Linear Algebra: Homework 3
|
|
|
- Teresa Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k ) 0 2k k 3 0 5k k 5 Exercise 49 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. k 2 u v k 2 3 u v 0 k 2 k 6 0 (k 3)(k + 2) 0 k 3 k 2 Exercise 50 Describe all vectors that are orthogonal to u [ ] 3. 3x + y 0 They are all parallel to the line described by y 3x.
2 Exercise 5 [ ] a Describe all vectors that are orthogonal to u. b They are all parallel to the line described by ax + by 0. Exercise 52 Under what conditions are the following true for vectors u and v in R 2 or R 3?. u + v u + v : This is true when the vectors are parallel. 2. u + v u v : This is true when the vectors are antiparallel. Exercise 53 Prove Theorem.2(b). Proof: u ( v + w) u v + u w u ( v + w) u i (v i + w i ) (u i v i + u i w i ) u i v i + u v + u w u i w i Exercise 54 Prove Theorem.2(d). Proof: u u 0 u u 0 iff u 0 u u u i u i (u i ) 2 (u i ) 2 is non-negative, therefore the summation must be greater than or equal to 0, and only equal to 0 when u 0. Exercise 55 Prove the stated property of distance between vectors. d( u, v) d( v, u) 2
3 Proof: d( u, v) n (u i v i ) 2 n ( ) 2 (v i u i ) 2 n (v i u i ) 2 d( v, u) Exercise 56 Prove the stated property of distance between vectors. d( u, w) d( u, v) + d( v, w) Proof: d( u, w) d( u, v) + d( v, w) u w u v + v w u w u v + v w (By the triangle inequality) u w u w Exercise 57 Prove the stated property of distance between vectors. d( u, v) 0 iff u v Proof: 0 d( u, v) 0 n (u i v i ) (u i v i ) 2 (u i v i ) u i 0 u v v u v i 3
4 Exercise 58 Prove that u c v c( u v). u c v c u i (cv i ) c(u i v i ) u i v i c( u v) Exercise 59 Prove that u v u v. Exercise 60 w + v w + v Let : w u v u v + v u v + v u u v + v u v u v u v u v (Triangle Inequality) Suppose know that u v u w. Does it follow that v w? If it does, give a proof that is valid in R n. Otherwise, give a counterexample. Suppose u 0. v and w can be any vector in R n. 0, 2 0 3, 4 Exercise 6 Prove that ( u + v) ( u v) u 2 v 2. ( u + v) ( u v) u u u v + v u v v u u v v u 2 v 2 Exercise 62a Prove that u + v 2 + u v 2 2 u v 2. u + v 2 + u v 2 ( u 2 + v 2 ) + ( u 2 + v 2 ) u 2 + v 2 + u 2 + v 2 2 u v 2 (Pythagorean Theorem) 4
5 Exercise 63 Prove that u v 4 u + v 2 4 u v 2. Exercise 64a 4 u + v 2 4 u v ( u + v) ( u + v) ( u v) ( u v) 4 4 ( u u + 2 u v + v v ( u u 2 u v + v v)) 4 u v Prove that u + v u v if and only if u and v are orthogonal. u + v u v ( u + v) ( u + v) ( u v) ( u v) ( u + v) ( u + v) ( u v) ( u v) u u + 2 u v + v v u u + v v 2 u v 0 u v 0 The dot product of two vectors is 0 if and only if the two vectors are orthogonal. Exercise 65a Prove that u + v and u v are orthogonal in R if and only if u v. Exercise 66 If u 2, v 3, and u v, find u + v. ( u + v) ( u v) 0 u u v v 0 u u v v u u v v u v u + v ( u + v) ( u + v) u u + 2 u v + v v u 2 + 2() + v
6 Exercise 67 Show that there are no vectors u and v such that u, v 2, and u v 3. u + v u + v u u v + v 2 u + v 2 + 2(3) Since this case violates the triangle inequality, there can be no such vectors. Exercise 68 Prove that if u is orthogonal to both v and w, then u is orthogonal to v + w. u v 0 u w 0 u v + u w 0 u ( v + w) 0 Prove that if u is orthogonal to both v and w, then u is orthogonal to s v + t w for all scalars s and t. Exercise 69 u v 0 u w 0 u v + u w 0 u ( v + w) 0 u i (v i + w i ) 0 u (v i + w i ) 0 Prove that u is orthogonal to v proj u v for all vectors u and v in R n, where u 0. u v u ( v proj u v) u ( v u u u) u v u v u u u u u v u v 0 6
7 Exercise 70a Prove that proj u (proj u v) proj u v. w proj u v u v u u u u v proj u (proj u v) proj u u u u proj u w u w u u u u v u u u u u u u u v u u u u u u u u v u u u proj u v Exercise 70b Prove that proj u ( v proj u v) 0. w proj u v u v u u u proj u ( v proj u v) proj u ( v w) u ( v w) u u u u v u w u u u u v u v u u u u u ( u u ) u v u v u u u u u u u u u ( ) u v u v u u u u u 0 u 0 7
