Physics 306, Honors Astronomy, Final Exam NAME
|
|
|
- Mary Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 306, Honors Astronomy, Final Exam NAME You are graded on your work, with partial credit where it is deserved. 1. Clearly describe how you (as an astronomer) would measure each of the following: (a) (2) Which elements are in the atmosphere of a star: (b) (2) How fast a star is moving away from us (or toward us): (c) (2) The distance to a Cepheid variable star: (d) (2) The surface temperature of a star: (e) (2) The mass of a heavy star which has a substantially lighter star as a companion in a binary system, if the distance between the stars can be determined with, e.g., parallax. (Actually, this basic method works for both stars in any binary system, but for simplicity let us suppose that you can just think of the lighter star as revolving around the heavier one.)
2 2. Below, in Parts (a) (d), arrange the following cosmological eras in chronological order, with the earliest first and the latest last: era of atoms (with universe relatively transparent to light) GUT era and era of inflation era of nucleosynthesis Planck era Then briefly give some substantial information about each era. This information should include a very crude indication of the time and temperature, as well as the fundamental significance of each era. (a) (3) (b) (3) (c) (3) (d) (3)
3 3. List the 4 pillars of the Big Bang theory and briefly indicate how each one of them involves a comparison between theory and observation. (a) (2) (b) (2) (c) (2) (d) (2)
4 4. (a) (3) List 6 quantities that must be conserved in a nuclear reaction. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (b) (7) State whether each of the following reactions is possible. I.e., say whether it satisfies all the conservation laws, and if not say which conservation law is violated. Here n 0 is a neutron, p + a proton, e! an electron, e + a positron,! a photon,! a neutrino, and! an antineutrino. (i) n 0! p + + e " + # (ii) n 0! p + + e " + # (iii) n 0! p + + e " + # (iv) p +! e + + " (v) p + + p +! p + + n 0 + e + + " (vi) p + + p +! p + + n 0 + e + + " Now, one of the reactions above represents beta decay, and one represents a fusion reaction within our Sun. Mark these 2 reactions with beta decay and fusion respectively, with the relevant phrase to the right of the reaction.
5 5. (a) (5) Once again (just as in class, and even on a previous exam) recall that a mass m, moving with velocity v, must be subjected to a centripetal force F = m v2 r if it is to be kept in a circular orbit of radius r. If this force is due to the gravitational attraction of a much larger mass M, then we also have F = G mm r 2 where G = 6..67! 10 "11 m 3 /kg s 2. Combine these equations to find the expression for M in terms of m, v, and r. (b) (5) Hydrogen atoms revolving around a galaxy are typically found to have larger velocities than can be accounted for with only luminous matter, and this is one of the strong arguments for the presence of dark matter. Use the graph below to approximately calculate the mass contained within 10 kpc of the center of the galaxy M33. From 1 km = 1 kilometer = 10 3 m 1 kpc = 1 kiloparsec = 3.26! 10 3 light years 1 light year = 9.46! m
6 6. (a) (5) A planet discovered around the star 51 Pegasi has an orbital period of 4.23 days. Calculate the distance of the planet from its star (or more precisely, the semimajor axis a of the planet s elliptical orbit). Since 51 Pegasi has about the same mass as our Sun, you can use the simple form of Kepler s third law p 2 = a 3 where the period p is measured in years and a is measured in AU (astronomical units). 1 AU! 1.50 " 10 8 km and 1 year! 365 days (b) (5) Describe 3 major methods used to detect extrasolar planets, saying briefly what each method tells you about the planet. (i) (ii) (iii)
7 7. A planet is found to block 1% of the light from its star when it is making a transit. The star has a radius of 500,000 km. (a) (4) Calculate the radius of the planet. (b) (4) The mass of the planet is found to be 4.0! kg. Calculate the mass density in g/cm 3. (c) (2) Is this planet more like Earth or more like Jupiter? Explain.
