B.2 Wave-particle duality
|
|
|
- Matilda Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 97 B.2 Wave-particle duality Perform the double-slit experiment with three di erent kinds of objects. B.2.a Classical Particles 1. Define P j (x) istheprobabilityofaparticlearrivingatx with just slit j open. Define P 12 (x) istheprobabilityofaparticlearrivingatx with both open. 2. We observe P 12 = P 1 + P 2,asexpected. B.2.b Classical Waves 1. The energy I of a water wave depends on the square of its height H, which may be positive or negative. 2. Hence I 12 = H 2 12 =(H 1 + H 2 ) 2 = H H 1 H 2 + H 2 2 = I 1 +2H 1 H 2 + I The 2H 1 H 2 term may be positive or negative, which leads to constructive and destructive interference. B.2.c Quantum Particles 1. The probability of observing a particle is given by the rule for waves. 2. The probability P is given by the square of a complex amplitude A. 3. P 12 = A 1 + A 2 2 = P 1 + A 1 A 2 + A 1 A 2 + P How does a particle going through one slit know whether or not the other slit is open?
2 98 CHAPTER III. QUANTUM COMPUTATION B.3 Uncertainty principle B.3.a Informally 1. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: The uncertainty principle states a lower bound on the precision with which certain pairs of variables can be measured. 2. Conjugate variables: These are such pairs as position and momentum, and energy and time. For example, the same state can be represented by the wave function (x) asafunctionofspaceandby (p) asafunctionofmomentum. 3. Example: x p ~/2. ~ = h/2, whereh is Planck s constant. They are defined E = h (Hertz, or cycles per second) and E = ~! (radians per second). 4. Observer e ect: While it is true that measurements in quantum mechanics cause disturbance to the system being measured, this is most emphatically not the content of the uncertainty principle. 1 (The disturbance is called the observer e ect.) 5. Typically the uncertainty principle is a result of the variables representing measurements in two bases that are Fourier transforms of each other. For example, time and energy are conjugate; note (t) and (E) = ( ), where E = h. (For momentum, the de Broglie relation is p = h, where =wavelength,orp = ~k, wherek =2 / is the angular wavenumber, the number of wavelengths per 2 units of distance.) 6. Example: Consider an audio signal (t) anditsfouriertransform ( ). Note that is a function of time, with dimension t, andits spectrum is a function of frequency, with dimension t 1. They are reciprocals of each other, and that is always the case with Fourier transforms. 1 NC 89.
3 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY For more details on this, including an intuitive explanation, see FFC, ch. 6.) 8. Non-commutative operators: More generally, the observables are represented by Hermitian operators P, Q that donot commute. Thatis, to the extent they do not compute, to that extent you cannot measure them both (because you would have to do either PQ or QP,butthey do not give the same result). 9. Best interpretation: If you set up the experiment multiple times, and measure the outcomes, you will find 2 P Q h[p, Q]i, where P and Q are conjugate observables. 10. Note that this is a purely mathematical result. Any system obeying the QM postulates will have uncertainty principles for every pair of non-commuting observables. B.3.b Formally Optional! The following is from FFC, ch Definition B.1 (commutator) If L, M : H!Hare linear operators, then their commutator is defined: [L, M] =LM ML. (III.2) Remark B.1 In e ect, [L, M] distills out the non-commutative part of the product of L and M. If the operators commute, then [L, M] =0, the identically zero operator. Constant-valued operators always commute (cl = Lc), and so [c, L] =0. 2. Definition B.2 (anti-commutator) If L, M : H! H are linear operators, then their anti-commutator is defined: {L, M} = LM + ML. If {L, M} = 0, we say that L and M anti-commute, LM = (III.3) ML.
4 100 CHAPTER III. QUANTUM COMPUTATION 3. See B.1.c (p. 93) for the justification of the following definitions. Definition B.3 (mean of measurement) If M is a Hermitian operator representing an observable, then the mean value of the measurement of a state i is hmi = h M i. 4. Definition B.4 (variance and standard deviation of measurement) If M is a Hermitian operator representing an observable, then the variance in the measurement of a state i is Var{M} = h(m hmi 2 )i = hm 2 i hmi 2. As usual, the standard deviation M of the measurement is defined M = p Var{M}. 5. Proposition B.1 If L and M are Hermitian operators on H and i 2 H, then 4h L 2 i h M 2 i h [L, M] i 2 + h {L, M} i 2. More briefly, in terms of average measurements, 4hL 2 ihm 2 i h[l, M]i 2 + h{l, M}i 2. Proof: Letx + iy = h LM i. Then, 2x = h LM i +(h LM i) = h LM i + h M L i = h LM i + h ML i since L, M are Hermitian = h {L, M} i. Likewise, 2iy = h LM i (h LM i) = h LM i h ML i = h [L, M] i.
