The energy of the Mycielskian of a regular graph
|
|
|
- Tobias Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 5 (1), Pages The energy of the Mycielskian of a regular graph R. Balakrishnan Department of Mathematics Bharathidasan University Tiruchirappalli-64 India mathbala@sify.com T. Kavaskar Department of Mathematics SRC, SASTRA University Kumbakonam 61 1 India t kavaskar@yahoo.com Wasin So Department of Mathematics San Jose State University San Jose, CA U.S.A. so@math.sjsu.edu Abstract Let G be a finite connected simple graph and μ(g) be the Mycielskian of G. We show that for connected graphs G and H, μ(g) is isomorphic to μ(h) if and only if G is isomorphic to H. Furthermore, we determine the energy of the Mycielskian of a connected regular graph G in terms of the energy E(G) of G, where the energy of G is the sum of the absolute values of the eigenvalues of G. The energy of a graph has its origin in chemistry in that the energy of a conjugated hydrocarbon molecule computed using the Hückel theory in quantum chemistry coincides with the graph energy of the corresponding molecular graph. We show that if G is a regular graph of order n with E(G) > 3n, thenμ(g) is hyperenergetic.
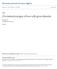
2 164 R. BALAKRISHNAN, T. KAVASKAR AND W. SO Figure 1: μ(k 1,3 + e) 1 Introduction We consider only finite simple connected graphs. The construction of triangle-free k-chromatic graphs, where k 3, was raised in the middle of the th century. In answer to this question, Mycielski [1] developed an interesting graph transformation known as the Mycielskian as follows: For a graph G =(V,E), the Mycielskian of G is the graph μ(g) with vertex set consisting of the disjoint union V V {u}, where V = {x : x V }, andedgesete {x y : xy E} {x u : x V }. We denote V (μ(g)) by the triad (V,V,u). We call x the twin of x in μ(g) and vice versa, and call u the root of μ(g). Figure 1 displays the Mycielskian of the graph K 1,3 + e. It is well-known [1] that if G is triangle free, then so is μ(g), and that the chromatic number χ(μ(g)) = χ(g) + 1. The generalized Mycielskian μ m (G) ofg is obtained by iterating the construction of V, m times. For the precise definition and a study of generalized Mycielskians, see [4, ]. For a vertex v of G, N G (v) stands for the set of neighbors of v in G, theopen neighborhood of v in G, andn G [v] =N(v) {v} denotes the closed neighborhood of v in G. We recall that two simple graphs G 1 =(V 1,E 1 )andg =(V,E )are isomorphic if and only if there exists a bijection φ : V 1 V such that uv E 1 if and only if φ(u)φ(v) E. Moreover, graph isomorphism defines an equivalence relation on the class of all simple graphs. Lemma 1.1. Let f : G H be a graph isomorphism of G onto H. Thenf(N G (x)) = N H (f(x)). Furthermore,G x = H f(x), andg N G [x] = H N H [f(x)] under the restriction maps of f to the respective domains. Proof. The proof follows from the definition of graph isomorphism.
3 THE MYCIELSKIAN OF A REGULAR GRAPH 165 Isomorphism of Mycielskians For a vertex v of a graph G, let d G (v) denote the degree of v in G. We first prove that the Mycielskian of a graph determines the graph uniquely up to isomorphism. Theorem.1. For connected graphs G and H, μ(g) = μ(h) if and only if G = H. Proof. If G = H, then trivially μ(g) = μ(h). So assume that G and H are connected and that μ(g) = μ(h). When n = or 3, the result is trivial. So assume that n 4. If G is of order n, thenμ(g) andμ(h) are both of order n +1, andsoh is also of order n. Letf : μ(g) μ(h) be the given isomorphism, where V (μ(g)) and V (μ(h)) are given by the triads (V 1,V 1,u 1 )and(v,v,u ) respectively. We look at the possible images of the root u 1 of μ(g) under f. Both u 1 and u are vertices of degree n. If f(u 1 )=u, then, by Lemma 1.1, G = μ(g) N[u 1 ] = μ(h) N[u ]=H. Next, we claim that f(u 1 ) / V. Suppose f(u 1 ) V. Since d µ(h) (f(u 1 )) = n d µ(g) (u 1 )=n, it follows from the definition of the Mycielskian, that in μ(h), neighbors of f(u 1 ) belong to V while another n neighbors (the twins) belong to V. (This forces n to be even). These n neighbors of f(u 1 ) form an independent subset of μ(h). Then H = μ(h) N µ(h) [f(u 1 )] = μ(g) N µ(g) [u 1 ]=G. Nowifx V is adjacent to f(u 1 )inμ(h), then x is adjacent to f(u 1 ),thetwinoff(u 1 ) belonging to V in μ(h). Further d H (f(u 1) )=1=d G (v), where v V 1 (the vertex set of G) corresponds to f(u 1 ) in μ(h). But then d µ(g) (v)=, while d µ(h) (f(u) )= n +1>, as n 4. Hence this case cannot arise. Finally, suppose that f(u 1 ) V. Set f(u 1 )=y. Then y, thetwinofy in μ(h), belongs to V. As d µ(g) (u 1 )=n, d µ(h) (y )=n. The vertex y has n 1 neighbors in V,say,x 1,x,...,x n 1. Then N H (y) ={x 1,x,...,x n 1 }, and hence y is also adjacent to x 1,x,...,x n 1 in V. Further, as N µ(g)(u 1 ) is independent, N µ(h) (y ) is also independent. Therefore H =stark 1,n 1 consisting of the edges yx 1,yx,...,yx n 1. Moreover, G = μ(g) N[u 1 ] = μ(h) N[y ]= star K 1,n 1 consisting of the edges yx 1,yx,...,yx n 1.ThusG = K 1,n 1 = H. We note that the Mycielskian of a simple disconnected graph can be defined in an analogous way and that Theorem.1 has a natural extension to the case of disconnected graphs. A connected graph G is fall colorable [6] using k colors if G has a proper k-vertex coloring {V 1,V,...,V k } such that each vertex of G is a color dominating vertex, that is, if v V i,thenv has a neighbor in each V j,1 j k, i j. For any graph G, define G as follows [3]: If G is of order n and has vertex set V = {v 1,v,...,v n }, G is the supergraph of G of order n got by choosing a new vertex v i for each vertex v i of G and making v i adjacent in G to all the vertices in V {v i }.LetV = {v 1,v,...,v n }.WecallV the set of external vertices of G and V, the set of internal vertices.
4 166 R. BALAKRISHNAN, T. KAVASKAR AND W. SO Let V i = {v i,v i },1 i n. Then {V 1,V,...,V n } is a fall color partition of G so that G is fall colorable. Theorem.. For (connected) graphs G and H, G = H if and only if G = H. Proof. Suppose G = H.IfG is of order n, G and H are both of order n, and hence H is also of order n. LetA denote the set of external vertices of G and B, the set of external vertices of H. Then in G, each vertex of A has degree n 1 andeach vertex of V (G ) \ A has degree at least n, while in H, each vertex of B has degree n 1 and each vertex of V (H ) \ B has degree at least n. Hence the isomorphism f maps A onto B. Further, by Lemma 1.1, G A = H B and hence G = H. Theorem.3 ([4]). For any (connected) graph G, μ(g) is non-fall colorable. Theorems.1 and. show that for any graph G both the derived graphs μ(g) and G determine G uniquely upto isomorphism. However, with regard to fall coloring, they behave in exactly the opposite ways in that for any graph G, μ(g) is non-fall colorable while G is fall colorable. Moreover, Theorems.1 and. show that the cardinalities of the set of all Mycielskians and the set of all graphs G are at least as large as the set of all connected graphs. Since the set of all connected graphs is countably infinite, we have the following result: Corollary.4. The cardinalities of the set of all (connected) fall colorable graphs and the set of all (connected) non-fall colorable graphs are both countably infinite. We remark that Corollary.4 can be inferred by other means as well. 3 Energy of the Mycielskian of a regular graph Let G =(V,E) be a simple graph of order n with vertex set V = {v 1,...,v n }. The adjacency matrix of G is the n n matrix A =(a ij ), where a ij = 1 or according as v i v j E or not. A is a real symmetric matrix and hence its spectrum, namely, the set of its eigenvalues, is real. Let the spectrum of G (= the spectrum of A) be {λ 1 λ n }. Then the energy E(G) ofg is defined as n λ i. The concept of i=1 graph energy arose in quantum chemistry where certain numerical quantities, such as the heat conduction of hydrocarbon molecules, are related to the total π-electron energy of conjugated hydrocarbon molecules. Indeed, the π-electron energy of any conjugated hydrocarbon molecule coincides with the energy of the corresponding molecular graph [5, 9, 1]. We now determine the energy of the Mycielskian of a k-regular graph G in terms of the energy of G. Some recent papers that deal with the energy of regular graphs are [1, 11, 14, 15, 19].
