ON RADIO NUMBER OF STACKED-BOOK GRAPHS arxiv: v1 [math.co] 2 Jan 2019
|
|
|
- Alan Leslie Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ON RADIO NUMBER OF STACKED-BOOK GRAPHS arxiv: v1 [math.co] Ja 019 TAYO CHARLES ADEFOKUN 1 AND DEBORAH OLAYIDE AJAYI Abstract. A Stacked-book graph G m, results from the Cartesia product of a stargraphs m adpath P, wheremadarethe ordersofs m adp respectively. A radio labelig problem of a simple ad coected graph, G, ivolves a oegative iteger fuctio f : V(G) Z + o the vertex set V(G) of G, such that for all u,v V(G), f(u) f(v) diam(g) + 1 d(u,v), where diam(g) is the diameter of G ad d(u,v) is the shortest distace betwee u ad v. Suppose that f mi ad f max are the respective least ad largestvalues of f o V(G), the, spaf, the absolute differece of f mi ad f max, is the spa of f while the radio umber r(g) of G is the least value of spaf over all the possible radio labels o V(G). I this paper, we obtai the radio umber for the stacked-book graph G m, where m 4 ad is eve, ad obtai bouds for m = 3 which improves existig upper ad lower bouds for G m, where m = Itroductio The graph G cosidered i this paper is simple ad udirected. The vertex ad edge sets of G are V(G) ad E(G). For e = uv E(G), e coects two vertices u ad v while d(u,v) is the distace betwee u,v ad diam(g) is the diameter of G. Radio umber labelig problem, which is mostly applied i frequecy assigmet for sigal trasmissio, where it mitigates the problems of sigal iterferece. It was first suggested i 1980 by Hale[6]. Let f be a o egative iteger fuctio o V(G) such that the radio labelig coditio, f(u) f(v) diamg+1 d(u,v) is satisfied for every pair u,v V(G). The spa of f, spaf, is the differece betwee f mi ad f max, the miimum ad the maximum radio label o G respectively. Thus the smallest possible value of spaf is the radio umber, r(g), of G. The radio labelig coditio guaratees that every vertex o G has uique radio label. Therefore, r(g) V(G) 1 is trivially true. However, establishig the radio umber of graphs has proved to be quite tedious. Eve so, such umbers have bee completely determied for some graphs. Liu ad Zhu [10] showed that for path, P, 3, { k(k 1)+1 if = k; r(p ) = k + if = k +1. Key words ad phrases. Radio labelig, radio umber, stacked-book graph, Cartesia product of graphs 010 Mathematics Subject Classificatio. Primary: 05C78; 05C15. 1
2 T.C ADEFOKUN AND D.O. AJAYI This improves results i [4] ad [5] by Chatrad, et. al. where the upper ad lower bouds for the same class of graph are obtaied. Furthermore, Liu ad Xie, [8], foud the radio umber for the square of a path, P { as: k r(p) = + if 1(mod 4), 9; k +1 if otherwise. Similar results are obtaied i [9] for square of cycles. Jiag [7] completely solved the radioumberproblemforthegridgraph(p m P ), whereform, >, itisotedthat r(p m P ) = m +m m m+, for m-odd ad eve. Saha ad Paigrahi [1] ad Ajayi ad Adefoku [1] obtaied results o the radio umbers of Cartesia products of two cycles (toroidal grid) ad of path ad star graph(stacked-book graph) respectively. I the case of stacked-book graph G = S P m, r(g) m+1, which the authors oted is ot tight. Recet results o radio umber iclude those o middle graph of path [], trees, [3] ad edge-joit graphs [11]. I this paper, for eve positive iteger, we cosider the stacked-book graph G m, ad derive the r(g m, ) for the case m 4. Furthermore, ew lower ad upper bouds of the umber are obtaied for m = 3, which improve similar results i [1].. Prelimiaries Let S m be a star of order m 3 ad for each vertex v i V(S m ), i m, v i is adjacet to v 1, the ceter vertex of S m. Also, let P be a path such that V(P ) =. The Graph G m, = S m P, is obtaied by the Cartesia product of S m ad P. The vertex set V(G m, ) is the Cartesia product V(S m ) V(P ), such that for ay u i v j V(G m, ), the, u i V(S m ) ad v j E(P ). For E(G m, ), u i v j u k v l is cotaied i E(G m, ) for u i v j, u k v l V(G m, ), the either u i = u k ad v j v l E(P m ) or u i u k E(S m ) ad v j = v l. Geometrically, V(G m, ) cotais umber of S m stars, amely S m(1),s m(),,s m(), such that for every pair v i S m(i) ad v i+1 S m(i+1), v i v i+1 E(G m, ). These are, i fact, the oly type of edges o G m, apart from those o its S m stars. This geometry fetched G m, the ame stacked-book graph. Remark.1. It is easy to see that diam(g m, ) = +1, beig the umber of edges from u i v 1 u 1 v 1 u 1 v u 1 v u j v, where i j. Remark.1. For coveiece, we write u i v j as u i,j i certai cases ad u i,j u k,l is the edge iduced by u i v j ad u k v l. Defiitio.1. Let G m, = S m P. The vertex set V (i) V(G m, ) is the set of vertices o star S m(i), defied by the set {u 1 v i,u v i,,u m v i }. We itroduce the followig defiitio: Defiitio.. Let G m, = S m P. The, the pair G(i) G m, iduced by V (i) ad V (i+ ). S m(i),s m(i+ ) is a subgraph Remark.. The maximum umber of G(i) subgraph i a G m, graph, eve, is ad the diam(g(i)) = +.
3 Remark.3. Let { V (i+ ) = u 1, i+ RADIO NUMBER OF STACKED-BOOK GRAPHS 3 V (i),v (i+ ),u, i+,,u m, i+ iduce G(i), such that V (i) = {u 1,i,u,i,,u m,i } ad }. The, for u V (i), v V (i+ ) ad d(u,v) = p, where p {, +1, +} ad for u k,i,v t,i+, if k = t; p = +1 if t = 1,k t; + if t 1,k 1,k t. 3. results I this sectio, we estimate the radio umber of stacked-book graphs ad obtai the exact radio umber for G m,, for m 4, eve. Lemma 3.1. Let S m be a star o G m, ad f, a radio label fuctio o G m,. The spaf o S m is (m 1)+1. Proof. Let the ceter vertex of S m be v 1 ad let f(v 1 ) be the radio label o v 1. There exists some v V(S m ) such that d(v 1,v ) = 1. Therefore, by the defiitio, f(v ) f(v 1 ) Suppose that k / {1,}. For v k, d(v,v k ) =, for all v k V(S m ). Thus, without loss of geerality, suppose that v m is the last vertex o V(S m ), the f(v m ) f(v 0 )+(+1)+(m ) ad the claim follows. Remark 3.1. It is easy to cofirm that give a star S m with ceter vertex v 1, if for a positive iteger α, r(s m ) = α, the either f(v 1 ) is f mi or f max. Now we establish lower boud for G(i). Lemma 3.. Let G(i) be a subgraph of G m, ad let f be the radio label o V(G m, ). The, r(g(i)) f(v 1 )+m +, where v 1 is the ceter vertex of S m(i+ ). Proof. Let S m(i) ad S m(j) be the stars o G(i) G m,, where j = i+. By Lemma 3.1, f(v m ) = f(v 1 ) + m + 1, with f(v m ) = max{f(v t ) : v t V(S m (j))}, ad v 1 the ceter of S m(j). Now, let u 1 be the ceter vertex of S m(i). It is clear that d(u 1,v 1 ) = +. Thus, f(u 1) f(v 1 ) + m = f(v 1 ) + m +. Claim: For optimal radio labelig of G(i), maximum label o S m(i) is at least f(u 1 ). Reaso: Cosider some u m V(S m ), such that m 1 ad d(u m,v m ) = +. The f(u m ) = f(v 1 )+m +1. By Lemma 3.1, thespaf off for a star S m ism +1. Now, f(u m ) (m +1) = f(v i )+. Thus, by Remark 3.1, f(u 1) = f(v 1 + ). This is a cotradictio, cosiderig that d(u 1,v 1 ) =. Lemma 3.3. Let G + (i) G m, be G(i) w 1, where w 1 is the ceter vertex of S m(j+1) ad let f be a radio labelig o G m,, where is eve. The, the spaf of f o G + (i) m+3 Proof. Let u 1 be the ceter vertex of S m(i). It ca be verified that d(u 1,w 1 ) =. By the proof of Lemma 3., f(u 1 ) f(v 1 )+m +, where v 1 is the ceter vertex
