Quantum Physics Notes-7 Operators, Observables, Understanding QM. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 1
|
|
|
- Debra Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quantum Physics 2005 Notes-7 Operators, Observables, Understanding QM Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005
2 A summary of this section This section of notes is a brief overview of the ideas in chapters 0-2 of Morrison. These chapters are the intellectual core of uantum mechanics (as opposed to uantum physics). You will address the material in chapters 0-2 with greater care in Intro to Quantum Mechanics. The purpose of these notes is only to introduce these ideas, especially for those students who will not take Intro to Quantum Mechanics. I will therefore skip lightly through these chapters, picking only the most important concepts. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 2
3 Operators Dirac notation Dirac Notation - "bra"= "ket"= Q =! Qˆ! =! Qˆ! dx * allspace! Qˆ! =! Qˆ! dx * 2 2 allspace * 2 allspace!! =!! dx =expectation value =matrix element =overlap integral ) Take the complex conjugate of the function inside the 2) Act with the operator on the function to its right. 3) Integrate the integrand over all space. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 3
4 Hermitian Operators Qˆ is Hermitian if for any two physically admissible state functions! Qˆ! = Qˆ!! 2 2 ( * ) * Qˆ!! ˆ 2 " Q!! 2dx If an operator is Hermitian, the expectation value of that operator will be real. All operators for physical uantities are Hermitian. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 4
5 Is p Hermitian? We will check explicitly whether % pˆ = $ ih % x Start by integrating! pˆ! 2! pˆ! = pˆ!!. by parts. 2 2 # # * % * # % *! ˆ p! 2 =! $ ih! 2 dx i 2 2 dx x = $ h!! $!! $# $# % $# % x # % # * % = ih! 2! dx =! 2 $ i! $# % x h % x $# Therefore p ˆ is Hermitian. * dx = pˆ!! 2 Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 5
6 Exercise Show by writing out the real space integral representation that the operator x ˆ is Hermitian. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 6
7 Operators and Eigenvalues In uantum physics, the form of the eigenvalue euation for an observable Aˆ with eigenstate & and eigenvalue a is: Aˆ & = a&. a The collection of all eigenvalues is called the spectrum of this operator. a The most familiar eigenstate is the stationary state. & $ iet / h which satisfies: ˆ! e H E E = E! =! In an eigenstate of an observable, the uncertainty in that observable is zero. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 7
8 The eigenstate of one observable might not be an eigenstate of another observable (but it can happen ). Example- An energy eigenstate of the suare well is: 2 ( x E h( ( x, t) Acos e with ' L h 2mL $ i' t! = = = % Is this an energy eigenstate of momentum pˆ = $ ih? % x % ( x $ i' t ( ( x $ i' t pˆ! = $ ih Acos e = iha sin e ) p! NO! % x L L L Another example: An energy eigenstate of the free wave is:! = % i( kx-' t) pˆ! = $ ih Ae = hk! YES> % x ( -' t) Notes 6 Quantum Physics F Ae i kx.
9 Hermiticity: Real eigenvalues and orthonormal eigenfunctions The eigenvalues of a Hermitian operator are real. The eigenvalues of a Hermitian operator are the only values that we can observe in a measurement of that observable. AND The eigenfunctions of a Hermitian operator are orthogonal, constitute a complete set, and satisfy closure. (p 465, Morrison). Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 9
10 Proof of orthogonality Take two different eigenstates of the same observable: ) Qˆ & = & and 2) Qˆ & = '& ' ' We want to demonstrate that & Qˆ & = & & = ' ' Notes 6 Quantum Physics F ' = 0. Multiply both sides of ) by complex conjugate of & : Use Hermiticity of Q ˆ to simplfy the LHS: & Qˆ & = Qˆ & & = '& & = '* & & = ' & & ' ' ' ' ' So we have so & ' & ( ) = 0 ' & - ' & & = 0, but we assumed ) ' & '
11 Hermiticity: Completeness Completeness of a set of eigenfunctions means that any well-behaved function of the variables on which the eigenfunctions depend can be expanded upon the set. ) f = c & We can choose to represent any function in a given range of variables by an expansion in a set of eigenfunctions of any operator. It's easy to find the coefficients ' ' ' ' Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 c. Multiply ) by & f = & c & = c & c & = c The coefficient c is the "projection" of f onto the eigenfunction & & '
12 Summarizing Eigenfunction Expansions Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 2
13 The meaning and use of expansions The collection of coefficients in the expansion of a state function in any complete set is merely an alternate way to represent the state function. These coefficients and the eigenfunctions contain the same information as the state function. Expressing a state function in terms of eigenfunctions can make apparent some properties of the state function. Expressing the state function in terms of eigenfunctions can allow us to get information about other variables. (Expressing the wavefunction (position variable) in terms of momentum eigenfunctions allows us to determine the momentum properties of the state function.) Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 3
14 Using expansions to calculate expectation values If we have a wavefunction that is not an eigenfunction of a given operator, the expectation value may be hard to calculate in the old way. Expanding the wavefunction in terms of the eigenfunctions of that operator may make things easier. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 4
15 Calculation of the mean Q ( t) =! * Qˆ! dx [ & ] = c t x Qˆ c t x dx * n' ( ) n' ( ) n ( )& n( ) * [ ( )& ( )] [ ( ) & ( )] = c t x c t x dx n' n' n n n * 2 cn' cn & n' & n cn n n' n n = = If we know the projection coefficients, we know the expectation value. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 5
