Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator Inertial Vibrations
|
|
|
- Moris Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 15, No. 2 (2011) c Technical University of Lodz Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator Inertial Vibrations Przemys law Szumiński Division of Dynamics, Technical University of Lódź, Stefanowskiego 1/15, Lódź, Poland Received (10 June 2011) Revised (12 June 2011) Accepted (20 June 2011) An analysis of inertial component of mechanical vibrations induced during a motion of the MAR industrial manipulator is presented. The mathematical analysis of vibrations is based on the perturbation method. The presented considerations include an analytical description of inertial vibrations as well as results of the numerical analysis for the RPP type manipulator. Keywords: Robot dynamics, perturbations, mechanical vibrations 1. Introduction On one hand, manipulator structures should be light weighted also due to their drives, but on the other hand, velocities and accelerations achieved by links attain higher and higher values in subsequent manipulator designs [1, 3]. As a result, mechanical vibrations can be induced during motion. Simultaneously, the accuracy with which the gripping device follows the given motion trajectory belongs to basic characteristics of its quantitative evaluation [6, 10, 12]. Errors in following the motion trajectory by the gripping device depend on many factors, for instance the preciseness of the relative arrangement of links in kinematic pairs that results from the way the robot is controlled and driven, tolerance in the execution of individual element dimensions, elastic strains and clearances in kinematic pairs caused by errors in manufacturing, assembly and wear [2, 4, 5, 11]. The experimental measurement of link vibrations allows for a general analysis of vibration sources only [7, 8, 9]. A possibility to describe the components of link vibrations from the viewpoint of their sources is essential. However, analytical descriptions of mutual relations between components of the vibrations induced by various sources can be hardly found in the literature.
2 150 Szumiński, P. 2. Perturbation analysis of vibrations The equations of perturbations of the manipulator nominal motion are based on equations of the manipulator dynamics [14] [M] [ q m ] + [C] [ q m ] + [K] [q m ] + [G] = [Q] (1) where: [M] matrix of the manipulator inertia; [D] matrix of the energy dissipation in driving systems; [C] matrix of effects of gyroscopic, centrifugal and Coriolis forces; [G] column matrix of gravity forces; [K] matrix of stiffness of driving systems; [Q] column matrix of generalized driving quantities; [x] column matrix of generalized coordinates of the manipulator. Let us introduce a nominal motion disturbance x n in the form x = x n + x (2) where x denotes displacement (angular or linear) of the link and its derivatives with respect to time, x n generalized coordinate of the nominal motion and its derivatives, x refers to a perturbation of the nominal value of the generalized coordinate and its derivative. We assume slight perturbations of the nominal motion. Now let us describe the link perturbation x as x = x 1 + x 2 (3) where x 1 denotes a perturbation of the nominal motion resulting from inertial vibrations of the link andx 2 denotes a perturbation of the link motion resulting from the perturbation occurring in the driving system. [M(x n + x)][ẍ n + ẍ] + [D][ẋ n + ẋ] + [K][x n + x] +[C(x n + x, ẋ n + ẋ)] + [G(x n + x)] = [Q n + Q] (4) Introducing inertial perturbations of links and perturbations in driving systems into equations (1), the following equations have been obtained In Eqs. (4), trigonometric functions of variables x have been expanded into power series, and then linearization through rejection of terms in the power series that are terms of the higher order has been conducted. Slight perturbations of the nominal motion are assumed. The equations of manipulator perturbations take then the following form [M(x n )][ ẍ] + [D(x n, ẋ n )][ ẋ] + [K(x n, ẋ n, ẍ n )][ x] +[G(x n, ẋ n, ẍ n, x, ẋ, ẍ)] + N[x n, ẋ n, ẍ n ] = [Q n + Q] (5) The analysis of vibration sources can concern a case when x 1 in equation (5) is equal to zero or when x 2 is equal to zero. Links of the manipulator that performs
3 Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator repeatable technological tasks move periodically. During such a motion, links can change their velocity, stop and start moving again. In the case when x 2 is equal to zero then Eq. (5) describes vibrations of inertial nature that originate in changes of accelerations of links. The inertial vibrations can be described as [A(x n )][ẍ 1 ] + [B(x n, ẋ n )][ẋ 1 ] + [C(x n, ẋ n, ẍ n )][x 1 ] +[Z(x n, ẋ n, ẍ n, x 1, ẋ 1, ẍ 1 )] = 0 By the numerical integration of equation (6) we can obtain the characteristic curves of inertial component of link mechanical vibrations. (6) Figure 1 Kinematic scheme of the MAR manipulator. 3. Model of the MAR manipulator A MAR manipulator, Fig. 1, has been subjected to analysis of mechanical vibrations. This is a modular robot with three degrees of freedom. The MAR manipulator is designed to displace continuously and repeatably tiny objects on the assembly, processing, control stands and to perform short-distance transportation activities. The MAR manipulator is a robot with a constant working cycle. In Tab. 1, the MAR manipulator main data are presented. A vector of generalized coordinates of the manipulator is q = [q 1, q 2, q 3 ] T (7) The energy of dissipation of the kinematic pair has been expressed by means of a resultant coefficient of energy dissipation as a function of square relative velocity
