Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos
|
|
|
- Miles Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos Issues with global models Possibility of smaller scales Consequences of this Magnetic flux concentrations Unusual dynamo effects Axel randenburg (Nordita, Stockholm CU oulder) 1
2 Global models suggest Distributed dynamo action Difference to flux transport dynamos Would require smaller turb. diff. h t =u rms /3k f =u rms l/3 Surface flux from upper layers Difference to deeply rooted tube picture Surface flux reamplification needed NEMPI: works best for large k f H p Mostly cylindrical W-contours Anti-solar differential rotation 2
3 Hanasoge
4 Do we need to rethink? In mixing length theory: l=h p only hypothesis cf. Nick Featherstone s talk Simulations: subgrid scale diffusion, viscosity Envisage reasons for (i) smaller scale flows and/or (ii) deeper parts subadiabatic? ut depth of convection zone still 200 Mm
5 Spruit97 A changing paradigm
6 Entropy rain
7 Stein & Nordlund (1998) simulations Filamentary, nonlocal shown: entropy fluctuations pos neg
8 Tau approximation u p i i s j j N c s g u N S u s / su p i j j i i i i N c s g S u u u s u s t F / 2 i su F N Closure hypothesis
9 Deardorff1
10 Deardorff2
11 Physical meaning? s / c 1 ln p ln p S pert coasting z s 0, u 0 u s z z 0
12 Physical meaning? s / c 1 ln p ln p S pert z s 0, u 0 u s z z 0
13 Why should only the top be unstable dt F K const rad dz e.g. if dt dz const K 3 16T 3 const Power law 0 a T b Polytropic index n T ab T 1 3 n
14 Deeper parts intrinsically stable Kramers opacity n=3.25 (interior): a=1, b=-7/2 Polytropic index n T ab T 1 3 n Entropy gradient positive (stable) for n > 3/2
15 Solar opacities n << -1 n = 3.25
16 Hydrostatic reference solutions Double Kramers-like H Kr Thickness only ~1Mm
17 Early work in the 1930s
18 Original mixing length model stable unstable weakly unstable stable surface assume interior F conv u S 1 3 rms
19 New solutions with Deardorff flux Entropy gradient d ln T d ln p d / ( S / cp) / dz ( ad ) H p old F conv ( ) ad new F conv ad ) ( D arxiv: v2
20 Consequences of small scales Larger k f less turb. Diffusion: h t =u rms /3k f Applications to dynamos: stronger, less turb diffusive Helps flux transport dynamos Two other important effect: Lambda effect differential rotation (Co smaller, Ta larger) aroclinic term stronger? Negative effective magnetic pressure spots 20
21 Flux emergence in global simulations Nelson, rown, run, Miesch, Toomre (2014) 21
22 3 scenarios Rising flux tubes? Hierachical convection? Self-organization as part of the dynamo g. u. g.w u.w A. 22
23 Sunspot decay 23
24 Self-assembly of a magnetic spot Minimalistic model 2 ingredients: Stratification & turbulence Extensions Coupled to dynamo Compete with rotation Radiation/ionization 24
25 A possible mechanism U i U j i j ij 3 ij U ij U 2 const Re M here based on forcing k Here 15 eddies per box scale Re M =70 means 70x15x2p=7000 based on box scale reakdown of quasi-linear theory randenburg et al (2011,ApJ 740, L50) 25
26 Negative effective magnetic pressure instability Kleeorin, Rogachevskii, Ruzmaikin (1989, 1990) Gas+turbulent+magnetic pressure; in pressure equil. increases turbulence is suppressed turbulent pressure decreases Net effect? 26
27 Sunspot formation that sucks Mean-field simulation: Neg pressure parameterized Typical downflow speeds Ma= randenbur et al (2014) 27
28 i-polar regions in simulations with corona Warnecke et al. (2013, ApJL 777, L37) 28
29 Coronal loops? Warnecke et al. (2013, ApJL 777, L37)
30 First dynamo-generated bi-polar regions Mitra et al. (2014, arxiv) 30
31 Still negative effective magnetic pressure? Or something new? Mitra et al. (2014, arxiv) 31
32 Jabbari et al. (2015, arxiv) Global models 32
33 33 New aspects in mean-field concept b u U E J t... J b u p 2 1 s,, t q q U U u u ij j i i j j i j i Ohm s law Theory and simulations: a effect and turbulent diffusivity Turbulent viscosity and other effects in momentum equation
34 Calculate full ij and ij tensors A t U ε J effect and turbulent magnetic diffusivity turbulent emf j ij j ε J ub * ij j Imposed-field method Convection (randenburg et al. 1990) Correlation method MRI accretion discs (randenburg & Sokoloff 2002) Galactic turbulence (Kowal et al. 2005, 2006) Test field method Stationary geodynamo (Schrinner et al. 2005, 2007) 34
35 35 Calculate full ij and ij tensors J U A t J b u U A t j b u b u u b U a t pq pq pq pq pq pq t j b u b u u b U a Original equation (uncurled) Mean-field equation fluctuations Response to arbitrary mean fields
36 36 Test fields 0 sin 0, 0 cos sin, 0 0 cos kz kz kz kz pq k j ijk pq j ij pq j, kz k kz kz k kz cos sin sin cos cos sin sin cos kz kz kz kz k * 22 * 21 * 12 * 11 Example:
37 Kinematic and t independent of Rm (2 200) ω u u 2 u k 1 rms f u u rms rms k 1 f Sur et al. (2008, MNRAS) 37
38 Nonlocality: convolution Multiplication convolution abcock-leighton effect is an example Sharp structures in mean-field dynamos artifacts Convolution in x-space multiplication in k 38
39 The 4 Roberts flows IV flow: negative eddy diffusivity dynamo ut positive diffusion at small scales Devlen et al. (2013) 39
40 40 Time-delay dynamo for Roberts II and III flows x z x z x t 2 2 ik k decay oscillatory With time delay x z x z x t t 2 ) ( x z x t x z x t 2
41 Time-delay dynamo for Roberts II and III flows t x z 2 x t x zx 2 ( k) k Re 2 [1 ( k) ] Growth when / 2 2 u rms k f 1 3 Rheinhardt et al. (2014) 41
42 Conclusions Small scale deep convection Deep convective flux: Deardorff Thus marginally stable (not unstable) Such flows yield weaker turb diffusion Favor spot formation by NEMPI Dynamo effect from time delay 42
Formation of Inhomogeneous Magnetic Structures in MHD Turbulence and Turbulent Convection
 Formation of Inhomogeneous Magnetic Structures in MHD Turbulence and Turbulent Convection Igor ROGACHEVSKII and Nathan KLEEORIN Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Beer-Sheva, Israel Axel BRANDENBURG and
Formation of Inhomogeneous Magnetic Structures in MHD Turbulence and Turbulent Convection Igor ROGACHEVSKII and Nathan KLEEORIN Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Beer-Sheva, Israel Axel BRANDENBURG and