5 THE MYCIELSKIAN OF A REGULAR GRAPH 167 Theorem 3.1. Let G be a k-regular graph on n vertices. Then the energy E(μ(G)) of μ(g) is given by: E(μ(G)) = 5E(G) ( 5 1)k + t 3, (3.1) where E(G) is the energy of G and t 3 is the unique negative root of the cubic t 3 kt (n + k )t + kn. (3.) Proof. Denote by A the adjacency matrix of G. AsA is real symmetric, A = PDP T, where D is the diagonal matrix diag(λ 1,...,λ n ), and P is an orthogonal matrix with orthonormal eigenvectors p i s, that is, Ap i = λ i p i for each i. In particular, if e denotes the n-vector with all entries equal 1, then p 1 = e n (G being regular). Hence e T p i = for i =,...,n, and consequently e T P =[ n,,...,]. Now, by the definition of μ(g), the adjacency matrix of μ(g) is the matrix of order (n + 1) given by A A μ(a) = A e. e T Since A = PDP T,wehave PDP T PDP T μ(a) = PDP e e T P D D P T = P D P T e P T. 1 e T P 1 Since P is an orthogonal matrix, the spectrum of μ(a) is the same as the spectrum of D D B = D [ n,,...,] T [. n,,...,] The determinant of the characteristic matrix of B is given by t λ 1 λ 1 t λ λ t λ n λ n λ 1 t n. λ t λ n t n t
6 168 R. BALAKRISHNAN, T. KAVASKAR AND W. SO We now expand det(ti B) along its first, (n +1) st and (n +1) st columns by Laplace s method [7]. In this expansion, only the 3 3 minor which is common to the above three columns and the 1 st, (n +1) st and the (n +1) st rows is nonzero. This minor is x λ 1 λ 1 M 1 = λ 1 n n. We now expand the complementary minor of M 1 along the nd and (n +) nd columns, and then the resulting complementary minor by the 3 rd and (n +3) rd columns and so on. These expansions give the spectrum of μ(a) to be the union of the spectra of the matrices λ 1 λ 1 [ ] [ ] λ 1 n λ λ, λn λ,..., n. λ n λ n Another way to see this is to observe that B is orthogonally similar to the direct sum of the above n matrices. Thus the spectrum of μ(a) is {t 1,t,t 3,λ (1 ± 5 ) (1 ± 5),...,λn } where t 1,t,t 3 are the roots of the cubic polynomial t 3 kt (n + k )t + kn, (note that since G is k-regular, λ 1 = k) which has two positive roots and one negative root, say, t 1 >t > >t 3. Let E(G) denote the energy of G. Then E(G) = i λ i = k + λ + + λ n. Hence the energy of the Mycielskian μ(g) ofg, when G is k-regular, is E(μ(G)) = t 1 + t + t 3 + ( = t 1 + t + t 3 + 5( λ + + λ n ) = k t 3 + t 3 + 5(E(G) k) = 5E(G) ( 5 1)k + t 3. ) ( λ + + λ n ) An application of Theorem 3.1. A simple graph G of order n is called hyperenergetic if E(G) > (n 1) = E(K n ), where K n is the complete graph on n vertices; otherwise it is called nonhyperenergetic. Hyperenergetic graphs are important because molecular graphs with maximum energy correspond to maximal stable π-electron systems [8, 13, 18, 3]. By definition, K n is non-hyperenergetic. For K n, t 3 ( 1, ), and substitution of k = n 1 in equation (3.1) shows that μ(k n ) is non-hyperenergetic.
7 THE MYCIELSKIAN OF A REGULAR GRAPH 169 It is known that the maximum energy that a graph G of order n can have is n 3 +n and that G has maximum energy if and only if it is a strongly regular graph with parameters ( ) n, n+ n, n+ n, n+ n 4 4 [1, 17]. If n>5, and G has maximum energy, then E(G) > 3n >(n 1) and hence G is hyperenergetic. Also from equation (3.1), E(μ(G)) > 3n (5) ( (5) 1)k + t 3 > 3n (5) ( (5) 1)(n 1) > (5)n + (5) + 1 > 4n = [(n +1) 1]. Hence the Mycielskians of maximal energy graphs of order n>5 are all hyperenergetic. More generally, if G is a regular graph of order n and E(G) > 3n, thenμ(g) is hyperenergetic. 3. Examples. We now present two examples. Consider two familiar regular graphs, namely, the Petersen graph P and a unitary Cayley graph. 1. The Petersen graph P. For P, n =1,m=15andk = 3. The spectrum of P is ( 3 (1), 1 (5), (4)), where a (b) means that a is repeated b times. Hence E(P ) = 16. Now for P, the polynomial (3.) is t 3 3t 19t + 3, and its unique negative root t 3 is Thus from equation (3.1), E(μ(P )) 16 5 ( 5 1)3+(3.889) = < 4 = (1 1), where 1 is the order of μ(p ). Consequently, μ(p ) is non-hyperenergetic.. The unitary Cayley graph G =Cay(Z 1,U) [, 13, 16, ]. Here U is the group of multiplicative units of the additive group (Z 1, +). Then E(G) = 4 φ(1) = 768 > 3 1 = 3n, where φ is the Euler totient function. Since n = 1, k= φ(1) = 48, the polynomial (3.) becomes t 3 48t 514t + 18 for which the unique negative root t 3 is Now from equation (3.1), E(μ(G)) ( 5 1)48 + (34.18) = > ((n +1) 1) = 84. Thus μ(cay(z 1,U)) is hyperenergetic, as expected. We conclude with an open problem. Open Problem: Does there exist an infinite family of non-hyperenergetic graphs whose Mycielskians are hyperenergetic? Acknowledgement For the first author, this research was supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, grant DST: SR /MS: 49 / 7 dated April 1, 8. The authors thank one of the referees for helpful comments and suggestions.
8 17 R. BALAKRISHNAN, T. KAVASKAR AND W. SO References [1] S. Akbari, F. Moazami and S. Zare, Kneser graphs and their complements are hyperenergetic, MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 61 (9), [] R. Balakrishnan, The energy of a graph, Linear Algebra Appl. 387 (4), [3] R. Balakrishnan and T. Kavaskar, Fall Coloring of Graphs -I, Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 3 (1), [4] R. Balakrishnan and T. Kavaskar, Fall coloring of graphs -II, J. Combin. Math. Combin. Comput. 76 (11), [5] R. Brualdi, Energy of a graph, Notes for AIM Workshop on spectra of families of matrices described by graphs, digraphs, and sign patterns, 6. [6] J.E. Dunbar, S.M. Hedetniemi, S.T. Hedetniemi, D.P. Jacobs, J. Knisely, R.C. Laskar and D.F. Rall, Fall coloring of graphs, J. Combin. Math. Combin. Comput. 33 (), [7] W. L. Ferrar, A Text-Book of Determinants, Matrices and Algebraic Forms, Oxford University Press, [8] I. Gutman, Hyperenergetic molecular graphs, J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 64 (1999), [9] I. Gutman, The energy of a graph: old and new results, in Algebraic Combinatorics and Applications, A. Betten, A. Kohner, R. Laue and A. Wassermann, eds., Springer, Berlin, 1, [1] I. Gutman and O. Polansky, Mathematical Concepts in Organic Chemistry, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, [11] I. Gutman, S.Z. Firoozabadi, J.A. de la Pẽna and J. Rada, On the energy of regular graphs, MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 57 (7), [1] W.H. Haemers, Strongly regular graphs with maximal energy, Linear Algebra Appl., 49 (8), [13] A. Ilić The energy of unitary Cayley graphs, Linear Algebra Appl. 431 (9), [14] A. Ilić, Distance spectra and distance energy of integral circulant graphs, Linear Algebra Appl. 433 (1), [15] A. Ilić, M. Bašić and I. Gutman, Calculating triply equienergetic graphs, MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 64 (1), 189.
