Physical Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (EN0291 S40) Sherief Reda Division of Engineering, Brown University Fall 2006
|
|
|
- Douglas Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physical Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (EN0291 S40) Sherief Reda Division of Engineering, Brown University Fall
2 Lecture 04: Timing Analysis Static timing analysis STA for sequential circuits Delay modeling: devices and interconnects Statistical static timing analysis 2
3 Propagation delay definition voltage a y Logic block V max (10)% 50% propagation delay time 10% 90% Definitions: rise/fall propagation delay transition time rise/fall transition delay (slew (slope): ΔV/transition delay) 3
4 Problem: Given a circuit, find the path(s) with the largest delay (critical paths) Solution: run SPICE and report the results of the simulation Problem: SPICE is computationally expensive to run except for small-size circuits WANTED: We need a fast method that produces relatively accurate timing results compared to SPICE 4
5 Static timing analysis simplified analysis I 1 I 2 I 3 I 4 I 5 I 6 C17 from ISCAS 85 benchmarks 1/2 2/4 1/2 1/2 2/4 1/2 3/5 1/2 All inputs are arrive at time 0 7/7 6/4 2/3 2/4 O 1 Assuming all interconnects have 0 delay 9/10 O 2 9/11 In reality, each input pin has its own rise/fall delay critical and wires have delays path Each gate has rise/fall delay slack = arrival time required arrival time paths with negative slacks need to be eliminated! 5
6 Finding the critical path through breadth first search I 1 I 2 2/1 3/2 O 1 I 3 4/2 1/1 I 4 I 5 3/2 2/2 4/3 O 2 I 6 Initialize queue Q to empty for all vertices i in V: nvisit[i]=0; Add all primary input vertices to queue Q While (Q 0) i = top of Q; remove i from Q; computer delay of i for every edge (i, j): nvisit[j]++; if(nvisit[j] == fanin[j]) add j to Q 6
7 STA can lead to false critical paths STA assumes a signal would propagate from a gate input to its output regardless of the values of other inputs a b delay = 5 delay = MUX delay = 5 delay 1 1 = MUX out What is critical path delay according to STA? Is this path realizable? No, actual delay is less than estimated by STA 7
8 Lecture 04: Timing Analysis Static timing analysis STA for sequential circuits Delay modeling: devices and interconnects Statistical static timing analysis 8
9 Timing analysis of sequential circuits Δ FF input [d min.. d max ] combinational circuit output Δ FF cycle time P hold time T h clock clock setup time T s 9
10 Timing analysis of sequential circuits under presence of clock skew Δ FF i clock input [d min.. d max ] combinational circuit output Δ FF j clock T=0 s i s j cycle time P 10
11 Sometimes introducing skew can be helpful FF k dmax =8ns FF i d max =10ns FF j s i s j Zero clock skew (s i =0 & s j = 0) clock period = 10ns, f max = 100MHz S i = -1 s j = 0 clock period = 9ns, f max = 111MHz (no timing violations) S i = -2 s j = 0 clock period = 8ns, f max = 125MHz (no timing violations) Introducing skew also helps minimize the simultaneous switching of FFs less load on the P/G network STA is relatively easy once we figure out how to calculate gate and interconnect delay 11
12 Lecture 04: Timing Analysis Static timing analysis STA for sequential circuits Delay modeling: devices and interconnects Statistical static timing analysis 12
13 Elmore delay model: An upper bound to actual delay in RC trees any tree structure R 1 R 2 R 3 R N step input C 1 C 2 C 3 C N Sum the result of multiplying each resistance by the capacitance down stream from it What is the runtime complexity? [see Gupta/Pileggi 97 for more info] 13
14 Switch-level device RC delay models NMOS model PMOS model [source: Weste/Harris] 14
15 Modeling the delay of an inverter loading affects gate delay Holes have half the mobility of electrons PMOS width = 2 of the NMOS device to get the same current (or resistance) during output rise equal rise and fall delays for CMOS inverter 15
16 Gate delay: rise delay step input A B x 6C 2C Y 4hC A B Y h copies R Y t = ( 6+ 4 ) (6+4h)C rise propagation delay pdr h RC Assumption: interconnect delay is ignored (for the moment) 16
17 Gate delay: fall delay step input (1) A B x 6C 2C Y 4hC A B Y h copies R/2 x R/2 2C Y (6+4h)C pdf ( 2 R R R )( 2) ( 6 4 ) ( 2 2) ( 7 4h) RC t = C + + h C + = + fall propagation delay fall delay is worse than rise delay in this case 17
18 Gate delay is input pattern dependant step input (1) A B x 6C 2C Y 4hC A B Y h copies fall propagation delay Connect the latest arriving signal closest to the output node whenever feasible 18
19 Impact of transition time on gate delay Input gate Output Δ time τ i Δ time In addition to capacitive load, input transition time affects delay: τ i > 0 Δ > Δ output transition time: 19
20 Why does transition time affect delay? During transition, gate current < saturation current higher effective output resistance larger delay Input transition time affects gate delay (and output transition time too!) stored in a lookup table for fast calculation t i τ i Gate Δ r/f (C, τ i ) total capacitance (intrinsic + loading + interconnects) T i +Δ r/f τ o 20
21 Interconnect delay: the lumped case V m V out 0V Upper bound on delays in RC trees [Pileggi 97] 21
22 Interconnect delay: lumped vs. distributed R 1 R 2 R 3 R N C 1 C 2 C 3 C N r = resistance per unit length c = capacitance per unit length lumped overestimates delay 22
