Sequences. We know that the functions can be defined on any subsets of R. As the set of positive integers
|
|
|
- Dwight Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sequences We know that the functions can be defined on any subsets of R. As the set of positive integers Z + is a subset of R, we can define a function on it in the following manner. f: Z + R f(n) = a n The range of this function is the infinite set {a 1, a, a 3, }. The set may not necessarily contain infinitely many distinct numbers because some of a i s could be equal. That set {a 1, a, a 3, } is called a sequence. We call a r the r th term of the sequence. For our convenience, we shall denote the whole sequence {a 1, a, } by {a n }. Example 1 Consider the sequence {a n } defined as a n = 1 n. Here, a 1 = 1 a = 1 = 0.5 a 3 = 1 3 = a = 1 = 0.5 One can see that as n gets bigger a n is getting closer to 0. For example, a 15 = a 0 = Because of the behaviour we have seen with the sequence {a n }, we suspect that by taking n large enough, we can make a n as close to 0 as we wish. Because a 0 is within 0.05 units of 0 and a 1 is within units of 0, we can expect that a will be even closer. These observations prepare us for our first definition. Definition 1 Let {a n } be a sequence. A number L is said to be the limit of {a n } if ε > 0, n 0 Z + such that n > n 0 a n L < ε When this happens, we write lim a n = L Now, let us consider the sequence in example 1. Let ε > 0.Then 1 ε R. By Archimedean property, n 0 Z + such that n 0 > 1 ε n > n 0 n > 1 ε 1 n < ε a n 0 = 1 0 < ε n lim a n = 0 1
2 Definition A sequence {a n } is said to be convergent if L R such that lim a n = L. Because we don t consider as a real number, this L is understood to be finite. The sequence in the example 1 is convergent. Not all the sequences are convergent. When a sequence is not convergent, it is said to be divergent. Example a n = n Assume {a n } is convergent. Then L R such that lim a n = L Because 1 > 0, n 0 Z + such that n L < 1 n > n 0 (n 0 + 1) L < 1 and (n 0 + 3) L < 1 = (n L) (n L) n L + n L < 1 contradiction The sequence {a n } is divergent. Theorem 1 A convergent sequence has a unique limit. Proof: Suppose a convergent sequence {a n } which doesn t have a unique limit. There are L, M R such that L M, lim a n = L and lim a n = M. Then > 0. n 1 Z + such that n > n 1 a n L < n Z + such that n > n a n M < Let n 0 be such that n 0 > n 1 and n 0 > n. Then = L a n0 + a n0 M a n0 L + a n0 M < + The limit is unique. = - contradiction Theorem Let {a n }, {b n } be two sequences such that lim a n = L and lim b n = M. Then, lim (a n + b n ) = L + M
3 Proof: Let ε > 0. n 1 Z + such that n > n 1 a n L < ε n Z + such that n > n b n M < ε Let n 0 = Max {n 1, n }. n > n 0 (a n + b n ) (L + M) a n L + b n M lim (a n + b n ) = L + M < ε + ε = ε Theorem 3 Let {a n }, {b n } be sequences such that lim Then the following claims are true. i) lim (ra n ) = rl r R ii) lim (a n b n ) = LM a n = L and lim b n = M. a n iii) lim = L b n M provided that M 0 The proof is an exercise for the student. Definition 3 Let {a n } be a sequence. i) If a n a n+1 n, then the sequence is said to be increasing. ii) If a n a n+1 n, then the sequence is said to be decreasing. iii) If a sequence is either increasing or decreasing, then it is said to be a monotonic sequence. If the strict inequalities are being used in i) or ii), then we say that the sequence is strictly increasing or strictly decreasing. Definition Let {a n } be a sequence. i) If A R such that a n A n, then {a n } is said to be bounded above. ii) If B R such that a n B n, then {a n } is said to be bounded below. iii) If there are A, B R such that B a n A n, then {a n } is said to be bounded. Theorem Every convergent sequence is bounded. Proof: Let {a n } be a convergent sequence. Then L R such that lim a n = L n 0 Z + such that n > n 0 a n L < 1 a n < L + 1 Let M = Max { a 1, a,., a n0, L + 1} Then a n M n M a n M n {a n } is bounded. 3
4 The student should realize that this theorem provides us with another way to make the claim we made in the example. The converse of theorem is false. Let a n = ( 1) n Then < a n < n It will be easy proving that the sequence {a n } is divergent. Suppose a sequence {a n } is bounded above. Then from the completeness axiom (chapter ), we can say that the supremum of {a n n Z + } exists. In the same way, if {a n } is bounded below, we can say that the infimum of {a n n Z + } exists. Theorem 5 If {a n } is increasing and bounded above, then lim a n = L where L = sup{a n n Z + }. Proof is a tutorial exercise. Theorem 6 If {a n } is decreasing and bounded below, then lim a n = M where M = inf{a n n Z + }. Proof is a tutorial exercise. Example 3 b n = n Clearly, {b n } is decreasing. 1 b n n So {b n } is bounded below. The student should be able to prove that 1 = inf{b n } From the above theorem, lim b n = 1 Cauchy Sequences We know that in a convergent sequence the terms get closer and closer to its limit. It may also be possible to have a sequence whose terms get closer and closer together and, we should be able to explain the behaviour of those terms without even mentioning a limit. The following definition will explain such a behaviour. Definition 5 A sequence {a n } is said to be a Cauchy sequence if and only if ε > 0, n 0 Z + such that m, n > n 0 a m a n < ε If the terms are getting closer and closer together, one would expect those to get closer and closer to a limit. In other words, one would expect such a sequence to be convergent. That fact needs to be proven and we will devote the next two theorems for that purpose.
