Rotational Kinematics. Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis Western HS AP Physics 1
|
|
|
- Pauline Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rotatonal Knematcs Rgd Object about a Fxed Axs Westen HS AP Physcs 1
2 Leanng Objectes
3 What we know Unfom Ccula Moton q s Centpetal Acceleaton : Centpetal Foce: Non-unfom a F c c m F F F t m ma t
4 What we know q s Angula elocty and acceleaton q t t s q Tangental elocty and acceleaton a
5 Do 10 (?) A student twls a 0.75 kg lead weght aound he head. The adus of the moton s 0.50 m. a) How many adans n 040 degees? b) At what angle wll the weght hae taeled 9.0 metes? c) At t=0, q=0 and the elocty s 1.5 m/s. What s the angula elocty? d) What angula acceleaton wll ge a tangental acceleaton of 9.8 m/s/s? e) What angula elocty wll ge a centpetal foce of 95.0N? a) 35.6 adans b) 1031degees, 18 adans c) 3 ad/sec d) 19.6 ad/sec e) 15.9 ad/sec
6 Constant Angula Acceleaton If angula acceleaton s constant, we can deelop angula equatons of moton just as we dd fo tanslatonal moton q s t t x x a t t at t x x t at f f f f ) ( Axs) (Fxed Rotatonal Tanslatonal f f f f q q q q
7 Do 11 A bowlng ball wth a mass of 5.0 kg olls down a amp. a) If the ball acceleates fom 0.5 ad/s to.5 ad/s n 3.0 sec, what s the angula acceleaton? b) What angle dd the ball oll though n ths tme? c) What would be the ball s fnal angula elocty f t olled though an angle of 1080 degees wth the same angula acceleaton? a) 0.67 ad/s/s b) 4.5 adans, 57 degees c) 5 ad/sec
8 Decton Angula Velocty and Acceleaton ae ectos Fo otatonal moton, you must specfy an axs of otaton Angula elocty ecto s paallel to the axs Decton detemned by ght hand ule Cul fnges of ght hand n the decton of otaton thumb ponts n decton of angula elocty
9 Rgd Object s Pont Patcle In tanslatonal moton an extended object can be model as f t wee a pont In otatonal moton, the moton can t be modeled as a patcle snce eey pont has dffeent eloctes and acceleatons Must be modeled as a collecton of patcles A gd object can t be defomed the elate locaton of the patcles emans constant
10 Rgd Object Rotaton a a t c Each patcle that makes up the object has the same angula elocty and acceleaton Each patcle moes n a ccle about the axs of otaton Ccula moton equatons apply fo each patcle
11 Rotatonal Knetc Enegy Each patcle that makes up an object wll hae KE gen by: KE 1 m m 1 The total KE due to otaton then becomes: snce KE 1 m m 1
12 Example How many axes of otaton does ths object hae? +z =1.5m = =1.0m 3 How much otatonal KE does the object hae f t s otatng about the z-axs at.0 ad/s? KE KE KE 1 1 m m 1 (1) (1) 3(1.5) 3(1.5) 1 (17.5)(4) 35J
13 Do 1 A peson twls a 1.0 mete long baton n the a wth an angula elocty of.5 ad/sec aound ts cente of mass. The shaft has neglgble mass and one end has a mass of 0.5kg whle the othe end has a mass of 1.5kg. a) How fa fom the small end s the cente of mass? b) What s the otatonal knetc enegy of the baton? a) 0.71 m b) 1.1 J
14 Rotatonal Knetc Enegy KE 1 m m 1 The tem Sm occus n all otatonal moton poblems and s an object s Moment of Ineta, I I m Rotatonal Knetc Enegy KE 1 I
15 Rotatonal Ineta Ineta Is an object s esstance to a change n moton Moton can be lnea o otatonal Mass s a measue of an object s neta Rotatonal Ineta Is an object s esstance to a change n otatonal moton Rotatonal neta depends on whee the mass s located o an object s dstbuton of mass
16 Rotatonal Ineta The fathe an object s mass s located fom the axs, the geate ts otatonal neta An object s otatonal neta s measued by ts Moment of Ineta, I
