MATH 391 Test 1 Fall, (1) (12 points each)compute the general solution of each of the following differential equations: = 4x 2y.
|
|
|
- Dora Blanche Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATH 391 Test 1 Fall, 2018 (1) (12 points each)compute the general solution of each of the following differential equations: (a) (b) x dy dx + xy = x2 + y. (x + y) dy dx = 4x 2y. (c) yy + (y ) 2 = 0 (y is a function of x). dy (a) Linear: dx + [1 1 x ]y = x. µ = exp[ (1 1 )dx] = x 1 e x. So [x 1 e x y] = e x. The solution is x 1 e x y = e x + C. So y = x + Cxe x. (b) Homogeneous: Use z = y/x. x dz 1+z (z+4)(z 1) = A z+4 + B z 1. dx = 4 2z 1+z z = 4 3z z2 1+z = (z+4)(z 1) 1+z. So 1+z = A(z 1)+B(z+4). Substitute z = 1, 4 to get A = 3/5, B = 2/5. (3/5) ln((y/x)+4)+(2/5) ln((y/x) 1) = ln(x)+c. You need not simplify, but ln[(y + 4x) 3 x 2 ] + ln[(y x) 2 x 3 ] = C. (c) Reduction of Order: y = v, y = v dv dy dv and so yv and so y = C are solutions, but you need not include them]. dv v ln v = ln y + C 1 or dy dx = v = C 1y 1. So y 2 /2 = C 1 x + C 2. dy + v2 = 0. [v = 0 = dy y and so (a) (b) (2) (12 points each) Solve the following initial value problems: x 2 y dy dx + xy2 = x + 1. with y(3) = 1. dy dx = xy 2 + x 2 y 2. with y(0) = 1. (a) (x 2 y)dy + (xy 2 x 1)dx = 0 is exact with F = 1 2 x2 y 2 + H(x) and so xy 2 + H (x) = xy 2 x 1. So F = 1 2 [x2 y 2 x 2 2x]. The general solution is F = C. So 1 2 [ ] = C and 3 = C. Solution x 2 y 2 x 2 2x = 6. (b) Variables separable with y 2 dy = [x+x 2 ]dx. So y 1 = x 2 /2+x 3 /3+C. Since y = 1 when x = 0, C = 1.
2 (3) (10 points each)in the following equations y is a function of t. (a) Solve the initial value problem 2y + 3y 5y = 0, y(0) = 14, y (0) = 0. (b) Compute the general solution of 2y + 3y + 5y = 0. (a) The characteristic equation is 0 = 2r 2 + 3r 5 = (2r + 5)(r 1) with roots r = 5/2, 1. The general solution is y = C 1 e 5t/2 + C 2 e t. So 14 = y(0) = C 1 + C 2 and 0 = y (0) = 5C 1 /2 + C 2. Subtracting, 14 = 7C 1 /2 and so C 1 = 4, C 2 = 10. y = 4e 5t/2 + 10e t. (b) The characteristic equation is 0 = 2r 2 + 3r + 5 with roots the complex conjugate pair r = ( 3/4) ± i 31/4. The general solution is y = C 1 e 3t/4 cos( 31t/4) + C 2 e 3t/4 cos( 31t/4). (4)(10 points) Assume that y 1, y 2 are solutions of the equation y +py +qy = 0 where p and q are functions of t defined for all t. (a) Prove Abel s Theorem, that the Wronskian of of the pair y 1, y 2 satisfies a first order equation. (b) Explain why the solution of the equation in (a) shows that either the Wronskian is identically zero or never zero. q y 1 y 2 y 2 y 1 = 0 p y 1 y 2 y 2 y 1 = W 1 y 1 y 2 y 2 y 1 = W Adding we obtain 0 = pw + W with solution W = Cexp[ p(t)dt]. The exponential is positive and so if C 0 the Wronskian is never zero. (5) (10 points) I borrow $10, 000 which has an interest rate of 7% per year, compounded continuously. I pay it off continuously at a rate of $100 per month. Set up an initial value problem (differential equation and initial conditions) whose solution is the quantity P (t) of dollars that I have left to pay time t (until the loan is paid off). You need not solve the equation. The payoff rate is $1200 per year. dp dt =.07P 1200 with P (0) = 10, 000.
3 MATH 391 Test 2 Fall, 2018 (1)(18 points) Solve the initial value problem: y 3y = 18t + 36e 3t with y(0) = 0 and y (0) = 0. Characteristic equation for the homogeneous is r 2 3r = 0 with roots r = 0, 3. So y h = C 1 + C 2 e 3t. 18t has associated root 0 and 36e 3t has associated root 3. Yp 1 = (At + B) + (Ce 3t ) but we must multiply the first block by t. 0 [Y p = At 2 + Bt + + Ce 3t ], 3 [Y p = 2At + B 3Ce 3t ], 1 [Y p = + + 2A + 9Ce 3t ]. 18t + 36e 3t = 6At + ( 3B + 2A) + 18Ce 3t. So A = 3, B = 2, C = 2. y g = C 1 + C 2 e 3t 3t 2 2t + 2e 3t, y g = +3C 2 e 3t 6t 2 6e 3t. 0 = C 1 + C 2 + 2, 0 = 3C So C 2 = (8/3), C 1 = (14/3). y = (14/3) + (8/3)e 3t 3t 2 2t + 2e 3t. (2)(18 points) Consider the sixth order differential equation y (6) +2y +y = 3t 2 + te t/2 7e t/2 sin(( 3/2)t) + cos(( 3/2)t) + 1. (a) Compute the general solution of the associated homogeneous equation. (b) Write down the test function with the fewest terms which can be used to obtain a particular solution via the Method of Undetermined Coefficients. Do not solve for the constants. Characteristic equation for the homogeneous is r 6 + 2r = (r 3 + 1) 2 = 0. Since r 3 +1 = (r +1)(r 2 r +1) the roots are 1, (1/2)±( 3/2)i each repeated twice. y h = C 1 e t + C 2 te t + C 3 e (1/2)t cos(( 3/2)t) + +C 4 e (1/2)t sin(( 3/2)t)+ C 5 te (1/2)t cos(( 3/2)t) + C 6 te (1/2)t sin(( 3/2)t). Associated root for 3t 2 and 1 is 0, for te t/2 is (1/2), for 7e t/2 sin(( 3/2)t) is (1/2) ± ( 3/2)i and for cos(( 3/2)t) is ±( 3/2)i. Y 1 p = (At 2 + Bt + C) + (Dt + E)e t/2 + (F e t/2 cos(( 3/2)t) + Ge t/2 sin(( 3/2)t)) + (H cos(( 3/2)t) + I sin(( 3/2)t)).
