SVM optimization and Kernel methods
|
|
|
- Preston Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements SVM optimization and Kernel methods w 4 is up. Due in a week. Kaggle is up 4/13/17 1 4/13/17 2 Outline Review SVM optimization Non-linear transformations in SVM Soft-margin SVM Goal: Find margins that maximize separablility of classes Margins are defined by data points closest to the hyperplane. 4/13/17 3 4/13/17 4 1
2 Optimizing Maximize geometric (e.g. normalized) margins γ. Without misclassifying a point y # w % x # + b γ for all i And our normalizing constraint w = 1 This was horribly non-convex so we tried something else instead Substitute in the definition of functional margins γ =,- w Gets rid of the normalizing constraint Optimizing cont. Now because the functional margin can arbitrarily be scaled, we assign it to a value 1. Our maximization problem is now 1 max s. t. y # w % x # + b 1, i = 1,, N w,3 w Which is equivalent to minimizing min w % w s. t. y # w % x # + b 1, i = 1,, N w,3, Note that γ is gone from this equation. 4/13/17 5 4/13/17 6 Intuition that the problem is convex > min,,w,3? w? s. t y # w % x # + b 1, i = 1,, N Intuition that the problem is convex > min,,w,3? w? s. t y # w % x # + b 1, i = 1,, N w > w > w > w? w? w? 4/13/17 4/13/17 2
3 Lagrange formulation Minimize L w, b, α = 1 2 w? E α # (y # with respect to w and b And maximize with respect to each α # 0 M L = w E α # y # x # = 0 L b = E α #y # = 0 w % x # + b 1) 4/13/17 9 Substituting into the Lagrangian we get w = E α # y # x # and E α # y # = 0 L w, b, α = 1 2 w% w E α # (y # w % x # + b 1) L α = E α # 1 2 E E y #y P α # α P x #, x P PI> Where α # 0, i = 1,, N and α # y # = 0 4/13/17 10 New optimization requirements L α = E α # 1 2 E y #y P α # α P x #, x P #,PI> which we maximize with respect to α subject to α # 0 for i = 1,, N and α # y # = 0 Extending this idea to SVMs L α = E α # 1 2 E y #y P α # α P x #, x P #,PI> Let s replace x #, x P with z #, z P where z is higher dimension This is something we don t know how to optimize using our statistical/mathematical knowledge for this class But this is a standard form with a known solution 4/13/ /17/
4 Extending this idea to SVMs L α = E α # 1 2 E y #y P α # α P z #, z P #,PI> ow much more expensive is this? Increasing hypothesis complexity L α = α # >? #,PI> y #y P vs L α = α # >? #,PI> y #y P α # α P x #, x P α # α P z #, z P The number of parameters has not changed. α # is based on the number data points w = α # y # x # and α # y # w % x # + b 1 = 0 If z #, z P is easy to calculate, this problem isn t any harder. Inner products are cheap. So we can go to higher dimensions easily 4/17/ /17/17 14 igher dimensions: Non-linear hyperplane ere our support vectors live in Z space. In X space we have pre-images of our support vectors. Margins are maintained in Z space but to compute the margin we still only need dot products. Extending this idea to SVMs Our algorithm can be written in terms of inner products with the input features E.g. we don t need the input data (or its transformation) except for the inner product L α = E α # 1 2 E y #y P α # α P x #, x P #,PI> Let s replace x #, x P with φ(x # ), φ(x P ) Computing the inner product is a fairly cheap computation. This allows us to make much more complex models 4/13/ /17/
5 Kernel trick We can easily compute K x, z by finding φ(x) and φ z and taking the inner product. But it s easy to imagine how this can get computationally expensive There are some K x, z though where we don t actually need to compute the individual φ(x) and φ z s instead we get the inner product directly This allows us to get an SVM result in high dimensional feature space given by φ but without explicitly finding or representing φ x Effectively free higher dimensional hypotheses Generalizing the Kernel x % z + c X φ gives us some intuitions to how Kernels work c controls the relative weighting between x # (first order) terms and the x # x P (second order) terms. More broadly the kernel K x, z = x % z + c X corresponds to a feature mapping to a YZX X feature space, which includes all terms x, x?,, x X Whereas computing φ(x) takes O n X time, the kernel still takes only O n time. Don t explicitly representing feature vectors in our high d space 4/13/ /13/17 18 Kernels as a similarity measure If φ x and φ z are close together, what should K x, z be? Remember the Kernel is replacing our dot product (which measures the angle between two vectors). K x, z is some sort of (approximate) distance between x and z If φ x and φ z are close, K x, z is larger If φ x and φ z are far, K x, z is small Gaussian kernel K x, z = exp? x z 2σ? Captures similarity It s close to 1 when x and z are close And close to 0 when x and z are far apart 4/13/ /13/
