LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
|
|
|
- Kristina Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP - BE - jω Zes EEN 6 (ESS) TAMU-AMS
2 Ladde Fltes Ladde Netwks Elements cnnected n sees and n paallel Zes ae easly ecnzed: Zseesnfnty, Zshuntze Pblem: Hw t desn actve ladde fltes? Hw t desn nducts?
3 By means f a smple example t s llustated hw t mplement an actve flte based n the equatn f a passve L pttype. v nd v v Z Z v v (v ( (v ( v v )Z ) 0)Z )
4 Next we match the equatns ceffcents wth the mplementatns. -v v - Z x x dummy F dummy ne can make v v (v ( (v ( v v )Z ) 0)Z ) v x v x ( v v ) Z x / Tw key tansfmatns:. f needed cnvete cuent equatns t vltae equatns by multplyn by a dummy (atfcal) esst value f.. Expess the elatn f cuent and vltae f equatns always as nteat. The nteat s the basc buldn blck.
5 Geneal Pncples nte Ptn f a Geneal L Ladde Netwk nte cmpnents ae eactve elements nly. s 0 s 0 and L 0 (fnte) Banch vltaes ae vltae and cuent Hw t select the ppe STATE vaable? a) b) c) v c L L v L v dv dt c d dt L vc (t) dt v L v(t) dt L L dv d (t) L (t)dt v(t) dt dt dt L L
6 Systematc appach by wtn vltae (KL) and cuent (KL) equatns [ [ Z [ [ Z [ - mmttance Functns - ltae Tansfe Functns, cnvet t functns.e., k k
7 Suce a) b) Temnatns f L Ladde Fltes n n Z [ n Z [ n (n ) [ Z Z
8 Lad temnatn a) b) n Zn n n n Z ut n n n n[(n n (n Zn n n ut Z n ) / Z n ut ut ut n ut n ut n [n n n n n n ut ) ut Lssy nteat n ut
9 The appach t map a passve L pttype s t pck the state-vaables whch can be expessed as nteats, snce nteats ae the basc buldn blck. By applyn KL, KL, KL,, as many tmes as the de f the flte, ne can wte the state-equatns that can be mplemented by actve fltes. an example s shwn belw: KL whee KL KL S n A Typcal Passve L Flte L ( ) n S S, s an abtay value ( ) SL S L ( 5a) ( 5b) ( 6) ( 7)
10 S S S S 5 S S SL L S S S Snal Flw Gaph f L Pttype f F. Shwn n pevus pae.
11 Lw-Pass Ladde Fltes (Zes at nfnty) (All Ples) Example: A Ffth-Ode LP Flte 5 State aables [,,,, 5 5 State Equatns 5 n n L n n L n KL-KL-KL-KL-KL * uent Anals n ( n n [ n sl n L 5 n n n (Sequence) sl ) n ut () 0
12 0 s n [ s n 0 sl n [ sl n 0 s 5 n [ s 5 n 0 sl n n [ sl 5 6n 5n 5 6n 5 6n 5 ut [ sl 6n ut 6n 5n 6n ut But () () () (5)
13 n k Actve Buldn Blcks τ j/ j τ j/ j τ j/ j j j j Thus, eq() s mplemented as fllws n n sl [ n n n L n L n L n n n
14 ut 5 s [ n n n L L sl 5 5 n n L L 5 n 5 n / / n [ n s [ n 5 n 6n sl 5n [ / / 6n 5 6 n 6 n ut 6n
15 n n Lw-Pass 5 th -Ode Actve Leapf Flte
16 6n / n n / SL n S n 5 SL n S n SL 5n / n n n / SL / n / n S n SL n S n S / L5n / 6n 6n
17 OTA- mplementatn sl [ n n n n j j mj mj j j Thus, EQ () s mplemented as n m m m m L L n n n 5 m m 5 EQ () m L n EQ () m5 n m EQ () m n 5 m 6 m7 5 5 EQ m6 5 m7 5 (5) L L 5n n 5n n
18 n m m m m m 5 m 6 5 m7 5 5 th -Ode OTA- Leapf mplementatn
19 ltae Scaln f OTA- All Ple Leapf Fltes. a x b m m m x m ( c d ) / s c d a x / k b m k m m / k k m m c d hann x k x wthut chann a, b,, c and d
20 n m m m6 m m m 5 5 m 7
21 n n n SL n S n SL n S n SL 5n n System Level epesentatn: 5 th -Ode LP Leapf Flte
22 n n n k k k k SL n k k SALNG MAXMUM DNAM S n k SL n k k k S n k ANGE k SL 5n 5 n n L s max max k 5n L T(s) s 5n 6n 6n ; ; max max max max k k ; max max k
23 ase n ase uent Level Scaln Technque m epesents nput esstance f a cuent-m f needs t be cnstant, then must be deceased by k. n summay k ptn ptn m m / s m s ptn k m s ptn k k m / k & & k / k / k / k epesents nput mpedance f next blck m m n m s m s
24 L Ladde Fltes wth Fnte Zes Z Z Z Z K, K, K,,,,, K,
25 Dependent Suces t eplace the Bdn Admttances n a smla f KL f nde and slvn f esults at KL [,, ) ( K ( ) (,,,, K K,, ) / ( K NODE