4 Since (1/2) ± ( 3/2)i is repeated twice we must multiply the third block by t 2. Y p = (At 2 + Bt + C) + (Dt + E)e t/2 + t 2 (F e t/2 cos(( 3/2)t)+Ge t/2 sin(( 3/2)t))+(H cos(( 3/2)t)+I sin(( 3/2)t)). (3)(16 points) Compute the general solution of y + y = tan(t). Characteristic equation for the homogeneous is r = 0 with roots ±i and so y h = C 1 cos(t) + C 2 sin(t). We look for y p = u 1 cos(t) + u 2 sin(t). u 1(cos(t)) + u 2(sin(t)) = 0 u 1( sin(t)) + u 2(cos(t)) = tan(t). Wronskian is 1. u 1 = sin(t) tan(t) = sin 2 (t)/ cos(t) = (cos 2 (t) 1)/ cos(t) = cos(t) sec(t), u 2 = cos(t) tan(t) = sin(t). u 1 = sin(t) ln sec(t) + tan(t), u 2 = cos(t), y g = C 1 cos(t) + C 2 sin(t) sin(t) ln sec(t) + tan(t). (4)(16 points) For the differential equation, (x 1)y xy +y = 0, y 1 = e x is a solution. Use the method of Reduction of Order to compute a second solution y 2 which is independent of the first one. y 2 (x) = ue x. 1 [y 2 = ue x ] x [y 2 = ue x + u e x ] (x 1) [y 2 = ue x + 2u e x + u e x ] 0 = 0 + u (x 2)e x + u (x 1)e x (x 1)v = (x 2)v, and so dv v = x 1 dx. u = v = (x 1)e x, and so u = xe x and y 2 = uy 1 = x. (5)(14 points) A hanging spring is stretched 6 inches (=.5 feet) by a weight of 24 pounds. (a) Set up the initial value problem (differential equation and initial conditions) which describes the motion, neglecting friction, when the weight is pulled down an additional foot and is then released and is subjected to an external force of 6 cos(ωt). You need not solve the equation. (Recall that g, the acceleration due to gravity is 32 feet/second 2.)
5 (b) Write down the test function with the fewest terms which can be used to obtain a particular solution via the Method of Undetermined Coefficients when ω = 5. (c) Write down the test function with the fewest terms which can be used to obtain a particular solution via the Method of Undetermined Coefficients when ω is the resonance frequency. (a) w = 24 = mg = 32m, so m = 3/4. 24 = w = k L = k(1/2), so k = 48. c = 0. (3/4)y + 48y = 6 cos(ωt), or, y + 64y = 8 cos(ωt), y(0) = 1, y (0) = 0. (b) y p = A cos 5t + B sin 5t. (c) The natural frequency is ω = 8. y p = At cos 8t + Bt sin 8t. (6) (18 points) For the differential equation: (2 x 2 )y + x 2 y + (x 2x 3 )y = 0 Compute the recursion formula for the coefficients of the power series solution centered at x 0 = 0. Use it to compute the first three nonzero terms of the series for the solution with y(0) = 24 and y (0) = 0. 2y = Σ 2n(n 1)a n x n 2 [k = n 2] = Σ2(k + 2)(k + 1)a k+2 x k. x 2 y = Σ n(n 1)a n x n [k = n] = Σ k(k 1)a k x k. x 2 y = Σ na n x n+1 [k = n + 1] = Σ (k 1)a k 1 x k. xy = Σ a n x n+1 [k = n + 1] = Σ a k 1 x k. 2x 3 y = Σ 2a n x n+3 [k = n + 3] = Σ 2a k 3 x k. a k+2 = 1 2(k+2)(k+1) [k(k 1)a k (k 1)a k 1 a k 1 +2a k 3 ]. a 0 = 24, a 1 = 0. Recursion formula: a k+2 = 1 2(k + 2)(k + 1) [k(k 1)a k ka k 1 + 2a k 3 ]. k = 0 : a 2 = 1 4 [ ] = 0. k = 1 : a 3 = 1 12 [0 a 0 + 0] = 2. k = 2 : a 4 = 1 24 [2a 2 2a 1 + 0] = 0 k = 3 : a 5 = 1 40 [6a 3 3a 2 + 2a 0 ] = = y = x x
6 MATH 391 Test 3 Fall, 2018 (1) Compute the general solution for each of the differential equations, (y is a function of x in each case). (a) x 2 y + 7xy + 6y = 0, x > 0 (20 points) (b) y + 7y + 6y = 6x. (a) Euler Equation: Indicial Equation r(r 1) + 7r + 6 = r 2 + 6r + 6 = 0 with roots r = 3 ± 3. General solution is: y = C 1 x C 2 x 3 3. (b) For the homogeneous equation y + 7y + 6y = 0 the characteristic equation is r 2 + 7r + 6 = (r + 6)(r + 1) = 0 with roots r = 6, 1. So y h = C 1 e 6x + C 2 e x. The associated root for 6x is 0 and so Y p = Ax + B. Y p = A, Y p = 0. So Y p + 7Y p + 6Y p = 6Ax + (6B + 7A) = 6x. So A = 1, B = 7/6. y = C 1 e 6x + C 2 e x + x (7/6). (2) (a) State the definition of the Laplace transform and use it to compute to compute for a function f(t) = e t the Laplace Transform L(f)(s). (b) Compute the Laplace Transform L(y) for the solution of the initial value problem: (15 points) 3y 3y + 2y = e t, y(0) = 5 and y (0) = 2. (a) L(f)(s) = e st f(t) dt. With f(t) = e t, 0 L(f)(s) = (b) 0 e st e t dt = 0 e (s+1)t dt = 1 s + 1 e (s+1)t 0 = 1 s + 1. L(y ) = sl(y) y(0), L(y ) = sl(y ) y (0) = s 2 L(y) sy(0) y (0). L(3y 3y + 2y) = 3[s 2 L(y) s5 ( 2)] 3[sL(y) 5] + 2L(y) = 1 s + 1. So L(y) = [ 1 s s 21] [3s2 3s + 2]. (3) For the differential equation: xy (2 + x)y = 0
7 (a) The point x 0 = 2 is an ordinary point. Compute the recursion formula for the coefficients of the power series solution centered at x 0 = 2. (15 points) (b) Solve the equation explicitly, by using the method of Reduction of Order. (10 points) (c) The point x = 0 is a regular singular point. Compute the associated Euler equation and compute the recursion formula for the coefficients of the series solution centered at x 0 = 0 which is associated with the larger root.(20 points) (a) Let X = x+2 so that x = X 2. The equation becomes (X 2)y Xy = 0. y = Σa n X n. 2y = Σ 2n(n 1)a n X n 2 [k = n 2] = Σ 2(k + 2)(k + 1)a k+2 X k. +Xy = Σ n(n 1)a n X n 1 [k = n 1] = Σ (k + 1)ka k+1 X k. Xy = Σ na n X n [k = n] = Σ ka k X K Recursion formula: a k+2 = (k + 1)ka k+1 ka k. 2(k + 2)(k + 1) (b) Let v = y and v = y. x dv dx = (x + 2)v. dv ln(v) = v = x dx = x + 2 ln(x) + C 1. dy dx = C 1x 2 e x. So y = C 1 [x 2 e x 2xe x + 2e x ] + C 2. (c) Multiply by x to get x 2 y x(2+x)y = 0 with associated Euler equation x 2 y 2xy = 0. The indicial equation is r(r 1) 2r = r(r 3) = 0 with roots 0, 3. So that 3 is the larger root. y = x r Σa n x n = Σa n x n+r. x 2 y = Σ (n + r)(n + r 1)a n x n+r [k = n] = Σ(k + r)(k + r 1)a k x k+r. 2xy = Σ 2(n + r)a n x n+r [k = n] = Σ 2(k + r)a k x k+r. x 2 y = Σ (n + r)a n x n+r+1 [k = n + 1] = Σ (k 1 + r)a k 1 x k+r [(k + r)(k + r 1) 2(k + r)]a k = [(k + r)(k + r 3)]a k = (k 1 + r)a k 1. With r = 3 the Recursion Formula is: a k = (k + 2) k(k + 3) a k 1.
