Math 126: Homework 13 solutions
|
|
|
- Lawrence Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 6: Homework 3 lutions. (a) The initial data can be parameterized according to = f (s) = s, y = g(s) =, u( f (s), g(s)) = h(s) = sin s. The characteristics are determined by the ODE system Equation gives y = t, = y + y, () =, () = zy 4. (3) which gives = t + t = t + t log = C + log( + t ) for me constant C. Hence, the characteristic passing through (s, ) at t = is = s( + t ). Equation 3 then gives which can be integrated to give = zt 4 z = t 4 log z = t 8 + D for me constant D. By using the initial data, it can be seen that z = Z(s, t) = e t /8 sin s The family of characteristics for different values of s is shown is Fig.
2 3 y Figure : Characteristics of the partial differential equation considered in question, projected into the y plane. (b) From part (a), it can be seen that s = (c) Taking partial derivatives of Eq. 4 gives + y, t = y, ( ) u(, y) = Z(s, t) = e y /8 sin + y. (4) u (, y) = e y /8 ( ) + y cos + y ( u y (, y) = e y /8 y ( ) 4 sin + y y ( )) ( + y ) cos + y Hence and ( ) y + y u = ye y/8 ( + y ) cos + y ( ) y + y u + u y = ye y/8 sin 4 + y = yu 4
3 u y Figure : Three-dimensional plot of the lution u(, y) of question. since the terms involving cosine will cancel each other. Thus u(, y) satisfies the PDE. In addition ( ) u(, ) = e sin + y = sin the lution satisfies the initial data. (d) Figure shows a plot of the lution. It can be seen how the sinuidal initial data is transported along the parabolic characteristics. A small amount of decay is al visible in the y direction, due to the presence of the ep( y /8) term in the lution.. The characteristics will be given by which is equivalent to = y, = = ( y) = + y. 3
4 This has a first integral ψ(, y) = + y and thus the characteristics are given by the curves where ψ(, y) is constant. Hence a typical characteristic is + y = R for me constant R, which corresponds to a circle of radius R. The characteristics are a family of concentric circles centered on the origin. Since the lution is constant along each characteristic a general lution can then be written as u(, y) = G( + y ) for me function G(λ). The initial condition states that and similarly u(, ) = h() = G( ) u(, ) = h( ) = G(( ) ) = G( ). For a lution to eist it is therefore necessary that h() = h( ), h is even. This is reanable, since any characteristic circle of radius R will intersect the initial data at ±R, the values must be consistent. For any even choice of h, a general lution can be written as G(λ) = h( λ) defined for λ, that u(, y) = h( + y ). Hence h being even is both a necessary and sufficient condition for a general lution to eist. 3. (a) The characteristics are given by the ODE system =, = 3, = 3z and the initial data can be can be parameterized according to Hence and therefore = f (s) = s, y = g(s) =, u( f (s), g(s)) = h(s). = X(s, t) = s + t (5) = 3(s + t) y = Y(s, t) = (s + t) 3 s 3 (6) where the constants of integration have been chosen that the characteristics pass through the initial data when t =. 4
5 3 y Figure 3: Characteristics for the partial differential equation considered in question 3. (b) The characteristics are shown in Fig. 3. The Jacobian is given by J(s, t) = X s(s, t) Y s (s, t) X t (s, t) Y t (s, t) = 3(s + t) 3s 3(s + t) = 3(s + t) 3(s + t) + 3s = 3s and thus J(s, ) = 3s. At s =, the Jacobian vanishes, implying that the characteristics and the initial data are tangent, which is in agreement with shapes of characteristics shown in Fig. 3. As described in the tetbook, for a C lution to eist, ( ) a(,, z ) b(,, z rank ) c(,, z ) f () g () h =. () This can be written as h () =. ( rank h () ) = (c) To find the general lution, first consider the differential equation for z given above: = 3z. 5
6 Thus z = 3(s + t) log z = (s + t) 3 + C for me integration constant C. Using the initial condition shows that Equations 5 and 6 show that and the general lution is z = Z(s, t) = h(s)e (s+t)3 s 3. s = S(, y) = 3 3 y t = T(, y) = 3 3 y u(, y) = Z(S(, y), T(, y)) = h( 3 3 y)e y If h() =, then h () = h() =, the condition from part (b) is satisfied. However, u(, y) = ( 3 y) /3 e y ( ) u y (, y) = y + (3 y) /3 u y (, y) = ( ) 3 3 y + ( y)/3 e y which is unbounded as y and thus u is not C in a neighborhood of the ais. This implies that while the condition from part (b) is necessary for a C lution to eist, it is not sufficient. Note that other choices of h(s) would lead to a C lution: if h(s) = s 3, then which is C everywhere. 4. This problem can be epressed as u(, y) = ( 3 y)e y F(, y, u, u, u y ) = u + u y 4u =. e y 6