5 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 101 Hence, h LM i 2 = 4(x 2 + y 2 ) = h [L, M] i 2 + h {L, M} i 2. Let i = L i and µi = M i. By the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, k ik k µik h µi and so h ihµ µi h µi 2. Hence, The result follows. h L 2 i h M 2 i h LM i Proposition B.2 Prop. B.1 can be weakened into a more useful form: 4h L 2 i h M 2 i h [L, M] i 2, or 4hL 2 ihm 2 i h[l, M]i 2 7. Proposition B.3 (uncertainty principle) If Hermitian operators P and Q are measurements (observables), then P Q 1 h [P, Q] i. 2 That is, P Q h[p, Q]i /2. So the product of the variances is bounded below by the degree to which the operators do not commute. Proof: LetL = P hp i and M = Q hqi. ByProp.B.2wehave 4Var{P } Var{Q} = 4hL 2 ihm 2 i h[l, M]i 2 = h[p hp i,q hqi]i 2 = h[p, Q]i 2. Hence, 2 P Q h[p, Q]i
6 102 CHAPTER III. QUANTUM COMPUTATION B.4 Dynamics B.4.a Continuous time 1. Schrödinger equation: The time evolution of a closed QM system is given by the Schrödinger equation: i~ d (t)i = H (t)i, dt or more compactly, i~ i = H i. H is the Hamiltonian of the system (a fixed Hermitian operator). ~ is Planck s constant (often absorbed into H). 2. Since H is Hermitian, it has a spectral decomposition, H = P E E EihE, where the normalized Ei are energy eigenstates (or stationary states) with corresponding energies E. The lowest energy is the ground state energy. B.4.b Discrete time 1. Stone s theorem shows that the solution to the Schrödinger equation is: (t + s)i = e iht/~ (s)i. 2. Define U(t) def =exp( iht/~); then (t + s)i = U(t) (s)i. 3. U is unitary (Exer. III.3). 4. Hence the evolution of a closed QM system from a state i at time t to a state 0 i at time t 0 can be described by a unitary operator, 0 i = U i. 5. For any unitary operator U there is a Hermitian K such that U = exp(ik) (Exer.III.4).
B.7 Uncertainty principle (supplementary)
 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 93 B.7 Uncertainty principle (supplementary) You might be surprised that the famous Heisenberg uncertainty principle is not among the postulates of quantum mechanics.
B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 93 B.7 Uncertainty principle (supplementary) You might be surprised that the famous Heisenberg uncertainty principle is not among the postulates of quantum mechanics.
Basic concepts from quantum theory
 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 77 B Basic concepts from quantum theory B.1 Introduction B.1.a Bases In quantum mechanics certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron
B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 77 B Basic concepts from quantum theory B.1 Introduction B.1.a Bases In quantum mechanics certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron
Basic concepts from quantum theory
 80 CHAPTER III. QUANTUM COMPUTATION Figure III.1: Probability density of first six hydrogen orbitals. The main quantum number (n =1, 2, 3) and the angular momentum quantum number (` =0, 1, 2=s,p,d)areshown.
80 CHAPTER III. QUANTUM COMPUTATION Figure III.1: Probability density of first six hydrogen orbitals. The main quantum number (n =1, 2, 3) and the angular momentum quantum number (` =0, 1, 2=s,p,d)areshown.
Basic concepts from quantum theory
 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 59 Figure III.1: Probability density of first six hydrogen orbitals. The main quantum number (n =1, 2, 3) and the angular momentum quantum number (` =0, 1, 2=s,p,d)areshown.
B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 59 Figure III.1: Probability density of first six hydrogen orbitals. The main quantum number (n =1, 2, 3) and the angular momentum quantum number (` =0, 1, 2=s,p,d)areshown.
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics
 2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
2. Introduction to quantum mechanics 2.1 Linear algebra Dirac notation Complex conjugate Vector/ket Dual vector/bra Inner product/bracket Tensor product Complex conj. matrix Transpose of matrix Hermitian
Problems and Multiple Choice Questions
 Problems and Multiple Choice Questions 1. A momentum operator in one dimension is 2. A position operator in 3 dimensions is 3. A kinetic energy operator in 1 dimension is 4. If two operator commute, a)
Problems and Multiple Choice Questions 1. A momentum operator in one dimension is 2. A position operator in 3 dimensions is 3. A kinetic energy operator in 1 dimension is 4. If two operator commute, a)
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics. EE270 Fall 2017
 Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12 In this lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to this course. Topics
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell 10/06/07 Fall 2009 Lecture 12 In this lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to this course. Topics
This is the important completeness relation,
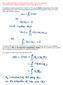 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 03/19/2018 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics The postulates (axioms) of quantum mechanics
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 03/19/2018 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics The postulates (axioms) of quantum mechanics
2.2 Schrödinger s wave equation
 2.2 Schrödinger s wave equation Slides: Video 2.2.1 Schrödinger wave equation introduction Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Section Chapter 2 introduction Schrödinger s wave
2.2 Schrödinger s wave equation Slides: Video 2.2.1 Schrödinger wave equation introduction Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Section Chapter 2 introduction Schrödinger s wave
Lecture 3 Dynamics 29
 Lecture 3 Dynamics 29 30 LECTURE 3. DYNAMICS 3.1 Introduction Having described the states and the observables of a quantum system, we shall now introduce the rules that determine their time evolution.
Lecture 3 Dynamics 29 30 LECTURE 3. DYNAMICS 3.1 Introduction Having described the states and the observables of a quantum system, we shall now introduce the rules that determine their time evolution.