5 Theorem 7 Every Cauchy sequence is bounded. Proof: Let {a n } be a Cauchy sequence. n 0 Z + such that m, n > n 0 a m a n < 1 m > n 0, a m a n0 +1 < 1 m > n 0 a m a n0 +1 < 1 a m < a n Let M = Max{ a 1, a,., a n0, a n } Then a m < M m Z + {a m } is bounded. Theorem 8 sequence. Let {a n } be a sequence. Then {a n } is convergent if and only if {a n } is a Cauchy Proof: Suppose {a n } is convergent. Let ε > 0. Then n 0 Z + such that n > n 0 a n L < ε where L is the limit of {a n}. Take m, n such that m > n 0, n > n 0. a m a n = a m L + L a n a m L + a n L < ε {a n } is a Cauchy sequence. Proving the converse is not necessary for engineering students. Theorem 7 and some other material will be needed for that proof. Because of this theorem, we can establish the convergence of a sequence without knowing the limit. Example : Suppose there is a sequence with the property a n+ = a n + a n+1 n Z + For this sequence, a i+1 a i = a i 1 + a i a i = a i 1 a i = a i 1 ( a i + a i 1 ) = a i 1 a i It follows that a i+1 a i = a i a i 1 = a i 1 a i 5
6 = = a a 1 i 1 If m = n, then a m a n = 0 So, without loss of generality, take m > n. m 1 a m a n = (a i+1 a i ) i=n m 1 a m a n a i+1 a i i=n m 1 = a a 1 ( 1 i 1 ) < a a 1 ( 1 n ) i=n Let ε > 0. If a = a 1, then a m a n < ε So let a a 1 Choose n 0 such that n0 > a a 1 ε n > n 0 n > a a 1 ε a a 1 n < ε a m a n < ε {a n } is a Cauchy sequence. Hence, {a n } is convergent. Note that we were able to establish the convergence without knowing the limit. U. A. Senevirathne Dept. of Mathematics University of Moratuwa. 6
7 7
MATH202 Introduction to Analysis (2007 Fall and 2008 Spring) Tutorial Note #7
 MATH202 Introduction to Analysis (2007 Fall and 2008 Spring) Tutorial Note #7 Real Number Summary of terminology and theorems: Definition: (Supremum & infimum) A supremum (or least upper bound) of a non-empty
MATH202 Introduction to Analysis (2007 Fall and 2008 Spring) Tutorial Note #7 Real Number Summary of terminology and theorems: Definition: (Supremum & infimum) A supremum (or least upper bound) of a non-empty
Structure of R. Chapter Algebraic and Order Properties of R
 Chapter Structure of R We will re-assemble calculus by first making assumptions about the real numbers. All subsequent results will be rigorously derived from these assumptions. Most of the assumptions
Chapter Structure of R We will re-assemble calculus by first making assumptions about the real numbers. All subsequent results will be rigorously derived from these assumptions. Most of the assumptions
MATH 101, FALL 2018: SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE REAL LINE
 MATH 101, FALL 2018: SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE REAL LINE SEBASTIEN VASEY These notes describe the material for November 26, 2018 (while similar content is in Abbott s book, the presentation here is different).
MATH 101, FALL 2018: SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON THE REAL LINE SEBASTIEN VASEY These notes describe the material for November 26, 2018 (while similar content is in Abbott s book, the presentation here is different).
2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom
 60 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom In this section, we use the fact that R is complete to establish some important results. First, we will prove that
60 CHAPTER 2. IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF R 2.2 Some Consequences of the Completeness Axiom In this section, we use the fact that R is complete to establish some important results. First, we will prove that
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 .1 Limits of Sequences. CHAPTER.1.0. a) True. If converges, then there is an M > 0 such that M. Choose by Archimedes an N N such that N > M/ε. Then n N implies /n M/n M/N < ε. b) False. = n does not converge,
.1 Limits of Sequences. CHAPTER.1.0. a) True. If converges, then there is an M > 0 such that M. Choose by Archimedes an N N such that N > M/ε. Then n N implies /n M/n M/N < ε. b) False. = n does not converge,
Midterm Review Math 311, Spring 2016
 Midterm Review Math 3, Spring 206 Material Review Preliminaries and Chapter Chapter 2. Set theory (DeMorgan s laws, infinite collections of sets, nested sets, cardinality) 2. Functions (image, preimage,
Midterm Review Math 3, Spring 206 Material Review Preliminaries and Chapter Chapter 2. Set theory (DeMorgan s laws, infinite collections of sets, nested sets, cardinality) 2. Functions (image, preimage,
Sequences. Limits of Sequences. Definition. A real-valued sequence s is any function s : N R.
 Sequences Limits of Sequences. Definition. A real-valued sequence s is any function s : N R. Usually, instead of using the notation s(n), we write s n for the value of this function calculated at n. We
Sequences Limits of Sequences. Definition. A real-valued sequence s is any function s : N R. Usually, instead of using the notation s(n), we write s n for the value of this function calculated at n. We
REVIEW OF ESSENTIAL MATH 346 TOPICS
 REVIEW OF ESSENTIAL MATH 346 TOPICS 1. AXIOMATIC STRUCTURE OF R Doğan Çömez The real number system is a complete ordered field, i.e., it is a set R which is endowed with addition and multiplication operations
REVIEW OF ESSENTIAL MATH 346 TOPICS 1. AXIOMATIC STRUCTURE OF R Doğan Çömez The real number system is a complete ordered field, i.e., it is a set R which is endowed with addition and multiplication operations
1. Supremum and Infimum Remark: In this sections, all the subsets of R are assumed to be nonempty.
 1. Supremum and Infimum Remark: In this sections, all the subsets of R are assumed to be nonempty. Let E be a subset of R. We say that E is bounded above if there exists a real number U such that x U for
1. Supremum and Infimum Remark: In this sections, all the subsets of R are assumed to be nonempty. Let E be a subset of R. We say that E is bounded above if there exists a real number U such that x U for
MATH3283W LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 6 = 5 13, = 2 5, 1 13
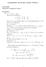 MATH383W LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 6 //00 Recursive sequences (cont.) Examples: () a =, a n+ = 3 a n. The first few terms are,,, 5 = 5, 3 5 = 5 3, Since 5
MATH383W LECTURE NOTES: WEEK 6 //00 Recursive sequences (cont.) Examples: () a =, a n+ = 3 a n. The first few terms are,,, 5 = 5, 3 5 = 5 3, Since 5
Suppose R is an ordered ring with positive elements P.