7 Following the notation of the tetbook, the last two variables of F can be denoted as p = u and q = u y, F(, y, u, p, q) = p + q 4u. (7) The characteristic system is then given by The initial data is dp dq = F p = p (8) = F q = q (9) = pf p + qf q = p + q () = F pf u = 4p () = F y qf u = 4q. () f (s) = cos s, g(s) = sin s, h(s) =. Let ϕ(s) and ψ(s) be the initial conditions on p and q respectively. Equation 7 requires that ϕ + ψ = 4 and the condition h (s) = ϕ(s) f (s) + ψ(s)g (s) requires that This gives one lution as ϕ sin s + ψ cos s =. ϕ = cos s, ψ = sin s and a second lution as ϕ = cos s, ψ = sin s. Consider the first lution for the initial data. Equation shows that q = Ce 4t for me constant C, and to be consistent with the initial data, this leads to q = e 4t sin s. Equation 9 then becomes = 4e4t sin s y = e 4t sin s + C 7
8 for me constant C. Using the initial data g(s) = sin s gives y = e 4t sin s. A similar consideration of Eqs. and 8 gives Thus p = e 4t cos s, = e 4t cos s. = 8e8t (cos s + sin s) = 8e 8t z = e 8t. To find a general lution u(, y), note that and thus + y = e 8t (cos s + sin s) = e 8t u(, y) = z = + y. Now consider the second case for the initial data. Then q = e 4t sin s Eq. 9 becomes = 4e4t sin s, and by considering the initial data g(s) = sin s, Similarly y = ( e 4t ) sin s. p = e 4t cos s, = ( e 4t ) cos s. The equation for / is the same with the same initial data z = e 8t still holds. To find a general lution u(, y), note that and thus the general lution is + y = ( e 4t ) u(, y) = e 4t = + y ( ) + y. Note that etending this lution outside of the disk + y = 4 would require further analysis, since t as + y 4. 8
Math512 PDE Homework 2
 Math51 PDE Homework October 11, 009 Exercise 1.3. Solve u = xu x +yu y +(u x+y y/ = 0 with initial conditon u(x, 0 = 1 x. Proof. In this case, we have F = xp + yq + (p + q / z = 0 and Γ parameterized as
Math51 PDE Homework October 11, 009 Exercise 1.3. Solve u = xu x +yu y +(u x+y y/ = 0 with initial conditon u(x, 0 = 1 x. Proof. In this case, we have F = xp + yq + (p + q / z = 0 and Γ parameterized as
Math 147, Homework 1 Solutions Due: April 10, 2012
 1. For what values of a is the set: Math 147, Homework 1 Solutions Due: April 10, 2012 M a = { (x, y, z) : x 2 + y 2 z 2 = a } a smooth manifold? Give explicit parametrizations for open sets covering M
1. For what values of a is the set: Math 147, Homework 1 Solutions Due: April 10, 2012 M a = { (x, y, z) : x 2 + y 2 z 2 = a } a smooth manifold? Give explicit parametrizations for open sets covering M
University of Regina Department of Mathematics and Statistics
 u z v 1. Consider the map Universit of Regina Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH431/831 Differential Geometr Winter 2014 Homework Assignment No. 3 - Solutions ϕ(u, v) = (cosusinv, sin u sin
u z v 1. Consider the map Universit of Regina Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH431/831 Differential Geometr Winter 2014 Homework Assignment No. 3 - Solutions ϕ(u, v) = (cosusinv, sin u sin
z x = f x (x, y, a, b), z y = f y (x, y, a, b). F(x, y, z, z x, z y ) = 0. This is a PDE for the unknown function of two independent variables.
 Chapter 2 First order PDE 2.1 How and Why First order PDE appear? 2.1.1 Physical origins Conservation laws form one of the two fundamental parts of any mathematical model of Continuum Mechanics. These
Chapter 2 First order PDE 2.1 How and Why First order PDE appear? 2.1.1 Physical origins Conservation laws form one of the two fundamental parts of any mathematical model of Continuum Mechanics. These
The first order quasi-linear PDEs
 Chapter 2 The first order quasi-linear PDEs The first order quasi-linear PDEs have the following general form: F (x, u, Du) = 0, (2.1) where x = (x 1, x 2,, x 3 ) R n, u = u(x), Du is the gradient of u.
Chapter 2 The first order quasi-linear PDEs The first order quasi-linear PDEs have the following general form: F (x, u, Du) = 0, (2.1) where x = (x 1, x 2,, x 3 ) R n, u = u(x), Du is the gradient of u.