17 Rotatonal Ineta Examples
18 On you own Poe that I fo a thn cylndcal shell about ts long axs (z) s MR.
19 Any Questons?
Dynamics of Rigid Bodies
 Dynamcs of Rgd Bodes A gd body s one n whch the dstances between consttuent patcles s constant thoughout the moton of the body,.e. t keeps ts shape. Thee ae two knds of gd body moton: 1. Tanslatonal Rectlnea
Dynamcs of Rgd Bodes A gd body s one n whch the dstances between consttuent patcles s constant thoughout the moton of the body,.e. t keeps ts shape. Thee ae two knds of gd body moton: 1. Tanslatonal Rectlnea
Physics 1501 Lecture 19
 Physcs 1501 ectue 19 Physcs 1501: ectue 19 Today s Agenda Announceents HW#7: due Oct. 1 Mdte 1: aveage 45 % Topcs otatonal Kneatcs otatonal Enegy Moents of Ineta Physcs 1501: ectue 19, Pg 1 Suay (wth copason
Physcs 1501 ectue 19 Physcs 1501: ectue 19 Today s Agenda Announceents HW#7: due Oct. 1 Mdte 1: aveage 45 % Topcs otatonal Kneatcs otatonal Enegy Moents of Ineta Physcs 1501: ectue 19, Pg 1 Suay (wth copason
Physics 1: Mechanics
 Physcs : Mechancs Đào Ngọc Hạnh Tâm Offce: A.503, Emal: dnhtam@hcmu.edu.vn HCMIU, Vetnam Natonal Unvesty Acknowledgment: Sldes ae suppoted by Pof. Phan Bao Ngoc Contents of Physcs Pat A: Dynamcs of Mass
Physcs : Mechancs Đào Ngọc Hạnh Tâm Offce: A.503, Emal: dnhtam@hcmu.edu.vn HCMIU, Vetnam Natonal Unvesty Acknowledgment: Sldes ae suppoted by Pof. Phan Bao Ngoc Contents of Physcs Pat A: Dynamcs of Mass
Chapter 5 Circular Motion
 Chapte 5 Ccula Moton In a gd body, the dstances between the pats o the body eman constant. We begn nestgatng the otaton o a gd body. We conclude ou nestgaton n Chapte 8. The language used to descbe otatonal
Chapte 5 Ccula Moton In a gd body, the dstances between the pats o the body eman constant. We begn nestgatng the otaton o a gd body. We conclude ou nestgaton n Chapte 8. The language used to descbe otatonal
Description Linear Angular position x displacement x rate of change of position v x x v average rate of change of position
 Chapte 5 Ccula Moton The language used to descbe otatonal moton s ey smla to the language used to descbe lnea moton. The symbols ae deent. Descpton Lnea Angula poston dsplacement ate o change o poston
Chapte 5 Ccula Moton The language used to descbe otatonal moton s ey smla to the language used to descbe lnea moton. The symbols ae deent. Descpton Lnea Angula poston dsplacement ate o change o poston
PHY126 Summer Session I, 2008
 PHY6 Summe Sesson I, 8 Most of nfomaton s avalable at: http://nngoup.phscs.sunsb.edu/~chak/phy6-8 ncludng the sllabus and lectue sldes. Read sllabus and watch fo mpotant announcements. Homewok assgnment
PHY6 Summe Sesson I, 8 Most of nfomaton s avalable at: http://nngoup.phscs.sunsb.edu/~chak/phy6-8 ncludng the sllabus and lectue sldes. Read sllabus and watch fo mpotant announcements. Homewok assgnment
Chapter 10 and elements of 11, 12 Rotation of Rigid Bodies
 Chapte 10 and elements of 11, 1 Rotaton of Rgd Bodes What s a Rgd Body? Rotatonal Knematcs Angula Velocty ω and Acceleaton α Rotaton wth Constant Acceleaton Angula vs. Lnea Knematcs Enegy n Rotatonal Moton:
Chapte 10 and elements of 11, 1 Rotaton of Rgd Bodes What s a Rgd Body? Rotatonal Knematcs Angula Velocty ω and Acceleaton α Rotaton wth Constant Acceleaton Angula vs. Lnea Knematcs Enegy n Rotatonal Moton:
Chapter 13 - Universal Gravitation
 Chapte 3 - Unesal Gataton In Chapte 5 we studed Newton s thee laws of moton. In addton to these laws, Newton fomulated the law of unesal gataton. Ths law states that two masses ae attacted by a foce gen
Chapte 3 - Unesal Gataton In Chapte 5 we studed Newton s thee laws of moton. In addton to these laws, Newton fomulated the law of unesal gataton. Ths law states that two masses ae attacted by a foce gen
Physics 207 Lecture 16
 Physcs 07 Lectue 6 Goals: Lectue 6 Chapte Extend the patcle odel to gd-bodes Undestand the equlbu of an extended object. Analyze ollng oton Undestand otaton about a fxed axs. Eploy consevaton of angula
Physcs 07 Lectue 6 Goals: Lectue 6 Chapte Extend the patcle odel to gd-bodes Undestand the equlbu of an extended object. Analyze ollng oton Undestand otaton about a fxed axs. Eploy consevaton of angula
Capítulo. Three Dimensions
 Capítulo Knematcs of Rgd Bodes n Thee Dmensons Mecánca Contents ntoducton Rgd Bod Angula Momentum n Thee Dmensons Pncple of mpulse and Momentum Knetc Eneg Sample Poblem 8. Sample Poblem 8. Moton of a Rgd
Capítulo Knematcs of Rgd Bodes n Thee Dmensons Mecánca Contents ntoducton Rgd Bod Angula Momentum n Thee Dmensons Pncple of mpulse and Momentum Knetc Eneg Sample Poblem 8. Sample Poblem 8. Moton of a Rgd
One-dimensional kinematics
 Phscs 45 Fomula Sheet Eam 3 One-dmensonal knematcs Vectos dsplacement: Δ total dstance taveled aveage speed total tme Δ aveage veloct: vav t t Δ nstantaneous veloct: v lm Δ t v aveage acceleaton: aav t
Phscs 45 Fomula Sheet Eam 3 One-dmensonal knematcs Vectos dsplacement: Δ total dstance taveled aveage speed total tme Δ aveage veloct: vav t t Δ nstantaneous veloct: v lm Δ t v aveage acceleaton: aav t
Physics 111 Lecture 11