23 Carryout STA after annotating your circuit with gate/interconnect delays Annotate your circuit with gate/interconnect delay, and carry out STA Don t ignore interconnect delay because it is currently responsible for ~80% of total path delays! 23
24 Lecture 04: Timing Analysis Static timing analysis STA for sequential circuits Delay modeling: devices and interconnects Statistical static timing analysis 24
25 In Statistical STA (SSTA), delay is no longer deterministic I 1 I 2 x pdf pdf delay z? delay O 1 I 3 I 4 pdf delay y I 5 O 2 I 6 Replace deterministic gate delay by a random delay variable that has a normal pdf What is the pdf of z = max(x, y), where x and y are two random normal variables? z is not normal, but can be approximated reasonable using random variables [Jacobs/Berkelaar 00] 25
26 Gate variations impact critical path(s) delay leading to an increase in the average delay Intra-chip (within-die) variations: arises within devices in the same die Inter-chip (die-to-die) variations: arises between different chips 26
27 Assignments for next lecture Reading assignments: Statistical Timing Analysis for Intra-Die Process Variations with Spatial Correlations, ICCAD'03 (Kundan + (Yiwen) (judge)) Incremental timing analysis, US Patent (Cesare) Industrial products: Cadence SignalStorm (Elif) Synopsys PrimeTime (Brendan) Projects overview: mins presentation on previous work + proposal 1½ 2 page report 27
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002
 CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 18-322 DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002 Final Examination, Monday Dec. 16, 2002 NAME: SECTION: Time: 180 minutes Closed
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 18-322 DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002 Final Examination, Monday Dec. 16, 2002 NAME: SECTION: Time: 180 minutes Closed
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (6.374) - Fall 2003 Quiz #2 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Analysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (6.374) - Fall 2003 Quiz #2 Prof. Anantha Chandrakasan
Lecture 4: DC & Transient Response
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: DC & Transient Response David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 004 Outline DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response Delay Estimation Slide
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: DC & Transient Response David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 004 Outline DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response Delay Estimation Slide
Lecture 5: DC & Transient Response
 Lecture 5: DC & Transient Response Outline q Pass Transistors q DC Response q Logic Levels and Noise Margins q Transient Response q RC Delay Models q Delay Estimation 2 Activity 1) If the width of a transistor
Lecture 5: DC & Transient Response Outline q Pass Transistors q DC Response q Logic Levels and Noise Margins q Transient Response q RC Delay Models q Delay Estimation 2 Activity 1) If the width of a transistor
Homework Assignment #5 EE 477 Spring 2017 Professor Parker
 Homework Assignment #5 EE 477 Spring 2017 Professor Parker Question 1: (15%) Compute the worst-case rising and falling RC time constants at point B of the circuit below using the Elmore delay method. Assume
Homework Assignment #5 EE 477 Spring 2017 Professor Parker Question 1: (15%) Compute the worst-case rising and falling RC time constants at point B of the circuit below using the Elmore delay method. Assume
Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
 Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Lecture 4 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ah_madian@hotmail.com Dr. Ahmed H. Madian-VLSI Contents Delay estimation Simple RC model Penfield-Rubenstein Model Logical effort Delay
Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Lecture 4 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ah_madian@hotmail.com Dr. Ahmed H. Madian-VLSI Contents Delay estimation Simple RC model Penfield-Rubenstein Model Logical effort Delay
EE5780 Advanced VLSI CAD
 EE5780 Advanced VLSI CAD Lecture 4 DC and Transient Responses, Circuit Delays Zhuo Feng 4.1 Outline Pass Transistors DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response RC Delay Models Delay
EE5780 Advanced VLSI CAD Lecture 4 DC and Transient Responses, Circuit Delays Zhuo Feng 4.1 Outline Pass Transistors DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response RC Delay Models Delay
Lecture 6: DC & Transient Response
 Lecture 6: DC & Transient Response Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline Pass Transistors DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins
Lecture 6: DC & Transient Response Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline Pass Transistors DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins
TAU 2014 Contest Pessimism Removal of Timing Analysis v1.6 December 11 th,
 TU 2014 Contest Pessimism Removal of Timing nalysis v1.6 ecember 11 th, 2013 https://sites.google.com/site/taucontest2014 1 Introduction This document outlines the concepts and implementation details necessary
TU 2014 Contest Pessimism Removal of Timing nalysis v1.6 ecember 11 th, 2013 https://sites.google.com/site/taucontest2014 1 Introduction This document outlines the concepts and implementation details necessary
Delay and Power Estimation
 EEN454 Digital Integrated ircuit Design Delay and Power Estimation EEN 454 Delay Estimation We would like to be able to easily estimate delay Not as accurate as simulation But make it easier to ask What