9 THE MYCIELSKIAN OF A REGULAR GRAPH 171 [16] D. Kiani, M.M.H. Aghaei, Y. Meemark and B. Suntornpoch, Energy of unitary Cayley graphs and gcd-graphs, Linear Algebra Appl. 435 (11), [17] J.H. Koolen and V. Moulton, Maximal energy graphs, Advances Appl. Math. 6 (1), [18] J.H. Koolen, V. Moulton, I. Gutman and D. Vidovic, More hyperenergetic molecular graphs, J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 65 (), [19] X. Li, Y. Li and Y. Shi, Note on the energy of regular graphs, Linear Algebra Appl. 43 (1), [] W. Liu, J. Wu, P.C.B. Lam and G. Gu, Several parameters of generalized Mycielskians, Discr. Appl. Math. 154 (6), [1] J. Mycielski, Sur le coloriage des graphs, Colloq. Math. 3 (1955), [] H.N. Ramaswamy and C.R. Veena, On the energy of unitary Cayley graphs, Electron.J.Combin.16 (9), Note 4, 8 pp. [3] H.B. Walikar, I. Gutman, P.R. Hampiholi and H.S. Ramane, Non-hyperenergetic graphs, Graph Theory Notes, New York Acad. Sci. 41 (1), (Received 8 Apr 11; revised 3 Aug 11)
EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS
 5 Kragujevac J. Math. 26 (2004) 5 13. EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS Harishchandra S. Ramane, 1 Hanumappa B. Walikar, 2 Siddani Bhaskara Rao, 3 B. Devadas Acharya, 4 Prabhakar R. Hampiholi, 1 Sudhir R. Jog, 1 Ivan
5 Kragujevac J. Math. 26 (2004) 5 13. EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS Harishchandra S. Ramane, 1 Hanumappa B. Walikar, 2 Siddani Bhaskara Rao, 3 B. Devadas Acharya, 4 Prabhakar R. Hampiholi, 1 Sudhir R. Jog, 1 Ivan
STRONGLY REGULAR INTEGRAL CIRCULANT GRAPHS AND THEIR ENERGIES
 BULLETIN OF INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN 1840-4367 Vol. 2(2012), 9-16 Former BULLETIN OF SOCIETY OF MATHEMATICIANS BANJA LUKA ISSN 0354-5792 (o), ISSN 1986-521X (p) STRONGLY REGULAR
BULLETIN OF INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN 1840-4367 Vol. 2(2012), 9-16 Former BULLETIN OF SOCIETY OF MATHEMATICIANS BANJA LUKA ISSN 0354-5792 (o), ISSN 1986-521X (p) STRONGLY REGULAR
ON EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS AND MOLECULAR GRAPHS
 Kragujevac J. Sci. 29 2007) 73 84. UDC 541.66:547.318 ON EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS AND MOLECULAR GRAPHS Hanumappa B. Walikar, a Harishchandra S. Ramane, b Ivan Gutman, c Sabeena B. Halkarni a a Department of
Kragujevac J. Sci. 29 2007) 73 84. UDC 541.66:547.318 ON EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS AND MOLECULAR GRAPHS Hanumappa B. Walikar, a Harishchandra S. Ramane, b Ivan Gutman, c Sabeena B. Halkarni a a Department of
The energy of integral circulant graphs
 Applied Linear Algebra ALA 200 Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics University of Niš, Serbia Novi Sad, May 200 Graph energy Integral circulant graphs Recent applications Let G be a simple graph with n
Applied Linear Algebra ALA 200 Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics University of Niš, Serbia Novi Sad, May 200 Graph energy Integral circulant graphs Recent applications Let G be a simple graph with n
Multi-coloring and Mycielski s construction
 Multi-coloring and Mycielski s construction Tim Meagher Fall 2010 Abstract We consider a number of related results taken from two papers one by W. Lin [1], and the other D. C. Fisher[2]. These articles
Multi-coloring and Mycielski s construction Tim Meagher Fall 2010 Abstract We consider a number of related results taken from two papers one by W. Lin [1], and the other D. C. Fisher[2]. These articles
ENERGY OF SOME CLUSTER GRAPHS
 51 Kragujevac J. Sci. 23 (2001) 51-62. ENERGY OF SOME CLUSTER GRAPHS H. B. Walikar a and H. S. Ramane b a Karnatak University s Kittur Rani Chennama Post Graduate Centre, Department of Mathematics, Post
51 Kragujevac J. Sci. 23 (2001) 51-62. ENERGY OF SOME CLUSTER GRAPHS H. B. Walikar a and H. S. Ramane b a Karnatak University s Kittur Rani Chennama Post Graduate Centre, Department of Mathematics, Post
arxiv: v2 [math.co] 4 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v2 [math.co] 4 Sep 2009 arxiv: v2 [math.co] 4 Sep 2009](/thumbs/89/97983448.jpg) Bounds for the Hückel energy of a graph Ebrahim Ghorbani a,b,, Jack H. Koolen c,d,, Jae Young Yang c a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Sharif University of Technology, P.O. Box 11155-9415, Tehran,
Bounds for the Hückel energy of a graph Ebrahim Ghorbani a,b,, Jack H. Koolen c,d,, Jae Young Yang c a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Sharif University of Technology, P.O. Box 11155-9415, Tehran,
Tilburg University. Strongly Regular Graphs with Maximal Energy Haemers, W. H. Publication date: Link to publication
 Tilburg University Strongly Regular Graphs with Maximal Energy Haemers, W. H. Publication date: 2007 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Haemers, W. H. (2007). Strongly Regular Graphs
Tilburg University Strongly Regular Graphs with Maximal Energy Haemers, W. H. Publication date: 2007 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Haemers, W. H. (2007). Strongly Regular Graphs
Journal of Mathematical Nanoscience. On borderenergetic and L-borderenergetic graphs
 Journal of Mathematical Nanoscienese 7 (2) (2017) 71 77 Journal of Mathematical Nanoscience Available Online at: http://jmathnano.sru.ac.ir On borderenergetic and L-borderenergetic graphs Mardjan Hakimi-Nezhaad
Journal of Mathematical Nanoscienese 7 (2) (2017) 71 77 Journal of Mathematical Nanoscience Available Online at: http://jmathnano.sru.ac.ir On borderenergetic and L-borderenergetic graphs Mardjan Hakimi-Nezhaad
Solutions to Unsolved Problems on the Minimal Energies of Two Classes of Graphs
 MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 66 (2011) 943-958 ISSN 0340-6253 Solutions to Unsolved Problems on the Minimal Energies of Two Classes of
MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 66 (2011) 943-958 ISSN 0340-6253 Solutions to Unsolved Problems on the Minimal Energies of Two Classes of
Maximal Energy Graphs
 Advances in Applied Mathematics 6, 47 5 (001) doi:10.1006/aama.000.0705, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Maximal Energy Graphs Jack H. Koolen 1 FSPM-Strukturbildungsprozesse, University
Advances in Applied Mathematics 6, 47 5 (001) doi:10.1006/aama.000.0705, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Maximal Energy Graphs Jack H. Koolen 1 FSPM-Strukturbildungsprozesse, University
Normalized Laplacian spectrum of two new types of join graphs
 Journal of Linear and Topological Algebra Vol. 6, No. 1, 217, 1-9 Normalized Laplacian spectrum of two new types of join graphs M. Hakimi-Nezhaad a, M. Ghorbani a a Department of Mathematics, Faculty of
Journal of Linear and Topological Algebra Vol. 6, No. 1, 217, 1-9 Normalized Laplacian spectrum of two new types of join graphs M. Hakimi-Nezhaad a, M. Ghorbani a a Department of Mathematics, Faculty of
SEIDEL ENERGY OF ITERATED LINE GRAPHS OF REGULAR GRAPHS
 Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 39(1) (015), Pages 7 1. SEIDEL ENERGY OF ITERATED LINE GRAPHS OF REGULAR GRAPHS HARISHCHANDRA S. RAMANE 1, IVAN GUTMAN, AND MAHADEVAPPA M. GUNDLOOR 3 Abstract.
Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 39(1) (015), Pages 7 1. SEIDEL ENERGY OF ITERATED LINE GRAPHS OF REGULAR GRAPHS HARISHCHANDRA S. RAMANE 1, IVAN GUTMAN, AND MAHADEVAPPA M. GUNDLOOR 3 Abstract.