8 8. List and clearly describe the 3 different processes that can lead to internal heat and volcanic activity in a planet or large moon, making reference to the example that is provided in each case. (a) (2) Early Earth: (b) (4) Present-day Earth: (c) (4) Io:
9 9. Starting with the Sun, then moving outward (with the object nearest the Sun first) list 10 of your favorite objects in the Solar System, including the 8 that are still officially classified as planets. In each case, clearly describe one substantial and nontrivial feature about each object that you find interesting. (a) (2) (b) (2) (c) (2) (d) (2) (e) (2)
10 (f) (2) (g) (2) (h) (2) (i) (2) (j) (2)
11 10. (5 points extra credit) Briefly describe the significance of each of the following experiments: (a) Wilson and Penzias, 1964: (b) COBE (Cosmic Background Explorer), early 1990s: (c) WMAP (Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe), early 2000s: 11. (5 points extra credit) Qualitatively describe the particles in the Standard Model of particle physics, including the 3 generations of quarks and leptons and the various force-carrying particles. List all 4 members of the first generation of quarks and leptons. What is the quark content of a proton and of a neutron? What are the charges of these quarks? Happy Holidays, and have a Merry Christmas!
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS FINAL EXAM: THURSDAY, May 14 th, 11:15am Last Astronomy public talk, May 8 th (up to 3% Extra class credit (see Blackboard announcement for details)
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS FINAL EXAM: THURSDAY, May 14 th, 11:15am Last Astronomy public talk, May 8 th (up to 3% Extra class credit (see Blackboard announcement for details)
Physics 306, Honors Astronomy, Exam 3 NAME
 Physics 306, Honors Astronomy, Exam 3 NAME You are graded on your work, with partial credit where it is deserved. 1. (4) A very tough friend of yours (who can withstand the tidal forces) sits in his spaceship
Physics 306, Honors Astronomy, Exam 3 NAME You are graded on your work, with partial credit where it is deserved. 1. (4) A very tough friend of yours (who can withstand the tidal forces) sits in his spaceship
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. OUR Universe: Accelerating Universe
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies FINAL: Saturday, Dec 12th, 7:30pm, HERE ALTERNATE FINAL: Monday, Dec 7th, 5:30pm in Muenzinger E131 Last OBSERVING session, Tue, Dec.8th, 7pm Please check
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies FINAL: Saturday, Dec 12th, 7:30pm, HERE ALTERNATE FINAL: Monday, Dec 7th, 5:30pm in Muenzinger E131 Last OBSERVING session, Tue, Dec.8th, 7pm Please check
Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time
 Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Back to the Big Bang The early Universe was both dense and hot. Equivalent mass density of radiation (E=mc
Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Back to the Big Bang The early Universe was both dense and hot. Equivalent mass density of radiation (E=mc
Chapter 27: The Early Universe
 Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes
 Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how much bigger in radius is the Sun than the Earth? The ratio of the Sun's radius to the Earth's radius is 1,392,000/12756 = 109.1 How big is an astronomical
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how much bigger in radius is the Sun than the Earth? The ratio of the Sun's radius to the Earth's radius is 1,392,000/12756 = 109.1 How big is an astronomical
4 The Big Bang, the genesis of the Universe, the origin of the microwave background
 4 The Big Bang, the genesis of the Universe, the origin of the microwave background a(t) = 0 The origin of the universe: a(t) = 0 Big Bang coined by Fred Hoyle he calculated the ratio of elements created
4 The Big Bang, the genesis of the Universe, the origin of the microwave background a(t) = 0 The origin of the universe: a(t) = 0 Big Bang coined by Fred Hoyle he calculated the ratio of elements created
Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes. Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017
 Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017 Reminders Last star party of the semester tomorrow night! Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm The first three minutes
Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017 Reminders Last star party of the semester tomorrow night! Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm The first three minutes
Answer Key for Exam C
 Answer Key for Exam C 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam C 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B
 Answer Key for Exam B 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Chapter 27 The Early Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 27 The Early Universe Units of Chapter 27 27.1 Back to the Big Bang 27.2 The Evolution of the Universe More on Fundamental Forces 27.3 The Formation of Nuclei and Atoms 27.4 The Inflationary Universe
Chapter 27 The Early Universe Units of Chapter 27 27.1 Back to the Big Bang 27.2 The Evolution of the Universe More on Fundamental Forces 27.3 The Formation of Nuclei and Atoms 27.4 The Inflationary Universe
Answer Key for Exam D
 Answer Key for Exam D 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam D 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE?
 i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3
 October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
October 31, 2004 Name: Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Review Exam 3 Instructions: Write your answers in the space provided; indicate clearly if you continue on the back of a page. No books, notes, or
Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online.
