ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
|
|
|
- Darren White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot engine? Yes/no 3. (10 pt) Write the equation for the COP of Carnot refrigerator below: CO P r L H L 4. (10 pt) Write the equation for the COP of a Carnot heat pump below. COP hp H H L 5. (20pt) List the completely reversible processes of a Carnot cycle below: (A) Isothermal expansion (B) Adiabatic expansion (C) Isothermal compression (D) Adiabatic compression 6. (10 pt) Write the inequality of Clausius below: Q 0 7. (5 pt) he inequality of Clausius is consistent with the Kelvin-Planck statement of the Second Law. 8. (15 pt) Write the inequality of Clausius for an internally reversible cycle below. Q 0 9. he of an actual heat engine must be positive/zero/negative.
2 Lesson (5 pt) he entropy of a phase-change substance is found using tables. 2. (5 pt) Specific entropy of phase-changers is found in the same manner as all the other specific properties. 3. (5 pt) If s f <= s <= s g, the substance is a saturated mixture. 4. (5 pt) If s > s g, the substance is a superheated vapor. 5. (5 pt) If s < sf, the substance is a subcooled liquid. 6. (20 pt) Sketch the -s state diagram for a phase-changing substance below. Include one isobar and one constant volume process line. 7. (10 pt) If the substance is a subcooled liquid, s is approximately s f at the same temperature. 8. (5 pt) Quality is used in the same way for specific entropy as for other specific properties. 9. (10 pt) Is it possible to convert a superheated vapor to a compressed liquid with a constant entropy process? Yes/No 10. (10 pt) Is it possible to convert a superheated vapor to a compressed liquid in an isothermal process? Yes/No 11. (10 pt) Is it possible to convert a superheated vapor to a compressed liquid in an isobaric process? Yes/No 12. (10 pt) Is it possible to convert a superheated vapor to a compressed liquid in a constant volume process? Yes/No
3 Lesson (10 pt) A Mollier diagram is a h-s state diagram. 2. (10 pt) When a closed system consisting of a phase-changing substance undergoes an isobaric process such that the entropy increases, the temperature will always increase. rue/false 3. (10 pt) Ideal turbines and compressors execute constant entropy processes. 4. (10 pt) Ideal nozzles and diffusers execute constant entropy processes. 5. (10 pt) Entropy can only be transferred by heat, not work. 6. (10 pt) Heat is a form of disorganized energy while work is not. 7. (10 pt) During a constant volume process, like a rigid container, the ds equation reduces to: ds = du 8. (10 pt) During a constant pressure process, like flow through a pipe, the ds equation reduces to: ds = dh 9. (20 pt) During an isobaric phase change from a saturated liquid to a saturated vapor, the relationship between the enthalpy of vaporization and entropy of vaporization is: s fg = h fg /
4 Lesson (10pt) Oil in an automobile engine is stirred by the action of the internal parts. If this is done with no heat transfer, you would expect the entropy of the oil to increase/decrease. 11. (10 pt) he Carnot cycle processes form a rectangle when drawn on a -s state diagram. 12. (10 pt) Constant entropy processes form a _Vertical line when drawn of a -s state diagram. 13. (10 pt) Areas below reversible processes on -s state diagrams represent transfer. 14. (10 pt) he heat transfer during a reversible, isobaric conversion of a saturated liquid to a saturated vapor is given by: s fg 15. (10 pt)he change in the entropy (in terms of the specific volume) of an ideal gas with constant specific heats as it undergoes an isothermal process is given by: s 2 -s 1 = Rln(v 2 /v 1 ) 16. (10 pt)he change in the entropy (in terms of the absolute temperature) of an ideal gas with constant specific heats as it undergoes an isobaric process is given by: s 2 -s 1 = c p ln( 2 / 1 ) 17. (10 pt)he change in the entropy (in terms of the pressure) of an ideal gas with variable specific heats as it undergoes an isothermal process is given by: s 2 -s 1 = -Rln(P 2 /P 1 ) 18. (10 pt)he change in the entropy (in terms of the absolute temperature) of an ideal gas with variable specific heats as it undergoes an isobaric process is given by: s 2 -s 1 = integral (c P d/) 19. he entropy change of an incompressible substance with constant specific heat is given by: s 2 -s 1 = cln( 2 / 1 )
5 Lesson (10 pt) he entropy change of a system is always greater than of equal to Q /. 2. (5 pt) dq / can be considered as an entropy transfer with heat. 3. (5 pt) Entropy is produced by irreversible processes. 4. (5 pt) Entropy production is a property of a system. rue/false 5. (10 pt) he entropy of an isolated system must always increase or remain fixed. 6. (10 pt) Entropy production of a closed system equals the sum of the entropy change of the system and system heat transfers. 7. (10 pt) If S prod is negative, the process is impossible. 8. (10 pt) If S prod is positive, the process is irreversible. 9. (10 pt) he entropy production for the most effective process is zero. 10. (10 pt) Processes always proceed in directions in which the entropy production is positive or zero. 11. (10 pt) Entropy is not conserved, but is always being produced. 12. (5 pt) Entropy production is a measure of the irreversibility of a process.
