, R.H.P.; Wu, G. Deposited on : 2018-04-17 Resolution : 2.00 Å(reported)
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 06:13 pm GMT PDB ID : 5G5C Title : Structure of the Pyrococcus furiosus Esterase Pf2001 with space group C2221 Authors : Varejao, N.; Reverter,
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 06:13 pm GMT PDB ID : 5G5C Title : Structure of the Pyrococcus furiosus Esterase Pf2001 with space group C2221 Authors : Varejao, N.; Reverter,
Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08 Å resolution: comparison with the Azotobacter vinelandii MoFe protein
 Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table S1 Kinetic Analyses of the AMSH-LP mutants AMSH-LP K M (μm) k cat x 10-3 (s -1 ) WT 71.8 ± 6.3 860 ± 65.4 T353A 76.8 ± 11.7 46.3 ± 3.7 F355A 58.9 ± 10.4 5.33 ± 0.30 proximal S358A 75.1
Supplementary Table S1 Kinetic Analyses of the AMSH-LP mutants AMSH-LP K M (μm) k cat x 10-3 (s -1 ) WT 71.8 ± 6.3 860 ± 65.4 T353A 76.8 ± 11.7 46.3 ± 3.7 F355A 58.9 ± 10.4 5.33 ± 0.30 proximal S358A 75.1
Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics. Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2
 Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2 Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell
Table 1. Crystallographic data collection, phasing and refinement statistics Native Hg soaked Mn soaked 1 Mn soaked 2 Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Jan 14, 2019 11:10 AM EST PDB ID : 6GYW Title : Crystal structure of DacA from Staphylococcus aureus Authors : Tosi, T.; Freemont, P.S.; Grundling, A. Deposited
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Jan 14, 2019 11:10 AM EST PDB ID : 6GYW Title : Crystal structure of DacA from Staphylococcus aureus Authors : Tosi, T.; Freemont, P.S.; Grundling, A. Deposited
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Proteins: Characteristics and Properties of Amino Acids
 SBI4U:Biochemistry Macromolecules Eachaminoacidhasatleastoneamineandoneacidfunctionalgroupasthe nameimplies.thedifferentpropertiesresultfromvariationsinthestructuresof differentrgroups.thergroupisoftenreferredtoastheaminoacidsidechain.
SBI4U:Biochemistry Macromolecules Eachaminoacidhasatleastoneamineandoneacidfunctionalgroupasthe nameimplies.thedifferentpropertiesresultfromvariationsinthestructuresof differentrgroups.thergroupisoftenreferredtoastheaminoacidsidechain.
What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and peptides at aqueous graphene interfaces: Electronic Supplementary
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 21 What makes a good graphene-binding peptide? Adsorption of amino acids and
Rho1 binding site PtdIns(4,5)P2 binding site Both sites
 localization Mutation site DMSO LatB WT F77A I115A I131A K134A Rho1 binding site PtdIns(4,5)P2 binding site Both sites E186A E199A N201A R84A-E186A-E199A L131A-K136A-E186A L131A-E186A-E199A K136A-E186A-E199A
localization Mutation site DMSO LatB WT F77A I115A I131A K134A Rho1 binding site PtdIns(4,5)P2 binding site Both sites E186A E199A N201A R84A-E186A-E199A L131A-K136A-E186A L131A-E186A-E199A K136A-E186A-E199A
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 08:34 pm GMT PDB ID : 1RUT Title : Complex of LMO4 LIM domains 1 and 2 with the ldb1 LID domain Authors : Deane, J.E.; Ryan, D.P.; Maher, M.J.;
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 08:34 pm GMT PDB ID : 1RUT Title : Complex of LMO4 LIM domains 1 and 2 with the ldb1 LID domain Authors : Deane, J.E.; Ryan, D.P.; Maher, M.J.;
Programme Last week s quiz results + Summary Fold recognition Break Exercise: Modelling remote homologues
