arxiv: v1 [cs.ce] 3 Apr 2016
|
|
|
- Veronica Farmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
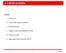
1 Two Dimensional Angle of Arrival Estimation arxiv: v1 [csce] 3 Apr Introduction Santhosh Kumar, Pradip Sircar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Kanpur , Uttar Pradesh, India We present a new method for the estimation of two dimensional (2D) angles of arrival (AOAs), namely, azimuth and incidence angles of multiple narrowband signals of same frequency in the far field of antenna array In this report, we propose an algorithm which uses an L-shape array configuration [1] We extend the polynomial based approach presented in [2] to two dimensional AOA estimation We Consider an L-shaped antenna array as shown in Figure 1 in the XZ plane [1] Figure 1: The L-shaped array configuration The gain of an element at a position (x, y, z) for a signal with reference to 1
2 origin from the direction (θ, φ) is given by a(θ, φ) = e j(2π/λ)(x sin θ cos φ+y sin θ sin φ+z cos θ) (1) Suppose that there are q narrow band sources, with same wavelength λ impinging on each sensor An lth source has an incidence angle θ l and an azimuth angle φ l, l = 1, 2,, q The signal received at the ith element of the Z-subarray is given by [1] z i (t) = a z,i (θ l, φ l )s l (t) + n z,i (t) (2) a z,i (θ l, φ l ) = e jβd cos θ l = e j2π(i 1)(d/λ) cos θ l = e j(i 1)ψ l ψ l = 2π(d/λ) cos θ l (3) s l (t) is the complex envelope of the lth signal arriving from the direction (θ l, φ l ) and n z,i (t) is the zero-mean additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) whose properties are mentioned in Section 22 The signal received at the ith element of the X-subarray is given by x i (t) = a x,i (θ l, φ l )s l (t) + n x,i (t) (4) a x,i (θ l, φ l ) = e j2π(i 1)(d/λ) sin θ l cos φ l = e j(i 1)ξ l, ξ l = 2π(d/λ) sin θ l cos φ l (5) and n x,i (t) is the zero-mean AWGN If we collect outputs of all the sensors on the Z-subarray into an m 1 vector, we have z(t) = a z (θ l, φ l )s l (t) + n z (t) (6) z(t) = [z 1 (t) z 2 (t) z m (t)] T a z (θ l, φ l ) is the m 1 steering vector of the Z-subarray towards the direction (θ l, φ l ) given by a z (θ l, φ l ) = [a z,1 (θ l, φ l a z,2 (θ l, φ l ) a z,m (θ l, φ l )] T 2
3 and We can rewrite (6) as n z (t) = [ n z,1 (t) n z,2 (t) n z,m (t) ] T a z,1(θ 1, φ 1) a z,1(θ 2, φ 2) a z,1(θ q, φ q) a z,2(θ 1, φ 1) a z,2(θ 2, φ 2) a z,2(θ q, φ q) z(t) = a z,m(θ 1, φ 1) a z,m(θ 2, φ 2) a z,m(θ q, φ q) Similarly for the X-subarray, we have s 1(t) s 2(t) s q(t) + n z,1(t) n z,2(t) n z,m(t) (7) x(t) = a x (θ l, φ l )s l (t) + n x (t) (8) x(t) = [x 1 (t) x 2 (t) x m (t)] T and a x (θ l, φ l ) = [a x,1 (θ l, φ l a x,2 (θ l, φ l ) a x,m (θ l, φ l )] T n x (t) = [n x,1 (t) n x,2 (t) n x,m (t)] T Note that (8) can be rewritten as a x,1(θ 1, φ 1) a x,1(θ 2, φ 2) a x,1(θ q, φ q) a x,2(θ 1, φ 1) a x,2(θ 2, φ 2) a x,2(θ q, φ q) x(t) = a x,m(θ 1, φ 1) a x,m(θ 2, φ 2) a x,m(θ q, φ q) s 1(t) s 2(t) s q(t) + n x,1(t) n x,2(t) n x,m(t) (9) 2 Proposed Method Consider the Z-subarray: On substituting the values of a z,i (θ l, φ l ) in (7) for i = 1, 2,, m and l = 1, 2,, q, we have z(t) = e jψ1 e jψ2 e jψq e j(m 1)ψ1 e j(m 1)ψ2 e j(m 1)ψq {ψ l } are defined in (3) s 1 (t) s 2 (t) s q (t) + n z,1 (t) n z,2 (t) n z,m (t) (10) 3
4 By collecting M equispaced snapshots from each sensor, a data matrix Z is formed as follows s 1 (t 1 ) s 1 (t 2 ) s 1 (t M ) e jψ1 e jψ2 e jψq s 2 (t 1 ) s 2 (t 2 ) s 2 (t M ) Z = e j(m 1)ψ1 e j(m 1)ψ2 e j(m 1)ψq s q (t 1 ) s q (t 2 ) s q (t M ) or Z = + n z,1 (t 1 ) n z,1 (t 2 ) n z,1 (t M ) n z,2 (t 1 ) n z,2 (t 2 ) n z,2 (t M ) n z,m (t 1 ) n z,m (t 2 ) n z,m (t M ) (11) Z = A z S + N z (12) z 1 (t 1 ) z 1 (t 2 ) z 1 (t M ) z 2 (t 1 ) z 2 (t 2 ) z 2 (t M ) z m (t 1 ) z m (t 2 ) z m (t M ) The matrices A z and S are unknown, and are not rank-deficient by assumption Now, let y 1 = e jψ1, y 2 = e jψ2,, y q = e jψq and assume that y 1, y 2,, y q are the roots of a polynomial equation P(y) = 1 + c 1 y + c 2 y c m 1 y m 1 = 0 (13) Now our aim is to calculate the coefficients which satisfy this assumption and then to solve for the roots 21 Method without Noise From (13) and (11), it can easily be shown that the following equations hold for no noise case z 1 (t 1 ) + c 1 z 2 (t 1 ) + c 2 z 3 (t 1 ) + + c m 1 z m (t 1 ) = 0 z 1 (t 2 ) + c 1 z 2 (t 2 ) + c 2 z 3 (t 2 ) + + c m 1 z m (t 2 ) = 0 z 1 (t M ) + c 1 z 2 (t M ) + c 2 z 3 (t M ) + + c m 1 z m (t M ) = 0 4
5 After simple manipulations, c 1 z 2 (t 1 ) + c 2 z 3 (t 1 ) + + c m 1 z m (t 1 ) = z 1 (t 1 ) c 1 z 2 (t 2 ) + c 2 z 3 (t 2 ) + + c m 1 z m (t 2 ) = z 1 (t 2 ) c 1 z 2 (t M ) + c 2 z 3 (t M ) + + c m 1 z m (t M ) = z 1 (t M ) The above set of equations can be written in matrix form as z 2 (t 1 ) z 3 (t 1 ) z m (t 1 ) c 1 z 2 (t 2 ) z 3 (t 2 ) z m (t 2 ) or z 2 (t M ) z 3 (t M ) z m (t M ) c 2 c m 1 = z 1 (t 1 ) z 1 (t 2 ) z 1 (t M ) (14) P C = P 1 (15) This is an overdetermined system of equations The best solution in the least square sense for the coefficient vector C is given by P # is the Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse of P, C = P # P 1 (16) P # = (P H P ) 1 P H Substitute c 1, c 2,, c m 1 obtained in (16) into (13) and solve for the roots of P(y) There are (m 1) roots, and among those only q solutions are of our interest From the (m 1) roots choose q roots say {γ l }, whose magnitudes are nearer to unity: Then, the estimate of ψ l is γ l = e j2π(d/λ) cos θ l l = 1, 2,, q (17) ˆψ l = angle{γ l } (18) Follow the similar approach for the X-subarray to calculate {β l } defined by β l = e j2π(d/λ) sin θ l cos φ l l = 1, 2,, q (19) and hence ˆξ l = angle{β l } (20) Now the estimates of θ l and φ l are given by ( ) ˆψ ˆθ l = sin 1 l 2π(d/λ) ( ) ˆξ ˆφ l = cos 1 l (2π(d/λ) sin ˆθ l ) l = 1, 2,, q (21) l = 1, 2,, q (22) 5