 1. The real numbers. 1.1. Ordered rings. Definition 1.1. By an ordered commutative ring with unity we mean an ordered sextuple (R, +, 0,, 1, P ) such that (R, +, 0,, 1) is a commutative ring with unity
1. The real numbers. 1.1. Ordered rings. Definition 1.1. By an ordered commutative ring with unity we mean an ordered sextuple (R, +, 0,, 1, P ) such that (R, +, 0,, 1) is a commutative ring with unity
ADVANCED CALCULUS - MTH433 LECTURE 4 - FINITE AND INFINITE SETS
 ADVANCED CALCULUS - MTH433 LECTURE 4 - FINITE AND INFINITE SETS 1. Cardinal number of a set The cardinal number (or simply cardinal) of a set is a generalization of the concept of the number of elements
ADVANCED CALCULUS - MTH433 LECTURE 4 - FINITE AND INFINITE SETS 1. Cardinal number of a set The cardinal number (or simply cardinal) of a set is a generalization of the concept of the number of elements
Scalar multiplication and addition of sequences 9
 8 Sequences 1.2.7. Proposition. Every subsequence of a convergent sequence (a n ) n N converges to lim n a n. Proof. If (a nk ) k N is a subsequence of (a n ) n N, then n k k for every k. Hence if ε >
8 Sequences 1.2.7. Proposition. Every subsequence of a convergent sequence (a n ) n N converges to lim n a n. Proof. If (a nk ) k N is a subsequence of (a n ) n N, then n k k for every k. Hence if ε >
The Real Number System
 MATH 337 The Real Number System Sets of Numbers Dr. Neal, WKU A set S is a well-defined collection of objects, with well-defined meaning that there is a specific description from which we can tell precisely
MATH 337 The Real Number System Sets of Numbers Dr. Neal, WKU A set S is a well-defined collection of objects, with well-defined meaning that there is a specific description from which we can tell precisely
Sequences CHAPTER 3. Definition. A sequence is a function f : N R.
 CHAPTER 3 Sequences 1. Limits and the Archimedean Property Our first basic object for investigating real numbers is the sequence. Before we give the precise definition of a sequence, we will give the intuitive
CHAPTER 3 Sequences 1. Limits and the Archimedean Property Our first basic object for investigating real numbers is the sequence. Before we give the precise definition of a sequence, we will give the intuitive
MIDTERM REVIEW FOR MATH The limit
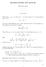 MIDTERM REVIEW FOR MATH 500 SHUANGLIN SHAO. The limit Define lim n a n = A: For any ε > 0, there exists N N such that for any n N, a n A < ε. The key in this definition is to realize that the choice of
MIDTERM REVIEW FOR MATH 500 SHUANGLIN SHAO. The limit Define lim n a n = A: For any ε > 0, there exists N N such that for any n N, a n A < ε. The key in this definition is to realize that the choice of
Week 2: Sequences and Series
 QF0: Quantitative Finance August 29, 207 Week 2: Sequences and Series Facilitator: Christopher Ting AY 207/208 Mathematicians have tried in vain to this day to discover some order in the sequence of prime
QF0: Quantitative Finance August 29, 207 Week 2: Sequences and Series Facilitator: Christopher Ting AY 207/208 Mathematicians have tried in vain to this day to discover some order in the sequence of prime
Characterisation of Accumulation Points. Convergence in Metric Spaces. Characterisation of Closed Sets. Characterisation of Closed Sets
 Convergence in Metric Spaces Functional Analysis Lecture 3: Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces Bengt Ove Turesson September 4, 2016 Suppose that (X, d) is a metric space. A sequence (x n ) X is
Convergence in Metric Spaces Functional Analysis Lecture 3: Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces Bengt Ove Turesson September 4, 2016 Suppose that (X, d) is a metric space. A sequence (x n ) X is
Sequences. Chapter 3. n + 1 3n + 2 sin n n. 3. lim (ln(n + 1) ln n) 1. lim. 2. lim. 4. lim (1 + n)1/n. Answers: 1. 1/3; 2. 0; 3. 0; 4. 1.
 Chapter 3 Sequences Both the main elements of calculus (differentiation and integration) require the notion of a limit. Sequences will play a central role when we work with limits. Definition 3.. A Sequence
Chapter 3 Sequences Both the main elements of calculus (differentiation and integration) require the notion of a limit. Sequences will play a central role when we work with limits. Definition 3.. A Sequence
M17 MAT25-21 HOMEWORK 6
 M17 MAT25-21 HOMEWORK 6 DUE 10:00AM WEDNESDAY SEPTEMBER 13TH 1. To Hand In Double Series. The exercises in this section will guide you to complete the proof of the following theorem: Theorem 1: Absolute
M17 MAT25-21 HOMEWORK 6 DUE 10:00AM WEDNESDAY SEPTEMBER 13TH 1. To Hand In Double Series. The exercises in this section will guide you to complete the proof of the following theorem: Theorem 1: Absolute
MAS221 Analysis Semester Chapter 2 problems
 MAS221 Analysis Semester 1 2018-19 Chapter 2 problems 20. Consider the sequence (a n ), with general term a n = 1 + 3. Can you n guess the limit l of this sequence? (a) Verify that your guess is plausible
MAS221 Analysis Semester 1 2018-19 Chapter 2 problems 20. Consider the sequence (a n ), with general term a n = 1 + 3. Can you n guess the limit l of this sequence? (a) Verify that your guess is plausible
Definition 2.1. A metric (or distance function) defined on a non-empty set X is a function d: X X R that satisfies: For all x, y, and z in X :
 MATH 337 Metric Spaces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a non-empty set. The elements of X shall be called points. We shall define the general means of determining the distance between two points. Throughout we
MATH 337 Metric Spaces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a non-empty set. The elements of X shall be called points. We shall define the general means of determining the distance between two points. Throughout we
Econ Slides from Lecture 1
 Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 1 Joel Sobel August 23, 2010 Warning I can t start without assuming that something is common knowledge. You can find basic definitions of Sets and Set Operations
Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 1 Joel Sobel August 23, 2010 Warning I can t start without assuming that something is common knowledge. You can find basic definitions of Sets and Set Operations
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers
 Chapter 1 The Real Numbers In a beginning course in calculus, the emphasis is on introducing the techniques of the subject;i.e., differentiation and integration and their applications. An advanced calculus
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers In a beginning course in calculus, the emphasis is on introducing the techniques of the subject;i.e., differentiation and integration and their applications. An advanced calculus
C.7. Numerical series. Pag. 147 Proof of the converging criteria for series. Theorem 5.29 (Comparison test) Let a k and b k be positive-term series
 C.7 Numerical series Pag. 147 Proof of the converging criteria for series Theorem 5.29 (Comparison test) Let and be positive-term series such that 0, for any k 0. i) If the series converges, then also
C.7 Numerical series Pag. 147 Proof of the converging criteria for series Theorem 5.29 (Comparison test) Let and be positive-term series such that 0, for any k 0. i) If the series converges, then also
Section 3.2 : Sequences
 Section 3.2 : Sequences Note: Chapter 11 of Stewart s Calculus is a good reference for this chapter of our lecture notes. Definition 52 A sequence is an infinite ordered list a 1, a 2, a 3,... The items