4 152 Szumiński, P. Table 1 Number of the link Length of the link [m] Mass of the link [kg] Static stiffness [Nm/rad, N/m] Damping [Nms/rad], [Ns/m] S 3 =0.18 m of kinematic pair links. The electric and mechanical model of the driving system covers torsional flexibilities and viscous damping. It has been assumed that each link is driven by an independent driving system and consists of an electric motor, a mechanical gear and driving shafts. The general equations of the MAR manipulator motion are as follows [M] [ q m ] + [C] [ q m ] + [K] [q m ] + [G] = [Q] (8) where [M] matrix of inertia of the manipulator, [K] matrix of stiffness; [C] - matrix of effects of gyroscopic forces, centrifugal forces and Coriolis forces, [G] matrix of gravity forces, [Q] matrix of driving quantities, [q] matrix of generalized coordinates of the manipulator. The manipulator performs its technological task in two steps. The first one means a motion in the first driving system and the second one a motion of the second and third degree of freedom, whereas the first degree is stationary. The presented analysis concerns the second step of motion Inertial component of vibrations of the MAR manipulator During the second step of motion of the MAR manipulator, after introducing perturbations of second and third generalized coordinates, we receive equations of links vibrations. The inertial vibrations, Eq. (6), have the form [A][ẍ 1 ] + [B][ẋ 1 ] + [C][x 1 ] + [Z] = 0 (9) where [A] = [ [ 1 3 m 2L m 3 12 L2 3 + L (s 3 + q 3 ) 2] m 3 L 2 m 3 L 2 m 3 ] [B] = [ ] 2m3 q 3 (s 3 + q 3 ) + c 2 2m 3 q 2 (s 3 + q 3 ) 2m 3 q 2 (s 3 + q 3 ) c 3 (10)
5 [C] = Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator [m 3 (s 3 + q 3 ) sin(q 2 ) m 3 {2[(s 3 + q 3 ) q 2 + q 2 q 3 ] +(m m 2)g cos(q 1 ) cos(q 2 ))L 2 cos(q 2 )] +g cos(q 1 ) + k 2 m 3 g cos(q 1 ) cos(q 2 ) k 3 m 3 q 2 2} [Z] = q 2 { 1 3 m 2L m 3 [L L2 3 + (s 3 + q 3 ) 2 + x 2 13]} m 3 L 2 q 3 +2m 3 [(s 3 + q 3 )( q 2 q 3 + ẍ 12 x 13 + ẋ 12 ẋ 13 ) + x 13 ( q 2 ẋ 13 + q 3 ẋ 12 )t] { 1 2 m 2L 2 sin(q 2 ) + m 3 [(L 2 + x 12 x 13 t) sin(q 2 ) (s 3 + q 3 ) cos(q 2 )]t}g cos(q 1 ) m 3 [ q3 L 2 q 2 (s 3 + q 3 )( q ẋ 2 12) 2 q 2 x 13 ẋ 12 + g cos(q 1 ) sin(q 2 ) ] c i, k i coefficients of damping and dynamic stiffness of the i-th driving system, Tab. 1. Figure 2 Parameters of the trajectory of the gripping device motion 3.2. Trajectory of the gripping device motion The trajectory of the manipulator gripping device motion is presented in Fig. 2. This is a flat motion trajectory described with a combination of trigonometric functions. A detailed mathematical description of the trajectory is to be found in [13]. The geometrical data of the gripping device trajectory can be found in Tab. 2. Table 2 Parameters of the trajectory of motion Q [m] L [m] K [m] R [m]
6 154 Szumiński, P. The assumed trajectory shows a possibility of occurrence of manipulator stops and start ups, Fig. 3. The position of the gripping device on its trajectory is described by an angle β in the local coordinate system X 1 Y 1 0 1, see Fig. 2. a) b) Figure 3 Velocity and acceleration of the gripping device as a function of the angle β
7 Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator a) b) Figure 4 Generalized coordinates q 2 andq 3 as a function of the angle β
8 156 Szumiński, P Reverse task of kinematics and dynamics of the MAR mmanipulator For the proposed analysis of manipulator mechanical vibrations, it is necessary to solve reverse tasks of kinematics and dynamics [3, 10 12]. The kinematics reverse task allows us to determine generalized coordinates, their velocities and accelerations as a function of the gripping device position. A solution to the kinematics reverse task of the MAR manipulator can be found in [13]. On the other hand, the reverse task in dynamics allows for calculating values of forces and driving moments for the imposed trajectory of the gripping device motion. The Newton Euler method [10] was used to solve the dynamics tasks. The velocity and acceleration of the gripping device are presented in Fig. 3. The generalized coordinates of the manipulator and the generalized driving quantities of the nominal motion, for the configuration under consideration, are presented in Figs 4, 5. Figure 5 Generalized driving quantities of the nominal motion Table 3 Parameter Second gear Third gear Radius of the gear r 1 [m] Radius of the gear r 2 [m] Radius of the gear r 3 [m] Length a, b, c[m] Mechanical ratio n i [-] Rolling bearings SKF [15] 7200B 7200B
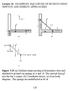
9 Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator Figure 6 Scheme of mechanical gears Figure 7 Perturbations of the links position due to the links motion 4. Numerical analysis of inertial vibrations of the MAR robot The numerical analysis is aimed at an analysis of inertial vibrations. The analysis takes into account stiffnesses of rolling bearings of the driving system, Fig. 6. Main data of the driving systems can be found in Tab. 3. A model of analysis of stiffness of manipulator rolling bearings and bearing systems is to be found in [14]. This algorithm has been applied in calculations of stiffness of individual bearings and
10 158 Szumiński, P. a) b) Figure 8 Accelerations of vibrations of the links due to the links motion, a) 2 nd link, b) 3 rd link
11 Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator then bearing systems occurring in driving systems, Fig. 6. Figs 7 and 8 show perturbations of links position and accelerations of inertial vibrations. 5. Conclusions In the paper, an analysis of vibrations due to the motion of the linkage mechanism itself is presented. The presented method for analysis of mechanical vibrations allows for a mathematical description of components of links vibrations. As an example, a three degree of freedom manipulator has been analyzed to show and solve numerically the problem. The plots presented allow for an evaluation of sources of mechanical vibrations in the working space of the robot. The experimental results obtain can be employed by designers to improve an accuracy of the robot positioning. References [1] Eschmann, P. and, Hasbargen, L.: Ball and roller bearings theory design and application, Willey & Sons, New York, [2] Hać, M. and Osiński, J.: Stability analysis of parametric vibration of flexible mechanisms, Machine Dynamics Problems, 3, , [3] Jezierski, E.: Dynamics of robots, Scientific Technical Publisher, Warsaw, (in olish), [4] Knapczyk, J. and Lebiediew, P.A.: Theory of 3D mechanisms and manipulators, Scientific Technical Publishers, Poland, (in Polish), [5] Koz lowski, K., Dutkiewicz, P. and