Flux concentrations in turbulent convection
 Solar and Astrophysical Dynamos and Magnetic Activity Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 294, 2012 c International Astronomical Union 2013 A.G. Kosovichev, E.M. de Gouveia Dal Pino, & Y. Yan, eds. doi:10.1017/s1743921313002640
Solar and Astrophysical Dynamos and Magnetic Activity Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 294, 2012 c International Astronomical Union 2013 A.G. Kosovichev, E.M. de Gouveia Dal Pino, & Y. Yan, eds. doi:10.1017/s1743921313002640
Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection
 Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection André Giesecke Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam An der Sternwarte 16 14482 Potsdam MHD-Group seminar, 2006 André Giesecke (AIP) Anisotropic turbulence
Anisotropic turbulence in rotating magnetoconvection André Giesecke Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam An der Sternwarte 16 14482 Potsdam MHD-Group seminar, 2006 André Giesecke (AIP) Anisotropic turbulence
Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo
 Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo Manfred Küker 1 1 Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany Abstract. Mean field models of rotating
Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo Manfred Küker 1 1 Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany Abstract. Mean field models of rotating
Theory and modelling of turbulent transport in astrophysical phenomena
 MHD 2017 Tokyo, 29 August 2017 Theory and modelling of turbulent transport in astrophysical phenomena Nobumitsu YOKOI Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), University of Tokyo In collaboration with Akira
MHD 2017 Tokyo, 29 August 2017 Theory and modelling of turbulent transport in astrophysical phenomena Nobumitsu YOKOI Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), University of Tokyo In collaboration with Akira
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 30 2007 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv: ) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita)
 IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv:1505.06632) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita) Solar Seminar at MPS Oct 25, 2015 Large-scale magnetic field
IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv:1505.06632) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita) Solar Seminar at MPS Oct 25, 2015 Large-scale magnetic field
Helicity and Large Scale Dynamos; Lessons From Mean Field Theory and Astrophysical Implications
 Helicity and Large Scale Dynamos; Lessons From Mean Field Theory and Astrophysical Implications Eric Blackman (U. Rochester) 21st century theory based on incorporating mag. hel conservation has predictive
Helicity and Large Scale Dynamos; Lessons From Mean Field Theory and Astrophysical Implications Eric Blackman (U. Rochester) 21st century theory based on incorporating mag. hel conservation has predictive
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Oct 2014 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.sr] 31 Oct 2014](/thumbs/93/111897112.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2018 July 1, 2018 Magnetic flux concentrations from dynamo-generated fields S. Jabbari 1,2, A. Brandenburg 1,2, I. R. Losada 1,2, N. Kleeorin 3,1,4,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2018 July 1, 2018 Magnetic flux concentrations from dynamo-generated fields S. Jabbari 1,2, A. Brandenburg 1,2, I. R. Losada 1,2, N. Kleeorin 3,1,4,
Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul]
![Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul]](/thumbs/82/84973983.jpg) Dynamo tutorial Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] ISSI Dynamo tutorial 1 1 Dynamo tutorial
Dynamo tutorial Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] ISSI Dynamo tutorial 1 1 Dynamo tutorial
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields
 Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Theoretical Geomagnetism. Lecture 2: Self- Exciting Dynamos: Kinematic Theory
 Theoretical Geomagnetism Lecture 2: Self- Exciting Dynamos: Kinematic Theory 1 2.0 What is a self-exciting dynamo? Dynamo = A device that converts kinetic energy into electromagnetic energy. Dynamos use
Theoretical Geomagnetism Lecture 2: Self- Exciting Dynamos: Kinematic Theory 1 2.0 What is a self-exciting dynamo? Dynamo = A device that converts kinetic energy into electromagnetic energy. Dynamos use
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 16 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 16 Oct 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 16 Oct 2014](/thumbs/72/66481597.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 20 October 2014 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Intense bipolar structures from stratified helical dynamos Dhrubaditya Mitra 1, A. Brandenburg 1,2, N. Kleeorin
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 20 October 2014 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Intense bipolar structures from stratified helical dynamos Dhrubaditya Mitra 1, A. Brandenburg 1,2, N. Kleeorin
Dynamo Simulations in Solar Convection Zone
 Dynamo Simulations in Solar Convection Zone Bidya Binay Karak (Nordita fellow & Visitor at MPS) Collaborators: Axel Brandenburg (Nordita), Petri Käpylä and Maarit Käpylä (Aalto University) Thanks to organisers
Dynamo Simulations in Solar Convection Zone Bidya Binay Karak (Nordita fellow & Visitor at MPS) Collaborators: Axel Brandenburg (Nordita), Petri Käpylä and Maarit Käpylä (Aalto University) Thanks to organisers
Solar cycle & Dynamo Modeling
 Solar cycle & Dynamo Modeling Andrés Muñoz-Jaramillo www.solardynamo.org Georgia State University University of California - Berkeley Stanford University THE SOLAR CYCLE: A MAGNETIC PHENOMENON Sunspots
Solar cycle & Dynamo Modeling Andrés Muñoz-Jaramillo www.solardynamo.org Georgia State University University of California - Berkeley Stanford University THE SOLAR CYCLE: A MAGNETIC PHENOMENON Sunspots
Outline. What is overshoot? Why is overshoot interesting? Overshoot at the base of the solar convection zone. What is overshoot?