8 Exercise 73 Use the fact that proj u v c u for some scalar c together with Figure.4 to find c and derive the formula for proj u v. Exercise 74 c u ( v c u) 0 (c u v) (c u c u) 0 c( u v) c 2 ( u u) u v u u c proj u v c u u v u u u Using mathematical induction, prove the following generalization of the Triangle Inequality: Basis: Assumption: Induction: v + v v n v + v v n u + v u + v v + v v n v + v v n v + v v n + v n+ v + v v n + v n+ v + v v n + v n+ Section.3 Exercise Write the equation of the line passing through P with normal vector n in normal form and general form. [ ] 3 P (0, 0) n 2 [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] 3 x y 0 2 3x + 2y 0 Exercise 3 Write the equation of the line passing through P with direction vector d in vector form and parametric form. [ ] P (, 0) d 3 [ ] [ ] [ ] x + t y 0 3 { x t l y 3t 8
9 Exercise 5 Write the equation of the line passing through P with direction vector d in vector form and parametric form. P (0,, 0) d 4 x 0 y + t z 0 4 x t l y t z 4t Exercise 7 Write the equation of the line passing through P with normal vector n in normal form and general form. 3 P (0,, 0) n 2 3 x y 2 z 0 Exercise 9 3x + 2y + z 2 Write the equation of the plane passing through P with vectors u and v in vector form and parametric form. 2 3 P (0, 0, 0) u v 2 2 x y 0 + s + t 2 z 0 2 x 2s t3 Π y s + 2t z 2s + t Exercise Give the vector equation of the line passing through P and Q. P (, 2) Q (3, 0) [ ] 2 d 2 [ ] [ ] [ ] x t y 0 2 9
10 Exercise 3 Give the vector equation of the plane passing through P, Q, R. Exercise 5 P (,, ) Q (4, 0, 2) R (0,, ) 3 u v 0 2 x 3 y + s + t 0 z 2 Find parametric equations and an equation in vector form for the lines in R 2 with the following equations: Exercise 7 y 3x { x t l y 3t [ ] [ ] [ ] x 0 + t y 3 Suggest a vector proof of the fact that in R 2, two lines with slope m and m 2 are perpendicular if and only if m m 2. u m, v m 2, u v 0 m m m m 2 0
11 Exercise 9 The plane P has the equation 4x y +5z 2. For each of the planes P in Exercise 8. determine whether P and P are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. a : 2x + 3y z n 4,, 5 n a 2, 3, n c n a n n a 8 + ( 3) + ( 5) 0 b : 4x y + 5z 0 n b 4,, 5 n c n a c : x y z 3 n c,, n c n c n n c ( 5) 0 d : 4x + 6y 2z 0 n d 4, 6, 2 2, 3, n c n d n n d 8 + ( 3) + ( 5) 0 Perpendicular Parallel Perpendicular Perpendicular Exercise 2 Find the vector form of the equation of the line in R 2 that passes through P (2, ) and is parallel to the line with general equation 2x 3y. d 2, 3 Exercise 23 [ ] x y [ 2 ] + t Find the vector form of the equation of the line in R 3 that passes through P (, 0, 3) and is parallel to the line with parametric equations: x t l y 2 + 3t z 2 t x y 0 + t 3 z 3 Section 2. Exercise Determine which equations are linear in the variables x, y, z. [ ] 2 3 x πy + 3 5z 0
12 Linear. Exercise 3 Determine which equations are linear in the variables x, y, z. Nonlinear, x is not st degree. x + 7y + z sin π 9 Exercise 5 Nonlinear, cos(x) is a function of x. 3 cos(x) 4y + z 3 Exercise Find the solution set of each equation. 3x 6y 0 All points that lie on the line y 2 x. Exercise 3 Find the solution set of each equation. x + 2y + 3z 4 All points that lie on the plane x + 2y + 3z 4 or [4 3t 2s, s, t]. Exercise 5 Determine geometrically whether each system has a unique solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solution. Then solve each system algebraically to confirm your answer. Two intersecting lines, one solution at (3,-3). x + y 0 2x + y 3 Exercise 7 Determine geometrically whether each system has a unique solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solution. Then solve each system algebraically to confirm your answer. Two parallel lines, no solution. 3x 6y 3 x + 2y Exercise 9 Solve the given system by back substitution. x 2y y 3 x 7 2
13 Exercise 2 Solve the given system by back substitution. x y + z 0 2y z 3z z 3 y 3 x 2 3 Exercise 23 Solve the given system by back substitution. Exercise 25 Solve these systems. Exercise 27 Find the augmented matrices of the linear systems. x + x 2 x 3 x 4 x 2 + x 3 + x 4 0 x 3 x 4 0 x 4 x 3 x 2 2 x x 2 2x + y 3 3x 4y + z x y 0 y 7 z 23 2x + y 3 [ ] 0 A 2 3 3