Wróblewski, W.: Modeling and control of robots, State Scientific Publishers, Warsaw, (in Polish), [6] Kucharski, T.: Mechanical vibrations, Scientific Technical Publishers, Warsaw, (in Polish, )2004. [7] Lisowski, W., Giergiel, J. and Uhl, T.: Application of modal models for vibration control of manipulators, Proceedings of Noise Control, AGH Cracow, 73 78, [8] Liu, Y.C. and Yang S.M.: Vibration control experiment of a slewing flexible beam, ASME J. of Dynamic Sys., Measur.,Control, 117, , [9] Morecki, A. and Knapczyk, J.: Foundations of robotics, theory and elements of manipulators and robots, Scientific Technical Publishers, Warsaw, (in Polish), [10] Sciaviccio, L.and Siciliano, B.: Modeling and control of robot manipulators, Springer, London, [11] Spong, M.W. and Vidyasagar, M.: Robot dynamics and control, J.Wiley & Sons, New York, [12] Stȩpniewski, A.: Effect of the manipulator driving system flexibility on accuracy of the trajectory representation, XIV TMM Polish Scientific and Didactic Conference, (in Polish), [13] Szumiński, P. and Kapitaniak, T.: Stability regions of periodic trajectories of the manipulator motion, Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 17, 67 78, [14] Szumiński, P.: Determination of the stiffness of rolling kinematic pairs of manipulators, Mechanism and Machine Theory, 42(9), , [15] SKF catalogue of rolling bearings.
12
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms
 Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and X. Ding School of Computing, Info. Sys. & Maths. South Bank University London SE1 0AA, U.K. (seligjm@sbu.ac.uk) Abstract This article develops a
Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and X. Ding School of Computing, Info. Sys. & Maths. South Bank University London SE1 0AA, U.K. (seligjm@sbu.ac.uk) Abstract This article develops a
SAMCEF For ROTORS. Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics. This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF A, Page 1
 SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
Selection of Servomotors and Reducer Units for a 2 DoF PKM
 Selection of Servomotors and Reducer Units for a 2 DoF PKM Hermes GIBERTI, Simone CINQUEMANI Mechanical Engineering Department, Politecnico di Milano, Campus Bovisa Sud, via La Masa 34, 20156, Milano,
Selection of Servomotors and Reducer Units for a 2 DoF PKM Hermes GIBERTI, Simone CINQUEMANI Mechanical Engineering Department, Politecnico di Milano, Campus Bovisa Sud, via La Masa 34, 20156, Milano,
STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS
 Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
Int. J. of Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 04, vol.9, No.3, pp.609-69 DOI: 0.478/ijame-04-004 STATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A PUMP IMPELLER WITH A BALANCING DEVICE PART I: STATIC ANALYSIS C. KUNDERA
1820. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation
 8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
Vibrations in Mechanical Systems
 Maurice Roseau Vibrations in Mechanical Systems Analytical Methods and Applications With 112 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Contents Chapter I. Forced Vibrations
Maurice Roseau Vibrations in Mechanical Systems Analytical Methods and Applications With 112 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Contents Chapter I. Forced Vibrations
Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES
 Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES Figure 5.29 (a) Uniform beam moving in frictionless slots and attached to ground via springs at A and B. The vertical force
Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES Figure 5.29 (a) Uniform beam moving in frictionless slots and attached to ground via springs at A and B. The vertical force
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
PROJECT 2 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514
 PROJECT 2 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514 Dynamics of Rotor-Bearing System Lateral Vibrations and Stability Threshold of Rotors Supported On Hydrodynamic Bearing and Ball Bearing. Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Prof.
PROJECT 2 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514 Dynamics of Rotor-Bearing System Lateral Vibrations and Stability Threshold of Rotors Supported On Hydrodynamic Bearing and Ball Bearing. Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Prof.
Case Study: The Pelican Prototype Robot
 5 Case Study: The Pelican Prototype Robot The purpose of this chapter is twofold: first, to present in detail the model of the experimental robot arm of the Robotics lab. from the CICESE Research Center,
5 Case Study: The Pelican Prototype Robot The purpose of this chapter is twofold: first, to present in detail the model of the experimental robot arm of the Robotics lab. from the CICESE Research Center,
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS USED IN INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
 International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VIII, No. 1 / 2016 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS
International Journal of Modern Manufacturing Technologies ISSN 2067 3604, Vol. VIII, No. 1 / 2016 EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH REGARDING TRANSIENT REGIME OF KINEMATIC CHAINS INCLUDING PLANETARY TRANSMISSIONS
EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION
 1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
Virtual Passive Controller for Robot Systems Using Joint Torque Sensors
 NASA Technical Memorandum 110316 Virtual Passive Controller for Robot Systems Using Joint Torque Sensors Hal A. Aldridge and Jer-Nan Juang Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia January 1997 National
NASA Technical Memorandum 110316 Virtual Passive Controller for Robot Systems Using Joint Torque Sensors Hal A. Aldridge and Jer-Nan Juang Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia January 1997 National
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
Linear guide drives. Synchronous shafts The use of synchronous shafts enables several linear axes to be operated with one drive.
 Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
Linear guide drives Drive concept The linear guides are driven via the hollow shaft in the drive head. The drive head is used to directly install a motor or alternatively (in connection with a center shaft)
Dynamics Modeling and Identification of the Amigobot Robot
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, No. 1 (2010) 65 79 c Technical University of Lodz Dynamics Modeling and Identification of the Amigobot Robot Tomasz Buratowski Department of Robotics and Mechatronics,
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, No. 1 (2010) 65 79 c Technical University of Lodz Dynamics Modeling and Identification of the Amigobot Robot Tomasz Buratowski Department of Robotics and Mechatronics,
ON NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENT VERIFICATION OF CHARACTERISTIC FREQUENCY OF ANGULAR CONTACT BALL-BEARING IN HIGH SPEED SPINDLE SYSTEM
 ON NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENT VERIFICATION OF CHARACTERISTIC FREQUENCY OF ANGULAR CONTACT BALL-BEARING IN HIGH SPEED SPINDLE SYSTEM Tian-Yau Wu and Chun-Che Sun Department of Mechanical Engineering,
ON NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND EXPERIMENT VERIFICATION OF CHARACTERISTIC FREQUENCY OF ANGULAR CONTACT BALL-BEARING IN HIGH SPEED SPINDLE SYSTEM Tian-Yau Wu and Chun-Che Sun Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Contents. Dynamics and control of mechanical systems. Focus on
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM J. E. Jam, F. Meisami Composite Materials and Technology Center Tehran, IRAN jejaam@gmail.com N. G. Nia Iran Polymer & Petrochemical Institute, Tehran,
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM J. E. Jam, F. Meisami Composite Materials and Technology Center Tehran, IRAN jejaam@gmail.com N. G. Nia Iran Polymer & Petrochemical Institute, Tehran,
Table of Contents. Preface... 13
 Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements
 A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
Deriving 1 DOF Equations of Motion Worked-Out Examples. MCE371: Vibrations. Prof. Richter. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Handout 3 Fall 2017
 MCE371: Vibrations Prof. Richter Department of Mechanical Engineering Handout 3 Fall 2017 Masses with Rectilinear Motion Follow Palm, p.63, 67-72 and Sect.2.6. Refine your skill in drawing correct free
MCE371: Vibrations Prof. Richter Department of Mechanical Engineering Handout 3 Fall 2017 Masses with Rectilinear Motion Follow Palm, p.63, 67-72 and Sect.2.6. Refine your skill in drawing correct free
Model Reference Adaptive Control of Underwater Robotic Vehicle in Plane Motion
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on SSTEMS Agios ikolaos Crete Island Greece July 23-25 27 38 Model Reference Adaptive Control of Underwater Robotic Vehicle in Plane Motion j.garus@amw.gdynia.pl
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on SSTEMS Agios ikolaos Crete Island Greece July 23-25 27 38 Model Reference Adaptive Control of Underwater Robotic Vehicle in Plane Motion j.garus@amw.gdynia.pl
Dynamic Model of a Badminton Stroke
 ISEA 28 CONFERENCE Dynamic Model of a Badminton Stroke M. Kwan* and J. Rasmussen Department of Mechanical Engineering, Aalborg University, 922 Aalborg East, Denmark Phone: +45 994 9317 / Fax: +45 9815
ISEA 28 CONFERENCE Dynamic Model of a Badminton Stroke M. Kwan* and J. Rasmussen Department of Mechanical Engineering, Aalborg University, 922 Aalborg East, Denmark Phone: +45 994 9317 / Fax: +45 9815
DYNAMICS OF ELECTROMECHANICAL DRIVE OF SUSPENDED TIMBERTRANSPORTING ROPE SYSTEM
 Technical Sciences, 2016, 19(3) 245 256 DYNAMICS OF ELECTROMECHANICAL DRIVE OF SUSPENDED TIMBERTRANSPORTING ROPE SYSTEM Lidiya Dzyuba 1, Vasyl Baryliak 2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,
Technical Sciences, 2016, 19(3) 245 256 DYNAMICS OF ELECTROMECHANICAL DRIVE OF SUSPENDED TIMBERTRANSPORTING ROPE SYSTEM Lidiya Dzyuba 1, Vasyl Baryliak 2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,
Contents. Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter 2 Unacceptable Cam Curves Chapter 3 Double-Dwell Cam Curves... 27
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.0 Cam-Follower Systems... 1 1.1 Fundamentals... 1 1.2 Terminology... 4 Type of Follower Motion... 4 Type of Joint Closure... 4 Type of Follower... 5 Type of Cam...
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.0 Cam-Follower Systems... 1 1.1 Fundamentals... 1 1.2 Terminology... 4 Type of Follower Motion... 4 Type of Joint Closure... 4 Type of Follower... 5 Type of Cam...
The basic principle to be used in mechanical systems to derive a mathematical model is Newton s law,
 Chapter. DYNAMIC MODELING Understanding the nature of the process to be controlled is a central issue for a control engineer. Thus the engineer must construct a model of the process with whatever information
Chapter. DYNAMIC MODELING Understanding the nature of the process to be controlled is a central issue for a control engineer. Thus the engineer must construct a model of the process with whatever information
Effects of Structural Forces on the Dynamic Performance of High Speed Rotating Impellers.