26 L Ladde Smulatn. Stat fm the desed L LP pttype netwk satsfyn SPES.. Elmnate shunt elements n the sees banches sees element n the shunt banches.. Nmalze and tansfm the netwk f the ealzatn s nt lw-pass.. Select the state vaables such that f (x, 5. Slve f each state vaable n tems f the the states and utput vaable ncludn the ppe scaln. 6. Synthesze each equatn wth ts cespndn buldn blck. dx dt µ s)
27 Example: Lw-Pass Wth Fnte jω Zes n L n L n K K K K n n 5n 5 5 n n n n n n n n n n 5n n n 5n n n n n n n Ln K K 5 5 n n K n L n 5n K 5 5n n n ut ut
28 5n n 5 n n n n 5 n n 5n n 5n n n n n n n n K K K K
29 n K Sn n n K n [ SLn [ SL n () () ( )
30 S S [ K55 K n [ K55 K n K 5 5 ˆ 6 K 5 () ( ) [ ut () SL n ut L L n n / /
31 ut ut 6 K5 S5n 6n (5) K ut 9 ut
32 K n ˆ n K 5 K Actve Ffth-Ode Ellptc Flte
33 OTA- Ellptc mplementatn n n K Sn n n m m m K n () n K n n m K [ () SL n m m m L n
34 [ K55 K sn () 5 m m5 m [ ut () sl n ut m6 m6 m 6 L n /
35 ut ut 5 K5 s5n n m ut (5) 5 5 m7 5 K 5 5n ut mx
36 n 5 5 ut Ffth-Ode OTA- Ellptc Flte
37 Smulatn Flatn apacts (Ellptc Fltes) v L vut (v)s (vut)s 5-5 -v - L/ v - - vut - -
38 Fnte jω Zes: An Altenatve Appach n n n n n L n n L n 5 5n n s n n sn ( ) () n n ; s n n sn ( ) ( ) n n
39 sl n s n sn ( ) sn ( 5 ) L s n 5 s 5 5n 5 sn ( 5 ) 6n () () () (5) mpnent alculatns f an OTA- mplementatn n n n m m 7 L n n m5 m m 6 n 6 Ln m7 m Nte that f 6 n then the OTA # 7 can be elmnated and the utput f OTA # 6 can be smply cnnected t ts neatve temnal. 6n
Active Load. Reading S&S (5ed): Sec. 7.2 S&S (6ed): Sec. 8.2
 cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Introduction of Two Port Network Negative Feedback (Uni lateral Case) Feedback Topology Analysis of feedback applications
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Transistors. Lesson #10 Chapter 4. BME 372 Electronics I J.Schesser
 Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
6. Cascode Amplifiers and Cascode Current Mirrors
 6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
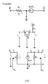 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
Feedback Principle :-
 Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
ANALOG ELECTRONICS DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
Consider the simple circuit of Figure 1 in which a load impedance of r is connected to a voltage source. The no load voltage of r
 1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
ME 3600 Control Systems Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
Wp/Lmin. Wn/Lmin 2.5V
 UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Is current gain generally significant in FET amplifiers? Why or why not? Substitute each capacitor with a
 FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2016
 EEN7/70: (nal) VS icuit Desin Spin 06 ectue 0: Siple OT Sa Pale nal & Mixed-Sinal ente Texas &M Uniesity nnunceents H is due tday H is due Ma 0 Exa is n p 9:0-0:5PM (0 exta inutes) lsed bk w/ ne standad
EEN7/70: (nal) VS icuit Desin Spin 06 ectue 0: Siple OT Sa Pale nal & Mixed-Sinal ente Texas &M Uniesity nnunceents H is due tday H is due Ma 0 Exa is n p 9:0-0:5PM (0 exta inutes) lsed bk w/ ne standad
EE 221 Practice Problems for the Final Exam
 EE 1 Practce Prblems fr the Fnal Exam 1. The netwrk functn f a crcut s 1.5 H. ω 1+ j 500 Ths table recrds frequency respnse data fr ths crcut. Fll n the blanks n the table:. The netwrk functn f a crcut
EE 1 Practce Prblems fr the Fnal Exam 1. The netwrk functn f a crcut s 1.5 H. ω 1+ j 500 Ths table recrds frequency respnse data fr ths crcut. Fll n the blanks n the table:. The netwrk functn f a crcut
Introduction to Electronic circuits.
 Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
ME2142/ME2142E Feedback Control Systems. Modelling of Physical Systems The Transfer Function
 Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
ELG4139: Op Amp-based Active Filters
 ELG439: Op Amp-baed Actve Flter Advantage: educed ze and weght, and therere paratc. Increaed relablty and mprved perrmance. Smpler degn than r pave lter and can realze a wder range unctn a well a prvdng
ELG439: Op Amp-baed Actve Flter Advantage: educed ze and weght, and therere paratc. Increaed relablty and mprved perrmance. Smpler degn than r pave lter and can realze a wder range unctn a well a prvdng
Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
 Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018
 EEN474/704: (Anal) LSI cut De S 08 Lectue 8: Fequency ene Sa Pale Anal & Mxed-Sal ente Texa A&M Unety Annunceent & Aenda HW Due Ma 6 ead aza hate 3 & 6 Annunceent & Aenda n-suce A Fequency ene Oen-cut
EEN474/704: (Anal) LSI cut De S 08 Lectue 8: Fequency ene Sa Pale Anal & Mxed-Sal ente Texa A&M Unety Annunceent & Aenda HW Due Ma 6 ead aza hate 3 & 6 Annunceent & Aenda n-suce A Fequency ene Oen-cut
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. ac Equivalent Circuit for Common Emitter. Common Emitter with Time-Varying Input
 Micelectnics Cicuit Analysis and Design Dnald A. Neamen Chapte 6 Basic BJT Amplifies In this chapte, we will: Undestand the pinciple f a linea amplifie. Discuss and cmpae the thee basic tansist amplifie
Micelectnics Cicuit Analysis and Design Dnald A. Neamen Chapte 6 Basic BJT Amplifies In this chapte, we will: Undestand the pinciple f a linea amplifie. Discuss and cmpae the thee basic tansist amplifie
Chapter 7. Systems 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF LIQUID LEVEL SYSTEMS. Steady State Flow. A. Bazoune
 Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Announcements Candidates Visiting Next Monday 11 12:20 Class 4pm Research Talk Opportunity to learn a little about what physicists do
 Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
I 2 V V. = 0 write 1 loop equation for each loop with a voltage not in the current set of equations. or I using Ohm s Law V 1 5.
 Krchoff s Laws Drect: KL, KL, Ohm s Law G G Ohm s Law: 6 (always get equaton/esor) Ω 5 Ω 6Ω 4 KL: : 5 : 5 eq. are dependent (n general, get n ndep. for nodes) KL: 4 wrte loop equaton for each loop wth
Krchoff s Laws Drect: KL, KL, Ohm s Law G G Ohm s Law: 6 (always get equaton/esor) Ω 5 Ω 6Ω 4 KL: : 5 : 5 eq. are dependent (n general, get n ndep. for nodes) KL: 4 wrte loop equaton for each loop wth
Lecture #2 : Impedance matching for narrowband block
 Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. NMOS Common-Source Circuit. NMOS Common-Source Circuit 10/15/2013. In this chapter, we will:
 Mcrelectrncs Crcut Analyss and Desn Dnald A. Neaen Chapter 4 Basc FET Aplfers In ths chapter, we wll: Inestate a snle-transstr crcut that can aplfy a sall, te-aryn nput snal Deelp sall-snal dels that are
Mcrelectrncs Crcut Analyss and Desn Dnald A. Neaen Chapter 4 Basc FET Aplfers In ths chapter, we wll: Inestate a snle-transstr crcut that can aplfy a sall, te-aryn nput snal Deelp sall-snal dels that are
5.1 Moment of a Force Scalar Formation
 Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
OBJECTIVE To investigate the parallel connection of R, L, and C. 1 Electricity & Electronics Constructor EEC470
 Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectional Mathematics 2006 Solution Set
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
Example 11: The man shown in Figure (a) pulls on the cord with a force of 70
 Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Electric potential energy Electrostatic force does work on a particle : Potential energy (: i initial state f : final state):
 Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
A) (0.46 î ) N B) (0.17 î ) N
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
hitt Phy2049: Magnetism 6/10/2011 Magnetic Field Units Force Between Two Parallel Currents Force Between Two Anti-Parallel Currents
 6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Winter 2011, F. Najmabadi
 Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
9/12/2013. Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. Modes of Operation. Cross Section of Integrated Circuit npn Transistor
 Mcoelectoncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Donald A. Neamen Chapte 5 The pola Juncton Tanssto In ths chapte, we wll: Dscuss the physcal stuctue and opeaton of the bpola juncton tanssto. Undestand the dc analyss
Mcoelectoncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Donald A. Neamen Chapte 5 The pola Juncton Tanssto In ths chapte, we wll: Dscuss the physcal stuctue and opeaton of the bpola juncton tanssto. Undestand the dc analyss
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONVERTER
 70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
Outline. Steady Heat Transfer with Conduction and Convection. Review Steady, 1-D, Review Heat Generation. Review Heat Generation II
 Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Exercises for Differential Amplifiers. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Execises f iffeential mplifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najmabai Execise : Cmpute,, an G if m, 00 Ω, O, an ientical Q &Q with µ n C x 8 m, t, λ 0. F G 0 an B F G. epeat the execise f λ 0. -. This execise shws
Execises f iffeential mplifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najmabai Execise : Cmpute,, an G if m, 00 Ω, O, an ientical Q &Q with µ n C x 8 m, t, λ 0. F G 0 an B F G. epeat the execise f λ 0. -. This execise shws
EEE2146 Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. MIC2: Investigation of Amplifier Parameters of a Common-Collector Amplifier
 EEE2146 Mcelectncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Expement MIC2 MIC2: Inestgatn f Amplfe Paametes f a Cmmn-Cllect Amplfe Ttal Pecentage: 5% (Fm 40% Cusewk Mak) 1. Objecte T nestgate the ltage and cuent gans and
EEE2146 Mcelectncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Expement MIC2 MIC2: Inestgatn f Amplfe Paametes f a Cmmn-Cllect Amplfe Ttal Pecentage: 5% (Fm 40% Cusewk Mak) 1. Objecte T nestgate the ltage and cuent gans and
Combustion Chamber. (0.1 MPa)
 ME 354 Tutial #10 Winte 001 Reacting Mixtues Pblem 1: Detemine the mle actins the pducts cmbustin when ctane, C 8 18, is buned with 00% theetical ai. Als, detemine the dew-pint tempeatue the pducts i the
ME 354 Tutial #10 Winte 001 Reacting Mixtues Pblem 1: Detemine the mle actins the pducts cmbustin when ctane, C 8 18, is buned with 00% theetical ai. Als, detemine the dew-pint tempeatue the pducts i the
Module B3. VLoad = = V S V LN
 Mdule B Prblem The -hase lads are cnnected n arallel. One s a urely resste lad cnnected n wye. t cnsumes 00kW. The secnd s a urely nducte 00kR lad cnnected n wye. The thrd s a urely caacte 00kR lad cnnected
Mdule B Prblem The -hase lads are cnnected n arallel. One s a urely resste lad cnnected n wye. t cnsumes 00kW. The secnd s a urely nducte 00kR lad cnnected n wye. The thrd s a urely caacte 00kR lad cnnected
Summary 7. ELECTROMAGNETIC JOINT. ROTATING MAGNETIC FIELD. SPACE-PHASOR THEORY... 2
 uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
4. The material balances for isothermal ideal reactor models
 Summay Geneal mateal balane f eatng system Bath eat Cntnuus-flw eats: CST (Cntnuus Sted Tank eat) P (Plug lw eat) Steady state f CST and P Desgn tasks : utlet (fnal nvesn), gven vlume f eat x vlume f eat,
Summay Geneal mateal balane f eatng system Bath eat Cntnuus-flw eats: CST (Cntnuus Sted Tank eat) P (Plug lw eat) Steady state f CST and P Desgn tasks : utlet (fnal nvesn), gven vlume f eat x vlume f eat,
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
Exercises for Cascode Amplifiers. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Execises f Cascde plifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabadi F. Najabadi, ECE0, Fall 0 /6 Execise : Cpute assue and Eey Cascde stae inceases by uble Cascde Execise : Cpute all indicated s, s, and i s. ssue tansists
Execises f Cascde plifies ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabadi F. Najabadi, ECE0, Fall 0 /6 Execise : Cpute assue and Eey Cascde stae inceases by uble Cascde Execise : Cpute all indicated s, s, and i s. ssue tansists
Common Gate Amplifier
 mmn Gate Ampler Fure (a) shs a cmmn ate ampler th deal current surce lad. Fure (b) shs the deal current surce mplemented by PMOS th cnstant ate t surce vltae. DD DD G M G M G M (a) (b) Fure. mmn ate ampler.