EEN454 Digital Integrated ircuit Design Delay and Power Estimation EEN 454 Delay Estimation We would like to be able to easily estimate delay Not as accurate as simulation But make it easier to ask What
Lecture 8: Combinational Circuit Design
 Lecture 8: Combinational Circuit Design Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at ustin 9/5/8 Verilog to Gates module mux(input s, d0, d, output y); assign y = s? d
Lecture 8: Combinational Circuit Design Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at ustin 9/5/8 Verilog to Gates module mux(input s, d0, d, output y); assign y = s? d
EECS 141: SPRING 09 MIDTERM 2
 University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences J. Rabaey WeFr 2-3:30pm We, April 22, 2:00-3:30pm EECS 141: SPRING 09 MIDTERM 2 NAME Last First
University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences J. Rabaey WeFr 2-3:30pm We, April 22, 2:00-3:30pm EECS 141: SPRING 09 MIDTERM 2 NAME Last First
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences nalysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (6.374) - Fall 2003 Quiz #1 Prof. nantha Chandrakasan Student
MSSCHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences nalysis and Design of Digital Integrated Circuits (6.374) - Fall 2003 Quiz #1 Prof. nantha Chandrakasan Student
Lecture 7 Circuit Delay, Area and Power
 Lecture 7 Circuit Delay, Area and Power lecture notes from S. Mitra Intro VLSI System course (EE271) Introduction to VLSI Systems 1 Circuits and Delay Introduction to VLSI Systems 2 Power, Delay and Area:
Lecture 7 Circuit Delay, Area and Power lecture notes from S. Mitra Intro VLSI System course (EE271) Introduction to VLSI Systems 1 Circuits and Delay Introduction to VLSI Systems 2 Power, Delay and Area:
EECS 151/251A Homework 5
 EECS 151/251A Homework 5 Due Monday, March 5 th, 2018 Problem 1: Timing The data-path shown below is used in a simple processor. clk rd1 rd2 0 wr regfile 1 0 ALU REG 1 The elements used in the design have
EECS 151/251A Homework 5 Due Monday, March 5 th, 2018 Problem 1: Timing The data-path shown below is used in a simple processor. clk rd1 rd2 0 wr regfile 1 0 ALU REG 1 The elements used in the design have
9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter III CMOS Device, Inverter, Combinational circuit Logic and Layout Part 3 Combinational Logic Gates (textbook chapter 6) 9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter III CMOS Device, Inverter, Combinational circuit Logic and Layout Part 3 Combinational Logic Gates (textbook chapter 6) 9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
5. CMOS Gate Characteristics CS755
 5. CMOS Gate Characteristics Last module: CMOS Transistor theory This module: DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response Delay Estimation Transistor ehavior 1) If the width of a transistor
5. CMOS Gate Characteristics Last module: CMOS Transistor theory This module: DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response Delay Estimation Transistor ehavior 1) If the width of a transistor
Lecture 5: DC & Transient Response
 Lecture 5: DC & Transient Response Outline Pass Transistors DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response RC Delay Models Delay Estimation 2 Pass Transistors We have assumed source is grounded
Lecture 5: DC & Transient Response Outline Pass Transistors DC Response Logic Levels and Noise Margins Transient Response RC Delay Models Delay Estimation 2 Pass Transistors We have assumed source is grounded
ESE570 Spring University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 2018 Final Monday, Apr 0 5 Problems with point weightings shown.
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 2018 Final Monday, Apr 0 5 Problems with point weightings shown.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Elad Alon Homework #9 EECS141 PROBLEM 1: TIMING Consider the simple state machine shown
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Elad Alon Homework #9 EECS141 PROBLEM 1: TIMING Consider the simple state machine shown
Problem Set 9 Solutions
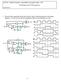 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Lecture 12 CMOS Delay & Transient Response
 EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 12 CMOS Delay & Transient Response Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 12 CMOS Delay & Transient Response Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
EE 466/586 VLSI Design. Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University
 EE 466/586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 9 Propagation delay Power and delay Tradeoffs Follow board notes Propagation Delay Switching Time
EE 466/586 VLSI Design Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Lecture 9 Propagation delay Power and delay Tradeoffs Follow board notes Propagation Delay Switching Time
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan,
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan,
DELAYS IN ASIC DESIGN
 DELAYS IN ASIC DESIGN We encounter several types of delays in ASIC design. They are as follows: Gate delay or Intrinsic delay Net delay or Interconnect delay or Wire delay or Extrinsic delay or Flight
DELAYS IN ASIC DESIGN We encounter several types of delays in ASIC design. They are as follows: Gate delay or Intrinsic delay Net delay or Interconnect delay or Wire delay or Extrinsic delay or Flight
DC and Transient. Courtesy of Dr. Daehyun Dr. Dr. Shmuel and Dr.