Section 3.2 : Sequences Note: Chapter 11 of Stewart s Calculus is a good reference for this chapter of our lecture notes. Definition 52 A sequence is an infinite ordered list a 1, a 2, a 3,... The items
DR.RUPNATHJI( DR.RUPAK NATH )
 Contents 1 Sets 1 2 The Real Numbers 9 3 Sequences 29 4 Series 59 5 Functions 81 6 Power Series 105 7 The elementary functions 111 Chapter 1 Sets It is very convenient to introduce some notation and terminology
Contents 1 Sets 1 2 The Real Numbers 9 3 Sequences 29 4 Series 59 5 Functions 81 6 Power Series 105 7 The elementary functions 111 Chapter 1 Sets It is very convenient to introduce some notation and terminology
Math 410 Homework 6 Due Monday, October 26
 Math 40 Homework 6 Due Monday, October 26. Let c be any constant and assume that lim s n = s and lim t n = t. Prove that: a) lim c s n = c s We talked about these in class: We want to show that for all
Math 40 Homework 6 Due Monday, October 26. Let c be any constant and assume that lim s n = s and lim t n = t. Prove that: a) lim c s n = c s We talked about these in class: We want to show that for all
Math 1b Sequences and series summary
 Math b Sequences and series summary December 22, 2005 Sequences (Stewart p. 557) Notations for a sequence: or a, a 2, a 3,..., a n,... {a n }. The numbers a n are called the terms of the sequence.. Limit
Math b Sequences and series summary December 22, 2005 Sequences (Stewart p. 557) Notations for a sequence: or a, a 2, a 3,..., a n,... {a n }. The numbers a n are called the terms of the sequence.. Limit
Advanced Calculus: MATH 410 Real Numbers Professor David Levermore 5 December 2010
 Advanced Calculus: MATH 410 Real Numbers Professor David Levermore 5 December 2010 1. Real Number System 1.1. Introduction. Numbers are at the heart of mathematics. By now you must be fairly familiar with
Advanced Calculus: MATH 410 Real Numbers Professor David Levermore 5 December 2010 1. Real Number System 1.1. Introduction. Numbers are at the heart of mathematics. By now you must be fairly familiar with
A Few Examples. A Few Examples
 Section 3.2 : Sequences Note: Chapter of Stewart s Calculus is a good reference for this chapter of our lecture notes. Definition 52 A sequence is an infinite ordered list A Few Examples (( ) n + ) n=
Section 3.2 : Sequences Note: Chapter of Stewart s Calculus is a good reference for this chapter of our lecture notes. Definition 52 A sequence is an infinite ordered list A Few Examples (( ) n + ) n=
Iowa State University. Instructor: Alex Roitershtein Summer Exam #1. Solutions. x u = 2 x v
 Math 501 Iowa State University Introduction to Real Analysis Department of Mathematics Instructor: Alex Roitershtein Summer 015 Exam #1 Solutions This is a take-home examination. The exam includes 8 questions.
Math 501 Iowa State University Introduction to Real Analysis Department of Mathematics Instructor: Alex Roitershtein Summer 015 Exam #1 Solutions This is a take-home examination. The exam includes 8 questions.
2.1 Convergence of Sequences
 Chapter 2 Sequences 2. Convergence of Sequences A sequence is a function f : N R. We write f) = a, f2) = a 2, and in general fn) = a n. We usually identify the sequence with the range of f, which is written
Chapter 2 Sequences 2. Convergence of Sequences A sequence is a function f : N R. We write f) = a, f2) = a 2, and in general fn) = a n. We usually identify the sequence with the range of f, which is written
MATH 324 Summer 2011 Elementary Number Theory. Notes on Mathematical Induction. Recall the following axiom for the set of integers.
 MATH 4 Summer 011 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction Principle of Mathematical Induction Recall the following axiom for the set of integers. Well-Ordering Axiom for the Integers If
MATH 4 Summer 011 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction Principle of Mathematical Induction Recall the following axiom for the set of integers. Well-Ordering Axiom for the Integers If
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES
 MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics. Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics
 Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics An Introductory Single Variable Real Analysis: A Learning Approach through Problem Solving Marcel B. Finan c All Rights
Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics An Introductory Single Variable Real Analysis: A Learning Approach through Problem Solving Marcel B. Finan c All Rights
Logical Connectives and Quantifiers
 Chapter 1 Logical Connectives and Quantifiers 1.1 Logical Connectives 1.2 Quantifiers 1.3 Techniques of Proof: I 1.4 Techniques of Proof: II Theorem 1. Let f be a continuous function. If 1 f(x)dx 0, then
Chapter 1 Logical Connectives and Quantifiers 1.1 Logical Connectives 1.2 Quantifiers 1.3 Techniques of Proof: I 1.4 Techniques of Proof: II Theorem 1. Let f be a continuous function. If 1 f(x)dx 0, then
Math 324 Summer 2012 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction
 Math 4 Summer 01 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction Principle of Mathematical Induction Recall the following axiom for the set of integers. Well-Ordering Axiom for the Integers If
Math 4 Summer 01 Elementary Number Theory Notes on Mathematical Induction Principle of Mathematical Induction Recall the following axiom for the set of integers. Well-Ordering Axiom for the Integers If
Chapter One. The Real Number System
 Chapter One. The Real Number System We shall give a quick introduction to the real number system. It is imperative that we know how the set of real numbers behaves in the way that its completeness and
Chapter One. The Real Number System We shall give a quick introduction to the real number system. It is imperative that we know how the set of real numbers behaves in the way that its completeness and
Foundations of Mathematical Analysis
 Foundations of Mathematical Analysis Fabio Bagagiolo Dipartimento di Matematica, Università di Trento email:fabio.bagagiolo@unitn.it Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Basic concepts in mathematical analysis
Foundations of Mathematical Analysis Fabio Bagagiolo Dipartimento di Matematica, Università di Trento email:fabio.bagagiolo@unitn.it Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Basic concepts in mathematical analysis
Math 421, Homework #7 Solutions. We can then us the triangle inequality to find for k N that (x k + y k ) (L + M) = (x k L) + (y k M) x k L + y k M
 Math 421, Homework #7 Solutions (1) Let {x k } and {y k } be convergent sequences in R n, and assume that lim k x k = L and that lim k y k = M. Prove directly from definition 9.1 (i.e. don t use Theorem
Math 421, Homework #7 Solutions (1) Let {x k } and {y k } be convergent sequences in R n, and assume that lim k x k = L and that lim k y k = M. Prove directly from definition 9.1 (i.e. don t use Theorem
Numerical Sequences and Series
 Numerical Sequences and Series Written by Men-Gen Tsai email: b89902089@ntu.edu.tw. Prove that the convergence of {s n } implies convergence of { s n }. Is the converse true? Solution: Since {s n } is
Numerical Sequences and Series Written by Men-Gen Tsai email: b89902089@ntu.edu.tw. Prove that the convergence of {s n } implies convergence of { s n }. Is the converse true? Solution: Since {s n } is