MATH 173: PRACTICE MIDTERM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 73: PACTICE MIDTEM SOLUTIONS This is a closed book, closed notes, no electronic devices exam. There are 5 problems. Solve all of them. Write your solutions to problems and in blue book #, and your
MATH 73: PACTICE MIDTEM SOLUTIONS This is a closed book, closed notes, no electronic devices exam. There are 5 problems. Solve all of them. Write your solutions to problems and in blue book #, and your
Solutions Of Homework 4
 Solutions Of Homework 1. Two parallel sides of a rectangle are being lengthened at the rate of 3 in/sec, while the other two sides are shortened in such a way that the figure remains a rectangle with constant
Solutions Of Homework 1. Two parallel sides of a rectangle are being lengthened at the rate of 3 in/sec, while the other two sides are shortened in such a way that the figure remains a rectangle with constant
b) The system of ODE s d x = v(x) in U. (2) dt
 How to solve linear and quasilinear first order partial differential equations This text contains a sketch about how to solve linear and quasilinear first order PDEs and should prepare you for the general
How to solve linear and quasilinear first order partial differential equations This text contains a sketch about how to solve linear and quasilinear first order PDEs and should prepare you for the general
TRIG REVIEW NOTES. Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents will equal)
 TRIG REVIEW NOTES Convert from radians to degrees: multiply by 0 180 Convert from degrees to radians: multiply by 0. 180 Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents
TRIG REVIEW NOTES Convert from radians to degrees: multiply by 0 180 Convert from degrees to radians: multiply by 0. 180 Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents
3.5 Continuity of a Function One Sided Continuity Intermediate Value Theorem... 23
 Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
(ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9
![(ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9 (ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9](/thumbs/89/100579300.jpg) Study Guide for Eam 1 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its epression to be well-defined. Some eamples of the conditions are: What is inside
Study Guide for Eam 1 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its epression to be well-defined. Some eamples of the conditions are: What is inside
MATH 220 solution to homework 1
 MATH solution to homework Problem. Define z(s = u( + s, y + s, then z (s = u u ( + s, y + s + y ( + s, y + s = e y, z( y = u( y, = f( y, u(, y = z( = z( y + y If we prescribe the data u(, = f(, then z
MATH solution to homework Problem. Define z(s = u( + s, y + s, then z (s = u u ( + s, y + s + y ( + s, y + s = e y, z( y = u( y, = f( y, u(, y = z( = z( y + y If we prescribe the data u(, = f(, then z
Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 05 notes Summer
 Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 0 notes Summer 0 Trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions often arise in physical applications with periodic motion. They do not arise often
Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 0 notes Summer 0 Trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions often arise in physical applications with periodic motion. They do not arise often
Transition to College Math
 Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
MTHE 227 Problem Set 10 Solutions. (1 y2 +z 2., 0, 0), y 2 + z 2 < 4 0, Otherwise.
 MTHE 7 Problem Set Solutions. (a) Sketch the cross-section of the (hollow) clinder + = in the -plane, as well as the vector field in this cross-section. ( +,, ), + < F(,, ) =, Otherwise. This is a simple
MTHE 7 Problem Set Solutions. (a) Sketch the cross-section of the (hollow) clinder + = in the -plane, as well as the vector field in this cross-section. ( +,, ), + < F(,, ) =, Otherwise. This is a simple
4 Introduction to First-Order Partial Differential
 4 Introduction to First-Order Partial Differential Equations You have already encountered examples of first-order PDEs in Section 3 when we discussed the pure advection mechanism, and mentioning the interesting
4 Introduction to First-Order Partial Differential Equations You have already encountered examples of first-order PDEs in Section 3 when we discussed the pure advection mechanism, and mentioning the interesting
is the curve of intersection of the plane y z 2 and the cylinder x oriented counterclockwise when viewed from above.
 The questions below are representative or actual questions that have appeared on final eams in Math from pring 009 to present. The questions below are in no particular order. There are tpicall 10 questions
The questions below are representative or actual questions that have appeared on final eams in Math from pring 009 to present. The questions below are in no particular order. There are tpicall 10 questions
problem score possible Total 60
 Math 32 A: Midterm 1, Oct. 24, 2008 Name: ID Number: Section: problem score possible 1. 10 2. 10 3. 10 4. 10 5. 10 6. 10 Total 60 1 1. Determine whether the following points are coplanar: a. P = (8, 14,
Math 32 A: Midterm 1, Oct. 24, 2008 Name: ID Number: Section: problem score possible 1. 10 2. 10 3. 10 4. 10 5. 10 6. 10 Total 60 1 1. Determine whether the following points are coplanar: a. P = (8, 14,
Name of the Student:
 Engineering Mathematics 016 SUBJECT NAME : Engineering Mathematics - I SUBJECT CODE : MA111 MATERIAL NAME : Universit Questions REGULATION : R008 WEBSITE : wwwhariganeshcom UPDATED ON : Januar 016 TEXTBOOK
Engineering Mathematics 016 SUBJECT NAME : Engineering Mathematics - I SUBJECT CODE : MA111 MATERIAL NAME : Universit Questions REGULATION : R008 WEBSITE : wwwhariganeshcom UPDATED ON : Januar 016 TEXTBOOK
Mathematics Trigonometry: Unit Circle
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
Lecture 10. (2) Functions of two variables. Partial derivatives. Dan Nichols February 27, 2018
 Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
Lecture 10 Partial derivatives Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts February 27, 2018 Last time: functions of two variables f(x, y) x and y are the independent
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Constrained Optimization
 MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Constrained Optimization Xiaojing Ye Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Xiaojing Ye, Math & Stat, Georgia State University 0 Constrained optimization
MATH 4211/6211 Optimization Constrained Optimization Xiaojing Ye Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Xiaojing Ye, Math & Stat, Georgia State University 0 Constrained optimization
Surfaces JWR. February 13, 2014
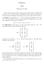 Surfaces JWR February 13, 214 These notes summarize the key points in the second chapter of Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces by Manfredo P. do Carmo. I wrote them to assure that the terminology
Surfaces JWR February 13, 214 These notes summarize the key points in the second chapter of Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces by Manfredo P. do Carmo. I wrote them to assure that the terminology
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (104 points)
 AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (0 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
AP Calculus (BC) Summer Assignment (0 points) This packet is a review of some Precalculus topics and some Calculus topics. It is to be done NEATLY and on a SEPARATE sheet of paper. Use your discretion
MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework
 MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
MATH 332, (Vector Analysis), Summer 2005: Homework 1 Instructor: Ivan Avramidi MATH 332: Vector Analysis Summer 2005 Homework Set 1. (Scalar Product, Equation of a Plane, Vector Product) Sections: 1.9,
Math 263 Final. (b) The cross product is. i j k c. =< c 1, 1, 1 >
 Math 63 Final Problem 1: [ points, 5 points to each part] Given the points P : (1, 1, 1), Q : (1,, ), R : (,, c 1), where c is a parameter, find (a) the vector equation of the line through P and Q. (b)
Math 63 Final Problem 1: [ points, 5 points to each part] Given the points P : (1, 1, 1), Q : (1,, ), R : (,, c 1), where c is a parameter, find (a) the vector equation of the line through P and Q. (b)
Homework #12 corrections
 Homework #2 corrections April 25, 205 (284) Let f() = 2 sin for 0 and f(0) = 0 (a) Use Theorems 283 and 284 to show f is differentiable at each a 0 and calculate f (a) Use, without proof, the fact that
Homework #2 corrections April 25, 205 (284) Let f() = 2 sin for 0 and f(0) = 0 (a) Use Theorems 283 and 284 to show f is differentiable at each a 0 and calculate f (a) Use, without proof, the fact that
Green s Theorem. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Green s Theorem
 Green s Theorem MATH 311, alculus III J. obert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Main Idea Main idea: the line integral around a positively oriented, simple closed curve is related to a double
Green s Theorem MATH 311, alculus III J. obert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Main Idea Main idea: the line integral around a positively oriented, simple closed curve is related to a double
The slope, m, compares the change in y-values to the change in x-values. Use the points (2, 4) and (6, 6) to determine the slope.
 LESSON Relating Slope and -intercept to Linear Equations UNDERSTAND The slope of a line is the ratio of the line s vertical change, called the rise, to its horizontal change, called the run. You can find
LESSON Relating Slope and -intercept to Linear Equations UNDERSTAND The slope of a line is the ratio of the line s vertical change, called the rise, to its horizontal change, called the run. You can find
1985 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
Limits and the derivative function. Limits and the derivative function
 The Velocity Problem A particle is moving in a straight line. t is the time that has passed from the start of motion (which corresponds to t = 0) s(t) is the distance from the particle to the initial position
The Velocity Problem A particle is moving in a straight line. t is the time that has passed from the start of motion (which corresponds to t = 0) s(t) is the distance from the particle to the initial position
Calculus 1 (AP, Honors, Academic) Summer Assignment 2018
 Calculus (AP, Honors, Academic) Summer Assignment 08 The summer assignments for Calculus will reinforce some necessary Algebra and Precalculus skills. In order to be successful in Calculus, you must have
Calculus (AP, Honors, Academic) Summer Assignment 08 The summer assignments for Calculus will reinforce some necessary Algebra and Precalculus skills. In order to be successful in Calculus, you must have
Section 3.5 The Implicit Function Theorem
 Section 3.5 The Implicit Function Theorem THEOREM 11 (Special Implicit Function Theorem): Suppose that F : R n+1 R has continuous partial derivatives. Denoting points in R n+1 by (x, z), where x R n and
Section 3.5 The Implicit Function Theorem THEOREM 11 (Special Implicit Function Theorem): Suppose that F : R n+1 R has continuous partial derivatives. Denoting points in R n+1 by (x, z), where x R n and
MATH The Chain Rule Fall 2016 A vector function of a vector variable is a function F: R n R m. In practice, if x 1, x n is the input,
 MATH 20550 The Chain Rule Fall 2016 A vector function of a vector variable is a function F: R n R m. In practice, if x 1, x n is the input, F(x 1,, x n ) F 1 (x 1,, x n ),, F m (x 1,, x n ) where each
MATH 20550 The Chain Rule Fall 2016 A vector function of a vector variable is a function F: R n R m. In practice, if x 1, x n is the input, F(x 1,, x n ) F 1 (x 1,, x n ),, F m (x 1,, x n ) where each
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
AP Calculus.1 Worksheet Day 1 All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. The only way to guarantee the eistence of a it is to algebraically prove
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work
 Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
Chapter 6: The Laplace Transform. Chih-Wei Liu
 Chapter 6: The Laplace Transform Chih-Wei Liu Outline Introduction The Laplace Transform The Unilateral Laplace Transform Properties of the Unilateral Laplace Transform Inversion of the Unilateral Laplace
Chapter 6: The Laplace Transform Chih-Wei Liu Outline Introduction The Laplace Transform The Unilateral Laplace Transform Properties of the Unilateral Laplace Transform Inversion of the Unilateral Laplace
4. (6 points) Express the domain of the following function in interval notation:
 Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
Warm up: Unit circle Fill in the exact values for quadrant 1 reference angles.