8 (4) (a) Compute the Fourier series for the function f(x) = x 2 on the interval [ 1, 1]. (b) Compute the solution u(x, t) for the partial differential equation on the interval [0, 1]: u t = 16u xx with u(0, t) = u(1, t) = 0 for t > 0 (boundary conditions) u(x, 0) = 3 sin(2πx) 5 sin(5πx) + sin(6πx). for 0 < x < 1 (initial conditions) (20 points) (a) y = x 2 is even and so b n = 0 for all n. a 0 = x2 dx = 2/3. a n = x 2 cos(nπx)dx = 2[(x 2 )( 1 nπ (b) L = 1, α = sin(nπx)) (2x)( cos(nπx))+(2)( (nπ) 2 (nπ) 3 sin(nπx))]1 0 = (0 0) + ( 4( 1)n 4( 1)n ((nπ) 2 0) + (0 0) = ) ((nπ) 2 ). y = (2/3) (1/2) + Σ 4( 1) n n=1 ((nπ) 2 ) cos(nπx). u(x, t) = 3e (8π)2t sin(2πx) 5e (20π)2t sin(5πx) + e (24π)2t sin(6πx).
Math K (24564) - Homework Solutions 02
 Math 39100 K (24564) - Homework Solutions 02 Ethan Akin Office: NAC 6/287 Phone: 650-5136 Email: ethanakin@earthlink.net Spring, 2018 Contents Reduction of Order, B & D Chapter 3, p. 174 Constant Coefficient
Math 39100 K (24564) - Homework Solutions 02 Ethan Akin Office: NAC 6/287 Phone: 650-5136 Email: ethanakin@earthlink.net Spring, 2018 Contents Reduction of Order, B & D Chapter 3, p. 174 Constant Coefficient
Math K (24564) - Lectures 02
 Math 39100 K (24564) - Lectures 02 Ethan Akin Office: NAC 6/287 Phone: 650-5136 Email: ethanakin@earthlink.net Spring, 2018 Contents Second Order Linear Equations, B & D Chapter 4 Second Order Linear Homogeneous
Math 39100 K (24564) - Lectures 02 Ethan Akin Office: NAC 6/287 Phone: 650-5136 Email: ethanakin@earthlink.net Spring, 2018 Contents Second Order Linear Equations, B & D Chapter 4 Second Order Linear Homogeneous
Math 266 Midterm Exam 2
 Math 266 Midterm Exam 2 March 2st 26 Name: Ground Rules. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use one 4-by-6
Math 266 Midterm Exam 2 March 2st 26 Name: Ground Rules. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use one 4-by-6
Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA 2132 Final Practice Answers Fall 2012
 Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA Final Practice Answers Fall Studying from past or sample exams is NOT recommended. If you do, it should be only AFTER you know how to do all of the homework and worksheet
Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA Final Practice Answers Fall Studying from past or sample exams is NOT recommended. If you do, it should be only AFTER you know how to do all of the homework and worksheet
Ma 221 Final Exam Solutions 5/14/13
 Ma 221 Final Exam Solutions 5/14/13 1. Solve (a) (8 pts) Solution: The equation is separable. dy dx exy y 1 y0 0 y 1e y dy e x dx y 1e y dy e x dx ye y e y dy e x dx ye y e y e y e x c The last step comes
Ma 221 Final Exam Solutions 5/14/13 1. Solve (a) (8 pts) Solution: The equation is separable. dy dx exy y 1 y0 0 y 1e y dy e x dx y 1e y dy e x dx ye y e y dy e x dx ye y e y e y e x c The last step comes
A: Brief Review of Ordinary Differential Equations
 A: Brief Review of Ordinary Differential Equations Because of Principle # 1 mentioned in the Opening Remarks section, you should review your notes from your ordinary differential equations (odes) course
A: Brief Review of Ordinary Differential Equations Because of Principle # 1 mentioned in the Opening Remarks section, you should review your notes from your ordinary differential equations (odes) course
Graded and supplementary homework, Math 2584, Section 4, Fall 2017
 Graded and supplementary homework, Math 2584, Section 4, Fall 2017 (AB 1) (a) Is y = cos(2x) a solution to the differential equation d2 y + 4y = 0? dx2 (b) Is y = e 2x a solution to the differential equation
Graded and supplementary homework, Math 2584, Section 4, Fall 2017 (AB 1) (a) Is y = cos(2x) a solution to the differential equation d2 y + 4y = 0? dx2 (b) Is y = e 2x a solution to the differential equation
Review for Exam 2. Review for Exam 2.
 Review for Exam 2. 5 or 6 problems. No multiple choice questions. No notes, no books, no calculators. Problems similar to homeworks. Exam covers: Regular-singular points (5.5). Euler differential equation
Review for Exam 2. 5 or 6 problems. No multiple choice questions. No notes, no books, no calculators. Problems similar to homeworks. Exam covers: Regular-singular points (5.5). Euler differential equation
Ex. 1. Find the general solution for each of the following differential equations:
 MATH 261.007 Instr. K. Ciesielski Spring 2010 NAME (print): SAMPLE TEST # 2 Solve the following exercises. Show your work. (No credit will be given for an answer with no supporting work shown.) Ex. 1.
MATH 261.007 Instr. K. Ciesielski Spring 2010 NAME (print): SAMPLE TEST # 2 Solve the following exercises. Show your work. (No credit will be given for an answer with no supporting work shown.) Ex. 1.