On the Energy of Some Graphs
 nnals of Pure and pplied Mathematics Vol. 7, No., 08, 5- ISSN: 79-087X P, 79-0888online Published on pril 08 www.researchmathsci.org DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.57/apam.v7na nnals of On the Energy of Some
nnals of Pure and pplied Mathematics Vol. 7, No., 08, 5- ISSN: 79-087X P, 79-0888online Published on pril 08 www.researchmathsci.org DOI: http://dx.doi.org/0.57/apam.v7na nnals of On the Energy of Some
D-EQUIENERGETIC SELF-COMPLEMENTARY GRAPHS
 123 Kragujevac J. Math. 32 (2009) 123 131. D-EQUIENERGETIC SELF-COMPLEMENTARY GRAPHS Gopalapillai Indulal 1 and Ivan Gutman 2 1 Department of Mathematics, St. Aloysius College, Edathua, Alappuzha 689573,
123 Kragujevac J. Math. 32 (2009) 123 131. D-EQUIENERGETIC SELF-COMPLEMENTARY GRAPHS Gopalapillai Indulal 1 and Ivan Gutman 2 1 Department of Mathematics, St. Aloysius College, Edathua, Alappuzha 689573,
Equitable Coloring On Mycielskian Of Wheels And Bigraphs
 Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 1(201), 174-182 c ISSN 1607-2510 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/ amen/ Equitable Coloring On Mycielskian Of Wheels And Bigraphs Kaliraj Kalimuthu,
Applied Mathematics E-Notes, 1(201), 174-182 c ISSN 1607-2510 Available free at mirror sites of http://www.math.nthu.edu.tw/ amen/ Equitable Coloring On Mycielskian Of Wheels And Bigraphs Kaliraj Kalimuthu,
Energy of Graphs. Sivaram K. Narayan Central Michigan University. Presented at CMU on October 10, 2015
 Energy of Graphs Sivaram K. Narayan Central Michigan University Presented at CMU on October 10, 2015 1 / 32 Graphs We will consider simple graphs (no loops, no multiple edges). Let V = {v 1, v 2,..., v
Energy of Graphs Sivaram K. Narayan Central Michigan University Presented at CMU on October 10, 2015 1 / 32 Graphs We will consider simple graphs (no loops, no multiple edges). Let V = {v 1, v 2,..., v
SIMPLICES AND SPECTRA OF GRAPHS
 University of Ljubljana Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Mechanics Department of Mathematics Jadranska 9, 000 Ljubljana, Slovenia Preprint series, Vol. 47 (2009), 07 SIMPLICES AND SPECTRA OF GRAPHS
University of Ljubljana Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Mechanics Department of Mathematics Jadranska 9, 000 Ljubljana, Slovenia Preprint series, Vol. 47 (2009), 07 SIMPLICES AND SPECTRA OF GRAPHS
Multi-colouring the Mycielskian of Graphs
 Multi-colouring the Mycielskian of Graphs Wensong Lin Daphne Der-Fen Liu Xuding Zhu December 1, 016 Abstract A k-fold colouring of a graph is a function that assigns to each vertex a set of k colours,
Multi-colouring the Mycielskian of Graphs Wensong Lin Daphne Der-Fen Liu Xuding Zhu December 1, 016 Abstract A k-fold colouring of a graph is a function that assigns to each vertex a set of k colours,
ON THE WIENER INDEX AND LAPLACIAN COEFFICIENTS OF GRAPHS WITH GIVEN DIAMETER OR RADIUS
 MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 63 (2010) 91-100 ISSN 0340-6253 ON THE WIENER INDEX AND LAPLACIAN COEFFICIENTS OF GRAPHS WITH GIVEN DIAMETER
MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 63 (2010) 91-100 ISSN 0340-6253 ON THE WIENER INDEX AND LAPLACIAN COEFFICIENTS OF GRAPHS WITH GIVEN DIAMETER
New Results on Equienergetic Graphs of Small Order
 International Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 1819-4966 Volume 12, Number 2 (2017), pp. 595 602 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcam.htm New Results on
International Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 1819-4966 Volume 12, Number 2 (2017), pp. 595 602 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcam.htm New Results on
Relations between edge removing and edge subdivision concerning domination number of a graph
 arxiv:1409.7508v1 [math.co] 26 Sep 2014 Relations between edge removing and edge subdivision concerning domination number of a graph Magdalena Lemańska 1, Joaquín Tey 2, Rita Zuazua 3 1 Gdansk University
arxiv:1409.7508v1 [math.co] 26 Sep 2014 Relations between edge removing and edge subdivision concerning domination number of a graph Magdalena Lemańska 1, Joaquín Tey 2, Rita Zuazua 3 1 Gdansk University
INDEPENDENT TRANSVERSAL DOMINATION IN GRAPHS
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 32 (2012) 5 17 INDEPENDENT TRANSVERSAL DOMINATION IN GRAPHS Ismail Sahul Hamid Department of Mathematics The Madura College Madurai, India e-mail: sahulmat@yahoo.co.in
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 32 (2012) 5 17 INDEPENDENT TRANSVERSAL DOMINATION IN GRAPHS Ismail Sahul Hamid Department of Mathematics The Madura College Madurai, India e-mail: sahulmat@yahoo.co.in
A Survey on Comparing Zagreb Indices
 MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 65 (2011) 581-593 ISSN 0340-6253 A Survey on Comparing Zagreb Indices Bolian Liu and Zhifu You School of
MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 65 (2011) 581-593 ISSN 0340-6253 A Survey on Comparing Zagreb Indices Bolian Liu and Zhifu You School of
On marker set distance Laplacian eigenvalues in graphs.
 Malaya Journal of Matematik, Vol 6, No 2, 369-374, 2018 https://doiorg/1026637/mjm0602/0011 On marker set distance Laplacian eigenvalues in graphs Medha Itagi Huilgol1 * and S Anuradha2 Abstract In our
Malaya Journal of Matematik, Vol 6, No 2, 369-374, 2018 https://doiorg/1026637/mjm0602/0011 On marker set distance Laplacian eigenvalues in graphs Medha Itagi Huilgol1 * and S Anuradha2 Abstract In our
Graph fundamentals. Matrices associated with a graph
 Graph fundamentals Matrices associated with a graph Drawing a picture of a graph is one way to represent it. Another type of representation is via a matrix. Let G be a graph with V (G) ={v 1,v,...,v n
Graph fundamentals Matrices associated with a graph Drawing a picture of a graph is one way to represent it. Another type of representation is via a matrix. Let G be a graph with V (G) ={v 1,v,...,v n
The least eigenvalue of the signless Laplacian of non-bipartite unicyclic graphs with k pendant vertices
 Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 26 Volume 26 (2013) Article 22 2013 The least eigenvalue of the signless Laplacian of non-bipartite unicyclic graphs with k pendant vertices Ruifang Liu rfliu@zzu.edu.cn
Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 26 Volume 26 (2013) Article 22 2013 The least eigenvalue of the signless Laplacian of non-bipartite unicyclic graphs with k pendant vertices Ruifang Liu rfliu@zzu.edu.cn
LAPLACIAN ENERGY OF UNION AND CARTESIAN PRODUCT AND LAPLACIAN EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS
 Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 39() (015), Pages 193 05. LAPLACIAN ENERGY OF UNION AND CARTESIAN PRODUCT AND LAPLACIAN EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS HARISHCHANDRA S. RAMANE 1, GOURAMMA A. GUDODAGI 1,
Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 39() (015), Pages 193 05. LAPLACIAN ENERGY OF UNION AND CARTESIAN PRODUCT AND LAPLACIAN EQUIENERGETIC GRAPHS HARISHCHANDRA S. RAMANE 1, GOURAMMA A. GUDODAGI 1,
On Dominator Colorings in Graphs
 On Dominator Colorings in Graphs Ralucca Michelle Gera Department of Applied Mathematics Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 994, USA ABSTRACT Given a graph G, the dominator coloring problem seeks a
On Dominator Colorings in Graphs Ralucca Michelle Gera Department of Applied Mathematics Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 994, USA ABSTRACT Given a graph G, the dominator coloring problem seeks a
Milovanović Bounds for Seidel Energy of a Graph
 Advances in Theoretical and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-4554 Volume 10, Number 1 (2016), pp. 37 44 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/atam.htm Milovanović Bounds for Seidel Energy
Advances in Theoretical and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-4554 Volume 10, Number 1 (2016), pp. 37 44 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/atam.htm Milovanović Bounds for Seidel Energy
RELATION BETWEEN ENERGY AND LAPLACIAN ENERGY
 MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 59 (200) 343-354 ISSN 0340-6253 RELATION BETWEEN ENERGY AND LAPLACIAN ENERGY Ivan Gutman, a NairMariaMaiadeAbreu,
MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 59 (200) 343-354 ISSN 0340-6253 RELATION BETWEEN ENERGY AND LAPLACIAN ENERGY Ivan Gutman, a NairMariaMaiadeAbreu,
A lower bound for the Laplacian eigenvalues of a graph proof of a conjecture by Guo
 A lower bound for the Laplacian eigenvalues of a graph proof of a conjecture by Guo A. E. Brouwer & W. H. Haemers 2008-02-28 Abstract We show that if µ j is the j-th largest Laplacian eigenvalue, and d
A lower bound for the Laplacian eigenvalues of a graph proof of a conjecture by Guo A. E. Brouwer & W. H. Haemers 2008-02-28 Abstract We show that if µ j is the j-th largest Laplacian eigenvalue, and d
Bulletin of the Iranian Mathematical Society
 ISSN: 117-6X (Print) ISSN: 1735-8515 (Online) Bulletin of the Iranian Mathematical Society Vol. 4 (14), No. 6, pp. 1491 154. Title: The locating chromatic number of the join of graphs Author(s): A. Behtoei
ISSN: 117-6X (Print) ISSN: 1735-8515 (Online) Bulletin of the Iranian Mathematical Society Vol. 4 (14), No. 6, pp. 1491 154. Title: The locating chromatic number of the join of graphs Author(s): A. Behtoei
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 3 May 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 3 May 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 3 May 2013](/thumbs/88/116922618.jpg) arxiv:1305.0601v1 [math.co] 3 May 2013 On the Cayley graph of a commutative ring with respect to its zero-divisors G. Aalipour a,b and S. Akbari a,b a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Sharif University
arxiv:1305.0601v1 [math.co] 3 May 2013 On the Cayley graph of a commutative ring with respect to its zero-divisors G. Aalipour a,b and S. Akbari a,b a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Sharif University
The Interlace Polynomial of Graphs at 1
 The Interlace Polynomial of Graphs at 1 PN Balister B Bollobás J Cutler L Pebody July 3, 2002 Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152 USA Abstract In this paper we
The Interlace Polynomial of Graphs at 1 PN Balister B Bollobás J Cutler L Pebody July 3, 2002 Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152 USA Abstract In this paper we
On the connectivity of the direct product of graphs
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 41 (2008), Pages 45 56 On the connectivity of the direct product of graphs Boštjan Brešar University of Maribor, FEECS Smetanova 17, 2000 Maribor Slovenia bostjan.bresar@uni-mb.si
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 41 (2008), Pages 45 56 On the connectivity of the direct product of graphs Boštjan Brešar University of Maribor, FEECS Smetanova 17, 2000 Maribor Slovenia bostjan.bresar@uni-mb.si
Eigenvalues and edge-connectivity of regular graphs
 Eigenvalues and edge-connectivity of regular graphs Sebastian M. Cioabă University of Delaware Department of Mathematical Sciences Newark DE 19716, USA cioaba@math.udel.edu August 3, 009 Abstract In this
Eigenvalues and edge-connectivity of regular graphs Sebastian M. Cioabă University of Delaware Department of Mathematical Sciences Newark DE 19716, USA cioaba@math.udel.edu August 3, 009 Abstract In this
2 β 0 -excellent graphs
 β 0 -excellent graphs A. P. Pushpalatha, G. Jothilakshmi Thiagarajar College of Engineering Madurai - 65 015 India Email: gjlmat@tce.edu, appmat@tce.edu S. Suganthi, V. Swaminathan Ramanujan Research Centre
β 0 -excellent graphs A. P. Pushpalatha, G. Jothilakshmi Thiagarajar College of Engineering Madurai - 65 015 India Email: gjlmat@tce.edu, appmat@tce.edu S. Suganthi, V. Swaminathan Ramanujan Research Centre
Discrete Mathematics
 Discrete Mathematics 310 (2010) 3398 303 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Discrete Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Maximal cliques in {P 2 P 3, C }-free graphs S.A.
Discrete Mathematics 310 (2010) 3398 303 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Discrete Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Maximal cliques in {P 2 P 3, C }-free graphs S.A.
Energy, Laplacian Energy and Zagreb Index of Line Graph, Middle Graph and Total Graph
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 21, no. 18, 895-9 Energy, Laplacian Energy and Zagreb Index of Line Graph, Middle Graph and Total Graph Zhongzhu Liu Department of Mathematics, South China Normal
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 21, no. 18, 895-9 Energy, Laplacian Energy and Zagreb Index of Line Graph, Middle Graph and Total Graph Zhongzhu Liu Department of Mathematics, South China Normal
CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIAL OF SOME CLUSTER GRAPHS
 Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 37(2) (2013), Pages 369 373 CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIAL OF SOME CLUSTER GRAPHS PRABHAKAR R HAMPIHOLI 1 AND BASAVRAJ S DURGI 2 Abstract The characteristic polynomial
Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 37(2) (2013), Pages 369 373 CHARACTERISTIC POLYNOMIAL OF SOME CLUSTER GRAPHS PRABHAKAR R HAMPIHOLI 1 AND BASAVRAJ S DURGI 2 Abstract The characteristic polynomial
On oriented graphs with minimal skew energy
 Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 7 Article 61 014 On oriented graphs with minimal skew energy Shi-Cai Gong Zhejiang A & F University, scgong@zafueducn Xueliang Li Nankai University, lxl@nankaieducn
Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 7 Article 61 014 On oriented graphs with minimal skew energy Shi-Cai Gong Zhejiang A & F University, scgong@zafueducn Xueliang Li Nankai University, lxl@nankaieducn
On sum of powers of the Laplacian and signless Laplacian eigenvalues of graphs
 On sum of powers of the Laplacian and signless Laplacian eigenvalues of graphs Saieed Akbari 1,2 Ebrahim Ghorbani 1,2 Jacobus H. Koolen 3,4 Mohammad Reza Oboudi 1,2 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences
On sum of powers of the Laplacian and signless Laplacian eigenvalues of graphs Saieed Akbari 1,2 Ebrahim Ghorbani 1,2 Jacobus H. Koolen 3,4 Mohammad Reza Oboudi 1,2 1 Department of Mathematical Sciences
Energies of Graphs and Matrices
 Energies of Graphs and Matrices Duy Nguyen T Parabola Talk October 6, 2010 Summary 1 Definitions Energy of Graph 2 Laplacian Energy Laplacian Matrices Edge Deletion 3 Maximum energy 4 The Integral Formula
Energies of Graphs and Matrices Duy Nguyen T Parabola Talk October 6, 2010 Summary 1 Definitions Energy of Graph 2 Laplacian Energy Laplacian Matrices Edge Deletion 3 Maximum energy 4 The Integral Formula
Hamilton Cycles in Digraphs of Unitary Matrices
 Hamilton Cycles in Digraphs of Unitary Matrices G. Gutin A. Rafiey S. Severini A. Yeo Abstract A set S V is called an q + -set (q -set, respectively) if S has at least two vertices and, for every u S,
Hamilton Cycles in Digraphs of Unitary Matrices G. Gutin A. Rafiey S. Severini A. Yeo Abstract A set S V is called an q + -set (q -set, respectively) if S has at least two vertices and, for every u S,
Some spectral inequalities for triangle-free regular graphs
 Filomat 7:8 (13), 1561 1567 DOI 198/FIL138561K Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://wwwpmfniacrs/filomat Some spectral inequalities for triangle-free
Filomat 7:8 (13), 1561 1567 DOI 198/FIL138561K Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://wwwpmfniacrs/filomat Some spectral inequalities for triangle-free
Hanna Furmańczyk EQUITABLE COLORING OF GRAPH PRODUCTS
 Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 6 No. 006 Hanna Furmańczyk EQUITABLE COLORING OF GRAPH PRODUCTS Abstract. A graph is equitably k-colorable if its vertices can be partitioned into k independent sets in such a
Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 6 No. 006 Hanna Furmańczyk EQUITABLE COLORING OF GRAPH PRODUCTS Abstract. A graph is equitably k-colorable if its vertices can be partitioned into k independent sets in such a
Graphs with Integer Matching Polynomial Roots
 Graphs with Integer Matching Polynomial Roots S. Akbari a, P. Csikvári b, A. Ghafari a, S. Khalashi Ghezelahmad c, M. Nahvi a a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
Graphs with Integer Matching Polynomial Roots S. Akbari a, P. Csikvári b, A. Ghafari a, S. Khalashi Ghezelahmad c, M. Nahvi a a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran,
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators.
 MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
3-Chromatic Cubic Graphs with Complementary Connected Domination Number Three
 Vol.3, Issue.1, Jan-Feb. 2013 pp-231-239 ISSN: 2249-6645 3-Chromatic Cubic Graphs with Complementary Connected Domination Number Three Selvam Avadayappan, 1 S. Kalaimathy, 2 G. Mahadevan 3 1, 2 Department
Vol.3, Issue.1, Jan-Feb. 2013 pp-231-239 ISSN: 2249-6645 3-Chromatic Cubic Graphs with Complementary Connected Domination Number Three Selvam Avadayappan, 1 S. Kalaimathy, 2 G. Mahadevan 3 1, 2 Department
On energy, Laplacian energy and p-fold graphs
 Electronic Journal of Graph Theory and Applications 3 (1) (2015), 94 107 On energy, Laplacian energy and p-fold graphs Hilal A. Ganie a, S. Pirzada b, Edy Tri Baskoro c a Department of Mathematics, University
Electronic Journal of Graph Theory and Applications 3 (1) (2015), 94 107 On energy, Laplacian energy and p-fold graphs Hilal A. Ganie a, S. Pirzada b, Edy Tri Baskoro c a Department of Mathematics, University
On Adjacent Vertex-distinguishing Total Chromatic Number of Generalized Mycielski Graphs. Enqiang Zhu*, Chanjuan Liu and Jin Xu
 TAIWANESE JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. xx, No. x, pp. 4, xx 20xx DOI: 0.650/tjm/6499 This paper is available online at http://journal.tms.org.tw On Adjacent Vertex-distinguishing Total Chromatic Number
TAIWANESE JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. xx, No. x, pp. 4, xx 20xx DOI: 0.650/tjm/6499 This paper is available online at http://journal.tms.org.tw On Adjacent Vertex-distinguishing Total Chromatic Number
Characteristic polynomials of skew-adjacency matrices of oriented graphs
 Characteristic polynomials of skew-adjacency matrices of oriented graphs Yaoping Hou Department of Mathematics Hunan Normal University Changsha, Hunan 410081, China yphou@hunnu.edu.cn Tiangang Lei Department
Characteristic polynomials of skew-adjacency matrices of oriented graphs Yaoping Hou Department of Mathematics Hunan Normal University Changsha, Hunan 410081, China yphou@hunnu.edu.cn Tiangang Lei Department
Some results on incidence coloring, star arboricity and domination number
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 54 (2012), Pages 107 114 Some results on incidence coloring, star arboricity and domination number Pak Kiu Sun Wai Chee Shiu Department of Mathematics Hong
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 54 (2012), Pages 107 114 Some results on incidence coloring, star arboricity and domination number Pak Kiu Sun Wai Chee Shiu Department of Mathematics Hong
Partial cubes: structures, characterizations, and constructions
 Partial cubes: structures, characterizations, and constructions Sergei Ovchinnikov San Francisco State University, Mathematics Department, 1600 Holloway Ave., San Francisco, CA 94132 Abstract Partial cubes
Partial cubes: structures, characterizations, and constructions Sergei Ovchinnikov San Francisco State University, Mathematics Department, 1600 Holloway Ave., San Francisco, CA 94132 Abstract Partial cubes
GENERALIZED INDEPENDENCE IN GRAPHS HAVING CUT-VERTICES
 GENERALIZED INDEPENDENCE IN GRAPHS HAVING CUT-VERTICES Vladimir D. Samodivkin 7th January 2008 (Dedicated to Mihail Konstantinov on his 60th birthday) Abstract For a graphical property P and a graph G,
GENERALIZED INDEPENDENCE IN GRAPHS HAVING CUT-VERTICES Vladimir D. Samodivkin 7th January 2008 (Dedicated to Mihail Konstantinov on his 60th birthday) Abstract For a graphical property P and a graph G,
arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 11 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 11 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 11 Oct 2018](/thumbs/89/97851698.jpg) Path matrix and path energy of graphs arxiv:1810.04870v1 [cs.ds] 11 Oct 018 Aleksandar Ilić Facebook Inc, Menlo Park, California, USA e-mail: aleksandari@gmail.com Milan Bašić Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics,
Path matrix and path energy of graphs arxiv:1810.04870v1 [cs.ds] 11 Oct 018 Aleksandar Ilić Facebook Inc, Menlo Park, California, USA e-mail: aleksandari@gmail.com Milan Bašić Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics,
Very few Moore Graphs
 Very few Moore Graphs Anurag Bishnoi June 7, 0 Abstract We prove here a well known result in graph theory, originally proved by Hoffman and Singleton, that any non-trivial Moore graph of diameter is regular
Very few Moore Graphs Anurag Bishnoi June 7, 0 Abstract We prove here a well known result in graph theory, originally proved by Hoffman and Singleton, that any non-trivial Moore graph of diameter is regular
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 27 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 27 Nov 2014 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 27 Nov 2014](/thumbs/92/110723314.jpg) Extremal matching energy of complements of trees Tingzeng Wu a,,1, Weigen Yan b,2, Heping Zhang c,1 a School of Mathematics and Statistics, Qinghai Nationalities University, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.
Extremal matching energy of complements of trees Tingzeng Wu a,,1, Weigen Yan b,2, Heping Zhang c,1 a School of Mathematics and Statistics, Qinghai Nationalities University, Xining, Qinghai 810007, P.
Cospectral graphs and the generalized adjacency matrix
 Linear Algebra and its Applications 42 2007) 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Cospectral graphs and the generalized adjacency matrix E.R. van Dam a,1, W.H. Haemers a,, J.H. Koolen b,2 a Tilburg University,
Linear Algebra and its Applications 42 2007) 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Cospectral graphs and the generalized adjacency matrix E.R. van Dam a,1, W.H. Haemers a,, J.H. Koolen b,2 a Tilburg University,
arxiv: v2 [math.co] 19 Jun 2018
![arxiv: v2 [math.co] 19 Jun 2018 arxiv: v2 [math.co] 19 Jun 2018](/thumbs/96/129281759.jpg) arxiv:1705.06268v2 [math.co] 19 Jun 2018 On the Nonexistence of Some Generalized Folkman Numbers Xiaodong Xu Guangxi Academy of Sciences Nanning 530007, P.R. China xxdmaths@sina.com Meilian Liang School
arxiv:1705.06268v2 [math.co] 19 Jun 2018 On the Nonexistence of Some Generalized Folkman Numbers Xiaodong Xu Guangxi Academy of Sciences Nanning 530007, P.R. China xxdmaths@sina.com Meilian Liang School
ON DOMINATING THE CARTESIAN PRODUCT OF A GRAPH AND K 2. Bert L. Hartnell
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 24 (2004 ) 389 402 ON DOMINATING THE CARTESIAN PRODUCT OF A GRAPH AND K 2 Bert L. Hartnell Saint Mary s University Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3H 3C3 e-mail: bert.hartnell@smu.ca
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 24 (2004 ) 389 402 ON DOMINATING THE CARTESIAN PRODUCT OF A GRAPH AND K 2 Bert L. Hartnell Saint Mary s University Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3H 3C3 e-mail: bert.hartnell@smu.ca
Acyclic and Oriented Chromatic Numbers of Graphs
 Acyclic and Oriented Chromatic Numbers of Graphs A. V. Kostochka Novosibirsk State University 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia X. Zhu Dept. of Applied Mathematics National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung,
Acyclic and Oriented Chromatic Numbers of Graphs A. V. Kostochka Novosibirsk State University 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia X. Zhu Dept. of Applied Mathematics National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung,
On Total Domination Polynomials of Certain Graphs
 Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 123-127 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING S. Sanal 1 and H. E. Vatsalya 2 1. Faculty of Mathematics, Ibri College of Technology,
Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 123-127 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING S. Sanal 1 and H. E. Vatsalya 2 1. Faculty of Mathematics, Ibri College of Technology,
Bounds for the Zero Forcing Number of Graphs with Large Girth
 Theory and Applications of Graphs Volume 2 Issue 2 Article 1 2015 Bounds for the Zero Forcing Number of Graphs with Large Girth Randy Davila Rice University, rrd32@txstate.edu Franklin Kenter Rice University,
Theory and Applications of Graphs Volume 2 Issue 2 Article 1 2015 Bounds for the Zero Forcing Number of Graphs with Large Girth Randy Davila Rice University, rrd32@txstate.edu Franklin Kenter Rice University,
On the normalized Laplacian energy and general Randić index R 1 of graphs
 On the normalized Laplacian energy and general Randić index R of graphs Michael Cavers a Shaun Fallat a Steve Kirkland ab3 a Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Regina Regina SK Canada