4 4 T.C ADEFOKUN AND D.O. AJAYI of S m(j). Thus by defiitio, f(w 1 ) f(v 1 )+m Sice f(v 1 ) is the miimum label o G(i), the result follows = f(v 1 )+m+3. Now we preset the lower boud for stacked-book graph G m,, where is a eve iteger ad m 3. Theorem 3.1. Let G = G m, be a stacked-book graph with m 3 ad a eve iteger. Furthermore, let f be the radio labelig o G. The, r(g) m + 1. Proof. From the defiitio of G(i), graph G m, cotais umber of G(i) subgraphs. Likewise, it ca be see that G m, cotais 1 umber of G + (i) subgraphs. Now, let G( ), iduced by S m( ) ad S m() be the last G(i) subgraphs o G m, ad G + (1),G + (),,G + ( 1 1 ) be the umber of G + (i) graphs. By the earlier result, if f(v 1 ) = 0, the r(g m, ) ( ) 1 (m+3)+m m + = + 1. I what follows, we examie the upper boud of the stacked-book graph G m,. Lemma 3.4. Let G(i) be a subgraph of G m, iduced by V (i),v (i+ ). The for ay pair v V (i) ad u V (i+ ), such that d(u,v) +1, f(v) f(u). Proof. Let u = u k,i V (i) ad v = u t,i+ V (i+ ). Sice d(u,v) >, the by Remark.3, k t. Suppose that either u or v is the ceter vertex of their respective stars S m(i) ad S m(i+ ). The, d(u,v) = diam(g(i)). Now, let the radio label o u ad v be f(u) ad f(v) respectively. Suppose, without loss of geerality, that f(v) > f(u). The f(v) f(u)+diam(g m, )+1 diam(g(i)), which implies that f(v) f(u)+. This implies that f(v) f(u). Similarly, if f(u) f(v), the f(u) f(v) ad thus, the claim follows. The followig remarks ca be cofirmed by applyig similar methods as i proof of Lemma 3.4. Remark 3.1. Suppose that either of u,v i Lemma 3.4, say u, is such that for ay u V (i), uu E(S m(i) ). The d(u,u ) = +1 ad f(u) f(v) +1. Remark 3.. Let u,u V (i). If d(u,u ) = 1, the f(u) f(u ) + 1 ad f(u) f(u ) for d(u,u ) =. Theorem 3.. Let m > 3 be odd ad G(i) G m,, be iduced by V (i),v (i+ ). the, r(g(i)) f(v 1 )+m +, where v 1 is the ceter star S m(1+ ). Proof. Let V (i) = {u 1,i,u,i,,u m,i } ad V (t) = {u 1,t,u,t,,u m,t }, where t = i+. For r [1,m], set u r,i V (i) as α r ad u r,t V (t) as β r. From earlier remark, d(β r,α r ) { +1, +} for r s. Now, for every pair α s,β r, where α s V (i), ad β r V (t), let r s except otherwise stated. Let α 1 ad β 1 be the respective ceters of the stars S m(i) ad S m(t) iduced by V (i) ad V (t) ad let the radio label o β 1 be f(β 1 )
5 RADIO NUMBER OF STACKED-BOOK GRAPHS 5 such that f(β 1 ) =mi{f(β i ) : 1 i m}. Sice β 1 is the ceter of S m(t), the give α V (i), d(β 1,α ) = +1. Nowsetp = diam(g m,)+1 d(β 1,α r ), r 1. Hece, p = + ( +1) = +1. Suppose that α j V (i) ad β k V (t), such that 1 j k 1. The, d(α j,β k ) = +. So we set q = diam(g m,)+1 d(α j,β k ) =. For f(β 1) ad someα V (i), f(α ) = f(β 1 )+p. Also, forβ 3 V (t), f(β 3 ) = f(α )+q = f(β 1 )+p+q ad f(α 4 ) = f(β 1 )+q +p. We cotiue to label the vertices o both V (i) ad V (t) alteratively based o the last value attaied. Therefore, for m odd, f(β m ) = f(α m 1 )+ = f(β 1 )+(m )q +p. It ca be see that there does ot exist α d V (i), such that d > m. So, we reverse the order of labelig, such that for β m,α 3, f(α 3 ) = f(β m )+q = f(β 1 )+(m )q +p. Also, for the pair α 3,β, f(β ) = f(β 1 )+(m )q +q +p. This cotiues util we reach the pair α m, β m 1, ad obtai f(α m 1 ) = f(β 1 )+(m 3)q +p. Fially, we cosider the pair β m 1 ad α 1. Sice α 1 is the ceter of S (i), the d(α 1,β m 1 ) = +1 ad hece, f(α 1 ) = f(α m 1 )+p = f(β 1 )+(m 3)q+p = f(β 1 )+m +. Hece, r(g(i)) f(v 1 )+m +, where m is odd ad eve. Next we directly apply Theorem 3.. } Lemma 3.5. Let {S Ḡ(i) be iduced by m(i),s m(i+ ),γ 1, where γ 1 is the ceter of star S m(i+ +1), iduced by V (i+ +1). The, f(γ 1 ) f(β 1 )+m+3. Proof. For α 1 ad β 1 ceters of stars S (i) ad S (i+ ) respectively, let f(α 1 ) = f(β 1 )+ m +, as established i Theorem 3.. The, d(α 1,γ 1 ) = +1. Therefore, f(γ 1 ) = f(α 1 )+p = f(β 1 )+m+3. Now, for β 1, the ceter of S m(1+ ), iduced by V (1+ ). By settig f(β 1 ) = 0, we establish a upper boud for the radio umber of a stacked-book graph G m, i the ext results. Theorem 3.3. For G m,, m odd ad eve, r(g m, ) m + 1.
6 6 T.C ADEFOKUN AND D.O. AJAYI Proof. Let v 1(1),v (1),v 3(1),,v (1) be the set of the respective ceters of stars S m(1), S m(), S m(3),, S m() i G m,. Also, suppose that f(v +1(1) ) = 0. From the Lemma 3.5 f(v +(1) ) = m + 3; f(v +3(1) ) = (m + 3) ad so o. I the ed, f(v (1) ) = ( 1)(m+3). Also, let v (1) = v (1) be the ceter of S m( ) G m, ad let S m( ),S m() iduce the graph G( ) G m,. By Theorem 3., ( ( r G f(v (1) )+m )) + m + 1. Theorem 3.4. Let m, be eve. The r(g m, ) m + 1. Proof. The proof follows similar argumet ad techique as i Theorem 3., Lemma 3.5 ad Theorem Figure 1. A G 4,6 graph with r(g 4,6 ) 77 Theorems 3.1, 3.3, 3.4 establish the radio umber of G m,, where m 4 ad is eve, as recapped i the ext theorem. Theorem 3.5. Let G m, be a stacked-book graph with m 4 ad eve, the, r(g m, ) = m + 1. Next we cosider the case where m = 3. First we preset a result that is equivalet to Theorem 3. with respect to m = 3. Theorem { 3.6. Let } G 3, be a stacked-book graph, where is eve. Suppose that the pair S 3(i),S 3(i+ ) form a subgraph G(i) of G 3,. The, r(g(i)) f(u 1 )+ 5 +3, where u 1 is the ceter vertex of S 3(i+ ). Proof. Let V (i) = {v 1,v,v 3 } ad V (i+ ) = {u 1,u,u 3 } where V (i) ad V (i+ ) are vertex sets of stars S 3(i) ad S 3(i+ ) i G 3, respectively. Also, let v 1 ad u i be the respective ceter vertices of S 3(i) ad S 3(i+ ). From earlier remark, d(v 1,u 1 ) = +1. Suppose
7 RADIO NUMBER OF STACKED-BOOK GRAPHS 7 that f(u 1 ), the radio label of u 1 is the smallest possible radio label o G(i), the, f(v ) = f(v 1 )+diam(g 3, )+1 d(v 1,u 1 ) = f(u i )+ +1. For v,u 3 d(v,u 3 ) = +, f(u 3 ) = f(u 1 )++1 For u 3,v 1, d(u 3,v 1 ) = +1, f(v 1 ) = f(u 1 ) For v 1,u, d(v 1,u ) = +1 ad thus, f(u ) = f(u 1 )+ 3 ( ) = f(u 1 )++3. Ad fially, for the pair v 3,u, d(v 3,u 3 ) = + ad f(u 3 ) = f(u 1 ) Hece, r(g(i)) f(u 1 ) Next, we obtai the followig result. Lemma 3.6. Let κ 1 be the ceter of star S 3(i+ )+1 G 3, ad let H(1) be a subgraph of G (3,m) iduced by S 3(i),S 3(i+ ),κ 1. The f(κ 1 ) 3+1. Proof. The vertex with the maximum value of radio label i Theorem 3.6 is u 3. Let us adopt this, with f(u 3 ) = f(u 1 ) Now, d(u 3,κ 1 ) = +. Therefore, f(κ 1 ) = f(u 1 )+3+3. I the fial result here, we set f(u 1 ) = 0, for u i, the ceter of star S 3(1+ ). Theorem 3.7. Let be a eve positive iteger. The, r(g 3,m ) 3 +. Proof. Proof follows similar techique adopted i Theorem 3.4. Figure is a radio umberig for G 3,6. It shows that r(g 3,6 ) is ot more tha 60.