Bessel s Equation. MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics
 Bessel s Equation MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background Bessel s equation of order ν has the form where ν is a constant. x 2 y + xy
Bessel s Equation MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background Bessel s equation of order ν has the form where ν is a constant. x 2 y + xy
Elementary Differential Equations, Section 2 Prof. Loftin: Practice Test Problems for Test Find the radius of convergence of the power series
 Elementary Differential Equations, Section 2 Prof. Loftin: Practice Test Problems for Test 2 SOLUTIONS 1. Find the radius of convergence of the power series Show your work. x + x2 2 + x3 3 + x4 4 + + xn
Elementary Differential Equations, Section 2 Prof. Loftin: Practice Test Problems for Test 2 SOLUTIONS 1. Find the radius of convergence of the power series Show your work. x + x2 2 + x3 3 + x4 4 + + xn
Diff. Eq. App.( ) Midterm 1 Solutions
 Diff. Eq. App.(110.302) Midterm 1 Solutions Johns Hopkins University February 28, 2011 Problem 1.[3 15 = 45 points] Solve the following differential equations. (Hint: Identify the types of the equations
Diff. Eq. App.(110.302) Midterm 1 Solutions Johns Hopkins University February 28, 2011 Problem 1.[3 15 = 45 points] Solve the following differential equations. (Hint: Identify the types of the equations
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Math 308 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 38 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 38 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Name: ID.NO: Fall 97. PLEASE, BE NEAT AND SHOW ALL YOUR WORK; CIRCLE YOUR ANSWER. NO NOTES, BOOKS, CALCULATORS, TAPE PLAYERS, or COMPUTERS.
 MATH 303-2/6/97 FINAL EXAM - Alternate WILKERSON SECTION Fall 97 Name: ID.NO: PLEASE, BE NEAT AND SHOW ALL YOUR WORK; CIRCLE YOUR ANSWER. NO NOTES, BOOKS, CALCULATORS, TAPE PLAYERS, or COMPUTERS. Problem
MATH 303-2/6/97 FINAL EXAM - Alternate WILKERSON SECTION Fall 97 Name: ID.NO: PLEASE, BE NEAT AND SHOW ALL YOUR WORK; CIRCLE YOUR ANSWER. NO NOTES, BOOKS, CALCULATORS, TAPE PLAYERS, or COMPUTERS. Problem
APPLIED MATHEMATICS. Part 1: Ordinary Differential Equations. Wu-ting Tsai
 APPLIED MATHEMATICS Part 1: Ordinary Differential Equations Contents 1 First Order Differential Equations 3 1.1 Basic Concepts and Ideas................... 4 1.2 Separable Differential Equations................
APPLIED MATHEMATICS Part 1: Ordinary Differential Equations Contents 1 First Order Differential Equations 3 1.1 Basic Concepts and Ideas................... 4 1.2 Separable Differential Equations................
2. Determine whether the following pair of functions are linearly dependent, or linearly independent:
 Topics to be covered on the exam include: Recognizing, and verifying solutions to homogeneous second-order linear differential equations, and their corresponding Initial Value Problems Recognizing and
Topics to be covered on the exam include: Recognizing, and verifying solutions to homogeneous second-order linear differential equations, and their corresponding Initial Value Problems Recognizing and
Solutions to Math 53 Math 53 Practice Final
 Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
كلية العلوم قسم الرياضيات المعادالت التفاضلية العادية
 الجامعة اإلسالمية كلية العلوم غزة قسم الرياضيات المعادالت التفاضلية العادية Elementary differential equations and boundary value problems المحاضرون أ.د. رائد صالحة د. فاتن أبو شوقة 1 3 4 5 6 بسم هللا
الجامعة اإلسالمية كلية العلوم غزة قسم الرياضيات المعادالت التفاضلية العادية Elementary differential equations and boundary value problems المحاضرون أ.د. رائد صالحة د. فاتن أبو شوقة 1 3 4 5 6 بسم هللا
Equations with regular-singular points (Sect. 5.5).
 Equations with regular-singular points (Sect. 5.5). Equations with regular-singular points. s: Equations with regular-singular points. Method to find solutions. : Method to find solutions. Recall: The
Equations with regular-singular points (Sect. 5.5). Equations with regular-singular points. s: Equations with regular-singular points. Method to find solutions. : Method to find solutions. Recall: The
2. Second-order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 Advanced Engineering Mathematics 2. Second-order Linear ODEs 1 2. Second-order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations 2.1 Homogeneous linear ODEs 2.2 Homogeneous linear ODEs with constant coefficients
Advanced Engineering Mathematics 2. Second-order Linear ODEs 1 2. Second-order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations 2.1 Homogeneous linear ODEs 2.2 Homogeneous linear ODEs with constant coefficients
Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point
 Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background We will find a power series solution to the equation:
Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background We will find a power series solution to the equation:
Differential Equations
 Differential Equations Problem Sheet 1 3 rd November 2011 First-Order Ordinary Differential Equations 1. Find the general solutions of the following separable differential equations. Which equations are
Differential Equations Problem Sheet 1 3 rd November 2011 First-Order Ordinary Differential Equations 1. Find the general solutions of the following separable differential equations. Which equations are
MATH 2250 Final Exam Solutions
 MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
Lecture Notes on. Differential Equations. Emre Sermutlu
 Lecture Notes on Differential Equations Emre Sermutlu ISBN: Copyright Notice: To my wife Nurten and my daughters İlayda and Alara Contents Preface ix 1 First Order ODE 1 1.1 Definitions.............................
Lecture Notes on Differential Equations Emre Sermutlu ISBN: Copyright Notice: To my wife Nurten and my daughters İlayda and Alara Contents Preface ix 1 First Order ODE 1 1.1 Definitions.............................
dx n a 1(x) dy
 HIGHER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Theory of linear equations Initial-value and boundary-value problem nth-order initial value problem is Solve: a n (x) dn y dx n + a n 1(x) dn 1 y dx n 1 +... + a 1(x)
HIGHER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Theory of linear equations Initial-value and boundary-value problem nth-order initial value problem is Solve: a n (x) dn y dx n + a n 1(x) dn 1 y dx n 1 +... + a 1(x)
Exam Basics. midterm. 1 There will be 9 questions. 2 The first 3 are on pre-midterm material. 3 The next 1 is a mix of old and new material.
 Exam Basics 1 There will be 9 questions. 2 The first 3 are on pre-midterm material. 3 The next 1 is a mix of old and new material. 4 The last 5 questions will be on new material since the midterm. 5 60
Exam Basics 1 There will be 9 questions. 2 The first 3 are on pre-midterm material. 3 The next 1 is a mix of old and new material. 4 The last 5 questions will be on new material since the midterm. 5 60
Review For the Final: Problem 1 Find the general solutions of the following DEs. a) x 2 y xy y 2 = 0 solution: = 0 : homogeneous equation.
