Math 211/213 Calculus III-IV. Directions. Kenneth Massey. September 17, 2018
|
|
|
- Rolf Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mth 211/213 Clculus -V Kenneth Mssey Crson-Newmn University September 17, 2018 C-N Mth Mssey, 1 / 1 Directions You re t the origin nd giving directions to the point (4, 3). 1. n Mnhttn: go est 4 blocks, then north 3 blocks. 2. Supermn: ngle nd distnce C-N Mth Mssey, 2 / 1 Converting between (x, y) C nd (θ, r) P. r 2 = x 2 + y 2 x = r cos θ y = r sin θ tn θ = y x C-N Mth Mssey, 3 / 1
2 Alises Consider the point ( π 6, 8) P 1. Crtesin coordintes (unique) 2. List some lises in polr coordintes. 3. The set of ll lises is ( π 6 + kπ, ( 1)k 8 ) P, k Z C-N Mth Mssey, 4 / 1 Conversion When converting to polr, mke sure the qudrnts mtch. 1. ( π 4, 6) P 2. (2, 1) C 3. ( 1, 1) C 4. ( π 2, 1) P 5. ( 5π 6, 3) P 6. ( 3, 1) C C-N Mth Mssey, 5 / 1 Polr Grphs The grph of n eqution/inequlity is the set of points tht stisfy it. (Geogebr or Desmos) 1. r = 2 2. θ = 2 3. r < r 2 π 5. 6 θ π 3 6. r = θ 7. r = 1 θ, θ [1, 6π] 8. r = 2 sin(θ) 9. r = sin(2θ) 10. r = 1 sin θ+2 cos θ (convert to Crt.) 11. r 2 sin θ cos θ = 1 (convert to Crt.) 12. (x 2) 2 + y 2 = 4 (convert to polr) C-N Mth Mssey, 6 / 1
3 Nme tht Shpe Substitute nd complete the squre to identify the grph of r = cos θ + b sin θ. r r 2. = (x /r) + b(y/r) = x + by C-N Mth Mssey, 7 / 1 Tngents By the chin rule, dy dy dx = dθ. dx dθ Given point (x 0, y 0 ), nd slope m = dy dx, θ the tngent line is y = y 0 + m(x x 0 ) horizontl tngent = dy dθ = 0 (my need WA to solve) verticl tngent = dx dθ = 0 C-N Mth Mssey, 8 / 1 Crdioid The grph of r = 1 sin(θ) is [crdioid]. 1. Plot points nd sketch. 2. Corresponding prmetric equtions: x = (1 sin(t)) cos(t) y = (1 sin(t)) sin(t) 3. Find the tngent line when θ = π Find ll verticl or horizontl tngents. C-N Mth Mssey, 9 / 1
4 Lineriztion Consider polr function r(θ). Suppose r(1) = 8 nd dr θ=1 = Find dx 2. Find eqn tngent line where θ = Estimte the point (x (1.05), y(1.05)). r dr dθ θ dθ, dy dθ dθ, nd dy dx. C-N Mth Mssey, 10 / 1 Prbol y = x 2 for x [0, 2] just sttic pth x indep., y dep. x = t, y = t 2 for t [0, 2] dynmic motion long pth t indep., both x nd y dep. mke it go bckwrds, nd tke 5 seconds (2.4t, (2.4t) 2 ) mke it strt t (0, 0), nd oscillte bck-nd-forth forever C-N Mth Mssey, 11 / 1 Crdiod r = 1 cos(θ) for θ [0, 2π] just sttic pth nchored to origin x = (1 sin(t)) cos(t) y = (1 sin(t)) sin(t) dynmic motion, esier to modify move cusp to (3, 4), nd t [0, 1] no longer function r(θ) (RFOT) x (t) = (1 sin(2πt)) cos(2πt) + 3 y(t) = (1 sin(2πt)) cos(2πt) + 4 C-N Mth Mssey, 12 / 1
5 t D is the independent prmeter in the domin D (think time or thet) x (t ) gives dependent x s function of t y(t ) gives dependent y s function of t s coordintes (x (t ), y(t )) x (t ) or vector y(t ) generlizes y(x ) nd r (θ), nd to higher dimensionl spce C-N Mth Mssey, 13 / 1 Unit Circle Describe the unit circle 1. implicitly x 2 + y 2 = 1 2. two functions y = ± 1 x 2 3. polr r = 1 4. prmetriclly [x = cos(t ); y = sin(t )] independent vrible t [0, 2π] initil/terminl point (0, 1) counter-clockwise ngulr velocity ω = 1 rdin/sec. How would you chnge rdius? center? C-N Mth Mssey, 14 / 1 Vritions 1. Experiment with softwre to control rdius center ω period 2π, frequency 2π, speed ωr ω strting position clockwise / counter-clockwise 2. ellipse 3. spirl x h 2 C-N Mth Mssey, 15 / 1 + y k b 2 =1
6 Prmetric Grphs Any function y = f (x ) cn be prmeterized by x = t, y = f (t). f x = cos(t), y = sin 2 (t), write y s function of x nd stte the domin. GeoGebr: x = sin(2t), y = cos(t) for 1± t [0, 2π]. y = ± 1 x 2 2 Mke tble of points to sketch by hnd. e.g. (cos(3t), sin(t)) C-N Mth Mssey, 16 / 1 Chnging Forms prmetric x = t + 1, y = t eliminte prmeter solve for t, then substitute function y = x 2 1 implicit x 2 y 2 = 1 prmetric x = t 2 + 1, y = t or x = t, y = t 2 1 or x = sec(t), y = tn(t) C-N Mth Mssey, 17 / 1 Exmples Describe the pth s function y = f (x ), nd stte the domin. [ ] [ ] t t for t 2 t t [ ] [ ] t + 1 cos(t 2. t ) sin(t 2 ) C-N Mth Mssey, 18 / 1
7 Polr to Prmetric Exmple: r = θ, θ [0, ) Often r is written s function of θ. Corresponding prmetric equtions: x (θ) = r(θ) cos θ y(θ) = r(θ) sin θ Sketch by plotting points. symmetric bout the x -xis if r(θ) is even symmetric bout the y-xis if r(θ) is odd C-N Mth Mssey, 19 / 1 Lines 1. Prmeterize y = 3 + 2(x 1) x = t, y = 3 + 2(t 1) x = t + 1, y = 3 + 2t x = t 2 + 1, y = 3 + 2t 2 x = cos(t) + 1, y = cos(t) if y = t, wht is x? 2. The line segment (x 0, y 0 ) (x 1, y 1 ) cn be prmeterized for t [0, 1] by x (t) = x 0 + (x 1 x 0 )t y(t) = y 0 + (y 1 y 0 )t C-N Mth Mssey, 20 / 1 Cycloid [Pth] of point on wheel with rdius r feet, rolling horizontlly t h feet per second. center (ht, r) frequency h 2πr 2πr ; period h sec. ngulr velocity ω = h r rdins per sec. ngle θ = ωt = ht/r point reltive to center ( r sin(θ), r cos(θ)) prmetric equtions x (t) = ht r sin(ht/r) y(t) = r r cos(ht/r) C-N Mth Mssey, 21 / 1
8 Prmetric Clculus llustrte with x (t) = cos(t), y(t) = sin(2t). nottion ẋ = dx chin rule dy d 2 y dx 2 = d dx ( dy dx = dy dx dx ) = d ( dy dx ) dx, so dy dx = dy dx re A = x 1 x 0 ydx = t 1 t 0 y dx C-N Mth Mssey, 22 / 1 Length of Curves Segment: distnce over time is Tking limits, define speed s(t) = (dx rc length L = Specil cses: y(x ), L = r(θ), L = b b C-N Mth Mssey, 23 / 1 t1 ) ( ) dy t 0 s(t) 1 + (dy/dx )2 dx r 2 + (dr/dθ) 2 dθ ( x )2 + ( y) 2 t Are Enclosed by Curves Tke cre for ± re, intersections, overlp. b For simple closed curve: A = ydx 1 Polr with boundry rys: A = b 2 r 2 dθ (integrte circulr sectors with re θ 2 r 2 ) e.g. between x -xis nd r = θ. Show tht re works out to π3 6 both wys. C-N Mth Mssey, 24 / 1
9 Exmples 1. perimeter of region bdb y = 1 x 2, y = 0 2. perimeter of r = 5 sin(3θ) 3. x = t 2, y = t 3 4t, t [0, 2] Use the speed (squred) function to find fstest, slowest. Find pth length nd re between curve nd x -xis. 4. show tht circumference of unit circle is 2π 5. re of ellipse is πb 6. [x = e t cos(t), y = e t sin(t)], t [0, T ] find speed, rc length s functions of T 7. cycloid rc length is 8r, enclosing re 3πr 2 (indep. of h) C-N Mth Mssey, 25 / 1 Fishing t [0, 10] x = 4t 2 40t y = t 3 15t t 1. tble/plot points t = 0, 1, 2, 5, 8, 9, find dx, dy, dy dx, nd d 2 y dx 2 3. tngent line nd concvity where t = 2 4. where is tngent either horiz or verticl? 5. where does tngent hve slope 1? 6. enclosed re 7. speed when t = 2 8. totl rc length C-N Mth Mssey, 26 / 1 Polr Are/Length C-N Mth Mssey, 27 / 1