 Programme 8.00-8.20 Last week s quiz results + Summary 8.20-9.00 Fold recognition 9.00-9.15 Break 9.15-11.20 Exercise: Modelling remote homologues 11.20-11.40 Summary & discussion 11.40-12.00 Quiz 1 Feedback
Programme 8.00-8.20 Last week s quiz results + Summary 8.20-9.00 Fold recognition 9.00-9.15 Break 9.15-11.20 Exercise: Modelling remote homologues 11.20-11.40 Summary & discussion 11.40-12.00 Quiz 1 Feedback
Experimental and Computational Mutagenesis to Investigate the. Positioning of a General Base within an Enzyme Active Site
 Experimental and Computational Mutagenesis to Investigate the Positioning of a General Base within an Enzyme Active Site Jason P. Schwans, Philip Hanoian, Benjamin J. Lengerich, Fanny Sunden, Ana Gonzalez
Experimental and Computational Mutagenesis to Investigate the Positioning of a General Base within an Enzyme Active Site Jason P. Schwans, Philip Hanoian, Benjamin J. Lengerich, Fanny Sunden, Ana Gonzalez
NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile virus NS2B-NS3 protease
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 NMR study of complexes between low molecular mass inhibitors and the West Nile
Ramachandran Plot. 4ysz Phi (degrees) Plot statistics
 B Ramachandran Plot ~b b 135 b ~b ~l l Psi (degrees) 5-5 a A ~a L - -135 SER HIS (F) 59 (G) SER (B) ~b b LYS ASP ASP 315 13 13 (A) (F) (B) LYS ALA ALA 315 173 (E) 173 (E)(A) ~p p ~b - -135 - -5 5 135 (degrees)
B Ramachandran Plot ~b b 135 b ~b ~l l Psi (degrees) 5-5 a A ~a L - -135 SER HIS (F) 59 (G) SER (B) ~b b LYS ASP ASP 315 13 13 (A) (F) (B) LYS ALA ALA 315 173 (E) 173 (E)(A) ~p p ~b - -135 - -5 5 135 (degrees)
Amino Acid Side Chain Induced Selectivity in the Hydrolysis of Peptides Catalyzed by a Zr(IV)-Substituted Wells-Dawson Type Polyoxometalate
 Amino Acid Side Chain Induced Selectivity in the Hydrolysis of Peptides Catalyzed by a Zr(IV)-Substituted Wells-Dawson Type Polyoxometalate Stef Vanhaecht, Gregory Absillis, Tatjana N. Parac-Vogt* Department
Amino Acid Side Chain Induced Selectivity in the Hydrolysis of Peptides Catalyzed by a Zr(IV)-Substituted Wells-Dawson Type Polyoxometalate Stef Vanhaecht, Gregory Absillis, Tatjana N. Parac-Vogt* Department
ml. ph 7.5 ph 6.5 ph 5.5 ph 4.5. β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS
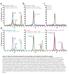 a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
a UV28 absorption (mau) 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex + GDP β 2 AR-Gs complex + GTPγS β 2 AR-Gs complex dissociated complex excess nucleotides b 9 8 7 5 3 β 2 AR-Gs complex β 2 AR-Gs complex
Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants. GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
Supplementary Figures
 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Type I FGFR1 inhibitors (a) Chemical structures of a pyrazolylaminopyrimidine inhibitor (henceforth referred to as PAPI; PDB-code of the FGFR1-PAPI complex:
1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Type I FGFR1 inhibitors (a) Chemical structures of a pyrazolylaminopyrimidine inhibitor (henceforth referred to as PAPI; PDB-code of the FGFR1-PAPI complex:
Supplementary Information. Broad Spectrum Anti-Influenza Agents by Inhibiting Self- Association of Matrix Protein 1
 Supplementary Information Broad Spectrum Anti-Influenza Agents by Inhibiting Self- Association of Matrix Protein 1 Philip D. Mosier 1, Meng-Jung Chiang 2, Zhengshi Lin 2, Yamei Gao 2, Bashayer Althufairi