 Review For the Final: Problem 1 Find the general solutions of the following DEs. a) x 2 y xy y 2 = 0 solution: y y x y2 = 0 : homogeneous equation. x2 v = y dy, y = vx, and x v + x dv dx = v + v2. dx =
Review For the Final: Problem 1 Find the general solutions of the following DEs. a) x 2 y xy y 2 = 0 solution: y y x y2 = 0 : homogeneous equation. x2 v = y dy, y = vx, and x v + x dv dx = v + v2. dx =
4 Differential Equations
 Advanced Calculus Chapter 4 Differential Equations 65 4 Differential Equations 4.1 Terminology Let U R n, and let y : U R. A differential equation in y is an equation involving y and its (partial) derivatives.
Advanced Calculus Chapter 4 Differential Equations 65 4 Differential Equations 4.1 Terminology Let U R n, and let y : U R. A differential equation in y is an equation involving y and its (partial) derivatives.
ODE. Philippe Rukimbira. Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAP / 92
 ODE Philippe Rukimbira Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAP 2302 1 / 92 4.4 The method of Variation of parameters 1. Second order differential equations (Normalized,
ODE Philippe Rukimbira Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAP 2302 1 / 92 4.4 The method of Variation of parameters 1. Second order differential equations (Normalized,
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 8, 2015 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Second Order Linear Equations
 October 13, 2016 1 Second And Higher Order Linear Equations In first part of this chapter, we consider second order linear ordinary linear equations, i.e., a differential equation of the form L[y] = d
October 13, 2016 1 Second And Higher Order Linear Equations In first part of this chapter, we consider second order linear ordinary linear equations, i.e., a differential equation of the form L[y] = d
Final Exam May 4, 2016
 1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
Fourier transforms. c n e inπx. f (x) = Write same thing in an equivalent form, using n = 1, f (x) = l π
 Fourier transforms We can imagine our periodic function having periodicity taken to the limits ± In this case, the function f (x) is not necessarily periodic, but we can still use Fourier transforms (related
Fourier transforms We can imagine our periodic function having periodicity taken to the limits ± In this case, the function f (x) is not necessarily periodic, but we can still use Fourier transforms (related
Differential Equations, Math 315 Midterm 2 Solutions
 Name: Section: Differential Equations, Math 35 Midterm 2 Solutions. A mass of 5 kg stretches a spring 0. m (meters). The mass is acted on by an external force of 0 sin(t/2)n (newtons) and moves in a medium
Name: Section: Differential Equations, Math 35 Midterm 2 Solutions. A mass of 5 kg stretches a spring 0. m (meters). The mass is acted on by an external force of 0 sin(t/2)n (newtons) and moves in a medium
MA22S3 Summary Sheet: Ordinary Differential Equations
 MA22S3 Summary Sheet: Ordinary Differential Equations December 14, 2017 Kreyszig s textbook is a suitable guide for this part of the module. Contents 1 Terminology 1 2 First order separable 2 2.1 Separable
MA22S3 Summary Sheet: Ordinary Differential Equations December 14, 2017 Kreyszig s textbook is a suitable guide for this part of the module. Contents 1 Terminology 1 2 First order separable 2 2.1 Separable
LINEAR EQUATIONS OF HIGHER ORDER. EXAMPLES. General framework
 Differential Equations Grinshpan LINEAR EQUATIONS OF HIGHER ORDER. EXAMPLES. We consider linear ODE of order n: General framework (1) x (n) (t) + P n 1 (t)x (n 1) (t) + + P 1 (t)x (t) + P 0 (t)x(t) = 0
Differential Equations Grinshpan LINEAR EQUATIONS OF HIGHER ORDER. EXAMPLES. We consider linear ODE of order n: General framework (1) x (n) (t) + P n 1 (t)x (n 1) (t) + + P 1 (t)x (t) + P 0 (t)x(t) = 0
Understand the existence and uniqueness theorems and what they tell you about solutions to initial value problems.
 Review Outline To review for the final, look over the following outline and look at problems from the book and on the old exam s and exam reviews to find problems about each of the following topics.. Basics
Review Outline To review for the final, look over the following outline and look at problems from the book and on the old exam s and exam reviews to find problems about each of the following topics.. Basics
M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 2013
 M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 013 Section.6 3. Consider the equation: (3x xy + )dx + (6y x + 3)dy = 0. Let M(x, y) = 3x xy + and N(x, y) = 6y x + 3. Since: y = x = N We can conclude that this
M343 Homework 3 Enrique Areyan May 17, 013 Section.6 3. Consider the equation: (3x xy + )dx + (6y x + 3)dy = 0. Let M(x, y) = 3x xy + and N(x, y) = 6y x + 3. Since: y = x = N We can conclude that this
MATH 23 Exam 2 Review Solutions
 MATH 23 Exam 2 Review Solutions Problem 1. Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the given differential equation x 2 y (x 0.1875)y = 0, x > 0, y 1 (x) = x 1/4 e 2 x Solution
MATH 23 Exam 2 Review Solutions Problem 1. Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the given differential equation x 2 y (x 0.1875)y = 0, x > 0, y 1 (x) = x 1/4 e 2 x Solution
