Problem info Geometry model Labelled Objects Results Nonlinear dependencies
|
|
|
- Ashley Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problem info Problem type: Transient Magnetics (integration time: E-09 s.) Geometry model class: Plane-Parallel Problem database file names: Problem: circuit.pbm Geometry: Circuit.mod Material Data: Circuit.dms Material Data 2 (library): none Electric circuit: circuit.qcr Results taken from other problems: none
2 Geometry model
3 Table 1. Geometry model statistics With Label Total Blocks 1 1 Edges 1 3 Vertices 0 3 Number of nodes: 3.
4 Electric circuit Coupled electric circuit Circuit elements: Inductor L1= [H] Voltage source V1=2*impulse(t,0.75e-9,6e-9) [V] Resistor R=95.5 [Ohm] Resistor Load=50 [Ohm] Resistor R1= [Ohm] Capacitor C1= [F]
5 Inductor L2= [H] Capacitor C2= [F] Inductor L3= [H] Capacitor C3= [F] Inductor L4= [H] Capacitor C4= [F] Inductor L5= [H] Capacitor C5= [F] Inductor L6= [H] Capacitor C6= [F] Inductor L7= [H] Capacitor C7= [F] Inductor L8= [H] Capacitor C8= [F] Inductor L9= [H] Capacitor C9= [F] Inductor L10= [H] Capacitor C10= [F] Inductor L11= [H] Capacitor C11= [F] Inductor L12= [H] Capacitor C12= [F] Inductor L13= [H] Capacitor C13= [F] Inductor L14= [H] Capacitor C14= [F] Inductor L15= [H] Capacitor C15= [F] Inductor L16= [H] Capacitor C16= [F] Inductor L17= [H]
6 Capacitor C17= [F] Inductor L18= [H] Capacitor C18= [F] Inductor L19= [H] Capacitor C19= [F] Inductor L20= [H] Capacitor C20= [F] Inductor L21= [H] Capacitor C21= [F] Inductor L22= [H] Capacitor C22= [F] Inductor L23= [H] Capacitor C23= [F] Inductor L24= [H] Capacitor C24= [F] Inductor L25= [H] Capacitor C25= [F] Inductor L26= [H] Capacitor C26= [F] Inductor L27= [H] Capacitor C27= [F] Inductor L28= [H] Capacitor C28= [F] Inductor L29= [H] Capacitor C29= [F] Inductor L30= [H] Capacitor C30= [F]
7 Labelled objects There are following labelled objects in the geometry model (Material Data file could contain more labels, but only those labels that assigned to geometric objects are listed) Blocks: a1 Edges: a0 Vertices: Detailed information about each label is listed below.
8 Labelled objects: block "a1" There are (1) objects with this label Relative magnetic permeability: mu_x=1, mu_y=1 Current density: j=0 [A/m2] Conductor's connection: in parallel
9 Labelled objects: edge "a0" There are (1) objects with this label Magnetic potential: A=0 [Wb/m]
10
11 Results Field lines
12 Results Electric circuit currents Circuit elements: L1. I= [A] V1. I= [A] R. I= [A] Load. I= [A]
13 R1. I= [A] C1. I= [A] L2. I= [A] C2. I= [A] L3. I= [A] C3. I= [A] L4. I= [A] C4. I= [A] L5. I= [A] C5. I= [A] L6. I= [A] C6. I= [A] L7. I= [A] C7. I= [A] L8. I= [A] C8. I= [A] L9. I= [A] C9. I= [A] L10. I= [A] C10. I= [A] L11. I= [A] C11. I= [A] L12. I= [A] C12. I= [A]
14 L13. I= [A] C13. I= [A] L14. I= [A] C14. I= [A] L15. I= [A] C15. I= [A] L16. I= [A] C16. I= [A] L17. I= [A] C17. I= [A] L18. I= [A] C18. I= [A] L19. I= [A] C19. I= [A] L20. I= [A] C20. I= [A] L21. I= [A] C21. I= [A] L22. I= [A] C22. I= [A] L23. I= [A] C23. I= [A] L24. I= [A] C24. I= [A]
15 L25. I= [A] C25. I= [A] L26. I= [A] C26. I= [A] L27. I= [A] C27. I= [A] L28. I= [A] C28. I= [A] L29. I= [A] C29. I= [A] L30. I= [A] C30. I= [A]
16 Results Color map of Strength H [A/m]
17 Nonlinear dependencies No non-linear dependencies are used in this problem data
Texas A & M University Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 364 Dynamic Systems and Controls Dr. Alexander G. Parlos
 Texas A & M University Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 364 Dynamic Systems and Controls Dr. Alexander G. Parlos Lecture 5: Electrical and Electromagnetic System Components The objective of this
Texas A & M University Department of Mechanical Engineering MEEN 364 Dynamic Systems and Controls Dr. Alexander G. Parlos Lecture 5: Electrical and Electromagnetic System Components The objective of this
Chapter 2. Engr228 Circuit Analysis. Dr Curtis Nelson
 Chapter 2 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 2 Objectives Understand symbols and behavior of the following circuit elements: Independent voltage and current sources; Dependent voltage and
Chapter 2 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 2 Objectives Understand symbols and behavior of the following circuit elements: Independent voltage and current sources; Dependent voltage and
Exercise 2: Kirchhoff s Current Law/2 Sources
 Exercise 2: Kirchhoff s Current Law/2 Sources EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to apply Kirchhoff s current law to a circuit having two voltage sources. You will
Exercise 2: Kirchhoff s Current Law/2 Sources EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to apply Kirchhoff s current law to a circuit having two voltage sources. You will
Kirchhoff's Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC 2)
 Kirchhoff's Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC ) Circuit analysis: solving for I and V at each element Linear circuits: involve resistors, capacitors, inductors Initial analysis uses only resistors Power sources,
Kirchhoff's Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC ) Circuit analysis: solving for I and V at each element Linear circuits: involve resistors, capacitors, inductors Initial analysis uses only resistors Power sources,
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit.