16 Example Calculate the expected value of the energy for the following non-stationary state of the SHO. $ i' t $ i' 2t!( x, t) = & e + & e $ i' 7 t $ i' 2t c ( t) = e ; c2( t) = e (all others=0) # E ( t) = cn En = h' 0 + h' 0 = h' 0 n= Note that any individual measurement of E will yield an eigenenergy. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 6
17 The Commutator A simultaneous eigenstate is one whose state function is an eigenstate of two operators: Qˆ & = & and Rˆ & = r&, r, r, r, r Because they are eigenstates: Q = * Q = 0 and R = r * R = 0 Qˆ, Rˆ = QR ˆ ˆ - RQ ˆ ˆ = 0 ) Operators that commute define a complete set of simultaneous eigenfunctions. 2) Two operators that share a complete set of eigenfunctions commute. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 7
18 Commutators and uncertainty principles If operators R ˆ and Q ˆ commute, then they share simultaneous eigenfunctions. Measurement of each observable for an eigenfunction yields a precise value. The only uncertainty relation that can apply is: * Q* R, 0. A Generalized Uncertainty Principle: * Q* R, 2 i Qˆ, Rˆ (For momentum and position: [ xˆ pˆ ], = ih) ˆ If Qˆ, Rˆ ) 0 then there exist no eigenstates of either observable. (Think about + ( x) and e - i( kx-' t ).) Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 8
19 Commutators of x and p Notes 6 Quantum Physics F2005 9
20 An aside Charles Hermite (December 24, January 4, 90) was a French mathematician who did research on number theory, uadratic forms, invariant theory, orthogonal polynomials, elliptic functions, and algebra. Hermite polynomials, Hermite normal form, Hermitian operators, and cubic Hermite splines are named in his honor. He was the first to prove that e, the base of natural logarithms, is a transcendental number. His methods were later used by Ferdinand von Lindemann for the proof of his celebrated theorem that π is transcendental. Upon Weierstrass' discovery in 86 of continuous curves that are nowhere differentiable - they possess no tangent at any point - Hermite famously remarked: I turn aside with a shudder of horror from this lamentable plague of functions which have no derivatives. Notes 6 Quantum Physics F
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics
 II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
II. The Machinery of Quantum Mechanics Based on the results of the experiments described in the previous section, we recognize that real experiments do not behave quite as we expect. This section presents
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS. Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5
 BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements
 Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements Today s Program: 1. Simple Harmonic Oscillator (SHO). Principle of spectral decomposition. 3. Predicting the results of measurements, fourth postulate
Lecture 6 Quantum Mechanical Systems and Measurements Today s Program: 1. Simple Harmonic Oscillator (SHO). Principle of spectral decomposition. 3. Predicting the results of measurements, fourth postulate
Harmonic Oscillator with raising and lowering operators. We write the Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator in one dimension as follows:
 We write the Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator in one dimension as follows: H ˆ! = "!2 d 2! + 1 2µ dx 2 2 kx 2! = E! T ˆ = "! 2 2µ d 2 dx 2 V ˆ = 1 2 kx 2 H ˆ = ˆ T + ˆ V (1) where µ is
We write the Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator in one dimension as follows: H ˆ! = "!2 d 2! + 1 2µ dx 2 2 kx 2! = E! T ˆ = "! 2 2µ d 2 dx 2 V ˆ = 1 2 kx 2 H ˆ = ˆ T + ˆ V (1) where µ is
The Schrodinger Wave Equation (Engel 2.4) In QM, the behavior of a particle is described by its wave function Ψ(x,t) which we get by solving:
 When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
1. Quantum Mechanics, Cohen Tannoudji, Chapters Linear Algebra, Schaum Series 3. Quantum Chemistry Ch. 6
 Lecture # Today s Program 1. Recap: Classical States, Hamiltonians and time evolution. First postulate The description of a state of a system. 3. Second postulate physical quantities. 4. Linear operators.
Lecture # Today s Program 1. Recap: Classical States, Hamiltonians and time evolution. First postulate The description of a state of a system. 3. Second postulate physical quantities. 4. Linear operators.
Page 404. Lecture 22: Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 2008/11/19 Date Revised: 2008/11/19
 Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
Page 404 Lecture : Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Energy Basis Date Given: 008/11/19 Date Revised: 008/11/19 Coordinate Basis Section 6. The One-Dimensional Simple Harmonic Oscillator: Coordinate Basis Page
Properties of Commutators and Schroedinger Operators and Applications to Quantum Computing
 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Research Technology (IJEART) Properties of Commutators and Schroedinger Operators and Applications to Quantum Computing N. B. Okelo Abstract In this paper
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Research Technology (IJEART) Properties of Commutators and Schroedinger Operators and Applications to Quantum Computing N. B. Okelo Abstract In this paper
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
 The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules The postulates of quantum mechanics Dr Grant Ritchie The postulates.. 1. Associated with any particle moving in a conservative field of force is a wave function,
Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics
 Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics In classical mechanics the angular momentum L = r p of any particle moving in a central field of force is conserved. For the reduced two-body problem this is the content
Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics In classical mechanics the angular momentum L = r p of any particle moving in a central field of force is conserved. For the reduced two-body problem this is the content
An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually).
 Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case:
 The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2004 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics II (8.5) Fall 24 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 3, 24 September 23, 24 7:pm This week we continue to study the basic principles of quantum
Quantum Physics II (8.5) Fall 24 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 3, 24 September 23, 24 7:pm This week we continue to study the basic principles of quantum
Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Classical harmonic oscillator Linear force acting on a particle (Hooke s law): F =!kx From Newton s law: F = ma = m d x dt =!kx " d x dt + # x = 0, # = k / m Position and momentum solutions oscillate in
Classical harmonic oscillator Linear force acting on a particle (Hooke s law): F =!kx From Newton s law: F = ma = m d x dt =!kx " d x dt + # x = 0, # = k / m Position and momentum solutions oscillate in
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics. EE270 Fall 2017
 Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
Supplementary information I Hilbert Space, Dirac Notation, and Matrix Mechanics Properties of Vector Spaces Unit vectors ~xi form a basis which spans the space and which are orthonormal ( if i = j ~xi
Statistical Interpretation
 Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
Physics 342 Lecture 15 Statistical Interpretation Lecture 15 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Friday, February 29th, 2008 Quantum mechanics is a theory of probability densities given that we now have an
The Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 The Simple Harmonic Oscillator Asaf Pe er 1 November 4, 215 This part of the course is based on Refs [1] [3] 1 Introduction We return now to the study of a 1-d stationary problem: that of the simple harmonic
The Simple Harmonic Oscillator Asaf Pe er 1 November 4, 215 This part of the course is based on Refs [1] [3] 1 Introduction We return now to the study of a 1-d stationary problem: that of the simple harmonic
1 Mathematical preliminaries
 1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
1 Mathematical preliminaries The mathematical language of quantum mechanics is that of vector spaces and linear algebra. In this preliminary section, we will collect the various definitions and mathematical
Summary: angular momentum derivation
 Summary: angular momentum derivation L = r p L x = yp z zp y, etc. [x, p y ] = 0, etc. (-) (-) (-3) Angular momentum commutation relations [L x, L y ] = i hl z (-4) [L i, L j ] = i hɛ ijk L k (-5) Levi-Civita
Summary: angular momentum derivation L = r p L x = yp z zp y, etc. [x, p y ] = 0, etc. (-) (-) (-3) Angular momentum commutation relations [L x, L y ] = i hl z (-4) [L i, L j ] = i hɛ ijk L k (-5) Levi-Civita
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1
 Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 February 1, 2017 1 / 13
Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University February 1, 2017 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Linear Algebra and Dirac Notation, Pt. 1 February 1, 2017 1 / 13
Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space
 Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation
 1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors,
 chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 5, January 27, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
df(x) = h(x) dx Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 2009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation
 Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
Chemistry 4531 Mathematical Preliminaries Spring 009 I. A Primer on Differential Equations Order of differential equation Linearity of differential equation Partial vs. Ordinary Differential Equations
Quantum mechanics in one hour
 Chapter 2 Quantum mechanics in one hour 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to refresh your knowledge of quantum mechanics and to establish notation. Depending on your background you might
Chapter 2 Quantum mechanics in one hour 2.1 Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to refresh your knowledge of quantum mechanics and to establish notation. Depending on your background you might
8.04 Spring 2013 March 12, 2013 Problem 1. (10 points) The Probability Current
 Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
Prolem Set 5 Solutions 8.04 Spring 03 March, 03 Prolem. (0 points) The Proaility Current We wish to prove that dp a = J(a, t) J(, t). () dt Since P a (t) is the proaility of finding the particle in the
Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Dirac Notation Formalism of Quantum Mechanics We can use a shorthand notation for the normalization integral I = "! (r,t) 2 dr = "! * (r,t)! (r,t) dr =!! The state! is called a ket. The complex conjugate
Dirac Notation Formalism of Quantum Mechanics We can use a shorthand notation for the normalization integral I = "! (r,t) 2 dr = "! * (r,t)! (r,t) dr =!! The state! is called a ket. The complex conjugate
Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle
 Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle Superposition add states together, get new states. Math quantity associated with states must also have this property. Vectors have this property.
Mathematical Formulation of the Superposition Principle Superposition add states together, get new states. Math quantity associated with states must also have this property. Vectors have this property.
Can we derive Newton s F = ma from the SE?