3. Identify and find the general solution of each of the following first order differential equations.
 Final Exam MATH 33, Sample Questions. Fall 7. y = Cx 3 3 is the general solution of a differential equation. Find the equation. Answer: y = 3y + 9 xy. y = C x + C x is the general solution of a differential
Final Exam MATH 33, Sample Questions. Fall 7. y = Cx 3 3 is the general solution of a differential equation. Find the equation. Answer: y = 3y + 9 xy. y = C x + C x is the general solution of a differential
Math 216 Second Midterm 19 March, 2018
 Math 26 Second Midterm 9 March, 28 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 26 Second Midterm 9 March, 28 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 222 Spring 2013 Exam 3 Review Problem Answers
 . (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
. (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
MATH 307: Problem Set #7
 MATH 307: Problem Set #7 Due on: Feb 11, 2016 Problem 1 First-order Variation of Parameters The method of variation of parameters uses the homogeneous solutions of a linear ordinary differential equation
MATH 307: Problem Set #7 Due on: Feb 11, 2016 Problem 1 First-order Variation of Parameters The method of variation of parameters uses the homogeneous solutions of a linear ordinary differential equation
Practice Problems For Test 3
 Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Math 125 Final Examination Spring 2015
 Math 125 Final Examination Spring 2015 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name This exam is closed book. You may use one 8.5 11 sheet of handwritten notes (both sides
Math 125 Final Examination Spring 2015 Your Name Your Signature Student ID # Quiz Section Professor s Name TA s Name This exam is closed book. You may use one 8.5 11 sheet of handwritten notes (both sides
Math 4B Notes. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: T 12:45 1:45pm Last updated 7/24/2016
 Math 4B Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: T 2:45 :45pm Last updated 7/24/206 Classification of Differential Equations The order of a differential equation is the
Math 4B Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: T 2:45 :45pm Last updated 7/24/206 Classification of Differential Equations The order of a differential equation is the
Second In-Class Exam Solutions Math 246, Professor David Levermore Thursday, 31 March 2011
 Second In-Class Exam Solutions Math 246, Professor David Levermore Thursday, 31 March 211 (1) [6] Give the interval of definition for the solution of the initial-value problem d 4 y dt 4 + 7 1 t 2 dy dt
Second In-Class Exam Solutions Math 246, Professor David Levermore Thursday, 31 March 211 (1) [6] Give the interval of definition for the solution of the initial-value problem d 4 y dt 4 + 7 1 t 2 dy dt
Assignment # 3, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS:
 Assignment # 3, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations: (a) y (1 + x)e x y 2 = xy, (i) y(0) = 1, (ii) y(0) = 0. On what intervals are the solution of the IVP defined? (b) 2y + y
Assignment # 3, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations: (a) y (1 + x)e x y 2 = xy, (i) y(0) = 1, (ii) y(0) = 0. On what intervals are the solution of the IVP defined? (b) 2y + y
Math Ordinary Differential Equations Sample Test 3 Solutions
 Solve the following Math - Ordinary Differential Equations Sample Test Solutions (i x 2 y xy + 8y y(2 2 y (2 (ii x 2 y + xy + 4y y( 2 y ( (iii x 2 y xy + y y( 2 y ( (i The characteristic equation is m(m
Solve the following Math - Ordinary Differential Equations Sample Test Solutions (i x 2 y xy + 8y y(2 2 y (2 (ii x 2 y + xy + 4y y( 2 y ( (iii x 2 y xy + y y( 2 y ( (i The characteristic equation is m(m
Higher-order ordinary differential equations
 Higher-order ordinary differential equations 1 A linear ODE of general order n has the form a n (x) dn y dx n +a n 1(x) dn 1 y dx n 1 + +a 1(x) dy dx +a 0(x)y = f(x). If f(x) = 0 then the equation is called
Higher-order ordinary differential equations 1 A linear ODE of general order n has the form a n (x) dn y dx n +a n 1(x) dn 1 y dx n 1 + +a 1(x) dy dx +a 0(x)y = f(x). If f(x) = 0 then the equation is called
Problem Score Possible Points Total 150
 Math 250 Fall 2010 Final Exam NAME: ID No: SECTION: This exam contains 17 problems on 13 pages (including this title page) for a total of 150 points. There are 10 multiple-choice problems and 7 partial
Math 250 Fall 2010 Final Exam NAME: ID No: SECTION: This exam contains 17 problems on 13 pages (including this title page) for a total of 150 points. There are 10 multiple-choice problems and 7 partial
1 Solution to Homework 4
 Solution to Homework Section. 5. The characteristic equation is r r + = (r )(r ) = 0 r = or r =. y(t) = c e t + c e t y = c e t + c e t. y(0) =, y (0) = c + c =, c + c = c =, c =. To find the maximum value
Solution to Homework Section. 5. The characteristic equation is r r + = (r )(r ) = 0 r = or r =. y(t) = c e t + c e t y = c e t + c e t. y(0) =, y (0) = c + c =, c + c = c =, c =. To find the maximum value
Second-Order Linear ODEs
 C0.tex /4/011 16: 3 Page 13 Chap. Second-Order Linear ODEs Chapter presents different types of second-order ODEs and the specific techniques on how to solve them. The methods are systematic, but it requires
C0.tex /4/011 16: 3 Page 13 Chap. Second-Order Linear ODEs Chapter presents different types of second-order ODEs and the specific techniques on how to solve them. The methods are systematic, but it requires
for any C, including C = 0, because y = 0 is also a solution: dy
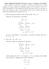 Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
Form A. 1. Which of the following is a second-order, linear, homogenous differential equation? 2
 Form A Math 4 Common Part of Final Exam December 6, 996 INSTRUCTIONS: Please enter your NAME, ID NUMBER, FORM designation, and INDEX NUMBER on your op scan sheet. The index number should be written in
Form A Math 4 Common Part of Final Exam December 6, 996 INSTRUCTIONS: Please enter your NAME, ID NUMBER, FORM designation, and INDEX NUMBER on your op scan sheet. The index number should be written in
Practice Problems For Test 3
 Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
Practice Problems For Test 3 Power Series Preliminary Material. Find the interval of convergence of the following. Be sure to determine the convergence at the endpoints. (a) ( ) k (x ) k (x 3) k= k (b)
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Terminology Most of the phenomena studied in the sciences and engineering involve processes that change with time. For example, it is well known
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Terminology Most of the phenomena studied in the sciences and engineering involve processes that change with time. For example, it is well known
FINAL EXAM, MATH 353 SUMMER I 2015
 FINAL EXAM, MATH 353 SUMMER I 25 9:am-2:pm, Thursday, June 25 I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam and I have conducted myself within the guidelines of the Duke Community
FINAL EXAM, MATH 353 SUMMER I 25 9:am-2:pm, Thursday, June 25 I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam and I have conducted myself within the guidelines of the Duke Community
Practice Midterm Solutions
 Practice Midterm Solutions Math 4B: Ordinary Differential Equations Winter 20 University of California, Santa Barbara TA: Victoria Kala DO NOT LOOK AT THESE SOLUTIONS UNTIL YOU HAVE ATTEMPTED EVERY PROBLEM
Practice Midterm Solutions Math 4B: Ordinary Differential Equations Winter 20 University of California, Santa Barbara TA: Victoria Kala DO NOT LOOK AT THESE SOLUTIONS UNTIL YOU HAVE ATTEMPTED EVERY PROBLEM
Math 20D Final Exam 8 December has eigenvalues 3, 3, 0 and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. ( 2) det
 Math D Final Exam 8 December 9. ( points) Show that the matrix 4 has eigenvalues 3, 3, and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. 4 λ det λ λ λ = (4 λ) det λ ( ) det + det λ = (4 λ)(( λ) 4) + ( λ + )
Math D Final Exam 8 December 9. ( points) Show that the matrix 4 has eigenvalues 3, 3, and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. 4 λ det λ λ λ = (4 λ) det λ ( ) det + det λ = (4 λ)(( λ) 4) + ( λ + )
HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]
![HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]](/thumbs/73/68538384.jpg) HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
Higher Order Linear Equations