 I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors
 Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Voltage vs. Current in a Resistor, Capacitor or Inductor
 Voltage vs. Current in a Resistor, Capacitor or Inductor Voltage vs. Current in a Resistor, Capacitor or Inductor Elements in an electrical system behave differently if they are exposed to direct current
Voltage vs. Current in a Resistor, Capacitor or Inductor Voltage vs. Current in a Resistor, Capacitor or Inductor Elements in an electrical system behave differently if they are exposed to direct current
EE-201 Review Exam I. 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6) None of above
 EE-201, Review Probs Test 1 page-1 Spring 98 EE-201 Review Exam I Multiple Choice (5 points each, no partial credit.) 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6)
EE-201, Review Probs Test 1 page-1 Spring 98 EE-201 Review Exam I Multiple Choice (5 points each, no partial credit.) 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6)
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors)
 Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM In the circuit shown above, resistors 1 and 2 of resistance R 1 and R 2, respectively, and an inductor of inductance L are connected to a battery of emf e and
2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM In the circuit shown above, resistors 1 and 2 of resistance R 1 and R 2, respectively, and an inductor of inductance L are connected to a battery of emf e and
Series & Parallel Resistors 3/17/2015 1
 Series & Parallel Resistors 3/17/2015 1 Series Resistors & Voltage Division Consider the single-loop circuit as shown in figure. The two resistors are in series, since the same current i flows in both
Series & Parallel Resistors 3/17/2015 1 Series Resistors & Voltage Division Consider the single-loop circuit as shown in figure. The two resistors are in series, since the same current i flows in both
Exam 2 Fall 2014
 1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
1 95.144 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Section instructor Section number Last/First name Last 3 Digits of Student ID Number: Show all work. Show all formulas used for each problem prior to substitution of numbers.
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors
 Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Induction & Inductors 1 Revision of Electromagnetic Induction and Inductors (Much of this material has come from Electrical & Electronic Principles & Technology by John Bird) Magnetic Field
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, series and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, series and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Maxwell s Equations:
 Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A-337 Phone: (915) 747-6958 E-Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu Maxwell s Equations: Terms & Definitions EE-3321 Electromagnetic Field Theory Outline Maxwell s Equations
Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A-337 Phone: (915) 747-6958 E-Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu Maxwell s Equations: Terms & Definitions EE-3321 Electromagnetic Field Theory Outline Maxwell s Equations
Lecture #3. Review: Power
 Lecture #3 OUTLINE Power calculations Circuit elements Voltage and current sources Electrical resistance (Ohm s law) Kirchhoff s laws Reading Chapter 2 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Review: Power If an element is
Lecture #3 OUTLINE Power calculations Circuit elements Voltage and current sources Electrical resistance (Ohm s law) Kirchhoff s laws Reading Chapter 2 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Review: Power If an element is
1 Phasors and Alternating Currents
 Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
Physics 4 Chapter : Alternating Current 0/5 Phasors and Alternating Currents alternating current: current that varies sinusoidally with time ac source: any device that supplies a sinusoidally varying potential
PRACTICE EXAM 2 for Midterm 2
 PRACTICE EXAM 2 for Midterm 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1) In the circuit shown in the figure, all the lightbulbs are identical. Which of the following is the correct ranking of the brightness of the bulbs?
PRACTICE EXAM 2 for Midterm 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1) In the circuit shown in the figure, all the lightbulbs are identical. Which of the following is the correct ranking of the brightness of the bulbs?
IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le2
 Le1 Le3 Le4 Le6 Le8 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le2 Ex1 Ex2 Ex4 Ex5 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Kirchhoffs laws
Le1 Le3 Le4 Le6 Le8 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le2 Ex1 Ex2 Ex4 Ex5 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Kirchhoffs laws
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
Page 3. - At first glance, this looks just like a resistor, but Impedance is the generic expression that includes time & frequency dependence.
 EEE 46/56 Digital System Design Module #2 nterconnect Modeling with umped Elements Topics. Modeling Techniques 2. pedance of sistors, Capacitors and nductors Textbook ading Assignments. 3.-3.7 What you
EEE 46/56 Digital System Design Module #2 nterconnect Modeling with umped Elements Topics. Modeling Techniques 2. pedance of sistors, Capacitors and nductors Textbook ading Assignments. 3.-3.7 What you
REVIEW EXERCISES. 2. What is the resulting action if switch (S) is opened after the capacitor (C) is fully charged? Se figure 4.27.
 REVIEW EXERCISES Circle the letter of the correct answer to each question. 1. What is the current and voltage relationship immediately after the switch is closed in the circuit in figure 4-27, which shows
REVIEW EXERCISES Circle the letter of the correct answer to each question. 1. What is the current and voltage relationship immediately after the switch is closed in the circuit in figure 4-27, which shows
QUIZ 1 SOLUTION. One way of labeling voltages and currents is shown below.
 F 14 1250 QUIZ 1 SOLUTION EX: Find the numerical value of v 2 in the circuit below. Show all work. SOL'N: One method of solution is to use Kirchhoff's and Ohm's laws. The first step in this approach is
F 14 1250 QUIZ 1 SOLUTION EX: Find the numerical value of v 2 in the circuit below. Show all work. SOL'N: One method of solution is to use Kirchhoff's and Ohm's laws. The first step in this approach is
Electrical Circuits I
 Electrical Circuits I This lecture discusses the mathematical modeling of simple electrical linear circuits. When modeling a circuit, one ends up with a set of implicitly formulated algebraic and differential
Electrical Circuits I This lecture discusses the mathematical modeling of simple electrical linear circuits. When modeling a circuit, one ends up with a set of implicitly formulated algebraic and differential
Capacitor Action. 3. Capacitor Action Theory Support. Electronics - AC Circuits
 Capacitor Action Topics covered in this presentation: Capacitors on DC Capacitors on AC Capacitor Charging Capacitor Discharging 1 of 18 Charging a Capacitor (DC) Before looking at how capacitors charge
Capacitor Action Topics covered in this presentation: Capacitors on DC Capacitors on AC Capacitor Charging Capacitor Discharging 1 of 18 Charging a Capacitor (DC) Before looking at how capacitors charge
RC Circuits (32.9) Neil Alberding (SFU Physics) Physics 121: Optics, Electricity & Magnetism Spring / 1
 (32.9) We have only been discussing DC circuits so far. However, using a capacitor we can create an RC circuit. In this example, a capacitor is charged but the switch is open, meaning no current flows.
(32.9) We have only been discussing DC circuits so far. However, using a capacitor we can create an RC circuit. In this example, a capacitor is charged but the switch is open, meaning no current flows.
Exploring Operations Involving Complex Numbers. (3 + 4x) (2 x) = 6 + ( 3x) + +
 Name Class Date 11.2 Complex Numbers Essential Question: What is a complex number, and how can you add, subtract, and multiply complex numbers? Explore Exploring Operations Involving Complex Numbers In
Name Class Date 11.2 Complex Numbers Essential Question: What is a complex number, and how can you add, subtract, and multiply complex numbers? Explore Exploring Operations Involving Complex Numbers In
R 2, R 3, and R 4 are in parallel, R T = R 1 + (R 2 //R 3 //R 4 ) + R 5. C-C Tsai
 Chapter 07 Series-Parallel Circuits The Series-Parallel Network Complex circuits May be separated both series and/or parallel elements Combinations which are neither series nor parallel To analyze a circuit
Chapter 07 Series-Parallel Circuits The Series-Parallel Network Complex circuits May be separated both series and/or parallel elements Combinations which are neither series nor parallel To analyze a circuit
PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 2
 PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1) The figure shows three identical lightbulbs connected to a battery having a constant voltage across its terminals. What happens to the brightness
PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 2 Multiple Choice Questions 1) The figure shows three identical lightbulbs connected to a battery having a constant voltage across its terminals. What happens to the brightness
Introduction to Electric Circuit Analysis
 EE110300 Practice of Electrical and Computer Engineering Lecture 2 and Lecture 4.1 Introduction to Electric Circuit Analysis Prof. Klaus Yung-Jane Hsu 2003/2/20 What Is An Electric Circuit? Electrical
EE110300 Practice of Electrical and Computer Engineering Lecture 2 and Lecture 4.1 Introduction to Electric Circuit Analysis Prof. Klaus Yung-Jane Hsu 2003/2/20 What Is An Electric Circuit? Electrical
Introduction to Basic Electronics Lecture -2
 Introduction to Basic Electronics Lecture -2 Basic Electronics What is electricity? Voltage, Current, Resistance DC/AC Ohm s Law Capacitors & Inductors Conductor & Insulator What is Electricity? Everything
Introduction to Basic Electronics Lecture -2 Basic Electronics What is electricity? Voltage, Current, Resistance DC/AC Ohm s Law Capacitors & Inductors Conductor & Insulator What is Electricity? Everything
Exercise 4 Modeling transient currents and voltages
 Exercise 4 Modeling transient currents and voltages Basic A circuit elements In a D circuit, the electro-motive forces push the electrons along the circuit and resistors remove that energy by conversion
Exercise 4 Modeling transient currents and voltages Basic A circuit elements In a D circuit, the electro-motive forces push the electrons along the circuit and resistors remove that energy by conversion
Homework 2 SJTU233. Part A. Part B. Problem 2. Part A. Problem 1. Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω.
 Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Module 3 Electrical Fundamentals
 3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
Outline. Week 5: Circuits. Course Notes: 3.5. Goals: Use linear algebra to determine voltage drops and branch currents.
 Outline Week 5: Circuits Course Notes: 3.5 Goals: Use linear algebra to determine voltage drops and branch currents. Components in Resistor Networks voltage source current source resistor Components in
Outline Week 5: Circuits Course Notes: 3.5 Goals: Use linear algebra to determine voltage drops and branch currents. Components in Resistor Networks voltage source current source resistor Components in
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work Solutions
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits. Home Work s 21.1 Problem 21.11 What is the time constant of the circuit in Figure (21.19). 10 Ω 10 Ω 5.0 Ω 2.0µF 2.0µF 2.0µF 3.0µF Figure 21.19: Given: The circuit
PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT ES/CE/MAG. Class XII
 PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT ES/CE/MAG Class XII MM : 70 1. What is dielectric strength of a medium? Give its value for vacuum. 1 2. What is the physical importance of the line integral of an electrostatic field?
PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT ES/CE/MAG Class XII MM : 70 1. What is dielectric strength of a medium? Give its value for vacuum. 1 2. What is the physical importance of the line integral of an electrostatic field?
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Electromagnetic Oscillations Physics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 8! We have been working with circuits that have a constant current a current that increases to a constant current
Electromagnetic Oscillations Physics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 8! We have been working with circuits that have a constant current a current that increases to a constant current
Physics 212. Lecture 9. Electric Current
 Physics 212 Lecture 9 Electric Current Exam Here, Tuesday, June 26, 8 9:30 AM Will begin at 7:30 for those who must leave by 9. Office hours 1-7 PM, Rm 232 Loomis Bring your ID! Physics 212 Lecture 9,
Physics 212 Lecture 9 Electric Current Exam Here, Tuesday, June 26, 8 9:30 AM Will begin at 7:30 for those who must leave by 9. Office hours 1-7 PM, Rm 232 Loomis Bring your ID! Physics 212 Lecture 9,
1. Review of Circuit Theory Concepts
 1. Review of Circuit Theory Concepts Lecture notes: Section 1 ECE 65, Winter 2013, F. Najmabadi Circuit Theory is an pproximation to Maxwell s Electromagnetic Equations circuit is made of a bunch of elements
1. Review of Circuit Theory Concepts Lecture notes: Section 1 ECE 65, Winter 2013, F. Najmabadi Circuit Theory is an pproximation to Maxwell s Electromagnetic Equations circuit is made of a bunch of elements
To find the step response of an RC circuit
 To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
Physics 212 Midterm 2 Form A
 1. A wire contains a steady current of 2 A. The charge that passes a cross section in 2 s is: A. 3.2 10-19 C B. 6.4 10-19 C C. 1 C D. 2 C E. 4 C 2. In a Physics 212 lab, Jane measures the current versus
1. A wire contains a steady current of 2 A. The charge that passes a cross section in 2 s is: A. 3.2 10-19 C B. 6.4 10-19 C C. 1 C D. 2 C E. 4 C 2. In a Physics 212 lab, Jane measures the current versus
Physics 6B Summer 2007 Final
 Physics 6B Summer 2007 Final Question 1 An electron passes through two rectangular regions that contain uniform magnetic fields, B 1 and B 2. The field B 1 is stronger than the field B 2. Each field fills
Physics 6B Summer 2007 Final Question 1 An electron passes through two rectangular regions that contain uniform magnetic fields, B 1 and B 2. The field B 1 is stronger than the field B 2. Each field fills
What happens when things change. Transient current and voltage relationships in a simple resistive circuit.