 Overshoot at the base of the solar convection zone What can we learn from numerical simulations? Matthias Rempel HAO / NCAR Outline What is overshoot? Why is overshoot interesting? Overshoot modeling different
Overshoot at the base of the solar convection zone What can we learn from numerical simulations? Matthias Rempel HAO / NCAR Outline What is overshoot? Why is overshoot interesting? Overshoot modeling different
Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence
 Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence Oliver Gressel, Axel Brandenburg Astrophysics group, NORDITA, Stockholm Abhijit Bendre, Detlef Elstner, Udo Ziegler &
Dynamic simulations of the Galactic Dynamo based on supernova-driven ISM turbulence Oliver Gressel, Axel Brandenburg Astrophysics group, NORDITA, Stockholm Abhijit Bendre, Detlef Elstner, Udo Ziegler &
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL
 DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
DYNAMO THEORY: THE PROBLEM OF THE GEODYNAMO PRESENTED BY: RAMANDEEP GILL MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE EARTH DIPOLE Field Structure Permanent magnetization of Core? 80% of field is dipole 20 % is non dipole 2)
Hydrodynamic simulations with a radiative surface
 Hydrodynamic simulations with a radiative surface Atefeh Barekat Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University, Sweden Nordita, KTH Royal Institute of Technology and Stockholm University, Sweden Department
Hydrodynamic simulations with a radiative surface Atefeh Barekat Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University, Sweden Nordita, KTH Royal Institute of Technology and Stockholm University, Sweden Department
"Heinrich Schwabe's holistic detective agency
 "Heinrich Schwabe's holistic detective agency, Ricky Egeland* High Altitude Observatory, NCAR 1. Sun alone is a complex system, emergence, total is > Σ of parts=> holistic 2. The Sun alone has provided
"Heinrich Schwabe's holistic detective agency, Ricky Egeland* High Altitude Observatory, NCAR 1. Sun alone is a complex system, emergence, total is > Σ of parts=> holistic 2. The Sun alone has provided
Creation and destruction of magnetic fields
 HAO/NCAR July 20 2011 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
HAO/NCAR July 20 2011 Magnetic fields in the Universe Earth Magnetic field present for 3.5 10 9 years, much longer than Ohmic decay time ( 10 4 years) Strong variability on shorter time scales (10 3 years)
Stratified Convection Driven by Internal Heating
 Stratified Convection Driven by Internal Heating (a convective amplitudes talk) Nick Featherstone Collaborators: Brad Hindman Mark Miesch Juri Toomre The Rossby Number typical velocity v Rotational Timescale
Stratified Convection Driven by Internal Heating (a convective amplitudes talk) Nick Featherstone Collaborators: Brad Hindman Mark Miesch Juri Toomre The Rossby Number typical velocity v Rotational Timescale
COMPLETE LIST OF PUBLICATIONS OF ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI
 COMPLETE LIST OF PUBLICATIONS OF ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI Publications (Book) : The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas: An Introduction for Astrophysicists Arnab Rai Choudhuri (1998) Cambridge University Press.
COMPLETE LIST OF PUBLICATIONS OF ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI Publications (Book) : The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas: An Introduction for Astrophysicists Arnab Rai Choudhuri (1998) Cambridge University Press.
Prediction of solar activity cycles by assimilating sunspot data into a dynamo model
 Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992638
Solar and Stellar Variability: Impact on Earth and Planets Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 264, 2009 A. G. Kosovichev, A. H. Andrei & J.-P. Rozelot, eds. c International Astronomical Union 2010 doi:10.1017/s1743921309992638
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 18 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 18 Jul 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 18 Jul 2013](/thumbs/72/66481700.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2013 July 19, 2013 Magnetic flux concentrations in a polytropic atmosphere I. R. Losada 1,2, A. Brandenburg 1,2, N. Kleeorin 3,1,4, I. Rogachevskii 3,1,4
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2013 July 19, 2013 Magnetic flux concentrations in a polytropic atmosphere I. R. Losada 1,2, A. Brandenburg 1,2, N. Kleeorin 3,1,4, I. Rogachevskii 3,1,4
Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields?
 Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields? Dana Longcope Montana State University w/ liberal borrowing from Bagenal, Stanley, Christensen, Schrijver, Charbonneau, Q: Why do the Sun and planets
Q: Why do the Sun and planets have magnetic fields? Dana Longcope Montana State University w/ liberal borrowing from Bagenal, Stanley, Christensen, Schrijver, Charbonneau, Q: Why do the Sun and planets
Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number
 MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
MRI Turbulence Workshop, IAS, Princeton, 17.06.08 Small-Scale Dynamo and the Magnetic Prandtl Number Alexander Schekochihin (Imperial College) with Steve Cowley (Culham & Imperial) Greg Hammett (Princeton)
A simple subgrid-scale model for astrophysical turbulence
 CfCA User Meeting NAOJ, 29-30 November 2016 A simple subgrid-scale model for astrophysical turbulence Nobumitsu Yokoi Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), Univ. of Tokyo Collaborators Axel Brandenburg
CfCA User Meeting NAOJ, 29-30 November 2016 A simple subgrid-scale model for astrophysical turbulence Nobumitsu Yokoi Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), Univ. of Tokyo Collaborators Axel Brandenburg
Solar photosphere. Michal Sobotka Astronomical Institute AS CR, Ondřejov, CZ. ISWI Summer School, August 2011, Tatranská Lomnica
 Solar photosphere Michal Sobotka Astronomical Institute AS CR, Ondřejov, CZ ISWI Summer School, August 2011, Tatranská Lomnica Contents General characteristics Structure Small-scale magnetic fields Sunspots
Solar photosphere Michal Sobotka Astronomical Institute AS CR, Ondřejov, CZ ISWI Summer School, August 2011, Tatranská Lomnica Contents General characteristics Structure Small-scale magnetic fields Sunspots