 C H A P T E R 4 Higher Order Linear Equations 4.1 1. The differential equation is in standard form. Its coefficients, as well as the function g(t) = t, are continuous everywhere. Hence solutions are valid
C H A P T E R 4 Higher Order Linear Equations 4.1 1. The differential equation is in standard form. Its coefficients, as well as the function g(t) = t, are continuous everywhere. Hence solutions are valid
MATH 251 Week 6 Not collected, however you are encouraged to approach all problems to prepare for exam
 MATH 51 Week 6 Not collected, however you are encouraged to approach all problems to prepare for exam A collection of previous exams could be found at the coordinator s web: http://www.math.psu.edu/tseng/class/m51samples.html
MATH 51 Week 6 Not collected, however you are encouraged to approach all problems to prepare for exam A collection of previous exams could be found at the coordinator s web: http://www.math.psu.edu/tseng/class/m51samples.html
The method of Fröbenius
 Note III.5 1 1 April 008 The method of Fröbenius For the general homogeneous ordinary differential equation y (x) + p(x)y (x) + q(x)y(x) = 0 (1) the series method works, as in the Hermite case, where both
Note III.5 1 1 April 008 The method of Fröbenius For the general homogeneous ordinary differential equation y (x) + p(x)y (x) + q(x)y(x) = 0 (1) the series method works, as in the Hermite case, where both
2r 2 e rx 5re rx +3e rx = 0. That is,
 Math 4, Exam 1, Solution, Spring 013 Write everything on the blank paper provided. You should KEEP this piece of paper. If possible: turn the problems in order (use as much paper as necessary), use only
Math 4, Exam 1, Solution, Spring 013 Write everything on the blank paper provided. You should KEEP this piece of paper. If possible: turn the problems in order (use as much paper as necessary), use only
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 1 - ODEs Page 1.01
 ENGI 940 Lecture Notes - ODEs Page.0. Ordinary Differential Equations An equation involving a function of one independent variable and the derivative(s) of that function is an ordinary differential equation
ENGI 940 Lecture Notes - ODEs Page.0. Ordinary Differential Equations An equation involving a function of one independent variable and the derivative(s) of that function is an ordinary differential equation
Math53: Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 2004
 Math53: Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 2004 Unit 2 Summary Second- and Higher-Order Ordinary Differential Equations Extremely Important: Euler s formula Very Important: finding solutions to linear
Math53: Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 2004 Unit 2 Summary Second- and Higher-Order Ordinary Differential Equations Extremely Important: Euler s formula Very Important: finding solutions to linear
Department of Mathematics. MA 108 Ordinary Differential Equations
 Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Powai, Mumbai 476, INDIA. MA 8 Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 23 Instructor Santanu Dey Name : Roll No : Syllabus and Course Outline
Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Powai, Mumbai 476, INDIA. MA 8 Ordinary Differential Equations Autumn 23 Instructor Santanu Dey Name : Roll No : Syllabus and Course Outline
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
Physics 116C Solutions to the Practice Final Exam Fall The method of Frobenius fails because it works only for Fuchsian equations, of the type
 Physics 6C Solutions to the Practice Final Exam Fall 2 Consider the differential equation x y +x(x+)y y = () (a) Explain why the method of Frobenius method fails for this problem. The method of Frobenius
Physics 6C Solutions to the Practice Final Exam Fall 2 Consider the differential equation x y +x(x+)y y = () (a) Explain why the method of Frobenius method fails for this problem. The method of Frobenius
Virginia Tech Math 1226 : Past CTE problems
 Virginia Tech Math 16 : Past CTE problems 1. It requires 1 in-pounds of work to stretch a spring from its natural length of 1 in to a length of 1 in. How much additional work (in inch-pounds) is done in
Virginia Tech Math 16 : Past CTE problems 1. It requires 1 in-pounds of work to stretch a spring from its natural length of 1 in to a length of 1 in. How much additional work (in inch-pounds) is done in
Math 3313: Differential Equations Second-order ordinary differential equations
 Math 3313: Differential Equations Second-order ordinary differential equations Thomas W. Carr Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX Outline Mass-spring & Newton s 2nd law Properties
Math 3313: Differential Equations Second-order ordinary differential equations Thomas W. Carr Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX Outline Mass-spring & Newton s 2nd law Properties
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Problem 1 (Equations with the dependent variable missing) By means of the substitutions. v = dy dt, dv
 V Problem 1 (Equations with the dependent variable missing) By means of the substitutions v = dy dt, dv dt = d2 y dt 2 solve the following second-order differential equations 1. t 2 d2 y dt + 2tdy 1 =
V Problem 1 (Equations with the dependent variable missing) By means of the substitutions v = dy dt, dv dt = d2 y dt 2 solve the following second-order differential equations 1. t 2 d2 y dt + 2tdy 1 =
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Terminology A differential equation is an equation that contains an unknown function together with one or more of its derivatives. 1 Examples: 1. y = 2x + cos x 2. dy dt =
Consider an ideal pendulum as shown below. l θ is the angular acceleration θ is the angular velocity
 1 Second Order Ordinary Differential Equations 1.1 The harmonic oscillator Consider an ideal pendulum as shown below. θ l Fr mg l θ is the angular acceleration θ is the angular velocity A point mass m
1 Second Order Ordinary Differential Equations 1.1 The harmonic oscillator Consider an ideal pendulum as shown below. θ l Fr mg l θ is the angular acceleration θ is the angular velocity A point mass m
Find the Fourier series of the odd-periodic extension of the function f (x) = 1 for x ( 1, 0). Solution: The Fourier series is.
 Review for Final Exam. Monday /09, :45-:45pm in CC-403. Exam is cumulative, -4 problems. 5 grading attempts per problem. Problems similar to homeworks. Integration and LT tables provided. No notes, no
Review for Final Exam. Monday /09, :45-:45pm in CC-403. Exam is cumulative, -4 problems. 5 grading attempts per problem. Problems similar to homeworks. Integration and LT tables provided. No notes, no
Introductory Differential Equations
 Introductory Differential Equations Lecture Notes June 3, 208 Contents Introduction Terminology and Examples 2 Classification of Differential Equations 4 2 First Order ODEs 5 2 Separable ODEs 5 22 First
Introductory Differential Equations Lecture Notes June 3, 208 Contents Introduction Terminology and Examples 2 Classification of Differential Equations 4 2 First Order ODEs 5 2 Separable ODEs 5 22 First
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs)
 c01.tex 8/10/2010 22: 55 Page 1 PART A Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Chap. 1 First-Order ODEs Sec. 1.1 Basic Concepts. Modeling To get a good start into this chapter and this section, quickly
c01.tex 8/10/2010 22: 55 Page 1 PART A Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) Chap. 1 First-Order ODEs Sec. 1.1 Basic Concepts. Modeling To get a good start into this chapter and this section, quickly
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014
 Page 1 of 12 Please go to the next page... Sample Midterm 1 ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014 50 points 1. Find the solution of the following initial-value problem 1. Solution (S.O.V) dt = ty2,
Page 1 of 12 Please go to the next page... Sample Midterm 1 ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014 50 points 1. Find the solution of the following initial-value problem 1. Solution (S.O.V) dt = ty2,
Math Applied Differential Equations
 Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Basic Definitions and Concepts A differential equation is an equation that involves one or more of the derivatives (first derivative, second derivative,
Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Basic Definitions and Concepts A differential equation is an equation that involves one or more of the derivatives (first derivative, second derivative,
Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-12) Solution 1 From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have.