Supplementary Information Broad Spectrum Anti-Influenza Agents by Inhibiting Self- Association of Matrix Protein 1 Philip D. Mosier 1, Meng-Jung Chiang 2, Zhengshi Lin 2, Yamei Gao 2, Bashayer Althufairi
Supporting information to: Time-resolved observation of protein allosteric communication. Sebastian Buchenberg, Florian Sittel and Gerhard Stock 1
 Supporting information to: Time-resolved observation of protein allosteric communication Sebastian Buchenberg, Florian Sittel and Gerhard Stock Biomolecular Dynamics, Institute of Physics, Albert Ludwigs
Supporting information to: Time-resolved observation of protein allosteric communication Sebastian Buchenberg, Florian Sittel and Gerhard Stock Biomolecular Dynamics, Institute of Physics, Albert Ludwigs
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but not the only one!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids repeated
Oxygen Binding in Hemocyanin
 Supporting Information for Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study of Oxygen Binding in Hemocyanin Toru Saito and Walter Thiel* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung, Kaiser-Wilhelm-Platz 1, D-45470
Supporting Information for Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study of Oxygen Binding in Hemocyanin Toru Saito and Walter Thiel* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung, Kaiser-Wilhelm-Platz 1, D-45470
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Feb 17, 2018 01:16 am GMT PDB ID : 1IFT Title : RICIN A-CHAIN (RECOMBINANT) Authors : Weston, S.A.; Tucker, A.D.; Thatcher, D.R.; Derbyshire, D.J.; Pauptit,
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Feb 17, 2018 01:16 am GMT PDB ID : 1IFT Title : RICIN A-CHAIN (RECOMBINANT) Authors : Weston, S.A.; Tucker, A.D.; Thatcher, D.R.; Derbyshire, D.J.; Pauptit,
Course Notes: Topics in Computational. Structural Biology.
 Course Notes: Topics in Computational Structural Biology. Bruce R. Donald June, 2010 Copyright c 2012 Contents 11 Computational Protein Design 1 11.1 Introduction.........................................
Course Notes: Topics in Computational Structural Biology. Bruce R. Donald June, 2010 Copyright c 2012 Contents 11 Computational Protein Design 1 11.1 Introduction.........................................
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/243/ra68/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Superbinder SH2 Domains Act as Antagonists of Cell Signaling Tomonori Kaneko, Haiming Huang, Xuan Cao, Xing Li, Chengjun
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Bacterial protease uses distinct thermodynamic signatures for substrate recognition
 Bacterial protease uses distinct thermodynamic signatures for substrate recognition Gustavo Arruda Bezerra, Yuko Ohara-Nemoto, Irina Cornaciu, Sofiya Fedosyuk, Guillaume Hoffmann, Adam Round, José A. Márquez,
Bacterial protease uses distinct thermodynamic signatures for substrate recognition Gustavo Arruda Bezerra, Yuko Ohara-Nemoto, Irina Cornaciu, Sofiya Fedosyuk, Guillaume Hoffmann, Adam Round, José A. Márquez,
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
Using Higher Calculus to Study Biologically Important Molecules Julie C. Mitchell
 Using Higher Calculus to Study Biologically Important Molecules Julie C. Mitchell Mathematics and Biochemistry University of Wisconsin - Madison 0 There Are Many Kinds Of Proteins The word protein comes
Using Higher Calculus to Study Biologically Important Molecules Julie C. Mitchell Mathematics and Biochemistry University of Wisconsin - Madison 0 There Are Many Kinds Of Proteins The word protein comes
Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4.
 Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4. Field Desorption 5. MS MS techniques Matrix assisted
Other Methods for Generating Ions 1. MALDI matrix assisted laser desorption ionization MS 2. Spray ionization techniques 3. Fast atom bombardment 4. Field Desorption 5. MS MS techniques Matrix assisted
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information A Sensitive Phosphorescent Thiol Chemosensor Based on an Iridium(III) Complex with α,β-unsaturated Ketone Functionalized 2,2 -Bipyridyl Ligand Na Zhao, a Yu-Hui Wu,
Electronic Supplementary Information A Sensitive Phosphorescent Thiol Chemosensor Based on an Iridium(III) Complex with α,β-unsaturated Ketone Functionalized 2,2 -Bipyridyl Ligand Na Zhao, a Yu-Hui Wu,
7.012 Problem Set 1. i) What are two main differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
 ame 7.01 Problem Set 1 Section Question 1 a) What are the four major types of biological molecules discussed in lecture? Give one important function of each type of biological molecule in the cell? b)
ame 7.01 Problem Set 1 Section Question 1 a) What are the four major types of biological molecules discussed in lecture? Give one important function of each type of biological molecule in the cell? b)
Supplementary Information. Viral immunoevasin targeting of a Natural Killer cell receptor family
 Supplementary Information Viral immunoevasin targeting of a Natural Killer cell receptor family Richard Berry 1, Natasha Ng 1, Philippa M. Saunders 2, Julian P. Vivian 1, Jie Lin 2, Felix A. Deuss 1, Alexandra
Supplementary Information Viral immunoevasin targeting of a Natural Killer cell receptor family Richard Berry 1, Natasha Ng 1, Philippa M. Saunders 2, Julian P. Vivian 1, Jie Lin 2, Felix A. Deuss 1, Alexandra
Supplementary Information Intrinsic Localized Modes in Proteins
 Supplementary Information Intrinsic Localized Modes in Proteins Adrien Nicolaï 1,, Patrice Delarue and Patrick Senet, 1 Department of Physics, Applied Physics and Astronomy, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute,
Supplementary Information Intrinsic Localized Modes in Proteins Adrien Nicolaï 1,, Patrice Delarue and Patrick Senet, 1 Department of Physics, Applied Physics and Astronomy, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute,
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2
 2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
2 Viewing and Analyzing Proteins, Ligands and their Complexes 2 Overview Viewing the accessible surface Analyzing the properties of proteins containing thousands of atoms is best accomplished by representing
Central Dogma. modifications genome transcriptome proteome
 entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
entral Dogma DA ma protein post-translational modifications genome transcriptome proteome 83 ierarchy of Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids There are 20 n possible sequences for a protein of n residues!
Physiochemical Properties of Residues
 Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Physiochemical Properties of Residues Various Sources C N Cα R Slide 1 Conformational Propensities Conformational Propensity is the frequency in which a residue adopts a given conformation (in a polypeptide)
Computational Protein Design
 11 Computational Protein Design This chapter introduces the automated protein design and experimental validation of a novel designed sequence, as described in Dahiyat and Mayo [1]. 11.1 Introduction Given
11 Computational Protein Design This chapter introduces the automated protein design and experimental validation of a novel designed sequence, as described in Dahiyat and Mayo [1]. 11.1 Introduction Given
Supplementary information for:
 SUPPLEMETARY IFRMATI Supplementary information for: Structure of a β 1 -adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor Tony Warne, Maria J. Serrano-Vega, Jillian G. Baker#, Rouslan Moukhametzianov, Patricia C.
SUPPLEMETARY IFRMATI Supplementary information for: Structure of a β 1 -adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor Tony Warne, Maria J. Serrano-Vega, Jillian G. Baker#, Rouslan Moukhametzianov, Patricia C.
Model Mélange. Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins
 Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Exam III. Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information.