14 Exercise 29 Find the augmented matrices of the linear systems. Exercise 3 x + 5y x + y 5 2x + 4y 4 A Find a system of linear equations that has the given matrix as its augmented matrix. 0 A 0 2 Exercise 33 y + z x y 2x y + z Solve the linear systems in the given equations. x y 0 2x + y 3 [ ] 0 A 2 3 2R + R 2 R 2 [ ] 0 A R 2 R 2 [ ] 0 A 0 R 2 + R R [ ] 0 A 0 x y 4
15 Exercise 35 Solve the linear systems in the given equations. x + 5y x + y 5 2x + 4y 4 A R + R 2 R R + R 3 R 3 5 A R 2 R 2 6 R 3 R 3 5 A 0 0 5R 3 + R R 0 4 A 0 0 x 4 y 5
16 Exercise 37 Solve the linear systems in the given equations. Exercise 39 A R 2 R R + R 3 R R 3 R 2 R (Inconsistent) Find a system of two linear equations in the variables x and y whose solution set is given by the parametric equations x t and y 3 2t. y 3 2x 3x 5 Find another parametric solution to the system in the first part in which the parameter is s and y s. y s x s 3 2 If you have any questions, comments, or concerns, please contact me at alvin@omgimanerd.tech 6
Linear Algebra. Alvin Lin. August December 2017
 Linear Algebra Alvin Lin August 207 - December 207 Linear Algebra The study of linear algebra is about two basic things. We study vector spaces and structure preserving maps between vector spaces. A vector
Linear Algebra Alvin Lin August 207 - December 207 Linear Algebra The study of linear algebra is about two basic things. We study vector spaces and structure preserving maps between vector spaces. A vector
MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11
 MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11 August 7 & 11, 2014 Contents 8 Lines and Planes 1 8.1 Equations of Lines in Two-Space and Three-Space............ 1 8.2 Equations of Planes........................... 5 8.3 Properties
MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11 August 7 & 11, 2014 Contents 8 Lines and Planes 1 8.1 Equations of Lines in Two-Space and Three-Space............ 1 8.2 Equations of Planes........................... 5 8.3 Properties
Math 51, Homework-2. Section numbers are from the course textbook.
 SSEA Summer 2017 Math 51, Homework-2 Section numbers are from the course textbook. 1. Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 1 1 1 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 0 t R.
SSEA Summer 2017 Math 51, Homework-2 Section numbers are from the course textbook. 1. Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 1 1 1 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 0 t R.
Matrices. A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. Cells in a matrix can be referenced in the form.
 Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Math 241, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
Inner Product Spaces 6.1 Length and Dot Product in R n
 Inner Product Spaces 6.1 Length and Dot Product in R n Summer 2017 Goals We imitate the concept of length and angle between two vectors in R 2, R 3 to define the same in the n space R n. Main topics are:
Inner Product Spaces 6.1 Length and Dot Product in R n Summer 2017 Goals We imitate the concept of length and angle between two vectors in R 2, R 3 to define the same in the n space R n. Main topics are:
Math Linear Algebra
 Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
Math 220 - Linear Algebra (Summer 208) Solutions to Homework #7 Exercise 6..20 (a) TRUE. u v v u = 0 is equivalent to u v = v u. The latter identity is true due to the commutative property of the inner
8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]
![8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4] 8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]](/thumbs/95/122742655.jpg) Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
Linear Algebra Exam 1 Spring 2007
 Linear Algebra Exam 1 Spring 2007 March 15, 2007 Name: SOLUTION KEY (Total 55 points, plus 5 more for Pledged Assignment.) Honor Code Statement: Directions: Complete all problems. Justify all answers/solutions.