6 Lesson (15 pt) Write the general rate form of the entropy balance below. Q ds ms ms prd in out dt 2. (15 pt) Entropy is transferred into and out of a system by mass transfer and heat transfer but not by work transfer. 3. (10 pt) Write the equation for the rate of entropy transfer by heat below: q S da A 4. (10 pt) Write the equation for the total entropy change of a internally reversible, isothermal system below: S = Q/ 5. (10 pt) When there is no heat transfer between a system and its surroundings, the entropy production must be either zero or positive. 6. (10 pt) Write the equation for the entropy production for a closed system below: Q m ( s ) 0 2 s 1 prd 7. (10pt) Write the equation for the entropy production for a single-stream, steady-state system below: q s s prd 8. (10 pt)he entropy of an isolated system must always increase or remain fixed. 9. (10 pt) Write the equation for the entropy production for a multi-stream, steady-state system below: Q ms ms 0 prd in out
7 Lesson (15 pt) Write the general for the r3eversible work of a single stream, steady-state system below: w vdp ke pe 2. (15 pt) Rewrite the equation of Problem 1 for an incompressible substance with negligible ke and pe below: w v( P P ) (10 pt) Write Bernoullis equation below: 2 2 V V 2 1 vdp g( z z ) (15 pt) On P-v state diagrams, the area to the _left_ of a reversible process line represents work consumed by a single-stream, _steady-state_ system. 5. (10 pt) he larger the specific _volume_ in a flowing system, the larger the work transfer. 6. (10 pt) Reversible work production is always _greater than_ or _equal to_ the actual work production. 7. (5 pt) he reversible process that require the least reversible work consumed by a compressor is the _reversible_ process. 8. (15 pt) Write the equation for the reversible work production of a single-stream, steady-state device through which an ideal gas experiences a polytropic process in terms of the inlet and outlet temperatures below: Rn w ( ) n 9. (5 pt) An isentropic process is a special case of a polytropic process where n = _k_.
8 Lesson (10 pt) An isentropic process is also a reversible and adiabatic process. (15 pt) An isentropic expansion process is one in which the pressure and temperature decrease while the entropy remains constant. (15 pt) An isentropic compression is one in which the pressure and temperature increase while the entropy remains constant. (10 pt) For an ideal gas with constant specific heats undergoing an isentropic process, the relationship between pressure and specific volume is given by: Pv k = constant (10 pt) For an ideal gas with constant specific heats undergoing an isentropic process, the relationship between pressure and temperature is given by: (/ r ) = (P/P r ) (k-1)/k (10 pt) For an ideal gas with constant specific heats undergoing an isentropic process, the relationship between specific volume and temperature is given by: (/ r ) = (v r /v) (k-1) 7. (10 pt)he ideal process for the isentropic efficiency is the isentropic process between the same pressures. 8. (10 pt)he isentropic process is also the reversible and adiabatic process. 9. (10 pt) In order to produce the maximum amount of work for a given enthalpy or specific internal energy change, there must be no heat trsansfer.
9 Lesson (15 pt) Write the equation for the work transfer for a single-stream, steady-state, internally reversible system below: w vdp ke pe 2. (10 pt) How much work is produced by a single-stream, steady-state, internally reversible system with an isobaric process (you may neglect ke and pe)? zero 3. (10 pt) Work consumed by a single-stream, steady-state system undergoing an internally reversible process is represented by the area to the left of the process line on a P-v state diagram. 4. (15 pt) Write the equation for the work produced by a single-stream, steady-state, internally reversible system undergoing a constant volume process below: w = -v(p 2 -P 1 ) 5. (15 pt) Write the equation for the work produced by a single-stream, steady-state, internally reversible system through which an ideal gas (with constant specific heats) flows while maintaining a constant temperature below: w = -Rln(P 2 /P 1 ) 6. (15 pt) Write the equation for the work produced by a single-stream, steady-state, internally reversible system through which an ideal gas (with constant specific heats) flows while maintaining a constant entropy below: R P ( k1)/ k 1 2 w k 1 P (10 pt) During an adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas from a high to a low pressure, the final temperature is greater than or equal to that predicted by the isentropic expansion equations. 8. (10 pt) During an adiabatic compression of an ideal gas from a low to a high pressure, the final temperature is greater than or equal to that predicted by the isentropic expansion equations.