 Name: 4-1 Unit Circle and Exact Values Learning Goals: 1) How can we use the unit circle to find the value of sine, cosine, and tangent? 2) Given a point on a circle and the radius of the circle, how can
Name: 4-1 Unit Circle and Exact Values Learning Goals: 1) How can we use the unit circle to find the value of sine, cosine, and tangent? 2) Given a point on a circle and the radius of the circle, how can
1 Basic Second-Order PDEs
 Partial Differential Equations A. Visintin a.a. 2011-12 These pages are in progress. They contain: an abstract of the classes; notes on some (few) specific issues. These notes are far from providing a
Partial Differential Equations A. Visintin a.a. 2011-12 These pages are in progress. They contain: an abstract of the classes; notes on some (few) specific issues. These notes are far from providing a
4. Functions of one variable
 4. Functions of one variable These lecture notes present my interpretation of Ruth Lawrence s lecture notes (in Hebrew) 1 In this chapter we are going to meet one of the most important concepts in mathematics:
4. Functions of one variable These lecture notes present my interpretation of Ruth Lawrence s lecture notes (in Hebrew) 1 In this chapter we are going to meet one of the most important concepts in mathematics:
Solution: As x approaches 3, (x 2) approaches 1, so ln(x 2) approaches ln(1) = 0. Therefore we have a limit of the form 0/0 and can apply the.
 MATH, solutions to practice problems for the final eam. Compute the it: a) 3 e / Answer: e /3. b) 3 ln( 3) Answer:. c) 3 ln( ) 3 Solution: As approaches 3, ( ) approaches, so ln( ) approaches ln() =. Therefore
MATH, solutions to practice problems for the final eam. Compute the it: a) 3 e / Answer: e /3. b) 3 ln( 3) Answer:. c) 3 ln( ) 3 Solution: As approaches 3, ( ) approaches, so ln( ) approaches ln() =. Therefore
Math 5335 Section 2 Fall 2005 Solutions to December 8 homework problems
 Math 5335 Section 2 Fall 2005 Solutions to December 8 homework problems PROBLEM 9.7 To find an intersection points, we have to solve the following sstem of equations: 2 + 2 = 6, ( ) 2 + 2 =. We epand (and
Math 5335 Section 2 Fall 2005 Solutions to December 8 homework problems PROBLEM 9.7 To find an intersection points, we have to solve the following sstem of equations: 2 + 2 = 6, ( ) 2 + 2 =. We epand (and
Chain Rule. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets
 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets Equation of Continuity Our equations of hydrogeology are a combination of o Conservation of mass o Some empirical
1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets Equation of Continuity Our equations of hydrogeology are a combination of o Conservation of mass o Some empirical
18 19 Find the extreme values of f on the region described by the inequality. 20. Consider the problem of maximizing the function
 940 CHAPTER 14 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 14.8 EXERCISES 1. Pictured are a contour map of f and a curve with equation t, y 8. Estimate the maimum and minimum values of f subject to the constraint that t, y 8.
940 CHAPTER 14 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES 14.8 EXERCISES 1. Pictured are a contour map of f and a curve with equation t, y 8. Estimate the maimum and minimum values of f subject to the constraint that t, y 8.
Answers to Even-Numbered Exercises
 Answers to Even-Numbered Eercises Chapter Eercises. page ) 9 0.45 0 8) z yz 0) y 6 y 8 y y 4 y Eercises. page 6 ) p 9 8 8 5 8) 0) y y y ) w 5, 8 y y y, 857 000 Eercises. page 9 5 6 5 ) 8) 0) 8 6 9 66 y
Answers to Even-Numbered Eercises Chapter Eercises. page ) 9 0.45 0 8) z yz 0) y 6 y 8 y y 4 y Eercises. page 6 ) p 9 8 8 5 8) 0) y y y ) w 5, 8 y y y, 857 000 Eercises. page 9 5 6 5 ) 8) 0) 8 6 9 66 y
D In, RS=10, sin R
 FEBRUARY 7, 08 Invitational Sickles The abbreviation NOTA means None of These Answers and should be chosen if choices A, B, C and D are not correct Solve for over the Real Numbers: ln( ) ln() The trigonometric
FEBRUARY 7, 08 Invitational Sickles The abbreviation NOTA means None of These Answers and should be chosen if choices A, B, C and D are not correct Solve for over the Real Numbers: ln( ) ln() The trigonometric
Stokes Theorem. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Summer Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Stokes Theorem
 tokes Theorem MATH 311, alculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics ummer 2011 Background (1 of 2) Recall: Green s Theorem, M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = R ( N x M ) da y where is a piecewise
tokes Theorem MATH 311, alculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics ummer 2011 Background (1 of 2) Recall: Green s Theorem, M(x, y) dx + N(x, y) dy = R ( N x M ) da y where is a piecewise
How big is the family of stationary null scrolls?