Linear Algebra Exam 1 Spring 2007 March 15, 2007 Name: SOLUTION KEY (Total 55 points, plus 5 more for Pledged Assignment.) Honor Code Statement: Directions: Complete all problems. Justify all answers/solutions.
MTH 2310, FALL Introduction
 MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
Inner products. Theorem (basic properties): Given vectors u, v, w in an inner product space V, and a scalar k, the following properties hold:
 Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8
 MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
Unit 2: Lines and Planes in 3 Space. Linear Combinations of Vectors
 Lesson10.notebook November 28, 2012 Unit 2: Lines and Planes in 3 Space Linear Combinations of Vectors Today's goal: I can write vectors as linear combinations of each other using the appropriate method
Lesson10.notebook November 28, 2012 Unit 2: Lines and Planes in 3 Space Linear Combinations of Vectors Today's goal: I can write vectors as linear combinations of each other using the appropriate method
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 211: Linear Algebra
 Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
Section 1.1 System of Linear Equations College of Science MATHS 211: Linear Algebra (University of Bahrain) Linear System 1 / 33 Goals:. 1 Define system of linear equations and their solutions. 2 To represent
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra. Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations. Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve:
 MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations Finding the solution to a set of two equations in two variables: Example 1: Solve: x x = 3 1 2 2x + 4x = 12 1 2 Geometric meaning: Do these
Linear Algebra: Homework 7
 Linear Algebra: Homework 7 Alvin Lin August 6 - December 6 Section 3.5 Exercise x Let S be the collection of vectors in R y that satisfy the given property. In each case, either prove that S forms a subspace
Linear Algebra: Homework 7 Alvin Lin August 6 - December 6 Section 3.5 Exercise x Let S be the collection of vectors in R y that satisfy the given property. In each case, either prove that S forms a subspace
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
Worksheet for Lecture 23 (due December 4) Section 6.1 Inner product, length, and orthogonality
 Worksheet for Lecture (due December 4) Name: Section 6 Inner product, length, and orthogonality u Definition Let u = u n product or dot product to be and v = v v n be vectors in R n We define their inner
Worksheet for Lecture (due December 4) Name: Section 6 Inner product, length, and orthogonality u Definition Let u = u n product or dot product to be and v = v v n be vectors in R n We define their inner
Math 51, Homework-2 Solutions
 SSEA Summer 27 Math 5, Homework-2 Solutions Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 t R 5 4 By substituting t = and t =, we get two points
SSEA Summer 27 Math 5, Homework-2 Solutions Write the parametric equation of the plane that contains the following point and line: 3 2, 4 2 + t 3 t R 5 4 By substituting t = and t =, we get two points
Chapter 6: Orthogonality
 Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in
 Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in R 2 In this section, we begin with a discussion about how to find the vector and parametric equations of a line in R 2. To find the vector and parametric
Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in R 2 In this section, we begin with a discussion about how to find the vector and parametric equations of a line in R 2. To find the vector and parametric
Vector equations of lines in the plane and 3-space (uses vector addition & scalar multiplication).
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Solution to Homework 1
 Solution to Homework 1 Olena Bormashenko September, 0 Section 1.1:, 5b)d), 7b)f), 8a)b), ; Section 1.:, 5, 7, 9, 10, b)c), 1, 15b), 3 Section 1.1. In each of the following cases, find a point that is two-thirds
Solution to Homework 1 Olena Bormashenko September, 0 Section 1.1:, 5b)d), 7b)f), 8a)b), ; Section 1.:, 5, 7, 9, 10, b)c), 1, 15b), 3 Section 1.1. In each of the following cases, find a point that is two-thirds
web: HOMEWORK 1
 MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
Kevin James. MTHSC 206 Section 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 MTHSC 206 Section 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Definition A line in R 3 can be described by a point and a direction vector. Given the point r 0 and the direction vector v. Any point r on the line
MTHSC 206 Section 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Definition A line in R 3 can be described by a point and a direction vector. Given the point r 0 and the direction vector v. Any point r on the line
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10
 Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
Review of Coordinate Systems
 Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
Vector Geometry. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at
Chapter 5 Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at