8 8 T.C ADEFOKUN AND D.O. AJAYI Figure. A G 3,6 graph with r(g 3,6 ) Coclusio It is oteworthy to look at some of the results i [7]. A G 3, is a 3 grid. By [7], it is see that r(g 3,6 ) = 59, which is better tha the result i Figure above by 1. But this is still a cosiderable improvemet compared with a upper boud of 109 suggested i [1]. I establishig the upper boud for G 3,, it is observed that the umber of the pair u,v V(G 3, ) for which d(u,v) = diam(g 3,)+1 is more tha the case where d(u,v) = i each of the segmets of radio labelig of the stacked-graph. However, the reverse proves to be the case i G m,, m 4. Refereces [1] D. O. Ajayi ad T. C. Adefoku O bouds of radio umber of certai product graphs, J. Nigeria Math. Soc. 37() (018) [] D. Batva, S Vaidya ad S. Zhou Radio umbers of trees, Electro. Notes i Discrete Math. 48 (015) [3] D. Batva Radio umbers of middle graph of paths, Electro. Notes i Discrete Math. 66 (017) [4] G. Chartrad, D. Erwi, F Harary ad P. Zhag, Radio labeligs of graphs, Bull. Ist. Combi. Appl. 33 (001) [5] G. Chartrad, D. Erwi ad P. Zhag, A graph labelig problem suggested by FM Chael Restrictios, Bull. Ist. Combi. Appl. 43 (005) [6] W. K. Hale, Frequecy assigmet theory ad applicatios, Proc. IEEE, 68 (1980) [7] T-S Jiag, The radio umber of grid graphs, arxiv: v [8] D.D.-F. Liu ad M. Xie Radio umber for square paths, Ars Combi. 90 (009) [9] D.D.-F. Liu ad M. Xie Radio umber for square cycles, Cogr. Numer. 169 (004) [10] D. Liu ad X. Zhu, Multilevel distace labeligs for paths ad cycles, SIAM J. Discrete Math. 19 (005) [11] A. Naseem, K. Shabbir ad H. Shaker The radio umber of edge-joit graphs, ARS Comb. 139 (018) [1] L. Saha ad P. Paigrahi, O the radio umbers of toroidal grid, Aust. Jour. Combi. 55 (013)
9 RADIO NUMBER OF STACKED-BOOK GRAPHS 9 1 Departmet of Computer ad Mathematical Scieces, Crawford Uiversity, Nigeria address: tayoadefoku@crawforduiversity.edu.g Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Ibada, Ibada, Nigeria address: olayide.ajayi@mail.ui.edu.g; adelaideajayi@yahoo.com
RADIO NUMBER FOR CROSS PRODUCT P n (P 2 ) Gyeongsang National University Jinju, , KOREA 2,4 Department of Mathematics
 Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 97 No. 4 014, 515-55 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.173/ijpam.v97i4.11
Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 97 No. 4 014, 515-55 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.173/ijpam.v97i4.11
γ-max Labelings of Graphs
 γ-max Labeligs of Graphs Supapor Saduakdee 1 & Varaoot Khemmai 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Sriakhariwirot Uiversity, Bagkok, Thailad Joural of Mathematics Research; Vol. 9, No. 1; February 017 ISSN 1916-9795
γ-max Labeligs of Graphs Supapor Saduakdee 1 & Varaoot Khemmai 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Sriakhariwirot Uiversity, Bagkok, Thailad Joural of Mathematics Research; Vol. 9, No. 1; February 017 ISSN 1916-9795
PAijpam.eu IRREGULAR SET COLORINGS OF GRAPHS
 Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 109 No. 7 016, 143-150 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: 10.173/ijpam.v109i7.18 PAijpam.eu
Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 109 No. 7 016, 143-150 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: 10.173/ijpam.v109i7.18 PAijpam.eu
Absolutely Harmonious Labeling of Graphs
 Iteratioal J.Math. Combi. Vol. (011), 40-51 Absolutely Harmoious Labelig of Graphs M.Seeivasa (Sri Paramakalyai College, Alwarkurichi-6741, Idia) A.Lourdusamy (St.Xavier s College (Autoomous), Palayamkottai,
Iteratioal J.Math. Combi. Vol. (011), 40-51 Absolutely Harmoious Labelig of Graphs M.Seeivasa (Sri Paramakalyai College, Alwarkurichi-6741, Idia) A.Lourdusamy (St.Xavier s College (Autoomous), Palayamkottai,
Randić index, diameter and the average distance
 Radić idex, diameter ad the average distace arxiv:0906.530v1 [math.co] 9 Ju 009 Xueliag Li, Yogtag Shi Ceter for Combiatorics ad LPMC-TJKLC Nakai Uiversity, Tiaji 300071, Chia lxl@akai.edu.c; shi@cfc.akai.edu.c
Radić idex, diameter ad the average distace arxiv:0906.530v1 [math.co] 9 Ju 009 Xueliag Li, Yogtag Shi Ceter for Combiatorics ad LPMC-TJKLC Nakai Uiversity, Tiaji 300071, Chia lxl@akai.edu.c; shi@cfc.akai.edu.c
k-equitable mean labeling
 Joural of Algorithms ad Comutatio joural homeage: htt://jac.ut.ac.ir k-euitable mea labelig P.Jeyathi 1 1 Deartmet of Mathematics, Govidammal Aditaar College for Wome, Tiruchedur- 628 215,Idia ABSTRACT
Joural of Algorithms ad Comutatio joural homeage: htt://jac.ut.ac.ir k-euitable mea labelig P.Jeyathi 1 1 Deartmet of Mathematics, Govidammal Aditaar College for Wome, Tiruchedur- 628 215,Idia ABSTRACT
EQUITABLE DOMINATING CHROMATIC SETS IN GRAPHS. Sethu Institute of Technology Kariapatti, Tamilnadu, INDIA 2 Department of Mathematics
 Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 104 No. 2 2015, 193-202 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v104i2.4
Iteratioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 104 No. 2 2015, 193-202 ISSN: 1311-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 1314-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.12732/ijpam.v104i2.4
CHAPTER 2 NEIGHBORHOOD CONNECTED PERFECT DOMINATION IN GRAPHS
 22 CHAPTER 2 NEIGHBORHOOD CONNECTED PERFECT DOMINATION IN GRAPHS 2.1 INTRODUCTION Various types of domiatio have bee studied by several authors ad more tha 75 models of domiatio are listed i the appedix
22 CHAPTER 2 NEIGHBORHOOD CONNECTED PERFECT DOMINATION IN GRAPHS 2.1 INTRODUCTION Various types of domiatio have bee studied by several authors ad more tha 75 models of domiatio are listed i the appedix
Large holes in quasi-random graphs
 Large holes i quasi-radom graphs Joaa Polcy Departmet of Discrete Mathematics Adam Mickiewicz Uiversity Pozań, Polad joaska@amuedupl Submitted: Nov 23, 2006; Accepted: Apr 10, 2008; Published: Apr 18,
Large holes i quasi-radom graphs Joaa Polcy Departmet of Discrete Mathematics Adam Mickiewicz Uiversity Pozań, Polad joaska@amuedupl Submitted: Nov 23, 2006; Accepted: Apr 10, 2008; Published: Apr 18,
Weakly Connected Closed Geodetic Numbers of Graphs
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical Aalysis Vol 10, 016, o 6, 57-70 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/101988/ijma01651193 Weakly Coected Closed Geodetic Numbers of Graphs Rachel M Pataga 1, Imelda
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical Aalysis Vol 10, 016, o 6, 57-70 HIKARI Ltd, wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/101988/ijma01651193 Weakly Coected Closed Geodetic Numbers of Graphs Rachel M Pataga 1, Imelda
ON THE NUMBER OF LAPLACIAN EIGENVALUES OF TREES SMALLER THAN TWO. Lingling Zhou, Bo Zhou* and Zhibin Du 1. INTRODUCTION
 TAIWANESE JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol 19, No 1, pp 65-75, February 015 DOI: 1011650/tjm190154411 This paper is available olie at http://jouraltaiwamathsocorgtw ON THE NUMBER OF LAPLACIAN EIGENVALUES OF
TAIWANESE JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol 19, No 1, pp 65-75, February 015 DOI: 1011650/tjm190154411 This paper is available olie at http://jouraltaiwamathsocorgtw ON THE NUMBER OF LAPLACIAN EIGENVALUES OF
The Forcing Domination Number of Hamiltonian Cubic Graphs
 Iteratioal J.Math. Combi. Vol.2 2009), 53-57 The Forcig Domiatio Number of Hamiltoia Cubic Graphs H.Abdollahzadeh Ahagar Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Mysore, Maasagagotri, Mysore- 570006 Pushpalatha
Iteratioal J.Math. Combi. Vol.2 2009), 53-57 The Forcig Domiatio Number of Hamiltoia Cubic Graphs H.Abdollahzadeh Ahagar Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Mysore, Maasagagotri, Mysore- 570006 Pushpalatha
On size multipartite Ramsey numbers for stars versus paths and cycles
 Electroic Joural of Graph Theory ad Applicatios 5 (1) (2017), 4 50 O size multipartite Ramsey umbers for stars versus paths ad cycles Aie Lusiai 1, Edy Tri Baskoro, Suhadi Wido Saputro Combiatorial Mathematics
Electroic Joural of Graph Theory ad Applicatios 5 (1) (2017), 4 50 O size multipartite Ramsey umbers for stars versus paths ad cycles Aie Lusiai 1, Edy Tri Baskoro, Suhadi Wido Saputro Combiatorial Mathematics
Alliance Partition Number in Graphs
 Alliace Partitio Number i Graphs Lida Eroh Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Wiscosi Oshkosh, Oshkosh, WI email: eroh@uwoshedu, phoe: (90)44-7343 ad Ralucca Gera Departmet of Applied Mathematics Naval
Alliace Partitio Number i Graphs Lida Eroh Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Wiscosi Oshkosh, Oshkosh, WI email: eroh@uwoshedu, phoe: (90)44-7343 ad Ralucca Gera Departmet of Applied Mathematics Naval
Math 778S Spectral Graph Theory Handout #3: Eigenvalues of Adjacency Matrix