1. Theorem. (Archimedean Property) Let x be any real number. There exists a positive integer n greater than x.
 Advanced Calculus I, Dr. Block, Chapter 2 notes. Theorem. (Archimedean Property) Let x be any real number. There exists a positive integer n greater than x. 2. Definition. A sequence is a real-valued function
Advanced Calculus I, Dr. Block, Chapter 2 notes. Theorem. (Archimedean Property) Let x be any real number. There exists a positive integer n greater than x. 2. Definition. A sequence is a real-valued function
Principle of Mathematical Induction
 Advanced Calculus I. Math 451, Fall 2016, Prof. Vershynin Principle of Mathematical Induction 1. Prove that 1 + 2 + + n = 1 n(n + 1) for all n N. 2 2. Prove that 1 2 + 2 2 + + n 2 = 1 n(n + 1)(2n + 1)
Advanced Calculus I. Math 451, Fall 2016, Prof. Vershynin Principle of Mathematical Induction 1. Prove that 1 + 2 + + n = 1 n(n + 1) for all n N. 2 2. Prove that 1 2 + 2 2 + + n 2 = 1 n(n + 1)(2n + 1)
MA103 Introduction to Abstract Mathematics Second part, Analysis and Algebra
 206/7 MA03 Introduction to Abstract Mathematics Second part, Analysis and Algebra Amol Sasane Revised by Jozef Skokan, Konrad Swanepoel, and Graham Brightwell Copyright c London School of Economics 206
206/7 MA03 Introduction to Abstract Mathematics Second part, Analysis and Algebra Amol Sasane Revised by Jozef Skokan, Konrad Swanepoel, and Graham Brightwell Copyright c London School of Economics 206
The Real Numbers. Chapter The Completeness Property of R
 Chapter 1 The Real Numbers 1.1 The Completeness Property of R Example 1.1.1 (Bartle 2.3.5 (a) Page 39). A nonempty set S 1 with a finite number of elements will have a least element, say u, and a largest
Chapter 1 The Real Numbers 1.1 The Completeness Property of R Example 1.1.1 (Bartle 2.3.5 (a) Page 39). A nonempty set S 1 with a finite number of elements will have a least element, say u, and a largest
Homework 1 (revised) Solutions
 Homework 1 (revised) Solutions 1. Textbook, 1.1.1, # 1.1.2 (p. 24) Let S be an ordered set. Let A be a non-empty finite subset. Then A is bounded and sup A, inf A A Solution. The hint was: Use induction,
Homework 1 (revised) Solutions 1. Textbook, 1.1.1, # 1.1.2 (p. 24) Let S be an ordered set. Let A be a non-empty finite subset. Then A is bounded and sup A, inf A A Solution. The hint was: Use induction,
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES. Contents. 1. Sets Functions Countability Axiom of choice Equivalence relations 9
 MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY
 A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY 1. NOTATION Before we begin some notational definitions are useful. (1) Z = {, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, }is the set of integers. (2) Q = { a b : aεz, bεz {0}} is the set
A LITTLE REAL ANALYSIS AND TOPOLOGY 1. NOTATION Before we begin some notational definitions are useful. (1) Z = {, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, }is the set of integers. (2) Q = { a b : aεz, bεz {0}} is the set
Chapter 3 Continuous Functions
 Continuity is a very important concept in analysis. The tool that we shall use to study continuity will be sequences. There are important results concerning the subsets of the real numbers and the continuity
Continuity is a very important concept in analysis. The tool that we shall use to study continuity will be sequences. There are important results concerning the subsets of the real numbers and the continuity
1.2 Functions What is a Function? 1.2. FUNCTIONS 11
 1.2. FUNCTIONS 11 1.2 Functions 1.2.1 What is a Function? In this section, we only consider functions of one variable. Loosely speaking, a function is a special relation which exists between two variables.
1.2. FUNCTIONS 11 1.2 Functions 1.2.1 What is a Function? In this section, we only consider functions of one variable. Loosely speaking, a function is a special relation which exists between two variables.
Problem Set 2 Solutions Math 311, Spring 2016
 Problem Set 2 Solutions Math 311, Spring 2016 Directions: Name: You must complete (at least) a total of 8 problems, some of which have multiple parts. You may complete more than 8 problems, for possible
Problem Set 2 Solutions Math 311, Spring 2016 Directions: Name: You must complete (at least) a total of 8 problems, some of which have multiple parts. You may complete more than 8 problems, for possible
We are going to discuss what it means for a sequence to converge in three stages: First, we define what it means for a sequence to converge to zero
 Chapter Limits of Sequences Calculus Student: lim s n = 0 means the s n are getting closer and closer to zero but never gets there. Instructor: ARGHHHHH! Exercise. Think of a better response for the instructor.
Chapter Limits of Sequences Calculus Student: lim s n = 0 means the s n are getting closer and closer to zero but never gets there. Instructor: ARGHHHHH! Exercise. Think of a better response for the instructor.