mmn Gate Ampler Fure (a) shs a cmmn ate ampler th deal current surce lad. Fure (b) shs the deal current surce mplemented by PMOS th cnstant ate t surce vltae. DD DD G M G M G M (a) (b) Fure. mmn ate ampler.
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Derivation of Lagrange Equations from D Alembert s Principle
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
V. Principles of Irreversible Thermodynamics. s = S - S 0 (7.3) s = = - g i, k. "Flux": = da i. "Force": = -Â g a ik k = X i. Â J i X i (7.
 Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
FYSE400 ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 YS400 NLOG LCONCS LCU 12 eedback plfer 1 uptn 1. he bac aplfer unlateral. 2. he gan OL f the bac aplfer deterned wthut feedback. 3. he calculated gan OL laded gan : ladng f the feedback netwrk, urce and
YS400 NLOG LCONCS LCU 12 eedback plfer 1 uptn 1. he bac aplfer unlateral. 2. he gan OL f the bac aplfer deterned wthut feedback. 3. he calculated gan OL laded gan : ladng f the feedback netwrk, urce and
A NEW FAMILY OF TRANSFORMERLESS MODULAR DC-DC CONVERTERS FOR HIGH POWER APPLICATIONS
 A NEW FAMIY OF TRANSFORMERESS MODUAR D-D ONVERTERS FOR HIGH POWER APPIATIONS by Abdelahman Haga A thess submtted n cnfmty wth the equements f the degee f Dct f Phlsphy Gaduate Depatment f Electcal and
A NEW FAMIY OF TRANSFORMERESS MODUAR D-D ONVERTERS FOR HIGH POWER APPIATIONS by Abdelahman Haga A thess submtted n cnfmty wth the equements f the degee f Dct f Phlsphy Gaduate Depatment f Electcal and
(8) Gain Stage and Simple Output Stage
 EEEB23 Electoncs Analyss & Desgn (8) Gan Stage and Smple Output Stage Leanng Outcome Able to: Analyze an example of a gan stage and output stage of a multstage amplfe. efeence: Neamen, Chapte 11 8.0) ntoducton
EEEB23 Electoncs Analyss & Desgn (8) Gan Stage and Smple Output Stage Leanng Outcome Able to: Analyze an example of a gan stage and output stage of a multstage amplfe. efeence: Neamen, Chapte 11 8.0) ntoducton
Set of square-integrable function 2 L : function space F
 Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. β f
 FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
Selective Convexity in Extended GDEA Model
 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 5, 20, n. 78, 386-3873 Selectve nvet n Etended GDEA Mdel Sevan Shaee a and Fahad Hssenadeh Ltf b a. Depatment f Mathematcs, ehan Nth Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian
Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 5, 20, n. 78, 386-3873 Selectve nvet n Etended GDEA Mdel Sevan Shaee a and Fahad Hssenadeh Ltf b a. Depatment f Mathematcs, ehan Nth Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian
CHAPTER 17. Solutions for Exercises. Using the expressions given in the Exercise statement for the currents, we have
 CHATER 7 Slutin f Execie E7. F Equatin 7.5, we have B gap Ki ( t ) c( θ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 0 ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 40 a b c ) Uing the expein given in the Execie tateent f the cuent, we have B gap K c( ωt )c(
CHATER 7 Slutin f Execie E7. F Equatin 7.5, we have B gap Ki ( t ) c( θ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 0 ) + Ki ( t ) c( θ 40 a b c ) Uing the expein given in the Execie tateent f the cuent, we have B gap K c( ωt )c(
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 PEATINAL AMPLIFIES Why do we study them at ths pont???. pamps are ery useful electronc components. We hae already the tools to analyze practcal crcuts usng pamps 3. The lnear models for pamps nclude dependent
PEATINAL AMPLIFIES Why do we study them at ths pont???. pamps are ery useful electronc components. We hae already the tools to analyze practcal crcuts usng pamps 3. The lnear models for pamps nclude dependent