 Announcements HW #5 Due Wed, Dec. 10th. Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online. NOTE: Planetarium: Large dome you sit inside.
Announcements HW #5 Due Wed, Dec. 10th. Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online. NOTE: Planetarium: Large dome you sit inside.
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 33 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
The first 400,000 years
 The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
Inflationary Universe and. Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation
 Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Survey questions. Inflationary Universe and. Survey Questions. Survey questions. Survey questions
 Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time
 Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Future of universe depends on the total amount of dark and normal matter Amount of matter
Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Future of universe depends on the total amount of dark and normal matter Amount of matter
Nucleosíntesis primordial
 Tema 5 Nucleosíntesis primordial Asignatura de Física Nuclear Curso académico 2009/2010 Universidad de Santiago de Compostela Big Bang cosmology 1.1 The Universe today The present state of the Universe
Tema 5 Nucleosíntesis primordial Asignatura de Física Nuclear Curso académico 2009/2010 Universidad de Santiago de Compostela Big Bang cosmology 1.1 The Universe today The present state of the Universe
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Relative Sizes of Stars. Today Exam#3 Review. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Blackbody Radiation
 Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers
 Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers Prof. Pradhan April 24, 2015 What is Science? 1. Explain the difference between astronomy and astrology. 2. What number is the metric system based around? What
Unity in the Whole Structure
 Cosmology II Unity in the Whole Structure How is it possible by any methods of observation yet known to the astronomer to learn anything about the universe as a whole? It is possible only because the universe,
Cosmology II Unity in the Whole Structure How is it possible by any methods of observation yet known to the astronomer to learn anything about the universe as a whole? It is possible only because the universe,
Cosmology. What is Cosmology?
 Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
Cosmology What is Cosmology? The study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe The idea is to form picture of the entire Universe: origin, size, and future We will make assumptions that what
V. Astronomy Section
 EAS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines V. Astronomy Section 1. Introduction, Astronomical Distances, Solar System Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of Earth s position in the solar
EAS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines V. Astronomy Section 1. Introduction, Astronomical Distances, Solar System Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of Earth s position in the solar
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
Exam #3. Final Exam. Exam 3 review. How do we measure properties of a star? A detailed outline of study topics is here:
 Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago
 Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller hgeller@gmu.edu http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George
Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller hgeller@gmu.edu http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline. The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) Inflationary Model Added. (10^-35 to 10^-33 Of A Second)
 The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. State the Cosmological Principle. [Total 2 marks] 2. Describe the important properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation and how the standard model of the Universe
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. State the Cosmological Principle. [Total 2 marks] 2. Describe the important properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation and how the standard model of the Universe
Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis
 Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. The CMB as seen by the WMAP satellite.!2
Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. The CMB as seen by the WMAP satellite.!2
IB Physics - Astronomy
 Solar System Our Solar System has eight planets. The picture below shows their relative sizes, but NOT their relative distances. A planet orbits the sun, and has gravitationally cleared its orbital area
Solar System Our Solar System has eight planets. The picture below shows their relative sizes, but NOT their relative distances. A planet orbits the sun, and has gravitationally cleared its orbital area
Lecture 13. Gravity in the Solar System
 Lecture 13 Gravity in the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How was the heliocentric model established? What are monumental steps in the history of the heliocentric model? 2. How do Kepler s three laws
Lecture 13 Gravity in the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How was the heliocentric model established? What are monumental steps in the history of the heliocentric model? 2. How do Kepler s three laws
John Ellison University of California, Riverside. Quarknet 2008 at UCR
 Overview of Particle Physics John Ellison University of California, Riverside Quarknet 2008 at UCR 1 Particle Physics What is it? Study of the elementary constituents of matter And the fundamental forces