On the normalized Laplacian energy and general Randić index R of graphs Michael Cavers a Shaun Fallat a Steve Kirkland ab3 a Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Regina Regina SK Canada
SOME RESULTS ON THE DISTANCE r-b-coloring IN GRAPHS
 TWMS J. App. Eng. Math. V.6, N.2, 2016, pp. 315-323 SOME RESULTS ON THE DISTANCE r-b-coloring IN GRAPHS G. JOTHILAKSHMI 1, A. P. PUSHPALATHA 1, S. SUGANTHI 2, V. SWAMINATHAN 3, Abstract. Given a positive
TWMS J. App. Eng. Math. V.6, N.2, 2016, pp. 315-323 SOME RESULTS ON THE DISTANCE r-b-coloring IN GRAPHS G. JOTHILAKSHMI 1, A. P. PUSHPALATHA 1, S. SUGANTHI 2, V. SWAMINATHAN 3, Abstract. Given a positive
A Characterization of (3+1)-Free Posets
 Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 93, 231241 (2001) doi:10.1006jcta.2000.3075, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on A Characterization of (3+1)-Free Posets Mark Skandera Department of
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 93, 231241 (2001) doi:10.1006jcta.2000.3075, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on A Characterization of (3+1)-Free Posets Mark Skandera Department of
Linear Algebra and its Applications
 Linear Algebra and its Applications xxx (2008) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Linear Algebra and its Applications journal homepage: wwwelseviercom/locate/laa Graphs with three distinct
Linear Algebra and its Applications xxx (2008) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Linear Algebra and its Applications journal homepage: wwwelseviercom/locate/laa Graphs with three distinct
Bipartite graphs with at most six non-zero eigenvalues
 Also available at http://amc-journal.eu ISSN 1855-3966 (printed edn.), ISSN 1855-3974 (electronic edn.) ARS MATHEMATICA CONTEMPORANEA 11 (016) 315 35 Bipartite graphs with at most six non-zero eigenvalues
Also available at http://amc-journal.eu ISSN 1855-3966 (printed edn.), ISSN 1855-3974 (electronic edn.) ARS MATHEMATICA CONTEMPORANEA 11 (016) 315 35 Bipartite graphs with at most six non-zero eigenvalues
On uniquely 3-colorable plane graphs without prescribed adjacent faces 1
 arxiv:509.005v [math.co] 0 Sep 05 On uniquely -colorable plane graphs without prescribed adjacent faces Ze-peng LI School of Electronics Engineering and Computer Science Key Laboratory of High Confidence
arxiv:509.005v [math.co] 0 Sep 05 On uniquely -colorable plane graphs without prescribed adjacent faces Ze-peng LI School of Electronics Engineering and Computer Science Key Laboratory of High Confidence
Some constructions of integral graphs
 Some constructions of integral graphs A. Mohammadian B. Tayfeh-Rezaie School of Mathematics, Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM), P.O. Box 19395-5746, Tehran, Iran ali m@ipm.ir tayfeh-r@ipm.ir
Some constructions of integral graphs A. Mohammadian B. Tayfeh-Rezaie School of Mathematics, Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences (IPM), P.O. Box 19395-5746, Tehran, Iran ali m@ipm.ir tayfeh-r@ipm.ir
Some Nordhaus-Gaddum-type Results
 Some Nordhaus-Gaddum-type Results Wayne Goddard Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, USA Michael A. Henning Department of Mathematics University of Natal Pietermaritzburg,
Some Nordhaus-Gaddum-type Results Wayne Goddard Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, USA Michael A. Henning Department of Mathematics University of Natal Pietermaritzburg,
Graphs and matrices with maximal energy
 Graphs and matrices with maximal energy arxiv:math/060375v1 [math.co] 30 Mar 006 Vladimir Nikiforov Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis, Memphis TN 3815, USA, e-mail: vnikifrv@memphis.edu
Graphs and matrices with maximal energy arxiv:math/060375v1 [math.co] 30 Mar 006 Vladimir Nikiforov Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis, Memphis TN 3815, USA, e-mail: vnikifrv@memphis.edu
DECOMPOSITIONS OF MULTIGRAPHS INTO PARTS WITH THE SAME SIZE
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 335 347 DECOMPOSITIONS OF MULTIGRAPHS INTO PARTS WITH THE SAME SIZE Jaroslav Ivančo Institute of Mathematics P.J. Šafári University, Jesenná 5 SK-041 54
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 335 347 DECOMPOSITIONS OF MULTIGRAPHS INTO PARTS WITH THE SAME SIZE Jaroslav Ivančo Institute of Mathematics P.J. Šafári University, Jesenná 5 SK-041 54
STRUCTURE OF THE SET OF ALL MINIMAL TOTAL DOMINATING FUNCTIONS OF SOME CLASSES OF GRAPHS
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 407 423 STRUCTURE OF THE SET OF ALL MINIMAL TOTAL DOMINATING FUNCTIONS OF SOME CLASSES OF GRAPHS K. Reji Kumar Department of Mathematics N.S.S College,
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 407 423 STRUCTURE OF THE SET OF ALL MINIMAL TOTAL DOMINATING FUNCTIONS OF SOME CLASSES OF GRAPHS K. Reji Kumar Department of Mathematics N.S.S College,
Minimizing the Laplacian eigenvalues for trees with given domination number
 Linear Algebra and its Applications 419 2006) 648 655 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Minimizing the Laplacian eigenvalues for trees with given domination number Lihua Feng a,b,, Guihai Yu a, Qiao Li b a School
Linear Algebra and its Applications 419 2006) 648 655 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Minimizing the Laplacian eigenvalues for trees with given domination number Lihua Feng a,b,, Guihai Yu a, Qiao Li b a School
New feasibility conditions for directed strongly regular graphs
 New feasibility conditions for directed strongly regular graphs Sylvia A. Hobart Jason Williford Department of Mathematics University of Wyoming Laramie, Wyoming, U.S.A sahobart@uwyo.edu, jwillif1@uwyo.edu
New feasibility conditions for directed strongly regular graphs Sylvia A. Hobart Jason Williford Department of Mathematics University of Wyoming Laramie, Wyoming, U.S.A sahobart@uwyo.edu, jwillif1@uwyo.edu
Laplacian Polynomial and Laplacian Energy of Some Cluster Graphs
 International Journal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Research (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2014, PP 448-452 ISSN 2347-307X (Print) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) wwwarcjournalsorg Laplacian Polynomial
International Journal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Research (IJSIMR) Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2014, PP 448-452 ISSN 2347-307X (Print) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) wwwarcjournalsorg Laplacian Polynomial
Dominator Colorings and Safe Clique Partitions
 Dominator Colorings and Safe Clique Partitions Ralucca Gera, Craig Rasmussen Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 994, USA {rgera,ras}@npsedu and Steve Horton United States Military Academy West Point,
Dominator Colorings and Safe Clique Partitions Ralucca Gera, Craig Rasmussen Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 994, USA {rgera,ras}@npsedu and Steve Horton United States Military Academy West Point,
1 Last time: least-squares problems
 MATH Linear algebra (Fall 07) Lecture Last time: least-squares problems Definition. If A is an m n matrix and b R m, then a least-squares solution to the linear system Ax = b is a vector x R n such that
MATH Linear algebra (Fall 07) Lecture Last time: least-squares problems Definition. If A is an m n matrix and b R m, then a least-squares solution to the linear system Ax = b is a vector x R n such that
Using Laplacian Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in the Analysis of Frequency Assignment Problems
 Using Laplacian Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in the Analysis of Frequency Assignment Problems Jan van den Heuvel and Snežana Pejić Department of Mathematics London School of Economics Houghton Street,
Using Laplacian Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in the Analysis of Frequency Assignment Problems Jan van den Heuvel and Snežana Pejić Department of Mathematics London School of Economics Houghton Street,
Journal of Science and Arts Year 17, No. 1(38), pp , 2017
 Journal of Science and Arts Year 17, No. 1(38), pp. 49-60, 2017 BOUNDS FOR THE ENERGY OF ( ) ORIGINAL PAPER ( ) USING 2-ADJACENCY SERIFE BUYUKKOSE 1, SEMIHA BASDAS NURKAHLI 1, NURSAH MUTLU 1 Manuscript
Journal of Science and Arts Year 17, No. 1(38), pp. 49-60, 2017 BOUNDS FOR THE ENERGY OF ( ) ORIGINAL PAPER ( ) USING 2-ADJACENCY SERIFE BUYUKKOSE 1, SEMIHA BASDAS NURKAHLI 1, NURSAH MUTLU 1 Manuscript
v iv j E(G) x u, for each v V(G).