is needed and this can be established by multiplying A, obtained in step 3, by, resulting V = A x y =. = x, located in 1 st quadrant rotated about 2
 Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
element k Using FEM to Solve Truss Problems
 sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
ANALOG ELECTRONICS 1 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
The Gradient and Applications This unit is based on Sections 9.5 and 9.6, Chapter 9. All assigned readings and exercises are from the textbook
 The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
March 15. Induction and Inductance Chapter 31
 Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
A) N B) 0.0 N C) N D) N E) N
 Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS
 P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
Oscillator. Introduction of Oscillator Linear Oscillator. Stability. Wien Bridge Oscillator RC Phase-Shift Oscillator LC Oscillator
 Oscillatr Intrductin f Oscillatr Linear Oscillatr Wien Bridge Oscillatr Phase-Shift Oscillatr L Oscillatr Stability Oscillatrs Oscillatin: an effect that repeatedly and regularly fluctuates abut the mean
Oscillatr Intrductin f Oscillatr Linear Oscillatr Wien Bridge Oscillatr Phase-Shift Oscillatr L Oscillatr Stability Oscillatrs Oscillatin: an effect that repeatedly and regularly fluctuates abut the mean
Electric Charge. Electric charge is quantized. Electric charge is conserved
 lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
Transient Conduction: Spatial Effects and the Role of Analytical Solutions
 Transent Cnductn: Spatal Effects and the Rle f Analytcal Slutns Slutn t the Heat Equatn fr a Plane Wall wth Symmetrcal Cnvectn Cndtns If the lumped capactance apprxmatn can nt be made, cnsderatn must be
Transent Cnductn: Spatal Effects and the Rle f Analytcal Slutns Slutn t the Heat Equatn fr a Plane Wall wth Symmetrcal Cnvectn Cndtns If the lumped capactance apprxmatn can nt be made, cnsderatn must be
BASIC ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND ANALYSIS. Ref: Horowitz, P, & W. Hill, The Art of Electronics, 2nd. ed., Cambridge (1989).
 BASC ELECTCAL CCUTS AND ANALYSS ef: Horowitz, P, & W. Hill, The Art of Electronics, nd. ed., Cambridge (989). CHAGE - symbol C, unit is coulomb; coulomb 6.45 0 8 electrons CUENT - symbol or i, unit is
BASC ELECTCAL CCUTS AND ANALYSS ef: Horowitz, P, & W. Hill, The Art of Electronics, nd. ed., Cambridge (989). CHAGE - symbol C, unit is coulomb; coulomb 6.45 0 8 electrons CUENT - symbol or i, unit is
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:041 Electonic icuits BJT eview Sections in hapte 5 & 6 in Textbook A. Kuge BJT eview, Page- 1 npn Output Family of uves A. Kuge BJT eview, Page- 2 npn BJT dc Equivalent evese biased Fowad biased i B
55:041 Electonic icuits BJT eview Sections in hapte 5 & 6 in Textbook A. Kuge BJT eview, Page- 1 npn Output Family of uves A. Kuge BJT eview, Page- 2 npn BJT dc Equivalent evese biased Fowad biased i B
Power Flow in Electromagnetic Waves. The time-dependent power flow density of an electromagnetic wave is given by the instantaneous Poynting vector
 Pwer Flw in Electrmagnetic Waves Electrmagnetic Fields The time-dependent pwer flw density f an electrmagnetic wave is given by the instantaneus Pynting vectr P t E t H t ( ) = ( ) ( ) Fr time-varying
Pwer Flw in Electrmagnetic Waves Electrmagnetic Fields The time-dependent pwer flw density f an electrmagnetic wave is given by the instantaneus Pynting vectr P t E t H t ( ) = ( ) ( ) Fr time-varying
CHAPTER 3: FEEDBACK. Dr. Wan Mahani Hafizah binti Wan Mahmud