 Physcs 111 ectue 11 Angula Momentum SJ 8th Ed.: Chap 11.1 11.4 Recap and Ovevew Coss Poduct Revsted Toque Revsted Angula Momentum Angula Fom o Newton s Second aw Angula Momentum o a System o Patcles Angula
Physcs 111 ectue 11 Angula Momentum SJ 8th Ed.: Chap 11.1 11.4 Recap and Ovevew Coss Poduct Revsted Toque Revsted Angula Momentum Angula Fom o Newton s Second aw Angula Momentum o a System o Patcles Angula
7/1/2008. Adhi Harmoko S. a c = v 2 /r. F c = m x a c = m x v 2 /r. Ontang Anting Moment of Inertia. Energy
 7//008 Adh Haoko S Ontang Antng Moent of neta Enegy Passenge undego unfo ccula oton (ccula path at constant speed) Theefoe, thee ust be a: centpetal acceleaton, a c. Theefoe thee ust be a centpetal foce,
7//008 Adh Haoko S Ontang Antng Moent of neta Enegy Passenge undego unfo ccula oton (ccula path at constant speed) Theefoe, thee ust be a: centpetal acceleaton, a c. Theefoe thee ust be a centpetal foce,
PHY121 Formula Sheet
 HY Foula Sheet One Denson t t Equatons o oton l Δ t Δ d d d d a d + at t + at a + t + ½at² + a( - ) ojectle oton y cos θ sn θ gt ( cos θ) t y ( sn θ) t ½ gt y a a sn θ g sn θ g otatonal a a a + a t Ccula
HY Foula Sheet One Denson t t Equatons o oton l Δ t Δ d d d d a d + at t + at a + t + ½at² + a( - ) ojectle oton y cos θ sn θ gt ( cos θ) t y ( sn θ) t ½ gt y a a sn θ g sn θ g otatonal a a a + a t Ccula
DYNAMICS VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Kinematics of Rigid Bodies in Three Dimensions. Seventh Edition CHAPTER
 Edton CAPTER 8 VECTOR MECANCS FOR ENGNEERS: DYNAMCS Fednand P. Bee E. Russell Johnston, J. Lectue Notes: J. Walt Ole Teas Tech Unvest Knematcs of Rgd Bodes n Thee Dmensons 003 The McGaw-ll Companes, nc.
Edton CAPTER 8 VECTOR MECANCS FOR ENGNEERS: DYNAMCS Fednand P. Bee E. Russell Johnston, J. Lectue Notes: J. Walt Ole Teas Tech Unvest Knematcs of Rgd Bodes n Thee Dmensons 003 The McGaw-ll Companes, nc.
COLLEGE OF FOUNDATION AND GENERAL STUDIES PUTRAJAYA CAMPUS FINAL EXAMINATION TRIMESTER /2017
 COLLEGE OF FOUNDATION AND GENERAL STUDIES PUTRAJAYA CAMPUS FINAL EXAMINATION TRIMESTER 1 016/017 PROGRAMME SUBJECT CODE : Foundaton n Engneeng : PHYF115 SUBJECT : Phscs 1 DATE : Septembe 016 DURATION :
COLLEGE OF FOUNDATION AND GENERAL STUDIES PUTRAJAYA CAMPUS FINAL EXAMINATION TRIMESTER 1 016/017 PROGRAMME SUBJECT CODE : Foundaton n Engneeng : PHYF115 SUBJECT : Phscs 1 DATE : Septembe 016 DURATION :
Review. Physics 231 fall 2007
 Reew Physcs 3 all 7 Man ssues Knematcs - moton wth constant acceleaton D moton, D pojectle moton, otatonal moton Dynamcs (oces) Enegy (knetc and potental) (tanslatonal o otatonal moton when detals ae not
Reew Physcs 3 all 7 Man ssues Knematcs - moton wth constant acceleaton D moton, D pojectle moton, otatonal moton Dynamcs (oces) Enegy (knetc and potental) (tanslatonal o otatonal moton when detals ae not
1. A body will remain in a state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line unless it
 Pncples of Dnamcs: Newton's Laws of moton. : Foce Analss 1. A bod wll eman n a state of est, o of unfom moton n a staght lne unless t s acted b etenal foces to change ts state.. The ate of change of momentum
Pncples of Dnamcs: Newton's Laws of moton. : Foce Analss 1. A bod wll eman n a state of est, o of unfom moton n a staght lne unless t s acted b etenal foces to change ts state.. The ate of change of momentum
Scalars and Vectors Scalar
 Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
TEST-03 TOPIC: MAGNETISM AND MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT Q.1 Find the magnetic field intensity due to a thin wire carrying current I in the Fig.
 TEST-03 TPC: MAGNETSM AND MAGNETC EFFECT F CURRENT Q. Fnd the magnetc feld ntensty due to a thn we cayng cuent n the Fg. - R 0 ( + tan) R () 0 ( ) R 0 ( + ) R 0 ( + tan ) R Q. Electons emtted wth neglgble
TEST-03 TPC: MAGNETSM AND MAGNETC EFFECT F CURRENT Q. Fnd the magnetc feld ntensty due to a thn we cayng cuent n the Fg. - R 0 ( + tan) R () 0 ( ) R 0 ( + ) R 0 ( + tan ) R Q. Electons emtted wth neglgble
Rigid Bodies: Equivalent Systems of Forces
 Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
a v2 r a' (4v) 2 16 v2 mg mg (2.4kg)(9.8m / s 2 ) 23.52N 23.52N N
 Conceptual ewton s Law Applcaton Test Revew 1. What s the decton o centpetal acceleaton? see unom ccula moton notes 2. What aects the magntude o a ctonal oce? see cton notes 3. What s the deence between
Conceptual ewton s Law Applcaton Test Revew 1. What s the decton o centpetal acceleaton? see unom ccula moton notes 2. What aects the magntude o a ctonal oce? see cton notes 3. What s the deence between
Rotary motion
 ectue 8 RTARY TN F THE RGD BDY Notes: ectue 8 - Rgd bod Rgd bod: j const numbe of degees of feedom 6 3 tanslatonal + 3 ota motons m j m j Constants educe numbe of degees of feedom non-fee object: 6-p
ectue 8 RTARY TN F THE RGD BDY Notes: ectue 8 - Rgd bod Rgd bod: j const numbe of degees of feedom 6 3 tanslatonal + 3 ota motons m j m j Constants educe numbe of degees of feedom non-fee object: 6-p
Physics 2A Chapter 11 - Universal Gravitation Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Test 1 phy What mass of a material with density ρ is required to make a hollow spherical shell having inner radius r i and outer radius r o?