 DC and Transient Courtesy of Dr. Daehyun Lim@WSU, Dr. Harris@HMC, Dr. Shmuel Wimer@BIU and Dr. Choi@PSU http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-604 yrpeng@uark.edu Pass Transistors We have assumed source is
DC and Transient Courtesy of Dr. Daehyun Lim@WSU, Dr. Harris@HMC, Dr. Shmuel Wimer@BIU and Dr. Choi@PSU http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-604 yrpeng@uark.edu Pass Transistors We have assumed source is
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #4
 EE115 Digital Electronic ircuits Homework #4 Problem 1 Power Dissipation Solution Vdd =1.0V onsider the source follower circuit used to drive a load L =20fF shown above. M1 and M2 are both NMOS transistors
EE115 Digital Electronic ircuits Homework #4 Problem 1 Power Dissipation Solution Vdd =1.0V onsider the source follower circuit used to drive a load L =20fF shown above. M1 and M2 are both NMOS transistors
EE213, Spr 2017 HW#3 Due: May 17 th, in class. Figure 1
 RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermediate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero
RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermediate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero
EEE 421 VLSI Circuits
 EEE 421 CMOS Properties Full rail-to-rail swing high noise margins» Logic levels not dependent upon the relative device sizes transistors can be minimum size ratioless Always a path to V dd or GND in steady
EEE 421 CMOS Properties Full rail-to-rail swing high noise margins» Logic levels not dependent upon the relative device sizes transistors can be minimum size ratioless Always a path to V dd or GND in steady
Spiral 2 7. Capacitance, Delay and Sizing. Mark Redekopp
 2-7.1 Spiral 2 7 Capacitance, Delay and Sizing Mark Redekopp 2-7.2 Learning Outcomes I understand the sources of capacitance in CMOS circuits I understand how delay scales with resistance, capacitance
2-7.1 Spiral 2 7 Capacitance, Delay and Sizing Mark Redekopp 2-7.2 Learning Outcomes I understand the sources of capacitance in CMOS circuits I understand how delay scales with resistance, capacitance
TAU 2015 Contest Incremental Timing Analysis and Incremental Common Path Pessimism Removal (CPPR) Contest Education. v1.9 January 19 th, 2015
 TU 2015 Contest Incremental Timing nalysis and Incremental Common Path Pessimism Removal CPPR Contest Education v1.9 January 19 th, 2015 https://sites.google.com/site/taucontest2015 Contents 1 Introduction
TU 2015 Contest Incremental Timing nalysis and Incremental Common Path Pessimism Removal CPPR Contest Education v1.9 January 19 th, 2015 https://sites.google.com/site/taucontest2015 Contents 1 Introduction
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation *
 PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas A&M University
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas A&M University
Lecture 8: Logic Effort and Combinational Circuit Design
 Lecture 8: Logic Effort and Combinational Circuit Design Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q Logical Effort q Delay in a Logic Gate
Lecture 8: Logic Effort and Combinational Circuit Design Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q Logical Effort q Delay in a Logic Gate
Static CMOS Circuits. Example 1
 Static CMOS Circuits Conventional (ratio-less) static CMOS Covered so far Ratio-ed logic (depletion load, pseudo nmos) Pass transistor logic ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Example 1 module mux(input s, d0,
Static CMOS Circuits Conventional (ratio-less) static CMOS Covered so far Ratio-ed logic (depletion load, pseudo nmos) Pass transistor logic ECE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Example 1 module mux(input s, d0,
Lecture 9: Combinational Circuit Design
 Lecture 9: Combinational Circuit Design Outline Bubble Pushing Compound Gates Logical Effort Example Input Ordering symmetric Gates Skewed Gates Best P/N ratio 0: Combinational Circuits CMOS VLSI Design
Lecture 9: Combinational Circuit Design Outline Bubble Pushing Compound Gates Logical Effort Example Input Ordering symmetric Gates Skewed Gates Best P/N ratio 0: Combinational Circuits CMOS VLSI Design
Fig. 1 CMOS Transistor Circuits (a) Inverter Out = NOT In, (b) NOR-gate C = NOT (A or B)
 1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
Lecture 5. MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects
 Lecture 5 MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects Introduction C load = (C gd,n + C gd,p + C db,n + C db,p ) + (C int + C g ) Lumped linear capacitance intrinsic cap. extrinsic
Lecture 5 MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects Introduction C load = (C gd,n + C gd,p + C db,n + C db,p ) + (C int + C g ) Lumped linear capacitance intrinsic cap. extrinsic
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 2017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 1. This homework is due September 5, 2017, at 11:59AM.