MATH 102 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS. 1. Some Fundamentals
 MATH 02 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS Properties of Real Numbers Some Fundamentals The whole course will be based entirely on the study of sequence of numbers and functions defined on the real
MATH 02 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS Properties of Real Numbers Some Fundamentals The whole course will be based entirely on the study of sequence of numbers and functions defined on the real
L p Functions. Given a measure space (X, µ) and a real number p [1, ), recall that the L p -norm of a measurable function f : X R is defined by
 L p Functions Given a measure space (, µ) and a real number p [, ), recall that the L p -norm of a measurable function f : R is defined by f p = ( ) /p f p dµ Note that the L p -norm of a function f may
L p Functions Given a measure space (, µ) and a real number p [, ), recall that the L p -norm of a measurable function f : R is defined by f p = ( ) /p f p dµ Note that the L p -norm of a function f may
MATH115. Sequences and Infinite Series. Paolo Lorenzo Bautista. June 29, De La Salle University. PLBautista (DLSU) MATH115 June 29, / 16
 MATH115 Sequences and Infinite Series Paolo Lorenzo Bautista De La Salle University June 29, 2014 PLBautista (DLSU) MATH115 June 29, 2014 1 / 16 Definition A sequence function is a function whose domain
MATH115 Sequences and Infinite Series Paolo Lorenzo Bautista De La Salle University June 29, 2014 PLBautista (DLSU) MATH115 June 29, 2014 1 / 16 Definition A sequence function is a function whose domain
Calculus (Real Analysis I)
 Calculus (Real Analysis I) (MAT122β) Department of Mathematics University of Ruhuna A.W.L. Pubudu Thilan Department of Mathematics University of Ruhuna Calculus (Real Analysis I)(MAT122β) 1/172 Chapter
Calculus (Real Analysis I) (MAT122β) Department of Mathematics University of Ruhuna A.W.L. Pubudu Thilan Department of Mathematics University of Ruhuna Calculus (Real Analysis I)(MAT122β) 1/172 Chapter
Seunghee Ye Ma 8: Week 2 Oct 6
 Week 2 Summary This week, we will learn about sequences and real numbers. We first define what we mean by a sequence and discuss several properties of sequences. Then, we will talk about what it means
Week 2 Summary This week, we will learn about sequences and real numbers. We first define what we mean by a sequence and discuss several properties of sequences. Then, we will talk about what it means
REAL ANALYSIS: INTRODUCTION
 REAL ANALYSIS: INTRODUCTION DR. RITU AGARWAL EMAIL: RAGARWAL.MATHS@MNIT.AC.IN MALVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. The real number system 1 2. Field Axioms 1 3. Order Axioms 2 4.
REAL ANALYSIS: INTRODUCTION DR. RITU AGARWAL EMAIL: RAGARWAL.MATHS@MNIT.AC.IN MALVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR Contents 1. The real number system 1 2. Field Axioms 1 3. Order Axioms 2 4.
Due date: Monday, February 6, 2017.
 Modern Analysis Homework 3 Solutions Due date: Monday, February 6, 2017. 1. If A R define A = {x R : x A}. Let A be a nonempty set of real numbers, assume A is bounded above. Prove that A is bounded below
Modern Analysis Homework 3 Solutions Due date: Monday, February 6, 2017. 1. If A R define A = {x R : x A}. Let A be a nonempty set of real numbers, assume A is bounded above. Prove that A is bounded below
MATH 131A: REAL ANALYSIS (BIG IDEAS)
 MATH 131A: REAL ANALYSIS (BIG IDEAS) Theorem 1 (The Triangle Inequality). For all x, y R we have x + y x + y. Proposition 2 (The Archimedean property). For each x R there exists an n N such that n > x.
MATH 131A: REAL ANALYSIS (BIG IDEAS) Theorem 1 (The Triangle Inequality). For all x, y R we have x + y x + y. Proposition 2 (The Archimedean property). For each x R there exists an n N such that n > x.
Solutions Manual for Homework Sets Math 401. Dr Vignon S. Oussa
 1 Solutions Manual for Homework Sets Math 401 Dr Vignon S. Oussa Solutions Homework Set 0 Math 401 Fall 2015 1. (Direct Proof) Assume that x and y are odd integers. Then there exist integers u and v such
1 Solutions Manual for Homework Sets Math 401 Dr Vignon S. Oussa Solutions Homework Set 0 Math 401 Fall 2015 1. (Direct Proof) Assume that x and y are odd integers. Then there exist integers u and v such
Math 117: Infinite Sequences
 Math 7: Infinite Sequences John Douglas Moore November, 008 The three main theorems in the theory of infinite sequences are the Monotone Convergence Theorem, the Cauchy Sequence Theorem and the Subsequence
Math 7: Infinite Sequences John Douglas Moore November, 008 The three main theorems in the theory of infinite sequences are the Monotone Convergence Theorem, the Cauchy Sequence Theorem and the Subsequence
Foundations of Mathematical Analysis
 Foundations of Mathematical Analysis Fabio Bagagiolo Dipartimento di Matematica, Università di Trento email:bagagiol@science.unitn.it Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Basic concepts in mathematical analysis
Foundations of Mathematical Analysis Fabio Bagagiolo Dipartimento di Matematica, Università di Trento email:bagagiol@science.unitn.it Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Basic concepts in mathematical analysis
Continuity. Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
Math LM (24543) Lectures 01
 Math 32300 LM (24543) Lectures 01 Ethan Akin Office: NAC 6/287 Phone: 650-5136 Email: ethanakin@earthlink.net Spring, 2018 Contents Introduction, Ross Chapter 1 and Appendix The Natural Numbers N and The
Math 32300 LM (24543) Lectures 01 Ethan Akin Office: NAC 6/287 Phone: 650-5136 Email: ethanakin@earthlink.net Spring, 2018 Contents Introduction, Ross Chapter 1 and Appendix The Natural Numbers N and The
Solutions to Homework Assignment 2
 Solutions to Homework Assignment Real Analysis I February, 03 Notes: (a) Be aware that there maybe some typos in the solutions. If you find any, please let me know. (b) As is usual in proofs, most problems
Solutions to Homework Assignment Real Analysis I February, 03 Notes: (a) Be aware that there maybe some typos in the solutions. If you find any, please let me know. (b) As is usual in proofs, most problems
THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4
 FOUNDATIONS OF ANALYSIS FALL 2008 TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4 (1) Every element in a field has a multiplicative inverse. (2) In a field the additive inverse of 1 is 0. (3) In a field
FOUNDATIONS OF ANALYSIS FALL 2008 TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS THE REAL NUMBERS Chapter #4 (1) Every element in a field has a multiplicative inverse. (2) In a field the additive inverse of 1 is 0. (3) In a field
Introduction to Mathematical Analysis I. Second Edition. Beatriz Lafferriere Gerardo Lafferriere Nguyen Mau Nam
 Introduction to Mathematical Analysis I Second Edition Beatriz Lafferriere Gerardo Lafferriere Nguyen Mau Nam Introduction to Mathematical Analysis I Second Edition Beatriz Lafferriere Gerardo Lafferriere
Introduction to Mathematical Analysis I Second Edition Beatriz Lafferriere Gerardo Lafferriere Nguyen Mau Nam Introduction to Mathematical Analysis I Second Edition Beatriz Lafferriere Gerardo Lafferriere
Math 430/530: Advanced Calculus I Chapter 1: Sequences
 Math 430/530: Advanced Calculus I Chapter 1: Sequences Fall 2018 Sequences A sequence is just a list of real numbers a 1, a 2,... with a definite order. We write a = (a n ) n=1 for a sequence a with n
Math 430/530: Advanced Calculus I Chapter 1: Sequences Fall 2018 Sequences A sequence is just a list of real numbers a 1, a 2,... with a definite order. We write a = (a n ) n=1 for a sequence a with n
means is a subset of. So we say A B for sets A and B if x A we have x B holds. BY CONTRAST, a S means that a is a member of S.