 Effects of Structural Forces on the Dynamic Performance of High Speed Rotating Impellers. G Shenoy 1, B S Shenoy 1 and Raj C Thiagarajan 2 * 1 Dept. of Mechanical & Mfg. Engineering, Manipal Institute
Effects of Structural Forces on the Dynamic Performance of High Speed Rotating Impellers. G Shenoy 1, B S Shenoy 1 and Raj C Thiagarajan 2 * 1 Dept. of Mechanical & Mfg. Engineering, Manipal Institute
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly
 Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Influence of electromagnetic stiffness on coupled micro vibrations generated by solar array drive assembly Mariyam Sattar 1, Cheng Wei 2, Awais Jalali 3 1, 2 Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,
Linköping University Electronic Press
 Linköping University Electronic Press Report Simulation Model of a 2 Degrees of Freedom Industrial Manipulator Patrik Axelsson Series: LiTH-ISY-R, ISSN 400-3902, No. 3020 ISRN: LiTH-ISY-R-3020 Available
Linköping University Electronic Press Report Simulation Model of a 2 Degrees of Freedom Industrial Manipulator Patrik Axelsson Series: LiTH-ISY-R, ISSN 400-3902, No. 3020 ISRN: LiTH-ISY-R-3020 Available
Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs
 DOI 10.1007/s00542-016-2850-2 TECHNICAL PAPER Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs Bumcho Kim 1,2 Minho Lee 3 Gunhee Jang 3 Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00542-016-2850-2 TECHNICAL PAPER Robust shaft design to compensate deformation in the hub press fitting and disk clamping process of 2.5 HDDs Bumcho Kim 1,2 Minho Lee 3 Gunhee Jang 3 Received:
Research Article On Equations of Motion of Elastic Linkages by FEM
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 13, Article ID 6876, 1 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/6876 Research Article On Equations of Motion of Elastic Linkages by FEM MichaB HaT Institute of Machine
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 13, Article ID 6876, 1 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/13/6876 Research Article On Equations of Motion of Elastic Linkages by FEM MichaB HaT Institute of Machine
Excel Spreadsheet in Mechanical Engineering Technology Education
 Excel Spreadsheet in Mechanical Engineering Technology Education Prof. Ti Lin, Liu Department of Manufacturing & Mechanical Engineering Technology Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY 14623
Excel Spreadsheet in Mechanical Engineering Technology Education Prof. Ti Lin, Liu Department of Manufacturing & Mechanical Engineering Technology Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY 14623
TOPIC : 8 : Balancing
 TOPIC : 8 : Balancing --------------------------------------------------------------- Q.1. What is balancing? What are its objectives? What are types of balancing? BALANCING: Balancing is the technique
TOPIC : 8 : Balancing --------------------------------------------------------------- Q.1. What is balancing? What are its objectives? What are types of balancing? BALANCING: Balancing is the technique
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations
 Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering the Effect of a Rotating or Stationary Herringbone Groove
 G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 133-791, Korea Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering
G. H. Jang e-mail: ghjang@hanyang.ac.kr J. W. Yoon PREM, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, 133-791, Korea Nonlinear Dynamic Analysis of a Hydrodynamic Journal Bearing Considering
PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 208(1), 1 14 PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 208(1), 1 14 PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
Shape Optimization of Revolute Single Link Flexible Robotic Manipulator for Vibration Suppression
 15 th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms NaCoMM011-157 Shape Optimization of Revolute Single Link Flexible Robotic Manipulator for Vibration Suppression Sachindra Mahto Abstract In this work,
15 th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms NaCoMM011-157 Shape Optimization of Revolute Single Link Flexible Robotic Manipulator for Vibration Suppression Sachindra Mahto Abstract In this work,
Design and Control of Compliant Humanoids. Alin Albu-Schäffer. DLR German Aerospace Center Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics
 Design and Control of Compliant Humanoids Alin Albu-Schäffer DLR German Aerospace Center Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics Torque Controlled Light-weight Robots Torque sensing in each joint Mature
Design and Control of Compliant Humanoids Alin Albu-Schäffer DLR German Aerospace Center Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics Torque Controlled Light-weight Robots Torque sensing in each joint Mature
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
WORK SHEET FOR MEP311
 EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
INVESTIGATION OF BALL SCREWS FOR FEED DRIVE 1. INTRODUCTION
 Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 4, 203 ball screws, machine tools, rigidity, impact forces Jerzy Z. SOBOLEWSKI INVESTIGATION OF BALL SCEWS FO FEED DIVE The paper presents a method which enables
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 4, 203 ball screws, machine tools, rigidity, impact forces Jerzy Z. SOBOLEWSKI INVESTIGATION OF BALL SCEWS FO FEED DIVE The paper presents a method which enables
1 Introduction. Minho Lee 1 Jihoon Lee 1 Gunhee Jang 1
 DOI 10.1007/s005-015-5-5 TECHNICAL PAPER Stability analysis of a whirling rigid rotor supported by stationary grooved FDBs considering the five degrees of freedom of a general rotor bearing system Minho
DOI 10.1007/s005-015-5-5 TECHNICAL PAPER Stability analysis of a whirling rigid rotor supported by stationary grooved FDBs considering the five degrees of freedom of a general rotor bearing system Minho
Dynamic Analysis of Pelton Turbine and Assembly
 Dynamic Analysis of Pelton Turbine and Assembly Aman Rajak, Prateek Shrestha, Manoj Rijal, Bishal Pudasaini, Mahesh Chandra Luintel Department of Mechanical Engineering, Central Campus, Pulchowk, Institute
Dynamic Analysis of Pelton Turbine and Assembly Aman Rajak, Prateek Shrestha, Manoj Rijal, Bishal Pudasaini, Mahesh Chandra Luintel Department of Mechanical Engineering, Central Campus, Pulchowk, Institute