10 Length Theorem 1 Arc length of the curve r = f (θ), θ b b ( ) 2 dr L = r 2 + dθ dθ llustrte with picture, or derive vi prmetric eqns. Verify re nd circumference of circle. Perimeter of crdioid r = 1 sin θ. C-N Mth Mssey, 28 / 1 Are Theorem 2 The re bounded by r = f (θ), θ =, θ = b b 1 A = 2 r 2 dθ llustrte with picture. Find re of crdioid r = 1 sin θ. C-N Mth Mssey, 29 / 1 Crft Your Own 1. Design prmetric equtions to produce this horseshoe pth for t [0, 10]. (sketch x nd y s functions of t) 2. Let R be region below curve nd bove x -xis. Find the perimeter nd re of R. (note +/ re just works!) 3. Tn. line thru (0, 12) with negtive slope. C-N Mth Mssey, 30 / 1
11 For Everything Else Find the re of intersection of the two circles: r = 1 nd r = 2 cos θ. ( ) π π (2 cos θ)2 dθ [WA] π 3 π 3 1 π π 2 (2 cos θ)2 1 2 (1)2 dθ [WA] 3 Wht bout the re of the circles union? C-N Mth Mssey, 31 / 1
k ) and directrix x = h p is A focal chord is a line segment which passes through the focus of a parabola and has endpoints on the parabola.
 Stndrd Eqution of Prol with vertex ( h, k ) nd directrix y = k p is ( x h) p ( y k ) = 4. Verticl xis of symmetry Stndrd Eqution of Prol with vertex ( h, k ) nd directrix x = h p is ( y k ) p( x h) = 4.
Stndrd Eqution of Prol with vertex ( h, k ) nd directrix y = k p is ( x h) p ( y k ) = 4. Verticl xis of symmetry Stndrd Eqution of Prol with vertex ( h, k ) nd directrix x = h p is ( y k ) p( x h) = 4.
Math 0230 Calculus 2 Lectures
 Mth Clculus Lectures Chpter 9 Prmetric Equtions nd Polr Coordintes Numertion of sections corresponds to the text Jmes Stewrt, Essentil Clculus, Erly Trnscendentls, Second edition Section 91 Prmetric Curves
Mth Clculus Lectures Chpter 9 Prmetric Equtions nd Polr Coordintes Numertion of sections corresponds to the text Jmes Stewrt, Essentil Clculus, Erly Trnscendentls, Second edition Section 91 Prmetric Curves
ES.182A Topic 32 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 ES.8A Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Polr coordintes nd double integrls 3. Polr Coordintes (, ) = (r cos(θ), r sin(θ)) r θ Stndrd,, r, θ tringle Polr coordintes re just stndrd trigonometric reltions. In
ES.8A Topic 3 Notes Jerem Orloff 3 Polr coordintes nd double integrls 3. Polr Coordintes (, ) = (r cos(θ), r sin(θ)) r θ Stndrd,, r, θ tringle Polr coordintes re just stndrd trigonometric reltions. In
Space Curves. Recall the parametric equations of a curve in xy-plane and compare them with parametric equations of a curve in space.
 Clculus 3 Li Vs Spce Curves Recll the prmetric equtions of curve in xy-plne nd compre them with prmetric equtions of curve in spce. Prmetric curve in plne x = x(t) y = y(t) Prmetric curve in spce x = x(t)
Clculus 3 Li Vs Spce Curves Recll the prmetric equtions of curve in xy-plne nd compre them with prmetric equtions of curve in spce. Prmetric curve in plne x = x(t) y = y(t) Prmetric curve in spce x = x(t)
Geometric and Mechanical Applications of Integrals
 5 Geometric nd Mechnicl Applictions of Integrls 5.1 Computing Are 5.1.1 Using Crtesin Coordintes Suppose curve is given by n eqution y = f(x), x b, where f : [, b] R is continuous function such tht f(x)
5 Geometric nd Mechnicl Applictions of Integrls 5.1 Computing Are 5.1.1 Using Crtesin Coordintes Suppose curve is given by n eqution y = f(x), x b, where f : [, b] R is continuous function such tht f(x)
Mathematics of Motion II Projectiles
 Chmp+ Fll 2001 Dn Stump 1 Mthemtics of Motion II Projectiles Tble of vribles t time v velocity, v 0 initil velocity ccelertion D distnce x position coordinte, x 0 initil position x horizontl coordinte
Chmp+ Fll 2001 Dn Stump 1 Mthemtics of Motion II Projectiles Tble of vribles t time v velocity, v 0 initil velocity ccelertion D distnce x position coordinte, x 0 initil position x horizontl coordinte
US01CMTH02 UNIT Curvature
 Stu mteril of BSc(Semester - I) US1CMTH (Rdius of Curvture nd Rectifiction) Prepred by Nilesh Y Ptel Hed,Mthemtics Deprtment,VPnd RPTPScience College US1CMTH UNIT- 1 Curvture Let f : I R be sufficiently
Stu mteril of BSc(Semester - I) US1CMTH (Rdius of Curvture nd Rectifiction) Prepred by Nilesh Y Ptel Hed,Mthemtics Deprtment,VPnd RPTPScience College US1CMTH UNIT- 1 Curvture Let f : I R be sufficiently
(6.5) Length and area in polar coordinates
 86 Chpter 6 SLICING TECHNIQUES FURTHER APPLICATIONS Totl mss 6 x ρ(x)dx + x 6 x dx + 9 kg dx + 6 x dx oment bout origin 6 xρ(x)dx x x dx + x + x + ln x ( ) + ln 6 kg m x dx + 6 6 x x dx Centre of mss +
86 Chpter 6 SLICING TECHNIQUES FURTHER APPLICATIONS Totl mss 6 x ρ(x)dx + x 6 x dx + 9 kg dx + 6 x dx oment bout origin 6 xρ(x)dx x x dx + x + x + ln x ( ) + ln 6 kg m x dx + 6 6 x x dx Centre of mss +
Math 231E, Lecture 33. Parametric Calculus
 Mth 31E, Lecture 33. Prmetric Clculus 1 Derivtives 1.1 First derivtive Now, let us sy tht we wnt the slope t point on prmetric curve. Recll the chin rule: which exists s long s /. = / / Exmple 1.1. Reconsider
Mth 31E, Lecture 33. Prmetric Clculus 1 Derivtives 1.1 First derivtive Now, let us sy tht we wnt the slope t point on prmetric curve. Recll the chin rule: which exists s long s /. = / / Exmple 1.1. Reconsider
ES 111 Mathematical Methods in the Earth Sciences Lecture Outline 1 - Thurs 28th Sept 17 Review of trigonometry and basic calculus
 ES 111 Mthemticl Methods in the Erth Sciences Lecture Outline 1 - Thurs 28th Sept 17 Review of trigonometry nd bsic clculus Trigonometry When is it useful? Everywhere! Anything involving coordinte systems
ES 111 Mthemticl Methods in the Erth Sciences Lecture Outline 1 - Thurs 28th Sept 17 Review of trigonometry nd bsic clculus Trigonometry When is it useful? Everywhere! Anything involving coordinte systems
AP Calculus Multiple Choice: BC Edition Solutions
 AP Clculus Multiple Choice: BC Edition Solutions J. Slon Mrch 8, 04 ) 0 dx ( x) is A) B) C) D) E) Divergent This function inside the integrl hs verticl symptotes t x =, nd the integrl bounds contin this
AP Clculus Multiple Choice: BC Edition Solutions J. Slon Mrch 8, 04 ) 0 dx ( x) is A) B) C) D) E) Divergent This function inside the integrl hs verticl symptotes t x =, nd the integrl bounds contin this
Loudoun Valley High School Calculus Summertime Fun Packet
 Loudoun Vlley High School Clculus Summertime Fun Pcket We HIGHLY recommend tht you go through this pcket nd mke sure tht you know how to do everything in it. Prctice the problems tht you do NOT remember!