6 Non-separable case Non-separable case By placing the input features in high dimensional space, Kernels We re increasing the likelihood that the data is actually separable Either because the data is already linearly separable Or can be made so by a (potentially non-linear) transformation 4/13/ /13/17 22 Non-separable case Some cases, we don t want to find a separating hyperplane It can be susceptible to outliers Sometimes we want a robust rather than accurate hypothesis Regularization in Optimal Margin Classifiers Extend optimal margin (linear SVMs) to non-linearly separable data Makes the margin less sensitive to outliers Introduce ll > regularization Like ridge regression, penalize the values for being in the margin Or penalize for being incorrectly classified. 1 min,,w,3 2 w? + C E ξ # s. t. y # w % x # + b 1 ξ #, i = 1,, n and ξ # 0 4/17/ /17/
7 Regularization and SVMs 1 min,,w,3 2 w? + C E ξ # s. t. y # w % x # + b 1 ξ #, i = 1,, n and ξ # 0 Training data points can now have a (functional) margin less than 1 If a data point has a functional margin 1 ξ # (with ξ # > 0) There s a cost in or objective fxn of Cξ # C controls the relative weighting between minimizing w? and having functional margins at least 1. Regularization As in ridge regression, we can control the penalty C In ridge we called it λ And it controlled the size of the βs compared to the ability to fit the training data Now we re trading off between Large margins (making w? small) And functional margins of at least 1 (ξ # = 0) As C goes to 0, we get the optimal margin classifier 4/17/ /17/17 26 Solving for w and b Need to construct the Lagrangian again, this time with regularization. We have two Lagrange multipliers One for the constraint y # w % x # + b 1 ξ # And another for ξ # 0 L w, b, ξ, α, r = 1 2 w% w + C E ξ # E α # y # w % x + b 1 + ξ # E r # ξ # Solving for w and b L w, b, ξ, α, r = 1 2 w% w + C E ξ # E α # y # w % x + b 1 + ξ # E r # ξ # α # and r # are Lagrange multipliers so α #, r # 0 We solve for the derivative w.r.t. w and b, set it to 0 Simplifying, we obtain max W α = E α # 1 j 2 E y #y P α # α P x #, x P #,PI> s.t. 0 α # C, i = 1,, N and α # y # = 0 4/17/ /17/
8 Solving for w and b max E α # 1 j 2 E y #y P α # α P x #, x P #,PI> s.t. 0 α # C, i = 1,, N and α # y # = 0 Note that we now have an upper bound C for α # w can be expressed in terms of α # s Support vectors Considering the values α # we could tell if something was a support vector If it was greater than 0, it was a support vector Otherwise, we knew the data point was not near the decision boundary Now though, we can have points in the margins. ow do we determine if something is a support vector? The only change from regularization is that we put an upper bound on α # 4/17/ /17/17 30 Support vectors Considering the values α # we could tell if something was a support vector α # = 0 y # w % x # + b 1 far from boundary α # = C y # w % x # + b 1 in the margin/misclassifed 0 < α # < C y # w % x # + b = 1 support vector 4/17/ /17/
9 Algorithms for solving SVMs We saw that we needed quadratic programming And Lagrange multipliers for standard SVMs ow about an algorithm for the soft-margin (e.g. non separable) SVMs? 4/17/17 33 Aside: Coordinate ascent Let s say we have some function max W(α >, α?,, α ) that j we re trying to optimize What methods have we ween to optimize such a problem? A new algorithm: Loop until convergence: { } For i = 1,, n { α # argmax j- # W(α >,, α #>, α - #, α #Z>,, α ) } 4/17/17 34 Intermediate step: Coordinate ascent Loop until convergence: { For i = 1,, n { α # argmax j- # W(α >,, α #>, α - #, α #Z>,, α ) } } old all variables except for α # fixed Reoptimize W α with respect to just parameter α # ere we re just visiting α s in order But you could imagine other selection algorithms (e.g. one that maximizes the increase for W α ) Sequential minimal optimization SMO algorithm We want to solve max W α = E α # 1 j 2 E y #y P α # α P x #, x P #,PI> s.t. 0 α # C, i = 1,, N and α # y # = 0 Let s say we have a set of α # s that satisfy our constraints What happens if we try coordinate ascent? 4/17/ /17/
10 We re stuck Because we know that α # y # = 0 We can see that α > y > = #I? α # y # Equivalently, α > = y # #I? α # y # So we can t get a better estimate for α > here Instead we ll consider two α s at a time SMO algorithm Loop until convergence { 1. Select some pair α # and α P to update next } (usually we use a heuristic that picks two that will allow the largest progress toward the global minimum) 2. Reoptimize our estimate of w (W α ) with respect to α # and α #, while holding all α (k i, j) fixed. 4/17/ /17/
Support Vector Machine (continued)
 Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
Statistical Pattern Recognition
 Statistical Pattern Recognition Support Vector Machine (SVM) Hamid R. Rabiee Hadi Asheri, Jafar Muhammadi, Nima Pourdamghani Spring 2013 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/91-92/2/ce725-1/ Agenda Introduction
Statistical Pattern Recognition Support Vector Machine (SVM) Hamid R. Rabiee Hadi Asheri, Jafar Muhammadi, Nima Pourdamghani Spring 2013 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/91-92/2/ce725-1/ Agenda Introduction
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2014 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2014 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2016 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2016 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2015 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Kernel Methods CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Fall 2015 Soleymani Outline Margin concept Hard-Margin SVM Soft-Margin SVM Dual Problems of Hard-Margin