Overview of Particle Physics John Ellison University of California, Riverside Quarknet 2008 at UCR 1 Particle Physics What is it? Study of the elementary constituents of matter And the fundamental forces
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science Astronomy
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science Astronomy ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM Formation of the Solar System Motion and Position Kepler s Laws Newton
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science Astronomy ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM Formation of the Solar System Motion and Position Kepler s Laws Newton
Implications of the Hubble Law: - it is not static, unchanging - Universe had a beginning!! - could not have been expanding forever HUBBLE LAW:
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe. Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is changing (getting bigger!) - it is not static, unchanging
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Name: unid: Foundations of Astronomy ASTR/PHYS Final Exam
 Name: unid: Physical Constants * Foundations of Astronomy ASTR/PHYS 2500 Final Exam Gravitational constant G 6.673 x 10-11 m 3 kg - 1 s - 2 Elementary charge e 1.602 x 10-19 C Vacuum permittivity ε 0 8.854
Name: unid: Physical Constants * Foundations of Astronomy ASTR/PHYS 2500 Final Exam Gravitational constant G 6.673 x 10-11 m 3 kg - 1 s - 2 Elementary charge e 1.602 x 10-19 C Vacuum permittivity ε 0 8.854
OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and determining
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram and determining
Cosmology. An Analogy 11/28/2010. Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe
 Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang. Expansion of the Universe. Big Bang Theory. Age of the Universe. Hubble s Law. Hubble s Law
 Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
COSMOLOGY and DARK MATTER
 Physics 10 1 st Lecture September 28, 2004 COSMOLOGY and DARK MATTER Joel Primack Introduction Modern cosmology the study of the universe as a whole is undergoing a scientific revolution. New ground- and
Physics 10 1 st Lecture September 28, 2004 COSMOLOGY and DARK MATTER Joel Primack Introduction Modern cosmology the study of the universe as a whole is undergoing a scientific revolution. New ground- and
The performance expectation above was developed using the following elements from A Framework for K-12 Science Education: Disciplinary Core Ideas
 HS-ESS1-1 HS-ESS1-1. Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the life span of the sun and the role of nuclear fusion in the sun s core to release energy in the form of radiation. [Clarification
HS-ESS1-1 HS-ESS1-1. Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the life span of the sun and the role of nuclear fusion in the sun s core to release energy in the form of radiation. [Clarification
Crab Nebula. Hubble Telescope (optical) Consists of Debris from 1054 Supernova in our Milky Way Galaxy
 Crab Nebula Hubble Telescope (optical) Consists of Debris from 1054 Supernova in our Milky Way Galaxy The Crab Nebula is the remnant of a star which, at the end of its lifespan, exploded in a supernova,
Crab Nebula Hubble Telescope (optical) Consists of Debris from 1054 Supernova in our Milky Way Galaxy The Crab Nebula is the remnant of a star which, at the end of its lifespan, exploded in a supernova,
IB Test. Astrophysics HL. Name_solution / a) Describe what is meant by a nebula [1]
![IB Test. Astrophysics HL. Name_solution / a) Describe what is meant by a nebula [1] IB Test. Astrophysics HL. Name_solution / a) Describe what is meant by a nebula [1]](/thumbs/73/69495220.jpg) IB Test Astrophysics HL Name_solution / 47 1. a) Describe what is meant by a nebula [1] an intergalactic cloud of gas and dust where all stars begin to form b) Explain how the Jeans criterion applies to
IB Test Astrophysics HL Name_solution / 47 1. a) Describe what is meant by a nebula [1] an intergalactic cloud of gas and dust where all stars begin to form b) Explain how the Jeans criterion applies to
The Universe. What is it? What is in it? How did it form? How will it end? How do we know?
 The Universe What is it? What is in it? How did it form? How will it end? How do we know? What is your place in the Universe? What is the universe? a. The study of the universe its nature, origins, and
The Universe What is it? What is in it? How did it form? How will it end? How do we know? What is your place in the Universe? What is the universe? a. The study of the universe its nature, origins, and
Cosmology. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16
 Cosmology Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16 Expansion of the Universe 1923 - Edwin Hubble resolved Andromeda Nebula into separate stars. 1929 - Hubble compared radial velocity versus distance for 18 nearest galaxies.
Cosmology Thornton and Rex, Ch. 16 Expansion of the Universe 1923 - Edwin Hubble resolved Andromeda Nebula into separate stars. 1929 - Hubble compared radial velocity versus distance for 18 nearest galaxies.
Name Date Period. 10. convection zone 11. radiation zone 12. core
 240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: # Marks: XX Raw Score: IB Curve: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: # Marks: XX Raw Score: IB Curve: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS OPTION E, ASTROPHYSICS TEST REVIEW S1. This question is about the nature of certain stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
Island Universes. Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe.
 Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
HNRS 227 Lecture 18 October 2007 Chapter 12. Stars, Galaxies and the Universe presented by Dr. Geller
 HNRS 227 Lecture 18 October 2007 Chapter 12 Stars, Galaxies and the Universe presented by Dr. Geller Recall from Chapters 1-11 Units of length, mass, density, time, and metric system The Scientific Method
HNRS 227 Lecture 18 October 2007 Chapter 12 Stars, Galaxies and the Universe presented by Dr. Geller Recall from Chapters 1-11 Units of length, mass, density, time, and metric system The Scientific Method
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture
 (Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
Chapter 22 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. The Birth of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
Early (Expanding) Universe. Average temperature decreases with expansion.
 Early (Expanding) Universe Average temperature decreases with expansion. Particles & Anti-Particles Very short wavelength photons collide and form electron-positron pairs. E=mc 2 electron=matter positron=antimatter
Early (Expanding) Universe Average temperature decreases with expansion. Particles & Anti-Particles Very short wavelength photons collide and form electron-positron pairs. E=mc 2 electron=matter positron=antimatter
ASTRONOMY. S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c,
 ASTRONOMY S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c, UNIVERSE Age 13.7 billion years old The Big Bang Theory Protons and Neutrons formed hydrogen and helium. This created heat that formed the stars. Other elements
ASTRONOMY S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c, UNIVERSE Age 13.7 billion years old The Big Bang Theory Protons and Neutrons formed hydrogen and helium. This created heat that formed the stars. Other elements
Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm. Astronomy 100. Tom Burbine
 Astronomy 100 Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm Tom Burbine tburbine@mtholyoke.edu www.xanga.com/astronomy100 Schedule Today (end and beginning of the universe) May 3 (Does Life Exist Elsewhere in the Universe)
Astronomy 100 Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm Tom Burbine tburbine@mtholyoke.edu www.xanga.com/astronomy100 Schedule Today (end and beginning of the universe) May 3 (Does Life Exist Elsewhere in the Universe)
Name: P8 SPACE PHYSICS. Class: Question Practice. Date: 140 minutes. Time: 140 marks. Marks: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY. Comments:
 P8 SPACE PHYSICS Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 40 minutes Marks: 40 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 52 In 929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from galaxies moving
P8 SPACE PHYSICS Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 40 minutes Marks: 40 marks Comments: GCSE PHYSICS ONLY Page of 52 In 929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from galaxies moving
Describe the lifecycle of a star in chronological order and explain the main stages, relating the stellar evolution to initial mass
 Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Explain the major events in the evolution of the universe according to the Big Bang Theory, in chronological order, backing up your arguments
Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Explain the major events in the evolution of the universe according to the Big Bang Theory, in chronological order, backing up your arguments
USAAAO First Round 2015
 USAAAO First Round 2015 This round consists of 30 multiple-choice problems to be completed in 75 minutes. You may only use a scientific calculator and a table of constants during the test. The top 50%
USAAAO First Round 2015 This round consists of 30 multiple-choice problems to be completed in 75 minutes. You may only use a scientific calculator and a table of constants during the test. The top 50%
Q2 S PA C E S C I E N C E
 EARTH & SPACE SCIENCE 8 MRS. DUDDLES Q2 S PA C E S C I E N C E FRIDAY 01/19/2018 HALF DAY PM (RECORDS DAY) Students will relate Earth s days, years, and seasons to Earth s movement in space Students will
EARTH & SPACE SCIENCE 8 MRS. DUDDLES Q2 S PA C E S C I E N C E FRIDAY 01/19/2018 HALF DAY PM (RECORDS DAY) Students will relate Earth s days, years, and seasons to Earth s movement in space Students will
The Big Bang Theory. Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra
 The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
The Big Bang Theory Rachel Fludd and Matthijs Hoekstra Theories from Before the Big Bang came from a black hole from another universe? our universe is part of a multiverse? just random particles? The Big
g = Gm / r 2 The Big Idea
 The Big Idea Over 2500 years ago Aristotle proposed two laws of physics governing motion. One for Earthly bodies (objects on Earth) that states objects naturally go in straight lines and one for Heavenly
The Big Idea Over 2500 years ago Aristotle proposed two laws of physics governing motion. One for Earthly bodies (objects on Earth) that states objects naturally go in straight lines and one for Heavenly
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006
 Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
Astronomy 162, Week 10 Cosmology Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Information Makeup quiz Wednesday, May 31, 5-6PM, Planetarium Review Session, Monday, June 5 6PM, Planetarium Cosmology Study of the universe
The 64th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places
 The 64th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places Brian Odom Fall 2006 http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 2: From the Big Bang to
The 64th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places Brian Odom Fall 2006 http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 2: From the Big Bang to
Interactions. Laws. Evolution
 Lecture Origin of the Elements MODEL: Origin of the Elements or Nucleosynthesis Fundamental Particles quarks, gluons, leptons, photons, neutrinos + Basic Forces gravity, electromagnetic, nuclear Interactions
Lecture Origin of the Elements MODEL: Origin of the Elements or Nucleosynthesis Fundamental Particles quarks, gluons, leptons, photons, neutrinos + Basic Forces gravity, electromagnetic, nuclear Interactions
Astronomy 100 Exploring the Universe Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday. Tom Burbine
 Astronomy 100 Exploring the Universe Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday Tom Burbine tomburbine@astro.umass.edu Mass-to-Light Ratio You can compare the measured mass to the luminosity of a galaxy Milky Way Milky
Astronomy 100 Exploring the Universe Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday Tom Burbine tomburbine@astro.umass.edu Mass-to-Light Ratio You can compare the measured mass to the luminosity of a galaxy Milky Way Milky
Lecture 19 Nuclear Astrophysics. Baryons, Dark Matter, Dark Energy. Experimental Nuclear Physics PHYS 741
 Lecture 19 Nuclear Astrophysics Baryons, Dark Matter, Dark Energy Experimental Nuclear Physics PHYS 741 heeger@wisc.edu References and Figures from: - Haxton, Nuclear Astrophysics - Basdevant, Fundamentals
Lecture 19 Nuclear Astrophysics Baryons, Dark Matter, Dark Energy Experimental Nuclear Physics PHYS 741 heeger@wisc.edu References and Figures from: - Haxton, Nuclear Astrophysics - Basdevant, Fundamentals
Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3.
 Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology. Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 4/21/2011
 New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 Agenda Introduction Space, Time and Matter Early views of the cosmos Important Ideas from Classical Physics Two 20 th Century revolutions
New Ideas from Astronomy and Cosmology Martin Buoncristiani Session 5 Agenda Introduction Space, Time and Matter Early views of the cosmos Important Ideas from Classical Physics Two 20 th Century revolutions
Brief Introduction to Cosmology
 Brief Introduction to Cosmology Matias Zaldarriaga Harvard University August 2006 Basic Questions in Cosmology: How does the Universe evolve? What is the universe made off? How is matter distributed? How
Brief Introduction to Cosmology Matias Zaldarriaga Harvard University August 2006 Basic Questions in Cosmology: How does the Universe evolve? What is the universe made off? How is matter distributed? How
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Spring 2003 Final Exam Review Topics
 Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Spring 2003 Final Exam Review Topics The final exam will cover material from the whole course (including the galaxies and cosmology material from after Exam 3). The topics
Astronomy 102: Stars and Galaxies Spring 2003 Final Exam Review Topics The final exam will cover material from the whole course (including the galaxies and cosmology material from after Exam 3). The topics
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
3. It is expanding: the galaxies are moving apart, accelerating slightly The mystery of Dark Energy
 II. Cosmology: How the universe developed Outstanding features of the universe today: 1. It is big, and full of galaxies. 2. It has structure: the galaxies are clumped in filaments and sheets The structure
II. Cosmology: How the universe developed Outstanding features of the universe today: 1. It is big, and full of galaxies. 2. It has structure: the galaxies are clumped in filaments and sheets The structure
Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3)
 Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3) Key Ideas Physics of the Early Universe Informed by experimental & theoretical physics Later stages confirmed by observations
Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3) Key Ideas Physics of the Early Universe Informed by experimental & theoretical physics Later stages confirmed by observations
A brief history of cosmological ideas
 A brief history of cosmological ideas Cosmology: Science concerned with the origin and evolution of the universe, using the laws of physics. Cosmological principle: Our place in the universe is not special
A brief history of cosmological ideas Cosmology: Science concerned with the origin and evolution of the universe, using the laws of physics. Cosmological principle: Our place in the universe is not special