 Test 1 phy 0 1. a) What s the pupose of measuement? b) Wte all fou condtons, whch must be satsfed by a scala poduct. (Use dffeent symbols to dstngush opeatons on ectos fom opeatons on numbes.) c) What
Test 1 phy 0 1. a) What s the pupose of measuement? b) Wte all fou condtons, whch must be satsfed by a scala poduct. (Use dffeent symbols to dstngush opeatons on ectos fom opeatons on numbes.) c) What
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unfom Ccul Moton Unfom ccul Moton An object mong t constnt sped n ccle The ntude of the eloct emns constnt The decton of the eloct chnges contnuousl!!!! Snce cceleton s te of chnge of eloct:!! Δ Δt The
Unfom Ccul Moton Unfom ccul Moton An object mong t constnt sped n ccle The ntude of the eloct emns constnt The decton of the eloct chnges contnuousl!!!! Snce cceleton s te of chnge of eloct:!! Δ Δt The
Objectives. Chapter 6. Learning Outcome. Newton's Laws in Action. Reflection: Reflection: 6.2 Gravitational Field
 Chapte 6 Gataton Objectes 6. Newton's Law o nesal Gataton 6. Gatatonal Feld 6. Gatatonal Potental 6. Satellte oton n Ccula Obts 6.5 scape Velocty Leanng Outcoe (a and use the oula / (b explan the eanng
Chapte 6 Gataton Objectes 6. Newton's Law o nesal Gataton 6. Gatatonal Feld 6. Gatatonal Potental 6. Satellte oton n Ccula Obts 6.5 scape Velocty Leanng Outcoe (a and use the oula / (b explan the eanng
Chapter I Matrices, Vectors, & Vector Calculus 1-1, 1-9, 1-10, 1-11, 1-17, 1-18, 1-25, 1-27, 1-36, 1-37, 1-41.
 Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
10/15/2013. PHY 113 C General Physics I 11 AM-12:15 PM MWF Olin 101
 10/15/01 PHY 11 C Geneal Physcs I 11 AM-1:15 PM MWF Oln 101 Plan fo Lectue 14: Chapte 1 Statc equlbu 1. Balancng foces and toques; stablty. Cente of gavty. Wll dscuss elastcty n Lectue 15 (Chapte 15) 10/14/01
10/15/01 PHY 11 C Geneal Physcs I 11 AM-1:15 PM MWF Oln 101 Plan fo Lectue 14: Chapte 1 Statc equlbu 1. Balancng foces and toques; stablty. Cente of gavty. Wll dscuss elastcty n Lectue 15 (Chapte 15) 10/14/01
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics. In the current chapter, you will study the motion of systems of particles.
 Seeth Edto CHPTER 4 VECTOR MECHNICS FOR ENINEERS: DYNMICS Fedad P. ee E. Russell Johsto, J. Systems of Patcles Lectue Notes: J. Walt Ole Texas Tech Uesty 003 The Mcaw-Hll Compaes, Ic. ll ghts eseed. Seeth
Seeth Edto CHPTER 4 VECTOR MECHNICS FOR ENINEERS: DYNMICS Fedad P. ee E. Russell Johsto, J. Systems of Patcles Lectue Notes: J. Walt Ole Texas Tech Uesty 003 The Mcaw-Hll Compaes, Ic. ll ghts eseed. Seeth
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Dynamics of Rotational Motion Toque: the otational analogue of foce Toque = foce x moment am τ = l moment am = pependicula distance though which the foce acts a.k.a. leve am l l l l τ = l = sin φ = tan
Dynamics of Rotational Motion Toque: the otational analogue of foce Toque = foce x moment am τ = l moment am = pependicula distance though which the foce acts a.k.a. leve am l l l l τ = l = sin φ = tan
Physics Exam II Chapters 25-29
 Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
Physcs 114 1 Exam II Chaptes 5-9 Answe 8 of the followng 9 questons o poblems. Each one s weghted equally. Clealy mak on you blue book whch numbe you do not want gaded. If you ae not sue whch one you do
24-2: Electric Potential Energy. 24-1: What is physics
 D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
D. Iyad SAADEDDIN Chapte 4: Electc Potental Electc potental Enegy and Electc potental Calculatng the E-potental fom E-feld fo dffeent chage dstbutons Calculatng the E-feld fom E-potental Potental of a
CSU ATS601 Fall Other reading: Vallis 2.1, 2.2; Marshall and Plumb Ch. 6; Holton Ch. 2; Schubert Ch r or v i = v r + r (3.
 3 Eath s Rotaton 3.1 Rotatng Famewok Othe eadng: Valls 2.1, 2.2; Mashall and Plumb Ch. 6; Holton Ch. 2; Schubet Ch. 3 Consde the poston vecto (the same as C n the fgue above) otatng at angula velocty.
3 Eath s Rotaton 3.1 Rotatng Famewok Othe eadng: Valls 2.1, 2.2; Mashall and Plumb Ch. 6; Holton Ch. 2; Schubet Ch. 3 Consde the poston vecto (the same as C n the fgue above) otatng at angula velocty.