MA 242 LINEAR ALGEBRA C1, Solutions to First Midterm Exam
 MA 242 LINEAR ALGEBRA C Solutions to First Midterm Exam Prof Nikola Popovic October 2 9:am - :am Problem ( points) Determine h and k such that the solution set of x + = k 4x + h = 8 (a) is empty (b) contains
MA 242 LINEAR ALGEBRA C Solutions to First Midterm Exam Prof Nikola Popovic October 2 9:am - :am Problem ( points) Determine h and k such that the solution set of x + = k 4x + h = 8 (a) is empty (b) contains
v = v 1 2 +v 2 2. Two successive applications of this idea give the length of the vector v R 3 :
 Length, Angle and the Inner Product The length (or norm) of a vector v R 2 (viewed as connecting the origin to a point (v 1,v 2 )) is easily determined by the Pythagorean Theorem and is denoted v : v =
Length, Angle and the Inner Product The length (or norm) of a vector v R 2 (viewed as connecting the origin to a point (v 1,v 2 )) is easily determined by the Pythagorean Theorem and is denoted v : v =
MATH 1210 Assignment 3 Solutions 17R-T2
 MATH 1210 Assignment 3 Solutions 17R-T2 This assignment is optional and does not need to be handed in. Attempt all questions, write out nicely written solutions (showing all your work), and the solutions
MATH 1210 Assignment 3 Solutions 17R-T2 This assignment is optional and does not need to be handed in. Attempt all questions, write out nicely written solutions (showing all your work), and the solutions
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
4.3 Equations in 3-space
 4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning:
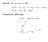 Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
Recall: Dot product on R 2 : u v = (u 1, u 2 ) (v 1, v 2 ) = u 1 v 1 + u 2 v 2, u u = u 2 1 + u 2 2 = u 2. Geometric Meaning: u v = u v cos θ. u θ v 1 Reason: The opposite side is given by u v. u v 2 =
Lecture 3: Vectors. In Song Kim. September 1, 2011
 Lecture 3: Vectors In Song Kim September 1, 211 1 Solving Equations Up until this point we have been looking at different types of functions, often times graphing them. Each point on a graph is a solution
Lecture 3: Vectors In Song Kim September 1, 211 1 Solving Equations Up until this point we have been looking at different types of functions, often times graphing them. Each point on a graph is a solution
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP Contents. 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2
 MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
F F. proj cos( ) v. v proj v
 Geometric Definition of Dot Product 1.2 The Dot Product Suppose you are pulling up on a rope attached to a box, as shown above. How would you find the force moving the box towards you? As stated above,
Geometric Definition of Dot Product 1.2 The Dot Product Suppose you are pulling up on a rope attached to a box, as shown above. How would you find the force moving the box towards you? As stated above,
Identify the graph of a function, and obtain information from or about the graph of a function.
 PS 1 Graphs: Graph equations using rectangular coordinates and graphing utilities, find intercepts, discuss symmetry, graph key equations, solve equations using a graphing utility, work with lines and
PS 1 Graphs: Graph equations using rectangular coordinates and graphing utilities, find intercepts, discuss symmetry, graph key equations, solve equations using a graphing utility, work with lines and
which are not all zero. The proof in the case where some vector other than combination of the other vectors in S is similar.
 It follows that S is linearly dependent since the equation is satisfied by which are not all zero. The proof in the case where some vector other than combination of the other vectors in S is similar. is
It follows that S is linearly dependent since the equation is satisfied by which are not all zero. The proof in the case where some vector other than combination of the other vectors in S is similar. is
BSc (Hons) in Computer Games Development. vi Calculate the components a, b and c of a non-zero vector that is orthogonal to
 1 APPLIED MATHEMATICS INSTRUCTIONS Full marks will be awarded for the correct solutions to ANY FIVE QUESTIONS. This paper will be marked out of a TOTAL MAXIMUM MARK OF 100. Credit will be given for clearly
1 APPLIED MATHEMATICS INSTRUCTIONS Full marks will be awarded for the correct solutions to ANY FIVE QUESTIONS. This paper will be marked out of a TOTAL MAXIMUM MARK OF 100. Credit will be given for clearly
1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus Rectangular Coordinate Systems... 4
 MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
Calculus Vector Principia Mathematica. Lynne Ryan Associate Professor Mathematics Blue Ridge Community College
 Calculus Vector Principia Mathematica Lynne Ryan Associate Professor Mathematics Blue Ridge Community College Defining a vector Vectors in the plane A scalar is a quantity that can be represented by a
Calculus Vector Principia Mathematica Lynne Ryan Associate Professor Mathematics Blue Ridge Community College Defining a vector Vectors in the plane A scalar is a quantity that can be represented by a