 09-107 onors Chemistry ame Exam III Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information. 1. A series of octahedral metal compounds are made from 1 mol
09-107 onors Chemistry ame Exam III Please read through each question carefully, and make sure you provide all of the requested information. 1. A series of octahedral metal compounds are made from 1 mol
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1: Amplitudes of three current levels. Level 0 (pa) Level 1 (pa) Level 2 (pa) TrkA- TrkH WT 200 K 0.01 ± 0.01 9.5 ± 0.01 18.7 ± 0.03 200 Na * 0.001 ± 0.01 3.9 ± 0.01 12.5 ± 0.03 200
Supplementary Table 1: Amplitudes of three current levels. Level 0 (pa) Level 1 (pa) Level 2 (pa) TrkA- TrkH WT 200 K 0.01 ± 0.01 9.5 ± 0.01 18.7 ± 0.03 200 Na * 0.001 ± 0.01 3.9 ± 0.01 12.5 ± 0.03 200
Unraveling the degradation of artificial amide bonds in Nylon oligomer hydrolase: From induced-fit to acylation processes
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Supporting Information for Unraveling the degradation of artificial amide bonds
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2015 Supporting Information for Unraveling the degradation of artificial amide bonds
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
NB-DNJ/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 4.5
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
Peptide Syntheses. Illustrative Protection: BOC/ t Bu. A. Introduction. do not acid
 Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptide yntheses from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction do not acid -Met-e- -Met-Met- -e-e- -e-met- dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide diketopiperazine
Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptide yntheses from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction do not acid -Met-e- -Met-Met- -e-e- -e-met- dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide dipeptide diketopiperazine
Protein Fragment Search Program ver Overview: Contents:
 Protein Fragment Search Program ver 1.1.1 Developed by: BioPhysics Laboratory, Faculty of Life and Environmental Science, Shimane University 1060 Nishikawatsu-cho, Matsue-shi, Shimane, 690-8504, Japan
Protein Fragment Search Program ver 1.1.1 Developed by: BioPhysics Laboratory, Faculty of Life and Environmental Science, Shimane University 1060 Nishikawatsu-cho, Matsue-shi, Shimane, 690-8504, Japan
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
doi:10.1038/nature11085 Supplementary Tables: Supplementary Table 1. Summary of crystallographic and structure refinement data Structure BRIL-NOP receptor Data collection Number of crystals 23 Space group
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantitation of the binding of pro53 peptide to sorla Vps10p measured by the AP reporter assay. The graph shows tracings of the typical chromogenic AP reaction observed with AP-pro53
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantitation of the binding of pro53 peptide to sorla Vps10p measured by the AP reporter assay. The graph shows tracings of the typical chromogenic AP reaction observed with AP-pro53
Supplement information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physil Chemistry Chemil Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 216 Supplement information Fullerenol C 6 (OH) 16 prevents amyloid fibrillization of Aβ
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physil Chemistry Chemil Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 216 Supplement information Fullerenol C 6 (OH) 16 prevents amyloid fibrillization of Aβ
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Jan 28, 2019 11:10 AM EST PDB ID : 6A5H Title : The structure of [4+2] and [6+4] cyclase in the biosynthetic pathway of unidentified natural product Authors
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Jan 28, 2019 11:10 AM EST PDB ID : 6A5H Title : The structure of [4+2] and [6+4] cyclase in the biosynthetic pathway of unidentified natural product Authors
Peptides And Proteins
 Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Kevin Burgess, May 3, 2017 1 Peptides And Proteins from chapter(s) in the recommended text A. Introduction B. omenclature And Conventions by amide bonds. on the left, right. 2 -terminal C-terminal triglycine
Amino Acids and Proteins at ZnO-water Interfaces in Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Electronic Supplementary Information
 Amino Acids and Proteins at ZnO-water Interfaces in Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Electronic Supplementary Information Grzegorz Nawrocki and Marek Cieplak Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences,