 EECS 16 Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 1 This homework is due September 5, 017, at 11:59M. 1. Fundamental Theorem of Solutions to Differential
EECS 16 Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 1 This homework is due September 5, 017, at 11:59M. 1. Fundamental Theorem of Solutions to Differential
7. Combinational Circuits
 7. Combinational Circuits Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 September 25, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas
7. Combinational Circuits Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 September 25, 2017 ECE Department, University of Texas
Objective and Outline. Acknowledgement. Objective: Power Components. Outline: 1) Acknowledgements. Section 4: Power Components
 Objective: Power Components Outline: 1) Acknowledgements 2) Objective and Outline 1 Acknowledgement This lecture note has been obtained from similar courses all over the world. I wish to thank all the
Objective: Power Components Outline: 1) Acknowledgements 2) Objective and Outline 1 Acknowledgement This lecture note has been obtained from similar courses all over the world. I wish to thank all the
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 igital Integrated Circuits esign Perspective esigning Combinational Logic Circuits 1 Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational Logic Circuit Out In Combinational Logic Circuit Out State Combinational
igital Integrated Circuits esign Perspective esigning Combinational Logic Circuits 1 Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational Logic Circuit Out In Combinational Logic Circuit Out State Combinational
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter Lecture 07: Timing II
 CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 07: Timing II CSE241 L3 ASICs.1 Delay Calculation Cell Fall Cap\Tr 0.05 0.2 0.5 0.01 0.02 0.16 0.30 0.5 2.0 0.04 0.32 0.178 0.08 0.64 0.60 1.20 0.1ns 0.147ns
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 07: Timing II CSE241 L3 ASICs.1 Delay Calculation Cell Fall Cap\Tr 0.05 0.2 0.5 0.01 0.02 0.16 0.30 0.5 2.0 0.04 0.32 0.178 0.08 0.64 0.60 1.20 0.1ns 0.147ns
Power Dissipation. Where Does Power Go in CMOS?
 Power Dissipation [Adapted from Chapter 5 of Digital Integrated Circuits, 2003, J. Rabaey et al.] Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit
Power Dissipation [Adapted from Chapter 5 of Digital Integrated Circuits, 2003, J. Rabaey et al.] Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Digital Integrated Circuits Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey nantha Chandrakasan orivoje Nikolić Designing Combinational Logic Circuits November 2002. 1 Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational
Digital Integrated Circuits Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey nantha Chandrakasan orivoje Nikolić Designing Combinational Logic Circuits November 2002. 1 Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 16 CMOS Combinational Circuits - 2 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 16 CMOS Combinational Circuits - 2 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
5.0 CMOS Inverter. W.Kucewicz VLSICirciuit Design 1
 5.0 CMOS Inverter W.Kucewicz VLSICirciuit Design 1 Properties Switching Threshold Dynamic Behaviour Capacitance Propagation Delay nmos/pmos Ratio Power Consumption Contents W.Kucewicz VLSICirciuit Design
5.0 CMOS Inverter W.Kucewicz VLSICirciuit Design 1 Properties Switching Threshold Dynamic Behaviour Capacitance Propagation Delay nmos/pmos Ratio Power Consumption Contents W.Kucewicz VLSICirciuit Design
DC & Transient Responses
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design DC & Transient Responses ECEN 454 DC Response DC Response: vs. for a gate Ex: Inverter When = -> = When = -> = In between, depends on transistor size and current
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design DC & Transient Responses ECEN 454 DC Response DC Response: vs. for a gate Ex: Inverter When = -> = When = -> = In between, depends on transistor size and current
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. Professor Oldham Fall 1999
 UNIVERSITY OF CLIFORNI College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Professor Oldham Fall 1999 EECS 40 FINL EXM 13 December 1999 Name: Last, First Student ID: T: Kusuma
UNIVERSITY OF CLIFORNI College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Professor Oldham Fall 1999 EECS 40 FINL EXM 13 December 1999 Name: Last, First Student ID: T: Kusuma
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * (Revised Version)
 PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * (Revised Version) Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas
PARADE: PARAmetric Delay Evaluation Under Process Variation * (Revised Version) Xiang Lu, Zhuo Li, Wangqi Qiu, D. M. H. Walker, Weiping Shi Dept. of Electrical Engineering Dept. of Computer Science Texas
Lecture 6: Circuit design part 1
 Lecture 6: Circuit design part 6. Combinational circuit design 6. Sequential circuit design 6.3 Circuit simulation 6.4. Hardware description language Combinational Circuit Design. Combinational circuit
Lecture 6: Circuit design part 6. Combinational circuit design 6. Sequential circuit design 6.3 Circuit simulation 6.4. Hardware description language Combinational Circuit Design. Combinational circuit
VLSI Design, Fall Logical Effort. Jacob Abraham
 6. Logical Effort 6. Logical Effort Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 207 September 20, 207 ECE Department, University of
6. Logical Effort 6. Logical Effort Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 207 September 20, 207 ECE Department, University of
Lecture 1: Gate Delay Models
 High Speed CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1: Gate Delay Models (c) 1997 David Harris 1.0 Designing for Speed on the Back of an Envelope Custom IC design is all about speed. For a small amount of money, one synthesize
High Speed CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 1: Gate Delay Models (c) 1997 David Harris 1.0 Designing for Speed on the Back of an Envelope Custom IC design is all about speed. For a small amount of money, one synthesize
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction
 DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction Saraju P. Mohanty Dept of Computer Science and Engineering University of North Texas smohanty@cs.unt.edu http://www.cs.unt.edu/~smohanty/
DKDT: A Performance Aware Dual Dielectric Assignment for Tunneling Current Reduction Saraju P. Mohanty Dept of Computer Science and Engineering University of North Texas smohanty@cs.unt.edu http://www.cs.unt.edu/~smohanty/
Logic Synthesis and Verification
 Logic Synthesis and Verification Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall Timing Analysis & Optimization Reading: Logic Synthesis in a Nutshell Sections
Logic Synthesis and Verification Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Fall Timing Analysis & Optimization Reading: Logic Synthesis in a Nutshell Sections
Name: Answers. Mean: 83, Standard Deviation: 12 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Total. ESE370 Fall 2015
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems ESE370, Fall 2015 Final Tuesday, December 15 Problem weightings
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems ESE370, Fall 2015 Final Tuesday, December 15 Problem weightings
Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements.