Loudoun Vlley High School Clculus Summertime Fun Pcket We HIGHLY recommend tht you go through this pcket nd mke sure tht you know how to do everything in it. Prctice the problems tht you do NOT remember!
. Double-angle formulas. Your answer should involve trig functions of θ, and not of 2θ. cos(2θ) = sin(2θ) =.
 Review of some needed Trig Identities for Integrtion Your nswers should be n ngle in RADIANS rccos( 1 2 ) = rccos( - 1 2 ) = rcsin( 1 2 ) = rcsin( - 1 2 ) = Cn you do similr problems? Review of Bsic Concepts
Review of some needed Trig Identities for Integrtion Your nswers should be n ngle in RADIANS rccos( 1 2 ) = rccos( - 1 2 ) = rcsin( 1 2 ) = rcsin( - 1 2 ) = Cn you do similr problems? Review of Bsic Concepts
. Double-angle formulas. Your answer should involve trig functions of θ, and not of 2θ. sin 2 (θ) =
 Review of some needed Trig. Identities for Integrtion. Your nswers should be n ngle in RADIANS. rccos( 1 ) = π rccos( - 1 ) = 2π 2 3 2 3 rcsin( 1 ) = π rcsin( - 1 ) = -π 2 6 2 6 Cn you do similr problems?
Review of some needed Trig. Identities for Integrtion. Your nswers should be n ngle in RADIANS. rccos( 1 ) = π rccos( - 1 ) = 2π 2 3 2 3 rcsin( 1 ) = π rcsin( - 1 ) = -π 2 6 2 6 Cn you do similr problems?
Exploring parametric representation with the TI-84 Plus CE graphing calculator
 Exploring prmetric representtion with the TI-84 Plus CE grphing clcultor Richrd Prr Executive Director Rice University School Mthemtics Project rprr@rice.edu Alice Fisher Director of Director of Technology
Exploring prmetric representtion with the TI-84 Plus CE grphing clcultor Richrd Prr Executive Director Rice University School Mthemtics Project rprr@rice.edu Alice Fisher Director of Director of Technology
Math 1102: Calculus I (Math/Sci majors) MWF 3pm, Fulton Hall 230 Homework 2 solutions
 Mth 1102: Clculus I (Mth/Sci mjors) MWF 3pm, Fulton Hll 230 Homework 2 solutions Plese write netly, nd show ll work. Cution: An nswer with no work is wrong! Do the following problems from Chpter III: 6,
Mth 1102: Clculus I (Mth/Sci mjors) MWF 3pm, Fulton Hll 230 Homework 2 solutions Plese write netly, nd show ll work. Cution: An nswer with no work is wrong! Do the following problems from Chpter III: 6,
Review: Velocity: v( t) r '( t) speed = v( t) Initial speed v, initial height h, launching angle : 1 Projectile motion: r( ) j v r
 13.3 Arc Length Review: curve in spce: r t f t i g t j h t k Tngent vector: r '( t ) f ' t i g ' t j h' t k Tngent line t t t : s r( t ) sr '( t ) Velocity: v( t) r '( t) speed = v( t) Accelertion ( t)
13.3 Arc Length Review: curve in spce: r t f t i g t j h t k Tngent vector: r '( t ) f ' t i g ' t j h' t k Tngent line t t t : s r( t ) sr '( t ) Velocity: v( t) r '( t) speed = v( t) Accelertion ( t)
CHAPTER 10 PARAMETRIC, VECTOR, AND POLAR FUNCTIONS. dy dx
 CHAPTER 0 PARAMETRIC, VECTOR, AND POLAR FUNCTIONS 0.. PARAMETRIC FUNCTIONS A) Recll tht for prmetric equtions,. B) If the equtions x f(t), nd y g(t) define y s twice-differentile function of x, then t
CHAPTER 0 PARAMETRIC, VECTOR, AND POLAR FUNCTIONS 0.. PARAMETRIC FUNCTIONS A) Recll tht for prmetric equtions,. B) If the equtions x f(t), nd y g(t) define y s twice-differentile function of x, then t
Mathematics. Area under Curve.
 Mthemtics Are under Curve www.testprepkrt.com Tle of Content 1. Introduction.. Procedure of Curve Sketching. 3. Sketching of Some common Curves. 4. Are of Bounded Regions. 5. Sign convention for finding
Mthemtics Are under Curve www.testprepkrt.com Tle of Content 1. Introduction.. Procedure of Curve Sketching. 3. Sketching of Some common Curves. 4. Are of Bounded Regions. 5. Sign convention for finding
Integration Techniques
 Integrtion Techniques. Integrtion of Trigonometric Functions Exmple. Evlute cos x. Recll tht cos x = cos x. Hence, cos x Exmple. Evlute = ( + cos x) = (x + sin x) + C = x + 4 sin x + C. cos 3 x. Let u
Integrtion Techniques. Integrtion of Trigonometric Functions Exmple. Evlute cos x. Recll tht cos x = cos x. Hence, cos x Exmple. Evlute = ( + cos x) = (x + sin x) + C = x + 4 sin x + C. cos 3 x. Let u
In-Class Problems 2 and 3: Projectile Motion Solutions. In-Class Problem 2: Throwing a Stone Down a Hill
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Deprtment of Physics Physics 8T Fll Term 4 In-Clss Problems nd 3: Projectile Motion Solutions We would like ech group to pply the problem solving strtegy with the
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Deprtment of Physics Physics 8T Fll Term 4 In-Clss Problems nd 3: Projectile Motion Solutions We would like ech group to pply the problem solving strtegy with the
dt. However, we might also be curious about dy
 Section 0. The Clculus of Prmetric Curves Even though curve defined prmetricly my not be function, we cn still consider concepts such s rtes of chnge. However, the concepts will need specil tretment. For
Section 0. The Clculus of Prmetric Curves Even though curve defined prmetricly my not be function, we cn still consider concepts such s rtes of chnge. However, the concepts will need specil tretment. For
Disclaimer: This Final Exam Study Guide is meant to help you start studying. It is not necessarily a complete list of everything you need to know.