Solar Structure. Connections between the solar interior and solar activity. Deep roots of solar activity
 Deep roots of solar activity Michael Thompson University of Sheffield Sheffield, U.K. michael.thompson@sheffield.ac.uk With thanks to: Alexander Kosovichev, Rudi Komm, Steve Tobias Connections between
Deep roots of solar activity Michael Thompson University of Sheffield Sheffield, U.K. michael.thompson@sheffield.ac.uk With thanks to: Alexander Kosovichev, Rudi Komm, Steve Tobias Connections between
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters
 Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Magnetic Field in Galaxies and clusters Kandaswamy Subramanian Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune 411 007, India. The Magnetic Universe, February 16, 2015 p.0/27 Plan Observing
Scaling laws for planetary dynamos driven by helical waves
 Scaling laws for planetary dynamos driven by helical waves P. A. Davidson A. Ranjan Cambridge What keeps planetary magnetic fields alive? (Earth, Mercury, Gas giants) Two ingredients of the early theories:
Scaling laws for planetary dynamos driven by helical waves P. A. Davidson A. Ranjan Cambridge What keeps planetary magnetic fields alive? (Earth, Mercury, Gas giants) Two ingredients of the early theories:
Reconstructing the Subsurface Three-Dimensional Magnetic Structure of Solar Active Regions Using SDO/HMI Observations
 Reconstructing the Subsurface Three-Dimensional Magnetic Structure of Solar Active Regions Using SDO/HMI Observations Georgios Chintzoglou*, Jie Zhang School of Physics, Astronomy and Computational Sciences,
Reconstructing the Subsurface Three-Dimensional Magnetic Structure of Solar Active Regions Using SDO/HMI Observations Georgios Chintzoglou*, Jie Zhang School of Physics, Astronomy and Computational Sciences,
Accretion Disks I. High Energy Astrophysics: Accretion Disks I 1/60
 Accretion Disks I References: Accretion Power in Astrophysics, J. Frank, A. King and D. Raine. High Energy Astrophysics, Vol. 2, M.S. Longair, Cambridge University Press Active Galactic Nuclei, J.H. Krolik,
Accretion Disks I References: Accretion Power in Astrophysics, J. Frank, A. King and D. Raine. High Energy Astrophysics, Vol. 2, M.S. Longair, Cambridge University Press Active Galactic Nuclei, J.H. Krolik,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Apr 2017](/thumbs/84/89559151.jpg) IAUS 327: Fine Structure and Dynamics of the Solar Atmosphere Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 327, 2016 c 2016 International Astronomical Union A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
IAUS 327: Fine Structure and Dynamics of the Solar Atmosphere Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 327, 2016 c 2016 International Astronomical Union A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X
where G is Newton s gravitational constant, M is the mass internal to radius r, and Ω 0 is the
 Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
Hydrodynamic simulations with a radiative surface
 Hydrodynamic simulations with a radiative surface Atefeh Barekat Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University, Sweden Nordita, KTH Royal Institute of Technology and Stockholm University, Sweden Image
Hydrodynamic simulations with a radiative surface Atefeh Barekat Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University, Sweden Nordita, KTH Royal Institute of Technology and Stockholm University, Sweden Image
Surface Convection INTRODUCTION
 Surface Convection Robert F. Stein, David Benson, Dali Georgobiani, Åke Nordlund Werner Schaffenberger and Physics and Astronomy Department, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA Department
Surface Convection Robert F. Stein, David Benson, Dali Georgobiani, Åke Nordlund Werner Schaffenberger and Physics and Astronomy Department, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA Department
Nonmodal Growth and the Unstratified MRI Dynamo
 MPPC general meeting, Berlin, June 24 Nonmodal Growth and the Unstratified MRI Dynamo Jonathan Squire!! and!! Amitava Bhattacharjee MRI turbulence Observed accretion rate in disks in astrophysical disks
MPPC general meeting, Berlin, June 24 Nonmodal Growth and the Unstratified MRI Dynamo Jonathan Squire!! and!! Amitava Bhattacharjee MRI turbulence Observed accretion rate in disks in astrophysical disks
THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS
 THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS Axel Brandenburg NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen 0, Denmark; and Department of Mathematics, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, NEl 7RU, UK brandenb@nordita.dk Abstract
THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS Axel Brandenburg NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen 0, Denmark; and Department of Mathematics, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, NEl 7RU, UK brandenb@nordita.dk Abstract
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Nov 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Nov 2014](/thumbs/90/102450208.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2017 December 30, 2017 Hydraulic effects in a radiative atmosphere with ionization P. Bhat 1,2 and A. Brandenburg 1,3 1 Nordita, KTH Royal Institute
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2017 December 30, 2017 Hydraulic effects in a radiative atmosphere with ionization P. Bhat 1,2 and A. Brandenburg 1,3 1 Nordita, KTH Royal Institute
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 29 Jul 2018](/thumbs/89/98758195.jpg) Nonkinematic solar dynamo models with double-cell meridional circulation V.V. Pipin Institute of Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Irkutsk, 664033, Russia arxiv:1803.09459v2 [astro-ph.sr]
Nonkinematic solar dynamo models with double-cell meridional circulation V.V. Pipin Institute of Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Irkutsk, 664033, Russia arxiv:1803.09459v2 [astro-ph.sr]
arxiv: v3 [physics.flu-dyn] 9 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v3 [physics.flu-dyn] 9 Jul 2018 arxiv: v3 [physics.flu-dyn] 9 Jul 2018](/thumbs/91/105716408.jpg) Under consideration for publication in J. Plasma Phys. 1 arxiv:1801.05384v3 [physics.flu-dyn] 9 Jul 2018 Advances in mean-field dynamo theory and applications to astrophysical turbulence Axel Brandenburg