 Module 4 AC Theory What happens when things change. What you'll learn in Module 4. 4.1 Resistors in DC Circuits Transient events in DC circuits. The difference between Ideal and Practical circuits Transient
Module 4 AC Theory What happens when things change. What you'll learn in Module 4. 4.1 Resistors in DC Circuits Transient events in DC circuits. The difference between Ideal and Practical circuits Transient
M. C. Escher: Waterfall. 18/9/2015 [tsl425 1/29]
![M. C. Escher: Waterfall. 18/9/2015 [tsl425 1/29] M. C. Escher: Waterfall. 18/9/2015 [tsl425 1/29]](/thumbs/76/73138710.jpg) M. C. Escher: Waterfall 18/9/2015 [tsl425 1/29] Direct Current Circuit Consider a wire with resistance R = ρl/a connected to a battery. Resistor rule: In the direction of I across a resistor with resistance
M. C. Escher: Waterfall 18/9/2015 [tsl425 1/29] Direct Current Circuit Consider a wire with resistance R = ρl/a connected to a battery. Resistor rule: In the direction of I across a resistor with resistance
Complete all the identification fields below or 10% of the lab value will be deduced from your final mark for this lab.
 Simple circuits 3 hr Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you
Simple circuits 3 hr Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you
ELECTRONICS E # 1 FUNDAMENTALS 2/2/2011
 FE Review 1 ELECTRONICS E # 1 FUNDAMENTALS Electric Charge 2 In an electric circuit it there is a conservation of charge. The net electric charge is constant. There are positive and negative charges. Like
FE Review 1 ELECTRONICS E # 1 FUNDAMENTALS Electric Charge 2 In an electric circuit it there is a conservation of charge. The net electric charge is constant. There are positive and negative charges. Like
COOKBOOK KVL AND KCL A COMPLETE GUIDE
 1250 COOKBOOK KVL AND KCL A COMPLETE GUIDE Example circuit: 1) Label all source and component values with a voltage drop measurement (+,- ) and a current flow measurement (arrow): By the passive sign convention,
1250 COOKBOOK KVL AND KCL A COMPLETE GUIDE Example circuit: 1) Label all source and component values with a voltage drop measurement (+,- ) and a current flow measurement (arrow): By the passive sign convention,
Modeling of Electrical Elements
 Modeling of Electrical Elements Dr. Bishakh Bhattacharya Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc - Funded by MHRD This Lecture Contains Modeling of
Modeling of Electrical Elements Dr. Bishakh Bhattacharya Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc - Funded by MHRD This Lecture Contains Modeling of
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 14 121011 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Steady-State Analysis RC Circuits RL Circuits 3 DC Steady-State
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 14 121011 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Steady-State Analysis RC Circuits RL Circuits 3 DC Steady-State
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency
 Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
Chapter 3. Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiency 3.1. The dc transformer model 3.2. Inclusion of inductor copper loss 3.3. Construction of equivalent circuit model 3.4. How to
PHYS 241 EXAM #2 November 9, 2006
 1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
1. ( 5 points) A resistance R and a 3.9 H inductance are in series across a 60 Hz AC voltage. The voltage across the resistor is 23 V and the voltage across the inductor is 35 V. Assume that all voltages
Assessment Schedule 2016 Physics: Demonstrate understanding electrical systems (91526)
 NCEA evel 3 Physics (91526) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Physics: Demonstrate understanding electrical systems (91526) Evidence Statement NØ N1 N 2 A 3 A 4 M 5 M 6 E 7 E 8 0 1A 2A 3A 4A or
NCEA evel 3 Physics (91526) 2016 page 1 of 5 Assessment Schedule 2016 Physics: Demonstrate understanding electrical systems (91526) Evidence Statement NØ N1 N 2 A 3 A 4 M 5 M 6 E 7 E 8 0 1A 2A 3A 4A or
Chapter 26 & 27. Electric Current and Direct- Current Circuits
 Chapter 26 & 27 Electric Current and Direct- Current Circuits Electric Current and Direct- Current Circuits Current and Motion of Charges Resistance and Ohm s Law Energy in Electric Circuits Combination
Chapter 26 & 27 Electric Current and Direct- Current Circuits Electric Current and Direct- Current Circuits Current and Motion of Charges Resistance and Ohm s Law Energy in Electric Circuits Combination
Exam 3--PHYS 102--S14
 Name: Exam 3--PHYS 102--S14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these statements is always true? a. resistors in parallel have the
Name: Exam 3--PHYS 102--S14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these statements is always true? a. resistors in parallel have the
Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004
 Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004 David E. Pellett Draft v.0.9 Notes Copyright 2004 David E. Pellett unless stated otherwise. References: Text for course: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, second edition,
Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004 David E. Pellett Draft v.0.9 Notes Copyright 2004 David E. Pellett unless stated otherwise. References: Text for course: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, second edition,
Circuit Analysis-II. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 5 Monday 23 rd April, 18
 Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
Circuit Analysis-II Capacitors in AC Circuits Introduction ü The instantaneous capacitor current is equal to the capacitance times the instantaneous rate of change of the voltage across the capacitor.