Synopsis : 8. ELECTROMAGNETISM
 Synopss : 8. ELECTROMAGNETISM MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT: 1. Electomagnetsm s the banch of physcs whch deals wth elaton between electcty and magnetsm.. A statc chage poduces only electc feld but movng
Synopss : 8. ELECTROMAGNETISM MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT: 1. Electomagnetsm s the banch of physcs whch deals wth elaton between electcty and magnetsm.. A statc chage poduces only electc feld but movng
CHAPTER 3 SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES
 HAPTER 3 SYSTEMS O PARTILES 3. Intoducton By systes of patcles I ean such thngs as a swa of bees, a sta cluste, a cloud of gas, an ato, a bck. A bck s ndeed coposed of a syste of patcles atos whch ae constaned
HAPTER 3 SYSTEMS O PARTILES 3. Intoducton By systes of patcles I ean such thngs as a swa of bees, a sta cluste, a cloud of gas, an ato, a bck. A bck s ndeed coposed of a syste of patcles atos whch ae constaned
PHYS Week 5. Reading Journals today from tables. WebAssign due Wed nite
 PHYS 015 -- Week 5 Readng Jounals today fom tables WebAssgn due Wed nte Fo exclusve use n PHYS 015. Not fo e-dstbuton. Some mateals Copyght Unvesty of Coloado, Cengage,, Peason J. Maps. Fundamental Tools
PHYS 015 -- Week 5 Readng Jounals today fom tables WebAssgn due Wed nte Fo exclusve use n PHYS 015. Not fo e-dstbuton. Some mateals Copyght Unvesty of Coloado, Cengage,, Peason J. Maps. Fundamental Tools
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton Torque: the rotatonal analogue of force Torque = force x moment arm = Fl moment arm = perpendcular dstance through whch the force acts a.k.a. leer arm l F l F l F l F = Fl =
Physics 11b Lecture #2. Electric Field Electric Flux Gauss s Law
 Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
Part V: Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms
 Pat V: Velocty an Acceleaton Analyss of Mechansms Ths secton wll evew the most common an cuently pactce methos fo completng the knematcs analyss of mechansms; escbng moton though velocty an acceleaton.
Pat V: Velocty an Acceleaton Analyss of Mechansms Ths secton wll evew the most common an cuently pactce methos fo completng the knematcs analyss of mechansms; escbng moton though velocty an acceleaton.
Engineering Mechanics. Force resultants, Torques, Scalar Products, Equivalent Force systems
 Engneeng echancs oce esultants, Toques, Scala oducts, Equvalent oce sstems Tata cgaw-hll Companes, 008 Resultant of Two oces foce: acton of one bod on anothe; chaacteed b ts pont of applcaton, magntude,
Engneeng echancs oce esultants, Toques, Scala oducts, Equvalent oce sstems Tata cgaw-hll Companes, 008 Resultant of Two oces foce: acton of one bod on anothe; chaacteed b ts pont of applcaton, magntude,
Energy in Closed Systems
 Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
19 The Born-Oppenheimer Approximation
 9 The Bon-Oppenheme Appoxmaton The full nonelatvstc Hamltonan fo a molecule s gven by (n a.u.) Ĥ = A M A A A, Z A + A + >j j (883) Lets ewte the Hamltonan to emphasze the goal as Ĥ = + A A A, >j j M A
9 The Bon-Oppenheme Appoxmaton The full nonelatvstc Hamltonan fo a molecule s gven by (n a.u.) Ĥ = A M A A A, Z A + A + >j j (883) Lets ewte the Hamltonan to emphasze the goal as Ĥ = + A A A, >j j M A
r cos, and y r sin with the origin of coordinate system located at
 Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
Rotational Dynamics. Physics 1425 Lecture 19. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
Chap13. Universal Gravitation
 Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
Chap13. Uniesal Gaitation Leel : AP Physics Instucto : Kim 13.1 Newton s Law of Uniesal Gaitation - Fomula fo Newton s Law of Gaitation F g = G m 1m 2 2 F21 m1 F12 12 m2 - m 1, m 2 is the mass of the object,
ALL QUESTIONS ARE WORTH 20 POINTS. WORK OUT FIVE PROBLEMS.
 GNRAL PHYSICS PH -3A (D. S. Mov) Test (/3/) key STUDNT NAM: STUDNT d #: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GNRAL PHYSICS PH -3A (D. S. Mov) Test (/3/) key STUDNT NAM: STUDNT d #: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PROJECTILE MOTION. At any given point in the motion, the velocity vector is always a tangent to the path.