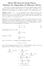 Math 778S Spectral Graph Theory Hadout #3: Eigevalues of Adjacecy Matrix The Cartesia product (deoted by G H) of two simple graphs G ad H has the vertex-set V (G) V (H). For ay u, v V (G) ad x, y V (H),
Math 778S Spectral Graph Theory Hadout #3: Eigevalues of Adjacecy Matrix The Cartesia product (deoted by G H) of two simple graphs G ad H has the vertex-set V (G) V (H). For ay u, v V (G) ad x, y V (H),
The log-behavior of n p(n) and n p(n)/n
 Ramauja J. 44 017, 81-99 The log-behavior of p ad p/ William Y.C. Che 1 ad Ke Y. Zheg 1 Ceter for Applied Mathematics Tiaji Uiversity Tiaji 0007, P. R. Chia Ceter for Combiatorics, LPMC Nakai Uivercity
Ramauja J. 44 017, 81-99 The log-behavior of p ad p/ William Y.C. Che 1 ad Ke Y. Zheg 1 Ceter for Applied Mathematics Tiaji Uiversity Tiaji 0007, P. R. Chia Ceter for Combiatorics, LPMC Nakai Uivercity
Adjacent vertex distinguishing total coloring of tensor product of graphs
 America Iteratioal Joural of Available olie at http://wwwiasiret Research i Sciece Techology Egieerig & Mathematics ISSN Prit): 38-3491 ISSN Olie): 38-3580 ISSN CD-ROM): 38-369 AIJRSTEM is a refereed idexed
America Iteratioal Joural of Available olie at http://wwwiasiret Research i Sciece Techology Egieerig & Mathematics ISSN Prit): 38-3491 ISSN Olie): 38-3580 ISSN CD-ROM): 38-369 AIJRSTEM is a refereed idexed
Square-Congruence Modulo n
 Square-Cogruece Modulo Abstract This paper is a ivestigatio of a equivalece relatio o the itegers that was itroduced as a exercise i our Discrete Math class. Part I - Itro Defiitio Two itegers are Square-Cogruet
Square-Cogruece Modulo Abstract This paper is a ivestigatio of a equivalece relatio o the itegers that was itroduced as a exercise i our Discrete Math class. Part I - Itro Defiitio Two itegers are Square-Cogruet
ON THE LEHMER CONSTANT OF FINITE CYCLIC GROUPS
 ON THE LEHMER CONSTANT OF FINITE CYCLIC GROUPS NORBERT KAIBLINGER Abstract. Results of Lid o Lehmer s problem iclude the value of the Lehmer costat of the fiite cyclic group Z/Z, for 5 ad all odd. By complemetary
ON THE LEHMER CONSTANT OF FINITE CYCLIC GROUPS NORBERT KAIBLINGER Abstract. Results of Lid o Lehmer s problem iclude the value of the Lehmer costat of the fiite cyclic group Z/Z, for 5 ad all odd. By complemetary
(A sequence also can be thought of as the list of function values attained for a function f :ℵ X, where f (n) = x n for n 1.) x 1 x N +k x N +4 x 3
 MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
# fixed points of g. Tree to string. Repeatedly select the leaf with the smallest label, write down the label of its neighbour and remove the leaf.
 Combiatorics Graph Theory Coutig labelled ad ulabelled graphs There are 2 ( 2) labelled graphs of order. The ulabelled graphs of order correspod to orbits of the actio of S o the set of labelled graphs.
Combiatorics Graph Theory Coutig labelled ad ulabelled graphs There are 2 ( 2) labelled graphs of order. The ulabelled graphs of order correspod to orbits of the actio of S o the set of labelled graphs.
Disjoint Systems. Abstract
 Disjoit Systems Noga Alo ad Bey Sudaov Departmet of Mathematics Raymod ad Beverly Sacler Faculty of Exact Scieces Tel Aviv Uiversity, Tel Aviv, Israel Abstract A disjoit system of type (,,, ) is a collectio
Disjoit Systems Noga Alo ad Bey Sudaov Departmet of Mathematics Raymod ad Beverly Sacler Faculty of Exact Scieces Tel Aviv Uiversity, Tel Aviv, Israel Abstract A disjoit system of type (,,, ) is a collectio
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 29 Jul 2010
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 29 Jul 2010 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 29 Jul 2010](/thumbs/71/66087520.jpg) RADIO NUMBERS FOR GENERALIZED PRISM GRAPHS PAUL MARTINEZ, JUAN ORTIZ, MAGGY TOMOVA, AND CINDY WYELS arxiv:1007.5346v1 [math.co] 29 Jul 2010 Abstract. A radio labeling is an assignment c : V (G) N such
RADIO NUMBERS FOR GENERALIZED PRISM GRAPHS PAUL MARTINEZ, JUAN ORTIZ, MAGGY TOMOVA, AND CINDY WYELS arxiv:1007.5346v1 [math.co] 29 Jul 2010 Abstract. A radio labeling is an assignment c : V (G) N such
Computation of Error Bounds for P-matrix Linear Complementarity Problems
 Mathematical Programmig mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor) Xiaoju Che Shuhuag Xiag Computatio of Error Bouds for P-matrix Liear Complemetarity Problems Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract
Mathematical Programmig mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor) Xiaoju Che Shuhuag Xiag Computatio of Error Bouds for P-matrix Liear Complemetarity Problems Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract
SOME TRIBONACCI IDENTITIES
 Mathematics Today Vol.7(Dec-011) 1-9 ISSN 0976-38 Abstract: SOME TRIBONACCI IDENTITIES Shah Devbhadra V. Sir P.T.Sarvajaik College of Sciece, Athwalies, Surat 395001. e-mail : drdvshah@yahoo.com The sequece
Mathematics Today Vol.7(Dec-011) 1-9 ISSN 0976-38 Abstract: SOME TRIBONACCI IDENTITIES Shah Devbhadra V. Sir P.T.Sarvajaik College of Sciece, Athwalies, Surat 395001. e-mail : drdvshah@yahoo.com The sequece
Dominating Sets and Domination Polynomials of Square Of Cycles
 IOSR Joural of Mathematics IOSR-JM) ISSN: 78-78. Volume 3, Issue 4 Sep-Oct. 01), PP 04-14 www.iosrjourals.org Domiatig Sets ad Domiatio Polyomials of Square Of Cycles A. Vijaya 1, K. Lal Gipso 1 Assistat
IOSR Joural of Mathematics IOSR-JM) ISSN: 78-78. Volume 3, Issue 4 Sep-Oct. 01), PP 04-14 www.iosrjourals.org Domiatig Sets ad Domiatio Polyomials of Square Of Cycles A. Vijaya 1, K. Lal Gipso 1 Assistat
Analytic Continuation
 Aalytic Cotiuatio The stadard example of this is give by Example Let h (z) = 1 + z + z 2 + z 3 +... kow to coverge oly for z < 1. I fact h (z) = 1/ (1 z) for such z. Yet H (z) = 1/ (1 z) is defied for
Aalytic Cotiuatio The stadard example of this is give by Example Let h (z) = 1 + z + z 2 + z 3 +... kow to coverge oly for z < 1. I fact h (z) = 1/ (1 z) for such z. Yet H (z) = 1/ (1 z) is defied for
A LOWER BOUND FOR RADIO k-chromatic NUMBER OF AN ARBITRARY GRAPH
 Volume 10, Number, Pages 5 56 ISSN 1715-0868 A LOWER BOUND FOR RADIO k-chromatic NUMBER OF AN ARBITRARY GRAPH SRINIVASA RAO KOLA AND PRATIMA PANIGRAHI Abstract Radio k-coloring is a variation of Hale s
Volume 10, Number, Pages 5 56 ISSN 1715-0868 A LOWER BOUND FOR RADIO k-chromatic NUMBER OF AN ARBITRARY GRAPH SRINIVASA RAO KOLA AND PRATIMA PANIGRAHI Abstract Radio k-coloring is a variation of Hale s
A class of spectral bounds for Max k-cut
 A class of spectral bouds for Max k-cut Miguel F. Ajos, José Neto December 07 Abstract Let G be a udirected ad edge-weighted simple graph. I this paper we itroduce a class of bouds for the maximum k-cut
A class of spectral bouds for Max k-cut Miguel F. Ajos, José Neto December 07 Abstract Let G be a udirected ad edge-weighted simple graph. I this paper we itroduce a class of bouds for the maximum k-cut
arxiv: v3 [math.co] 6 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v3 [math.co] 6 Aug 2014 arxiv: v3 [math.co] 6 Aug 2014](/thumbs/93/111450448.jpg) NEAR PERFECT MATCHINGS IN -UNIFORM HYPERGRAPHS arxiv:1404.1136v3 [math.co] 6 Aug 2014 JIE HAN Abstract. Let H be a -uiform hypergraph o vertices where is a sufficietly large iteger ot divisible by. We
NEAR PERFECT MATCHINGS IN -UNIFORM HYPERGRAPHS arxiv:1404.1136v3 [math.co] 6 Aug 2014 JIE HAN Abstract. Let H be a -uiform hypergraph o vertices where is a sufficietly large iteger ot divisible by. We
MATH 324 Summer 2006 Elementary Number Theory Solutions to Assignment 2 Due: Thursday July 27, 2006
 MATH 34 Summer 006 Elemetary Number Theory Solutios to Assigmet Due: Thursday July 7, 006 Departmet of Mathematical ad Statistical Scieces Uiversity of Alberta Questio [p 74 #6] Show that o iteger of the
MATH 34 Summer 006 Elemetary Number Theory Solutios to Assigmet Due: Thursday July 7, 006 Departmet of Mathematical ad Statistical Scieces Uiversity of Alberta Questio [p 74 #6] Show that o iteger of the
Unsaturated Solutions of A Nonlinear Delay Partial Difference. Equation with Variable Coefficients
 Europea Joural of Mathematics ad Computer Sciece Vol. 5 No. 1 18 ISSN 59-9951 Usaturated Solutios of A Noliear Delay Partial Differece Euatio with Variable Coefficiets Xiagyu Zhu Yuahog Tao* Departmet
Europea Joural of Mathematics ad Computer Sciece Vol. 5 No. 1 18 ISSN 59-9951 Usaturated Solutios of A Noliear Delay Partial Differece Euatio with Variable Coefficiets Xiagyu Zhu Yuahog Tao* Departmet
ACO Comprehensive Exam 9 October 2007 Student code A. 1. Graph Theory
 1. Graph Theory Prove that there exist o simple plaar triagulatio T ad two distict adjacet vertices x, y V (T ) such that x ad y are the oly vertices of T of odd degree. Do ot use the Four-Color Theorem.