 1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 35 CMOS Delay Model
 ECE 34 Electronic Circuits Lecture 35 CMOS Delay Model Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 34 Jose Schutt Aine 1 Digital Circuits V IH : Input
ECE 34 Electronic Circuits Lecture 35 CMOS Delay Model Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 34 Jose Schutt Aine 1 Digital Circuits V IH : Input
Digital Integrated Circuits
 Chapter 6 The CMOS Inverter 1 Contents Introduction (MOST models) 0, 1 st, 2 nd order The CMOS inverter : The static behavior: o DC transfer characteristics, o Short-circuit current The CMOS inverter :
Chapter 6 The CMOS Inverter 1 Contents Introduction (MOST models) 0, 1 st, 2 nd order The CMOS inverter : The static behavior: o DC transfer characteristics, o Short-circuit current The CMOS inverter :
CMOS Transistors, Gates, and Wires
 CMOS Transistors, Gates, and Wires Should the hardware abstraction layers make today s lecture irrelevant? pplication R P C W / R W C W / 6.375 Complex Digital Systems Christopher atten February 5, 006
CMOS Transistors, Gates, and Wires Should the hardware abstraction layers make today s lecture irrelevant? pplication R P C W / R W C W / 6.375 Complex Digital Systems Christopher atten February 5, 006
LECTURE 28. Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State
 Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
EECS 141: FALL 05 MIDTERM 1
 University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences D. Markovic TuTh 11-1:3 Thursday, October 6, 6:3-8:pm EECS 141: FALL 5 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last SOLUTION
University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences D. Markovic TuTh 11-1:3 Thursday, October 6, 6:3-8:pm EECS 141: FALL 5 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last SOLUTION
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Lecture 23. CMOS Logic Gates and Digital VLSI I
 ecture 3 CMOS ogic Gates and Digital SI I In this lecture you will learn: Digital ogic The CMOS Inverter Charge and Discharge Dynamics Power Dissipation Digital evels and Noise NFET Inverter Cut-off Saturation
ecture 3 CMOS ogic Gates and Digital SI I In this lecture you will learn: Digital ogic The CMOS Inverter Charge and Discharge Dynamics Power Dissipation Digital evels and Noise NFET Inverter Cut-off Saturation
ECE 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems. Simulation. Instructor: Maria K. Michael. Overview
 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems Simulation Instructor: Maria K. Michael Overview What is simulation? Design verification Modeling Levels Modeling circuits for simulation True-value simulation
407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems Simulation Instructor: Maria K. Michael Overview What is simulation? Design verification Modeling Levels Modeling circuits for simulation True-value simulation
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
Lecture 8: Combinational Circuits
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 8: Combinational Circuits David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 004 Outline ubble Pushing Compound Gates Logical Effort Example Input Ordering symmetric Gates
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 8: Combinational Circuits David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 004 Outline ubble Pushing Compound Gates Logical Effort Example Input Ordering symmetric Gates
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLSI Design I Delay Estimation. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville
 CPE/EE 47, CPE 57 VLSI Design I Delay Estimation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of labama in Huntsville leksandar Milenkovic ( www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka ) Review: CMOS Circuit
CPE/EE 47, CPE 57 VLSI Design I Delay Estimation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of labama in Huntsville leksandar Milenkovic ( www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka ) Review: CMOS Circuit
High-to-Low Propagation Delay t PHL
 High-to-Low Propagation Delay t PHL V IN switches instantly from low to high. Driver transistor (n-channel) immediately switches from cutoff to saturation; the p-channel pull-up switches from triode to
High-to-Low Propagation Delay t PHL V IN switches instantly from low to high. Driver transistor (n-channel) immediately switches from cutoff to saturation; the p-channel pull-up switches from triode to
Interconnect (2) Buffering Techniques.Transmission Lines. Lecture Fall 2003
 Interconnect (2) Buffering Techniques.Transmission Lines Lecture 12 18-322 Fall 2003 A few announcements Partners Lab Due Times Midterm 1 is nearly here Date: 10/14/02, time: 3:00-4:20PM, place: in class
Interconnect (2) Buffering Techniques.Transmission Lines Lecture 12 18-322 Fall 2003 A few announcements Partners Lab Due Times Midterm 1 is nearly here Date: 10/14/02, time: 3:00-4:20PM, place: in class
Dynamic operation 20
 Dynamic operation 20 A simple model for the propagation delay Symmetric inverter (rise and fall delays are identical) otal capacitance is linear t p Minimum length devices R W C L t = 0.69R C = p W L 0.69
Dynamic operation 20 A simple model for the propagation delay Symmetric inverter (rise and fall delays are identical) otal capacitance is linear t p Minimum length devices R W C L t = 0.69R C = p W L 0.69
University of Toronto. Final Exam
 University of Toronto Final Exam Date - Apr 18, 011 Duration:.5 hrs ECE334 Digital Electronics Lecturer - D. Johns ANSWER QUESTIONS ON THESE SHEETS USING BACKS IF NECESSARY 1. Equation sheet is on last