10 Lesson (10 pt) Cold-air standard analysis assumes the specific heats of the working gas are constant while hot-air standard analysis assumes the specific heats vary with temperature. 2. (10 pt) Air-standard analysis treats the combustion process as a heat addition process and the intake-exhaust processes as a heat rejection process. 3. (20 pt) he bore of a reciprocating engine is the diameter of the cylinder and the stroke is the distance travelled by the piston between bottom-dead-center and top-dead-center. 4. (10 pt) he displacement volume is the volume swept by the crown of the piston as it moves from bottom-dead-center to top-dead-center. 5. (10 pt) he mean effective pressure is the constant pressure required to produce the same net work for the same engine displacement volume. 6. (20 pt) Spark-ignition engines are either two-stroke or four-stroke engines that execute a complete cycle once per revolution or twice per revolution, respectively. 7. (10 pt) Write the definition of the reciprocating engine compression ratio of below. v r v max min 8. (10 pt) he Otto cycle is made up of two constant volume heat transfer processes and two isentropic processes.
11 Lesson (5 pt) he single parameter that influences the thermal efficiency of an Otto cycle is the compression ratio. 2. (15 pt) he diesel cycle is made up of a constant pressure heat addition, a constant volume heat rejection, and two isentropic processes. 3. (5 pt) he Brayton cycle represent s the ideal gas turbine. 4. (10 pt) he Brayton cycle is made up of two constant pressure heat transfer and two isentropic processes. Pmax 5. (10 pt) Write the definition of the gas turbine pressure ratio below. rp P 6. (10 pt) he principle deviations of actual gas turbines from the Brayton cycle are the efficiencies of the compressor and turbine. 7. (15 pt) List the components of the basic gas turbine below. (1) compressor, (2) combustor, and (3) turbine min 8. (5 pt) he maximum Brayton cycle temperature is limited by the turbine blades. 9. (10 pt) he back work ratio is defined as the ration of compressor work to the turbine work. 10. (10 pt) According to Carnot, the best way to increase the efficiency of a gas turbine is to increase the turbine inlet temperature. 11. (5 pt) he single most important parameter that influences the efficiency of a Brayton cycle is the pressure ratio.
12 Lesson (5 pt) he single parameter that influences the thermal efficiency of an Otto cycle is the compression ratio. 2. (15 pt) he diesel cycle is made up of a constant pressure heat addition, a constant volume heat rejection, and two isentropic processes. 3. (5 pt) he Brayton cycle represent s the ideal gas turbine. 4. (10 pt) he Brayton cycle is made up of two constant pressure heat transfer and two isentropic processes. Pmax 5. (10 pt) Write the definition of the gas turbine pressure ratio below. rp P 6. (10 pt) he principle deviations of actual gas turbines from the Brayton cycle are the efficiencies of the compressor and turbine. 7. (15 pt) List the components of the basic gas turbine below. (1) compressor, (2) combustor, and (3) turbine min 8. (5 pt) he maximum Brayton cycle temperature is limited by the turbine blades. 9. (10 pt) he back work ratio is defined as the ration of compressor work to the turbine work. 10. (10 pt) According to Carnot, the best way to increase the efficiency of a gas turbine is to increase the turbine inlet temperature. 11. (5 pt) he single most important parameter that influences the efficiency of a Brayton cycle is the pressure ratio.