 Disclimer: This is ment to help you strt studying. It is not necessrily complete list of everything you need to know. The MTH 33 finl exm minly consists of stndrd response questions where students must
Disclimer: This is ment to help you strt studying. It is not necessrily complete list of everything you need to know. The MTH 33 finl exm minly consists of stndrd response questions where students must
University of. d Class. 3 st Lecture. 2 nd
 University of Technology Electromechnicl Deprtment Energy Brnch Advnced Mthemtics Line Integrl nd d lss st Lecture nd Advnce Mthemtic Line Integrl lss Electromechnicl Engineer y Dr.Eng.Muhmmd.A.R.Yss Dr.Eng
University of Technology Electromechnicl Deprtment Energy Brnch Advnced Mthemtics Line Integrl nd d lss st Lecture nd Advnce Mthemtic Line Integrl lss Electromechnicl Engineer y Dr.Eng.Muhmmd.A.R.Yss Dr.Eng
r = cos θ + 1. dt ) dt. (1)
 MTHE 7 Proble Set 5 Solutions (A Crdioid). Let C be the closed curve in R whose polr coordintes (r, θ) stisfy () Sketch the curve C. r = cos θ +. (b) Find pretriztion t (r(t), θ(t)), t [, b], of C in polr
MTHE 7 Proble Set 5 Solutions (A Crdioid). Let C be the closed curve in R whose polr coordintes (r, θ) stisfy () Sketch the curve C. r = cos θ +. (b) Find pretriztion t (r(t), θ(t)), t [, b], of C in polr
I. Equations of a Circle a. At the origin center= r= b. Standard from: center= r=
 11.: Circle & Ellipse I cn Write the eqution of circle given specific informtion Grph circle in coordinte plne. Grph n ellipse nd determine ll criticl informtion. Write the eqution of n ellipse from rel
11.: Circle & Ellipse I cn Write the eqution of circle given specific informtion Grph circle in coordinte plne. Grph n ellipse nd determine ll criticl informtion. Write the eqution of n ellipse from rel
Properties of Integrals, Indefinite Integrals. Goals: Definition of the Definite Integral Integral Calculations using Antiderivatives
 Block #6: Properties of Integrls, Indefinite Integrls Gols: Definition of the Definite Integrl Integrl Clcultions using Antiderivtives Properties of Integrls The Indefinite Integrl 1 Riemnn Sums - 1 Riemnn
Block #6: Properties of Integrls, Indefinite Integrls Gols: Definition of the Definite Integrl Integrl Clcultions using Antiderivtives Properties of Integrls The Indefinite Integrl 1 Riemnn Sums - 1 Riemnn
APPLICATIONS OF THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL
 APPLICATIONS OF THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL. Volume: Slicing, disks nd wshers.. Volumes by Slicing. Suppose solid object hs boundries extending from x =, to x = b, nd tht its cross-section in plne pssing through
APPLICATIONS OF THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL. Volume: Slicing, disks nd wshers.. Volumes by Slicing. Suppose solid object hs boundries extending from x =, to x = b, nd tht its cross-section in plne pssing through
MORE FUNCTION GRAPHING; OPTIMIZATION. (Last edited October 28, 2013 at 11:09pm.)
 MORE FUNCTION GRAPHING; OPTIMIZATION FRI, OCT 25, 203 (Lst edited October 28, 203 t :09pm.) Exercise. Let n be n rbitrry positive integer. Give n exmple of function with exctly n verticl symptotes. Give
MORE FUNCTION GRAPHING; OPTIMIZATION FRI, OCT 25, 203 (Lst edited October 28, 203 t :09pm.) Exercise. Let n be n rbitrry positive integer. Give n exmple of function with exctly n verticl symptotes. Give
A. Limits - L Hopital s Rule ( ) How to find it: Try and find limits by traditional methods (plugging in). If you get 0 0 or!!, apply C.! 1 6 C.
 A. Limits - L Hopitl s Rule Wht you re finding: L Hopitl s Rule is used to find limits of the form f ( x) lim where lim f x x! c g x ( ) = or lim f ( x) = limg( x) = ". ( ) x! c limg( x) = 0 x! c x! c
A. Limits - L Hopitl s Rule Wht you re finding: L Hopitl s Rule is used to find limits of the form f ( x) lim where lim f x x! c g x ( ) = or lim f ( x) = limg( x) = ". ( ) x! c limg( x) = 0 x! c x! c
Definition of Continuity: The function f(x) is continuous at x = a if f(a) exists and lim
 Mth 9 Course Summry/Study Guide Fll, 2005 [1] Limits Definition of Limit: We sy tht L is the limit of f(x) s x pproches if f(x) gets closer nd closer to L s x gets closer nd closer to. We write lim f(x)
Mth 9 Course Summry/Study Guide Fll, 2005 [1] Limits Definition of Limit: We sy tht L is the limit of f(x) s x pproches if f(x) gets closer nd closer to L s x gets closer nd closer to. We write lim f(x)
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 6 (First moments of an arc) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.6 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 6 (First moments of n rc) by A.J.Hobson 13.6.1 Introduction 13.6. First moment of n rc bout the y-xis 13.6.3 First moment of n rc bout the x-xis
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.6 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 6 (First moments of n rc) by A.J.Hobson 13.6.1 Introduction 13.6. First moment of n rc bout the y-xis 13.6.3 First moment of n rc bout the x-xis
A. Limits - L Hopital s Rule. x c. x c. f x. g x. x c 0 6 = 1 6. D. -1 E. nonexistent. ln ( x 1 ) 1 x 2 1. ( x 2 1) 2. 2x x 1.
 A. Limits - L Hopitl s Rule Wht you re finding: L Hopitl s Rule is used to find limits of the form f ( ) lim where lim f or lim f limg. c g = c limg( ) = c = c = c How to find it: Try nd find limits by
A. Limits - L Hopitl s Rule Wht you re finding: L Hopitl s Rule is used to find limits of the form f ( ) lim where lim f or lim f limg. c g = c limg( ) = c = c = c How to find it: Try nd find limits by
P 1 (x 1, y 1 ) is given by,.