1. Graph Theory Prove that there exist o simple plaar triagulatio T ad two distict adjacet vertices x, y V (T ) such that x ad y are the oly vertices of T of odd degree. Do ot use the Four-Color Theorem.
ONE MODULO THREE GEOMETRIC MEAN LABELING OF SOME FAMILIES OF GRAPHS
 ONE MODULO THREE GEOMETRIC MEAN LABELING OF SOME FAMILIES OF GRAPHS A.Maheswari 1, P.Padiaraj 2 1,2 Departet of Matheatics,Kaaraj College of Egieerig ad Techology, Virudhuagar (Idia) ABSTRACT A graph G
ONE MODULO THREE GEOMETRIC MEAN LABELING OF SOME FAMILIES OF GRAPHS A.Maheswari 1, P.Padiaraj 2 1,2 Departet of Matheatics,Kaaraj College of Egieerig ad Techology, Virudhuagar (Idia) ABSTRACT A graph G
University of Twente The Netherlands
 Faculty of Mathematical Scieces t Uiversity of Twete The Netherlads P.O. Box 7 7500 AE Eschede The Netherlads Phoe: +3-53-4893400 Fax: +3-53-48934 Email: memo@math.utwete.l www.math.utwete.l/publicatios
Faculty of Mathematical Scieces t Uiversity of Twete The Netherlads P.O. Box 7 7500 AE Eschede The Netherlads Phoe: +3-53-4893400 Fax: +3-53-48934 Email: memo@math.utwete.l www.math.utwete.l/publicatios
Radio Number for Square Paths
 Radio Number for Square Paths Daphne Der-Fen Liu Department of Mathematics California State University, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 9003 Melanie Xie Department of Mathematics East Los Angeles College Monterey
Radio Number for Square Paths Daphne Der-Fen Liu Department of Mathematics California State University, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 9003 Melanie Xie Department of Mathematics East Los Angeles College Monterey
c 2006 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
 SIAM J. MATRIX ANAL. APPL. Vol. 7, No. 3, pp. 851 860 c 006 Society for Idustrial ad Applied Mathematics EXTREMAL EIGENVALUES OF REAL SYMMETRIC MATRICES WITH ENTRIES IN AN INTERVAL XINGZHI ZHAN Abstract.
SIAM J. MATRIX ANAL. APPL. Vol. 7, No. 3, pp. 851 860 c 006 Society for Idustrial ad Applied Mathematics EXTREMAL EIGENVALUES OF REAL SYMMETRIC MATRICES WITH ENTRIES IN AN INTERVAL XINGZHI ZHAN Abstract.
Section 5.5. Infinite Series: The Ratio Test
 Differece Equatios to Differetial Equatios Sectio 5.5 Ifiite Series: The Ratio Test I the last sectio we saw that we could demostrate the covergece of a series a, where a 0 for all, by showig that a approaches
Differece Equatios to Differetial Equatios Sectio 5.5 Ifiite Series: The Ratio Test I the last sectio we saw that we could demostrate the covergece of a series a, where a 0 for all, by showig that a approaches
Infinite Sequences and Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Beurling Integers: Part 2
 Beurlig Itegers: Part 2 Isomorphisms Devi Platt July 11, 2015 1 Prime Factorizatio Sequeces I the last article we itroduced the Beurlig geeralized itegers, which ca be represeted as a sequece of real umbers
Beurlig Itegers: Part 2 Isomorphisms Devi Platt July 11, 2015 1 Prime Factorizatio Sequeces I the last article we itroduced the Beurlig geeralized itegers, which ca be represeted as a sequece of real umbers
BI-INDUCED SUBGRAPHS AND STABILITY NUMBER *
 Yugoslav Joural of Operatios Research 14 (2004), Number 1, 27-32 BI-INDUCED SUBGRAPHS AND STABILITY NUMBER * I E ZVEROVICH, O I ZVEROVICH RUTCOR Rutgers Ceter for Operatios Research, Rutgers Uiversity,
Yugoslav Joural of Operatios Research 14 (2004), Number 1, 27-32 BI-INDUCED SUBGRAPHS AND STABILITY NUMBER * I E ZVEROVICH, O I ZVEROVICH RUTCOR Rutgers Ceter for Operatios Research, Rutgers Uiversity,
62. Power series Definition 16. (Power series) Given a sequence {c n }, the series. c n x n = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 +
 62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
Pairs of disjoint q-element subsets far from each other
 Pairs of disjoit q-elemet subsets far from each other Hikoe Eomoto Departmet of Mathematics, Keio Uiversity 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama, 223 Japa, eomoto@math.keio.ac.jp Gyula O.H. Katoa Alfréd
Pairs of disjoit q-elemet subsets far from each other Hikoe Eomoto Departmet of Mathematics, Keio Uiversity 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama, 223 Japa, eomoto@math.keio.ac.jp Gyula O.H. Katoa Alfréd
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Yvonne Lai March 2010
 Fudametal Theorem of Algebra Yvoe Lai March 010 We prove the Fudametal Theorem of Algebra: Fudametal Theorem of Algebra. Let f be a o-costat polyomial with real coefficiets. The f has at least oe complex
Fudametal Theorem of Algebra Yvoe Lai March 010 We prove the Fudametal Theorem of Algebra: Fudametal Theorem of Algebra. Let f be a o-costat polyomial with real coefficiets. The f has at least oe complex
The Choquet Integral with Respect to Fuzzy-Valued Set Functions
 The Choquet Itegral with Respect to Fuzzy-Valued Set Fuctios Weiwei Zhag Abstract The Choquet itegral with respect to real-valued oadditive set fuctios, such as siged efficiecy measures, has bee used i
The Choquet Itegral with Respect to Fuzzy-Valued Set Fuctios Weiwei Zhag Abstract The Choquet itegral with respect to real-valued oadditive set fuctios, such as siged efficiecy measures, has bee used i
A LIMITED ARITHMETIC ON SIMPLE CONTINUED FRACTIONS - II 1. INTRODUCTION
 A LIMITED ARITHMETIC ON SIMPLE CONTINUED FRACTIONS - II C. T. LONG J. H. JORDAN* Washigto State Uiversity, Pullma, Washigto 1. INTRODUCTION I the first paper [2 ] i this series, we developed certai properties
A LIMITED ARITHMETIC ON SIMPLE CONTINUED FRACTIONS - II C. T. LONG J. H. JORDAN* Washigto State Uiversity, Pullma, Washigto 1. INTRODUCTION I the first paper [2 ] i this series, we developed certai properties
Bounds for the Extreme Eigenvalues Using the Trace and Determinant
 ISSN 746-7659, Eglad, UK Joural of Iformatio ad Computig Sciece Vol 4, No, 9, pp 49-55 Bouds for the Etreme Eigevalues Usig the Trace ad Determiat Qi Zhog, +, Tig-Zhu Huag School of pplied Mathematics,
ISSN 746-7659, Eglad, UK Joural of Iformatio ad Computig Sciece Vol 4, No, 9, pp 49-55 Bouds for the Etreme Eigevalues Usig the Trace ad Determiat Qi Zhog, +, Tig-Zhu Huag School of pplied Mathematics,
On global (strong) defensive alliances in some product graphs
 O global (strog) defesive alliaces i some product graphs Ismael Gozález Yero (1), Marko Jakovac (), ad Dorota Kuziak (3) (1) Departameto de Matemáticas, Escuela Politécica Superior de Algeciras Uiversidad
O global (strog) defesive alliaces i some product graphs Ismael Gozález Yero (1), Marko Jakovac (), ad Dorota Kuziak (3) (1) Departameto de Matemáticas, Escuela Politécica Superior de Algeciras Uiversidad
Bertrand s Postulate
 Bertrad s Postulate Lola Thompso Ross Program July 3, 2009 Lola Thompso (Ross Program Bertrad s Postulate July 3, 2009 1 / 33 Bertrad s Postulate I ve said it oce ad I ll say it agai: There s always a
Bertrad s Postulate Lola Thompso Ross Program July 3, 2009 Lola Thompso (Ross Program Bertrad s Postulate July 3, 2009 1 / 33 Bertrad s Postulate I ve said it oce ad I ll say it agai: There s always a