An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually).
 Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send to
 Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
Energy levels and atomic structures lectures chapter one
 Structure of Atom An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are
Structure of Atom An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are
Quantum Computing Lecture 3. Principles of Quantum Mechanics. Anuj Dawar
 Quantum Computing Lecture 3 Principles of Quantum Mechanics Anuj Dawar What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum Mechanics is a framework for the development of physical theories. It is not itself a physical
Quantum Computing Lecture 3 Principles of Quantum Mechanics Anuj Dawar What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum Mechanics is a framework for the development of physical theories. It is not itself a physical
A more comprehensive theory was needed. 1925, Schrödinger and Heisenberg separately worked out a new theory Quantum Mechanics.
 Ch28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms Bohr s model was very successful to explain line spectra and the ionization energy for hydrogen. However, it also had many limitations: It was not able to predict the line
Ch28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms Bohr s model was very successful to explain line spectra and the ionization energy for hydrogen. However, it also had many limitations: It was not able to predict the line
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701
 Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/24//2017 Physics 5701 Lecture Commutation of Observables and First Consequences of the Postulates Outline 1 Commutation Relations 2 Uncertainty Relations
1 Fundamental physical postulates. C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
Atkins & de Paula: Atkins Physical Chemistry 9e Checklist of key ideas. Chapter 7: Quantum Theory: Introduction and Principles
 Atkins & de Paula: Atkins Physical Chemistry 9e Checklist of key ideas Chapter 7: Quantum Theory: Introduction and Principles classical mechanics, the laws of motion introduced in the seventeenth century
Atkins & de Paula: Atkins Physical Chemistry 9e Checklist of key ideas Chapter 7: Quantum Theory: Introduction and Principles classical mechanics, the laws of motion introduced in the seventeenth century
F R A N C E S C O B U S C E M I ( N A G OYA U N I V E R S I T Y ) C O L L O Q U I U D E P T. A P P L I E D M AT H E M AT I C S H A N YA N G U N I
 QUANTUM UNCERTAINT Y F R A N C E S C O B U S C E M I ( N A G OYA U N I V E R S I T Y ) C O L L O Q U I U M @ D E P T. A P P L I E D M AT H E M AT I C S H A N YA N G U N I V E R S I T Y ( E R I C A ) 2
QUANTUM UNCERTAINT Y F R A N C E S C O B U S C E M I ( N A G OYA U N I V E R S I T Y ) C O L L O Q U I U M @ D E P T. A P P L I E D M AT H E M AT I C S H A N YA N G U N I V E R S I T Y ( E R I C A ) 2
Bohr. Electronic Structure. Spectroscope. Spectroscope
 Bohr Electronic Structure Bohr proposed that the atom has only certain allowable energy states. Spectroscope Using a device called a it was found that gaseous elements emitted electromagnetic radiation
Bohr Electronic Structure Bohr proposed that the atom has only certain allowable energy states. Spectroscope Using a device called a it was found that gaseous elements emitted electromagnetic radiation
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
 Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
Fundamental of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Xinzhao Chu I 10 3.4. Principle of Uncertainty Indeterminacy 0. Expression of Heisenberg s Principle of Uncertainty It is worth to point out that
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics
 Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
Lecture 4: Postulates of quantum mechanics Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur The postulates of quantum mechanics provide us the mathematical formalism over which the physical theory is developed. For people studying
Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE Brooks/Cole - Thomson
 Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 7.1 The Nature of Light 2 Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation Light consists
Chapter 7 QUANTUM THEORY & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1 7.1 The Nature of Light 2 Most subatomic particles behave as PARTICLES and obey the physics of waves. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation Light consists
Intent. a little geometry of eigenvectors, two-dimensional example. classical analog of QM, briefly
 Intent a little geometry of eigenvectors, two-dimensional example classical analog of QM, briefly review of the underpinnings of QM, emphasizing Hilbert space operators with some simplifying assumptions???
Intent a little geometry of eigenvectors, two-dimensional example classical analog of QM, briefly review of the underpinnings of QM, emphasizing Hilbert space operators with some simplifying assumptions???