 MA00 Clculus nd Bsic Liner Alger I Chpter Coordinte Geometr nd Conic Sections Review In the rectngulr/crtesin coordintes sstem, we descrie the loction of points using coordintes. P (, ) P(, ) O The distnce
MA00 Clculus nd Bsic Liner Alger I Chpter Coordinte Geometr nd Conic Sections Review In the rectngulr/crtesin coordintes sstem, we descrie the loction of points using coordintes. P (, ) P(, ) O The distnce
r 0 ( ) cos( ) r( )sin( ). 1. Last time, we calculated that for the cardioid r( ) =1+sin( ),
 Wrm up Recll from lst time, given polr curve r = r( ),, dx dy dx = dy d = (r( )sin( )) d (r( ) cos( )) = r0 ( )sin( )+r( ) cos( ) r 0 ( ) cos( ) r( )sin( ).. Lst time, we clculted tht for crdioid r( )
Wrm up Recll from lst time, given polr curve r = r( ),, dx dy dx = dy d = (r( )sin( )) d (r( ) cos( )) = r0 ( )sin( )+r( ) cos( ) r 0 ( ) cos( ) r( )sin( ).. Lst time, we clculted tht for crdioid r( )
( x )( x) dx. Year 12 Extension 2 Term Question 1 (15 Marks) (a) Sketch the curve (x + 1)(y 2) = 1 2
 Yer Etension Term 7 Question (5 Mrks) Mrks () Sketch the curve ( + )(y ) (b) Write the function in prt () in the form y f(). Hence, or otherwise, sketch the curve (i) y f( ) (ii) y f () (c) Evlute (i)
Yer Etension Term 7 Question (5 Mrks) Mrks () Sketch the curve ( + )(y ) (b) Write the function in prt () in the form y f(). Hence, or otherwise, sketch the curve (i) y f( ) (ii) y f () (c) Evlute (i)
Chapter 2. Constraints, Lagrange s equations
 Chpter Constrints, Lgrnge s equtions Section Constrints The position of the prticle or system follows certin rules due to constrints: Holonomic constrint: f (r. r,... r n, t) = 0 Constrints tht re not
Chpter Constrints, Lgrnge s equtions Section Constrints The position of the prticle or system follows certin rules due to constrints: Holonomic constrint: f (r. r,... r n, t) = 0 Constrints tht re not
( dg. ) 2 dt. + dt. dt j + dh. + dt. r(t) dt. Comparing this equation with the one listed above for the length of see that
 Arc Length of Curves in Three Dimensionl Spce If the vector function r(t) f(t) i + g(t) j + h(t) k trces out the curve C s t vries, we cn mesure distnces long C using formul nerly identicl to one tht we
Arc Length of Curves in Three Dimensionl Spce If the vector function r(t) f(t) i + g(t) j + h(t) k trces out the curve C s t vries, we cn mesure distnces long C using formul nerly identicl to one tht we
Year 12 Mathematics Extension 2 HSC Trial Examination 2014
 Yer Mthemtics Etension HSC Tril Emintion 04 Generl Instructions. Reding time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using blck or blue pen. Blck pen is preferred. Bord-pproved clcultors my be used A tble of
Yer Mthemtics Etension HSC Tril Emintion 04 Generl Instructions. Reding time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using blck or blue pen. Blck pen is preferred. Bord-pproved clcultors my be used A tble of
Trignometric Substitution
 Trignometric Substitution Trigonometric substitution refers simply to substitutions of the form x sinu or x tnu or x secu It is generlly used in conjunction with the trignometric identities to sin θ+cos
Trignometric Substitution Trigonometric substitution refers simply to substitutions of the form x sinu or x tnu or x secu It is generlly used in conjunction with the trignometric identities to sin θ+cos
Trigonometric Functions
 Exercise. Degrees nd Rdins Chpter Trigonometric Functions EXERCISE. Degrees nd Rdins 4. Since 45 corresponds to rdin mesure of π/4 rd, we hve: 90 = 45 corresponds to π/4 or π/ rd. 5 = 7 45 corresponds
Exercise. Degrees nd Rdins Chpter Trigonometric Functions EXERCISE. Degrees nd Rdins 4. Since 45 corresponds to rdin mesure of π/4 rd, we hve: 90 = 45 corresponds to π/4 or π/ rd. 5 = 7 45 corresponds
We divide the interval [a, b] into subintervals of equal length x = b a n
![We divide the interval [a, b] into subintervals of equal length x = b a n We divide the interval [a, b] into subintervals of equal length x = b a n](/thumbs/80/80533932.jpg) Arc Length Given curve C defined by function f(x), we wnt to find the length of this curve between nd b. We do this by using process similr to wht we did in defining the Riemnn Sum of definite integrl:
Arc Length Given curve C defined by function f(x), we wnt to find the length of this curve between nd b. We do this by using process similr to wht we did in defining the Riemnn Sum of definite integrl:
Higher Checklist (Unit 3) Higher Checklist (Unit 3) Vectors
 Vectors Skill Achieved? Know tht sclr is quntity tht hs only size (no direction) Identify rel-life exmples of sclrs such s, temperture, mss, distnce, time, speed, energy nd electric chrge Know tht vector
Vectors Skill Achieved? Know tht sclr is quntity tht hs only size (no direction) Identify rel-life exmples of sclrs such s, temperture, mss, distnce, time, speed, energy nd electric chrge Know tht vector
5.2 Volumes: Disks and Washers
 4 pplictions of definite integrls 5. Volumes: Disks nd Wshers In the previous section, we computed volumes of solids for which we could determine the re of cross-section or slice. In this section, we restrict
4 pplictions of definite integrls 5. Volumes: Disks nd Wshers In the previous section, we computed volumes of solids for which we could determine the re of cross-section or slice. In this section, we restrict
Improper Integrals, and Differential Equations
 Improper Integrls, nd Differentil Equtions October 22, 204 5.3 Improper Integrls Previously, we discussed how integrls correspond to res. More specificlly, we sid tht for function f(x), the region creted
Improper Integrls, nd Differentil Equtions October 22, 204 5.3 Improper Integrls Previously, we discussed how integrls correspond to res. More specificlly, we sid tht for function f(x), the region creted
Section 17.2 Line Integrals
 Section 7. Line Integrls Integrting Vector Fields nd Functions long urve In this section we consider the problem of integrting functions, both sclr nd vector (vector fields) long curve in the plne. We
Section 7. Line Integrls Integrting Vector Fields nd Functions long urve In this section we consider the problem of integrting functions, both sclr nd vector (vector fields) long curve in the plne. We
Table of Contents. 1. Limits The Formal Definition of a Limit The Squeeze Theorem Area of a Circle
 Tble of Contents INTRODUCTION 5 CROSS REFERENCE TABLE 13 1. Limits 1 1.1 The Forml Definition of Limit 1. The Squeeze Theorem 34 1.3 Are of Circle 43. Derivtives 53.1 Eploring Tngent Lines 54. Men Vlue
Tble of Contents INTRODUCTION 5 CROSS REFERENCE TABLE 13 1. Limits 1 1.1 The Forml Definition of Limit 1. The Squeeze Theorem 34 1.3 Are of Circle 43. Derivtives 53.1 Eploring Tngent Lines 54. Men Vlue
Math 113 Exam 1-Review
 Mth 113 Exm 1-Review September 26, 2016 Exm 1 covers 6.1-7.3 in the textbook. It is dvisble to lso review the mteril from 5.3 nd 5.5 s this will be helpful in solving some of the problems. 6.1 Are Between
Mth 113 Exm 1-Review September 26, 2016 Exm 1 covers 6.1-7.3 in the textbook. It is dvisble to lso review the mteril from 5.3 nd 5.5 s this will be helpful in solving some of the problems. 6.1 Are Between
Section 14.3 Arc Length and Curvature
 Section 4.3 Arc Length nd Curvture Clculus on Curves in Spce In this section, we ly the foundtions for describing the movement of n object in spce.. Vector Function Bsics In Clc, formul for rc length in
Section 4.3 Arc Length nd Curvture Clculus on Curves in Spce In this section, we ly the foundtions for describing the movement of n object in spce.. Vector Function Bsics In Clc, formul for rc length in
Chapter 9. Arc Length and Surface Area
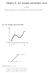 Chpter 9. Arc Length nd Surfce Are In which We ppl integrtion to stud the lengths of curves nd the re of surfces. 9. Arc Length (Tet 547 553) P n P 2 P P 2 n b P i ( i, f( i )) P i ( i, f( i )) distnce
Chpter 9. Arc Length nd Surfce Are In which We ppl integrtion to stud the lengths of curves nd the re of surfces. 9. Arc Length (Tet 547 553) P n P 2 P P 2 n b P i ( i, f( i )) P i ( i, f( i )) distnce
Mathematics Extension 2
 00 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Mthemtics Extension Generl Instructions Reding time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using blck or blue pen Bord-pproved clcultors m be used A tble of stndrd
00 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Mthemtics Extension Generl Instructions Reding time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using blck or blue pen Bord-pproved clcultors m be used A tble of stndrd
MATH 115: Review for Chapter 7
 MATH 5: Review for Chpter 7 Cn you stte the generl form equtions for the circle, prbol, ellipse, nd hyperbol? () Stte the stndrd form eqution for the circle. () Stte the stndrd form eqution for the prbol
MATH 5: Review for Chpter 7 Cn you stte the generl form equtions for the circle, prbol, ellipse, nd hyperbol? () Stte the stndrd form eqution for the circle. () Stte the stndrd form eqution for the prbol
Partial Derivatives. Limits. For a single variable function f (x), the limit lim
 Limits Prtil Derivtives For single vrible function f (x), the limit lim x f (x) exists only if the right-hnd side limit equls to the left-hnd side limit, i.e., lim f (x) = lim f (x). x x + For two vribles
Limits Prtil Derivtives For single vrible function f (x), the limit lim x f (x) exists only if the right-hnd side limit equls to the left-hnd side limit, i.e., lim f (x) = lim f (x). x x + For two vribles
( ) Same as above but m = f x = f x - symmetric to y-axis. find where f ( x) Relative: Find where f ( x) x a + lim exists ( lim f exists.