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Reading: Ben-Hur & Weston, A User s Guide to Support Vector Machines (linked from class web page) Notation Assume a binary classification problem. Instances are represented by vector
Support Vector Machines Reading: Ben-Hur & Weston, A User s Guide to Support Vector Machines (linked from class web page) Notation Assume a binary classification problem. Instances are represented by vector
Machine Learning. Support Vector Machines. Manfred Huber
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Manfred Huber 2015 1 Support Vector Machines Both logistic regression and linear discriminant analysis learn a linear discriminant function to separate the data
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Manfred Huber 2015 1 Support Vector Machines Both logistic regression and linear discriminant analysis learn a linear discriminant function to separate the data
Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators. Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators Binary classification can be viewed as the task of separating classes in feature space: w T x + b > 0 w T x + b = 0 w T x + b < 0 Department
Support Vector Machines Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators Binary classification can be viewed as the task of separating classes in feature space: w T x + b > 0 w T x + b = 0 w T x + b < 0 Department
Support Vector Machines. Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar
 Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Introduction to Support Vector Machines
 Introduction to Support Vector Machines Shivani Agarwal Support Vector Machines (SVMs) Algorithm for learning linear classifiers Motivated by idea of maximizing margin Efficient extension to non-linear
Introduction to Support Vector Machines Shivani Agarwal Support Vector Machines (SVMs) Algorithm for learning linear classifiers Motivated by idea of maximizing margin Efficient extension to non-linear
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Support Vector Machines
 CS229 Lecture notes Andrew Ng Part V Support Vector Machines This set of notes presents the Support Vector Machine (SVM) learning algorithm. SVMs are among the best (and many believe is indeed the best)
CS229 Lecture notes Andrew Ng Part V Support Vector Machines This set of notes presents the Support Vector Machine (SVM) learning algorithm. SVMs are among the best (and many believe is indeed the best)
L5 Support Vector Classification
 L5 Support Vector Classification Support Vector Machine Problem definition Geometrical picture Optimization problem Optimization Problem Hard margin Convexity Dual problem Soft margin problem Alexander
L5 Support Vector Classification Support Vector Machine Problem definition Geometrical picture Optimization problem Optimization Problem Hard margin Convexity Dual problem Soft margin problem Alexander
Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recognition 1 / 48 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht
Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recognition 1 / 48 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht
Statistical Machine Learning from Data
 Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Support Vector Machines Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole Polytechnique
Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Support Vector Machines Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole Polytechnique
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Introduction to SVM and RVM
 Introduction to SVM and RVM Machine Learning Seminar HUS HVL UIB Yushu Li, UIB Overview Support vector machine SVM First introduced by Vapnik, et al. 1992 Several literature and wide applications Relevance
Introduction to SVM and RVM Machine Learning Seminar HUS HVL UIB Yushu Li, UIB Overview Support vector machine SVM First introduced by Vapnik, et al. 1992 Several literature and wide applications Relevance
Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter
 Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
Support Vector Machines. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Support Vector Machines CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
Support Vector Machines CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 A Linearly Separable Problem Consider the binary classification
Support Vector Machines, Kernel SVM
 Support Vector Machines, Kernel SVM Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 27, 2017 1 / 40 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 SVM
Support Vector Machines, Kernel SVM Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 27, 2017 1 / 40 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 SVM
Machine Learning. Lecture 6: Support Vector Machine. Feng Li.
 Machine Learning Lecture 6: Support Vector Machine Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2018 Warm Up 2 / 80 Warm Up (Contd.)