 8.04 Quantum Physics Lecture XIII p = pˆ (13-1) ( ( ) ) = xψ Ψ (13-) ( ) = xψ Ψ (13-3) [ ] = x (ΨΨ ) Ψ Ψ (13-4) ( ) = xψ Ψ (13-5) = p, (13-6) where again we have use integration by parts an the fact that
8.04 Quantum Physics Lecture XIII p = pˆ (13-1) ( ( ) ) = xψ Ψ (13-) ( ) = xψ Ψ (13-3) [ ] = x (ΨΨ ) Ψ Ψ (13-4) ( ) = xψ Ψ (13-5) = p, (13-6) where again we have use integration by parts an the fact that
Lecture #1. Review. Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1
 L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
L1.P1 Lecture #1 Review Postulates of quantum mechanics (1-3) Postulate 1 The state of a system at any instant of time may be represented by a wave function which is continuous and differentiable. Specifically,
Quantum Mechanics- I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Quantum Mechanics- I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 6 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics II (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) In my last lecture,
Quantum Mechanics- I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 6 Postulates of Quantum Mechanics II (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) In my last lecture,
Quantum Mechanics-I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 21 Square-Integrable Functions
 Quantum Mechanics-I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Square-Integrable Functions (Refer Slide Time: 00:06) (Refer Slide Time: 00:14) We
Quantum Mechanics-I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Square-Integrable Functions (Refer Slide Time: 00:06) (Refer Slide Time: 00:14) We
Lecture 3 Dynamics 29
 Lecture 3 Dynamics 29 30 LECTURE 3. DYNAMICS 3.1 Introduction Having described the states and the observables of a quantum system, we shall now introduce the rules that determine their time evolution.
Lecture 3 Dynamics 29 30 LECTURE 3. DYNAMICS 3.1 Introduction Having described the states and the observables of a quantum system, we shall now introduce the rules that determine their time evolution.
( ) ( ) ( ) Invariance Principles & Conservation Laws. = P δx. Summary of key point of argument
 Invariance Principles & Conservation Laws Without invariance principles, there would be no laws of physics! We rely on the results of experiments remaining the same from day to day and place to place.
Invariance Principles & Conservation Laws Without invariance principles, there would be no laws of physics! We rely on the results of experiments remaining the same from day to day and place to place.
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 6, January 30, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 6, January 30, 2006 Solved Homework We are given that A" = a" and A * " = a" where
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Spring Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 6, January 30, 2006 Solved Homework We are given that A" = a" and A * " = a" where
CHAPTER NUMBER 7: Quantum Theory: Introduction and Principles
 CHAPTER NUMBER 7: Quantum Theory: Introduction and Principles Art PowerPoints Peter Atkins & Julio De Paula 2010 1 mm 1000 m 100 m 10 m 1000 nm 100 nm 10 nm 1 nm 10 Å 1 Å Quantum phenomena 7.1 Energy quantization
CHAPTER NUMBER 7: Quantum Theory: Introduction and Principles Art PowerPoints Peter Atkins & Julio De Paula 2010 1 mm 1000 m 100 m 10 m 1000 nm 100 nm 10 nm 1 nm 10 Å 1 Å Quantum phenomena 7.1 Energy quantization
1 Measurement and expectation values
 C/CS/Phys 191 Measurement and expectation values, Intro to Spin 2/15/05 Spring 2005 Lecture 9 1 Measurement and expectation values Last time we discussed how useful it is to work in the basis of energy
C/CS/Phys 191 Measurement and expectation values, Intro to Spin 2/15/05 Spring 2005 Lecture 9 1 Measurement and expectation values Last time we discussed how useful it is to work in the basis of energy
Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam 2 Solutions
 Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
Chemistry 46 Fall 7 Dr. Jean M. Standard Name SAMPE EXAM Sample Quantum Chemistry Exam Solutions.) ( points) Answer the following questions by selecting the correct answer from the choices provided. a.)
Lecture 6. Four postulates of quantum mechanics. The eigenvalue equation. Momentum and energy operators. Dirac delta function. Expectation values
 Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
Lecture 6 Four postulates of quantum mechanics The eigenvalue equation Momentum and energy operators Dirac delta function Expectation values Objectives Learn about eigenvalue equations and operators. Learn
Chapter III. Quantum Computation. Mathematical preliminaries. A.1 Complex numbers. A.2 Linear algebra review
 Chapter III Quantum Computation These lecture notes are exclusively for the use of students in Prof. MacLennan s Unconventional Computation course. c 2017, B. J. MacLennan, EECS, University of Tennessee,
Chapter III Quantum Computation These lecture notes are exclusively for the use of students in Prof. MacLennan s Unconventional Computation course. c 2017, B. J. MacLennan, EECS, University of Tennessee,
Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017)
 Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Lecture 1 8.321 Quantum Theory I, Fall 2017 1 Recitation 1 (Sep. 15, 2017) 1.1 Simultaneous Diagonalization In the last lecture, we discussed the situations in which two operators can be simultaneously
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers. David Miller
 Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector space Vector space We need a space in which our vectors exist
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector space Vector space We need a space in which our vectors exist
Section 9 Variational Method. Page 492
 Section 9 Variational Method Page 492 Page 493 Lecture 27: The Variational Method Date Given: 2008/12/03 Date Revised: 2008/12/03 Derivation Section 9.1 Variational Method: Derivation Page 494 Motivation