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, pm, Room TBA
 EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
a. Clockwise. b. Counterclockwise. c. Out of the board. d. Into the board. e. There will be no current induced in the wire
 Physics 1B Winter 2012: Final Exam For Practice Version A 1 Closed book. No work needs to be shown for multiple-choice questions. The first 10 questions are the makeup Quiz. The remaining questions are
Physics 1B Winter 2012: Final Exam For Practice Version A 1 Closed book. No work needs to be shown for multiple-choice questions. The first 10 questions are the makeup Quiz. The remaining questions are
LECTURE 8 RC AND RL FIRST-ORDER CIRCUITS (PART 1)
 CIRCUITS by Ulaby & Maharbiz LECTURE 8 RC AND RL FIRST-ORDER CIRCUITS (PART 1) 07/18/2013 ECE225 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute. 2013 National Technology and Science Press
CIRCUITS by Ulaby & Maharbiz LECTURE 8 RC AND RL FIRST-ORDER CIRCUITS (PART 1) 07/18/2013 ECE225 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS All rights reserved. Do not copy or distribute. 2013 National Technology and Science Press
Alternating Current Circuits
 Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Physics 122, Fall November 2012
 Today in Physics 1: inductance Mutual inductance elf inductance nductors in circuits: and circuits. it Energy stored in inductors 15 November 01 Physics 1, Fall 01 1 Mutual inductance onsider again a transformer
Today in Physics 1: inductance Mutual inductance elf inductance nductors in circuits: and circuits. it Energy stored in inductors 15 November 01 Physics 1, Fall 01 1 Mutual inductance onsider again a transformer
Physics 102 Spring 2006: Final Exam Multiple-Choice Questions
 Last Name: First Name: Physics 102 Spring 2006: Final Exam Multiple-Choice Questions For questions 1 and 2, refer to the graph below, depicting the potential on the x-axis as a function of x V x 60 40
Last Name: First Name: Physics 102 Spring 2006: Final Exam Multiple-Choice Questions For questions 1 and 2, refer to the graph below, depicting the potential on the x-axis as a function of x V x 60 40
r where the electric constant
 1.0 ELECTROSTATICS At the end of this topic, students will be able to: 10 1.1 Coulomb s law a) Explain the concepts of electrons, protons, charged objects, charged up, gaining charge, losing charge, charging
1.0 ELECTROSTATICS At the end of this topic, students will be able to: 10 1.1 Coulomb s law a) Explain the concepts of electrons, protons, charged objects, charged up, gaining charge, losing charge, charging
Transient Analysis of First-Order Circuits: Approaches and Recommendations
 Transient Analysis of First-Order Circuits: Approaches and Recommendations Khalid Al-Olimat Heath LeBlanc ECCS Department ECCS Department Ohio Northern University Ohio Northern University Ada, OH 45810
Transient Analysis of First-Order Circuits: Approaches and Recommendations Khalid Al-Olimat Heath LeBlanc ECCS Department ECCS Department Ohio Northern University Ohio Northern University Ada, OH 45810
ENGR 2405 Class No Electric Circuits I
 ENGR 2405 Class No. 48056 Electric Circuits I Dr. R. Williams Ph.D. rube.williams@hccs.edu Electric Circuit An electric circuit is an interconnec9on of electrical elements Charge Charge is an electrical
ENGR 2405 Class No. 48056 Electric Circuits I Dr. R. Williams Ph.D. rube.williams@hccs.edu Electric Circuit An electric circuit is an interconnec9on of electrical elements Charge Charge is an electrical
PHY 131 Review Session Fall 2015 PART 1:
 PHY 131 Review Session Fall 2015 PART 1: 1. Consider the electric field from a point charge. As you move farther away from the point charge, the electric field decreases at a rate of 1/r 2 with r being
PHY 131 Review Session Fall 2015 PART 1: 1. Consider the electric field from a point charge. As you move farther away from the point charge, the electric field decreases at a rate of 1/r 2 with r being
/20 /20 /20 /60. Dr. Galeazzi PHY207 Test #3 November 20, I.D. number:
 Signature: Name: I.D. number: You must do ALL the problems Each problem is worth 0 points for a total of 60 points. TO GET CREDIT IN PROBLEMS AND 3 YOU MUST SHOW GOOD WORK. CHECK DISCUSSION SECTION ATTENDED:
Signature: Name: I.D. number: You must do ALL the problems Each problem is worth 0 points for a total of 60 points. TO GET CREDIT IN PROBLEMS AND 3 YOU MUST SHOW GOOD WORK. CHECK DISCUSSION SECTION ATTENDED:
CURRENT SOURCES EXAMPLE 1 Find the source voltage Vs and the current I1 for the circuit shown below SOURCE CONVERSIONS
 CURRENT SOURCES EXAMPLE 1 Find the source voltage Vs and the current I1 for the circuit shown below EXAMPLE 2 Find the source voltage Vs and the current I1 for the circuit shown below SOURCE CONVERSIONS
CURRENT SOURCES EXAMPLE 1 Find the source voltage Vs and the current I1 for the circuit shown below EXAMPLE 2 Find the source voltage Vs and the current I1 for the circuit shown below SOURCE CONVERSIONS