Engineering Science OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Swing-Up Problem of an Inverted Pendulum Energy Space Approach
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 22, No. 1 (2018) 33 40 c Lodz University of Technology Swing-Up Problem of an Inverted Pendulum Energy Space Approach Marek Balcerzak Division of Dynamics Lodz
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 22, No. 1 (2018) 33 40 c Lodz University of Technology Swing-Up Problem of an Inverted Pendulum Energy Space Approach Marek Balcerzak Division of Dynamics Lodz
T1 T e c h n i c a l S e c t i o n
 1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
Expedient Modeling of Ball Screw Feed Drives
 S. Frey a A. Dadalau a A. Verl a Expedient Modeling of Ball Screw Feed Drives Stuttgart, February 2011 a Institute for Control Engineering of Machine Tools and Manufacturing Units (ISW), University of
S. Frey a A. Dadalau a A. Verl a Expedient Modeling of Ball Screw Feed Drives Stuttgart, February 2011 a Institute for Control Engineering of Machine Tools and Manufacturing Units (ISW), University of
NON-LINEAR BEARING STIFFNESS PARAMETER EXTRACTION FROM RANDOM RESPONSE IN FLEXIBLE ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 3(3), 389 48 NON-LINEAR BEARING STIFFNESS PARAMETER EXTRACTION FROM RANDOM RESPONSE IN FLEXIBLE ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 3(3), 389 48 NON-LINEAR BEARING STIFFNESS PARAMETER EXTRACTION FROM RANDOM RESPONSE IN FLEXIBLE ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian
THE INFLUENCE OF CLEARANCES IN A DRIVE SYSTEM ON DYNAMICS AND KINEMATICS OF A TELESCOPIC CRANE
 THE INFLUENCE OF CLEARANCES IN A DRIVE SYSTEM ON DYNAMICS AND KINEMATICS OF A TELESCOPIC CRANE Arkadiusz TRĄBKA * * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Computer Science, Department of Engineering Fundamentals,
THE INFLUENCE OF CLEARANCES IN A DRIVE SYSTEM ON DYNAMICS AND KINEMATICS OF A TELESCOPIC CRANE Arkadiusz TRĄBKA * * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Computer Science, Department of Engineering Fundamentals,
A Benchmark Problem for Robust Control of a Multivariable Nonlinear Flexible Manipulator
 Proceedings of the 17th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Seoul, Korea, July 6-11, 28 A Benchmark Problem for Robust Control of a Multivariable Nonlinear Flexible Manipulator
Proceedings of the 17th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Seoul, Korea, July 6-11, 28 A Benchmark Problem for Robust Control of a Multivariable Nonlinear Flexible Manipulator
D DAVID PUBLISHING. Design of Torque Balancing Mechanisms. 1. Introduction. Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada
 Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (207) 32-320 doi: 0.7265/259-5275/207.06.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada Department of Engineering
Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (207) 32-320 doi: 0.7265/259-5275/207.06.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Bruno Zappa, Vittorio Lorenzi, Paolo Righettini and Roberto Strada Department of Engineering
Objectives. Fundamentals of Dynamics: Module 9 : Robot Dynamics & controls. Lecture 31 : Robot dynamics equation (LE & NE methods) and examples
 \ Module 9 : Robot Dynamics & controls Lecture 31 : Robot dynamics equation (LE & NE methods) and examples Objectives In this course you will learn the following Fundamentals of Dynamics Coriolis component
\ Module 9 : Robot Dynamics & controls Lecture 31 : Robot dynamics equation (LE & NE methods) and examples Objectives In this course you will learn the following Fundamentals of Dynamics Coriolis component
Name: Fall 2014 CLOSED BOOK
 Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Effect of an hourglass shaped sleeve on the performance of the fluid dynamic bearings of a HDD spindle motor
 DOI 10.1007/s00542-014-2136-5 Technical Paper Effect of an hourglass shaped sleeve on the performance of the fluid dynamic bearings of a HDD spindle motor Jihoon Lee Minho Lee Gunhee Jang Received: 14
DOI 10.1007/s00542-014-2136-5 Technical Paper Effect of an hourglass shaped sleeve on the performance of the fluid dynamic bearings of a HDD spindle motor Jihoon Lee Minho Lee Gunhee Jang Received: 14
ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS BASUDEB BHATTACHARYYA Assistant Professor Department of Applied Mechanics Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur, Howrah OXJFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Foreword Preface
ENGINEERING MECHANICS BASUDEB BHATTACHARYYA Assistant Professor Department of Applied Mechanics Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur, Howrah OXJFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Foreword Preface
ABSTRACT I. INTRODUCTION
 2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
Nonlinear Dynamics Analysis of a Gear-Shaft-Bearing System with Breathing Crack and Tooth Wear Faults
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 483-491 483 Open Access Nonlinear Dynamics Analysis of a Gear-Shaft-Bearing System with Breathing
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 483-491 483 Open Access Nonlinear Dynamics Analysis of a Gear-Shaft-Bearing System with Breathing
1 2 Models, Theories, and Laws 1.5 Distinguish between models, theories, and laws 2.1 State the origin of significant figures in measurement
 Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Chapter 15. Oscillatory Motion
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
Varuvan Vadivelan. Institute of Technology LAB MANUAL. : 2013 : B.E. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING : III Year / V Semester. Regulation Branch Year & Semester
 Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation Branch Year & Semester : 2013 : B.E. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING : III Year / V Semester ME 6511 - DYNAMICS LABORATORY GENERAL
Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation Branch Year & Semester : 2013 : B.E. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING : III Year / V Semester ME 6511 - DYNAMICS LABORATORY GENERAL
Topic wise Tests. Complex Variables, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Aeroelastic effects of large blade deflections for wind turbines