 For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
Second order linear equations
 Second order linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations - MA 266 Taken from Elementary differential equations by Boyce and DiPrima Samy T. Second order equations Differential
Second order linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations - MA 266 Taken from Elementary differential equations by Boyce and DiPrima Samy T. Second order equations Differential
6 Second Order Linear Differential Equations
 6 Second Order Linear Differential Equations A differential equation for an unknown function y = f(x) that depends on a variable x is any equation that ties together functions of x with y and its derivatives.
6 Second Order Linear Differential Equations A differential equation for an unknown function y = f(x) that depends on a variable x is any equation that ties together functions of x with y and its derivatives.
Chapter 3: Second Order Equations
 Exam 2 Review This review sheet contains this cover page (a checklist of topics from Chapters 3). Following by all the review material posted pertaining to chapter 3 (all combined into one file). Chapter
Exam 2 Review This review sheet contains this cover page (a checklist of topics from Chapters 3). Following by all the review material posted pertaining to chapter 3 (all combined into one file). Chapter
Math 226 Calculus Spring 2016 Practice Exam 1. (1) (10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = f(x) have inverse function x = f 1 (y).
 Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
Math 6 Calculus Spring 016 Practice Exam 1 1) 10 Points) Let the differentiable function y = fx) have inverse function x = f 1 y). a) Write down the formula relating the derivatives f x) and f 1 ) y).
MATH 4B Differential Equations, Fall 2016 Final Exam Study Guide
 MATH 4B Differential Equations, Fall 2016 Final Exam Study Guide GENERAL INFORMATION AND FINAL EXAM RULES The exam will have a duration of 3 hours. No extra time will be given. Failing to submit your solutions
MATH 4B Differential Equations, Fall 2016 Final Exam Study Guide GENERAL INFORMATION AND FINAL EXAM RULES The exam will have a duration of 3 hours. No extra time will be given. Failing to submit your solutions
x gm 250 L 25 L min y gm min
 Name NetID MATH 308 Exam 2 Spring 2009 Section 511 Hand Computations P. Yasskin Solutions 1 /10 4 /30 2 /10 5 /30 3 /10 6 /15 Total /105 1. (10 points) Tank X initially contains 250 L of sugar water with
Name NetID MATH 308 Exam 2 Spring 2009 Section 511 Hand Computations P. Yasskin Solutions 1 /10 4 /30 2 /10 5 /30 3 /10 6 /15 Total /105 1. (10 points) Tank X initially contains 250 L of sugar water with
Math 2930 Worksheet Final Exam Review
 Math 293 Worksheet Final Exam Review Week 14 November 3th, 217 Question 1. (* Solve the initial value problem y y = 2xe x, y( = 1 Question 2. (* Consider the differential equation: y = y y 3. (a Find the
Math 293 Worksheet Final Exam Review Week 14 November 3th, 217 Question 1. (* Solve the initial value problem y y = 2xe x, y( = 1 Question 2. (* Consider the differential equation: y = y y 3. (a Find the
Differential Equations 2280 Sample Midterm Exam 3 with Solutions Exam Date: 24 April 2015 at 12:50pm
 Differential Equations 228 Sample Midterm Exam 3 with Solutions Exam Date: 24 April 25 at 2:5pm Instructions: This in-class exam is 5 minutes. No calculators, notes, tables or books. No answer check is
Differential Equations 228 Sample Midterm Exam 3 with Solutions Exam Date: 24 April 25 at 2:5pm Instructions: This in-class exam is 5 minutes. No calculators, notes, tables or books. No answer check is
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 7 Spring Practice problems for April Exam Problem Use the method of elimination to find the x-component of the general solution of x y = 6x 9x + y = x 6y 9y Soln: The system
Differential equations Math 7 Spring Practice problems for April Exam Problem Use the method of elimination to find the x-component of the general solution of x y = 6x 9x + y = x 6y 9y Soln: The system
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON. A foreign language dictionary (paper version) is permitted provided it contains no notes, additions or annotations.
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON MATH055W SEMESTER EXAMINATION 03/4 MATHEMATICS FOR ELECTRONIC & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Duration: 0 min Solutions Only University approved calculators may be used. A foreign language
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON MATH055W SEMESTER EXAMINATION 03/4 MATHEMATICS FOR ELECTRONIC & ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Duration: 0 min Solutions Only University approved calculators may be used. A foreign language
MATH 307: Problem Set #3 Solutions
 : Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
: Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
Midterm 2: Sample solutions Math 118A, Fall 2013
 Midterm 2: Sample solutions Math 118A, Fall 213 1. Find all separated solutions u(r,t = F(rG(t of the radially symmetric heat equation u t = k ( r u. r r r Solve for G(t explicitly. Write down an ODE for
Midterm 2: Sample solutions Math 118A, Fall 213 1. Find all separated solutions u(r,t = F(rG(t of the radially symmetric heat equation u t = k ( r u. r r r Solve for G(t explicitly. Write down an ODE for
1 Series Solutions Near Regular Singular Points
 1 Series Solutions Near Regular Singular Points All of the work here will be directed toward finding series solutions of a second order linear homogeneous ordinary differential equation: P xy + Qxy + Rxy
1 Series Solutions Near Regular Singular Points All of the work here will be directed toward finding series solutions of a second order linear homogeneous ordinary differential equation: P xy + Qxy + Rxy
y x 3. Solve each of the given initial value problems. (a) y 0? xy = x, y(0) = We multiply the equation by e?x, and obtain Integrating both sides with
 Solutions to the Practice Problems Math 80 Febuary, 004. For each of the following dierential equations, decide whether the given function is a solution. (a) y 0 = (x + )(y? ), y =? +exp(x +x)?exp(x +x)
Solutions to the Practice Problems Math 80 Febuary, 004. For each of the following dierential equations, decide whether the given function is a solution. (a) y 0 = (x + )(y? ), y =? +exp(x +x)?exp(x +x)
MATH 425, FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 425, FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Each exercise is worth 50 points. Exercise. a The operator L is defined on smooth functions of (x, y by: Is the operator L linear? Prove your answer. L (u := arctan(xy u
MATH 425, FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Each exercise is worth 50 points. Exercise. a The operator L is defined on smooth functions of (x, y by: Is the operator L linear? Prove your answer. L (u := arctan(xy u