Provide a short and specific definition in YOUR OWN WORDS. Do not use the definition from the book. Electromagnetic Radiation
 Name: Provide a short and specific definition in YOUR OWN WORDS. Do not use the definition from the book Additional Notes: Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength Frequency Photoelectric
Name: Provide a short and specific definition in YOUR OWN WORDS. Do not use the definition from the book Additional Notes: Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength Frequency Photoelectric
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS
 MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics
 p. 1/23 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have reviewed the mathematics (complex linear algebra) necessary to understand quantum mechanics. We will now see how the physics of quantum mechanics fits
p. 1/23 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have reviewed the mathematics (complex linear algebra) necessary to understand quantum mechanics. We will now see how the physics of quantum mechanics fits
Many Body Quantum Mechanics
 Many Body Quantum Mechanics In this section, we set up the many body formalism for quantum systems. This is useful in any problem involving identical particles. For example, it automatically takes care
Many Body Quantum Mechanics In this section, we set up the many body formalism for quantum systems. This is useful in any problem involving identical particles. For example, it automatically takes care
4.3 Lecture 18: Quantum Mechanics
 CHAPTER 4. QUANTUM SYSTEMS 73 4.3 Lecture 18: Quantum Mechanics 4.3.1 Basics Now that we have mathematical tools of linear algebra we are ready to develop a framework of quantum mechanics. The framework
CHAPTER 4. QUANTUM SYSTEMS 73 4.3 Lecture 18: Quantum Mechanics 4.3.1 Basics Now that we have mathematical tools of linear algebra we are ready to develop a framework of quantum mechanics. The framework
Page 684. Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02
 Page 684 Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02 Time Transformations Section 12.5 Symmetries: Time Transformations Page 685 Time Translation
Page 684 Lecture 40: Coordinate Transformations: Time Transformations Date Revised: 2009/02/02 Date Given: 2009/02/02 Time Transformations Section 12.5 Symmetries: Time Transformations Page 685 Time Translation
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers
 Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Syllabus and Textbook references All the main lessons (e.g., 1.1) and units (e.g., 1.1.1) for this class are listed below. Mostly, there are three lessons
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Syllabus and Textbook references All the main lessons (e.g., 1.1) and units (e.g., 1.1.1) for this class are listed below. Mostly, there are three lessons
Early Quantum Theory & Models of the Atom (Ch 27) Discovery of electron. Blackbody Radiation. Blackbody Radiation. J. J. Thomson ( )
 Early Quantum Theory & Models of the Atom (Ch 27) Discovery of electron Modern physics special relativity quantum theory J. J. Thomson (1856-1940) measured e/m directly set-up was similar to mass spectrometer
Early Quantum Theory & Models of the Atom (Ch 27) Discovery of electron Modern physics special relativity quantum theory J. J. Thomson (1856-1940) measured e/m directly set-up was similar to mass spectrometer
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case:
 The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
Sparks CH301. Quantum Mechanics. Waves? Particles? What and where are the electrons!? UNIT 2 Day 3. LM 14, 15 & 16 + HW due Friday, 8:45 am
 Sparks CH301 Quantum Mechanics Waves? Particles? What and where are the electrons!? UNIT 2 Day 3 LM 14, 15 & 16 + HW due Friday, 8:45 am What are we going to learn today? The Simplest Atom - Hydrogen Relate
Sparks CH301 Quantum Mechanics Waves? Particles? What and where are the electrons!? UNIT 2 Day 3 LM 14, 15 & 16 + HW due Friday, 8:45 am What are we going to learn today? The Simplest Atom - Hydrogen Relate
Lecture 14: Superposition & Time-Dependent Quantum States
 Lecture 14: Superposition & Time-Dependent Quantum States U= y(x,t=0) 2 U= U= y(x,t 0 ) 2 U= x 0 x L 0 x L Lecture 14, p 1 Last Week Time-independent Schrodinger s Equation (SEQ): 2 2m d y ( x) U ( x)
Lecture 14: Superposition & Time-Dependent Quantum States U= y(x,t=0) 2 U= U= y(x,t 0 ) 2 U= x 0 x L 0 x L Lecture 14, p 1 Last Week Time-independent Schrodinger s Equation (SEQ): 2 2m d y ( x) U ( x)
Basics on quantum information
 Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2016 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 52 Brief
Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2016 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 52 Brief
Quantum Mechanics Basics II
 Quantum Mechanics Basics II VBS/MRC Quantum Mechanics Basics II 0 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1. State of a Particle Wave Functions 2. Physical Observables Hermitian Operators 3. Outcome of Experiment
Quantum Mechanics Basics II VBS/MRC Quantum Mechanics Basics II 0 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 1. State of a Particle Wave Functions 2. Physical Observables Hermitian Operators 3. Outcome of Experiment
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Quantum Theory. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 6
 Quantum Theory Thornton and Rex, Ch. 6 Matter can behave like waves. 1) What is the wave equation? 2) How do we interpret the wave function y(x,t)? Light Waves Plane wave: y(x,t) = A cos(kx-wt) wave (w,k)
Quantum Theory Thornton and Rex, Ch. 6 Matter can behave like waves. 1) What is the wave equation? 2) How do we interpret the wave function y(x,t)? Light Waves Plane wave: y(x,t) = A cos(kx-wt) wave (w,k)
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations
 Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
PHY 571: Quantum Physics
 PHY 571: Quantum Physics John Venables 5-1675, john.venables@asu.edu Spring 2008 The Transition to Quantum Mechanics Module 1, Lecture 6, 7 and 8 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Describe waves/particles
PHY 571: Quantum Physics John Venables 5-1675, john.venables@asu.edu Spring 2008 The Transition to Quantum Mechanics Module 1, Lecture 6, 7 and 8 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Describe waves/particles
Physics 1C Lecture 28C. "For those who are not shocked when they first come across quantum theory cannot possibly have understood it.
 Physics 1C Lecture 28C "For those who are not shocked when they first come across quantum theory cannot possibly have understood it." --Neils Bohr Outline CAPE and extra credit problems Wave-particle duality
Physics 1C Lecture 28C "For those who are not shocked when they first come across quantum theory cannot possibly have understood it." --Neils Bohr Outline CAPE and extra credit problems Wave-particle duality
Second quantization: where quantization and particles come from?