Section 9 Variational Method Page 492 Page 493 Lecture 27: The Variational Method Date Given: 2008/12/03 Date Revised: 2008/12/03 Derivation Section 9.1 Variational Method: Derivation Page 494 Motivation
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Assignment 3
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 00 Assignment Readings The readings below will take you through the material for Problem Sets and 4. Cohen-Tannoudji Ch. II, III. Shankar Ch. 1 continues to be helpful. Sakurai
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations
 PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
PHYS-454 The position and momentum representations 1 Τhe continuous spectrum-a n So far we have seen problems where the involved operators have a discrete spectrum of eigenfunctions and eigenvalues.! n
Postulates and Theorems of Quantum Mechanics
 Postulates and Theorems of Quantum Mechanics Literally, a postulate is something taen as self-evident or assumed without proof as a basis for reasoning. It is simply is Postulate 1: State of a physical
Postulates and Theorems of Quantum Mechanics Literally, a postulate is something taen as self-evident or assumed without proof as a basis for reasoning. It is simply is Postulate 1: State of a physical
Physics 215 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 1
 Physics 5 Quantum Mechanics Assignment Logan A. Morrison January 9, 06 Problem Prove via the dual correspondence definition that the hermitian conjugate of α β is β α. By definition, the hermitian conjugate
Physics 5 Quantum Mechanics Assignment Logan A. Morrison January 9, 06 Problem Prove via the dual correspondence definition that the hermitian conjugate of α β is β α. By definition, the hermitian conjugate
Optional Problems on the Harmonic Oscillator
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 9 Optional Problems on the Harmonic Oscillator. Coherent States Consider a state ϕ α which is an eigenstate
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 9 Optional Problems on the Harmonic Oscillator. Coherent States Consider a state ϕ α which is an eigenstate
6.2 Unitary and Hermitian operators
 6.2 Unitary and Hermitian operators Slides: Video 6.2.1 Using unitary operators Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Section 4.10 (starting from Changing the representation of
6.2 Unitary and Hermitian operators Slides: Video 6.2.1 Using unitary operators Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Section 4.10 (starting from Changing the representation of
Physics 70007, Fall 2009 Answers to Final Exam
 Physics 70007, Fall 009 Answers to Final Exam December 17, 009 1. Quantum mechanical pictures a Demonstrate that if the commutation relation [A, B] ic is valid in any of the three Schrodinger, Heisenberg,
Physics 70007, Fall 009 Answers to Final Exam December 17, 009 1. Quantum mechanical pictures a Demonstrate that if the commutation relation [A, B] ic is valid in any of the three Schrodinger, Heisenberg,
The Klein Gordon Equation
 December 30, 2016 7:35 PM 1. Derivation Let s try to write down the correct relativistic equation of motion for a single particle and then quantize as usual. a. So take (canonical momentum) The Schrödinger
December 30, 2016 7:35 PM 1. Derivation Let s try to write down the correct relativistic equation of motion for a single particle and then quantize as usual. a. So take (canonical momentum) The Schrödinger
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19. Problem Set 6. Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19 Problem Set 6 Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all, G, H Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga.
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Tuesday March 19 Problem Set 6 Due Wednesday April 3 at 10.00AM Assigned Reading: E&R 6 all, G, H Li. 7 1 9, 8 1 Ga.
Page 52. Lecture 3: Inner Product Spaces Dual Spaces, Dirac Notation, and Adjoints Date Revised: 2008/10/03 Date Given: 2008/10/03
 Page 5 Lecture : Inner Product Spaces Dual Spaces, Dirac Notation, and Adjoints Date Revised: 008/10/0 Date Given: 008/10/0 Inner Product Spaces: Definitions Section. Mathematical Preliminaries: Inner
Page 5 Lecture : Inner Product Spaces Dual Spaces, Dirac Notation, and Adjoints Date Revised: 008/10/0 Date Given: 008/10/0 Inner Product Spaces: Definitions Section. Mathematical Preliminaries: Inner
in terms of the classical frequency, ω = , puts the classical Hamiltonian in the form H = p2 2m + mω2 x 2
 One of the most important problems in quantum mechanics is the simple harmonic oscillator, in part because its properties are directly applicable to field theory. The treatment in Dirac notation is particularly
One of the most important problems in quantum mechanics is the simple harmonic oscillator, in part because its properties are directly applicable to field theory. The treatment in Dirac notation is particularly
Chapter 2. Linear Algebra. rather simple and learning them will eventually allow us to explain the strange results of
 Chapter 2 Linear Algebra In this chapter, we study the formal structure that provides the background for quantum mechanics. The basic ideas of the mathematical machinery, linear algebra, are rather simple
Chapter 2 Linear Algebra In this chapter, we study the formal structure that provides the background for quantum mechanics. The basic ideas of the mathematical machinery, linear algebra, are rather simple
Physics 505 Homework No. 1 Solutions S1-1
 Physics 505 Homework No s S- Some Preliminaries Assume A and B are Hermitian operators (a) Show that (AB) B A dx φ ABψ dx (A φ) Bψ dx (B (A φ)) ψ dx (B A φ) ψ End (b) Show that AB [A, B]/2+{A, B}/2 where
Physics 505 Homework No s S- Some Preliminaries Assume A and B are Hermitian operators (a) Show that (AB) B A dx φ ABψ dx (A φ) Bψ dx (B (A φ)) ψ dx (B A φ) ψ End (b) Show that AB [A, B]/2+{A, B}/2 where
Reading: Mathchapters F and G, MQ - Ch. 7-8, Lecture notes on hydrogen atom.