6 22 Method with Noise Note that in (6) and (8), the vectors n z (t) and n x (t) are random noise components on Z and X subarrays respectively The noise is assumed to be additive, temporally white Gaussian with zero mean This assumption is a valid assumption in real-world applications Mathematically, we can express the above stated properties of the noise as follows, E[n z (t)] = E[n x (t)] = 0 (23) and E[n z (t)n H z (t)] = E[n x (t)n H x (t)] = σ 2 I (24) E[n z (t)n T z (t)] = E[n x (t)n T x (t)] = 0 (25) E[n z (t i )n H z (t j )] = E[n z (t i )n T z (t j )] = 0 for i j (26) E[n x (t i )n H x (t j )] = E[n x (t i )n T x (t j )] = 0 for i j (27) E denotes the expectation operation, H denotes the Hermitian operation, T denotes the transposition, and t i and t j are the ith and jth time instants respectively The noise has an negative impact on the accuracy of estimates of the polynomial coefficients In order to reduce the effect of the noise, we follow the same procedure except for the calculation of inverse of the matrix P in (15) we use the singular value decomposition(svd) as discussed below Let the SVD of P be P = UΣV H (28) U and V are the unitary matrices containing the singular vectors of P and Σ is a diagonal matrix of same dimensions as P, and it is given by Σ = U H P V (29) The diagonal elements in Σ are non-negative and are sorted in decreasing order, ie, Σ = diag{τ 1, τ 2,, τ q,, τ m 1 } (30) τ 1 τ 2 τ q τ m 1 are the singular values of P To reduce the effect of noise, replace the last m q 1 singular values with zero in calculating the inverse of P, ie, Σ 1 = diag{τ 1, τ 2,, τ q, 0, } (31) and Σ 1 1 = diag{1/τ 1, 1/τ 2,, 1/τ q, 0, } (32) 6
7 The dimensions of Σ 1 1 are same as that of P H The lease squares approximation of P 1 is given by [3] hence, the estimate of coefficient vector in (15) is P 1 = V Σ 1 1 U H (33) C = V Σ 1 1 U H P 1 (34) Follow the same approach for X-subarray to obtain the coefficient vector and the roots The computation of AOAs from the roots is same as that for the noiseless case References [1] N Tayem and H M Kwon, L-shape 2-dimensional arrival angle estimation with propagator method, IEEE Trans Antennas and Propagation, vol 53, no 5, pp , May 2005 [2] P Singh and P Sircar, Time delays and angles of arrival estimation using known signals, Signal, Image and Video Processing, vol 6, no 2, pp , Feb 2011 [3] P Dewilde and E F Deprettere, Singular value decomposition: An introduction, In E F Deprettere (ed), SVD and Signal Processing: Algorithms, Applications, and Architectures, pp 3 41 Elsevier Science, North Holland,
DOA Estimation of Uncorrelated and Coherent Signals in Multipath Environment Using ULA Antennas
 DOA Estimation of Uncorrelated and Coherent Signals in Multipath Environment Using ULA Antennas U.Somalatha 1 T.V.S.Gowtham Prasad 2 T. Ravi Kumar Naidu PG Student, Dept. of ECE, SVEC, Tirupati, Andhra
DOA Estimation of Uncorrelated and Coherent Signals in Multipath Environment Using ULA Antennas U.Somalatha 1 T.V.S.Gowtham Prasad 2 T. Ravi Kumar Naidu PG Student, Dept. of ECE, SVEC, Tirupati, Andhra
Real-Valued Khatri-Rao Subspace Approaches on the ULA and a New Nested Array
 Real-Valued Khatri-Rao Subspace Approaches on the ULA and a New Nested Array Huiping Duan, Tiantian Tuo, Jun Fang and Bing Zeng arxiv:1511.06828v1 [cs.it] 21 Nov 2015 Abstract In underdetermined direction-of-arrival
Real-Valued Khatri-Rao Subspace Approaches on the ULA and a New Nested Array Huiping Duan, Tiantian Tuo, Jun Fang and Bing Zeng arxiv:1511.06828v1 [cs.it] 21 Nov 2015 Abstract In underdetermined direction-of-arrival
A New High-Resolution and Stable MV-SVD Algorithm for Coherent Signals Detection
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 35, 163 171, 2014 A New High-Resolution and Stable MV-SVD Algorithm for Coherent Signals Detection Basma Eldosouky, Amr H. Hussein *, and Salah Khamis Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 35, 163 171, 2014 A New High-Resolution and Stable MV-SVD Algorithm for Coherent Signals Detection Basma Eldosouky, Amr H. Hussein *, and Salah Khamis Abstract
Decoupled Nominal 2-D Direction-of -Arrival Estimation Algorithm for Coherently Distributed Source
 Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 8, No. 2, 577-583 2014 577 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/080215 Decoupled Nominal 2-D Direction-of -Arrival Estimation
Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 8, No. 2, 577-583 2014 577 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/080215 Decoupled Nominal 2-D Direction-of -Arrival Estimation
ADAPTIVE ANTENNAS. SPATIAL BF
 ADAPTIVE ANTENNAS SPATIAL BF 1 1-Spatial reference BF -Spatial reference beamforming may not use of embedded training sequences. Instead, the directions of arrival (DoA) of the impinging waves are used
ADAPTIVE ANTENNAS SPATIAL BF 1 1-Spatial reference BF -Spatial reference beamforming may not use of embedded training sequences. Instead, the directions of arrival (DoA) of the impinging waves are used
Z subarray. (d,0) (Nd-d,0) (Nd,0) X subarray Y subarray
 A Fast Algorithm for 2-D Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Yuntao Wu 1,Guisheng Liao 1 and H. C. So 2 1 Laboratory for Radar Signal Processing, Xidian University, Xian, China 2 Department of Computer Engineering
A Fast Algorithm for 2-D Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Yuntao Wu 1,Guisheng Liao 1 and H. C. So 2 1 Laboratory for Radar Signal Processing, Xidian University, Xian, China 2 Department of Computer Engineering
Generalization Propagator Method for DOA Estimation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 37, 119 125, 2014 Generalization Propagator Method for DOA Estimation Sheng Liu, Li Sheng Yang, Jian ua uang, and Qing Ping Jiang * Abstract A generalization
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 37, 119 125, 2014 Generalization Propagator Method for DOA Estimation Sheng Liu, Li Sheng Yang, Jian ua uang, and Qing Ping Jiang * Abstract A generalization
Azimuth-elevation direction finding, using one fourcomponent acoustic vector-sensor spread spatially along a straight line
 Volume 23 http://acousticalsociety.org/ 169th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 18-22 May 2015 Signal Processing in Acoustics: Paper 4aSP4 Azimuth-elevation direction
Volume 23 http://acousticalsociety.org/ 169th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 18-22 May 2015 Signal Processing in Acoustics: Paper 4aSP4 Azimuth-elevation direction
FAST AND ACCURATE DIRECTION-OF-ARRIVAL ESTIMATION FOR A SINGLE SOURCE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 6, 13 20, 2009 FAST AND ACCURATE DIRECTION-OF-ARRIVAL ESTIMATION FOR A SINGLE SOURCE Y. Wu School of Computer Science and Engineering Wuhan Institute of Technology
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 6, 13 20, 2009 FAST AND ACCURATE DIRECTION-OF-ARRIVAL ESTIMATION FOR A SINGLE SOURCE Y. Wu School of Computer Science and Engineering Wuhan Institute of Technology
This is a repository copy of Direction finding and mutual coupling estimation for uniform rectangular arrays.