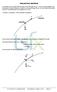 PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
PROJECTILE MOTION A pojectile is any object that has been thown though the ai. A foce must necessaily set the object in motion initially but, while it is moing though the ai, no foce othe than gaity acts
Chapter 8. Linear Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions
 Chapte 8 Lnea oentu, Ipulse, and Collsons 8. Lnea oentu and Ipulse The lnea oentu p of a patcle of ass ovng wth velocty v s defned as: p " v ote that p s a vecto that ponts n the sae decton as the velocty
Chapte 8 Lnea oentu, Ipulse, and Collsons 8. Lnea oentu and Ipulse The lnea oentu p of a patcle of ass ovng wth velocty v s defned as: p " v ote that p s a vecto that ponts n the sae decton as the velocty
Chapter 12 Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapte 12 Equlbum and Elastcty In ths chapte we wll defne equlbum and fnd the condtons needed so that an object s at equlbum. We wll then apply these condtons to a vaety of pactcal engneeng poblems of
Chapte 12 Equlbum and Elastcty In ths chapte we wll defne equlbum and fnd the condtons needed so that an object s at equlbum. We wll then apply these condtons to a vaety of pactcal engneeng poblems of
Circular Motion. x-y coordinate systems. Other coordinates... PHY circular-motion - J. Hedberg
 Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Cicula Motion PHY 207 - cicula-motion - J. Hedbeg - 2017 x-y coodinate systems Fo many situations, an x-y coodinate system is a geat idea. Hee is a map on Manhattan. The steets ae laid out in a ectangula
Lesson 8: Work, Energy, Power (Sections ) Chapter 6 Conservation of Energy
 Lesson 8: Wok, negy, Powe (Sectons 6.-6.8) Chapte 6 Conseaton o negy Today we begn wth a ey useul concept negy. We wll encounte many amla tems that now hae ey specc dentons n physcs. Conseaton o enegy
Lesson 8: Wok, negy, Powe (Sectons 6.-6.8) Chapte 6 Conseaton o negy Today we begn wth a ey useul concept negy. We wll encounte many amla tems that now hae ey specc dentons n physcs. Conseaton o enegy
Quiz 6--Work, Gravitation, Circular Motion, Torque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible)
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
RE 6.d Electric and Rest Energy RE 6.e EP6, HW6: Ch 6 Pr s 58, 59, 91, 99(a-c), 105(a-c)
 ed. Lab., Mon. Tues. ed. Lab. Mon. Tues. 6.1-.4 (.1) Intoducng Enegy & ok Quz 5 L5: Buoyancy, Ccles & Pendulums 6.5-.7 (.) Rest Mass,ok by Changng oces tudy Day tudy Day 6.8-.9(.18,.19) Intoducng Potental
ed. Lab., Mon. Tues. ed. Lab. Mon. Tues. 6.1-.4 (.1) Intoducng Enegy & ok Quz 5 L5: Buoyancy, Ccles & Pendulums 6.5-.7 (.) Rest Mass,ok by Changng oces tudy Day tudy Day 6.8-.9(.18,.19) Intoducng Potental
Lecture 22. PE = GMm r TE = GMm 2a. T 2 = 4π 2 GM. Main points of today s lecture: Gravitational potential energy: Total energy of orbit:
 Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
Lectue Main points of today s lectue: Gavitational potential enegy: Total enegy of obit: PE = GMm TE = GMm a Keple s laws and the elation between the obital peiod and obital adius. T = 4π GM a3 Midtem
CSJM University Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physics Paper-II Title: Electromagnetics Unit-1: Electrostatics Lecture: 1 to 4
 CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
PHYS 2135 Exam I February 13, 2018
 Exam Total /200 PHYS 2135 Exam I Febuay 13, 2018 Name: Recitation Section: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each Choose the best o most nealy coect answe Fo questions 6-9, solutions must begin
Exam Total /200 PHYS 2135 Exam I Febuay 13, 2018 Name: Recitation Section: Five multiple choice questions, 8 points each Choose the best o most nealy coect answe Fo questions 6-9, solutions must begin
Unit 6 Test Review Gravitation & Oscillation Chapters 13 & 15
 A.P. Physics C Unit 6 Test Review Gavitation & Oscillation Chaptes 13 & 15 * In studying fo you test, make sue to study this eview sheet along with you quizzes and homewok assignments. Multiple Choice
A.P. Physics C Unit 6 Test Review Gavitation & Oscillation Chaptes 13 & 15 * In studying fo you test, make sue to study this eview sheet along with you quizzes and homewok assignments. Multiple Choice
Remember: When an object falls due to gravity its potential energy decreases.
 Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
V. Principles of Irreversible Thermodynamics. s = S - S 0 (7.3) s = = - g i, k. "Flux": = da i. "Force": = -Â g a ik k = X i. Â J i X i (7.
 Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Rotational Motion. Lecture 6. Chapter 4. Physics I. Course website:
 Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
Rotational Motion. Every quantity that we have studied with translational motion has a rotational counterpart
 Rotational Motion & Angula Momentum Rotational Motion Evey quantity that we have studied with tanslational motion has a otational countepat TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angula Position Velocity
Rotational Motion & Angula Momentum Rotational Motion Evey quantity that we have studied with tanslational motion has a otational countepat TRANSLATIONAL ROTATIONAL Displacement x Angula Position Velocity
Physics 105: Mechanics Lecture 13
 Physcs 05: Mechancs Lecture 3 Wenda Cao NJIT Physcs Department Momentum and Momentum Conseraton Momentum Impulse Conseraton o Momentum Collsons Lnear Momentum A new undamental quantty, lke orce, energy
Physcs 05: Mechancs Lecture 3 Wenda Cao NJIT Physcs Department Momentum and Momentum Conseraton Momentum Impulse Conseraton o Momentum Collsons Lnear Momentum A new undamental quantty, lke orce, energy
Physics 201 Lecture 4
 Phscs 1 Lectue 4 ltoda: hapte 3 Lectue 4 v Intoduce scalas and vectos v Peom basc vecto aleba (addton and subtacton) v Inteconvet between atesan & Pola coodnates Stat n nteestn 1D moton poblem: ace 9.8
Phscs 1 Lectue 4 ltoda: hapte 3 Lectue 4 v Intoduce scalas and vectos v Peom basc vecto aleba (addton and subtacton) v Inteconvet between atesan & Pola coodnates Stat n nteestn 1D moton poblem: ace 9.8
s = rθ Chapter 10: Rotation 10.1: What is physics?