 1 Notation For those unfamiliar, we have := means equal by definition, N := {0, 1,... } or {1, 2,... } depending on context. (i.e. N is the set or collection of counting numbers.) In addition, means for
1 Notation For those unfamiliar, we have := means equal by definition, N := {0, 1,... } or {1, 2,... } depending on context. (i.e. N is the set or collection of counting numbers.) In addition, means for
Consequences of the Completeness Property
 Consequences of the Completeness Property Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of the Completeness Property Today 1 / 10 Introduction In this section, we use the fact that R
Consequences of the Completeness Property Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of the Completeness Property Today 1 / 10 Introduction In this section, we use the fact that R
Lecture 10. Riemann-Stieltjes Integration
 Lecture 10 Riemann-Stieltjes Integration In this section we will develop the basic definitions and some of the properties of the Riemann-Stieltjes Integral. The development will follow that of the Darboux
Lecture 10 Riemann-Stieltjes Integration In this section we will develop the basic definitions and some of the properties of the Riemann-Stieltjes Integral. The development will follow that of the Darboux
Advanced Calculus: MATH 410 Real Numbers Professor David Levermore 1 November 2017
 Advanced Calculus: MATH 410 Real Numbers Professor David Levermore 1 November 2017 1. Real Number System 1.1. Introduction. Numbers are at the heart of mathematics. By now you must be fairly familiar with
Advanced Calculus: MATH 410 Real Numbers Professor David Levermore 1 November 2017 1. Real Number System 1.1. Introduction. Numbers are at the heart of mathematics. By now you must be fairly familiar with
Section 2.5 : The Completeness Axiom in R
 Section 2.5 : The Completeness Axiom in R The rational numbers and real numbers are closely related. The set Q of rational numbers is countable and the set R of real numbers is not, and in this sense there
Section 2.5 : The Completeness Axiom in R The rational numbers and real numbers are closely related. The set Q of rational numbers is countable and the set R of real numbers is not, and in this sense there
INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 11 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES Infinite sequences and series were introduced briefly in A Preview of Calculus in connection with Zeno s paradoxes and the decimal representation
11 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES Infinite sequences and series were introduced briefly in A Preview of Calculus in connection with Zeno s paradoxes and the decimal representation
Solution of the 7 th Homework
 Solution of the 7 th Homework Sangchul Lee December 3, 2014 1 Preliminary In this section we deal with some facts that are relevant to our problems but can be coped with only previous materials. 1.1 Maximum
Solution of the 7 th Homework Sangchul Lee December 3, 2014 1 Preliminary In this section we deal with some facts that are relevant to our problems but can be coped with only previous materials. 1.1 Maximum
Real Analysis. Joe Patten August 12, 2018
 Real Analysis Joe Patten August 12, 2018 1 Relations and Functions 1.1 Relations A (binary) relation, R, from set A to set B is a subset of A B. Since R is a subset of A B, it is a set of ordered pairs.
Real Analysis Joe Patten August 12, 2018 1 Relations and Functions 1.1 Relations A (binary) relation, R, from set A to set B is a subset of A B. Since R is a subset of A B, it is a set of ordered pairs.
Chapter 8. Infinite Series
 8.4 Series of Nonnegative Terms Chapter 8. Infinite Series 8.4 Series of Nonnegative Terms Note. Given a series we have two questions:. Does the series converge? 2. If it converges, what is its sum? Corollary
8.4 Series of Nonnegative Terms Chapter 8. Infinite Series 8.4 Series of Nonnegative Terms Note. Given a series we have two questions:. Does the series converge? 2. If it converges, what is its sum? Corollary
+ = x. ± if x > 0. if x < 0, x
 2 Set Functions Notation Let R R {, + } and R + {x R : x 0} {+ }. Here + and are symbols satisfying obvious conditions: for any real number x R : < x < +, (± + (± x + (± (± + x ±, (± (± + and (± (, ± if
2 Set Functions Notation Let R R {, + } and R + {x R : x 0} {+ }. Here + and are symbols satisfying obvious conditions: for any real number x R : < x < +, (± + (± x + (± (± + x ±, (± (± + and (± (, ± if
Read carefully the instructions on the answer book and make sure that the particulars required are entered on each answer book.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION: January 2011 Analysis I Time Allowed: 1.5 hours Read carefully the instructions on the answer book and make sure that the particulars required are entered
THE UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION: January 2011 Analysis I Time Allowed: 1.5 hours Read carefully the instructions on the answer book and make sure that the particulars required are entered
Standard forms for writing numbers
 Standard forms for writing numbers In order to relate the abstract mathematical descriptions of familiar number systems to the everyday descriptions of numbers by decimal expansions and similar means,
Standard forms for writing numbers In order to relate the abstract mathematical descriptions of familiar number systems to the everyday descriptions of numbers by decimal expansions and similar means,
This exam contains 5 pages (including this cover page) and 4 questions. The total number of points is 100. Grade Table
 MAT25-2 Summer Session 2 207 Practice Final August 24th, 207 Time Limit: Hour 40 Minutes Name: Instructor: Nathaniel Gallup This exam contains 5 pages (including this cover page) and 4 questions. The total
MAT25-2 Summer Session 2 207 Practice Final August 24th, 207 Time Limit: Hour 40 Minutes Name: Instructor: Nathaniel Gallup This exam contains 5 pages (including this cover page) and 4 questions. The total
Math 140: Foundations of Real Analysis. Todd Kemp
 Math 140: Foundations of Real Analysis Todd Kemp Contents Part 1. Math 140A 5 Chapter 1. Ordered Sets, Ordered Fields, and Completeness 7 1. Lecture 1: January 5, 2016 7 2. Lecture 2: January 7, 2016
Math 140: Foundations of Real Analysis Todd Kemp Contents Part 1. Math 140A 5 Chapter 1. Ordered Sets, Ordered Fields, and Completeness 7 1. Lecture 1: January 5, 2016 7 2. Lecture 2: January 7, 2016
4130 HOMEWORK 4. , a 2
 4130 HOMEWORK 4 Due Tuesday March 2 (1) Let N N denote the set of all sequences of natural numbers. That is, N N = {(a 1, a 2, a 3,...) : a i N}. Show that N N = P(N). We use the Schröder-Bernstein Theorem.