 How big is the family of stationary null scrolls? Manuel Barros 1 and Angel Ferrández 2 1 Departamento de Geometría y Topología, Facultad de Ciencias Universidad de Granada, 1807 Granada, Spain. E-mail
How big is the family of stationary null scrolls? Manuel Barros 1 and Angel Ferrández 2 1 Departamento de Geometría y Topología, Facultad de Ciencias Universidad de Granada, 1807 Granada, Spain. E-mail
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC. Complex Fractions
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4]
![It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4] It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4]](/thumbs/79/79759146.jpg) It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4] f ( ) =.. It has a vertical asymptote at =, a) What are the critical numbers of f? b)
It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4] f ( ) =.. It has a vertical asymptote at =, a) What are the critical numbers of f? b)
1. Which of the following defines a function f for which f ( x) = f( x) 2. ln(4 2 x) < 0 if and only if
 . Which of the following defines a function f for which f ( ) = f( )? a. f ( ) = + 4 b. f ( ) = sin( ) f ( ) = cos( ) f ( ) = e f ( ) = log. ln(4 ) < 0 if and only if a. < b. < < < < > >. If f ( ) = (
. Which of the following defines a function f for which f ( ) = f( )? a. f ( ) = + 4 b. f ( ) = sin( ) f ( ) = cos( ) f ( ) = e f ( ) = log. ln(4 ) < 0 if and only if a. < b. < < < < > >. If f ( ) = (
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Textbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012
 Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
Sophomore Year: Algebra II Tetbook: Algebra II, Common Core Edition Larson, Boswell, Kanold, Stiff Holt McDougal 2012 Course Description: The purpose of this course is to give students a strong foundation
MATH 241 FALL 2009 HOMEWORK 3 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 41 FALL 009 HOMEWORK 3 SOLUTIONS H3P1 (i) We have the points A : (0, 0), B : (3, 0), and C : (x, y) We now from the distance formula that AC/BC = if and only if x + y (3 x) + y = which is equivalent
MATH 41 FALL 009 HOMEWORK 3 SOLUTIONS H3P1 (i) We have the points A : (0, 0), B : (3, 0), and C : (x, y) We now from the distance formula that AC/BC = if and only if x + y (3 x) + y = which is equivalent
C) 2 D) 4 E) 6. ? A) 0 B) 1 C) 1 D) The limit does not exist.
 . The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric equations = t, y = t t + are A) =, y = B) = only C) =, y = D) = only E) =, y =. What are the coordinates of the inflection point on the graph of y = ( +
. The asymptotes of the graph of the parametric equations = t, y = t t + are A) =, y = B) = only C) =, y = D) = only E) =, y =. What are the coordinates of the inflection point on the graph of y = ( +
( ) 2 + 2x 3! ( x x ) 2
 Review for The Final Math 195 1. Rewrite as a single simplified fraction: 1. Rewrite as a single simplified fraction:. + 1 + + 1! 3. Rewrite as a single simplified fraction:! 4! 4 + 3 3 + + 5! 3 3! 4!
Review for The Final Math 195 1. Rewrite as a single simplified fraction: 1. Rewrite as a single simplified fraction:. + 1 + + 1! 3. Rewrite as a single simplified fraction:! 4! 4 + 3 3 + + 5! 3 3! 4!
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. B) 94 C) ) A) 1 2
 Chapter Calculus MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the average rate of change of the function over the given interval. ) = 73-5
Chapter Calculus MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the average rate of change of the function over the given interval. ) = 73-5
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART 1 MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI PART 1: 135 POINTS, PART 2: 115 POINTS, TOTAL: 250 POINTS
 SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
Math 461 Homework 8. Paul Hacking. November 27, 2018
 Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 (1) Let S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F :
Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 (1) Let S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F :
Circles Print Activity. Use the Explore It mode to answer the following questions. 1. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions:
 Name: Circles Print Activity Use the Explore It mode to answer the following questions. 1. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions: a. A is a/an angle. (central/inscribed) b. A is subtended
Name: Circles Print Activity Use the Explore It mode to answer the following questions. 1. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions: a. A is a/an angle. (central/inscribed) b. A is subtended
Partial Differential Equations with Applications
 Universit of Leeds MATH 33 Partial Differential Eqations with Applications Eamples to spplement Chapter on First Order PDEs Eample (Simple linear eqation, k + = 0, (, 0) = ϕ(), k a constant.) The characteristic
Universit of Leeds MATH 33 Partial Differential Eqations with Applications Eamples to spplement Chapter on First Order PDEs Eample (Simple linear eqation, k + = 0, (, 0) = ϕ(), k a constant.) The characteristic
MATH 250 TOPIC 11 LIMITS. A. Basic Idea of a Limit and Limit Laws. Answers to Exercises and Problems
 Math 5 T-Limits Page MATH 5 TOPIC LIMITS A. Basic Idea of a Limit and Limit Laws B. Limits of the form,, C. Limits as or as D. Summary for Evaluating Limits Answers to Eercises and Problems Math 5 T-Limits
Math 5 T-Limits Page MATH 5 TOPIC LIMITS A. Basic Idea of a Limit and Limit Laws B. Limits of the form,, C. Limits as or as D. Summary for Evaluating Limits Answers to Eercises and Problems Math 5 T-Limits
3.3.1 Linear functions yet again and dot product In 2D, a homogenous linear scalar function takes the general form:
 3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri 3 3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri Overview: Differentiable functions have a local linear approimation. Near a given point, local changes are determined by
3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri 3 3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri Overview: Differentiable functions have a local linear approimation. Near a given point, local changes are determined by
Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018
 (1) Let Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 +y 2 +z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F : S
(1) Let Math 461 Homework 8 Paul Hacking November 27, 2018 S 2 = {(x, y, z) x 2 +y 2 +z 2 = 1} R 3 be the sphere with center the origin and radius 1. Let N = (0, 0, 1) S 2 be the north pole. Let F : S
1 k. cos tan? Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. 1. A sequence is defined by the recurrence relation u 2u 1, u 3.
 Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
SECTION A Time allowed: 20 minutes Marks: 20
 Mathcity.org Merging man and maths Federal Board HSSC-II Eamination Mathematics Model Question Paper Roll No: Answer Sheet No: FBISE WE WORK FOR EXCELLENCE Signature of Candidate: Signature of Invigilator:
Mathcity.org Merging man and maths Federal Board HSSC-II Eamination Mathematics Model Question Paper Roll No: Answer Sheet No: FBISE WE WORK FOR EXCELLENCE Signature of Candidate: Signature of Invigilator:
(6, 4, 0) = (3, 2, 0). Find the equation of the sphere that has the line segment from P to Q as a diameter.
 Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF 11am, Fulton Hall 425 Homework 8 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible.
 Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF am, Fulton Hall 45 Homework 8 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book:.4.,.4.0,.4.-.4.6, 4.., 4..,
Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF am, Fulton Hall 45 Homework 8 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book:.4.,.4.0,.4.-.4.6, 4.., 4..,
Math 53 Homework 7 Solutions
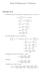 Math 5 Homework 7 Solutions Section 5.. To find the mass of the lamina, we integrate ρ(x, y over the box: m a b a a + x + y dy y + x y + y yb y b + bx + b bx + bx + b x ab + a b + ab a b + ab + ab. We
Math 5 Homework 7 Solutions Section 5.. To find the mass of the lamina, we integrate ρ(x, y over the box: m a b a a + x + y dy y + x y + y yb y b + bx + b bx + bx + b x ab + a b + ab a b + ab + ab. We
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Differentiating Functions & Expressions - Edexcel Past Exam Questions
 - Edecel Past Eam Questions. (a) Differentiate with respect to (i) sin + sec, (ii) { + ln ()}. 5-0 + 9 Given that y =, ¹, ( -) 8 (b) show that = ( -). (6) June 05 Q. f() = e ln, > 0. (a) Differentiate
- Edecel Past Eam Questions. (a) Differentiate with respect to (i) sin + sec, (ii) { + ln ()}. 5-0 + 9 Given that y =, ¹, ( -) 8 (b) show that = ( -). (6) June 05 Q. f() = e ln, > 0. (a) Differentiate
(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)
![(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2) (a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)](/thumbs/85/92620692.jpg) . f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
. f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables.
 Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables. Partial derivatives and directional derivatives. Directional derivative of functions of
Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables. Partial derivatives and directional derivatives. Directional derivative of functions of
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment School Year
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment School Year 018-019 Objective of the summer assignment: The AP Calculus summer assignment is designed to serve as a review for many of the prerequisite math skills required
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment School Year 018-019 Objective of the summer assignment: The AP Calculus summer assignment is designed to serve as a review for many of the prerequisite math skills required
Vector-Valued Functions
 Vector-Valued Functions 1 Parametric curves 8 ' 1 6 1 4 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure 1: Which curve is a graph of a function? 1 4 6 8 1 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure : A graph of a function: = f() 8 ' 1 6 4 1 1
Vector-Valued Functions 1 Parametric curves 8 ' 1 6 1 4 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure 1: Which curve is a graph of a function? 1 4 6 8 1 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure : A graph of a function: = f() 8 ' 1 6 4 1 1
PDEs in Spherical and Circular Coordinates
 Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) This lecture Laplacian in spherical & circular polar coordinates Laplace s PDE in electrostatics Schrödinger
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations part of EM, Scalar and Vector Fields module (PHY2064) This lecture Laplacian in spherical & circular polar coordinates Laplace s PDE in electrostatics Schrödinger
and y c from x 0 to x 1
 Math 44 Activity 9 (Due by end of class August 6). Find the value of c, c, that minimizes the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region between the graphs of y 4 and y c from to about the line
Math 44 Activity 9 (Due by end of class August 6). Find the value of c, c, that minimizes the volume of the solid generated by revolving the region between the graphs of y 4 and y c from to about the line
abc Mathematics Further Pure General Certificate of Education SPECIMEN UNITS AND MARK SCHEMES
 abc General Certificate of Education Mathematics Further Pure SPECIMEN UNITS AND MARK SCHEMES ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY MATHEMATICS (56) ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY PURE MATHEMATICS (566) ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY FURTHER
abc General Certificate of Education Mathematics Further Pure SPECIMEN UNITS AND MARK SCHEMES ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY MATHEMATICS (56) ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY PURE MATHEMATICS (566) ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY FURTHER
MATH 2 - PROBLEM SETS
 MATH - PROBLEM SETS Problem Set 1: 1. Simplify and write without negative eponents or radicals: a. c d p 5 y cd b. 5p 1 y. Joe is standing at the top of a 100-foot tall building. Mike eits the building
MATH - PROBLEM SETS Problem Set 1: 1. Simplify and write without negative eponents or radicals: a. c d p 5 y cd b. 5p 1 y. Joe is standing at the top of a 100-foot tall building. Mike eits the building
Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Mathematics
 Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Mathematics GROUPS Trinity Term 06 MA3: Advanced Calculus SAMPLE EXAM, Solutions DAY PLACE TIME Prof. Larry Rolen Instructions to Candidates: Attempt
Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Mathematics GROUPS Trinity Term 06 MA3: Advanced Calculus SAMPLE EXAM, Solutions DAY PLACE TIME Prof. Larry Rolen Instructions to Candidates: Attempt
Feedback D. Incorrect! Exponential functions are continuous everywhere. Look for features like square roots or denominators that could be made 0.