Amino Acids and Proteins at ZnO-water Interfaces in Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Electronic Supplementary Information Grzegorz Nawrocki and Marek Cieplak Institute of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences,
Sequential resonance assignments in (small) proteins: homonuclear method 2º structure determination
 Lecture 9 M230 Feigon Sequential resonance assignments in (small) proteins: homonuclear method 2º structure determination Reading resources v Roberts NMR of Macromolecules, Chap 4 by Christina Redfield
Lecture 9 M230 Feigon Sequential resonance assignments in (small) proteins: homonuclear method 2º structure determination Reading resources v Roberts NMR of Macromolecules, Chap 4 by Christina Redfield
Exam I Answer Key: Summer 2006, Semester C
 1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i
 Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 10:24 pm GMT PDB ID : 1A30 Title : HIV-1 PROTEASE COMPLEXED WITH A TRIPEPTIDE INHIBITOR Authors : Louis, J.M.; Dyda, F.; Nashed, N.T.; Kimmel,
Full wwpdb X-ray Structure Validation Report i Mar 8, 2018 10:24 pm GMT PDB ID : 1A30 Title : HIV-1 PROTEASE COMPLEXED WITH A TRIPEPTIDE INHIBITOR Authors : Louis, J.M.; Dyda, F.; Nashed, N.T.; Kimmel,
Monomeric Clavularia CFP July 19, 2006
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table 1S Rationale for design of the synthetic gene library. Residue number Mutation Codon a Rationale His42 Leu44 Gln66 (residue of chromophore) His, Asn, Gln, Lys Leu, Val, Ala,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table 1S Rationale for design of the synthetic gene library. Residue number Mutation Codon a Rationale His42 Leu44 Gln66 (residue of chromophore) His, Asn, Gln, Lys Leu, Val, Ala,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
C H E M I S T R Y N A T I O N A L Q U A L I F Y I N G E X A M I N A T I O N SOLUTIONS GUIDE
 C H E M I S T R Y 2 0 0 0 A T I A L Q U A L I F Y I G E X A M I A T I SLUTIS GUIDE Answers are a guide only and do not represent a preferred method of solving problems. Section A 1B, 2A, 3C, 4C, 5D, 6D,
C H E M I S T R Y 2 0 0 0 A T I A L Q U A L I F Y I G E X A M I A T I SLUTIS GUIDE Answers are a guide only and do not represent a preferred method of solving problems. Section A 1B, 2A, 3C, 4C, 5D, 6D,
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1.
 Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
Table S1. Overview of used PDZK1 constructs and their binding affinities to peptides. Related to figure 1. PDZK1 constru cts Amino acids MW [kda] KD [μm] PEPT2-CT- FITC KD [μm] NHE3-CT- FITC KD [μm] PDZK1-CT-
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 5 N 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 a b 0 9 8 7 H c (kda) 95 0 57 4 28 2 5.5 Precipitate before NMR expt. Supernatant before NMR expt. Precipitate after hrs NMR expt. Supernatant after hrs NMR expt.
5 N 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 a b 0 9 8 7 H c (kda) 95 0 57 4 28 2 5.5 Precipitate before NMR expt. Supernatant before NMR expt. Precipitate after hrs NMR expt. Supernatant after hrs NMR expt.
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Combinatorial Readout of Unmodified H3R2 and Acetylated H3K14 by the Tandem PHD Finger of MOZ Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism for HOXA9 Transcription Yu Qiu 1, Lei Liu 1, Chen Zhao
Supplemental Information Combinatorial Readout of Unmodified H3R2 and Acetylated H3K14 by the Tandem PHD Finger of MOZ Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism for HOXA9 Transcription Yu Qiu 1, Lei Liu 1, Chen Zhao
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a
 Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Supplementary figure 1 Application of tmfret in LeuT. (a) To assess the feasibility of using tmfret for distance-dependent measurements in LeuT, a series of tmfret-pairs comprised of single cysteine mutants
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5751/1159/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Structure of the Quaternary Complex of Interleukin-2 with Its α, β, and γ c Receptors Xinquan Wang, Mathias Rickert,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5751/1159/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Structure of the Quaternary Complex of Interleukin-2 with Its α, β, and γ c Receptors Xinquan Wang, Mathias Rickert,
Molecular Structure Prediction by Global Optimization
 Molecular Structure Prediction by Global Optimization K.A. DILL Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco, CA 94118 A.T. PHILLIPS Computer Science
Molecular Structure Prediction by Global Optimization K.A. DILL Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco, CA 94118 A.T. PHILLIPS Computer Science
Translation. A ribosome, mrna, and trna.
 Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
Translation The basic processes of translation are conserved among prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic Translation A ribosome, mrna, and trna. In the initiation of translation in prokaryotes, the Shine-Dalgarno
ENZYME MECHANISMS, PROTEASES, STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY
 Supplementary Information SUBJECT AREAS: ENZYME MECHANISMS, PROTEASES, STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to N.T. (ntanaka@pharm.showa-u.ac.jp) or W.O. (owataru@vos.nagaokaut.ac.jp)
Supplementary Information SUBJECT AREAS: ENZYME MECHANISMS, PROTEASES, STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to N.T. (ntanaka@pharm.showa-u.ac.jp) or W.O. (owataru@vos.nagaokaut.ac.jp)
Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling. Patrice Koehl
 Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling Patrice Koehl Structural Bioinformatics: Proteins Proteins: Sources of Structure Information Proteins: Homology Modeling Proteins: Ab initio prediction Proteins:
Protein Structures: Experiments and Modeling Patrice Koehl Structural Bioinformatics: Proteins Proteins: Sources of Structure Information Proteins: Homology Modeling Proteins: Ab initio prediction Proteins:
Background BIOCHEMISTRY LAB CHE-554. Experiment #1 Spectrophotometry
 BIOCHEMISTRY LAB Experiment #1 Spectrophotometry CHE-554 In day 1 we will use spectrophotometry as an analytical technique using a known extinction coefficient to assess the precision and accuracy of common
BIOCHEMISTRY LAB Experiment #1 Spectrophotometry CHE-554 In day 1 we will use spectrophotometry as an analytical technique using a known extinction coefficient to assess the precision and accuracy of common
IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23
 Supplementary Information IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23 Balvinder Dhaliwal 1*, Marie O. Y. Pang 2, Anthony H. Keeble 2,3, Louisa K. James 2,4, Hannah J. Gould 2, James M. McDonnell
Supplementary Information IgE binds asymmetrically to its B cell receptor CD23 Balvinder Dhaliwal 1*, Marie O. Y. Pang 2, Anthony H. Keeble 2,3, Louisa K. James 2,4, Hannah J. Gould 2, James M. McDonnell
Protein Structure Bioinformatics Introduction
 1 Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Protein Structure Bioinformatics Introduction Basel, 27. September 2004 Torsten Schwede Biozentrum - Universität Basel Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Klingelbergstr
1 Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Protein Structure Bioinformatics Introduction Basel, 27. September 2004 Torsten Schwede Biozentrum - Universität Basel Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics Klingelbergstr
A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of
 Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures?
 1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
Supplementary Information. Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization
 Supplementary Information Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization Kunhua Li 1,3, Heather L. Condurso 1,3, Gengnan Li 1, Yousong Ding 2 and Steven D. Bruner 1*
Supplementary Information Structural basis for precursor protein-directed ribosomal peptide macrocyclization Kunhua Li 1,3, Heather L. Condurso 1,3, Gengnan Li 1, Yousong Ding 2 and Steven D. Bruner 1*
Supplemental Information. Molecular Basis of Spectral Diversity. in Near-Infrared Phytochrome-Based. Fluorescent Proteins
 Chemistry & Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Molecular Basis of Spectral Diversity in Near-Infrared Phytochrome-Based Fluorescent Proteins Daria M. Shcherbakova, Mikhail Baloban, Sergei Pletnev,
Chemistry & Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Molecular Basis of Spectral Diversity in Near-Infrared Phytochrome-Based Fluorescent Proteins Daria M. Shcherbakova, Mikhail Baloban, Sergei Pletnev,
*Corresponding Author *K. F.: *T. H.:
 Theoretical Analysis of Activity Cliffs among Benzofuranone Class Pim1 Inhibitors Using the Fragment Molecular Orbital Method with Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area (FMO+MM-PBSA) Approach
Theoretical Analysis of Activity Cliffs among Benzofuranone Class Pim1 Inhibitors Using the Fragment Molecular Orbital Method with Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area (FMO+MM-PBSA) Approach
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers.