 Aeroelastic effects of large blade deflections for wind turbines Torben J. Larsen Anders M. Hansen Risoe, National Laboratory Risoe, National Laboratory P.O. Box 49, 4 Roskilde, Denmark P.O. Box 49, 4
Aeroelastic effects of large blade deflections for wind turbines Torben J. Larsen Anders M. Hansen Risoe, National Laboratory Risoe, National Laboratory P.O. Box 49, 4 Roskilde, Denmark P.O. Box 49, 4
Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System
 American Journal of Modern Physics and Application 2017; 4(2): 6-11 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajmpa Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System Petr Hrubý 1, Zdeněk Hlaváč 2,
American Journal of Modern Physics and Application 2017; 4(2): 6-11 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajmpa Cardan s Coupling Shaft as a Dynamic Evolutionary System Petr Hrubý 1, Zdeněk Hlaváč 2,
ROLLER BEARING FAILURES IN REDUCTION GEAR CAUSED BY INADEQUATE DAMPING BY ELASTIC COUPLINGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIONS
 ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session. Dr. David Herrin March 27, 2012
 Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Stability analysis of a whirling disk-spindle system supported by FDBs with rotating grooves
 Microsyst Technol (011) 17:787 797 DOI 10.1007/s0054-010-111-9 TECHNICAL PAPER Stability analysis of a whirling disk-spindle system supported by FDBs with rotating grooves Jihoon Lee Gunhee Jang Kyungmoon
Microsyst Technol (011) 17:787 797 DOI 10.1007/s0054-010-111-9 TECHNICAL PAPER Stability analysis of a whirling disk-spindle system supported by FDBs with rotating grooves Jihoon Lee Gunhee Jang Kyungmoon
In this section of notes, we look at the calculation of forces and torques for a manipulator in two settings:
 Introduction Up to this point we have considered only the kinematics of a manipulator. That is, only the specification of motion without regard to the forces and torques required to cause motion In this
Introduction Up to this point we have considered only the kinematics of a manipulator. That is, only the specification of motion without regard to the forces and torques required to cause motion In this
Circular motion minutes. 62 marks. theonlinephysicstutor.com. facebook.com/theonlinephysicstutor Page 1 of 22. Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks:
 Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Application of the Lyapunov Exponent Based on Current Vibration Control Parameter (CVC) in Control of an Industrial Robot
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 18, No. 1 (2015) 51 61 c Lodz University of Technology Application of the Lyapunov Exponent Based on Current Vibration Control Parameter (CVC) in Control of an
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 18, No. 1 (2015) 51 61 c Lodz University of Technology Application of the Lyapunov Exponent Based on Current Vibration Control Parameter (CVC) in Control of an
41514 Dynamics of Machinery
 41514 Dynamics of Machinery Theory, Experiment, Phenomenology and Industrial Applications Ilmar Ferreira Santos 1. Recapitulation Mathematical Modeling & Steps 2. Example System of Particle 3. Example
41514 Dynamics of Machinery Theory, Experiment, Phenomenology and Industrial Applications Ilmar Ferreira Santos 1. Recapitulation Mathematical Modeling & Steps 2. Example System of Particle 3. Example
Chapter 14. Oscillations. Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion:
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion: Kinematics Energy Examples of Simple Harmonic Oscillators Damped and Forced Oscillations. Resonance. Periodic Motion
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion: Kinematics Energy Examples of Simple Harmonic Oscillators Damped and Forced Oscillations. Resonance. Periodic Motion
EFFECTIVE MODAL MASS & MODAL PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F
 EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
Dispersion of critical rotational speeds of gearbox: effect of bearings stiffnesses
 Dispersion of critical rotational speeds of gearbox: effect of bearings stiffnesses F. Mayeux, E. Rigaud, J. Perret-Liaudet Ecole Centrale de Lyon Laboratoire de Tribologie et Dynamique des Systèmes Batiment
Dispersion of critical rotational speeds of gearbox: effect of bearings stiffnesses F. Mayeux, E. Rigaud, J. Perret-Liaudet Ecole Centrale de Lyon Laboratoire de Tribologie et Dynamique des Systèmes Batiment
Sound Propagation through Media. Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
 Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-13 WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOLIDS Longitudinal Vibrations In Thin Plates Unlike 3-D solids, thin plates have surfaces
Sound Propagation through Media Nachiketa Tiwari Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur LECTURE-13 WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOLIDS Longitudinal Vibrations In Thin Plates Unlike 3-D solids, thin plates have surfaces
STATICS & DYNAMICS. Engineering Mechanics. Gary L. Gray. Francesco Costanzo. Michael E. Plesha. University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Engineering Mechanics STATICS & DYNAMICS SECOND EDITION Francesco Costanzo Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Penn State University Michael E. Plesha Department of Engineering Physics University
Engineering Mechanics STATICS & DYNAMICS SECOND EDITION Francesco Costanzo Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Penn State University Michael E. Plesha Department of Engineering Physics University
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Vibration Dynamics and Control
 Giancarlo Genta Vibration Dynamics and Control Spri ringer Contents Series Preface Preface Symbols vii ix xxi Introduction 1 I Dynamics of Linear, Time Invariant, Systems 23 1 Conservative Discrete Vibrating
Giancarlo Genta Vibration Dynamics and Control Spri ringer Contents Series Preface Preface Symbols vii ix xxi Introduction 1 I Dynamics of Linear, Time Invariant, Systems 23 1 Conservative Discrete Vibrating
Numerical Methods for Solving the Dynamic Behavior of Real Systems
 SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS OF THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NOVI PAZAR SER. A: APPL. MATH. INFORM. AND MECH. vol. 6, 1 (2014), 25-34. Numerical Methods for Solving the Dynamic Behavior of Real Systems V. Nikolić,