4130 HOMEWORK 4 Due Tuesday March 2 (1) Let N N denote the set of all sequences of natural numbers. That is, N N = {(a 1, a 2, a 3,...) : a i N}. Show that N N = P(N). We use the Schröder-Bernstein Theorem.
B553 Lecture 1: Calculus Review
 B553 Lecture 1: Calculus Review Kris Hauser January 10, 2012 This course requires a familiarity with basic calculus, some multivariate calculus, linear algebra, and some basic notions of metric topology.
B553 Lecture 1: Calculus Review Kris Hauser January 10, 2012 This course requires a familiarity with basic calculus, some multivariate calculus, linear algebra, and some basic notions of metric topology.
5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions
 5.5. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 195 5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 5.5.1 Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested
5.5. DEEPER PROPERTIES OF CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS 195 5.5 Deeper Properties of Continuous Functions 5.5.1 Intermediate Value Theorem and Consequences When one studies a function, one is usually interested
Introduction to Real Analysis
 Christopher Heil Introduction to Real Analysis Chapter 0 Online Expanded Chapter on Notation and Preliminaries Last Updated: January 9, 2018 c 2018 by Christopher Heil Chapter 0 Notation and Preliminaries:
Christopher Heil Introduction to Real Analysis Chapter 0 Online Expanded Chapter on Notation and Preliminaries Last Updated: January 9, 2018 c 2018 by Christopher Heil Chapter 0 Notation and Preliminaries:
Continuity. Chapter 4
 Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
Chapter 4 Continuity Throughout this chapter D is a nonempty subset of the real numbers. We recall the definition of a function. Definition 4.1. A function from D into R, denoted f : D R, is a subset of
Introduction and Preliminaries
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Preliminaries This chapter serves two purposes. The first purpose is to prepare the readers for the more systematic development in later chapters of methods of real analysis
Chapter 1 Introduction and Preliminaries This chapter serves two purposes. The first purpose is to prepare the readers for the more systematic development in later chapters of methods of real analysis
F (x) = P [X x[. DF1 F is nondecreasing. DF2 F is right-continuous
 7: /4/ TOPIC Distribution functions their inverses This section develops properties of probability distribution functions their inverses Two main topics are the so-called probability integral transformation
7: /4/ TOPIC Distribution functions their inverses This section develops properties of probability distribution functions their inverses Two main topics are the so-called probability integral transformation
Lecture 4: Constructing the Integers, Rationals and Reals
 Math/CS 20: Intro. to Math Professor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 4: Constructing the Integers, Rationals and Reals Week 5 UCSB 204 The Integers Normally, using the natural numbers, you can easily define
Math/CS 20: Intro. to Math Professor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 4: Constructing the Integers, Rationals and Reals Week 5 UCSB 204 The Integers Normally, using the natural numbers, you can easily define
Lecture 2: A crash course in Real Analysis
 EE5110: Probability Foundations for Electrical Engineers July-November 2015 Lecture 2: A crash course in Real Analysis Lecturer: Dr. Krishna Jagannathan Scribe: Sudharsan Parthasarathy This lecture is
EE5110: Probability Foundations for Electrical Engineers July-November 2015 Lecture 2: A crash course in Real Analysis Lecturer: Dr. Krishna Jagannathan Scribe: Sudharsan Parthasarathy This lecture is
3.4 Introduction to power series
 3.4 Introduction to power series Definition 3.4.. A polynomial in the variable x is an expression of the form n a i x i = a 0 + a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n + a n x n i=0 or a n x n + a n x n + + a 2 x 2
3.4 Introduction to power series Definition 3.4.. A polynomial in the variable x is an expression of the form n a i x i = a 0 + a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n + a n x n i=0 or a n x n + a n x n + + a 2 x 2
Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement. sentential connectives. negation. conjunction. disjunction
 Copyright & License Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement sentential connectives negation conjunction disjunction implication or conditional antecedant & consequent hypothesis
Copyright & License Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. statement sentential connectives negation conjunction disjunction implication or conditional antecedant & consequent hypothesis
THE RADIUS OF CONVERGENCE FORMULA. a n (z c) n, f(z) =
 THE RADIUS OF CONVERGENCE FORMULA Every complex power series, f(z) = (z c) n, n=0 has a radius of convergence, nonnegative-real or infinite, R = R(f) [0, + ], that describes the convergence of the series,
THE RADIUS OF CONVERGENCE FORMULA Every complex power series, f(z) = (z c) n, n=0 has a radius of convergence, nonnegative-real or infinite, R = R(f) [0, + ], that describes the convergence of the series,
Examples of Dual Spaces from Measure Theory
 Chapter 9 Examples of Dual Spaces from Measure Theory We have seen that L (, A, µ) is a Banach space for any measure space (, A, µ). We will extend that concept in the following section to identify an
Chapter 9 Examples of Dual Spaces from Measure Theory We have seen that L (, A, µ) is a Banach space for any measure space (, A, µ). We will extend that concept in the following section to identify an
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
Lecture 3 - Tuesday July 5th
 Lecture 3 - Tuesday July 5th jacques@ucsd.edu Key words: Identities, geometric series, arithmetic series, difference of powers, binomial series Key concepts: Induction, proofs of identities 3. Identities
Lecture 3 - Tuesday July 5th jacques@ucsd.edu Key words: Identities, geometric series, arithmetic series, difference of powers, binomial series Key concepts: Induction, proofs of identities 3. Identities
Math 118B Solutions. Charles Martin. March 6, d i (x i, y i ) + d i (y i, z i ) = d(x, y) + d(y, z). i=1
 Math 8B Solutions Charles Martin March 6, Homework Problems. Let (X i, d i ), i n, be finitely many metric spaces. Construct a metric on the product space X = X X n. Proof. Denote points in X as x = (x,
Math 8B Solutions Charles Martin March 6, Homework Problems. Let (X i, d i ), i n, be finitely many metric spaces. Construct a metric on the product space X = X X n. Proof. Denote points in X as x = (x,