13 Lesson (20 pt) List the 4 components of the basic Rankine cycle below: Pump, Boiler, turbine, condenser 2. (15 pt) he process occurring in the Rankine cycle boiler is an isobaric process that converts saturated liquid water into a superheated vapor. 3. (15 pt) Ideally, the turbine in a Rankine cycle is a adiabatic, reversible device in which the working fluid undergoes an isentropic process. 4. (10 pt) he Rankine cycle condenser is an isobaric process that converts water mixture into a saturated liquid. 5. (5 pt) he water passing through the pump is an incompressible substance. 6. (10 pt) he change in the enthalpy across the pump is given by: h v P 7. (10 pt) Write the definition of the heat rate below. 8. (5 pt)he boiler is also known as the. 9. (10 pt) Rankine cycles are not operated as Carnot cycles because of the problems with equipment operating with a 2-phase working fluid? rue/false
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 6. Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6.1 Introduction
 Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 206 Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 206 Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY. PROOF: In Classroom
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY PROOF: In Classroom 2 RESULTS OF CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY For internally reversible cycles δq = 0 T int rev For irreversible cycles δq < 0 T irr A quantity whose cyclic
Chapter 7 ENTROPY CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY PROOF: In Classroom 2 RESULTS OF CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY For internally reversible cycles δq = 0 T int rev For irreversible cycles δq < 0 T irr A quantity whose cyclic
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 7. KFUPM Housam Binous CHE 303
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Boundary. Surroundings
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, Chapter 7 ENTROPY
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics II. Week 9
 hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles
 An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
An introduction to thermodynamics applied to Organic Rankine Cycles By : Sylvain Quoilin PhD Student at the University of Liège November 2008 1 Definition of a few thermodynamic variables 1.1 Main thermodynamics
ENTROPY. Chapter 7. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION
 CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Teaching schedule *15 18
 Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Chapter 6. Using Entropy
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 7-1 7-3 7-88, 7-131, 7-135 7-6 7-10 8-24, 8-44, 8-46, 8-60, 8-73, 8-99, 8-128, 8-132, 8-1 8-10, 8-13 8-135, 8-148, 8-152, 8-166, 8-168, 8-189
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 7-1 7-3 7-88, 7-131, 7-135 7-6 7-10 8-24, 8-44, 8-46, 8-60, 8-73, 8-99, 8-128, 8-132, 8-1 8-10, 8-13 8-135, 8-148, 8-152, 8-166, 8-168, 8-189
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Applied to Thermal Power Plants
 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Applied to Thermal Power Plants José R. Simões-Moreira Abstract In this chapter it is reviewed the fundamental principles of Thermodynamics aiming at its application to power
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Applied to Thermal Power Plants José R. Simões-Moreira Abstract In this chapter it is reviewed the fundamental principles of Thermodynamics aiming at its application to power
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics ME 04 BY Dr. Haitham Bahaidarah My Office Office Hours: :00 0:00 am SMW 03:00 04:00 pm UT Location: Building Room # 5.4
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics ME 04 BY Dr. Haitham Bahaidarah My Office Office Hours: :00 0:00 am SMW 03:00 04:00 pm UT Location: Building Room # 5.4
OVERVIEW. Air-Standard Power Cycles (open cycle)
 OVERVIEW OWER CYCLE The Rankine Cycle thermal efficiency effects of pressure and temperature Reheat cycle Regenerative cycle Losses and Cogeneration Air-Standard ower Cycles (open cycle) The Brayton cycle
OVERVIEW OWER CYCLE The Rankine Cycle thermal efficiency effects of pressure and temperature Reheat cycle Regenerative cycle Losses and Cogeneration Air-Standard ower Cycles (open cycle) The Brayton cycle
VEER SURENDRA SAI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY BURLA, ODISHA DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS.
 VEER SURENDRA SAI UNIVERSIY OF ECHNOLOGY BURLA, ODISHA DEPARMEN OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING HERMODYNAMICS Lecture Notes Disclaimer his document does not claim any originality and cannot be used
VEER SURENDRA SAI UNIVERSIY OF ECHNOLOGY BURLA, ODISHA DEPARMEN OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING HERMODYNAMICS Lecture Notes Disclaimer his document does not claim any originality and cannot be used
Part III: Planes, Trains, and Automobiles: Making Heat Work for You
 Contents at a Glance Introduction... 1 Part I: Covering the Basics in Thermodynamics... 7 Chapter 1: Thermodynamics in Everyday Life...9 Chapter 2: Laying the Foundation of Thermodynamics...15 Chapter
Contents at a Glance Introduction... 1 Part I: Covering the Basics in Thermodynamics... 7 Chapter 1: Thermodynamics in Everyday Life...9 Chapter 2: Laying the Foundation of Thermodynamics...15 Chapter
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles
 Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with aheat reservoir. (4.
 Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
MAE 11. Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018
 MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Spring_#8. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam
 Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
In the next lecture...
 16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
AME 436. Energy and Propulsion. Lecture 7 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines 2: Using P-V and T-s diagrams
 AME 46 Energy and ropulsion Lecture 7 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines : Using - and -s diagrams Outline! Air cycles! What are they?! Why use - and -s diagrams?! Using - and -s diagrams for air cycles!!!!!!
AME 46 Energy and ropulsion Lecture 7 Unsteady-flow (reciprocating) engines : Using - and -s diagrams Outline! Air cycles! What are they?! Why use - and -s diagrams?! Using - and -s diagrams for air cycles!!!!!!
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Name: I have observed the honor code and have neither given nor received aid on this exam.
 ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES. These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley.
 THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
10. Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka)
 10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
10 Heat devices: heat engines and refrigerators (Hiroshi Matsuoka) 1 In this chapter we will discuss how heat devices work Heat devices convert heat into work or work into heat and include heat engines
Scheme G. Sample Test Paper-I
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time: 1 hour 1) All questions are compulsory 2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3) Figures to the right indicate full marks 4) Assume suitable
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time: 1 hour 1) All questions are compulsory 2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary 3) Figures to the right indicate full marks 4) Assume suitable
ENERGY TRANSFER BY WORK: Electrical Work: When N Coulombs of electrical charge move through a potential difference V
 Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
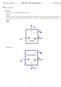 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
Chapter 1: Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts
 Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
Chapter 7: The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number: Instructions
 ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
Exergy and the Dead State
 EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
Existing Resources: Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics background and interests:
 Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
Existing Resources: Masters, G. (1991) Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science (Prentice Hall: NJ), pages 15 29. [ Masters_1991_Energy.pdf] Supplemental/reference for students with thermodynamics
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
9.1 Basic considerations in power cycle analysis. Thermal efficiency of a power cycle : th = Wnet/Qin
 Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES 9.1 Basic considerations in power cycle analysis. Thermal efficiency of a power cycle : th = Wnet/Qin Gas-power cycles vs. vapor-power cycles: T p 1 p 2 p 3 Vapor cycle Gas cycle
Chapter 9 GAS POWER CYCLES 9.1 Basic considerations in power cycle analysis. Thermal efficiency of a power cycle : th = Wnet/Qin Gas-power cycles vs. vapor-power cycles: T p 1 p 2 p 3 Vapor cycle Gas cycle
Chapter 7. Dr Ali Jawarneh. Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 8 Introduction to Vapour Power Cycle Today, we will continue
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 8 Introduction to Vapour Power Cycle Today, we will continue
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13
 Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW
 ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW 1. What is thermodynamics? It is a basic science that deals with energy and its transformations. The
ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW 1. What is thermodynamics? It is a basic science that deals with energy and its transformations. The
Previous lecture. Today lecture
 Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems
 ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
CHAPTER 8 THERMODYNAMICS. Common Data For Q. 3 and Q.4. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine operating at steady state with an enthalpy of 3251.
 CHAPER 8 HERMODYNAMICS YEAR 0 ONE MARK MCQ 8. MCQ 8. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine operating at steady state with an enthalpy of 35.0 kj/ kg and leaves as a saturated mixture at 5 kpa with quality
CHAPER 8 HERMODYNAMICS YEAR 0 ONE MARK MCQ 8. MCQ 8. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine operating at steady state with an enthalpy of 35.0 kj/ kg and leaves as a saturated mixture at 5 kpa with quality
Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics P Liquid P x 1 sat P 1 T sat T 2 T x 1 T x 1 T y 1 Liquid Vapour sat P 2 P x 1 P y 1 P y 1 Vapour sat T 1 x, y 1 1 x, y 1 1 Pradeep Ahuja Contents CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics P Liquid P x 1 sat P 1 T sat T 2 T x 1 T x 1 T y 1 Liquid Vapour sat P 2 P x 1 P y 1 P y 1 Vapour sat T 1 x, y 1 1 x, y 1 1 Pradeep Ahuja Contents CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems. Kwangheon Park Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering
 Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
ENT 254: Applied Thermodynamics
 ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
ES 202 Fluid and Thermal Systems
 ES Fluid and Thermal Systems Lecture : Power Cycles (/4/) Power cycle Road Map of Lecture use Rankine cycle as an example the ideal Rankine cycle representation on a T-s diagram divergence of constant
ES Fluid and Thermal Systems Lecture : Power Cycles (/4/) Power cycle Road Map of Lecture use Rankine cycle as an example the ideal Rankine cycle representation on a T-s diagram divergence of constant
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS
 FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS SEVENTH EDITION CLAUS BORGNAKKE RICHARD E. SONNTAG University of Michigan John Wiley & Sons, Inc. PUBLISHER ASSOCIATE PUBLISHER ACQUISITIONS EDITOR SENIOR PRODUCTION EDITOR
FUNDAMENTALS OF THERMODYNAMICS SEVENTH EDITION CLAUS BORGNAKKE RICHARD E. SONNTAG University of Michigan John Wiley & Sons, Inc. PUBLISHER ASSOCIATE PUBLISHER ACQUISITIONS EDITOR SENIOR PRODUCTION EDITOR
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Entropy ME 203 (2017) 2 / 27 T037
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