Under consideration for publication in J. Plasma Phys. 1 arxiv:1801.05384v3 [physics.flu-dyn] 9 Jul 2018 Advances in mean-field dynamo theory and applications to astrophysical turbulence Axel Brandenburg
A growing dynamo from a saturated Roberts flow dynamo
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 391, 1477 1481 (28) doi:1.1111/j.1365-2966.28.146.x A growing dynamo from a saturated Roberts flow dynamo Andreas Tilgner 1 and Axel Brandenburg 2 1 Institute of Geophysics, University
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 391, 1477 1481 (28) doi:1.1111/j.1365-2966.28.146.x A growing dynamo from a saturated Roberts flow dynamo Andreas Tilgner 1 and Axel Brandenburg 2 1 Institute of Geophysics, University
Stability of Vertically and Radially Stratified Protoplanetary Disks
 Stability of Vertically and Radially Stratified Protoplanetary Disks Figure from Stoll & Kley (2014) Glen Stewart Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado Vertical Shear instability
Stability of Vertically and Radially Stratified Protoplanetary Disks Figure from Stoll & Kley (2014) Glen Stewart Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics University of Colorado Vertical Shear instability
Supercomputers simulation of solar granulation
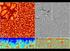 Supercomputers simulation of solar granulation simulation by Stein et al (2006), visualization by Henze (2008) Beyond Solar Dermatology But still stops at 0.97R! what lies deeper still? Supercomputers
Supercomputers simulation of solar granulation simulation by Stein et al (2006), visualization by Henze (2008) Beyond Solar Dermatology But still stops at 0.97R! what lies deeper still? Supercomputers
Mid Term Activity Report
 Department B: Scientific Department Project No: 227952 Project Acronym: AstroDyn Project Full Title: Astrophysical dynamos ERC GRANT Mid Term Activity Report Period covered: from 1 February 2009 to 31
Department B: Scientific Department Project No: 227952 Project Acronym: AstroDyn Project Full Title: Astrophysical dynamos ERC GRANT Mid Term Activity Report Period covered: from 1 February 2009 to 31
Magnetic Field Intensification and Small-scale Dynamo Action in Compressible Convection
 Magnetic Field Intensification and Small-scale Dynamo Action in Compressible Convection Paul Bushby (Newcastle University) Collaborators: Steve Houghton (Leeds), Nigel Weiss, Mike Proctor (Cambridge) Magnetic
Magnetic Field Intensification and Small-scale Dynamo Action in Compressible Convection Paul Bushby (Newcastle University) Collaborators: Steve Houghton (Leeds), Nigel Weiss, Mike Proctor (Cambridge) Magnetic
Solar and stellar dynamo models
 Solar and stellar dynamo models Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal From MHD to simple dynamo models Mean-field models Babcock-Leighton models Stochastic forcing Cycle forecasting Stellar dynamos
Solar and stellar dynamo models Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal From MHD to simple dynamo models Mean-field models Babcock-Leighton models Stochastic forcing Cycle forecasting Stellar dynamos
3-Fold Decomposition EFB Closure for Convective Turbulence and Organized Structures
 3-Fold Decomposition EFB Closure for Convective Turbulence and Organized Structures Igor ROGACHEVSKII and Nathan KLEEORIN Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel N.I. Lobachevsky State University
3-Fold Decomposition EFB Closure for Convective Turbulence and Organized Structures Igor ROGACHEVSKII and Nathan KLEEORIN Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel N.I. Lobachevsky State University
Accretion disc dynamos
 Accretion disc dynamos (i) Relative field orientation (ii) Ambient field vs dynamo (iii) Spin-up vs spin-down B. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, 2004, A&A 420, 17-32. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, W. Dobler,
Accretion disc dynamos (i) Relative field orientation (ii) Ambient field vs dynamo (iii) Spin-up vs spin-down B. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, 2004, A&A 420, 17-32. von Rekowski, A. Brandenburg, W. Dobler,
Global magnetorotational instability with inflow The non-linear regime
 Global magnetorotational instability with inflow The non-linear regime Evy Kersalé PPARC Postdoctoral Research Associate Dept. of Appl. Math. University of Leeds Collaboration: D. Hughes & S. Tobias (Dept.
Global magnetorotational instability with inflow The non-linear regime Evy Kersalé PPARC Postdoctoral Research Associate Dept. of Appl. Math. University of Leeds Collaboration: D. Hughes & S. Tobias (Dept.
The Sun. The Sun. Bhishek Manek UM-DAE Centre for Excellence in Basic Sciences. May 7, 2016
 The Sun Bhishek Manek UM-DAE Centre for Excellence in Basic Sciences May 7, 2016 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Resume of the Sun 3 Structure of the Sun - Solar Interior and Atmosphere 4 Standard Solar Model -
The Sun Bhishek Manek UM-DAE Centre for Excellence in Basic Sciences May 7, 2016 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Resume of the Sun 3 Structure of the Sun - Solar Interior and Atmosphere 4 Standard Solar Model -
Effects of rotation and stratification on magnetic flux concentrations
 Department of Astronomy Nordita Licentiate thesis Effects of rotation and stratification on magnetic flux concentrations Author: Illa R. Losada Supervisor: Axel Brandenburg Second Supervisor: Dan Kiselman
Department of Astronomy Nordita Licentiate thesis Effects of rotation and stratification on magnetic flux concentrations Author: Illa R. Losada Supervisor: Axel Brandenburg Second Supervisor: Dan Kiselman
Astronomy. Astrophysics. Quantifying the effect of turbulent magnetic diffusion on the growth rate of the magneto rotational instability
 DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201322837 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics Quantifying the effect of turbulent magnetic diffusion on the growth rate of the magneto rotational instability M. S. Väisälä 1,2, A.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201322837 c ESO 2014 Astronomy & Astrophysics Quantifying the effect of turbulent magnetic diffusion on the growth rate of the magneto rotational instability M. S. Väisälä 1,2, A.