 This is a repository copy of Direction finding and mutual coupling estimation for uniform rectangular arrays. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/90492/ Version:
This is a repository copy of Direction finding and mutual coupling estimation for uniform rectangular arrays. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/90492/ Version:
Generalized Pencil Of Function Method
 Generalized Pencil Of Function Method In recent times, the methodology of approximating a function by a sum of complex exponentials has found applications in many areas of electromagnetics For example
Generalized Pencil Of Function Method In recent times, the methodology of approximating a function by a sum of complex exponentials has found applications in many areas of electromagnetics For example
JOINT AZIMUTH-ELEVATION/(-RANGE) ESTIMATION OF MIXED NEAR-FIELD AND FAR-FIELD SOURCES USING TWO-STAGE SEPARATED STEERING VECTOR- BASED ALGORITHM
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 113, 17 46, 2011 JOINT AZIMUTH-ELEVATION/(-RANGE) ESTIMATION OF MIXED NEAR-FIELD AND FAR-FIELD SOURCES USING TWO-STAGE SEPARATED STEERING VECTOR- BASED ALGORITHM
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 113, 17 46, 2011 JOINT AZIMUTH-ELEVATION/(-RANGE) ESTIMATION OF MIXED NEAR-FIELD AND FAR-FIELD SOURCES USING TWO-STAGE SEPARATED STEERING VECTOR- BASED ALGORITHM
Array Signal Processing
 I U G C A P G Array Signal Processing December 21 Supervisor: Zohair M. Abu-Shaban Chapter 2 Array Signal Processing In this chapter, the theoretical background will be thoroughly covered starting with
I U G C A P G Array Signal Processing December 21 Supervisor: Zohair M. Abu-Shaban Chapter 2 Array Signal Processing In this chapter, the theoretical background will be thoroughly covered starting with
A Root-MUSIC-Like Direction Finding Method for Cyclostationary Signals
 EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing 25:1, 69 73 c 25 Hindawi Publishing Corporation A Root-MUSIC-Like Direction Finding Method for Cyclostationary Signals Pascal Chargé LESIA, DGEI, INSA Toulouse,
EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing 25:1, 69 73 c 25 Hindawi Publishing Corporation A Root-MUSIC-Like Direction Finding Method for Cyclostationary Signals Pascal Chargé LESIA, DGEI, INSA Toulouse,
Enhancing Polynomial MUSIC Algorithm for Coherent Broadband Sources Through Spatial Smoothing
 Enhancing Polynomial MUSIC Algorithm for Coherent Broadband Sources Through Spatial Smoothing William Coventry, Carmine Clemente and John Soraghan University of Strathclyde, CESIP, EEE, 204, George Street,
Enhancing Polynomial MUSIC Algorithm for Coherent Broadband Sources Through Spatial Smoothing William Coventry, Carmine Clemente and John Soraghan University of Strathclyde, CESIP, EEE, 204, George Street,
PASSIVE NEAR-FIELD SOURCE LOCALIZATION BASED ON SPATIAL-TEMPORAL STRUCTURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 27 41, 29 PASSIVE NEAR-FIELD SOURCE LOCALIZATION BASED ON SPATIAL-TEMPORAL STRUCTURE Y. Wu Wuhan Institute of Technology Wuhan 4373, China H. C. So Department
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 27 41, 29 PASSIVE NEAR-FIELD SOURCE LOCALIZATION BASED ON SPATIAL-TEMPORAL STRUCTURE Y. Wu Wuhan Institute of Technology Wuhan 4373, China H. C. So Department
Generalized Sidelobe Canceller and MVDR Power Spectrum Estimation. Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego
 Generalized Sidelobe Canceller and MVDR Power Spectrum Estimation Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsd.edu Reference Books 1. Optimum Array Processing, H. L. Van Trees 2.
Generalized Sidelobe Canceller and MVDR Power Spectrum Estimation Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsd.edu Reference Books 1. Optimum Array Processing, H. L. Van Trees 2.
POLYNOMIAL-PHASE SIGNAL DIRECTION-FINDING AND SOURCE-TRACKING WITH A SINGLE ACOUSTIC VECTOR SENSOR. Xin Yuan and Jiaji Huang
 POLYNOMIAL-PHASE SIGNAL DIRECTION-FINDING AND SOURCE-TRACKING WITH A SINGLE ACOUSTIC VECTOR SENSOR Xin Yuan and Jiaji Huang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC,
POLYNOMIAL-PHASE SIGNAL DIRECTION-FINDING AND SOURCE-TRACKING WITH A SINGLE ACOUSTIC VECTOR SENSOR Xin Yuan and Jiaji Huang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC,
New Approaches for Two-Dimensional DOA Estimation of Coherent and Noncircular Signals with Acoustic Vector-sensor Array
 New Approaches for Two-Dimensional DOA stimation of Coherent and Noncircular Signals with Acoustic Vector-sensor Array Han Chen A Thesis in The Department of lectrical and Computer ngineering Presented
New Approaches for Two-Dimensional DOA stimation of Coherent and Noncircular Signals with Acoustic Vector-sensor Array Han Chen A Thesis in The Department of lectrical and Computer ngineering Presented
Direction of Arrival Estimation: Subspace Methods. Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego
 Direction of Arrival Estimation: Subspace Methods Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsdedu Reference Books and Papers 1 Optimum Array Processing, H L Van Trees 2 Stoica, P,
Direction of Arrival Estimation: Subspace Methods Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsdedu Reference Books and Papers 1 Optimum Array Processing, H L Van Trees 2 Stoica, P,
Spatial Smoothing and Broadband Beamforming. Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego
 Spatial Smoothing and Broadband Beamforming Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsd.edu Reference Books and Papers 1. Optimum Array Processing, H. L. Van Trees 2. Stoica, P.,
Spatial Smoothing and Broadband Beamforming Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsd.edu Reference Books and Papers 1. Optimum Array Processing, H. L. Van Trees 2. Stoica, P.,
THE estimation of covariance matrices is a crucial component
 1 A Subspace Method for Array Covariance Matrix Estimation Mostafa Rahmani and George K. Atia, Member, IEEE, arxiv:1411.0622v1 [cs.na] 20 Oct 2014 Abstract This paper introduces a subspace method for the
1 A Subspace Method for Array Covariance Matrix Estimation Mostafa Rahmani and George K. Atia, Member, IEEE, arxiv:1411.0622v1 [cs.na] 20 Oct 2014 Abstract This paper introduces a subspace method for the
Multi-Source DOA Estimation Using an Acoustic Vector Sensor Array Under a Spatial Sparse Representation Framework
 DOI 10.1007/s00034-015-0102-9 Multi-Source DOA Estimation Using an Acoustic Vector Sensor Array Under a Spatial Sparse Representation Framework Yue-Xian Zou 1 Bo Li 1 Christian H Ritz 2 Received: 22 May
DOI 10.1007/s00034-015-0102-9 Multi-Source DOA Estimation Using an Acoustic Vector Sensor Array Under a Spatial Sparse Representation Framework Yue-Xian Zou 1 Bo Li 1 Christian H Ritz 2 Received: 22 May
linearly indepedent eigenvectors as the multiplicity of the root, but in general there may be no more than one. For further discussion, assume matrice
 3. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, Spectral Representation 3.. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors A vector ' is eigenvector of a matrix K, if K' is parallel to ' and ' 6, i.e., K' k' k is the eigenvalue. If is
3. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, Spectral Representation 3.. Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors A vector ' is eigenvector of a matrix K, if K' is parallel to ' and ' 6, i.e., K' k' k is the eigenvalue. If is
DOA Estimation of Quasi-Stationary Signals Using a Partly-Calibrated Uniform Linear Array with Fewer Sensors than Sources
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 63, 185 193, 218 DOA Estimation of Quasi-Stationary Signals Using a Partly-Calibrated Uniform Linear Array with Fewer Sensors than Sources Kai-Chieh Hsu and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 63, 185 193, 218 DOA Estimation of Quasi-Stationary Signals Using a Partly-Calibrated Uniform Linear Array with Fewer Sensors than Sources Kai-Chieh Hsu and
ROBUST ADAPTIVE BEAMFORMING BASED ON CO- VARIANCE MATRIX RECONSTRUCTION FOR LOOK DIRECTION MISMATCH
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 25, 37 46, 2011 ROBUST ADAPTIVE BEAMFORMING BASED ON CO- VARIANCE MATRIX RECONSTRUCTION FOR LOOK DIRECTION MISMATCH R. Mallipeddi 1, J. P. Lie 2, S.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 25, 37 46, 2011 ROBUST ADAPTIVE BEAMFORMING BASED ON CO- VARIANCE MATRIX RECONSTRUCTION FOR LOOK DIRECTION MISMATCH R. Mallipeddi 1, J. P. Lie 2, S.
Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Using Distributed Body Area Networks: Error & Refraction Analysis
 Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Using Distributed Body Area Networks: Error & Refraction Analysis Kaveh Ghaboosi, Pranay Pratap Swar, and Kaveh Pahlavan Center for Wireless Information Network Studies
Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Using Distributed Body Area Networks: Error & Refraction Analysis Kaveh Ghaboosi, Pranay Pratap Swar, and Kaveh Pahlavan Center for Wireless Information Network Studies
arxiv:gr-qc/ v1 16 Feb 2007
 International Journal of Modern Physics D c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:gr-qc/0702096v1 16 Feb 2007 Data Analysis of Gravitational Waves Using A Network of Detectors Linqing Wen Max Planck
International Journal of Modern Physics D c World Scientific Publishing Company arxiv:gr-qc/0702096v1 16 Feb 2007 Data Analysis of Gravitational Waves Using A Network of Detectors Linqing Wen Max Planck
Performance Analysis of Coarray-Based MUSIC and the Cramér-Rao Bound
 Performance Analysis of Coarray-Based MUSIC and the Cramér-Rao Bound Mianzhi Wang, Zhen Zhang, and Arye Nehorai Preston M. Green Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering Washington University in
Performance Analysis of Coarray-Based MUSIC and the Cramér-Rao Bound Mianzhi Wang, Zhen Zhang, and Arye Nehorai Preston M. Green Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering Washington University in
ASYMPTOTIC PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOA ESTIMATION METHOD FOR AN INCOHERENTLY DISTRIBUTED SOURCE. 2πd λ. E[ϱ(θ, t)ϱ (θ,τ)] = γ(θ; µ)δ(θ θ )δ t,τ, (2)
![ASYMPTOTIC PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOA ESTIMATION METHOD FOR AN INCOHERENTLY DISTRIBUTED SOURCE. 2πd λ. E[ϱ(θ, t)ϱ (θ,τ)] = γ(θ; µ)δ(θ θ )δ t,τ, (2) ASYMPTOTIC PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOA ESTIMATION METHOD FOR AN INCOHERENTLY DISTRIBUTED SOURCE. 2πd λ. E[ϱ(θ, t)ϱ (θ,τ)] = γ(θ; µ)δ(θ θ )δ t,τ, (2)](/thumbs/92/109921582.jpg) ASYMPTOTIC PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOA ESTIMATION METHOD FOR AN INCOHERENTLY DISTRIBUTED SOURCE Jooshik Lee and Doo Whan Sang LG Electronics, Inc. Seoul, Korea Jingon Joung School of EECS, KAIST Daejeon,
ASYMPTOTIC PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DOA ESTIMATION METHOD FOR AN INCOHERENTLY DISTRIBUTED SOURCE Jooshik Lee and Doo Whan Sang LG Electronics, Inc. Seoul, Korea Jingon Joung School of EECS, KAIST Daejeon,
A Gain-Phase Error Calibration Method for the Vibration of Wing Conformal Array
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol 75, 111 119, 2017 A Gain-Phase Error Calibration Method for the Vibration of Wing Conformal Array Wen Hao Du, Wen Tao Li *, and Xiao Wei Shi Abstract Due to
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol 75, 111 119, 2017 A Gain-Phase Error Calibration Method for the Vibration of Wing Conformal Array Wen Hao Du, Wen Tao Li *, and Xiao Wei Shi Abstract Due to
UNIT 6: The singular value decomposition.
 UNIT 6: The singular value decomposition. María Barbero Liñán Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Bachelor in Statistics and Business Mathematical methods II 2011-2012 A square matrix is symmetric if A T
UNIT 6: The singular value decomposition. María Barbero Liñán Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Bachelor in Statistics and Business Mathematical methods II 2011-2012 A square matrix is symmetric if A T
σ 11 σ 22 σ pp 0 with p = min(n, m) The σ ii s are the singular values. Notation change σ ii A 1 σ 2
 HE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSIION he SVD existence - properties. Pseudo-inverses and the SVD Use of SVD for least-squares problems Applications of the SVD he Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) heorem For
HE SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSIION he SVD existence - properties. Pseudo-inverses and the SVD Use of SVD for least-squares problems Applications of the SVD he Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) heorem For
One-Dimensional Uniform Array. Linear Array Principle of Operation
 One-Dimensional Uniform Array Array Output Linear Array Principle of Operation d sin d d sin c Array Output Setting the delays to [(N 1) m]d sin θ τ m =, m =0,...,N 1 c causes the received signals to add
One-Dimensional Uniform Array Array Output Linear Array Principle of Operation d sin d d sin c Array Output Setting the delays to [(N 1) m]d sin θ τ m =, m =0,...,N 1 c causes the received signals to add
SELECTIVE ANGLE MEASUREMENTS FOR A 3D-AOA INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLE TMA ALGORITHM
 SELECTIVE ANGLE MEASUREMENTS FOR A 3D-AOA INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLE TMA ALGORITHM Kutluyıl Doğançay Reza Arablouei School of Engineering, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes, SA 595, Australia ABSTRACT
SELECTIVE ANGLE MEASUREMENTS FOR A 3D-AOA INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLE TMA ALGORITHM Kutluyıl Doğançay Reza Arablouei School of Engineering, University of South Australia, Mawson Lakes, SA 595, Australia ABSTRACT
Using an Oblique Projection Operator for Highly Correlated Signal Direction-of-Arrival Estimations
 Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 9, No. 5, 2663-2671 (2015) 2663 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/090552 Using an Oblique Projection Operator for
Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 9, No. 5, 2663-2671 (2015) 2663 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/090552 Using an Oblique Projection Operator for
DOA Estimation using MUSIC and Root MUSIC Methods
 DOA Estimation using MUSIC and Root MUSIC Methods EE602 Statistical signal Processing 4/13/2009 Presented By: Chhavipreet Singh(Y515) Siddharth Sahoo(Y5827447) 2 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2
DOA Estimation using MUSIC and Root MUSIC Methods EE602 Statistical signal Processing 4/13/2009 Presented By: Chhavipreet Singh(Y515) Siddharth Sahoo(Y5827447) 2 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2
LOW COMPLEXITY COVARIANCE-BASED DOA ESTIMATION ALGORITHM
 LOW COMPLEXITY COVARIANCE-BASED DOA ESTIMATION ALGORITHM Tadeu N. Ferreira, Sergio L. Netto, and Paulo S. R. Diniz Electrical Engineering Program COPPE/DEL-Poli/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro P.O.