 Volume 3, pp. 514-5, May 01 A NOTE ON THE LEAST EIGENVALUE OF A GRAPH WITH GIVEN MAXIMUM DEGREE BAO-XUAN ZHU Abstract. This note investigates the least eigenvalues of connected graphs with n vertices and
Volume 3, pp. 514-5, May 01 A NOTE ON THE LEAST EIGENVALUE OF A GRAPH WITH GIVEN MAXIMUM DEGREE BAO-XUAN ZHU Abstract. This note investigates the least eigenvalues of connected graphs with n vertices and
Laplacians of Graphs, Spectra and Laplacian polynomials
 Mednykh A. D. (Sobolev Institute of Math) Laplacian for Graphs 27 June - 03 July 2015 1 / 30 Laplacians of Graphs, Spectra and Laplacian polynomials Alexander Mednykh Sobolev Institute of Mathematics Novosibirsk
Mednykh A. D. (Sobolev Institute of Math) Laplacian for Graphs 27 June - 03 July 2015 1 / 30 Laplacians of Graphs, Spectra and Laplacian polynomials Alexander Mednykh Sobolev Institute of Mathematics Novosibirsk
Applicable Analysis and Discrete Mathematics available online at GRAPHS WITH TWO MAIN AND TWO PLAIN EIGENVALUES
 Applicable Analysis and Discrete Mathematics available online at http://pefmath.etf.rs Appl. Anal. Discrete Math. 11 (2017), 244 257. https://doi.org/10.2298/aadm1702244h GRAPHS WITH TWO MAIN AND TWO PLAIN
Applicable Analysis and Discrete Mathematics available online at http://pefmath.etf.rs Appl. Anal. Discrete Math. 11 (2017), 244 257. https://doi.org/10.2298/aadm1702244h GRAPHS WITH TWO MAIN AND TWO PLAIN
On the spectral radii of quasi-tree graphs and quasiunicyclic graphs with k pendent vertices
 Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 20 Volume 20 (2010) Article 30 2010 On the spectral radii of quasi-tree graphs and quasiunicyclic graphs with k pendent vertices Xianya Geng Shuchao Li lscmath@mail.ccnu.edu.cn
Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 20 Volume 20 (2010) Article 30 2010 On the spectral radii of quasi-tree graphs and quasiunicyclic graphs with k pendent vertices Xianya Geng Shuchao Li lscmath@mail.ccnu.edu.cn
An Introduction to Spectral Graph Theory
 An Introduction to Spectral Graph Theory Mackenzie Wheeler Supervisor: Dr. Gary MacGillivray University of Victoria WheelerM@uvic.ca Outline Outline 1. How many walks are there from vertices v i to v j
An Introduction to Spectral Graph Theory Mackenzie Wheeler Supervisor: Dr. Gary MacGillivray University of Victoria WheelerM@uvic.ca Outline Outline 1. How many walks are there from vertices v i to v j
Topics in Graph Theory
 Topics in Graph Theory September 4, 2018 1 Preliminaries A graph is a system G = (V, E) consisting of a set V of vertices and a set E (disjoint from V ) of edges, together with an incidence function End
Topics in Graph Theory September 4, 2018 1 Preliminaries A graph is a system G = (V, E) consisting of a set V of vertices and a set E (disjoint from V ) of edges, together with an incidence function End
Locating-Total Dominating Sets in Twin-Free Graphs: a Conjecture
 Locating-Total Dominating Sets in Twin-Free Graphs: a Conjecture Florent Foucaud Michael A. Henning Department of Pure and Applied Mathematics University of Johannesburg Auckland Park, 2006, South Africa
Locating-Total Dominating Sets in Twin-Free Graphs: a Conjecture Florent Foucaud Michael A. Henning Department of Pure and Applied Mathematics University of Johannesburg Auckland Park, 2006, South Africa
Changing and unchanging of Total Dominating Color Transversal number of Graphs
 International Journal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Research (IJSIMR) Volume 4, Issue 4, April 216, PP 44-49 ISSN 2347-37X (Print) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.2431/2347-3142.446
International Journal of Scientific and Innovative Mathematical Research (IJSIMR) Volume 4, Issue 4, April 216, PP 44-49 ISSN 2347-37X (Print) & ISSN 2347-3142 (Online) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.2431/2347-3142.446
Laplacians of Graphs, Spectra and Laplacian polynomials
 Laplacians of Graphs, Spectra and Laplacian polynomials Lector: Alexander Mednykh Sobolev Institute of Mathematics Novosibirsk State University Winter School in Harmonic Functions on Graphs and Combinatorial
Laplacians of Graphs, Spectra and Laplacian polynomials Lector: Alexander Mednykh Sobolev Institute of Mathematics Novosibirsk State University Winter School in Harmonic Functions on Graphs and Combinatorial
Bicyclic digraphs with extremal skew energy
 Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 3 Volume 3 (01) Article 01 Bicyclic digraphs with extremal skew energy Xiaoling Shen Yoaping Hou yphou@hunnu.edu.cn Chongyan Zhang Follow this and additional
Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 3 Volume 3 (01) Article 01 Bicyclic digraphs with extremal skew energy Xiaoling Shen Yoaping Hou yphou@hunnu.edu.cn Chongyan Zhang Follow this and additional
AUTOMORPHISM GROUPS AND SPECTRA OF CIRCULANT GRAPHS
 AUTOMORPHISM GROUPS AND SPECTRA OF CIRCULANT GRAPHS MAX GOLDBERG Abstract. We explore ways to concisely describe circulant graphs, highly symmetric graphs with properties that are easier to generalize
AUTOMORPHISM GROUPS AND SPECTRA OF CIRCULANT GRAPHS MAX GOLDBERG Abstract. We explore ways to concisely describe circulant graphs, highly symmetric graphs with properties that are easier to generalize
Graph coloring, perfect graphs
 Lecture 5 (05.04.2013) Graph coloring, perfect graphs Scribe: Tomasz Kociumaka Lecturer: Marcin Pilipczuk 1 Introduction to graph coloring Definition 1. Let G be a simple undirected graph and k a positive
Lecture 5 (05.04.2013) Graph coloring, perfect graphs Scribe: Tomasz Kociumaka Lecturer: Marcin Pilipczuk 1 Introduction to graph coloring Definition 1. Let G be a simple undirected graph and k a positive
NOTE ON THE SKEW ENERGY OF ORIENTED GRAPHS. Communicated by Ivan Gutman. 1. Introduction
 Transactions on Combinatorics ISSN (print): 2251-8657, ISSN (on-line): 2251-8665 Vol. 4 No. 1 (2015), pp. 57-61. c 2015 University of Isfahan www.combinatorics.ir www.ui.ac.ir NOTE ON THE SKEW ENERGY OF
Transactions on Combinatorics ISSN (print): 2251-8657, ISSN (on-line): 2251-8665 Vol. 4 No. 1 (2015), pp. 57-61. c 2015 University of Isfahan www.combinatorics.ir www.ui.ac.ir NOTE ON THE SKEW ENERGY OF
12.1 The Achromatic Number of a Graph
 Chapter 1 Complete Colorings The proper vertex colorings of a graph G in which we are most interested are those that use the smallest number of colors These are, of course, the χ(g)-colorings of G If χ(g)
Chapter 1 Complete Colorings The proper vertex colorings of a graph G in which we are most interested are those that use the smallest number of colors These are, of course, the χ(g)-colorings of G If χ(g)
ARRANGEABILITY AND CLIQUE SUBDIVISIONS. Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Emory University Atlanta, GA and
 ARRANGEABILITY AND CLIQUE SUBDIVISIONS Vojtěch Rödl* Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Emory University Atlanta, GA 30322 and Robin Thomas** School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology
ARRANGEABILITY AND CLIQUE SUBDIVISIONS Vojtěch Rödl* Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Emory University Atlanta, GA 30322 and Robin Thomas** School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology
On minimal energies of trees with given diameter
 Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 17 Volume 17 (2008) Article 29 2008 On minimal energies of trees with given diameter Shuchao Li lscmath@mail.ccnu.edu.cn Nana Li Follow this and additional works
Electronic Journal of Linear Algebra Volume 17 Volume 17 (2008) Article 29 2008 On minimal energies of trees with given diameter Shuchao Li lscmath@mail.ccnu.edu.cn Nana Li Follow this and additional works
Linear algebra and applications to graphs Part 1
 Linear algebra and applications to graphs Part 1 Written up by Mikhail Belkin and Moon Duchin Instructor: Laszlo Babai June 17, 2001 1 Basic Linear Algebra Exercise 1.1 Let V and W be linear subspaces
Linear algebra and applications to graphs Part 1 Written up by Mikhail Belkin and Moon Duchin Instructor: Laszlo Babai June 17, 2001 1 Basic Linear Algebra Exercise 1.1 Let V and W be linear subspaces