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields
 Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
Electromagnetic Field Theory Chapter 9: Time-varying EM Fields Faraday s law of induction We have learned that a constant current induces magnetic field and a constant charge (or a voltage) makes an electric
Exercise 1: RC Time Constants
 Exercise 1: RC EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to determine the time constant of an RC circuit by using calculated and measured values. You will verify your results
Exercise 1: RC EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to determine the time constant of an RC circuit by using calculated and measured values. You will verify your results
Resistance, Ohm s Law and Kirchoff s Laws
 Universiti Teknologi MR Fakulti Sains Gunaan Resistance, Ohm s Law and Kirchoff s Laws PHY631: Physical Science ctivity Name: HP: Lab#: Intro Objectives The goal of today s activity is to physically investigate
Universiti Teknologi MR Fakulti Sains Gunaan Resistance, Ohm s Law and Kirchoff s Laws PHY631: Physical Science ctivity Name: HP: Lab#: Intro Objectives The goal of today s activity is to physically investigate
Inductors. Hydraulic analogy Duality with capacitor Charging and discharging. Lecture 12: Inductors
 Lecture 12: nductors nductors Hydraulic analogy Duality with capacitor Charging and discharging Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado http://hilaroad.com/camp/projects/magnet.html 99 Lecture 12: nductors
Lecture 12: nductors nductors Hydraulic analogy Duality with capacitor Charging and discharging Robert R. McLeod, University of Colorado http://hilaroad.com/camp/projects/magnet.html 99 Lecture 12: nductors
AP Physics C. Electric Circuits III.C
 AP Physics C Electric Circuits III.C III.C.1 Current, Resistance and Power The direction of conventional current Suppose the cross-sectional area of the conductor changes. If a conductor has no current,
AP Physics C Electric Circuits III.C III.C.1 Current, Resistance and Power The direction of conventional current Suppose the cross-sectional area of the conductor changes. If a conductor has no current,
Physics 102 Spring 2007: Final Exam Multiple-Choice Questions
 Last Name: First Name: Physics 102 Spring 2007: Final Exam Multiple-Choice Questions 1. The circuit on the left in the figure below contains a battery of potential V and a variable resistor R V. The circuit
Last Name: First Name: Physics 102 Spring 2007: Final Exam Multiple-Choice Questions 1. The circuit on the left in the figure below contains a battery of potential V and a variable resistor R V. The circuit
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance
 Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
E E 2320 Circuit Analysis. Calculating Resistance
 E E 30 Circuit Analysis Lecture 03 Simple esistive Circuits it and Applications Calculating esistance l A 6 1.67 10 cm cu 6 al.7010 Area, A When conductor has uniform crosssection cm l 1 Temperature Coefficient
E E 30 Circuit Analysis Lecture 03 Simple esistive Circuits it and Applications Calculating esistance l A 6 1.67 10 cm cu 6 al.7010 Area, A When conductor has uniform crosssection cm l 1 Temperature Coefficient
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
Electric Circuits I. Nodal Analysis. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits I Nodal Analysis Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Nodal Analysis Without Voltage Source Nodal analysis, which is based on a systematic application of Kirchhoff s current law (KCL). A node is defined
Electric Circuits I Nodal Analysis Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Nodal Analysis Without Voltage Source Nodal analysis, which is based on a systematic application of Kirchhoff s current law (KCL). A node is defined
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Section Number:
 Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly
Electricity and Light Pre Lab Questions
 Electricity and Light Pre Lab Questions The pre lab questions can be answered by reading the theory and procedure for the related lab. You are strongly encouraged to answers these questions on your own.
Electricity and Light Pre Lab Questions The pre lab questions can be answered by reading the theory and procedure for the related lab. You are strongly encouraged to answers these questions on your own.
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194
 MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
MAY/JUNE 2006 Question & Model Answer IN BASIC ELECTRICITY 194 Question 1 (a) List three sources of heat in soldering (b) state the functions of flux in soldering (c) briefly describe with aid of diagram
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current. 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3.