LOW COMPLEXITY COVARIANCE-BASED DOA ESTIMATION ALGORITHM Tadeu N. Ferreira, Sergio L. Netto, and Paulo S. R. Diniz Electrical Engineering Program COPPE/DEL-Poli/Federal University of Rio de Janeiro P.O.
DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTIMATION BASED ON FOURTH-ORDER CUMULANT USING PROPAGATOR METHOD
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 18, 83 99, 2009 DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTIMATION BASED ON FOURTH-ORDER CUMULANT USING PROPAGATOR METHOD P. Palanisamy and N. Rao Department of Electronics and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 18, 83 99, 2009 DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTIMATION BASED ON FOURTH-ORDER CUMULANT USING PROPAGATOR METHOD P. Palanisamy and N. Rao Department of Electronics and
6 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring
 6 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring We will discuss the restoration of one-dimensional signals and two-dimensional gray-scale images that have been contaminated by blur and noise. After an
6 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring We will discuss the restoration of one-dimensional signals and two-dimensional gray-scale images that have been contaminated by blur and noise. After an
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra)
 AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 7: More on Householder Reflectors; Least Squares Problems Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 15 Outline
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 7: More on Householder Reflectors; Least Squares Problems Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 15 Outline
Joint Frequency and 2-D DOA Recovery with sub-nyquist Difference Space-Time Array
 Joint Frequency and 2-D DOA ecovery with sub-nyquist Difference Space-Time Array A Anil Kumar, M Girish Chandra and P Balamuralidhar TCS esearch and Innovation, Bangalore, India. Email:{achannaanil.kumar,
Joint Frequency and 2-D DOA ecovery with sub-nyquist Difference Space-Time Array A Anil Kumar, M Girish Chandra and P Balamuralidhar TCS esearch and Innovation, Bangalore, India. Email:{achannaanil.kumar,
Proposition 42. Let M be an m n matrix. Then (32) N (M M)=N (M) (33) R(MM )=R(M)
 RODICA D. COSTIN. Singular Value Decomposition.1. Rectangular matrices. For rectangular matrices M the notions of eigenvalue/vector cannot be defined. However, the products MM and/or M M (which are square,
RODICA D. COSTIN. Singular Value Decomposition.1. Rectangular matrices. For rectangular matrices M the notions of eigenvalue/vector cannot be defined. However, the products MM and/or M M (which are square,
On the Deterministic CRB for DOA Estimation in. Unknown Noise fields Using Sparse Sensor Arrays
 On the Deterministic CRB for DOA Estimation in Unknown Noise fields Using Sparse Sensor Arrays Martin Kleinsteuber and Abd-Krim Seghouane National ICT Australia Limited, Canberra Research Laboratory, Locked
On the Deterministic CRB for DOA Estimation in Unknown Noise fields Using Sparse Sensor Arrays Martin Kleinsteuber and Abd-Krim Seghouane National ICT Australia Limited, Canberra Research Laboratory, Locked
2. Review of Linear Algebra
 2. Review of Linear Algebra ECE 83, Spring 217 In this course we will represent signals as vectors and operators (e.g., filters, transforms, etc) as matrices. This lecture reviews basic concepts from linear
2. Review of Linear Algebra ECE 83, Spring 217 In this course we will represent signals as vectors and operators (e.g., filters, transforms, etc) as matrices. This lecture reviews basic concepts from linear
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering
 Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13 15, Tuesday 8 th and Friday 11 th November 016 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13 15, Tuesday 8 th and Friday 11 th November 016 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE
Polynomial Root-MUSIC Algorithm for Efficient Broadband Direction Of Arrival Estimation
 Polynomial Root-MUSIC Algorithm for Efficient Broadband Direction Of Arrival Estimation William Coventry, Carmine Clemente, and John Soraghan University of Strathclyde, CESIP, EEE, 204, George Street,
Polynomial Root-MUSIC Algorithm for Efficient Broadband Direction Of Arrival Estimation William Coventry, Carmine Clemente, and John Soraghan University of Strathclyde, CESIP, EEE, 204, George Street,
ECE 275A Homework # 3 Due Thursday 10/27/2016
 ECE 275A Homework # 3 Due Thursday 10/27/2016 Reading: In addition to the lecture material presented in class, students are to read and study the following: A. The material in Section 4.11 of Moon & Stirling
ECE 275A Homework # 3 Due Thursday 10/27/2016 Reading: In addition to the lecture material presented in class, students are to read and study the following: A. The material in Section 4.11 of Moon & Stirling
EXTENSION OF NESTED ARRAYS WITH THE FOURTH-ORDER DIFFERENCE CO-ARRAY ENHANCEMENT
 EXTENSION OF NESTED ARRAYS WITH THE FOURTH-ORDER DIFFERENCE CO-ARRAY ENHANCEMENT Qing Shen,2, Wei Liu 2, Wei Cui, Siliang Wu School of Information and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology Beijing,
EXTENSION OF NESTED ARRAYS WITH THE FOURTH-ORDER DIFFERENCE CO-ARRAY ENHANCEMENT Qing Shen,2, Wei Liu 2, Wei Cui, Siliang Wu School of Information and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology Beijing,
8 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring
 8 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring We will discuss the restoration of one-dimensional signals and two-dimensional gray-scale images that have been contaminated by blur and noise. After an
8 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring We will discuss the restoration of one-dimensional signals and two-dimensional gray-scale images that have been contaminated by blur and noise. After an
8 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring
 8 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring We will discuss the restoration of one-dimensional signals and two-dimensional gray-scale images that have been contaminated by blur and noise. After an
8 The SVD Applied to Signal and Image Deblurring We will discuss the restoration of one-dimensional signals and two-dimensional gray-scale images that have been contaminated by blur and noise. After an
IMPROVED BLIND 2D-DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTI- MATION WITH L-SHAPED ARRAY USING SHIFT IN- VARIANCE PROPERTY
 J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 23, 593 606, 2009 IMPROVED BLIND 2D-DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTI- MATION WITH L-SHAPED ARRAY USING SHIFT IN- VARIANCE PROPERTY X. Zhang, X. Gao, and W. Chen Department
J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 23, 593 606, 2009 IMPROVED BLIND 2D-DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTI- MATION WITH L-SHAPED ARRAY USING SHIFT IN- VARIANCE PROPERTY X. Zhang, X. Gao, and W. Chen Department
Real Time Implementation for DOA Estimation Methods on NI-PXI Platform
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 59, 103 121, 2014 Real Time Implementation for DOA Estimation Methods on NI-PXI Platform Nizar Tayem * Abstract In this paper, we present five different approaches
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 59, 103 121, 2014 Real Time Implementation for DOA Estimation Methods on NI-PXI Platform Nizar Tayem * Abstract In this paper, we present five different approaches
Polynomial Matrix Formulation-Based Capon Beamformer
 Alzin, Ahmed and Coutts, Fraser K. and Corr, Jamie and Weiss, Stephan and Proudler, Ian K. and Chambers, Jonathon A. (26) Polynomial matrix formulation-based Capon beamformer. In: th IMA International
Alzin, Ahmed and Coutts, Fraser K. and Corr, Jamie and Weiss, Stephan and Proudler, Ian K. and Chambers, Jonathon A. (26) Polynomial matrix formulation-based Capon beamformer. In: th IMA International
The Singular Value Decomposition
 The Singular Value Decomposition Philippe B. Laval KSU Fall 2015 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) SVD Fall 2015 1 / 13 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
The Singular Value Decomposition Philippe B. Laval KSU Fall 2015 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) SVD Fall 2015 1 / 13 Review of Key Concepts We review some key definitions and results about matrices that will
Joint Direction-of-Arrival and Order Estimation in Compressed Sensing using Angles between Subspaces
 Aalborg Universitet Joint Direction-of-Arrival and Order Estimation in Compressed Sensing using Angles between Subspaces Christensen, Mads Græsbøll; Nielsen, Jesper Kjær Published in: I E E E / S P Workshop
Aalborg Universitet Joint Direction-of-Arrival and Order Estimation in Compressed Sensing using Angles between Subspaces Christensen, Mads Græsbøll; Nielsen, Jesper Kjær Published in: I E E E / S P Workshop
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF COARRAY-BASED MUSIC AND THE CRAMÉR-RAO BOUND. Mianzhi Wang, Zhen Zhang, and Arye Nehorai
 PERFORANCE ANALYSIS OF COARRAY-BASED USIC AND THE CRAÉR-RAO BOUND ianzhi Wang, Zhen Zhang, and Arye Nehorai Preston. Green Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Washington University in St.