3 Scalar Product. 3.0 The Dot Product. ~v ~w := v 1 w 1 + v 2 w v n w n.
 3 Scalar Product Copyright 2017, Gregory G. Smith 28 September 2017 Although vector products on R n are rare, every coordinate space R n is equipped with a binary operation that sends two vectors to a
3 Scalar Product Copyright 2017, Gregory G. Smith 28 September 2017 Although vector products on R n are rare, every coordinate space R n is equipped with a binary operation that sends two vectors to a
Distance Formula in 3-D Given any two points P 1 (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and P 2 (x 2, y 2, z 2 ) the distance between them is ( ) ( ) ( )
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
4.1 Distance and Length
 Chapter Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at vectors
Chapter Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at vectors
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
COURSE OF STUDY MATHEMATICS
 COURSE OF STUDY MATHEMATICS Name of Course: Honors PreCalculus Course Number: 341 Grade Level: 11 Length of Course: 180 Days Type of Offering: Academic Credit Value: 1 credit Prerequisite/s: Honors Geometry
COURSE OF STUDY MATHEMATICS Name of Course: Honors PreCalculus Course Number: 341 Grade Level: 11 Length of Course: 180 Days Type of Offering: Academic Credit Value: 1 credit Prerequisite/s: Honors Geometry
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m
 Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
Detailed objectives are given in each of the sections listed below. 1. Cartesian Space Coordinates. 2. Displacements, Forces, Velocities and Vectors
 Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
SUPPLEMENT I. Example. Graph the vector 4, 3. Definition. Given two points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ), the vector represented by # AB is # AB =,
 SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Linear Algebra I for Science (NYC)
 Element No. 1: To express concrete problems as linear equations. To solve systems of linear equations using matrices. Topic: MATRICES 1.1 Give the definition of a matrix, identify the elements and the
Element No. 1: To express concrete problems as linear equations. To solve systems of linear equations using matrices. Topic: MATRICES 1.1 Give the definition of a matrix, identify the elements and the
Multiple Choice Questions
 Multiple Choice Questions There is no penalty for guessing. Three points per question, so a total of 48 points for this section.. What is the complete relationship between homogeneous linear systems of
Multiple Choice Questions There is no penalty for guessing. Three points per question, so a total of 48 points for this section.. What is the complete relationship between homogeneous linear systems of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide
 Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1
 11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review. Give complete answers to each of the following questions. Show all of your work.
 Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review Give complete answers to each of the following questions Show all of your work Note: You might struggle with some of these questions, either because it has
Assignment 1 Math 5341 Linear Algebra Review Give complete answers to each of the following questions Show all of your work Note: You might struggle with some of these questions, either because it has
Intro Vectors 2D implicit curves 2D parametric curves. Graphics 2011/2012, 4th quarter. Lecture 2: vectors, curves, and surfaces
 Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra
 MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 1 Material Dr. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University January 9, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH 464)
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 1 Material Dr. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University January 9, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH 464)
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS
 MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
Solutions to Math 51 First Exam October 13, 2015
 Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
10.4 The Cross Product
 Math 172 Chapter 10B notes Page 1 of 9 10.4 The Cross Product The cross product, or vector product, is defined in 3 dimensions only. Let aa = aa 1, aa 2, aa 3 bb = bb 1, bb 2, bb 3 then aa bb = aa 2 bb
Math 172 Chapter 10B notes Page 1 of 9 10.4 The Cross Product The cross product, or vector product, is defined in 3 dimensions only. Let aa = aa 1, aa 2, aa 3 bb = bb 1, bb 2, bb 3 then aa bb = aa 2 bb
6.1. Inner Product, Length and Orthogonality
 These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday November 13, and Monday November 1, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say on those days. They are guaranteed to be incorrect..1.
These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday November 13, and Monday November 1, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say on those days. They are guaranteed to be incorrect..1.