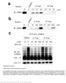 Supplementary Figure 1 CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers. (a) Competitive elution assay using thalidomide-immobilized beads coupled with racemic thalidomide. Beads were washed three times
Supplementary Figure 1 CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers. (a) Competitive elution assay using thalidomide-immobilized beads coupled with racemic thalidomide. Beads were washed three times
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Deciphering the Rules for Amino Acid Co- Assembly Based on Interlayer Distances
 Supporting Information Deciphering the Rules for Amino Acid Co- Assembly Based on Interlayer Distances Santu Bera, Sudipta Mondal, Yiming Tang, Guy Jacoby, Elad Arad, ǁ Tom Guterman, Raz Jelinek, ǁ Roy
Supporting Information Deciphering the Rules for Amino Acid Co- Assembly Based on Interlayer Distances Santu Bera, Sudipta Mondal, Yiming Tang, Guy Jacoby, Elad Arad, ǁ Tom Guterman, Raz Jelinek, ǁ Roy
Protein structure. Protein structure. Amino acid residue. Cell communication channel. Bioinformatics Methods
 Cell communication channel Bioinformatics Methods Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu SEQUENCE STRUCTURE DNA Sequence Protein Sequence Protein Structure Protein structure ATGAAATTTGGAAACTTCCTTCTCACTTATCAGCCACCT...
Cell communication channel Bioinformatics Methods Iosif Vaisman Email: ivaisman@gmu.edu SEQUENCE STRUCTURE DNA Sequence Protein Sequence Protein Structure Protein structure ATGAAATTTGGAAACTTCCTTCTCACTTATCAGCCACCT...
Diastereomeric resolution directed towards chirality. determination focussing on gas-phase energetics of coordinated. sodium dissociation
 Supplementary Information Diastereomeric resolution directed towards chirality determination focussing on gas-phase energetics of coordinated sodium dissociation Authors: samu Kanie*, Yuki Shioiri, Koji
Supplementary Information Diastereomeric resolution directed towards chirality determination focussing on gas-phase energetics of coordinated sodium dissociation Authors: samu Kanie*, Yuki Shioiri, Koji
β1 Structure Prediction and Validation
 13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
13 Chapter 2 β1 Structure Prediction and Validation 2.1 Overview Over several years, GPCR prediction methods in the Goddard lab have evolved to keep pace with the changing field of GPCR structure. Despite
Snork Synthesis Lab Lab Directions
 Snork Synthesis Lab Lab Directions This activity, modified from the original at The Biology Corner, will help you practice your understanding of protein synthesis. Submit your lab answers according to
Snork Synthesis Lab Lab Directions This activity, modified from the original at The Biology Corner, will help you practice your understanding of protein synthesis. Submit your lab answers according to
Protein Struktur. Biologen und Chemiker dürfen mit Handys spielen (leise) go home, go to sleep. wake up at slide 39
 Protein Struktur Biologen und Chemiker dürfen mit Handys spielen (leise) go home, go to sleep wake up at slide 39 Andrew Torda, Wintersemester 2016/ 2017 Andrew Torda 17.10.2016 [ 1 ] Proteins - who cares?
Protein Struktur Biologen und Chemiker dürfen mit Handys spielen (leise) go home, go to sleep wake up at slide 39 Andrew Torda, Wintersemester 2016/ 2017 Andrew Torda 17.10.2016 [ 1 ] Proteins - who cares?
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ottmann et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907587106 Fig. S1. Primary structure alignment of SBT3 with C5 peptidase from Streptococcus pyogenes. The Matchmaker tool in UCSF Chimera (http:// www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera)
Supporting Information Ottmann et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907587106 Fig. S1. Primary structure alignment of SBT3 with C5 peptidase from Streptococcus pyogenes. The Matchmaker tool in UCSF Chimera (http:// www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera)
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of GFP oligomer variants with different linkers. Oligomer mixtures were applied to a PAGE gel containing 0.1% SDS without boiling. The gel was analyzed by a fluorescent
Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation Morgan S. Gadd 1, Andrea Testa 1, Xavier Lucas 1, Kwok-Ho Chan, Wenzhang Chen, Douglas J.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Structural basis of PROTAC cooperative recognition for selective protein degradation Morgan S. Gadd 1, Andrea Testa 1, Xavier Lucas 1, Kwok-Ho Chan, Wenzhang Chen, Douglas J.