PERFORANCE ANALYSIS OF COARRAY-BASED USIC AND THE CRAÉR-RAO BOUND ianzhi Wang, Zhen Zhang, and Arye Nehorai Preston. Green Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Washington University in St.
Performance Analysis for Strong Interference Remove of Fast Moving Target in Linear Array Antenna
 Performance Analysis for Strong Interference Remove of Fast Moving Target in Linear Array Antenna Kwan Hyeong Lee Dept. Electriacal Electronic & Communicaton, Daejin University, 1007 Ho Guk ro, Pochen,Gyeonggi,
Performance Analysis for Strong Interference Remove of Fast Moving Target in Linear Array Antenna Kwan Hyeong Lee Dept. Electriacal Electronic & Communicaton, Daejin University, 1007 Ho Guk ro, Pochen,Gyeonggi,
AM 205: lecture 8. Last time: Cholesky factorization, QR factorization Today: how to compute the QR factorization, the Singular Value Decomposition
 AM 205: lecture 8 Last time: Cholesky factorization, QR factorization Today: how to compute the QR factorization, the Singular Value Decomposition QR Factorization A matrix A R m n, m n, can be factorized
AM 205: lecture 8 Last time: Cholesky factorization, QR factorization Today: how to compute the QR factorization, the Singular Value Decomposition QR Factorization A matrix A R m n, m n, can be factorized
Array Signal Processing Algorithms for Beamforming and Direction Finding
 Array Signal Processing Algorithms for Beamforming and Direction Finding This thesis is submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) Lei Wang Communications Research
Array Signal Processing Algorithms for Beamforming and Direction Finding This thesis is submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) Lei Wang Communications Research
Adaptive beamforming for uniform linear arrays with unknown mutual coupling. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters.
 Title Adaptive beamforming for uniform linear arrays with unknown mutual coupling Author(s) Liao, B; Chan, SC Citation IEEE Antennas And Wireless Propagation Letters, 2012, v. 11, p. 464-467 Issued Date
Title Adaptive beamforming for uniform linear arrays with unknown mutual coupling Author(s) Liao, B; Chan, SC Citation IEEE Antennas And Wireless Propagation Letters, 2012, v. 11, p. 464-467 Issued Date
ELEC E7210: Communication Theory. Lecture 10: MIMO systems
 ELEC E7210: Communication Theory Lecture 10: MIMO systems Matrix Definitions, Operations, and Properties (1) NxM matrix a rectangular array of elements a A. an 11 1....... a a 1M. NM B D C E ermitian transpose
ELEC E7210: Communication Theory Lecture 10: MIMO systems Matrix Definitions, Operations, and Properties (1) NxM matrix a rectangular array of elements a A. an 11 1....... a a 1M. NM B D C E ermitian transpose
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 46, NO. 1, JANUARY
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL 46, NO 1, JANUARY 1998 161 Simultaneous Schur Decomposition of Several Nonsymmetric Matrices to Achieve Automatic Pairing in Multidimensional Harmonic Retrieval
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL 46, NO 1, JANUARY 1998 161 Simultaneous Schur Decomposition of Several Nonsymmetric Matrices to Achieve Automatic Pairing in Multidimensional Harmonic Retrieval
Array Antennas. Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 Array Antennas An array antenna is a group of antenna elements with excitations coordinated in some way to achieve desired properties for the combined radiation pattern. When designing an array
Chapter 6 Array Antennas An array antenna is a group of antenna elements with excitations coordinated in some way to achieve desired properties for the combined radiation pattern. When designing an array
ECE 275A Homework #3 Solutions
 ECE 75A Homework #3 Solutions. Proof of (a). Obviously Ax = 0 y, Ax = 0 for all y. To show sufficiency, note that if y, Ax = 0 for all y, then it must certainly be true for the particular value of y =
ECE 75A Homework #3 Solutions. Proof of (a). Obviously Ax = 0 y, Ax = 0 for all y. To show sufficiency, note that if y, Ax = 0 for all y, then it must certainly be true for the particular value of y =
A Novel DOA Estimation Error Reduction Preprocessing Scheme of Correlated Waves for Khatri-Rao Product Extended-Array
 IEICE TRANS. COMMUN., VOL.E96 B, NO.0 OCTOBER 203 2475 PAPER Special Section on Recent Progress in Antennas and Propagation in Conjunction with Main Topics of ISAP202 A Novel DOA Estimation Error Reduction
IEICE TRANS. COMMUN., VOL.E96 B, NO.0 OCTOBER 203 2475 PAPER Special Section on Recent Progress in Antennas and Propagation in Conjunction with Main Topics of ISAP202 A Novel DOA Estimation Error Reduction
J. Liang School of Automation & Information Engineering Xi an University of Technology, China
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 18, 245 255, 211 A NOVEL DIAGONAL LOADING METHOD FOR ROBUST ADAPTIVE BEAMFORMING W. Wang and R. Wu Tianjin Key Lab for Advanced Signal Processing Civil Aviation
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 18, 245 255, 211 A NOVEL DIAGONAL LOADING METHOD FOR ROBUST ADAPTIVE BEAMFORMING W. Wang and R. Wu Tianjin Key Lab for Advanced Signal Processing Civil Aviation
Overview of Beamforming
 Overview of Beamforming Arye Nehorai Preston M. Green Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering Washington University in St. Louis March 14, 2012 CSSIP Lab 1 Outline Introduction Spatial and temporal
Overview of Beamforming Arye Nehorai Preston M. Green Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering Washington University in St. Louis March 14, 2012 CSSIP Lab 1 Outline Introduction Spatial and temporal
Pseudoinverse & Moore-Penrose Conditions
 ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego p. 1/1 Lecture 7 ECE 275A Pseudoinverse & Moore-Penrose Conditions ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego
ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego p. 1/1 Lecture 7 ECE 275A Pseudoinverse & Moore-Penrose Conditions ECE 275AB Lecture 7 Fall 2008 V1.0 c K. Kreutz-Delgado, UC San Diego
Adaptive beamforming. Slide 2: Chapter 7: Adaptive array processing. Slide 3: Delay-and-sum. Slide 4: Delay-and-sum, continued
 INF540 202 Adaptive beamforming p Adaptive beamforming Sven Peter Näsholm Department of Informatics, University of Oslo Spring semester 202 svenpn@ifiuiono Office phone number: +47 22840068 Slide 2: Chapter
INF540 202 Adaptive beamforming p Adaptive beamforming Sven Peter Näsholm Department of Informatics, University of Oslo Spring semester 202 svenpn@ifiuiono Office phone number: +47 22840068 Slide 2: Chapter
Master Thesis Separation of Non-Stationary Sources
 Master Thesis Separation of Non-Stationary Sources Lisbeth Andersson Perth, March 21 Australian Telecommunications Research Institute Curtin University of Technology Australia i Preface This master thesis
Master Thesis Separation of Non-Stationary Sources Lisbeth Andersson Perth, March 21 Australian Telecommunications Research Institute Curtin University of Technology Australia i Preface This master thesis
Research Article Computationally Efficient DOA and Polarization Estimation of Coherent Sources with Linear Electromagnetic Vector-Sensor Array
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 2011, Article ID 490289, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2011/490289 Research Article Computationally Efficient DOA and Polarization
Hindawi Publishing Corporation EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing Volume 2011, Article ID 490289, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2011/490289 Research Article Computationally Efficient DOA and Polarization
Sparse Sensing in Colocated MIMO Radar: A Matrix Completion Approach
 Sparse Sensing in Colocated MIMO Radar: A Matrix Completion Approach Athina P. Petropulu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Acknowledgments Shunqiao
Sparse Sensing in Colocated MIMO Radar: A Matrix Completion Approach Athina P. Petropulu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey Acknowledgments Shunqiao
POLI270 - Linear Algebra
 POLI7 - Linear Algebra Septemer 8th Basics a x + a x +... + a n x n b () is the linear form where a, b are parameters and x n are variables. For a given equation such as x +x you only need a variable and
POLI7 - Linear Algebra Septemer 8th Basics a x + a x +... + a n x n b () is the linear form where a, b are parameters and x n are variables. For a given equation such as x +x you only need a variable and
2. LINEAR ALGEBRA. 1. Definitions. 2. Linear least squares problem. 3. QR factorization. 4. Singular value decomposition (SVD) 5.