 AP Clculus Finl Review Sheet solutions When you see the words This is wht you think of doing Find the zeros Set function =, fctor or use qudrtic eqution if qudrtic, grph to find zeros on clcultor Find
AP Clculus Finl Review Sheet solutions When you see the words This is wht you think of doing Find the zeros Set function =, fctor or use qudrtic eqution if qudrtic, grph to find zeros on clcultor Find
A sequence is a list of numbers in a specific order. A series is a sum of the terms of a sequence.
 Core Module Revision Sheet The C exm is hour 30 minutes long nd is in two sections. Section A (36 mrks) 8 0 short questions worth no more thn 5 mrks ech. Section B (36 mrks) 3 questions worth mrks ech.
Core Module Revision Sheet The C exm is hour 30 minutes long nd is in two sections. Section A (36 mrks) 8 0 short questions worth no more thn 5 mrks ech. Section B (36 mrks) 3 questions worth mrks ech.
Math 100 Review Sheet
 Mth 100 Review Sheet Joseph H. Silvermn December 2010 This outline of Mth 100 is summry of the mteril covered in the course. It is designed to be study id, but it is only n outline nd should be used s
Mth 100 Review Sheet Joseph H. Silvermn December 2010 This outline of Mth 100 is summry of the mteril covered in the course. It is designed to be study id, but it is only n outline nd should be used s
Some Methods in the Calculus of Variations
 CHAPTER 6 Some Methods in the Clculus of Vritions 6-. If we use the vried function ( α, ) α sin( ) + () Then d α cos ( ) () d Thus, the totl length of the pth is d S + d d α cos ( ) + α cos ( ) d Setting
CHAPTER 6 Some Methods in the Clculus of Vritions 6-. If we use the vried function ( α, ) α sin( ) + () Then d α cos ( ) () d Thus, the totl length of the pth is d S + d d α cos ( ) + α cos ( ) d Setting
7.1 Integral as Net Change and 7.2 Areas in the Plane Calculus
 7.1 Integrl s Net Chnge nd 7. Ares in the Plne Clculus 7.1 INTEGRAL AS NET CHANGE Notecrds from 7.1: Displcement vs Totl Distnce, Integrl s Net Chnge We hve lredy seen how the position of n oject cn e
7.1 Integrl s Net Chnge nd 7. Ares in the Plne Clculus 7.1 INTEGRAL AS NET CHANGE Notecrds from 7.1: Displcement vs Totl Distnce, Integrl s Net Chnge We hve lredy seen how the position of n oject cn e
Unit #9 : Definite Integral Properties; Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties; Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Unit #9 : Definite Integrl Properties; Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus Gols: Identify properties of definite integrls Define odd nd even functions, nd reltionship to integrl vlues Introduce the Fundmentl
Multiple Integrals. Review of Single Integrals. Planar Area. Volume of Solid of Revolution
 Multiple Integrls eview of Single Integrls eding Trim 7.1 eview Appliction of Integrls: Are 7. eview Appliction of Integrls: olumes 7.3 eview Appliction of Integrls: Lengths of Curves Assignment web pge
Multiple Integrls eview of Single Integrls eding Trim 7.1 eview Appliction of Integrls: Are 7. eview Appliction of Integrls: olumes 7.3 eview Appliction of Integrls: Lengths of Curves Assignment web pge
First Semester Review Calculus BC
 First Semester Review lculus. Wht is the coordinte of the point of inflection on the grph of Multiple hoice: No lcultor y 3 3 5 4? 5 0 0 3 5 0. The grph of piecewise-liner function f, for 4, is shown below.
First Semester Review lculus. Wht is the coordinte of the point of inflection on the grph of Multiple hoice: No lcultor y 3 3 5 4? 5 0 0 3 5 0. The grph of piecewise-liner function f, for 4, is shown below.
4. Calculus of Variations
 4. Clculus of Vritions Introduction - Typicl Problems The clculus of vritions generlises the theory of mxim nd minim. Exmple (): Shortest distnce between two points. On given surfce (e.g. plne), nd the
4. Clculus of Vritions Introduction - Typicl Problems The clculus of vritions generlises the theory of mxim nd minim. Exmple (): Shortest distnce between two points. On given surfce (e.g. plne), nd the
Practice final exam solutions
 University of Pennsylvni Deprtment of Mthemtics Mth 26 Honors Clculus II Spring Semester 29 Prof. Grssi, T.A. Asher Auel Prctice finl exm solutions 1. Let F : 2 2 be defined by F (x, y (x + y, x y. If
University of Pennsylvni Deprtment of Mthemtics Mth 26 Honors Clculus II Spring Semester 29 Prof. Grssi, T.A. Asher Auel Prctice finl exm solutions 1. Let F : 2 2 be defined by F (x, y (x + y, x y. If
ntegration (p3) Integration by Inspection When differentiating using function of a function or the chain rule: If y = f(u), where in turn u = f(x)
 ntegrtion (p) Integrtion by Inspection When differentiting using function of function or the chin rule: If y f(u), where in turn u f( y y So, to differentite u where u +, we write ( + ) nd get ( + ) (.
ntegrtion (p) Integrtion by Inspection When differentiting using function of function or the chin rule: If y f(u), where in turn u f( y y So, to differentite u where u +, we write ( + ) nd get ( + ) (.
Math Calculus with Analytic Geometry II
 orem of definite Mth 5.0 with Anlytic Geometry II Jnury 4, 0 orem of definite If < b then b f (x) dx = ( under f bove x-xis) ( bove f under x-xis) Exmple 8 0 3 9 x dx = π 3 4 = 9π 4 orem of definite Problem
orem of definite Mth 5.0 with Anlytic Geometry II Jnury 4, 0 orem of definite If < b then b f (x) dx = ( under f bove x-xis) ( bove f under x-xis) Exmple 8 0 3 9 x dx = π 3 4 = 9π 4 orem of definite Problem
Unit 5. Integration techniques
 18.01 EXERCISES Unit 5. Integrtion techniques 5A. Inverse trigonometric functions; Hyperbolic functions 5A-1 Evlute ) tn 1 3 b) sin 1 ( 3/) c) If θ = tn 1 5, then evlute sin θ, cos θ, cot θ, csc θ, nd
18.01 EXERCISES Unit 5. Integrtion techniques 5A. Inverse trigonometric functions; Hyperbolic functions 5A-1 Evlute ) tn 1 3 b) sin 1 ( 3/) c) If θ = tn 1 5, then evlute sin θ, cos θ, cot θ, csc θ, nd
Linear Inequalities: Each of the following carries five marks each: 1. Solve the system of equations graphically.
 Liner Inequlities: Ech of the following crries five mrks ech:. Solve the system of equtions grphiclly. x + 2y 8, 2x + y 8, x 0, y 0 Solution: Considerx + 2y 8.. () Drw the grph for x + 2y = 8 by line.it
Liner Inequlities: Ech of the following crries five mrks ech:. Solve the system of equtions grphiclly. x + 2y 8, 2x + y 8, x 0, y 0 Solution: Considerx + 2y 8.. () Drw the grph for x + 2y = 8 by line.it
n=0 ( 1)n /(n + 1) converges, but not n=100 1/n2, is at most 1/100.
 Mth 07H Topics since the second exm Note: The finl exm will cover everything from the first two topics sheets, s well. Absolute convergence nd lternting series A series n converges bsolutely if n converges.
Mth 07H Topics since the second exm Note: The finl exm will cover everything from the first two topics sheets, s well. Absolute convergence nd lternting series A series n converges bsolutely if n converges.