Machine Learning Lecture 6: Support Vector Machine Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2018 Warm Up 2 / 80 Warm Up (Contd.)
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab.
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
10/05/2016. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES. Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
CS6375: Machine Learning Gautam Kunapuli. Support Vector Machines
 Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers)
 Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Bingyu Wang, Virgil Pavlu March 30, 2015 based on notes by Andrew Ng. 1 What s SVM The original SVM algorithm was invented by Vladimir N. Vapnik 1 and the current standard incarnation
Support Vector Machines Bingyu Wang, Virgil Pavlu March 30, 2015 based on notes by Andrew Ng. 1 What s SVM The original SVM algorithm was invented by Vladimir N. Vapnik 1 and the current standard incarnation
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick
 SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
SVMs, Duality and the Kernel Trick Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University February 26 th, 2007 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 1 SVMs reminder 2005-2007 Carlos Guestrin 2 Today
Incorporating detractors into SVM classification
 Incorporating detractors into SVM classification AGH University of Science and Technology 1 2 3 4 5 (SVM) SVM - are a set of supervised learning methods used for classification and regression SVM maximal
Incorporating detractors into SVM classification AGH University of Science and Technology 1 2 3 4 5 (SVM) SVM - are a set of supervised learning methods used for classification and regression SVM maximal
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine
 CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Statistical Methods for NLP
 Statistical Methods for NLP Text Categorization, Support Vector Machines Sameer Maskey Announcement Reading Assignments Will be posted online tonight Homework 1 Assigned and available from the course website
Statistical Methods for NLP Text Categorization, Support Vector Machines Sameer Maskey Announcement Reading Assignments Will be posted online tonight Homework 1 Assigned and available from the course website
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Announcements - Homework
 Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Support Vector Machines.
 Support Vector Machines www.cs.wisc.edu/~dpage 1 Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts the margin slack variables the linear support vector machine nonlinear SVMs the kernel
Support Vector Machines www.cs.wisc.edu/~dpage 1 Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts the margin slack variables the linear support vector machine nonlinear SVMs the kernel
LINEAR CLASSIFICATION, PERCEPTRON, LOGISTIC REGRESSION, SVC, NAÏVE BAYES. Supervised Learning
 LINEAR CLASSIFICATION, PERCEPTRON, LOGISTIC REGRESSION, SVC, NAÏVE BAYES Supervised Learning Linear vs non linear classifiers In K-NN we saw an example of a non-linear classifier: the decision boundary
LINEAR CLASSIFICATION, PERCEPTRON, LOGISTIC REGRESSION, SVC, NAÏVE BAYES Supervised Learning Linear vs non linear classifiers In K-NN we saw an example of a non-linear classifier: the decision boundary
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Support Vector Machines
 Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Support Vector Machines Explained
 December 23, 2008 Support Vector Machines Explained Tristan Fletcher www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/t.fletcher/ Introduction This document has been written in an attempt to make the Support Vector Machines (SVM),
December 23, 2008 Support Vector Machines Explained Tristan Fletcher www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/t.fletcher/ Introduction This document has been written in an attempt to make the Support Vector Machines (SVM),
1. Kernel ridge regression In contrast to ordinary least squares which has a cost function. m (θ T x (i) y (i) ) 2, J(θ) = 1 2.
 CS229 Problem Set #2 Solutions 1 CS 229, Public Course Problem Set #2 Solutions: Theory Kernels, SVMs, and 1. Kernel ridge regression In contrast to ordinary least squares which has a cost function J(θ)
CS229 Problem Set #2 Solutions 1 CS 229, Public Course Problem Set #2 Solutions: Theory Kernels, SVMs, and 1. Kernel ridge regression In contrast to ordinary least squares which has a cost function J(θ)
Support Vector Machines
 EE 17/7AT: Optimization Models in Engineering Section 11/1 - April 014 Support Vector Machines Lecturer: Arturo Fernandez Scribe: Arturo Fernandez 1 Support Vector Machines Revisited 1.1 Strictly) Separable
EE 17/7AT: Optimization Models in Engineering Section 11/1 - April 014 Support Vector Machines Lecturer: Arturo Fernandez Scribe: Arturo Fernandez 1 Support Vector Machines Revisited 1.1 Strictly) Separable
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING
 CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING 5: Vector Data: Support Vector Machine Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu October 18, 2017 Homework 1 Announcements Due end of the day of this Thursday (11:59pm)
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING 5: Vector Data: Support Vector Machine Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu October 18, 2017 Homework 1 Announcements Due end of the day of this Thursday (11:59pm)
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Sridhar Mahadevan mahadeva@cs.umass.edu University of Massachusetts Sridhar Mahadevan: CMPSCI 689 p. 1/32 Margin Classifiers margin b = 0 Sridhar Mahadevan: CMPSCI 689 p.