 2. LINEAR ALGEBRA Outline 1. Definitions 2. Linear least squares problem 3. QR factorization 4. Singular value decomposition (SVD) 5. Pseudo-inverse 6. Eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) 1 Definitions Vector
2. LINEAR ALGEBRA Outline 1. Definitions 2. Linear least squares problem 3. QR factorization 4. Singular value decomposition (SVD) 5. Pseudo-inverse 6. Eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) 1 Definitions Vector
An Adaptive Sensor Array Using an Affine Combination of Two Filters
 An Adaptive Sensor Array Using an Affine Combination of Two Filters Tõnu Trump Tallinn University of Technology Department of Radio and Telecommunication Engineering Ehitajate tee 5, 19086 Tallinn Estonia
An Adaptive Sensor Array Using an Affine Combination of Two Filters Tõnu Trump Tallinn University of Technology Department of Radio and Telecommunication Engineering Ehitajate tee 5, 19086 Tallinn Estonia
Lecture 5: Antenna Diversity and MIMO Capacity Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1. Overview. CommTh/EES/KTH
 : Antenna Diversity and Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications Wednesday, May 4, 206 9:00-2:00, Conference Room SIP Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication
: Antenna Diversity and Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications Wednesday, May 4, 206 9:00-2:00, Conference Room SIP Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication
Tensor polyadic decomposition for antenna array processing
 Tensor polyadic decomposition for antenna array processing Souleymen Sahnoun, Pierre Comon To cite this version: Souleymen Sahnoun, Pierre Comon. Tensor polyadic decomposition for antenna array processing.
Tensor polyadic decomposition for antenna array processing Souleymen Sahnoun, Pierre Comon To cite this version: Souleymen Sahnoun, Pierre Comon. Tensor polyadic decomposition for antenna array processing.
COMPLEX CONSTRAINED CRB AND ITS APPLICATION TO SEMI-BLIND MIMO AND OFDM CHANNEL ESTIMATION. Aditya K. Jagannatham and Bhaskar D.
 COMPLEX CONSTRAINED CRB AND ITS APPLICATION TO SEMI-BLIND MIMO AND OFDM CHANNEL ESTIMATION Aditya K Jagannatham and Bhaskar D Rao University of California, SanDiego 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093-0407
COMPLEX CONSTRAINED CRB AND ITS APPLICATION TO SEMI-BLIND MIMO AND OFDM CHANNEL ESTIMATION Aditya K Jagannatham and Bhaskar D Rao University of California, SanDiego 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA 92093-0407
DOA AND POLARIZATION ACCURACY STUDY FOR AN IMPERFECT DUAL-POLARIZED ANTENNA ARRAY. Miriam Häge, Marc Oispuu
 19th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 211) Barcelona, Spain, August 29 - September 2, 211 DOA AND POLARIZATION ACCURACY STUDY FOR AN IMPERFECT DUAL-POLARIZED ANTENNA ARRAY Miriam Häge, Marc
19th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 211) Barcelona, Spain, August 29 - September 2, 211 DOA AND POLARIZATION ACCURACY STUDY FOR AN IMPERFECT DUAL-POLARIZED ANTENNA ARRAY Miriam Häge, Marc
Applications of Robust Optimization in Signal Processing: Beamforming and Power Control Fall 2012
 Applications of Robust Optimization in Signal Processing: Beamforg and Power Control Fall 2012 Instructor: Farid Alizadeh Scribe: Shunqiao Sun 12/09/2012 1 Overview In this presentation, we study the applications
Applications of Robust Optimization in Signal Processing: Beamforg and Power Control Fall 2012 Instructor: Farid Alizadeh Scribe: Shunqiao Sun 12/09/2012 1 Overview In this presentation, we study the applications
Array Processing: Underwater Acoustic Source Localization
 2 Array Processing: Underwater Acoustic Source Localization Salah Bourennane, Caroline Fossati and Julien Marot Institut Fresnel, Ecole Centrale Marseille France. Introduction Array processing is used
2 Array Processing: Underwater Acoustic Source Localization Salah Bourennane, Caroline Fossati and Julien Marot Institut Fresnel, Ecole Centrale Marseille France. Introduction Array processing is used
Full-State Feedback Design for a Multi-Input System
 Full-State Feedback Design for a Multi-Input System A. Introduction The open-loop system is described by the following state space model. x(t) = Ax(t)+Bu(t), y(t) =Cx(t)+Du(t) () 4 8.5 A =, B =.5.5, C
Full-State Feedback Design for a Multi-Input System A. Introduction The open-loop system is described by the following state space model. x(t) = Ax(t)+Bu(t), y(t) =Cx(t)+Du(t) () 4 8.5 A =, B =.5.5, C
Two-Dimensional Sparse Arrays with Hole-Free Coarray and Reduced Mutual Coupling
 Two-Dimensional Sparse Arrays with Hole-Free Coarray and Reduced Mutual Coupling Chun-Lin Liu and P. P. Vaidyanathan Dept. of Electrical Engineering, 136-93 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Two-Dimensional Sparse Arrays with Hole-Free Coarray and Reduced Mutual Coupling Chun-Lin Liu and P. P. Vaidyanathan Dept. of Electrical Engineering, 136-93 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
A ROBUST BEAMFORMER BASED ON WEIGHTED SPARSE CONSTRAINT
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 16, 53 60, 2010 A ROBUST BEAMFORMER BASED ON WEIGHTED SPARSE CONSTRAINT Y. P. Liu and Q. Wan School of Electronic Engineering University of Electronic
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 16, 53 60, 2010 A ROBUST BEAMFORMER BASED ON WEIGHTED SPARSE CONSTRAINT Y. P. Liu and Q. Wan School of Electronic Engineering University of Electronic
ML ESTIMATION AND CRB FOR NARROWBAND AR SIGNALS ON A SENSOR ARRAY
 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing ICASSP ML ESTIMATION AND CRB FOR NARROWBAND AR SIGNALS ON A SENSOR ARRAY Langford B White School of Electrical and Electronic
2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing ICASSP ML ESTIMATION AND CRB FOR NARROWBAND AR SIGNALS ON A SENSOR ARRAY Langford B White School of Electrical and Electronic
Multiple Antennas. Mats Bengtsson, Björn Ottersten. Channel characterization and modeling 1 September 8, Signal KTH Research Focus
 Multiple Antennas Channel Characterization and Modeling Mats Bengtsson, Björn Ottersten Channel characterization and modeling 1 September 8, 2005 Signal Processing @ KTH Research Focus Channel modeling
Multiple Antennas Channel Characterization and Modeling Mats Bengtsson, Björn Ottersten Channel characterization and modeling 1 September 8, 2005 Signal Processing @ KTH Research Focus Channel modeling