 CHPTER 3: FEEDBCK Dr. Wan Mahan Hafzah bnt Wan Mahmud Feedback ntrductn Types f Feedback dvantages, Characterstcs and effect f Negatve Feedback mplfers Crcuts wth negatve feedback Pstve feedback and Oscllatr
CHPTER 3: FEEDBCK Dr. Wan Mahan Hafzah bnt Wan Mahmud Feedback ntrductn Types f Feedback dvantages, Characterstcs and effect f Negatve Feedback mplfers Crcuts wth negatve feedback Pstve feedback and Oscllatr
3. A Review of Some Existing AW (BT, CT) Algorithms
 3. A Revew of Some Exstng AW (BT, CT) Algothms In ths secton, some typcal ant-wndp algothms wll be descbed. As the soltons fo bmpless and condtoned tansfe ae smla to those fo ant-wndp, the pesented algothms
3. A Revew of Some Exstng AW (BT, CT) Algothms In ths secton, some typcal ant-wndp algothms wll be descbed. As the soltons fo bmpless and condtoned tansfe ae smla to those fo ant-wndp, the pesented algothms
EE 204 Lecture 25 More Examples on Power Factor and the Reactive Power
 EE 204 Lecture 25 Mre Examples n Pwer Factr and the Reactve Pwer The pwer factr has been defned n the prevus lecture wth an example n pwer factr calculatn. We present tw mre examples n ths lecture. Example
EE 204 Lecture 25 Mre Examples n Pwer Factr and the Reactve Pwer The pwer factr has been defned n the prevus lecture wth an example n pwer factr calculatn. We present tw mre examples n ths lecture. Example
Solution: (a) C 4 1 AI IC 4. (b) IBC 4
 C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
C A C C R A C R C R C sin 9 sin. A cuent f is maintaine in a single cicula lp f cicumfeence C. A magnetic fiel f is iecte paallel t the plane f the lp. (a) Calculate the magnetic mment f the lp. (b) What
BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS
 Brwn University Physics 0040 Intrductin BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS The measurements described here illustrate the peratin f resistrs and capacitrs in electric circuits, and the use f sme standard
Brwn University Physics 0040 Intrductin BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS The measurements described here illustrate the peratin f resistrs and capacitrs in electric circuits, and the use f sme standard
5. Differential Amplifiers
 5. iffeential plifies eain: Sea & Sith: Chapte 8 MOS ptins an Chapte.. ECE, Winte, F. Najabai iffeential an Cn-Me Sinals Cnsie a linea iuit with TWO inputs By supepsitin: efine: iffeene iffeential Me Cn
5. iffeential plifies eain: Sea & Sith: Chapte 8 MOS ptins an Chapte.. ECE, Winte, F. Najabai iffeential an Cn-Me Sinals Cnsie a linea iuit with TWO inputs By supepsitin: efine: iffeene iffeential Me Cn
Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 Chapte 4 Mtin in Tw and Thee Dimensins In this chapte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chapte t me aln a staiht line. Instead we will cnside mtin in a plane (tw dimensinal
Chapte 4 Mtin in Tw and Thee Dimensins In this chapte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chapte t me aln a staiht line. Instead we will cnside mtin in a plane (tw dimensinal
Optimization of the Electron Gun with a Permanent Ion Trap
 4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
Prof. Paolo Colantonio a.a
 Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
Big Data Analytics! Special Topics for Computer Science CSE CSE Mar 31
 Bg Data Analytcs! Specal Tpcs fr Cmputer Scence CSE 4095-001 CSE 5095-005! Mar 31 Fe Wang Asscate Prfessr Department f Cmputer Scence and Engneerng fe_wang@ucnn.edu Intrductn t Deep Learnng Perceptrn In
Bg Data Analytcs! Specal Tpcs fr Cmputer Scence CSE 4095-001 CSE 5095-005! Mar 31 Fe Wang Asscate Prfessr Department f Cmputer Scence and Engneerng fe_wang@ucnn.edu Intrductn t Deep Learnng Perceptrn In
The two main types of FETs are the junction field effect transistor (JFET) and the metal oxide field effect transistor (MOSFET).