 110 Phys460.nb 7 Second quantization: where quantization and particles come from? 7.1. Lagrangian mechanics and canonical quantization Q: How do we quantize a general system? 7.1.1.Lagrangian Lagrangian
110 Phys460.nb 7 Second quantization: where quantization and particles come from? 7.1. Lagrangian mechanics and canonical quantization Q: How do we quantize a general system? 7.1.1.Lagrangian Lagrangian
CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS
 CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Basics of Quantum Mechanics - Why Quantum Physics? - Classical mechanics (Newton's mechanics) and Maxwell's equations (electromagnetics theory) can explain MACROSCOPIC
CHAPTER 2: POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Basics of Quantum Mechanics - Why Quantum Physics? - Classical mechanics (Newton's mechanics) and Maxwell's equations (electromagnetics theory) can explain MACROSCOPIC
Closing the Debates on Quantum Locality and Reality: EPR Theorem, Bell's Theorem, and Quantum Information from the Brown-Twiss Vantage
 Closing the Debates on Quantum Locality and Reality: EPR Theorem, Bell's Theorem, and Quantum Information from the Brown-Twiss Vantage C. S. Unnikrishnan Fundamental Interactions Laboratory Tata Institute
Closing the Debates on Quantum Locality and Reality: EPR Theorem, Bell's Theorem, and Quantum Information from the Brown-Twiss Vantage C. S. Unnikrishnan Fundamental Interactions Laboratory Tata Institute
Physics 217 Problem Set 1 Due: Friday, Aug 29th, 2008
 Problem Set 1 Due: Friday, Aug 29th, 2008 Course page: http://www.physics.wustl.edu/~alford/p217/ Review of complex numbers. See appendix K of the textbook. 1. Consider complex numbers z = 1.5 + 0.5i and
Problem Set 1 Due: Friday, Aug 29th, 2008 Course page: http://www.physics.wustl.edu/~alford/p217/ Review of complex numbers. See appendix K of the textbook. 1. Consider complex numbers z = 1.5 + 0.5i and
8.05 Quantum Physics II, Fall 2011 FINAL EXAM Thursday December 22, 9:00 am -12:00 You have 3 hours.
 8.05 Quantum Physics II, Fall 0 FINAL EXAM Thursday December, 9:00 am -:00 You have 3 hours. Answer all problems in the white books provided. Write YOUR NAME and YOUR SECTION on your white books. There
8.05 Quantum Physics II, Fall 0 FINAL EXAM Thursday December, 9:00 am -:00 You have 3 hours. Answer all problems in the white books provided. Write YOUR NAME and YOUR SECTION on your white books. There
We also find the development of famous Schrodinger equation to describe the quantization of energy levels of atoms.
 Lecture 4 TITLE: Quantization of radiation and matter: Wave-Particle duality Objectives In this lecture, we will discuss the development of quantization of matter and light. We will understand the need
Lecture 4 TITLE: Quantization of radiation and matter: Wave-Particle duality Objectives In this lecture, we will discuss the development of quantization of matter and light. We will understand the need
Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics Units of Chapter 38 38-1 Quantum Mechanics A New Theory 37-2 The Wave Function and Its Interpretation; the Double-Slit Experiment 38-3 The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Chapter 38 Quantum Mechanics Units of Chapter 38 38-1 Quantum Mechanics A New Theory 37-2 The Wave Function and Its Interpretation; the Double-Slit Experiment 38-3 The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Electron in a Box. A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time.
 Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Electron in a Box A wave packet in a square well (an electron in a box) changing with time. Last Time: Light Wave model: Interference pattern is in terms of wave intensity Photon model: Interference in
Quantum Theory. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 6
 Quantum Theory Thornton and Rex, Ch. 6 Matter can behave like waves. 1) What is the wave equation? 2) How do we interpret the wave function y(x,t)? Light Waves Plane wave: y(x,t) = A cos(kx-wt) wave (w,k)
Quantum Theory Thornton and Rex, Ch. 6 Matter can behave like waves. 1) What is the wave equation? 2) How do we interpret the wave function y(x,t)? Light Waves Plane wave: y(x,t) = A cos(kx-wt) wave (w,k)
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case
 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 93
 B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 93 B.5 Superposition B.5.a Bases 1. In QM certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron in an atom. Therefore an atom might be in certain
B. BASIC CONCEPTS FROM QUANTUM THEORY 93 B.5 Superposition B.5.a Bases 1. In QM certain physical quantities are quantized, such as the energy of an electron in an atom. Therefore an atom might be in certain
0.1 Schrödinger Equation in 2-dimensional system
 0.1 Schrödinger Equation in -dimensional system In HW problem set 5, we introduced a simpleminded system describing the ammonia (NH 3 ) molecule, consisting of a plane spanned by the 3 hydrogen atoms and
0.1 Schrödinger Equation in -dimensional system In HW problem set 5, we introduced a simpleminded system describing the ammonia (NH 3 ) molecule, consisting of a plane spanned by the 3 hydrogen atoms and
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms
 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light Made up of electromagnetic radiation. Waves of electric and magnetic fields at right angles to each other. Parts of a wave Wavelength
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms 6.1 The Wave Nature of Light Made up of electromagnetic radiation. Waves of electric and magnetic fields at right angles to each other. Parts of a wave Wavelength
Theoretical Biophysics. Quantum Theory and Molecular Dynamics. Pawel Romanczuk WS 2017/18
 Theoretical Biophysics Quantum Theory and Molecular Dynamics Pawel Romanczuk WS 2017/18 http://lab.romanczuk.de/teaching/ 1 Introduction Two pillars of classical theoretical physics at the begin of 20th
Theoretical Biophysics Quantum Theory and Molecular Dynamics Pawel Romanczuk WS 2017/18 http://lab.romanczuk.de/teaching/ 1 Introduction Two pillars of classical theoretical physics at the begin of 20th
8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation
 8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation So far we have considered only free particles - i.e. particles whose energy consists entirely of its kinetic energy. In general, however, a particle moves under
8 Wavefunctions - Schrödinger s Equation So far we have considered only free particles - i.e. particles whose energy consists entirely of its kinetic energy. In general, however, a particle moves under
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys 191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/05 Fall 2005 Lecture 11 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation
 CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation In class we have discussed a thought experiment 1 that contrasts the behavior of classical particles, classical waves and quantum particles.