 Chemistry 356 017: Problem set No. 6; Reading: Mathchapters F and G, MQ - Ch. 7-8, Lecture notes on hydrogen atom. The H atom involves spherical coordinates and angular momentum, which leads to the shapes
Chemistry 356 017: Problem set No. 6; Reading: Mathchapters F and G, MQ - Ch. 7-8, Lecture notes on hydrogen atom. The H atom involves spherical coordinates and angular momentum, which leads to the shapes
B. Physical Observables Physical observables are represented by linear, hermitian operators that act on the vectors of the Hilbert space. If A is such
 G25.2651: Statistical Mechanics Notes for Lecture 12 I. THE FUNDAMENTAL POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS The fundamental postulates of quantum mechanics concern the following questions: 1. How is the physical
G25.2651: Statistical Mechanics Notes for Lecture 12 I. THE FUNDAMENTAL POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS The fundamental postulates of quantum mechanics concern the following questions: 1. How is the physical
Mathematical Methods wk 1: Vectors
 Mathematical Methods wk : Vectors John Magorrian, magog@thphysoxacuk These are work-in-progress notes for the second-year course on mathematical methods The most up-to-date version is available from http://www-thphysphysicsoxacuk/people/johnmagorrian/mm
Mathematical Methods wk : Vectors John Magorrian, magog@thphysoxacuk These are work-in-progress notes for the second-year course on mathematical methods The most up-to-date version is available from http://www-thphysphysicsoxacuk/people/johnmagorrian/mm
Mathematical Methods wk 1: Vectors
 Mathematical Methods wk : Vectors John Magorrian, magog@thphysoxacuk These are work-in-progress notes for the second-year course on mathematical methods The most up-to-date version is available from http://www-thphysphysicsoxacuk/people/johnmagorrian/mm
Mathematical Methods wk : Vectors John Magorrian, magog@thphysoxacuk These are work-in-progress notes for the second-year course on mathematical methods The most up-to-date version is available from http://www-thphysphysicsoxacuk/people/johnmagorrian/mm
Generators for Continuous Coordinate Transformations
 Page 636 Lecture 37: Coordinate Transformations: Continuous Passive Coordinate Transformations Active Coordinate Transformations Date Revised: 2009/01/28 Date Given: 2009/01/26 Generators for Continuous
Page 636 Lecture 37: Coordinate Transformations: Continuous Passive Coordinate Transformations Active Coordinate Transformations Date Revised: 2009/01/28 Date Given: 2009/01/26 Generators for Continuous
Lecture 8. 1 Uncovering momentum space 1. 2 Expectation Values of Operators 4. 3 Time dependence of expectation values 6
 Lecture 8 B. Zwiebach February 29, 206 Contents Uncovering momentum space 2 Expectation Values of Operators 4 Time dependence of expectation values 6 Uncovering momentum space We now begin a series of
Lecture 8 B. Zwiebach February 29, 206 Contents Uncovering momentum space 2 Expectation Values of Operators 4 Time dependence of expectation values 6 Uncovering momentum space We now begin a series of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS
 MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
( ) = 9φ 1, ( ) = 4φ 2.
 Chemistry 46 Dr Jean M Standard Homework Problem Set 6 Solutions The Hermitian operator A ˆ is associated with the physical observable A Two of the eigenfunctions of A ˆ are and These eigenfunctions are
Chemistry 46 Dr Jean M Standard Homework Problem Set 6 Solutions The Hermitian operator A ˆ is associated with the physical observable A Two of the eigenfunctions of A ˆ are and These eigenfunctions are
Physics 215 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 5
 Physics 15 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 5 Logan A. Morrison February 10, 016 Problem 1 A particle of mass m is confined to a one-dimensional region 0 x a. At t 0 its normalized wave function is 8 πx
Physics 15 Quantum Mechanics 1 Assignment 5 Logan A. Morrison February 10, 016 Problem 1 A particle of mass m is confined to a one-dimensional region 0 x a. At t 0 its normalized wave function is 8 πx
Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012
 PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
E = hν light = hc λ = ( J s)( m/s) m = ev J = ev
 Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
Problem The ionization potential tells us how much energy we need to use to remove an electron, so we know that any energy left afterwards will be the kinetic energy of the ejected electron. So first we
Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Exercises on Quantum Expectation Values (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) In the last couple
Quantum Mechanics - I Prof. Dr. S. Lakshmi Bala Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Exercises on Quantum Expectation Values (Refer Slide Time: 00:07) In the last couple
Lecture 4 (Sep. 18, 2017)
 Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
Lecture 4 8.3 Quantum Theory I, Fall 07 Lecture 4 (Sep. 8, 07) 4. Measurement 4.. Spin- Systems Last time, we said that a general state in a spin- system can be written as ψ = c + + + c, (4.) where +,
1 Fundamental physical postulates. C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12
 C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
C/CS/Phys C191 Quantum Mechanics in a Nutshell I 10/04/07 Fall 2007 Lecture 12 In this and the next lecture we summarize the essential physical and mathematical aspects of quantum mechanics relevant to
Lecture 10: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation. 1 Stationary States 1. 2 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3
 Contents Lecture 1: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation B. Zwiebach March 14, 16 1 Stationary States 1 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3 3 Free particle on a circle. 6 1 Stationary States
Contents Lecture 1: Solving the Time-Independent Schrödinger Equation B. Zwiebach March 14, 16 1 Stationary States 1 Solving for Energy Eigenstates 3 3 Free particle on a circle. 6 1 Stationary States
Lecture If two operators A, B commute then they have same set of eigenkets.