Differential Rotation and Emerging Flux in Solar Convective Dynamo Simulations
 Differential Rotation and Emerging Flux in Solar Convective Dynamo Simulations Yuhong Fan (HAO/NCAR), Fang Fang (LASP/CU) GTP workshop August 17, 2016 The High Altitude Observatory (HAO) at the National
Differential Rotation and Emerging Flux in Solar Convective Dynamo Simulations Yuhong Fan (HAO/NCAR), Fang Fang (LASP/CU) GTP workshop August 17, 2016 The High Altitude Observatory (HAO) at the National
Lecture 14: Solar Cycle. Observations of the Solar Cycle. Babcock-Leighton Model. Outline
 Lecture 14: Solar Cycle Outline 1 Observations of the Solar Cycle 2 Babcock-Leighton Model Observations of the Solar Cycle Sunspot Number 11-year (average) cycle period as short as 8 years as long as 15
Lecture 14: Solar Cycle Outline 1 Observations of the Solar Cycle 2 Babcock-Leighton Model Observations of the Solar Cycle Sunspot Number 11-year (average) cycle period as short as 8 years as long as 15
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 26 Feb 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 26 Feb 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 26 Feb 2018](/thumbs/93/114407668.jpg) Astronomische Nachrichten, 2 July 208 Small-scale dynamos in simulations of stratified turbulent convection Petri J. Käpylä,2,3,, Maarit J. Käpylä 3,2, and Axel Brandenburg 4,5,6,7 arxiv:802.09607v [astro-ph.sr]
Astronomische Nachrichten, 2 July 208 Small-scale dynamos in simulations of stratified turbulent convection Petri J. Käpylä,2,3,, Maarit J. Käpylä 3,2, and Axel Brandenburg 4,5,6,7 arxiv:802.09607v [astro-ph.sr]
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics
 Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
Selected Topics in Plasma Astrophysics Range of Astrophysical Plasmas and Relevant Techniques Stellar Winds (Lecture I) Thermal, Radiation, and Magneto-Rotational Driven Winds Connections to Other Areas
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal
 Stellar dynamos Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal Magnetohydrodynamics (ch. I.3) Simulations of solar/stellar dynamos (ch. III.5, +) Mean-field electrodynamics (ch. I.3, III.6) From MHD to simpler
Stellar dynamos Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal Magnetohydrodynamics (ch. I.3) Simulations of solar/stellar dynamos (ch. III.5, +) Mean-field electrodynamics (ch. I.3, III.6) From MHD to simpler
The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) in collaboration with Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma, Jim Stone, Greg Hammett Hydra A w/ Chandra Galactic
The Effects of Anisotropic Transport on Dilute Astrophysical Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) in collaboration with Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma, Jim Stone, Greg Hammett Hydra A w/ Chandra Galactic
The solar dynamo (critical comments on) SPD Hale talk 14 June 2011
 The solar dynamo (critical comments on) The solar dynamo (critical comments on) - what observations show - what they show is not the case - what is known from theory - interesting open questions quantitative
The solar dynamo (critical comments on) The solar dynamo (critical comments on) - what observations show - what they show is not the case - what is known from theory - interesting open questions quantitative
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018](/thumbs/88/116029012.jpg) Breaking Taylor-Proudman balance by magnetic field in stellar convection zone H. Hotta arxiv:1806.01452v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018 Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Chiba university, 1-33
Breaking Taylor-Proudman balance by magnetic field in stellar convection zone H. Hotta arxiv:1806.01452v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018 Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Chiba university, 1-33
Turbulent reconnection of magnetic bipoles in stratified turbulence
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 11 () Printed 12 April 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Turbulent reconnection of magnetic bipoles in stratified turbulence S. Jabbari 1,2, A. Brandenburg 1,2,3,4, Dhrubaditya
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 11 () Printed 12 April 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Turbulent reconnection of magnetic bipoles in stratified turbulence S. Jabbari 1,2, A. Brandenburg 1,2,3,4, Dhrubaditya
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory. Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008
 Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
Effect of the radiative background flux in convection
 Astron. Nachr. / AN 326, No. 8, 681 692 (2005) /DOI10.1002/asna.200510411 Effect of the radiative background flux in convection A. BRANDENBURG 1,K.L.CHAN 2, Å. NORDLUND 3,andR.F.STEIN 4 1 NORDITA, Blegdamsvej
Astron. Nachr. / AN 326, No. 8, 681 692 (2005) /DOI10.1002/asna.200510411 Effect of the radiative background flux in convection A. BRANDENBURG 1,K.L.CHAN 2, Å. NORDLUND 3,andR.F.STEIN 4 1 NORDITA, Blegdamsvej
The dynamics of Wolf numbers based on nonlinear dynamos with magnetic helicity: comparisons with observations
 Advance Access publication 2016 May 27 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1267 The dynamics of Wolf numbers based on nonlinear dynamos with magnetic helicity: comparisons with observations Y. Kleeorin, 1 N. Safiullin,
Advance Access publication 2016 May 27 doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1267 The dynamics of Wolf numbers based on nonlinear dynamos with magnetic helicity: comparisons with observations Y. Kleeorin, 1 N. Safiullin,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 14 Feb 2018
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 14 Feb 2018 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 14 Feb 2018](/thumbs/94/121680613.jpg) Draft version June 28, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1. GENERATION OF LARGE-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD IN CONVECTIVE FULL-SPHERE CROSS-HELICITY DYNAMO V.V. Pipin 1 and N. Yokoi 2 1 Institute
Draft version June 28, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style AASTeX6 v. 1. GENERATION OF LARGE-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD IN CONVECTIVE FULL-SPHERE CROSS-HELICITY DYNAMO V.V. Pipin 1 and N. Yokoi 2 1 Institute
Global Simulations of Black Hole Accretion. John F. Hawley Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia
 Global Simulations of Black Hole Accretion John F. Hawley Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia Collaborators and Acknowledgements Julian Krolik, Johns Hopkins University Scott Noble, JHU Jeremy
Global Simulations of Black Hole Accretion John F. Hawley Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia Collaborators and Acknowledgements Julian Krolik, Johns Hopkins University Scott Noble, JHU Jeremy
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere. Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin
 The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
The Madison Dynamo Experiment: magnetic instabilities driven by sheared flow in a sphere Cary Forest Department of Physics University of Wisconsin February 28, 2001 Planets, stars and perhaps the galaxy
NUMERICAL STUDIES OF DYNAMO ACTION IN A TURBULENT SHEAR FLOW. I.
 The Astrophysical Journal, 806:8 (0pp), 05 June 0 05. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. doi:0.088/0004-637x/806//8 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF DYNAMO ACTION IN A TURBULENT SHEAR FLOW. I.