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE
 VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II
 Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Quantile Textbook Report
 Quantile Textbook Report Algebra 1 Author Charles, Randall I., et al StateEdition West Virginia Grade Algebra 1 1 Foundations for Algebra 1.1 Variables and Expressions 750Q 1.2 Order of Operations and
Quantile Textbook Report Algebra 1 Author Charles, Randall I., et al StateEdition West Virginia Grade Algebra 1 1 Foundations for Algebra 1.1 Variables and Expressions 750Q 1.2 Order of Operations and
LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN
 LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN c W W L Chen, 1997, 2008. This chapter is available free to all individuals, on the understanding that it is not to be used for financial gain, and may be downloaded and/or photocopied,
LINEAR ALGEBRA W W L CHEN c W W L Chen, 1997, 2008. This chapter is available free to all individuals, on the understanding that it is not to be used for financial gain, and may be downloaded and/or photocopied,
Name: ID: Math 233 Exam 1. Page 1
 Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Ron Paul Curriculum Mathematics 8 Lesson List
 Ron Paul Curriculum Mathematics 8 Lesson List 1 Introduction 2 Algebraic Addition 3 Algebraic Subtraction 4 Algebraic Multiplication 5 Week 1 Review 6 Algebraic Division 7 Powers and Exponents 8 Order
Ron Paul Curriculum Mathematics 8 Lesson List 1 Introduction 2 Algebraic Addition 3 Algebraic Subtraction 4 Algebraic Multiplication 5 Week 1 Review 6 Algebraic Division 7 Powers and Exponents 8 Order
KIST DP Course Descriptions
 Grade: 11 Unit Number: 1 Unit Title: Algebra Sequence and Series; Exponents and Logarithms; The Binomial Theorem Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning Mathematics begins with axioms and uses deductive reasoning
Grade: 11 Unit Number: 1 Unit Title: Algebra Sequence and Series; Exponents and Logarithms; The Binomial Theorem Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning Mathematics begins with axioms and uses deductive reasoning
Mathematics 1350H Linear Algebra I: Matrix Algebra Trent University, Summer 2017 Solutions to the Quizzes
 Mathematics H Linear Algebra I: Matrix Algebra Trent University, Summer 7 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #. Wednesday, May, 7. [ minutes] Let a = and b = be vectors in R.. Find a + b and a b. []. Determine
Mathematics H Linear Algebra I: Matrix Algebra Trent University, Summer 7 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #. Wednesday, May, 7. [ minutes] Let a = and b = be vectors in R.. Find a + b and a b. []. Determine
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Null and Column Spaces Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./8 Announcements Study Guide posted HWK posted Math 9Applied
Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Null and Column Spaces Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./8 Announcements Study Guide posted HWK posted Math 9Applied
Extra Problems for Math 2050 Linear Algebra I
 Extra Problems for Math 5 Linear Algebra I Find the vector AB and illustrate with a picture if A = (,) and B = (,4) Find B, given A = (,4) and [ AB = A = (,4) and [ AB = 8 If possible, express x = 7 as
Extra Problems for Math 5 Linear Algebra I Find the vector AB and illustrate with a picture if A = (,) and B = (,4) Find B, given A = (,4) and [ AB = A = (,4) and [ AB = 8 If possible, express x = 7 as
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T. KEMP)
 MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB
 Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
Applied Linear Algebra in Geoscience Using MATLAB Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional Plots Programming in
Algebra II Learning Targets
 Chapter 0 Preparing for Advanced Algebra LT 0.1 Representing Functions Identify the domain and range of functions LT 0.2 FOIL Use the FOIL method to multiply binomials LT 0.3 Factoring Polynomials Use
Chapter 0 Preparing for Advanced Algebra LT 0.1 Representing Functions Identify the domain and range of functions LT 0.2 FOIL Use the FOIL method to multiply binomials LT 0.3 Factoring Polynomials Use
MTH 2032 SemesterII
 MTH 202 SemesterII 2010-11 Linear Algebra Worked Examples Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2011 ii Contents Table of Contents
MTH 202 SemesterII 2010-11 Linear Algebra Worked Examples Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education December 28, 2011 ii Contents Table of Contents
MyMathLab for School Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Common Core Edition 2016
 A Correlation of MyMathLab for School Precalculus Common Core Edition 2016 to the Tennessee Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-090-10 , Standard 1 Mathematical Processes Course
A Correlation of MyMathLab for School Precalculus Common Core Edition 2016 to the Tennessee Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-090-10 , Standard 1 Mathematical Processes Course
Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations.
 1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
Intro Vectors 2D implicit curves 2D parametric curves. Graphics 2012/2013, 4th quarter. Lecture 2: vectors, curves, and surfaces
 Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: TA sessions for tutorial 1 start today Tutorial 2 will go online after lecture 3 Practicals: Make sure to find a team partner very soon
Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: TA sessions for tutorial 1 start today Tutorial 2 will go online after lecture 3 Practicals: Make sure to find a team partner very soon
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017
 Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017 Since we didn t get a chance to discuss parametrized lines last week, we may spend some time discussing those before moving on to the dot
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017 Since we didn t get a chance to discuss parametrized lines last week, we may spend some time discussing those before moving on to the dot
Section 13.4 The Cross Product
 Section 13.4 The Cross Product Multiplying Vectors 2 In this section we consider the more technical multiplication which can be defined on vectors in 3-space (but not vectors in 2-space). 1. Basic Definitions
Section 13.4 The Cross Product Multiplying Vectors 2 In this section we consider the more technical multiplication which can be defined on vectors in 3-space (but not vectors in 2-space). 1. Basic Definitions
Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Media Update 7th Edition 2010, (Demana, et al)
 A Correlation of Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Media Update To the Virginia Standards of Learning for Mathematical Analysis February 2009 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how, meets
A Correlation of Precalculus Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic Media Update To the Virginia Standards of Learning for Mathematical Analysis February 2009 INTRODUCTION This document demonstrates how, meets
The Cross Product. In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications.