 Calculus Problem Solving Drill 07: Trigonometric Limits and Continuity No. of 0 Instruction: () Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully. () Do your work on a separate sheet of paper. (3)
Calculus Problem Solving Drill 07: Trigonometric Limits and Continuity No. of 0 Instruction: () Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully. () Do your work on a separate sheet of paper. (3)
Solutions to Problem Sheet for Week 11
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Solutions to Problem Sheet for Week MATH9: Differential Calculus (Advanced) Semester, 7 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math9/
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Solutions to Problem Sheet for Week MATH9: Differential Calculus (Advanced) Semester, 7 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math9/
8. THE FARY-MILNOR THEOREM
 Math 501 - Differential Geometry Herman Gluck Tuesday April 17, 2012 8. THE FARY-MILNOR THEOREM The curvature of a smooth curve in 3-space is 0 by definition, and its integral w.r.t. arc length, (s) ds,
Math 501 - Differential Geometry Herman Gluck Tuesday April 17, 2012 8. THE FARY-MILNOR THEOREM The curvature of a smooth curve in 3-space is 0 by definition, and its integral w.r.t. arc length, (s) ds,
Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals
 A. Line Integrals MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOY Department of Physics Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals The line integral of a scalar function f ( xyz),, along a path C is
A. Line Integrals MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOY Department of Physics Problem Solving 1: Line Integrals and Surface Integrals The line integral of a scalar function f ( xyz),, along a path C is
FINAL Exam REVIEW Math 1325 HCCS. Name
 FINAL Eam REVIEW Math 1325 HCCS Name ate MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1 The total cost to hand-produce large
FINAL Eam REVIEW Math 1325 HCCS Name ate MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1 The total cost to hand-produce large
Staple or bind all pages together. DO NOT dog ear pages as a method to bind.
 Math 3337 Homework Instructions: Staple or bind all pages together. DO NOT dog ear pages as a method to bind. Hand-drawn sketches should be neat, clear, of reasonable size, with axis and tick marks appropriately
Math 3337 Homework Instructions: Staple or bind all pages together. DO NOT dog ear pages as a method to bind. Hand-drawn sketches should be neat, clear, of reasonable size, with axis and tick marks appropriately
MATH 547 ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 4
 MATH 547 ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 4 ROI DOCAMPO ÁLVAREZ Chapter 0 Exercise We think of the torus T as the quotient of X = I I by the equivalence relation generated by the conditions (, s)
MATH 547 ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 4 ROI DOCAMPO ÁLVAREZ Chapter 0 Exercise We think of the torus T as the quotient of X = I I by the equivalence relation generated by the conditions (, s)
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Solution Midterm 2, Math 53, Summer (a) (10 points) Let f(x, y, z) be a differentiable function of three variables and define
 Solution Midterm, Math 5, Summer. (a) ( points) Let f(,, z) be a differentiable function of three variables and define F (s, t) = f(st, s + t, s t). Calculate the partial derivatives F s and F t in terms
Solution Midterm, Math 5, Summer. (a) ( points) Let f(,, z) be a differentiable function of three variables and define F (s, t) = f(st, s + t, s t). Calculate the partial derivatives F s and F t in terms
Franklin High School AB Calculus Prerequisite Work
 Franklin High School AB Calculus Prerequisite Work Below you will find an assignment set based on the prerequisites needed for the AB Calculus curriculum taught at Franklin High School. The problems assigned
Franklin High School AB Calculus Prerequisite Work Below you will find an assignment set based on the prerequisites needed for the AB Calculus curriculum taught at Franklin High School. The problems assigned
Math 10C - Fall Final Exam
 Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
Math 1C - Fall 217 - Final Exam Problem 1. Consider the function f(x, y) = 1 x 2 (y 1) 2. (i) Draw the level curve through the point P (1, 2). Find the gradient of f at the point P and draw the gradient
Higher. Specimen NAB Assessment
 hsn.uk.net Higher Mathematics UNIT Specimen NAB Assessment HSN0 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher
hsn.uk.net Higher Mathematics UNIT Specimen NAB Assessment HSN0 This document was produced speciall for the HSN.uk.net website, and we require that an copies or derivative works attribute the work to Higher
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2, Math 253
 SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #, Math 5. Find the equation of a sphere if one of its diameters has end points (, 0, 5) and (5, 4, 7). The length of the diameter is (5 ) + ( 4 0) + (7 5) = =, so the
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra
 Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
AP CALCULUS AB 2003 SCORING GUIDELINES
 CORING GUIDELINE Question Let R be the shaded region bounded by the graphs of y the vertical line =, as shown in the figure above. = and y = e and (b) Find the volume of the solid generated when R is revolved
CORING GUIDELINE Question Let R be the shaded region bounded by the graphs of y the vertical line =, as shown in the figure above. = and y = e and (b) Find the volume of the solid generated when R is revolved
Equations of motion in an accelerator (Lecture 7)
 Equations of motion in an accelerator (Lecture 7) January 27, 2016 130/441 Lecture outline We consider several types of magnets used in accelerators and write down the vector potential of the magnetic
Equations of motion in an accelerator (Lecture 7) January 27, 2016 130/441 Lecture outline We consider several types of magnets used in accelerators and write down the vector potential of the magnetic