The Astrophysical Journal, 806:8 (0pp), 05 June 0 05. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. doi:0.088/0004-637x/806//8 NUMERICAL STUDIES OF DYNAMO ACTION IN A TURBULENT SHEAR FLOW. I.
Non-spot magnetic fields
 Non-spot magnetic fields Non-spot fields Sunspots cover in general
Non-spot magnetic fields Non-spot fields Sunspots cover in general
Global Magnetorotational Instability with Inflow
 Global Magnetorotational Instability with Inflow Evy Kersalé PPARC Postdoctoral Research Associate Dept. of Appl. Maths University of Leeds Collaboration: D. Hughes & S. Tobias (Appl. Maths, Leeds) N.
Global Magnetorotational Instability with Inflow Evy Kersalé PPARC Postdoctoral Research Associate Dept. of Appl. Maths University of Leeds Collaboration: D. Hughes & S. Tobias (Appl. Maths, Leeds) N.
Turbulent transport coefficients in spherical wedge dynamo simulations of solar-like stars
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2017 July 30, 2017 Turbulent transport coefficients in spherical wedge dynamo simulations of solar-like stars J. Warnecke 1, 2,M.Rheinhardt 2,S.Tuomisto
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2017 July 30, 2017 Turbulent transport coefficients in spherical wedge dynamo simulations of solar-like stars J. Warnecke 1, 2,M.Rheinhardt 2,S.Tuomisto
Turbulence Modeling I!
 Outline! Turbulence Modeling I! Grétar Tryggvason! Spring 2010! Why turbulence modeling! Reynolds Averaged Numerical Simulations! Zero and One equation models! Two equations models! Model predictions!
Outline! Turbulence Modeling I! Grétar Tryggvason! Spring 2010! Why turbulence modeling! Reynolds Averaged Numerical Simulations! Zero and One equation models! Two equations models! Model predictions!
Predicting a solar cycle before its onset using a flux transport dynamo model
 *** TITLE *** Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 335, 2017 ***NAME OF EDITORS*** c 2017 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Predicting a solar cycle before its onset using a flux
*** TITLE *** Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 335, 2017 ***NAME OF EDITORS*** c 2017 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Predicting a solar cycle before its onset using a flux
Planetary dynamos: Dipole-multipole transition and dipole reversals
 Planetary dynamos: Dipole-multipole transition and dipole reversals Ulrich Christensen Max-Planck-Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany in collaboration with Hagay Amit, Julien
Planetary dynamos: Dipole-multipole transition and dipole reversals Ulrich Christensen Max-Planck-Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany in collaboration with Hagay Amit, Julien
Observable consequences
 Coronal Heating through braiding of magnetic field lines Solar eclipse, 11.8.1999, Wendy Carlos & John Kern Observable consequences 3D MHD model spectral synthesis results: Doppler shifts DEM variability
Coronal Heating through braiding of magnetic field lines Solar eclipse, 11.8.1999, Wendy Carlos & John Kern Observable consequences 3D MHD model spectral synthesis results: Doppler shifts DEM variability
Magnetic structuring at spatially unresolved scales. Jan Stenflo ETH Zurich and IRSOL, Locarno
 Magnetic structuring at spatially unresolved scales Jan Stenflo ETH Zurich and IRSOL, Locarno Magnetograms of the active and quiet Sun Question: What would the field look like with infinite resolution
Magnetic structuring at spatially unresolved scales Jan Stenflo ETH Zurich and IRSOL, Locarno Magnetograms of the active and quiet Sun Question: What would the field look like with infinite resolution
Rossby waves and solar activity variations
 Rossby waves and solar activity variations Teimuraz Zaqarashvili Institute für Geophysik, Astrophysik und Meteorologie University of Graz, Austria Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory at Ilia state University,
Rossby waves and solar activity variations Teimuraz Zaqarashvili Institute für Geophysik, Astrophysik und Meteorologie University of Graz, Austria Abastumani Astrophysical Observatory at Ilia state University,
A Discussion on The Effect of Mesh Resolution on Convective Boundary Layer Statistics and Structures Generated by Large-Eddy Simulation by Sullivan
 耶鲁 - 南京信息工程大学大气环境中心 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment A Discussion on The Effect of Mesh Resolution on Convective Boundary Layer Statistics and Structures Generated by Large-Eddy Simulation
耶鲁 - 南京信息工程大学大气环境中心 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment A Discussion on The Effect of Mesh Resolution on Convective Boundary Layer Statistics and Structures Generated by Large-Eddy Simulation
Accretion disks. AGN-7:HR-2007 p. 1. AGN-7:HR-2007 p. 2
 Accretion disks AGN-7:HR-2007 p. 1 AGN-7:HR-2007 p. 2 1 Quantitative overview Gas orbits in nearly circular fashion Each gas element has a small inward motion due to viscous torques, resulting in an outward
Accretion disks AGN-7:HR-2007 p. 1 AGN-7:HR-2007 p. 2 1 Quantitative overview Gas orbits in nearly circular fashion Each gas element has a small inward motion due to viscous torques, resulting in an outward
Energy transport: convection
 Outline Introduction: Modern astronomy and the power of quantitative spectroscopy Basic assumptions for classic stellar atmospheres: geometry, hydrostatic equilibrium, conservation of momentum-mass-energy,
Outline Introduction: Modern astronomy and the power of quantitative spectroscopy Basic assumptions for classic stellar atmospheres: geometry, hydrostatic equilibrium, conservation of momentum-mass-energy,
Vortex Dynamos. Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD)
 Vortex Dynamos Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD) An introduction to vortices Vortices are ubiquitous in geophysical and astrophysical fluid mechanics (stratification & rotation).
Vortex Dynamos Steve Tobias (University of Leeds) Stefan Llewellyn Smith (UCSD) An introduction to vortices Vortices are ubiquitous in geophysical and astrophysical fluid mechanics (stratification & rotation).