Support Vector Machines Sridhar Mahadevan mahadeva@cs.umass.edu University of Massachusetts Sridhar Mahadevan: CMPSCI 689 p. 1/32 Margin Classifiers margin b = 0 Sridhar Mahadevan: CMPSCI 689 p.
18.9 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods
 2018 CS420 Machine Learning, Lecture 3 Hangout from Prof. Andrew Ng. http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes3.pdf Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2018 CS420 Machine Learning, Lecture 3 Hangout from Prof. Andrew Ng. http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes3.pdf Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University
COMP 875 Announcements
 Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Announcements Tentative presentation order is out Remember: Monday before the week of the presentation you must send me the final paper list (for posting
CSE546: SVMs, Dual Formula5on, and Kernels Winter 2012
 CSE546: SVMs, Dual Formula5on, and Kernels Winter 2012 Luke ZeClemoyer Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin Linear classifiers Which line is becer? w. = j w (j) x (j) Data Example i Pick the one with the
CSE546: SVMs, Dual Formula5on, and Kernels Winter 2012 Luke ZeClemoyer Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin Linear classifiers Which line is becer? w. = j w (j) x (j) Data Example i Pick the one with the
Kernel Machines. Pradeep Ravikumar Co-instructor: Manuela Veloso. Machine Learning
 Kernel Machines Pradeep Ravikumar Co-instructor: Manuela Veloso Machine Learning 10-701 SVM linearly separable case n training points (x 1,, x n ) d features x j is a d-dimensional vector Primal problem:
Kernel Machines Pradeep Ravikumar Co-instructor: Manuela Veloso Machine Learning 10-701 SVM linearly separable case n training points (x 1,, x n ) d features x j is a d-dimensional vector Primal problem:
Non-Bayesian Classifiers Part II: Linear Discriminants and Support Vector Machines
 Non-Bayesian Classifiers Part II: Linear Discriminants and Support Vector Machines Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Fall 2018 CS 551, Fall
Non-Bayesian Classifiers Part II: Linear Discriminants and Support Vector Machines Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Fall 2018 CS 551, Fall
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials/ Where Should We Draw the Line????
Support Vector Machines Some material on these is slides borrowed from Andrew Moore's excellent machine learning tutorials located at: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~awm/tutorials/ Where Should We Draw the Line????
Lecture 10: A brief introduction to Support Vector Machine
 Lecture 10: A brief introduction to Support Vector Machine Advanced Applied Multivariate Analysis STAT 2221, Fall 2013 Sungkyu Jung Department of Statistics, University of Pittsburgh Xingye Qiao Department
Lecture 10: A brief introduction to Support Vector Machine Advanced Applied Multivariate Analysis STAT 2221, Fall 2013 Sungkyu Jung Department of Statistics, University of Pittsburgh Xingye Qiao Department
Review: Support vector machines. Machine learning techniques and image analysis
 Review: Support vector machines Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization min (w,w 0 ) 1 2 w 2 subject to y i (w 0 + w T x i ) 1 0, i = 1,..., n. Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization
Review: Support vector machines Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization min (w,w 0 ) 1 2 w 2 subject to y i (w 0 + w T x i ) 1 0, i = 1,..., n. Review: Support vector machines Margin optimization
Introduction to Machine Learning
 1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
1, DATA11002 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Teemu Roos TAs: Ville Hyvönen and Janne Leppä-aho Department of Computer Science University of Helsinki (based in part on material by Patrik Hoyer
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE Mainly based on https://nlp.stanford.edu/ir-book/pdf/15svm.pdf 1 Overview SVM is a huge topic Integration of MMDS, IIR, and Andrew Moore s slides here Our foci: Geometric intuition
SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE Mainly based on https://nlp.stanford.edu/ir-book/pdf/15svm.pdf 1 Overview SVM is a huge topic Integration of MMDS, IIR, and Andrew Moore s slides here Our foci: Geometric intuition
Linear, threshold units. Linear Discriminant Functions and Support Vector Machines. Biometrics CSE 190 Lecture 11. X i : inputs W i : weights
 Linear Discriminant Functions and Support Vector Machines Linear, threshold units CSE19, Winter 11 Biometrics CSE 19 Lecture 11 1 X i : inputs W i : weights θ : threshold 3 4 5 1 6 7 Courtesy of University
Linear Discriminant Functions and Support Vector Machines Linear, threshold units CSE19, Winter 11 Biometrics CSE 19 Lecture 11 1 X i : inputs W i : weights θ : threshold 3 4 5 1 6 7 Courtesy of University
Support Vector Machine
 Support Vector Machine Kernel: Kernel is defined as a function returning the inner product between the images of the two arguments k(x 1, x 2 ) = ϕ(x 1 ), ϕ(x 2 ) k(x 1, x 2 ) = k(x 2, x 1 ) modularity-
Support Vector Machine Kernel: Kernel is defined as a function returning the inner product between the images of the two arguments k(x 1, x 2 ) = ϕ(x 1 ), ϕ(x 2 ) k(x 1, x 2 ) = k(x 2, x 1 ) modularity-
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2018 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression
ML (cont.): SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 ML (cont.): SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES CS540 Bryan R Gibson University of Wisconsin-Madison Slides adapted from those used by Prof. Jerry Zhu, CS540-1 1 / 40 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) The No-Math Version
ML (cont.): SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES CS540 Bryan R Gibson University of Wisconsin-Madison Slides adapted from those used by Prof. Jerry Zhu, CS540-1 1 / 40 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) The No-Math Version
Lecture Notes on Support Vector Machine
 Lecture Notes on Support Vector Machine Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn Shandong University, China 1 Hyperplane and Margin In a n-dimensional space, a hyper plane is defined by ω T x + b = 0 (1) where ω R n is
Lecture Notes on Support Vector Machine Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn Shandong University, China 1 Hyperplane and Margin In a n-dimensional space, a hyper plane is defined by ω T x + b = 0 (1) where ω R n is
Support'Vector'Machines. Machine(Learning(Spring(2018 March(5(2018 Kasthuri Kannan
 Support'Vector'Machines Machine(Learning(Spring(2018 March(5(2018 Kasthuri Kannan kasthuri.kannan@nyumc.org Overview Support Vector Machines for Classification Linear Discrimination Nonlinear Discrimination
Support'Vector'Machines Machine(Learning(Spring(2018 March(5(2018 Kasthuri Kannan kasthuri.kannan@nyumc.org Overview Support Vector Machines for Classification Linear Discrimination Nonlinear Discrimination
Natural Language Processing. Classification. Features. Some Definitions. Classification. Feature Vectors. Classification I. Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Learning From Data Lecture 25 The Kernel Trick
 Learning From Data Lecture 25 The Kernel Trick Learning with only inner products The Kernel M. Magdon-Ismail CSCI 400/600 recap: Large Margin is Better Controling Overfitting Non-Separable Data 0.08 random
Learning From Data Lecture 25 The Kernel Trick Learning with only inner products The Kernel M. Magdon-Ismail CSCI 400/600 recap: Large Margin is Better Controling Overfitting Non-Separable Data 0.08 random
Support Vector Machines (SVM) in bioinformatics. Day 1: Introduction to SVM
 1 Support Vector Machines (SVM) in bioinformatics Day 1: Introduction to SVM Jean-Philippe Vert Bioinformatics Center, Kyoto University, Japan Jean-Philippe.Vert@mines.org Human Genome Center, University
1 Support Vector Machines (SVM) in bioinformatics Day 1: Introduction to SVM Jean-Philippe Vert Bioinformatics Center, Kyoto University, Japan Jean-Philippe.Vert@mines.org Human Genome Center, University
Mark your answers ON THE EXAM ITSELF. If you are not sure of your answer you may wish to provide a brief explanation.
 CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
COMP 652: Machine Learning. Lecture 12. COMP Lecture 12 1 / 37
 COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
Foundation of Intelligent Systems, Part I. SVM s & Kernel Methods
 Foundation of Intelligent Systems, Part I SVM s & Kernel Methods mcuturi@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp FIS - 2013 1 Support Vector Machines The linearly-separable case FIS - 2013 2 A criterion to select a linear classifier:
Foundation of Intelligent Systems, Part I SVM s & Kernel Methods mcuturi@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp FIS - 2013 1 Support Vector Machines The linearly-separable case FIS - 2013 2 A criterion to select a linear classifier:
CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 09, Kernel Methods
 CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 09, 207 Kernel Methods Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture They may or may not cover all the material discussed
CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 09, 207 Kernel Methods Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture They may or may not cover all the material discussed
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Perceptrons and Support Vector machines
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Multi-Class Classification; Kernel Methods
 Machine Learning (CSE 446): Multi-Class Classification; Kernel Methods Sham M Kakade c 2018 University of Washington cse446-staff@cs.washington.edu 1 / 12 Announcements HW3 due date as posted. make sure
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Multi-Class Classification; Kernel Methods Sham M Kakade c 2018 University of Washington cse446-staff@cs.washington.edu 1 / 12 Announcements HW3 due date as posted. make sure
Data Mining. Linear & nonlinear classifiers. Hamid Beigy. Sharif University of Technology. Fall 1396
 Data Mining Linear & nonlinear classifiers Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Data Mining Fall 1396 1 / 31 Table of contents 1 Introduction
Data Mining Linear & nonlinear classifiers Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Data Mining Fall 1396 1 / 31 Table of contents 1 Introduction
Convex Optimization and Support Vector Machine
 Convex Optimization and Support Vector Machine Problem 0. Consider a two-class classification problem. The training data is L n = {(x 1, t 1 ),..., (x n, t n )}, where each t i { 1, 1} and x i R p. We
Convex Optimization and Support Vector Machine Problem 0. Consider a two-class classification problem. The training data is L n = {(x 1, t 1 ),..., (x n, t n )}, where each t i { 1, 1} and x i R p. We
CMU-Q Lecture 24:
 CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 24: Supervised Learning 2 Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro SUPERVISED LEARNING Hypotheses space Hypothesis function Labeled Given Errors Performance criteria Given a collection of input
CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 24: Supervised Learning 2 Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro SUPERVISED LEARNING Hypotheses space Hypothesis function Labeled Given Errors Performance criteria Given a collection of input
Linear Models for Classification
 Linear Models for Classification Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 4 Classification: Hand-written Digit Recognition CHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 24, NO. 24, APRIL 2002 x i = t i = (0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
Linear Models for Classification Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 4 Classification: Hand-written Digit Recognition CHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 24, NO. 24, APRIL 2002 x i = t i = (0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support Vector Machines. CAP 5610: Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun QI
 Support Vector Machines CAP 5610: Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun QI 1 Linear Classifier Naive Bayes Assume each attribute is drawn from Gaussian distribution with the same variance Generative model:
Support Vector Machines CAP 5610: Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun QI 1 Linear Classifier Naive Bayes Assume each attribute is drawn from Gaussian distribution with the same variance Generative model:
Outline. Basic concepts: SVM and kernels SVM primal/dual problems. Chih-Jen Lin (National Taiwan Univ.) 1 / 22
 Outline Basic concepts: SVM and kernels SVM primal/dual problems Chih-Jen Lin (National Taiwan Univ.) 1 / 22 Outline Basic concepts: SVM and kernels Basic concepts: SVM and kernels SVM primal/dual problems
Outline Basic concepts: SVM and kernels SVM primal/dual problems Chih-Jen Lin (National Taiwan Univ.) 1 / 22 Outline Basic concepts: SVM and kernels Basic concepts: SVM and kernels SVM primal/dual problems
Classifier Complexity and Support Vector Classifiers
 Classifier Complexity and Support Vector Classifiers Feature 2 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 RBF kernel 10 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 Feature 1 David M.J. Tax Pattern Recognition Laboratory Delft University of Technology D.M.J.Tax@tudelft.nl
Classifier Complexity and Support Vector Classifiers Feature 2 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 RBF kernel 10 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 Feature 1 David M.J. Tax Pattern Recognition Laboratory Delft University of Technology D.M.J.Tax@tudelft.nl
Support Vector Machines MIT Course Notes Cynthia Rudin
 Support Vector Machines MIT 5.097 Course Notes Cynthia Rudin Credit: Ng, Hastie, Tibshirani, Friedan Thanks: Şeyda Ertekin Let s start with soe intuition about argins. The argin of an exaple x i = distance
Support Vector Machines MIT 5.097 Course Notes Cynthia Rudin Credit: Ng, Hastie, Tibshirani, Friedan Thanks: Şeyda Ertekin Let s start with soe intuition about argins. The argin of an exaple x i = distance
Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers)
 Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression. 1 Linearly Separable Data: Hard Margin SVMs
 E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
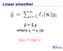 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Support Vector Machines. Maximizing the Margin
 Support Vector Machines Support vector achines (SVMs) learn a hypothesis: h(x) = b + Σ i= y i α i k(x, x i ) (x, y ),..., (x, y ) are the training exs., y i {, } b is the bias weight. α,..., α are the