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current 1. Electromagnetic oscillations and LC circuit 2. Alternating Current 3. RLC circuit in AC 1 RL and RC circuits RL RC Charging Discharging I = emf R
Magnetic Fields
 Magnetic circuits introduction Becomes aware of the similarities between the analysis of magnetic circuits and electric circuits. Develop a clear understanding of the important parameters of a magnetic
Magnetic circuits introduction Becomes aware of the similarities between the analysis of magnetic circuits and electric circuits. Develop a clear understanding of the important parameters of a magnetic
EE301 RESISTANCE AND OHM S LAW
 Learning Objectives a. Describe the concept of resistance b. Use Ohm s law to calculate current, voltage, and resistance values in a circuit c. Discuss the difference between an open circuit and a short
Learning Objectives a. Describe the concept of resistance b. Use Ohm s law to calculate current, voltage, and resistance values in a circuit c. Discuss the difference between an open circuit and a short
Midterm Exam 2. Prof. Miloš Popović
 Midterm Exam 2 Prof. Miloš Popović 100 min timed, closed book test. Write your name at top of every page (or initials on later pages) Aids: single page (single side) of notes, handheld calculator Work
Midterm Exam 2 Prof. Miloš Popović 100 min timed, closed book test. Write your name at top of every page (or initials on later pages) Aids: single page (single side) of notes, handheld calculator Work
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
 ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Chapter 1. Electric Fields 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Triboelectric Effect 1.3 Experiments with Pith Balls 1.4 Experiments with a Gold-leaf Electroscope 1.5 Coulomb s Law 1.6 Electric
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Chapter 1. Electric Fields 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Triboelectric Effect 1.3 Experiments with Pith Balls 1.4 Experiments with a Gold-leaf Electroscope 1.5 Coulomb s Law 1.6 Electric
Electric Circuit Theory
 Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 18 Two-Port Circuits Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 18.1 The Terminal Equations
Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 18 Two-Port Circuits Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 18.1 The Terminal Equations
Automatic Formulation of Circuit Equations
 ECE 570 Session 3 IC 752-E Computer Aided Engineering for Integrated Circuits Automatic Formulation of Circuit Equations Objective: Basics of computer aided analysis/simulation Outline:. Discussion of
ECE 570 Session 3 IC 752-E Computer Aided Engineering for Integrated Circuits Automatic Formulation of Circuit Equations Objective: Basics of computer aided analysis/simulation Outline:. Discussion of
MEP 382: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture 3: DC & AC Circuit Analysis
 Faculty of Engineering MEP 38: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture 3: DC & AC Circuit Analysis Outline oltage and Current Ohm s Law Kirchoff s laws esistors Series and Parallel oltage Dividers
Faculty of Engineering MEP 38: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture 3: DC & AC Circuit Analysis Outline oltage and Current Ohm s Law Kirchoff s laws esistors Series and Parallel oltage Dividers
Lecture # 2 Basic Circuit Laws
 CPEN 206 Linear Circuits Lecture # 2 Basic Circuit Laws Dr. Godfrey A. Mills Email: gmills@ug.edu.gh Phone: 026907363 February 5, 206 Course TA David S. Tamakloe CPEN 206 Lecture 2 205_206 What is Electrical
CPEN 206 Linear Circuits Lecture # 2 Basic Circuit Laws Dr. Godfrey A. Mills Email: gmills@ug.edu.gh Phone: 026907363 February 5, 206 Course TA David S. Tamakloe CPEN 206 Lecture 2 205_206 What is Electrical
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Mauro Forti October 27, 2018 Constitutive Relations in the Frequency Domain Consider a network with independent voltage and current sources at the same angular frequency
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Mauro Forti October 27, 2018 Constitutive Relations in the Frequency Domain Consider a network with independent voltage and current sources at the same angular frequency
Ohm s Law and Electronic Circuits
 Production Ohm s Law and Electronic Circuits Page 1 - Cyber Security Class ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS All you need to be an inventor is a good imagination and a pile of junk. -Thomas Edison Page 2 - Cyber Security
Production Ohm s Law and Electronic Circuits Page 1 - Cyber Security Class ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS All you need to be an inventor is a good imagination and a pile of junk. -Thomas Edison Page 2 - Cyber Security
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012
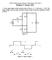 ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
ET4119 Electronic Power Conversion 2011/2012 Solutions 27 January 2012 1. In the single-phase rectifier shown below in Fig 1a., s = 1mH and I d = 10A. The input voltage v s has the pulse waveform shown
Alternating Current. Chapter 31. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman
 Chapter 31 Alternating Current PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 8_8_2008 Topics for Chapter 31
Chapter 31 Alternating Current PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 8_8_2008 Topics for Chapter 31
Objective Type Questions Instrumentation System & Devices (IDS)
 1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
1. A balance beam scale uses which of the following units? a. grams b.pounds c. ounces d. kilograms 2. Which of the following would be about the height of the average doorway? a. 2 meters b. 2 centimeters