 Lecture 14 Matrix representing of Operators While representing operators in terms of matrices, we use the basis kets to compute the matrix elements of the operator as shown below < Φ 1 x Φ 1 >< Φ 1 x Φ
Lecture 14 Matrix representing of Operators While representing operators in terms of matrices, we use the basis kets to compute the matrix elements of the operator as shown below < Φ 1 x Φ 1 >< Φ 1 x Φ
Spin Dynamics Basic Theory Operators. Richard Green SBD Research Group Department of Chemistry
 Spin Dynamics Basic Theory Operators Richard Green SBD Research Group Department of Chemistry Objective of this session Introduce you to operators used in quantum mechanics Achieve this by looking at:
Spin Dynamics Basic Theory Operators Richard Green SBD Research Group Department of Chemistry Objective of this session Introduce you to operators used in quantum mechanics Achieve this by looking at:
5.1 Uncertainty principle and particle current
 5.1 Uncertainty principle and particle current Slides: Video 5.1.1 Momentum, position, and the uncertainty principle Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Sections 3.1 3.13 Uncertainty
5.1 Uncertainty principle and particle current Slides: Video 5.1.1 Momentum, position, and the uncertainty principle Text reference: Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Sections 3.1 3.13 Uncertainty
Lecture-XXVI. Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation
 Lecture-XXVI Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation Time Independent Schrodinger Equation: The time-dependent Schrodinger equation: Assume that V is independent of time t. In that case the Schrodinger equation
Lecture-XXVI Time-Independent Schrodinger Equation Time Independent Schrodinger Equation: The time-dependent Schrodinger equation: Assume that V is independent of time t. In that case the Schrodinger equation
CHEM 301: Homework assignment #5
 CHEM 30: Homework assignment #5 Solutions. A point mass rotates in a circle with l =. Calculate the magnitude of its angular momentum and all possible projections of the angular momentum on the z-axis.
CHEM 30: Homework assignment #5 Solutions. A point mass rotates in a circle with l =. Calculate the magnitude of its angular momentum and all possible projections of the angular momentum on the z-axis.
Harmonic Oscillator. Robert B. Griffiths Version of 5 December Notation 1. 3 Position and Momentum Representations of Number Eigenstates 2
 qmd5 Harmonic Oscillator Robert B. Griffiths Version of 5 December 0 Contents Notation Eigenstates of the Number Operator N 3 Position and Momentum Representations of Number Eigenstates 4 Coherent States
qmd5 Harmonic Oscillator Robert B. Griffiths Version of 5 December 0 Contents Notation Eigenstates of the Number Operator N 3 Position and Momentum Representations of Number Eigenstates 4 Coherent States
SECOND QUANTIZATION PART I
 PART I SECOND QUANTIZATION 1 Elementary quantum mechanics We assume that the reader is already acquainted with elementary quantum mechanics. An introductory course in quantum mechanics usually addresses
PART I SECOND QUANTIZATION 1 Elementary quantum mechanics We assume that the reader is already acquainted with elementary quantum mechanics. An introductory course in quantum mechanics usually addresses
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I. September 19, ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer.
 D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I September 9, 003 ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of useful
D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I September 9, 003 ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of useful
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I Key. September 19, ) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer.
 D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I Key September 19, 003 1) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of
D Chemistry 350/450 Exam I Key September 19, 003 1) This is a multiple choice exam. Circle the correct answer. ) There is one correct answer to every problem. There is no partial credit. 3) A table of
26 Group Theory Basics
 26 Group Theory Basics 1. Reference: Group Theory and Quantum Mechanics by Michael Tinkham. 2. We said earlier that we will go looking for the set of operators that commute with the molecular Hamiltonian.
26 Group Theory Basics 1. Reference: Group Theory and Quantum Mechanics by Michael Tinkham. 2. We said earlier that we will go looking for the set of operators that commute with the molecular Hamiltonian.
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I. February 6, ) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems.