 Chape : oaon Angula poson, velocy, acceleaon Consan angula acceleaon Angula and lnea quanes oaonal knec enegy oaonal nea Toque Newon s nd law o oaon Wok and oaonal knec enegy.: Wha s physcs? In pevous
Chape : oaon Angula poson, velocy, acceleaon Consan angula acceleaon Angula and lnea quanes oaonal knec enegy oaonal nea Toque Newon s nd law o oaon Wok and oaonal knec enegy.: Wha s physcs? In pevous
Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynacs and Vbatons Fnal Exanaton Wednesday May 18 011 School of Engneeng own Unvesty NAME: Geneal Instuctons No collaboaton of any knd s petted on ths exanaton. You ay use double sded pages of efeence
EN40: Dynacs and Vbatons Fnal Exanaton Wednesday May 18 011 School of Engneeng own Unvesty NAME: Geneal Instuctons No collaboaton of any knd s petted on ths exanaton. You ay use double sded pages of efeence
Universal Gravitation
 Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
Chapte 1 Univesal Gavitation Pactice Poblem Solutions Student Textbook page 580 1. Conceptualize the Poblem - The law of univesal gavitation applies to this poblem. The gavitational foce, F g, between
III. Electromechanical Energy Conversion
 . Electoancal Enegy Coneson Schematc epesentaton o an toancal enegy coneson ece coppe losses coe losses (el losses) ancal losses Deental enegy nput om tcal souce: W V t Rt e t t W net ancal enegy output
. Electoancal Enegy Coneson Schematc epesentaton o an toancal enegy coneson ece coppe losses coe losses (el losses) ancal losses Deental enegy nput om tcal souce: W V t Rt e t t W net ancal enegy output
DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
2/24/2014. The point mass. Impulse for a single collision The impulse of a force is a vector. The Center of Mass. System of particles
 /4/04 Chapte 7 Lnea oentu Lnea oentu of a Sngle Patcle Lnea oentu: p υ It s a easue of the patcle s oton It s a vecto, sla to the veloct p υ p υ p υ z z p It also depends on the ass of the object, sla
/4/04 Chapte 7 Lnea oentu Lnea oentu of a Sngle Patcle Lnea oentu: p υ It s a easue of the patcle s oton It s a vecto, sla to the veloct p υ p υ p υ z z p It also depends on the ass of the object, sla
Review of Vector Algebra and Vector Calculus Operations
 Revew of Vecto Algeba and Vecto Calculus Opeatons Tpes of vaables n Flud Mechancs Repesentaton of vectos Dffeent coodnate sstems Base vecto elatons Scala and vecto poducts Stess Newton s law of vscost
Revew of Vecto Algeba and Vecto Calculus Opeatons Tpes of vaables n Flud Mechancs Repesentaton of vectos Dffeent coodnate sstems Base vecto elatons Scala and vecto poducts Stess Newton s law of vscost
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Course Outline. 1. MATLAB tutorial 2. Motion of systems that can be idealized as particles
 Couse Outlne. MATLAB tutoal. Moton of systems that can be dealzed as patcles Descpton of moton, coodnate systems; Newton s laws; Calculatng foces equed to nduce pescbed moton; Devng and solvng equatons
Couse Outlne. MATLAB tutoal. Moton of systems that can be dealzed as patcles Descpton of moton, coodnate systems; Newton s laws; Calculatng foces equed to nduce pescbed moton; Devng and solvng equatons
Motion in One Dimension
 Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Chapter 11: Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
(8) Gain Stage and Simple Output Stage
 EEEB23 Electoncs Analyss & Desgn (8) Gan Stage and Smple Output Stage Leanng Outcome Able to: Analyze an example of a gan stage and output stage of a multstage amplfe. efeence: Neamen, Chapte 11 8.0) ntoducton
EEEB23 Electoncs Analyss & Desgn (8) Gan Stage and Smple Output Stage Leanng Outcome Able to: Analyze an example of a gan stage and output stage of a multstage amplfe. efeence: Neamen, Chapte 11 8.0) ntoducton
Momentum. Momentum. Impulse. Momentum and Collisions
 Momentum Momentum and Collsons From Newton s laws: orce must be present to change an object s elocty (speed and/or drecton) Wsh to consder eects o collsons and correspondng change n elocty Gol ball ntally
Momentum Momentum and Collsons From Newton s laws: orce must be present to change an object s elocty (speed and/or drecton) Wsh to consder eects o collsons and correspondng change n elocty Gol ball ntally
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Angular Momentum and Fixed Axis Rotation. 8.01t Nov 10, 2004
 Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Circular motion. Objectives. Physics terms. Assessment. Equations 5/22/14. Describe the accelerated motion of objects moving in circles.
 Cicula motion Objectives Descibe the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles. Use equations to analyze the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles.. Descibe in you own wods what this equation
Cicula motion Objectives Descibe the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles. Use equations to analyze the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles.. Descibe in you own wods what this equation
ω = θ θ o = θ θ = s r v = rω
 Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
gravity r2,1 r2 r1 by m 2,1
 Gavtaton Many of the foundatons of classcal echancs wee fst dscoveed when phlosophes (ealy scentsts and atheatcans) ted to explan the oton of planets and stas. Newton s ost faous fo unfyng the oton of
Gavtaton Many of the foundatons of classcal echancs wee fst dscoveed when phlosophes (ealy scentsts and atheatcans) ted to explan the oton of planets and stas. Newton s ost faous fo unfyng the oton of
Physics C Rotational Motion Name: ANSWER KEY_ AP Review Packet
 Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
AP Physics 1 - Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test (Multiple Choice Section) Answer Section
 AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
PHYS 1410, 11 Nov 2015, 12:30pm.