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS OF THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NOVI PAZAR SER. A: APPL. MATH. INFORM. AND MECH. vol. 6, 1 (2014), 25-34. Numerical Methods for Solving the Dynamic Behavior of Real Systems V. Nikolić,
Program System for Machine Dynamics. Abstract. Version 5.0 November 2017
 Program System for Machine Dynamics Abstract Version 5.0 November 2017 Ingenieur-Büro Klement Lerchenweg 2 D 65428 Rüsselsheim Phone +49/6142/55951 hd.klement@t-online.de What is MADYN? The program system
Program System for Machine Dynamics Abstract Version 5.0 November 2017 Ingenieur-Büro Klement Lerchenweg 2 D 65428 Rüsselsheim Phone +49/6142/55951 hd.klement@t-online.de What is MADYN? The program system
(W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202)
 2016 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Schedule of Events Week Date Lecture (W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202) 1 27-Jul Introduction 2 Representing Position
2016 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Schedule of Events Week Date Lecture (W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202) 1 27-Jul Introduction 2 Representing Position
1541. A fast and reliable numerical method for analyzing loaded rolling element bearing displacements and stiffness
 1541. A fast and reliable numerical method for analyzing loaded rolling element bearing displacements and stiffness Yu Zhang 1 Guohua Sun 2 Teik C. Lim 3 Liyang Xie 4 1 4 School of Mechanical Engineering
1541. A fast and reliable numerical method for analyzing loaded rolling element bearing displacements and stiffness Yu Zhang 1 Guohua Sun 2 Teik C. Lim 3 Liyang Xie 4 1 4 School of Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical Principles
 Unit 8: Unit code Mechanical Principles F/615/1482 Unit level 4 Credit value 15 Introduction Mechanical principles have been crucial for engineers to convert the energy produced by burning oil and gas
Unit 8: Unit code Mechanical Principles F/615/1482 Unit level 4 Credit value 15 Introduction Mechanical principles have been crucial for engineers to convert the energy produced by burning oil and gas
Analysis and Calculation of Double Circular Arc Gear Meshing Impact Model
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscienceae 160 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 015, 9, 160-167 Open Access Analysis and Calculation of Double Circular Arc Gear Meshing Impact Model
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscienceae 160 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 015, 9, 160-167 Open Access Analysis and Calculation of Double Circular Arc Gear Meshing Impact Model
Control of constrained spatial three-link flexible manipulators
 Control of constrained spatial three-link flexible manipulators Sinan Kilicaslan, M. Kemal Ozgoren and S. Kemal Ider Gazi University/Mechanical Engineering Department, Ankara, Turkey Middle East Technical
Control of constrained spatial three-link flexible manipulators Sinan Kilicaslan, M. Kemal Ozgoren and S. Kemal Ider Gazi University/Mechanical Engineering Department, Ankara, Turkey Middle East Technical
Natural vibration frequency of classic MEMS structures
 Natural vibration frequency of classic MEMS structures Zacarias E. Fabrim PGCIMAT, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil Wang Chong, Manoel Martín Pérez Reimbold DeTec, UNIJUI, Ijuí, RS, Brazil Abstract This
Natural vibration frequency of classic MEMS structures Zacarias E. Fabrim PGCIMAT, UFRGS, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil Wang Chong, Manoel Martín Pérez Reimbold DeTec, UNIJUI, Ijuí, RS, Brazil Abstract This
Advanced Robotic Manipulation
 Advanced Robotic Manipulation Handout CS37A (Spring 017 Solution Set # Problem 1 - Redundant robot control The goal of this problem is to familiarize you with the control of a robot that is redundant with
Advanced Robotic Manipulation Handout CS37A (Spring 017 Solution Set # Problem 1 - Redundant robot control The goal of this problem is to familiarize you with the control of a robot that is redundant with
Robotics I. Figure 1: Initial placement of a rigid thin rod of length L in an absolute reference frame.
 Robotics I September, 7 Exercise Consider the rigid body in Fig., a thin rod of length L. The rod will be rotated by an angle α around the z axis, then by an angle β around the resulting x axis, and finally
Robotics I September, 7 Exercise Consider the rigid body in Fig., a thin rod of length L. The rod will be rotated by an angle α around the z axis, then by an angle β around the resulting x axis, and finally
Ball Bearing Model Performance on Various Sized Rotors with and without Centrifugal and Gyroscopic Forces
 Ball Bearing Model Performance on Various Sized Rotors with and without Centrifugal and Gyroscopic Forces Emil Kurvinen a,, Jussi Sopanen a, Aki Mikkola a a Lappeenranta University of Technology, Department
Ball Bearing Model Performance on Various Sized Rotors with and without Centrifugal and Gyroscopic Forces Emil Kurvinen a,, Jussi Sopanen a, Aki Mikkola a a Lappeenranta University of Technology, Department
Final Exam April 30, 2013
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF THIN-WALLED GIRDERS SUBJECTED TO COMBINED LOAD
 DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF THIN-WALLED GIRDERS SUBJECTED TO COMBINED LOAD P. WŁUKA, M. URBANIAK, T. KUBIAK Department of Strength of Materials, Lodz University of Technology, Stefanowskiego 1/15, 90-924 Łódź,
DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF THIN-WALLED GIRDERS SUBJECTED TO COMBINED LOAD P. WŁUKA, M. URBANIAK, T. KUBIAK Department of Strength of Materials, Lodz University of Technology, Stefanowskiego 1/15, 90-924 Łódź,
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Dynamics. Basilio Bona. Semester 1, DAUIN Politecnico di Torino. B. Bona (DAUIN) Dynamics Semester 1, / 18
 Dynamics Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Semester 1, 2016-17 B. Bona (DAUIN) Dynamics Semester 1, 2016-17 1 / 18 Dynamics Dynamics studies the relations between the 3D space generalized forces
Dynamics Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Semester 1, 2016-17 B. Bona (DAUIN) Dynamics Semester 1, 2016-17 1 / 18 Dynamics Dynamics studies the relations between the 3D space generalized forces