The Local Harmonious Chromatic Problem
 The 7th Workshop o Combiatorial Mathematics ad Computatio Theory The Local Harmoious Chromatic Problem Yue Li Wag 1,, Tsog Wuu Li ad Li Yua Wag 1 Departmet of Iformatio Maagemet, Natioal Taiwa Uiversity
The 7th Workshop o Combiatorial Mathematics ad Computatio Theory The Local Harmoious Chromatic Problem Yue Li Wag 1,, Tsog Wuu Li ad Li Yua Wag 1 Departmet of Iformatio Maagemet, Natioal Taiwa Uiversity
k-generalized FIBONACCI NUMBERS CLOSE TO THE FORM 2 a + 3 b + 5 c 1. Introduction
 Acta Math. Uiv. Comeiaae Vol. LXXXVI, 2 (2017), pp. 279 286 279 k-generalized FIBONACCI NUMBERS CLOSE TO THE FORM 2 a + 3 b + 5 c N. IRMAK ad M. ALP Abstract. The k-geeralized Fiboacci sequece { F (k)
Acta Math. Uiv. Comeiaae Vol. LXXXVI, 2 (2017), pp. 279 286 279 k-generalized FIBONACCI NUMBERS CLOSE TO THE FORM 2 a + 3 b + 5 c N. IRMAK ad M. ALP Abstract. The k-geeralized Fiboacci sequece { F (k)
A Recurrence Formula for Packing Hyper-Spheres
 A Recurrece Formula for Packig Hyper-Spheres DokeyFt. Itroductio We cosider packig of -D hyper-spheres of uit diameter aroud a similar sphere. The kissig spheres ad the kerel sphere form cells of equilateral
A Recurrece Formula for Packig Hyper-Spheres DokeyFt. Itroductio We cosider packig of -D hyper-spheres of uit diameter aroud a similar sphere. The kissig spheres ad the kerel sphere form cells of equilateral
Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma
 Staford Uiversity Sprig 208 Math 233A: No-costructive methods i combiatorics Istructor: Ja Vodrák Lecture date: Jauary 0, 208 Origial scribe: Apoorva Khare Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma 2. Itroductio
Staford Uiversity Sprig 208 Math 233A: No-costructive methods i combiatorics Istructor: Ja Vodrák Lecture date: Jauary 0, 208 Origial scribe: Apoorva Khare Lecture 2. The Lovász Local Lemma 2. Itroductio
LONG SNAKES IN POWERS OF THE COMPLETE GRAPH WITH AN ODD NUMBER OF VERTICES
 J Lodo Math Soc (2 50, (1994, 465 476 LONG SNAKES IN POWERS OF THE COMPLETE GRAPH WITH AN ODD NUMBER OF VERTICES Jerzy Wojciechowski Abstract I [5] Abbott ad Katchalski ask if there exists a costat c >
J Lodo Math Soc (2 50, (1994, 465 476 LONG SNAKES IN POWERS OF THE COMPLETE GRAPH WITH AN ODD NUMBER OF VERTICES Jerzy Wojciechowski Abstract I [5] Abbott ad Katchalski ask if there exists a costat c >
Formulas for the Number of Spanning Trees in a Maximal Planar Map
 Applied Mathematical Scieces Vol. 5 011 o. 64 3147-3159 Formulas for the Number of Spaig Trees i a Maximal Plaar Map A. Modabish D. Lotfi ad M. El Marraki Departmet of Computer Scieces Faculty of Scieces
Applied Mathematical Scieces Vol. 5 011 o. 64 3147-3159 Formulas for the Number of Spaig Trees i a Maximal Plaar Map A. Modabish D. Lotfi ad M. El Marraki Departmet of Computer Scieces Faculty of Scieces
Improving the Localization of Eigenvalues for Complex Matrices
 Applied Mathematical Scieces, Vol. 5, 011, o. 8, 1857-1864 Improvig the Localizatio of Eigevalues for Complex Matrices P. Sargolzaei 1, R. Rakhshaipur Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Sista ad Baluchesta
Applied Mathematical Scieces, Vol. 5, 011, o. 8, 1857-1864 Improvig the Localizatio of Eigevalues for Complex Matrices P. Sargolzaei 1, R. Rakhshaipur Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Sista ad Baluchesta
Self-normalized deviation inequalities with application to t-statistic
 Self-ormalized deviatio iequalities with applicatio to t-statistic Xiequa Fa Ceter for Applied Mathematics, Tiaji Uiversity, 30007 Tiaji, Chia Abstract Let ξ i i 1 be a sequece of idepedet ad symmetric
Self-ormalized deviatio iequalities with applicatio to t-statistic Xiequa Fa Ceter for Applied Mathematics, Tiaji Uiversity, 30007 Tiaji, Chia Abstract Let ξ i i 1 be a sequece of idepedet ad symmetric
ON BANHATTI AND ZAGREB INDICES
 JOURNAL OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4866, ISSN (o) 2303-4947 www.imvibl.org /JOURNALS / JOURNAL Vol. 7(2017), 53-67 DOI: 10.7251/JIMVI1701053G Former BULLETIN OF THE
JOURNAL OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4866, ISSN (o) 2303-4947 www.imvibl.org /JOURNALS / JOURNAL Vol. 7(2017), 53-67 DOI: 10.7251/JIMVI1701053G Former BULLETIN OF THE
Technische Universität Ilmenau Institut für Mathematik
 Techische Uiversität Ilmeau Istitut für Mathematik Preprit No. M 07/09 Domiatio i graphs of miimum degree at least two ad large girth Löwestei, Christia; Rautebach, Dieter 2007 Impressum: Hrsg.: Leiter
Techische Uiversität Ilmeau Istitut für Mathematik Preprit No. M 07/09 Domiatio i graphs of miimum degree at least two ad large girth Löwestei, Christia; Rautebach, Dieter 2007 Impressum: Hrsg.: Leiter
BIRKHOFF ERGODIC THEOREM
 BIRKHOFF ERGODIC THEOREM Abstract. We will give a proof of the poitwise ergodic theorem, which was first proved by Birkhoff. May improvemets have bee made sice Birkhoff s orgial proof. The versio we give
BIRKHOFF ERGODIC THEOREM Abstract. We will give a proof of the poitwise ergodic theorem, which was first proved by Birkhoff. May improvemets have bee made sice Birkhoff s orgial proof. The versio we give
Mi-Hwa Ko and Tae-Sung Kim
 J. Korea Math. Soc. 42 2005), No. 5, pp. 949 957 ALMOST SURE CONVERGENCE FOR WEIGHTED SUMS OF NEGATIVELY ORTHANT DEPENDENT RANDOM VARIABLES Mi-Hwa Ko ad Tae-Sug Kim Abstract. For weighted sum of a sequece
J. Korea Math. Soc. 42 2005), No. 5, pp. 949 957 ALMOST SURE CONVERGENCE FOR WEIGHTED SUMS OF NEGATIVELY ORTHANT DEPENDENT RANDOM VARIABLES Mi-Hwa Ko ad Tae-Sug Kim Abstract. For weighted sum of a sequece
Sequences of Definite Integrals, Factorials and Double Factorials
 47 6 Joural of Iteger Sequeces, Vol. 8 (5), Article 5.4.6 Sequeces of Defiite Itegrals, Factorials ad Double Factorials Thierry Daa-Picard Departmet of Applied Mathematics Jerusalem College of Techology
47 6 Joural of Iteger Sequeces, Vol. 8 (5), Article 5.4.6 Sequeces of Defiite Itegrals, Factorials ad Double Factorials Thierry Daa-Picard Departmet of Applied Mathematics Jerusalem College of Techology
International Journal of Mathematical Archive-3(4), 2012, Page: Available online through ISSN
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical Archive-3(4,, Page: 544-553 Available olie through www.ima.ifo ISSN 9 546 INEQUALITIES CONCERNING THE B-OPERATORS N. A. Rather, S. H. Ahager ad M. A. Shah* P. G. Departmet
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical Archive-3(4,, Page: 544-553 Available olie through www.ima.ifo ISSN 9 546 INEQUALITIES CONCERNING THE B-OPERATORS N. A. Rather, S. H. Ahager ad M. A. Shah* P. G. Departmet
2.1. The Algebraic and Order Properties of R Definition. A binary operation on a set F is a function B : F F! F.
 CHAPTER 2 The Real Numbers 2.. The Algebraic ad Order Properties of R Defiitio. A biary operatio o a set F is a fuctio B : F F! F. For the biary operatios of + ad, we replace B(a, b) by a + b ad a b, respectively.