 A Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
A Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra. Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 2014
 Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
Quantum Mechanics is Linear Algebra Noah Graham Middlebury College February 25, 24 Linear Algebra Cheat Sheet Column vector quantum state: v = v v 2. Row vector dual state: w = w w 2... Inner product:
1 Dirac Notation for Vector Spaces
 Theoretical Physics Notes 2: Dirac Notation This installment of the notes covers Dirac notation, which proves to be very useful in many ways. For example, it gives a convenient way of expressing amplitudes
Theoretical Physics Notes 2: Dirac Notation This installment of the notes covers Dirac notation, which proves to be very useful in many ways. For example, it gives a convenient way of expressing amplitudes
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Wednesday April Exam 2
 8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Wednesday April 18 2012 Exam 2 Last Name: First Name: Check Recitation Instructor Time R01 Barton Zwiebach 10:00 R02
8.04: Quantum Mechanics Professor Allan Adams Massachusetts Institute of Technology Wednesday April 18 2012 Exam 2 Last Name: First Name: Check Recitation Instructor Time R01 Barton Zwiebach 10:00 R02
Ch 125a Problem Set 1
 Ch 5a Problem Set Due Monday, Oct 5, 05, am Problem : Bra-ket notation (Dirac notation) Bra-ket notation is a standard and convenient way to describe quantum state vectors For example, φ is an abstract
Ch 5a Problem Set Due Monday, Oct 5, 05, am Problem : Bra-ket notation (Dirac notation) Bra-ket notation is a standard and convenient way to describe quantum state vectors For example, φ is an abstract
Solutions Final exam 633
 Solutions Final exam 633 S.J. van Enk (Dated: June 9, 2008) (1) [25 points] You have a source that produces pairs of spin-1/2 particles. With probability p they are in the singlet state, ( )/ 2, and with
Solutions Final exam 633 S.J. van Enk (Dated: June 9, 2008) (1) [25 points] You have a source that produces pairs of spin-1/2 particles. With probability p they are in the singlet state, ( )/ 2, and with
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline
 Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline 1. General structure of quantum mechanics. 8.04 was based primarily on wave mechanics. We review that foundation with the intent to build a more formal basis
Quantum Physics II (8.05) Fall 2002 Outline 1. General structure of quantum mechanics. 8.04 was based primarily on wave mechanics. We review that foundation with the intent to build a more formal basis
Physics 137A Quantum Mechanics Fall 2012 Midterm II - Solutions
 Physics 37A Quantum Mechanics Fall 0 Midterm II - Solutions These are the solutions to the exam given to Lecture Problem [5 points] Consider a particle with mass m charge q in a simple harmonic oscillator
Physics 37A Quantum Mechanics Fall 0 Midterm II - Solutions These are the solutions to the exam given to Lecture Problem [5 points] Consider a particle with mass m charge q in a simple harmonic oscillator
Quantum Computing Lecture 2. Review of Linear Algebra
 Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Basic Quantum Mechanics Prof. Ajoy Ghatak Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Basic Quantum Mechanics Prof. Ajoy Ghatak Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. # 07 Bra-Ket Algebra and Linear Harmonic Oscillator II Lecture No. # 02 Dirac s Bra and
Basic Quantum Mechanics Prof. Ajoy Ghatak Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. # 07 Bra-Ket Algebra and Linear Harmonic Oscillator II Lecture No. # 02 Dirac s Bra and
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/02/08 Fall 2008 Lecture 11
 C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
C/CS/Phys C191 Particle-in-a-box, Spin 10/0/08 Fall 008 Lecture 11 Last time we saw that the time dependent Schr. eqn. can be decomposed into two equations, one in time (t) and one in space (x): space
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case
 The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about the
QM and Angular Momentum
 Chapter 5 QM and Angular Momentum 5. Angular Momentum Operators In your Introductory Quantum Mechanics (QM) course you learned about the basic properties of low spin systems. Here we want to review that
Chapter 5 QM and Angular Momentum 5. Angular Momentum Operators In your Introductory Quantum Mechanics (QM) course you learned about the basic properties of low spin systems. Here we want to review that
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers
 Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Syllabus and Textbook references All the main lessons (e.g., 1.1) and units (e.g., 1.1.1) for this class are listed below. Mostly, there are three lessons
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers Syllabus and Textbook references All the main lessons (e.g., 1.1) and units (e.g., 1.1.1) for this class are listed below. Mostly, there are three lessons
Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory
 Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology June 2002 Last Revised: June 2003 1 Introduction The purpose of these
Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology June 2002 Last Revised: June 2003 1 Introduction The purpose of these
Chemistry 3502/4502. Exam I. February 6, ) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems.
 D Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
D Chemistry 3502/4502 Exam I February 6, 2006 1) Circle the correct answer on multiple-choice problems. 2) There is one correct answer to every multiple-choice problem. There is no partial credit. On the
PH425 Spins Homework 5 Due 4 pm. particles is prepared in the state: + + i 3 13
 PH45 Spins Homework 5 Due 10/5/18 @ 4 pm REQUIRED: 1. A beam of spin- 1 particles is prepared in the state: ψ + + i 1 1 (a) What are the possible results of a measurement of the spin component S z, and
PH45 Spins Homework 5 Due 10/5/18 @ 4 pm REQUIRED: 1. A beam of spin- 1 particles is prepared in the state: ψ + + i 1 1 (a) What are the possible results of a measurement of the spin component S z, and
This is the important completeness relation,
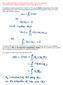 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