Parity of solar global magnetic field determined by turbulent diffusivity
 First Asia-Pacific Solar Physics Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 1, pp 117 122 Edited by Arnab Rai Choudhuri & Dipankar Banerjee Parity of solar global magnetic field determined by turbulent
First Asia-Pacific Solar Physics Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 1, pp 117 122 Edited by Arnab Rai Choudhuri & Dipankar Banerjee Parity of solar global magnetic field determined by turbulent
Summary: Mean field theory. ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism. Lecture 11 Tues 26 Feb Summary: Mean field theory. Summary: Mean field theory
 ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Summary: Mean fiel theory Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Average of inuction equation: ( ) = v + v η New solution properties arie from the term: E = v Assumption of
ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Summary: Mean fiel theory Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Average of inuction equation: ( ) = v + v η New solution properties arie from the term: E = v Assumption of
Logarithmic velocity profile in the atmospheric (rough wall) boundary layer
 Logarithmic velocity profile in the atmospheric (rough wall) boundary layer P =< u w > U z = u 2 U z ~ ε = u 3 /kz Mean velocity profile in the Atmospheric Boundary layer Experimentally it was found that
Logarithmic velocity profile in the atmospheric (rough wall) boundary layer P =< u w > U z = u 2 U z ~ ε = u 3 /kz Mean velocity profile in the Atmospheric Boundary layer Experimentally it was found that
Dynamo theory and its experimental validation
 Dynamo theory and its experimental validation Karl-Heinz Rädler Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Stockholm February 2009 Outline The idea of the self-exciting dynamo and elements of dynamo theory The Riga
Dynamo theory and its experimental validation Karl-Heinz Rädler Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Stockholm February 2009 Outline The idea of the self-exciting dynamo and elements of dynamo theory The Riga
Connecting solar radiance variability to the. solar dynamo using the virial theorem
 Connecting solar radiance variability to the solar dynamo using the virial theorem Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik, Freiburg i.br. steiner@kis.uni-freiburg.de http://www.uni-freiburg.de/ steiner/
Connecting solar radiance variability to the solar dynamo using the virial theorem Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik, Freiburg i.br. steiner@kis.uni-freiburg.de http://www.uni-freiburg.de/ steiner/
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales
 Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 29 Jan 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 29 Jan 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 29 Jan 2008](/thumbs/92/109576712.jpg) Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso?, 1 6, (2018) Non-dipolar magnetic fields in Ap stars arxiv:0801.4562v1 [astro-ph] 29 Jan 2008 J.Braithwaite 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics 60 St.
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso?, 1 6, (2018) Non-dipolar magnetic fields in Ap stars arxiv:0801.4562v1 [astro-ph] 29 Jan 2008 J.Braithwaite 1 Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics 60 St.
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 10 Dec 2008
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 10 Dec 2008 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 10 Dec 2008](/thumbs/76/73122006.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2017 December 3, 2017 Alpha effect and diffusivity in helical turbulence with shear Dhrubaditya Mitra 1, Petri J. Käpylä 2, Reza Tavakol 1, and Axel
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2017 December 3, 2017 Alpha effect and diffusivity in helical turbulence with shear Dhrubaditya Mitra 1, Petri J. Käpylä 2, Reza Tavakol 1, and Axel
LES Simulations of Quiet Sun Magnetism
 LES Simulations of Quiet Sun Magnetism Matthias Rempel HAO/NCAR Quiet sun magnetism Origin and spatial distribution of quiet sun field Small scale dynamo? Remnant field from large scale dynamo? Vögler,
LES Simulations of Quiet Sun Magnetism Matthias Rempel HAO/NCAR Quiet sun magnetism Origin and spatial distribution of quiet sun field Small scale dynamo? Remnant field from large scale dynamo? Vögler,
38. DYNAMOS; MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATION AND MAINTENANCE
 38. DYNAMOS; MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATION AND MAINTENANCE (Much of this Section derives from H. K. Moffatt, Magnetic Field Generation in Electrically Conducting Fluids, Cambridge, 978) The study of dynamos
38. DYNAMOS; MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATION AND MAINTENANCE (Much of this Section derives from H. K. Moffatt, Magnetic Field Generation in Electrically Conducting Fluids, Cambridge, 978) The study of dynamos
The Solar Surface Dynamo
 Overview of turbulent dynamo theory The Solar Surface Dynamo J. Pietarila Graham, 1 S. Danilovic, 1 M. Schüssler, 1 A. Vögler, 2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung 2 Sterrekundig Instituut,
Overview of turbulent dynamo theory The Solar Surface Dynamo J. Pietarila Graham, 1 S. Danilovic, 1 M. Schüssler, 1 A. Vögler, 2 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung 2 Sterrekundig Instituut,
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
The Physics of Collisionless Accretion Flows Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Accretion Disks: Physical Picture Simple Consequences of Mass, Momentum, & Energy Conservation Matter Inspirals on Approximately
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism. Lecture 9 Tues 19 Feb Magnetic fields in the Universe. Geomagnetism.
 Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
Scope of this lecture ASTR 7500: Solar & Stellar Magnetism Hale CGEG Solar & Space Physics Processes of magnetic field generation and destruction in turbulent plasma flows Introduction to general concepts
FLOW-NORDITA Spring School on Turbulent Boundary Layers1
 Jonathan F. Morrison, Ati Sharma Department of Aeronautics Imperial College, London & Beverley J. McKeon Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories, California Institute Technology FLOW-NORDITA Spring School on
Jonathan F. Morrison, Ati Sharma Department of Aeronautics Imperial College, London & Beverley J. McKeon Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories, California Institute Technology FLOW-NORDITA Spring School on
Large-scale Flows and Dynamo In Solar-Like Stars
 Large-scale Flows and Dynamo In Solar-Like Stars Gustavo Guerrero Physics Department Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais Brazil P. Smolarkiewicz (ECMWF) A. Kosovichev (NJIT), Elisabete M. de G. Dal Pino
Large-scale Flows and Dynamo In Solar-Like Stars Gustavo Guerrero Physics Department Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais Brazil P. Smolarkiewicz (ECMWF) A. Kosovichev (NJIT), Elisabete M. de G. Dal Pino