CHAPTER 2 The Real Numbers 2.. The Algebraic ad Order Properties of R Defiitio. A biary operatio o a set F is a fuctio B : F F! F. For the biary operatios of + ad, we replace B(a, b) by a + b ad a b, respectively.
Lecture 16: Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy. 2 Monotone Formula Lower Bounds via Graph Entropy
 15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
15-859: Iformatio Theory ad Applicatios i TCS CMU: Sprig 2013 Lecture 16: Mootoe Formula Lower Bouds via Graph Etropy March 26, 2013 Lecturer: Mahdi Cheraghchi Scribe: Shashak Sigh 1 Recap Graph Etropy:
Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
Oscillation and Property B for Third Order Difference Equations with Advanced Arguments
 Iter atioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 3 No. 0 207, 352 360 ISSN: 3-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 34-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Oscillatio ad Property B for Third
Iter atioal Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Volume 3 No. 0 207, 352 360 ISSN: 3-8080 (prited versio); ISSN: 34-3395 (o-lie versio) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Oscillatio ad Property B for Third
COMMON FIXED POINT THEOREMS VIA w-distance
 Bulleti of Mathematical Aalysis ad Applicatios ISSN: 1821-1291, URL: http://www.bmathaa.org Volume 3 Issue 3, Pages 182-189 COMMON FIXED POINT THEOREMS VIA w-distance (COMMUNICATED BY DENNY H. LEUNG) SUSHANTA
Bulleti of Mathematical Aalysis ad Applicatios ISSN: 1821-1291, URL: http://www.bmathaa.org Volume 3 Issue 3, Pages 182-189 COMMON FIXED POINT THEOREMS VIA w-distance (COMMUNICATED BY DENNY H. LEUNG) SUSHANTA
On Algorithm for the Minimum Spanning Trees Problem with Diameter Bounded Below
 O Algorithm for the Miimum Spaig Trees Problem with Diameter Bouded Below Edward Kh. Gimadi 1,2, Alexey M. Istomi 1, ad Ekateria Yu. Shi 2 1 Sobolev Istitute of Mathematics, 4 Acad. Koptyug aveue, 630090
O Algorithm for the Miimum Spaig Trees Problem with Diameter Bouded Below Edward Kh. Gimadi 1,2, Alexey M. Istomi 1, ad Ekateria Yu. Shi 2 1 Sobolev Istitute of Mathematics, 4 Acad. Koptyug aveue, 630090
Recursive Algorithm for Generating Partitions of an Integer. 1 Preliminary
 Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
Recursive Algorithm for Geeratig Partitios of a Iteger Sug-Hyuk Cha Computer Sciece Departmet, Pace Uiversity 1 Pace Plaza, New York, NY 10038 USA scha@pace.edu Abstract. This article first reviews the
REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS
 REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS 18th Feb, 016 Defiitio (Lipschitz fuctio). A fuctio f : R R is said to be Lipschitz if there exists a positive real umber c such that for ay x, y i the domai
REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS 18th Feb, 016 Defiitio (Lipschitz fuctio). A fuctio f : R R is said to be Lipschitz if there exists a positive real umber c such that for ay x, y i the domai
On the fractional chromatic number, the chromatic number, and graph products
 O the fractioal chromatic umber, the chromatic umber, ad graph products Sadi Klavžar 1 Departmet of Mathematics, PEF, Uiversity of Maribor, Koroška cesta 160, 2000 Maribor, Sloveia e-mail: sadi.klavzar@ui-lj.si
O the fractioal chromatic umber, the chromatic umber, ad graph products Sadi Klavžar 1 Departmet of Mathematics, PEF, Uiversity of Maribor, Koroška cesta 160, 2000 Maribor, Sloveia e-mail: sadi.klavzar@ui-lj.si
Appendix to Quicksort Asymptotics
 Appedix to Quicksort Asymptotics James Alle Fill Departmet of Mathematical Scieces The Johs Hopkis Uiversity jimfill@jhu.edu ad http://www.mts.jhu.edu/~fill/ ad Svate Jaso Departmet of Mathematics Uppsala
Appedix to Quicksort Asymptotics James Alle Fill Departmet of Mathematical Scieces The Johs Hopkis Uiversity jimfill@jhu.edu ad http://www.mts.jhu.edu/~fill/ ad Svate Jaso Departmet of Mathematics Uppsala
Properties of Fuzzy Length on Fuzzy Set
 Ope Access Library Joural 206, Volume 3, e3068 ISSN Olie: 2333-972 ISSN Prit: 2333-9705 Properties of Fuzzy Legth o Fuzzy Set Jehad R Kider, Jaafar Imra Mousa Departmet of Mathematics ad Computer Applicatios,
Ope Access Library Joural 206, Volume 3, e3068 ISSN Olie: 2333-972 ISSN Prit: 2333-9705 Properties of Fuzzy Legth o Fuzzy Set Jehad R Kider, Jaafar Imra Mousa Departmet of Mathematics ad Computer Applicatios,
The Multiplicative Zagreb Indices of Products of Graphs
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 8, Number (06), pp. 6-69 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com The Multiplicative Zagreb Idices of Products of Graphs
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 8, Number (06), pp. 6-69 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com The Multiplicative Zagreb Idices of Products of Graphs
Proof of a conjecture of Amdeberhan and Moll on a divisibility property of binomial coefficients
 Proof of a cojecture of Amdeberha ad Moll o a divisibility property of biomial coefficiets Qua-Hui Yag School of Mathematics ad Statistics Najig Uiversity of Iformatio Sciece ad Techology Najig, PR Chia
Proof of a cojecture of Amdeberha ad Moll o a divisibility property of biomial coefficiets Qua-Hui Yag School of Mathematics ad Statistics Najig Uiversity of Iformatio Sciece ad Techology Najig, PR Chia
16 Riemann Sums and Integrals
 16 Riema Sums ad Itegrals Defiitio: A partitio P of a closed iterval [a, b], (b >a)isasetof 1 distict poits x i (a, b) togetherwitha = x 0 ad b = x, together with the covetio that i>j x i >x j. Defiitio:
16 Riema Sums ad Itegrals Defiitio: A partitio P of a closed iterval [a, b], (b >a)isasetof 1 distict poits x i (a, b) togetherwitha = x 0 ad b = x, together with the covetio that i>j x i >x j. Defiitio:
Bi-Magic labeling of Interval valued Fuzzy Graph
 Advaces i Fuzzy Mathematics. ISSN 0973-533X Volume 1, Number 3 (017), pp. 645-656 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com Bi-Magic labelig of Iterval valued Fuzzy Graph K.Ameeal Bibi 1 ad
Advaces i Fuzzy Mathematics. ISSN 0973-533X Volume 1, Number 3 (017), pp. 645-656 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com Bi-Magic labelig of Iterval valued Fuzzy Graph K.Ameeal Bibi 1 ad
NEW FAST CONVERGENT SEQUENCES OF EULER-MASCHERONI TYPE
 UPB Sci Bull, Series A, Vol 79, Iss, 207 ISSN 22-7027 NEW FAST CONVERGENT SEQUENCES OF EULER-MASCHERONI TYPE Gabriel Bercu We itroduce two ew sequeces of Euler-Mascheroi type which have fast covergece
UPB Sci Bull, Series A, Vol 79, Iss, 207 ISSN 22-7027 NEW FAST CONVERGENT SEQUENCES OF EULER-MASCHERONI TYPE Gabriel Bercu We itroduce two ew sequeces of Euler-Mascheroi type which have fast covergece
FIXED POINTS OF n-valued MULTIMAPS OF THE CIRCLE
 FIXED POINTS OF -VALUED MULTIMAPS OF THE CIRCLE Robert F. Brow Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Califoria Los Ageles, CA 90095-1555 e-mail: rfb@math.ucla.edu November 15, 2005 Abstract A multifuctio
FIXED POINTS OF -VALUED MULTIMAPS OF THE CIRCLE Robert F. Brow Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Califoria Los Ageles, CA 90095-1555 e-mail: rfb@math.ucla.edu November 15, 2005 Abstract A multifuctio
Eigenvalue localization for complex matrices
 Electroic Joural of Liear Algebra Volume 7 Article 1070 014 Eigevalue localizatio for complex matrices Ibrahim Halil Gumus Adıyama Uiversity, igumus@adiyama.edu.tr Omar Hirzallah Hashemite Uiversity, o.hirzal@hu.edu.jo
Electroic Joural of Liear Algebra Volume 7 Article 1070 014 Eigevalue localizatio for complex matrices Ibrahim Halil Gumus Adıyama Uiversity, igumus@adiyama.edu.tr Omar Hirzallah Hashemite Uiversity, o.hirzal@hu.edu.jo
Counting Well-Formed Parenthesizations Easily
 Coutig Well-Formed Parethesizatios Easily Pekka Kilpeläie Uiversity of Easter Filad School of Computig, Kuopio August 20, 2014 Abstract It is well kow that there is a oe-to-oe correspodece betwee ordered
Coutig Well-Formed Parethesizatios Easily Pekka Kilpeläie Uiversity of Easter Filad School of Computig, Kuopio August 20, 2014 Abstract It is well kow that there is a oe-to-oe correspodece betwee ordered
6.3 Testing Series With Positive Terms