CHM 532 Notes on Wavefunctions and the Schrödinger Equation In class we have discussed a thought experiment 1 that contrasts the behavior of classical particles, classical waves and quantum particles.
Chapter 4. Development of a New Model
 Chapter 4 Development of a New Model Electrons behave like particles in some experiments, and like waves in others. The electron's 'wave/particle duality' has no real analogy in the everyday world. The
Chapter 4 Development of a New Model Electrons behave like particles in some experiments, and like waves in others. The electron's 'wave/particle duality' has no real analogy in the everyday world. The
The Two Level Atom. E e. E g. { } + r. H A { e e # g g. cos"t{ e g + g e } " = q e r g
 E e = h" 0 The Two Level Atom h" e h" h" 0 E g = " h# 0 g H A = h" 0 { e e # g g } r " = q e r g { } + r $ E r cos"t{ e g + g e } The Two Level Atom E e = µ bb 0 h" h" " r B = B 0ˆ z r B = B " cos#t x
E e = h" 0 The Two Level Atom h" e h" h" 0 E g = " h# 0 g H A = h" 0 { e e # g g } r " = q e r g { } + r $ E r cos"t{ e g + g e } The Two Level Atom E e = µ bb 0 h" h" " r B = B 0ˆ z r B = B " cos#t x
Attempts at relativistic QM
 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
PHY 396 K. Problem set #5. Due October 9, 2008.
 PHY 396 K. Problem set #5. Due October 9, 2008.. First, an exercise in bosonic commutation relations [â α, â β = 0, [â α, â β = 0, [â α, â β = δ αβ. ( (a Calculate the commutators [â αâ β, â γ, [â αâ β,
PHY 396 K. Problem set #5. Due October 9, 2008.. First, an exercise in bosonic commutation relations [â α, â β = 0, [â α, â β = 0, [â α, â β = δ αβ. ( (a Calculate the commutators [â αâ β, â γ, [â αâ β,
MESOSCOPIC QUANTUM OPTICS
 MESOSCOPIC QUANTUM OPTICS by Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ata Imamoglu A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Toronto Singapore Preface xi 1 Basic Concepts
MESOSCOPIC QUANTUM OPTICS by Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ata Imamoglu A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Toronto Singapore Preface xi 1 Basic Concepts
Learning Objectives and Worksheet I. Chemistry 1B-AL Fall 2016
 Learning Objectives and Worksheet I Chemistry 1B-AL Fall 2016 Lectures (1 2) Nature of Light and Matter, Quantization of Energy, and the Wave Particle Duality Read: Chapter 12, Pages: 524 526 Supplementary
Learning Objectives and Worksheet I Chemistry 1B-AL Fall 2016 Lectures (1 2) Nature of Light and Matter, Quantization of Energy, and the Wave Particle Duality Read: Chapter 12, Pages: 524 526 Supplementary
c = λν 10/23/13 What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
2.1 Green Functions in Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 2 Green Functions and Observables 2.1 Green Functions in Quantum Mechanics We will be interested in studying the properties of the ground state of a quantum mechanical many particle system. We
Chapter 2 Green Functions and Observables 2.1 Green Functions in Quantum Mechanics We will be interested in studying the properties of the ground state of a quantum mechanical many particle system. We
Uncertainty Principle
 Uncertainty Principle n n A Fourier transform of f is a function of frequency v Let be Δv the frequency range n It can be proved that ΔtΔv 1/(4 π) n n If Δt is small, f corresponds to a small interval
Uncertainty Principle n n A Fourier transform of f is a function of frequency v Let be Δv the frequency range n It can be proved that ΔtΔv 1/(4 π) n n If Δt is small, f corresponds to a small interval
Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 3 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 3. Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have introduced two concepts: (i the state of a particle or a quantum mechanical system is described by a wave
Chapter 3 Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics 3. Basic Postulates of Quantum Mechanics We have introduced two concepts: (i the state of a particle or a quantum mechanical system is described by a wave
Chapter 1 Recollections from Elementary Quantum Physics
 Chapter 1 Recollections from Elementary Quantum Physics Abstract We recall the prerequisites that we assume the reader to be familiar with, namely the Schrödinger equation in its time dependent and time
Chapter 1 Recollections from Elementary Quantum Physics Abstract We recall the prerequisites that we assume the reader to be familiar with, namely the Schrödinger equation in its time dependent and time
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
 The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
Basics on quantum information
 Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2014 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 49 Brief
Basics on quantum information Mika Hirvensalo Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Turku mikhirve@utu.fi Thessaloniki, May 2014 Mika Hirvensalo Basics on quantum information 1 of 49 Brief
Light. October 16, Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms Honors Chemistry. Bohr Model
 Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms Honors Chemistry Bohr Model Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist and a student of Rutherford improved Rutherford's model. Bohr proposed that an electron is found only in specific
Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms Honors Chemistry Bohr Model Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist and a student of Rutherford improved Rutherford's model. Bohr proposed that an electron is found only in specific
Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Introduction to Quantum Computing Petros Wallden Lecture 3: Basic Quantum Mechanics 26th September 2016 School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Resources 1. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information
Introduction to Quantum Computing Petros Wallden Lecture 3: Basic Quantum Mechanics 26th September 2016 School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Resources 1. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information
Quantum Computing Lecture 2. Review of Linear Algebra
 Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Physics 741 Graduate Quantum Mechanics 1 Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall x i x dx i x i x x i x dx
 Physics 74 Graduate Quantum Mechanics Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall 4. [ points] Consider the wave function x Nexp x ix (a) [6] What is the correct normaliation N? The normaliation condition is. exp,
Physics 74 Graduate Quantum Mechanics Solutions to Midterm Exam, Fall 4. [ points] Consider the wave function x Nexp x ix (a) [6] What is the correct normaliation N? The normaliation condition is. exp,
Lecture Outline Chapter 30. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 30 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 30 Quantum Physics Units of Chapter 30 Blackbody Radiation and Planck s Hypothesis of Quantized Energy Photons and the Photoelectric
Lecture Outline Chapter 30 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 30 Quantum Physics Units of Chapter 30 Blackbody Radiation and Planck s Hypothesis of Quantized Energy Photons and the Photoelectric
Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term Example Sheet 1. Values of some physical constants are given on the supplementary sheet
 Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term 2015 Quantum Mechanics Dr. J.M. Evans Example Sheet 1 Values of some physical constants are given on the supplementary sheet 1. Whenasampleofpotassiumisilluminatedwithlightofwavelength3
Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term 2015 Quantum Mechanics Dr. J.M. Evans Example Sheet 1 Values of some physical constants are given on the supplementary sheet 1. Whenasampleofpotassiumisilluminatedwithlightofwavelength3
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I Key. September 19, ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer.
 D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I Key September 19, 003 1) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of
D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I Key September 19, 003 1) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of
XI. INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS. C. Cohen-Tannoudji et al., Quantum Mechanics I, Wiley. Outline: Electromagnetic waves and photons
 XI. INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS C. Cohen-Tannoudji et al., Quantum Mechanics I, Wiley. Outline: Electromagnetic waves and photons Material particles and matter waves Quantum description of a particle:
XI. INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM MECHANICS C. Cohen-Tannoudji et al., Quantum Mechanics I, Wiley. Outline: Electromagnetic waves and photons Material particles and matter waves Quantum description of a particle:
Ch 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom (light and atomic structure)
 Ch 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom (light and atomic structure) Electromagnetic Radiation - Electromagnetic radiation consists of oscillations in electric and magnetic fields. The oscillations can be described
Ch 7 Quantum Theory of the Atom (light and atomic structure) Electromagnetic Radiation - Electromagnetic radiation consists of oscillations in electric and magnetic fields. The oscillations can be described
3.5 Finite Rotations in 3D Euclidean Space and Angular Momentum in QM
 3.5 Finite Rotations in 3D Euclidean Space and Angular Momentum in QM An active rotation in 3D position space is defined as the rotation of a vector about some point in a fixed coordinate system (a passive
3.5 Finite Rotations in 3D Euclidean Space and Angular Momentum in QM An active rotation in 3D position space is defined as the rotation of a vector about some point in a fixed coordinate system (a passive
Time evolution of states in quantum mechanics 1
 Time evolution of states in quantum mechanics 1 The time evolution from time t 0 to t of a quantum mechanical state is described by a linear operator Û(t, t 0. Thus a ket at time t that started out at
Time evolution of states in quantum mechanics 1 The time evolution from time t 0 to t of a quantum mechanical state is described by a linear operator Û(t, t 0. Thus a ket at time t that started out at
Electronic Structure of Atoms. Chapter 6
 Electronic Structure of Atoms Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms 1. The Wave Nature of Light All waves have: a) characteristic wavelength, λ b) amplitude, A Electronic Structure of Atoms 1. The Wave
Electronic Structure of Atoms Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms 1. The Wave Nature of Light All waves have: a) characteristic wavelength, λ b) amplitude, A Electronic Structure of Atoms 1. The Wave
Electrons in Atoms. Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy
 Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Path Integral for Spin