CLOSED-FORM 2D ANGLE ESTIMATION WITH A SPHERICAL ARRAY VIA SPHERICAL PHASE MODE EXCITATION AND ESPRIT. Roald Goossens and Hendrik Rogier
 CLOSED-FORM 2D AGLE ESTIMATIO WITH A SPHERICAL ARRAY VIA SPHERICAL PHASE MODE EXCITATIO AD ESPRIT Roald Goossens and Hendrik Rogier Ghent University Department of Information Technology St-Pietersnieuwstraat
CLOSED-FORM 2D AGLE ESTIMATIO WITH A SPHERICAL ARRAY VIA SPHERICAL PHASE MODE EXCITATIO AD ESPRIT Roald Goossens and Hendrik Rogier Ghent University Department of Information Technology St-Pietersnieuwstraat
arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 5 Mar 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 5 Mar 2013 arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 5 Mar 2013](/thumbs/92/108204613.jpg) REDUCED-RANK DOA ESTIMATION BASED ON JOINT ITERATIVE SUBSPACE OPTIMIZATION AND GRID SEARC Lei Wang and Rodrigo C. de Lamare Communications Research Group, Department of Electronics University of York,
REDUCED-RANK DOA ESTIMATION BASED ON JOINT ITERATIVE SUBSPACE OPTIMIZATION AND GRID SEARC Lei Wang and Rodrigo C. de Lamare Communications Research Group, Department of Electronics University of York,
ELG7177: MIMO Comunications. Lecture 3
 ELG7177: MIMO Comunications Lecture 3 Dr. Sergey Loyka EECS, University of Ottawa S. Loyka Lecture 3, ELG7177: MIMO Comunications 1 / 29 SIMO: Rx antenna array + beamforming single Tx antenna multiple
ELG7177: MIMO Comunications Lecture 3 Dr. Sergey Loyka EECS, University of Ottawa S. Loyka Lecture 3, ELG7177: MIMO Comunications 1 / 29 SIMO: Rx antenna array + beamforming single Tx antenna multiple
The Selection of Weighting Functions For Linear Arrays Using Different Techniques
 The Selection of Weighting Functions For Linear Arrays Using Different Techniques Dr. S. Ravishankar H. V. Kumaraswamy B. D. Satish 17 Apr 2007 Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering National Conference
The Selection of Weighting Functions For Linear Arrays Using Different Techniques Dr. S. Ravishankar H. V. Kumaraswamy B. D. Satish 17 Apr 2007 Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering National Conference
Underwater Direction-of-Arrival Finding: Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Performance Analysis
 Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship All Theses and Dissertations (ETDs) 5-24-2012 Underwater Direction-of-Arrival Finding: Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Performance
Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship All Theses and Dissertations (ETDs) 5-24-2012 Underwater Direction-of-Arrival Finding: Maximum Likelihood Estimation and Performance
Reduced-Rank Multi-Antenna Cyclic Wiener Filtering for Interference Cancellation
 Reduced-Rank Multi-Antenna Cyclic Wiener Filtering for Interference Cancellation Hong Zhang, Ali Abdi and Alexander Haimovich Center for Wireless Communications and Signal Processing Research Department
Reduced-Rank Multi-Antenna Cyclic Wiener Filtering for Interference Cancellation Hong Zhang, Ali Abdi and Alexander Haimovich Center for Wireless Communications and Signal Processing Research Department
Tensor MUSIC in Multidimensional Sparse Arrays
 Tensor MUSIC in Multidimensional Sparse Arrays Chun-Lin Liu 1 and P. P. Vaidyanathan 2 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, MC 136-93 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA cl.liu@caltech.edu
Tensor MUSIC in Multidimensional Sparse Arrays Chun-Lin Liu 1 and P. P. Vaidyanathan 2 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, MC 136-93 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA cl.liu@caltech.edu
Direction of Arrival Estimation Based on Heterogeneous Array
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol 69, 97 106, 2018 Direction of Arrival Estimation Based on Heterogeneous Array Xiaofei Ren 1, 2, * and Shuxi Gong 1 Abstract Traditionally, the direction of
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol 69, 97 106, 2018 Direction of Arrival Estimation Based on Heterogeneous Array Xiaofei Ren 1, 2, * and Shuxi Gong 1 Abstract Traditionally, the direction of
ECE Lecture Notes: Matrix Computations for Signal Processing
 ECE Lecture Notes: Matrix Computations for Signal Processing James P. Reilly c Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering McMaster University October 17, 2005 2 Lecture 2 This lecture discusses
ECE Lecture Notes: Matrix Computations for Signal Processing James P. Reilly c Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering McMaster University October 17, 2005 2 Lecture 2 This lecture discusses
Applied Numerical Linear Algebra. Lecture 8
 Applied Numerical Linear Algebra. Lecture 8 1/ 45 Perturbation Theory for the Least Squares Problem When A is not square, we define its condition number with respect to the 2-norm to be k 2 (A) σ max (A)/σ
Applied Numerical Linear Algebra. Lecture 8 1/ 45 Perturbation Theory for the Least Squares Problem When A is not square, we define its condition number with respect to the 2-norm to be k 2 (A) σ max (A)/σ
On the Simulatability Condition in Key Generation Over a Non-authenticated Public Channel
 On the Simulatability Condition in Key Generation Over a Non-authenticated Public Channel Wenwen Tu and Lifeng Lai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester,
On the Simulatability Condition in Key Generation Over a Non-authenticated Public Channel Wenwen Tu and Lifeng Lai Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester,
Lecture 6: Modeling of MIMO Channels Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1
 Fading : Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Thursday, May 3, 2018 9:30-12:00, Conference Room SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 23 Overview
Fading : Theoretical Foundations of Wireless Communications 1 Thursday, May 3, 2018 9:30-12:00, Conference Room SIP 1 Textbook: D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication 1 / 23 Overview
HIGH-SPEED data transmission and real-time multimedia
 5658 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL 55, NO 12, DECEMBER 2007 Reduced-Rank MDL Method for Source Enumeration in High-Resolution Array Processing Lei Huang, Member, IEEE, Shunjun Wu, Member,
5658 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL 55, NO 12, DECEMBER 2007 Reduced-Rank MDL Method for Source Enumeration in High-Resolution Array Processing Lei Huang, Member, IEEE, Shunjun Wu, Member,