Polynomials and Division Theory
 Higher Checklist (Unit ) Higher Checklist (Unit ) Polynomils nd Division Theory Skill Achieved? Know tht polynomil (expression) is of the form: n x + n x n + n x n + + n x + x + 0 where the i R re the
Higher Checklist (Unit ) Higher Checklist (Unit ) Polynomils nd Division Theory Skill Achieved? Know tht polynomil (expression) is of the form: n x + n x n + n x n + + n x + x + 0 where the i R re the
x 2 + n(n 1)(n 2) x 3 +
 Core 4 Module Revision Sheet The C4 exm is hour 30 minutes long nd is in two sections Section A 36 mrks 5 7 short questions worth t most 8 mrks ech Section B 36 mrks questions worth bout 8 mrks ech You
Core 4 Module Revision Sheet The C4 exm is hour 30 minutes long nd is in two sections Section A 36 mrks 5 7 short questions worth t most 8 mrks ech Section B 36 mrks questions worth bout 8 mrks ech You
Practice Final. Name: Problem 1. Show all of your work, label your answers clearly, and do not use a calculator.
 Nme: MATH 2250 Clculus Eric Perkerson Dte: December 11, 2015 Prctice Finl Show ll of your work, lbel your nswers clerly, nd do not use clcultor. Problem 1 Compute the following limits, showing pproprite
Nme: MATH 2250 Clculus Eric Perkerson Dte: December 11, 2015 Prctice Finl Show ll of your work, lbel your nswers clerly, nd do not use clcultor. Problem 1 Compute the following limits, showing pproprite
A REVIEW OF CALCULUS CONCEPTS FOR JDEP 384H. Thomas Shores Department of Mathematics University of Nebraska Spring 2007
 A REVIEW OF CALCULUS CONCEPTS FOR JDEP 384H Thoms Shores Deprtment of Mthemtics University of Nebrsk Spring 2007 Contents Rtes of Chnge nd Derivtives 1 Dierentils 4 Are nd Integrls 5 Multivrite Clculus
A REVIEW OF CALCULUS CONCEPTS FOR JDEP 384H Thoms Shores Deprtment of Mthemtics University of Nebrsk Spring 2007 Contents Rtes of Chnge nd Derivtives 1 Dierentils 4 Are nd Integrls 5 Multivrite Clculus
MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT 4 SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS WEEK 11 WRITTEN EXAMINATION 2 SOLUTIONS SECTION 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT 4 SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS WEEK WRITTEN EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES SECTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION QUESTION
MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT 4 SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS WEEK WRITTEN EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES SECTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION QUESTION
Lecture XVII. Vector functions, vector and scalar fields Definition 1 A vector-valued function is a map associating vectors to real numbers, that is
 Lecture XVII Abstrct We introduce the concepts of vector functions, sclr nd vector fields nd stress their relevnce in pplied sciences. We study curves in three-dimensionl Eucliden spce nd introduce the
Lecture XVII Abstrct We introduce the concepts of vector functions, sclr nd vector fields nd stress their relevnce in pplied sciences. We study curves in three-dimensionl Eucliden spce nd introduce the
The Wave Equation I. MA 436 Kurt Bryan
 1 Introduction The Wve Eqution I MA 436 Kurt Bryn Consider string stretching long the x xis, of indeterminte (or even infinite!) length. We wnt to derive n eqution which models the motion of the string
1 Introduction The Wve Eqution I MA 436 Kurt Bryn Consider string stretching long the x xis, of indeterminte (or even infinite!) length. We wnt to derive n eqution which models the motion of the string
Main topics for the Second Midterm
 Min topics for the Second Midterm The Midterm will cover Sections 5.4-5.9, Sections 6.1-6.3, nd Sections 7.1-7.7 (essentilly ll of the mteril covered in clss from the First Midterm). Be sure to know the
Min topics for the Second Midterm The Midterm will cover Sections 5.4-5.9, Sections 6.1-6.3, nd Sections 7.1-7.7 (essentilly ll of the mteril covered in clss from the First Midterm). Be sure to know the
4.4 Areas, Integrals and Antiderivatives
 . res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
. res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
12 TRANSFORMING BIVARIATE DENSITY FUNCTIONS
 1 TRANSFORMING BIVARIATE DENSITY FUNCTIONS Hving seen how to trnsform the probbility density functions ssocited with single rndom vrible, the next logicl step is to see how to trnsform bivrite probbility
1 TRANSFORMING BIVARIATE DENSITY FUNCTIONS Hving seen how to trnsform the probbility density functions ssocited with single rndom vrible, the next logicl step is to see how to trnsform bivrite probbility
Indefinite Integral. Chapter Integration - reverse of differentiation
 Chpter Indefinite Integrl Most of the mthemticl opertions hve inverse opertions. The inverse opertion of differentition is clled integrtion. For exmple, describing process t the given moment knowing the
Chpter Indefinite Integrl Most of the mthemticl opertions hve inverse opertions. The inverse opertion of differentition is clled integrtion. For exmple, describing process t the given moment knowing the
1 Line Integrals in Plane.
 MA213 thye Brief Notes on hpter 16. 1 Line Integrls in Plne. 1.1 Introduction. 1.1.1 urves. A piece of smooth curve is ssumed to be given by vector vlued position function P (t) (or r(t) ) s the prmeter
MA213 thye Brief Notes on hpter 16. 1 Line Integrls in Plne. 1.1 Introduction. 1.1.1 urves. A piece of smooth curve is ssumed to be given by vector vlued position function P (t) (or r(t) ) s the prmeter
Pre-Calculus TMTA Test 2018
 . For the function f ( x) ( x )( x )( x 4) find the verge rte of chnge from x to x. ) 70 4 8.4 8.4 4 7 logb 8. If logb.07, logb 4.96, nd logb.60, then ).08..867.9.48. For, ) sec (sin ) is equivlent to
. For the function f ( x) ( x )( x )( x 4) find the verge rte of chnge from x to x. ) 70 4 8.4 8.4 4 7 logb 8. If logb.07, logb 4.96, nd logb.60, then ).08..867.9.48. For, ) sec (sin ) is equivlent to
Multiple Integrals. Review of Single Integrals. Planar Area. Volume of Solid of Revolution
 Multiple Integrls eview of Single Integrls eding Trim 7.1 eview Appliction of Integrls: Are 7. eview Appliction of Integrls: Volumes 7.3 eview Appliction of Integrls: Lengths of Curves Assignment web pge
Multiple Integrls eview of Single Integrls eding Trim 7.1 eview Appliction of Integrls: Are 7. eview Appliction of Integrls: Volumes 7.3 eview Appliction of Integrls: Lengths of Curves Assignment web pge
(b) Let S 1 : f(x, y, z) = (x a) 2 + (y b) 2 + (z c) 2 = 1, this is a level set in 3D, hence
 Problem ( points) Find the vector eqution of the line tht joins points on the two lines L : r ( + t) i t j ( + t) k L : r t i + (t ) j ( + t) k nd is perpendiculr to both those lines. Find the set of ll
Problem ( points) Find the vector eqution of the line tht joins points on the two lines L : r ( + t) i t j ( + t) k L : r t i + (t ) j ( + t) k nd is perpendiculr to both those lines. Find the set of ll
AB Calculus Review Sheet
 AB Clculus Review Sheet Legend: A Preclculus, B Limits, C Differentil Clculus, D Applictions of Differentil Clculus, E Integrl Clculus, F Applictions of Integrl Clculus, G Prticle Motion nd Rtes This is
AB Clculus Review Sheet Legend: A Preclculus, B Limits, C Differentil Clculus, D Applictions of Differentil Clculus, E Integrl Clculus, F Applictions of Integrl Clculus, G Prticle Motion nd Rtes This is
B Veitch. Calculus I Study Guide
 Clculus I Stuy Guie This stuy guie is in no wy exhustive. As stte in clss, ny type of question from clss, quizzes, exms, n homeworks re fir gme. There s no informtion here bout the wor problems. 1. Some
Clculus I Stuy Guie This stuy guie is in no wy exhustive. As stte in clss, ny type of question from clss, quizzes, exms, n homeworks re fir gme. There s no informtion here bout the wor problems. 1. Some
Lecture 0. MATH REVIEW for ECE : LINEAR CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II
 Lecture 0 MATH REVIEW for ECE 000 : LINEAR CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II Aung Kyi Sn Grdute Lecturer School of Electricl nd Computer Engineering Purdue University Summer 014 Lecture 0 : Mth Review Lecture 0 is intended
Lecture 0 MATH REVIEW for ECE 000 : LINEAR CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II Aung Kyi Sn Grdute Lecturer School of Electricl nd Computer Engineering Purdue University Summer 014 Lecture 0 : Mth Review Lecture 0 is intended
Year 12 Trial Examination Mathematics Extension 1. Question One 12 marks (Start on a new page) Marks
 THGS Mthemtics etension Tril 00 Yer Tril Emintion Mthemtics Etension Question One mrks (Strt on new pge) Mrks ) If P is the point (-, 5) nd Q is the point (, -), find the co-ordintes of the point R which
THGS Mthemtics etension Tril 00 Yer Tril Emintion Mthemtics Etension Question One mrks (Strt on new pge) Mrks ) If P is the point (-, 5) nd Q is the point (, -), find the co-ordintes of the point R which
Homework Assignment 6 Solution Set
 Homework Assignment 6 Solution Set PHYCS 440 Mrch, 004 Prolem (Griffiths 4.6 One wy to find the energy is to find the E nd D fields everywhere nd then integrte the energy density for those fields. We know
Homework Assignment 6 Solution Set PHYCS 440 Mrch, 004 Prolem (Griffiths 4.6 One wy to find the energy is to find the E nd D fields everywhere nd then integrte the energy density for those fields. We know
MTH 4-16a Trigonometry
 MTH 4-16 Trigonometry Level 4 [UNIT 5 REVISION SECTION ] I cn identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse sides on right-ngled tringle. Identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse in the following right-ngled
MTH 4-16 Trigonometry Level 4 [UNIT 5 REVISION SECTION ] I cn identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse sides on right-ngled tringle. Identify the opposite, djcent nd hypotenuse in the following right-ngled
We partition C into n small arcs by forming a partition of [a, b] by picking s i as follows: a = s 0 < s 1 < < s n = b.