 Path Integral for Spin Altland-Simons have a good discussion in 3.3 Applications of the Feynman Path Integral to the quantization of spin, which is defined by the commutation relations [Ŝj, Ŝk = iɛ jk
Path Integral for Spin Altland-Simons have a good discussion in 3.3 Applications of the Feynman Path Integral to the quantization of spin, which is defined by the commutation relations [Ŝj, Ŝk = iɛ jk
Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term INTRODUCTION
 Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term 2017 Quantum Mechanics Dr. J.M. Evans 0. INTRODUCTION Quantum Mechanics (QM) is a radical generalisation of classical physics involving a new fundamental constant,
Mathematical Tripos Part IB Michaelmas Term 2017 Quantum Mechanics Dr. J.M. Evans 0. INTRODUCTION Quantum Mechanics (QM) is a radical generalisation of classical physics involving a new fundamental constant,
What needs to be known about the Collapse of Quantum-Mechanical Wave-Function
 1 What needs to be known about the Collapse of Quantum-Mechanical Wave-Function Hasmukh K. Tank Indian Space Research Organization, 22/693 Krishna Dham-2, Vejalpur, Ahmedabad-380015 India Abstract Quantum
1 What needs to be known about the Collapse of Quantum-Mechanical Wave-Function Hasmukh K. Tank Indian Space Research Organization, 22/693 Krishna Dham-2, Vejalpur, Ahmedabad-380015 India Abstract Quantum
Isospin. K.K. Gan L5: Isospin and Parity 1
 Isospin Isospin is a continuous symmetry invented by Heisenberg: Explain the observation that the strong interaction does not distinguish between neutron and proton. Example: the mass difference between
Isospin Isospin is a continuous symmetry invented by Heisenberg: Explain the observation that the strong interaction does not distinguish between neutron and proton. Example: the mass difference between
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics
 1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-5: QUANTUM THEORY AND THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE Introductory Video Quantum Mechanics IB Assessment Statements Topic 13.1, Quantum Physics:
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-5: QUANTUM THEORY AND THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE Introductory Video Quantum Mechanics IB Assessment Statements Topic 13.1, Quantum Physics:
Chapter 7 Atomic Structure -1 Quantum Model of Atom. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 7 Atomic Structure -1 Quantum Model of Atom Dr. Sapna Gupta The Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic spectrum includes many different types of radiation which travel in waves. Visible light
Chapter 7 Atomic Structure -1 Quantum Model of Atom Dr. Sapna Gupta The Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic spectrum includes many different types of radiation which travel in waves. Visible light
Chapter 7. The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom. Chapter 7 Lecture Lecture Presentation. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University
 Chapter 7 Lecture Lecture Presentation Chapter 7 The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University The Beginnings of Quantum Mechanics Until the beginning of the twentieth
Chapter 7 Lecture Lecture Presentation Chapter 7 The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University The Beginnings of Quantum Mechanics Until the beginning of the twentieth
Lecture 36 Chapter 31 Light Quanta Matter Waves Uncertainty Principle
 Lecture 36 Chapter 31 Light Quanta Matter Waves Uncertainty Principle 24-Nov-10 Birth of Quantum Theory There has been a long historical debate about the nature of light: Some believed it to be particle-like.
Lecture 36 Chapter 31 Light Quanta Matter Waves Uncertainty Principle 24-Nov-10 Birth of Quantum Theory There has been a long historical debate about the nature of light: Some believed it to be particle-like.
msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 189 #197
 msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 189 #197 Bibliography Dirac, P. A. M., The Principles of Quantum Mechanics, 4th Edition, (Oxford University Press, London, 1958). Feynman, R. P. and A. P. Hibbs, Quantum Mechanics
msqm 2011/8/14 21:35 page 189 #197 Bibliography Dirac, P. A. M., The Principles of Quantum Mechanics, 4th Edition, (Oxford University Press, London, 1958). Feynman, R. P. and A. P. Hibbs, Quantum Mechanics
2) The number of cycles that pass through a stationary point is called A) wavelength. B) amplitude. C) frequency. D) area. E) median.
 Chemistry Structure and Properties 2nd Edition Tro Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/chemistry-structure-and-properties-2nd-edition-tro-test-bank/ Chemistry: Structure & Properties,
Chemistry Structure and Properties 2nd Edition Tro Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/chemistry-structure-and-properties-2nd-edition-tro-test-bank/ Chemistry: Structure & Properties,
E = φ 1 A The dynamics of a particle with mass m and charge q is determined by the Hamiltonian
 Lecture 9 Relevant sections in text: 2.6 Charged particle in an electromagnetic field We now turn to another extremely important example of quantum dynamics. Let us describe a non-relativistic particle
Lecture 9 Relevant sections in text: 2.6 Charged particle in an electromagnetic field We now turn to another extremely important example of quantum dynamics. Let us describe a non-relativistic particle