 The Cross Product In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications. THE CROSS PRODUCT The cross product a x b of two vectors a and b, unlike the dot product, is a
The Cross Product In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications. THE CROSS PRODUCT The cross product a x b of two vectors a and b, unlike the dot product, is a
The value of a problem is not so much coming up with the answer as in the ideas and attempted ideas it forces on the would be solver I.N.
 Math 410 Homework Problems In the following pages you will find all of the homework problems for the semester. Homework should be written out neatly and stapled and turned in at the beginning of class
Math 410 Homework Problems In the following pages you will find all of the homework problems for the semester. Homework should be written out neatly and stapled and turned in at the beginning of class
Mathematics 2203, Test 1 - Solutions
 Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 6.1 Inner Product, Length & Orthogonality Math 2331 Linear Algebra 6.1 Inner Product, Length & Orthogonality Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/
6.1 Inner Product, Length & Orthogonality Math 2331 Linear Algebra 6.1 Inner Product, Length & Orthogonality Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/
Math 220: Summer Midterm 1 Questions
 Math 220: Summer 2015 Midterm 1 Questions MOST questions will either look a lot like a Homework questions This lists draws your attention to some important types of HW questions. SOME questions will have
Math 220: Summer 2015 Midterm 1 Questions MOST questions will either look a lot like a Homework questions This lists draws your attention to some important types of HW questions. SOME questions will have
2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution.
 1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
1. For matrices A, B, C, A + B = A + C if and only if A = B. 2. Every linear system with the same number of equations as unknowns has a unique solution. 3. Every linear system with the same number of equations
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Second Edition, Serge Lange
 Introduction to Linear Algebra, Second Edition, Serge Lange Chapter I: Vectors R n defined. Addition and scalar multiplication in R n. Two geometric interpretations for a vector: point and displacement.
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Second Edition, Serge Lange Chapter I: Vectors R n defined. Addition and scalar multiplication in R n. Two geometric interpretations for a vector: point and displacement.
Vectors, dot product, and cross product
 MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
Tennessee s State Mathematics Standards Precalculus
 Tennessee s State Mathematics Standards Precalculus Domain Cluster Standard Number Expressions (N-NE) Represent, interpret, compare, and simplify number expressions 1. Use the laws of exponents and logarithms
Tennessee s State Mathematics Standards Precalculus Domain Cluster Standard Number Expressions (N-NE) Represent, interpret, compare, and simplify number expressions 1. Use the laws of exponents and logarithms
Midterm 1 Review. Distance = (x 1 x 0 ) 2 + (y 1 y 0 ) 2.
 Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Calculus III (MAC )
 Calculus III (MAC2-) Test (25/9/7) Name (PRINT): Please show your work. An answer with no work receives no credit. You may use the back of a page if you need more space for a problem. You may not use any
Calculus III (MAC2-) Test (25/9/7) Name (PRINT): Please show your work. An answer with no work receives no credit. You may use the back of a page if you need more space for a problem. You may not use any
Brief Review of Exam Topics
 Math 32A Discussion Session Week 3 Notes October 17 and 19, 2017 We ll use this week s discussion session to prepare for the first midterm. We ll start with a quick rundown of the relevant topics, and
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 3 Notes October 17 and 19, 2017 We ll use this week s discussion session to prepare for the first midterm. We ll start with a quick rundown of the relevant topics, and
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 12.1 & 12.2 Vectors in the Plane
 MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
Linear Independence. MATH 322, Linear Algebra I. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Linear Independence MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Introduction Given a set of vectors {v 1, v 2,..., v r } and another vector v span{v 1, v 2,...,
Linear Independence MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Introduction Given a set of vectors {v 1, v 2,..., v r } and another vector v span{v 1, v 2,...,
Consequences of Orthogonality
 Consequences of Orthogonality Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of Orthogonality Today 1 / 23 Introduction The three kind of examples we did above involved Dirichlet, Neumann
Consequences of Orthogonality Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Consequences of Orthogonality Today 1 / 23 Introduction The three kind of examples we did above involved Dirichlet, Neumann