University of Toronto Final Exam Date - Apr 18, 011 Duration:.5 hrs ECE334 Digital Electronics Lecturer - D. Johns ANSWER QUESTIONS ON THESE SHEETS USING BACKS IF NECESSARY 1. Equation sheet is on last
Name: Grade: Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Total. ESE370 Fall 2015
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems ESE370, Fall 205 Midterm Wednesday, November 4 Point values
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems ESE370, Fall 205 Midterm Wednesday, November 4 Point values
Efficient Circuit Analysis under Multiple Input Switching (MIS) Anupama R. Subramaniam
 Efficient Circuit Analysis under Multiple Input Switching (MIS) by Anupama R. Subramaniam A Dissertation Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy Approved
Efficient Circuit Analysis under Multiple Input Switching (MIS) by Anupama R. Subramaniam A Dissertation Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy Approved
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Digital Integrated Circuits Design Perspective Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo School of Microelectronics,SJTU Introduction Digital IC Dynamic Logic Introduction Digital IC 2 EE141 Dynamic
Digital Integrated Circuits Design Perspective Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo School of Microelectronics,SJTU Introduction Digital IC Dynamic Logic Introduction Digital IC 2 EE141 Dynamic
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 20: Low Power Design
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 20: Low Power Design David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH E158
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 20: Low Power Design David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH E158
Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits. Fuyuzhuo
 Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo Introduction Digital IC Dynamic Logic Introduction Digital IC EE141 2 Dynamic logic outline Dynamic logic principle Dynamic logic
Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo Introduction Digital IC Dynamic Logic Introduction Digital IC EE141 2 Dynamic logic outline Dynamic logic principle Dynamic logic
ESE570 Spring University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 017 Final Wednesday, May 3 4 Problems with point weightings shown.
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Digital Integrated Cicruits AND VLSI Fundamentals ESE570, Spring 017 Final Wednesday, May 3 4 Problems with point weightings shown.
Interconnect (2) Buffering Techniques. Logical Effort
 Interconnect (2) Buffering Techniques. Logical Effort Lecture 14 18-322 Fall 2002 Textbook: [Sections 4.2.1, 8.2.3] A few announcements! M1 is almost over: The check-off is due today (by 9:30PM) Students
Interconnect (2) Buffering Techniques. Logical Effort Lecture 14 18-322 Fall 2002 Textbook: [Sections 4.2.1, 8.2.3] A few announcements! M1 is almost over: The check-off is due today (by 9:30PM) Students
Lecture 23. Dealing with Interconnect. Impact of Interconnect Parasitics
 Lecture 23 Dealing with Interconnect Impact of Interconnect Parasitics Reduce Reliability Affect Performance Classes of Parasitics Capacitive Resistive Inductive 1 INTERCONNECT Dealing with Capacitance
Lecture 23 Dealing with Interconnect Impact of Interconnect Parasitics Reduce Reliability Affect Performance Classes of Parasitics Capacitive Resistive Inductive 1 INTERCONNECT Dealing with Capacitance
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 19: Timing Analysis
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
Circuit A. Circuit B
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Last modified on November 19, 2006 by Karl Skucha (kskucha@eecs) Borivoje Nikolić Homework #9
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Last modified on November 19, 2006 by Karl Skucha (kskucha@eecs) Borivoje Nikolić Homework #9
Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 2010
 EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
Homework #2 10/6/2016. C int = C g, where 1 t p = t p0 (1 + C ext / C g ) = t p0 (1 + f/ ) f = C ext /C g is the effective fanout
 0/6/06 Homework # Lecture 8, 9: Sizing and Layout of omplex MOS Gates Reading: hapter 4, sections 4.3-4.5 October 3 & 5, 06 hapter, section.5.5 Prof. R. Iris ahar Weste & Harris vailable on course webpage
0/6/06 Homework # Lecture 8, 9: Sizing and Layout of omplex MOS Gates Reading: hapter 4, sections 4.3-4.5 October 3 & 5, 06 hapter, section.5.5 Prof. R. Iris ahar Weste & Harris vailable on course webpage
CMOS logic gates. João Canas Ferreira. March University of Porto Faculty of Engineering
 CMOS logic gates João Canas Ferreira University of Porto Faculty of Engineering March 2016 Topics 1 General structure 2 General properties 3 Cell layout João Canas Ferreira (FEUP) CMOS logic gates March
CMOS logic gates João Canas Ferreira University of Porto Faculty of Engineering March 2016 Topics 1 General structure 2 General properties 3 Cell layout João Canas Ferreira (FEUP) CMOS logic gates March
COMBINATIONAL LOGIC. Combinational Logic
 COMINTIONL LOGIC Overview Static CMOS Conventional Static CMOS Logic Ratioed Logic Pass Transistor/Transmission Gate Logic Dynamic CMOS Logic Domino np-cmos Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Logic
COMINTIONL LOGIC Overview Static CMOS Conventional Static CMOS Logic Ratioed Logic Pass Transistor/Transmission Gate Logic Dynamic CMOS Logic Domino np-cmos Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Logic