![We partition C into n small arcs by forming a partition of [a, b] by picking s i as follows: a = s 0 < s 1 < < s n = b. We partition C into n small arcs by forming a partition of [a, b] by picking s i as follows: a = s 0 < s 1 < < s n = b.](/thumbs/93/114277851.jpg) Mth 255 - Vector lculus II Notes 4.2 Pth nd Line Integrls We begin with discussion of pth integrls (the book clls them sclr line integrls). We will do this for function of two vribles, but these ides cn
Mth 255 - Vector lculus II Notes 4.2 Pth nd Line Integrls We begin with discussion of pth integrls (the book clls them sclr line integrls). We will do this for function of two vribles, but these ides cn
Overview of Calculus I
 Overview of Clculus I Prof. Jim Swift Northern Arizon University There re three key concepts in clculus: The limit, the derivtive, nd the integrl. You need to understnd the definitions of these three things,
Overview of Clculus I Prof. Jim Swift Northern Arizon University There re three key concepts in clculus: The limit, the derivtive, nd the integrl. You need to understnd the definitions of these three things,
Math 0230 Calculus 2 Lectures
 Mth Clculus Lectures Chpter 7 Applictions of Integrtion Numertion of sections corresponds to the text Jmes Stewrt, Essentil Clculus, Erly Trnscendentls, Second edition. Section 7. Ares Between Curves Two
Mth Clculus Lectures Chpter 7 Applictions of Integrtion Numertion of sections corresponds to the text Jmes Stewrt, Essentil Clculus, Erly Trnscendentls, Second edition. Section 7. Ares Between Curves Two
A LEVEL TOPIC REVIEW. factor and remainder theorems
 A LEVEL TOPIC REVIEW unit C fctor nd reminder theorems. Use the Fctor Theorem to show tht: ) ( ) is fctor of +. ( mrks) ( + ) is fctor of ( ) is fctor of + 7+. ( mrks) +. ( mrks). Use lgebric division
A LEVEL TOPIC REVIEW unit C fctor nd reminder theorems. Use the Fctor Theorem to show tht: ) ( ) is fctor of +. ( mrks) ( + ) is fctor of ( ) is fctor of + 7+. ( mrks) +. ( mrks). Use lgebric division
Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics (C2) Required Knowledge Information Sheet. Daniel Hammocks
 Edexcel GCE Core Mthemtics (C) Required Knowledge Informtion Sheet C Formule Given in Mthemticl Formule nd Sttisticl Tles Booklet Cosine Rule o = + c c cosine (A) Binomil Series o ( + ) n = n + n 1 n 1
Edexcel GCE Core Mthemtics (C) Required Knowledge Informtion Sheet C Formule Given in Mthemticl Formule nd Sttisticl Tles Booklet Cosine Rule o = + c c cosine (A) Binomil Series o ( + ) n = n + n 1 n 1
Chapters 4 & 5 Integrals & Applications
 Contents Chpters 4 & 5 Integrls & Applictions Motivtion to Chpters 4 & 5 2 Chpter 4 3 Ares nd Distnces 3. VIDEO - Ares Under Functions............................................ 3.2 VIDEO - Applictions
Contents Chpters 4 & 5 Integrls & Applictions Motivtion to Chpters 4 & 5 2 Chpter 4 3 Ares nd Distnces 3. VIDEO - Ares Under Functions............................................ 3.2 VIDEO - Applictions
( ) where f ( x ) is a. AB Calculus Exam Review Sheet. A. Precalculus Type problems. Find the zeros of f ( x).
 AB Clculus Exm Review Sheet A. Preclculus Type prolems A1 Find the zeros of f ( x). This is wht you think of doing A2 A3 Find the intersection of f ( x) nd g( x). Show tht f ( x) is even. A4 Show tht f
AB Clculus Exm Review Sheet A. Preclculus Type prolems A1 Find the zeros of f ( x). This is wht you think of doing A2 A3 Find the intersection of f ( x) nd g( x). Show tht f ( x) is even. A4 Show tht f
( ) as a fraction. Determine location of the highest
 AB Clculus Exm Review Sheet - Solutions A. Preclculus Type prolems A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 This is wht you think of doing Find the zeros of f ( x). Set function equl to 0. Fctor or use qudrtic eqution if
AB Clculus Exm Review Sheet - Solutions A. Preclculus Type prolems A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 This is wht you think of doing Find the zeros of f ( x). Set function equl to 0. Fctor or use qudrtic eqution if
df dx There is an infinite number of different paths from
 Integrl clculus line integrls Feb 7, 18 From clculus, in the cse of single vrible x1 F F x F x f x dx, where f x 1 x df dx Now, consider the cse tht two vribles re t ply. Suppose,, df M x y dx N x y dy
Integrl clculus line integrls Feb 7, 18 From clculus, in the cse of single vrible x1 F F x F x f x dx, where f x 1 x df dx Now, consider the cse tht two vribles re t ply. Suppose,, df M x y dx N x y dy
Main topics for the First Midterm
 Min topics for the First Midterm The Midterm will cover Section 1.8, Chpters 2-3, Sections 4.1-4.8, nd Sections 5.1-5.3 (essentilly ll of the mteril covered in clss). Be sure to know the results of the
Min topics for the First Midterm The Midterm will cover Section 1.8, Chpters 2-3, Sections 4.1-4.8, nd Sections 5.1-5.3 (essentilly ll of the mteril covered in clss). Be sure to know the results of the
1 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA and GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE
 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA nd GEOMETRY READINESS DIAGNOSTIC TEST PRACTICE Directions: Study the exmples, work the prolems, then check your nswers t the end of ech topic. If you don t get the nswer given, check