 PHYS 40, Nov 205, 2:30pm. A B = AB cos φ x = x 0 + v x0 t + a 2 xt 2 a ad = v2 2 m(v2 2 v) 2 θ = θ 0 + ω 0 t + 2 αt2 L = p fs µ s n 0 + αt K = 2 Iω2 cm = m +m 2 2 +... m +m 2 +... p = m v and L = I ω ω
PHYS 40, Nov 205, 2:30pm. A B = AB cos φ x = x 0 + v x0 t + a 2 xt 2 a ad = v2 2 m(v2 2 v) 2 θ = θ 0 + ω 0 t + 2 αt2 L = p fs µ s n 0 + αt K = 2 Iω2 cm = m +m 2 2 +... m +m 2 +... p = m v and L = I ω ω
COMPLEMENTARY ENERGY METHOD FOR CURVED COMPOSITE BEAMS
 ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
Physics 207: Lecture 20. Today s Agenda Homework for Monday
 Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
LINEAR MOMENTUM. product of the mass m and the velocity v r of an object r r
 LINEAR MOMENTUM Imagne beng on a skateboad, at est that can move wthout cton on a smooth suace You catch a heavy, slow-movng ball that has been thown to you you begn to move Altenatvely you catch a lght,
LINEAR MOMENTUM Imagne beng on a skateboad, at est that can move wthout cton on a smooth suace You catch a heavy, slow-movng ball that has been thown to you you begn to move Altenatvely you catch a lght,
Lab 10: Newton s Second Law in Rotation
 Lab 10: Newton s Second Law in Rotation We can descibe the motion of objects that otate (i.e. spin on an axis, like a popelle o a doo) using the same definitions, adapted fo otational motion, that we have
Lab 10: Newton s Second Law in Rotation We can descibe the motion of objects that otate (i.e. spin on an axis, like a popelle o a doo) using the same definitions, adapted fo otational motion, that we have
1. Physics for Scientists and Engineers by Serway and Jewett. V.1, 9 th ed. Chapter 11.5, pp
 Page of 6 THE GYROSCOPE The setup s not connected to a compute. You cannot get measued values dectly fom the compute o ente them nto the lab PC. Make notes dung the sesson to use them late fo composng
Page of 6 THE GYROSCOPE The setup s not connected to a compute. You cannot get measued values dectly fom the compute o ente them nto the lab PC. Make notes dung the sesson to use them late fo composng
VEKTORANALYS FLUX INTEGRAL LINE INTEGRAL. and. Kursvecka 2. Kapitel 4 5. Sidor 29 50
 VEKTORANAYS Ksecka INE INTEGRA and UX INTEGRA Kaptel 4 5 Sdo 9 5 A wnd TARGET PROBEM We want to psh a mne cat along a path fom A to B. Bt the wnd s blowng. How mch enegy s needed? (.e. how mch s the wok?
VEKTORANAYS Ksecka INE INTEGRA and UX INTEGRA Kaptel 4 5 Sdo 9 5 A wnd TARGET PROBEM We want to psh a mne cat along a path fom A to B. Bt the wnd s blowng. How mch enegy s needed? (.e. how mch s the wok?
Lecture 13. Rotational motion Moment of inertia
 Lectue 13 Rotational motion Moment of inetia EXAM 2 Tuesday Mach 6, 2018 8:15 PM 9:45 PM Today s Topics: Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement Angula Velocity and Acceleation Rotational Kinematics
Lectue 13 Rotational motion Moment of inetia EXAM 2 Tuesday Mach 6, 2018 8:15 PM 9:45 PM Today s Topics: Rotational Motion and Angula Displacement Angula Velocity and Acceleation Rotational Kinematics
τ rf = Iα I point = mr 2 L35 F 11/14/14 a*er lecture 1
 A mass s attached to a long, massless rod. The mass s close to one end of the rod. Is t easer to balance the rod on end wth the mass near the top or near the bottom? Hnt: Small α means sluggsh behavor
A mass s attached to a long, massless rod. The mass s close to one end of the rod. Is t easer to balance the rod on end wth the mass near the top or near the bottom? Hnt: Small α means sluggsh behavor
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec during recitations. If you have taken the post test, don t come to recitation!
 Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
RIGID BODY MOTION. Next, we rotate counterclockwise about ξ by angle. Next we rotate counterclockwise about γ by angle to get the final set (x,y z ).
 RGD BODY MOTON We now consder the moton of rgd bodes. The frst queston s what coordnates are needed to specf the locaton and orentaton of such an object. Clearl 6 are needed 3 to locate a partcular pont
RGD BODY MOTON We now consder the moton of rgd bodes. The frst queston s what coordnates are needed to specf the locaton and orentaton of such an object. Clearl 6 are needed 3 to locate a partcular pont
rt () is constant. We know how to find the length of the radius vector by r( t) r( t) r( t)
 Cicula Motion Fom ancient times cicula tajectoies hae occupied a special place in ou model of the Uniese. Although these obits hae been eplaced by the moe geneal elliptical geomety, cicula motion is still
Cicula Motion Fom ancient times cicula tajectoies hae occupied a special place in ou model of the Uniese. Although these obits hae been eplaced by the moe geneal elliptical geomety, cicula motion is still
Chapter 4. Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Chapter 7-8 Rotational Motion
 Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