Chapter 8. Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology
 VLSI Design hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Jin-Fu Li hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Introduction Low-Power Gate-Level Design Low-Power Architecture-Level Design Algorithmic-Level
VLSI Design hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Jin-Fu Li hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Introduction Low-Power Gate-Level Design Low-Power Architecture-Level Design Algorithmic-Level
! Dynamic Characteristics. " Delay
 EE 57: Digital Integrated ircuits and LI Fundamentals Lecture Outline! Dynamic haracteristics " Delay Lec : February, 8 MO Inverter and Interconnect Delay 3 Review: Propogation Delay Definitions Dynamic
EE 57: Digital Integrated ircuits and LI Fundamentals Lecture Outline! Dynamic haracteristics " Delay Lec : February, 8 MO Inverter and Interconnect Delay 3 Review: Propogation Delay Definitions Dynamic
and V DS V GS V T (the saturation region) I DS = k 2 (V GS V T )2 (1+ V DS )
 ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
ECE 342 Solid State Devices & Circuits 4. CMOS
 ECE 34 Solid State Devices & Circuits 4. CMOS Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu ECE 34 Jose Schutt Aine 1 Digital Circuits V IH : Input
ECE 34 Solid State Devices & Circuits 4. CMOS Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu ECE 34 Jose Schutt Aine 1 Digital Circuits V IH : Input
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring Lecture 14: Designing for Low Power
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 14: Designing for Low Power [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp12 CMPEN
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 14: Designing for Low Power [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp12 CMPEN
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #6
 Problem 1 Sizing of adder blocks Electrical Engineering Department Spring 2010 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #6 Solution Figure 1: Mirror adder. Study the mirror adder cell (textbook, pages
Problem 1 Sizing of adder blocks Electrical Engineering Department Spring 2010 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #6 Solution Figure 1: Mirror adder. Study the mirror adder cell (textbook, pages
Topic 4. The CMOS Inverter
 Topic 4 The CMOS Inverter Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Topic 4-1 Noise in Digital Integrated
Topic 4 The CMOS Inverter Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Topic 4-1 Noise in Digital Integrated
Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design
 Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design Section 5. -To achieve correct operation of integrated logic gates, we need to satisfy 1. Functional specification. Temporal (timing) constraint. (1) In CMOS, incorrect
Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design Section 5. -To achieve correct operation of integrated logic gates, we need to satisfy 1. Functional specification. Temporal (timing) constraint. (1) In CMOS, incorrect
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation. Physical issues verification (DSM)
 Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
Lecture 2: CMOS technology. Energy-aware computing
 Energy-Aware Computing Lecture 2: CMOS technology Basic components Transistors Two types: NMOS, PMOS Wires (interconnect) Transistors as switches Gate Drain Source NMOS: When G is @ logic 1 (actually over
Energy-Aware Computing Lecture 2: CMOS technology Basic components Transistors Two types: NMOS, PMOS Wires (interconnect) Transistors as switches Gate Drain Source NMOS: When G is @ logic 1 (actually over
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #5
 EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #5 Due Thursday, May 13, 6pm @ 56-147E EIV Problem 1 Elmore Delay Analysis Calculate the Elmore delay from node A to node B using the values for the resistors
EE115C Digital Electronic Circuits Homework #5 Due Thursday, May 13, 6pm @ 56-147E EIV Problem 1 Elmore Delay Analysis Calculate the Elmore delay from node A to node B using the values for the resistors
Designing Sequential Logic Circuits
 igital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 5: esigning Sequential Logic Circuits Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: r. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 26 April 2017 isclaimer: This course was
igital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 5: esigning Sequential Logic Circuits Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: r. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 26 April 2017 isclaimer: This course was
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 09: Resistance & Inverter Dynamic View [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic]
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 09: Resistance & Inverter Dynamic View [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic]
Variation-Resistant Dynamic Power Optimization for VLSI Circuits
 Process-Variation Variation-Resistant Dynamic Power Optimization for VLSI Circuits Fei Hu Department of ECE Auburn University, AL 36849 Ph.D. Dissertation Committee: Dr. Vishwani D. Agrawal Dr. Foster
Process-Variation Variation-Resistant Dynamic Power Optimization for VLSI Circuits Fei Hu Department of ECE Auburn University, AL 36849 Ph.D. Dissertation Committee: Dr. Vishwani D. Agrawal Dr. Foster