 Mcrelectrncs Chapter three: Feld Effect Transstr sall snal analyss Intrductn: Feld-effect transstr aplfers prde an excellent ltae an wth the added feature f hh nput pedance. They are als lw-pwercnsuptn
Mcrelectrncs Chapter three: Feld Effect Transstr sall snal analyss Intrductn: Feld-effect transstr aplfers prde an excellent ltae an wth the added feature f hh nput pedance. They are als lw-pwercnsuptn
III. Operational Amplifiers
 III. Operatnal Amplfers Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput vltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput vltage r current. Fur dfferent knds f amplfers ext: ltage amplfer: Current amplfer:
III. Operatnal Amplfers Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput vltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput vltage r current. Fur dfferent knds f amplfers ext: ltage amplfer: Current amplfer:
Summary of DLT method for stereo camera calibration, 3D reconstruction and robot-camera integration
 tes n T Smma f T meth f stee camea calbatn, ecnstctn an bt-camea ntegatn. amea calbatn Statng pnt: pespecte eqatns f a camea These eqatns map the cnates f a genec pnt n space,, nt the cespnng cnates n
tes n T Smma f T meth f stee camea calbatn, ecnstctn an bt-camea ntegatn. amea calbatn Statng pnt: pespecte eqatns f a camea These eqatns map the cnates f a genec pnt n space,, nt the cespnng cnates n
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 12: Applications of the Golden Rules for Negative Feedback
 PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
Summary chapter 4. Electric field s can distort charge distributions in atoms and molecules by stretching and rotating:
 Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up
 AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up S what d yu need t knw abut this mtin in tw-dimensin stuff t get a gd scre n the ld AP Physics Test? First ff, here are the equatins that yu ll have t wrk with: v v at x x
AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up S what d yu need t knw abut this mtin in tw-dimensin stuff t get a gd scre n the ld AP Physics Test? First ff, here are the equatins that yu ll have t wrk with: v v at x x
6. Introduction to Transistor Amplifiers: Concepts and Small-Signal Model
 6. ntoucton to anssto mples: oncepts an Small-Sgnal Moel Lectue notes: Sec. 5 Sea & Smth 6 th E: Sec. 5.4, 5.6 & 6.3-6.4 Sea & Smth 5 th E: Sec. 4.4, 4.6 & 5.3-5.4 EE 65, Wnte203, F. Najmaba Founaton o
6. ntoucton to anssto mples: oncepts an Small-Sgnal Moel Lectue notes: Sec. 5 Sea & Smth 6 th E: Sec. 5.4, 5.6 & 6.3-6.4 Sea & Smth 5 th E: Sec. 4.4, 4.6 & 5.3-5.4 EE 65, Wnte203, F. Najmaba Founaton o
β A Constant-G m Biasing
 p 2002 EE 532 Anal IC Des II Pae 73 Cnsan-G Bas ecall ha us a PTAT cuen efeence (see p f p. 66 he nes) bas a bpla anss pes cnsan anscnucance e epeaue (an als epenen f supply lae an pcess). Hw h we achee
p 2002 EE 532 Anal IC Des II Pae 73 Cnsan-G Bas ecall ha us a PTAT cuen efeence (see p f p. 66 he nes) bas a bpla anss pes cnsan anscnucance e epeaue (an als epenen f supply lae an pcess). Hw h we achee
Amplifier Constant Gain and Noise
 Amplfe Constant Gan and ose by Manfed Thumm and Wene Wesbeck Foschungszentum Kalsuhe n de Helmholtz - Gemenschaft Unvestät Kalsuhe (TH) Reseach Unvesty founded 85 Ccles of Constant Gan (I) If s taken to
Amplfe Constant Gan and ose by Manfed Thumm and Wene Wesbeck Foschungszentum Kalsuhe n de Helmholtz - Gemenschaft Unvestät Kalsuhe (TH) Reseach Unvesty founded 85 Ccles of Constant Gan (I) If s taken to
Copyright Paul Tobin 63
 DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
 Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Opeatinal Aplifies Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Fall 01, D. Guxing Wang 1 Outline Mdel f Opeatinal Aplifies Tw Stage CMOS Op Ap Telescpic Op Ap Flded-Cascde Op Ap Refeence
Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Opeatinal Aplifies Design f Analg Integated Cicuits Fall 01, D. Guxing Wang 1 Outline Mdel f Opeatinal Aplifies Tw Stage CMOS Op Ap Telescpic Op Ap Flded-Cascde Op Ap Refeence
Circuits Op-Amp. Interaction of Circuit Elements. Quick Check How does closing the switch affect V o and I o?
 Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Phys 331: Ch 9,.6-.7 Noninertial Frames: Centrifugal and Corriolis forces 1. And and
 Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
1. Transformer A transformer is used to obtain the approximate output voltage of the power supply. The output of the transformer is still AC.
 PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
A) 100 K B) 150 K C) 200 K D) 250 K E) 350 K
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
CHAPTER GAUSS'S LAW
 lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
ALL QUESTIONS ARE WORTH 20 POINTS. WORK OUT FIVE PROBLEMS.
 GNRAL PHYSICS PH -3A (D. S. Mov) Test (/3/) key STUDNT NAM: STUDNT d #: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GNRAL PHYSICS PH -3A (D. S. Mov) Test (/3/) key STUDNT NAM: STUDNT d #: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hotelling s Rule. Therefore arbitrage forces P(t) = P o e rt.
 Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