2. The evolution and structure of the universe is governed by General Relativity (GR).
 7/11 Chapter 12 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe. We start with two assumptions: 1. Cosmological Principle: On a large enough scale (large compared
7/11 Chapter 12 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe. We start with two assumptions: 1. Cosmological Principle: On a large enough scale (large compared
The Cosmic Microwave Background
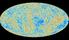 The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
ASTR Final Examination Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
 ASTR 1120-001 Final Examination Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson FINAL EXAM MAY 6 th 2006: Closed books and notes, 1.5 hours. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
ASTR 1120-001 Final Examination Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson FINAL EXAM MAY 6 th 2006: Closed books and notes, 1.5 hours. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
BROCK UNIVERSITY. Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015
 BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 9 Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50
BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 9 Test 2, March 2015 Number of pages: 9 Course: ASTR 1P02 Number of Students: 420 Date of Examination: March 5, 2015 Number of hours: 50 min Time of Examination: 18:00 18:50
Chapter 1 Introduction. Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS
 Chapter 1 Introduction Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS 2008 1 Ptolemäus (85 165 b.c.) Kopernicus (1473 1543) Kepler (1571 1630) Newton (1643 1727) Kant (1724 1630) Herschel (1738 1822) Einstein (1917)
Chapter 1 Introduction Particle Astrophysics & Cosmology SS 2008 1 Ptolemäus (85 165 b.c.) Kopernicus (1473 1543) Kepler (1571 1630) Newton (1643 1727) Kant (1724 1630) Herschel (1738 1822) Einstein (1917)
Universe Celestial Object Galaxy Solar System
 ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 13. Midterm review February 4th, 2008 1. Astronomy
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 13. Midterm review February 4th, 2008 1. Astronomy
Chapter 17 Cosmology
 Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department. Problem Set 6
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Astronomy 8.282J 12.402J March 17, 2006 Problem Set 6 Due: Friday, March 24 (in lecture) Reading:
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Astronomy 8.282J 12.402J March 17, 2006 Problem Set 6 Due: Friday, March 24 (in lecture) Reading:
Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN
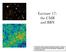 Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Peering out/back into the Universe As
Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Peering out/back into the Universe As
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam]
![Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam]](/thumbs/85/91935248.jpg) Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Although we can be certain that other stars are as complex as the Sun, we will try to
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17) [Material in smaller font on this page will not be present on the exam] Although we can be certain that other stars are as complex as the Sun, we will try to
Cosmology. Chapter 18. Cosmology. Observations of the Universe. Observations of the Universe. Motion of Galaxies. Cosmology
 Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
Cosmology Chapter 18 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the structure and evolution of the Universe as a whole How big is the Universe? What shape is it? How old is it? How did it form? What will happen
Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars
 Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Hubble's Law. H o = 71 km/s / Mpc. The further a galaxy is away, the faster it s moving away from us. V = H 0 D. Modern Data.
 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION E-6 GALAXIES Introductory Video: The Big Bang Theory Objectives Understand the Hubble classification scheme of galaxies and describe the
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION E-6 GALAXIES Introductory Video: The Big Bang Theory Objectives Understand the Hubble classification scheme of galaxies and describe the
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09. Astronomy 101
 The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
Astroparticle physics
 Timo Enqvist University of Oulu Oulu Southern institute lecture cource on Astroparticle physics 15.09.2009 15.12.2009 10 Cosmic microwave background Content 10.0 Small introduction 10.1 Cosmic microwave
Timo Enqvist University of Oulu Oulu Southern institute lecture cource on Astroparticle physics 15.09.2009 15.12.2009 10 Cosmic microwave background Content 10.0 Small introduction 10.1 Cosmic microwave
Potentially useful formulas: F = G m 1m 2 r 2 F = k q 1q 2 F = ma Distance = Speed Time
 PHY100 May 4, 2010 Final Exam Name: Aran Garcia-Bellido Please read the problems carefully and answer them in the space provided. Write on the back of the page, if necessary. Show your work where requested
PHY100 May 4, 2010 Final Exam Name: Aran Garcia-Bellido Please read the problems carefully and answer them in the space provided. Write on the back of the page, if necessary. Show your work where requested