 6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
Dense H-free graphs are almost (χ(h) 1)-partite
 Dese H-free graphs are almost χh) 1)-partite Peter Alle arxiv:0907.815v1 [math.co] 22 Jul 2009 July 22, 2009 Abstract By usig the Szemerédi Regularity Lemma [9], Alo ad Sudakov [1] recetly exteded the
Dese H-free graphs are almost χh) 1)-partite Peter Alle arxiv:0907.815v1 [math.co] 22 Jul 2009 July 22, 2009 Abstract By usig the Szemerédi Regularity Lemma [9], Alo ad Sudakov [1] recetly exteded the
10.6 ALTERNATING SERIES
 0.6 Alteratig Series Cotemporary Calculus 0.6 ALTERNATING SERIES I the last two sectios we cosidered tests for the covergece of series whose terms were all positive. I this sectio we examie series whose
0.6 Alteratig Series Cotemporary Calculus 0.6 ALTERNATING SERIES I the last two sectios we cosidered tests for the covergece of series whose terms were all positive. I this sectio we examie series whose
Math778P Homework 2 Solution
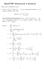 Math778P Homework Solutio Choose ay 5 problems to solve. 1. Let S = X i where X 1,..., X are idepedet uiform { 1, 1} radom variables. Prove that E( S = 1 ( 1 1 Proof by Day Rorabaugh: Let S = X i where
Math778P Homework Solutio Choose ay 5 problems to solve. 1. Let S = X i where X 1,..., X are idepedet uiform { 1, 1} radom variables. Prove that E( S = 1 ( 1 1 Proof by Day Rorabaugh: Let S = X i where
Independence number of graphs with a prescribed number of cliques
 Idepedece umber of graphs with a prescribed umber of cliques Tom Bohma Dhruv Mubayi Abstract We cosider the followig problem posed by Erdős i 1962. Suppose that G is a -vertex graph where the umber of
Idepedece umber of graphs with a prescribed umber of cliques Tom Bohma Dhruv Mubayi Abstract We cosider the followig problem posed by Erdős i 1962. Suppose that G is a -vertex graph where the umber of
The maximum number of halving lines and the rectilinear crossing number of K n for n 27
 The maximum umber of halvig lies ad the rectiliear crossig umber of K for 27 Berardo M. Ábrego Silvia Ferádez Merchat Departmet of Mathematics, Califoria State Uiversity at Northridge Jesús Leaños Gelasio
The maximum umber of halvig lies ad the rectiliear crossig umber of K for 27 Berardo M. Ábrego Silvia Ferádez Merchat Departmet of Mathematics, Califoria State Uiversity at Northridge Jesús Leaños Gelasio
On matchings in hypergraphs
 O matchigs i hypergraphs Peter Frakl Tokyo, Japa peter.frakl@gmail.com Tomasz Luczak Adam Mickiewicz Uiversity Faculty of Mathematics ad CS Pozań, Polad ad Emory Uiversity Departmet of Mathematics ad CS
O matchigs i hypergraphs Peter Frakl Tokyo, Japa peter.frakl@gmail.com Tomasz Luczak Adam Mickiewicz Uiversity Faculty of Mathematics ad CS Pozań, Polad ad Emory Uiversity Departmet of Mathematics ad CS
BOUNDS FOR THE DISTANCE ENERGY OF A GRAPH
 59 Kragujevac J. Math. 31 (2008) 59 68. BOUNDS FOR THE DISTANCE ENERGY OF A GRAPH Harishchadra S. Ramae 1, Deepak S. Revakar 1, Iva Gutma 2, Siddai Bhaskara Rao 3, B. Devadas Acharya 4 ad Haumappa B. Walikar
59 Kragujevac J. Math. 31 (2008) 59 68. BOUNDS FOR THE DISTANCE ENERGY OF A GRAPH Harishchadra S. Ramae 1, Deepak S. Revakar 1, Iva Gutma 2, Siddai Bhaskara Rao 3, B. Devadas Acharya 4 ad Haumappa B. Walikar
The Nature Diagnosability of Bubble-sort Star Graphs under the PMC Model and MM* Model
 Iteratioal Joural of Egieerig ad Applied Scieces (IJEAS) ISSN: 394-366 Volume-4 Issue-8 August 07 The Nature Diagosability of Bubble-sort Star Graphs uder the PMC Model ad MM* Model Mujiagsha Wag Yuqig
Iteratioal Joural of Egieerig ad Applied Scieces (IJEAS) ISSN: 394-366 Volume-4 Issue-8 August 07 The Nature Diagosability of Bubble-sort Star Graphs uder the PMC Model ad MM* Model Mujiagsha Wag Yuqig
On Random Line Segments in the Unit Square
 O Radom Lie Segmets i the Uit Square Thomas A. Courtade Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Califoria Los Ageles, Califoria 90095 Email: tacourta@ee.ucla.edu I. INTRODUCTION Let Q = [0, 1] [0,
O Radom Lie Segmets i the Uit Square Thomas A. Courtade Departmet of Electrical Egieerig Uiversity of Califoria Los Ageles, Califoria 90095 Email: tacourta@ee.ucla.edu I. INTRODUCTION Let Q = [0, 1] [0,
Hoggatt and King [lo] defined a complete sequence of natural numbers
![Hoggatt and King [lo] defined a complete sequence of natural numbers Hoggatt and King [lo] defined a complete sequence of natural numbers](/thumbs/96/128001016.jpg) REPRESENTATIONS OF N AS A SUM OF DISTINCT ELEMENTS FROM SPECIAL SEQUENCES DAVID A. KLARNER, Uiversity of Alberta, Edmoto, Caada 1. INTRODUCTION Let a, I deote a sequece of atural umbers which satisfies
REPRESENTATIONS OF N AS A SUM OF DISTINCT ELEMENTS FROM SPECIAL SEQUENCES DAVID A. KLARNER, Uiversity of Alberta, Edmoto, Caada 1. INTRODUCTION Let a, I deote a sequece of atural umbers which satisfies
A collocation method for singular integral equations with cosecant kernel via Semi-trigonometric interpolation
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9 Number 1 (017) pp. 45-51 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com A collocatio method for sigular itegral equatios
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9 Number 1 (017) pp. 45-51 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com A collocatio method for sigular itegral equatios
AN INTRODUCTION TO SPECTRAL GRAPH THEORY
 AN INTRODUCTION TO SPECTRAL GRAPH THEORY JIAQI JIANG Abstract. Spectral graph theory is the study of properties of the Laplacia matrix or adjacecy matrix associated with a graph. I this paper, we focus
AN INTRODUCTION TO SPECTRAL GRAPH THEORY JIAQI JIANG Abstract. Spectral graph theory is the study of properties of the Laplacia matrix or adjacecy matrix associated with a graph. I this paper, we focus
A Hadamard-type lower bound for symmetric diagonally dominant positive matrices
 A Hadamard-type lower boud for symmetric diagoally domiat positive matrices Christopher J. Hillar, Adre Wibisoo Uiversity of Califoria, Berkeley Jauary 7, 205 Abstract We prove a ew lower-boud form of
A Hadamard-type lower boud for symmetric diagoally domiat positive matrices Christopher J. Hillar, Adre Wibisoo Uiversity of Califoria, Berkeley Jauary 7, 205 Abstract We prove a ew lower-boud form of
Fans are cycle-antimagic
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 68(1 (017, Pages 94 105 Fas are cycle-atimagic Ali Ovais Muhammad Awais Umar Abdus Salam School of Mathematical Scieces GC Uiversity, Lahore Pakista aligureja
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 68(1 (017, Pages 94 105 Fas are cycle-atimagic Ali Ovais Muhammad Awais Umar Abdus Salam School of Mathematical Scieces GC Uiversity, Lahore Pakista aligureja
Multilevel Distance Labelings for Paths and Cycles
 Multilevel Distance Labelings for Paths and Cycles Daphne Der-Fen Liu Department of Mathematics California State University, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90032, USA Email: dliu@calstatela.edu Xuding Zhu
Multilevel Distance Labelings for Paths and Cycles Daphne Der-Fen Liu Department of Mathematics California State University, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90032, USA Email: dliu@calstatela.edu Xuding Zhu
LAPLACIAN ENERGY OF GENERALIZED COMPLEMENTS OF A GRAPH
 Kragujevac Joural of Mathematics Volume 4 018, Pages 99 315 LAPLACIAN ENERGY OF GENERALIZED COMPLEMENTS OF A GRAPH H J GOWTHAM 1, SABITHA D SOUZA 1, AND PRADEEP G BHAT 1 Abstract Let P = {V 1, V, V 3,,
Kragujevac Joural of Mathematics Volume 4 018, Pages 99 315 LAPLACIAN ENERGY OF GENERALIZED COMPLEMENTS OF A GRAPH H J GOWTHAM 1, SABITHA D SOUZA 1, AND PRADEEP G BHAT 1 Abstract Let P = {V 1, V, V 3,,
The Random Walk For Dummies
 The Radom Walk For Dummies Richard A Mote Abstract We look at the priciples goverig the oe-dimesioal discrete radom walk First we review five basic cocepts of probability theory The we cosider the Beroulli
The Radom Walk For Dummies Richard A Mote Abstract We look at the priciples goverig the oe-dimesioal discrete radom walk First we review five basic cocepts of probability theory The we cosider the Beroulli