Support Vector Machines Support vector achines (SVMs) learn a hypothesis: h(x) = b + Σ i= y i α i k(x, x i ) (x, y ),..., (x, y ) are the training exs., y i {, } b is the bias weight. α,..., α are the
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Support vector machines (SVMs) are one of the central concepts in all of machine learning. They are simply a combination of two ideas: linear classification via maximum (or optimal
Support Vector Machines Support vector machines (SVMs) are one of the central concepts in all of machine learning. They are simply a combination of two ideas: linear classification via maximum (or optimal
Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico
 Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico OWL RNA Bionformatics group Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Free University of Berlin 29 April, SoSe 2015 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) 1. One of
Applied Machine Learning Annalisa Marsico OWL RNA Bionformatics group Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Free University of Berlin 29 April, SoSe 2015 Support Vector Machines (SVMs) 1. One of
Max Margin-Classifier
 Max Margin-Classifier Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 7 Outline Maximum Margin Criterion Math Maximizing the Margin Non-Separable Data Kernels and Non-linear Mappings Where does the maximization
Max Margin-Classifier Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 7 Outline Maximum Margin Criterion Math Maximizing the Margin Non-Separable Data Kernels and Non-linear Mappings Where does the maximization
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Final Review. Henry Chai 12/4/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
Neural Networks. Prof. Dr. Rudolf Kruse. Computational Intelligence Group Faculty for Computer Science
 Neural Networks Prof. Dr. Rudolf Kruse Computational Intelligence Group Faculty for Computer Science kruse@iws.cs.uni-magdeburg.de Rudolf Kruse Neural Networks 1 Supervised Learning / Support Vector Machines
Neural Networks Prof. Dr. Rudolf Kruse Computational Intelligence Group Faculty for Computer Science kruse@iws.cs.uni-magdeburg.de Rudolf Kruse Neural Networks 1 Supervised Learning / Support Vector Machines
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find a plane that separates the classes in feature space. If we cannot, we get creative in two
Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find a plane that separates the classes in feature space. If we cannot, we get creative in two
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Support Vector Machines. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Support Vector Machines Kalev Kask Linear classifiers Which decision boundary is better? Both have zero training error (perfect training accuracy) But, one of them seems
Machine Learning and Data Mining Support Vector Machines Kalev Kask Linear classifiers Which decision boundary is better? Both have zero training error (perfect training accuracy) But, one of them seems
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines
 Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Lecture 10: Support Vector Machine and Large Margin Classifier
 Lecture 10: Support Vector Machine and Large Margin Classifier Applied Multivariate Analysis Math 570, Fall 2014 Xingye Qiao Department of Mathematical Sciences Binghamton University E-mail: qiao@math.binghamton.edu
Lecture 10: Support Vector Machine and Large Margin Classifier Applied Multivariate Analysis Math 570, Fall 2014 Xingye Qiao Department of Mathematical Sciences Binghamton University E-mail: qiao@math.binghamton.edu
LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Classification: Problem Statement 2 In regression, we are modeling the relationship between a continuous input variable x and a continuous target variable t. In classification, the input
LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Classification: Problem Statement 2 In regression, we are modeling the relationship between a continuous input variable x and a continuous target variable t. In classification, the input
Support Vector Machines: Maximum Margin Classifiers
 Support Vector Machines: Maximum Margin Classifiers Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition: September 16, 2008 Piotr Mirowski Based on slides by Sumit Chopra and Fu-Jie Huang 1 Outline What is behind
Support Vector Machines: Maximum Margin Classifiers Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition: September 16, 2008 Piotr Mirowski Based on slides by Sumit Chopra and Fu-Jie Huang 1 Outline What is behind
About this class. Maximizing the Margin. Maximum margin classifiers. Picture of large and small margin hyperplanes
 About this class Maximum margin classifiers SVMs: geometric derivation of the primal problem Statement of the dual problem The kernel trick SVMs as the solution to a regularization problem Maximizing the
About this class Maximum margin classifiers SVMs: geometric derivation of the primal problem Statement of the dual problem The kernel trick SVMs as the solution to a regularization problem Maximizing the
Support Vector Machine I
 Support Vector Machine I Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please use piazza. No emails. HW 0 grades are back. Re-grade request for one week. HW 1 due soon. HW
Support Vector Machine I Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please use piazza. No emails. HW 0 grades are back. Re-grade request for one week. HW 1 due soon. HW
Support Vector Machines for Classification: A Statistical Portrait
 Support Vector Machines for Classification: A Statistical Portrait Yoonkyung Lee Department of Statistics The Ohio State University May 27, 2011 The Spring Conference of Korean Statistical Society KAIST,
Support Vector Machines for Classification: A Statistical Portrait Yoonkyung Lee Department of Statistics The Ohio State University May 27, 2011 The Spring Conference of Korean Statistical Society KAIST,
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017
 COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University FEATURE EXPANSIONS FEATURE EXPANSIONS
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 10, 2/21/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University FEATURE EXPANSIONS FEATURE EXPANSIONS
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning
 SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
