is on the graph of y = f 1 (x).
|
|
|
- Jean Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f. for all in the domain We write f to denote the inverse function. Objective 2b How are the graphs of f and f related? If (a,b) is on the graph of = f(), then is on the graph of = f (). 77
2 Objective 2b Eample Select the graph of = f (). A function can be its own inverse. Consider Objective 2a Does ever function have an inverse? to be be the graph of a one- Graph of a function must pass the to-one function. 78
3 Which are one-to-one functions? {(,2),(,3),(5,4)} {(,2),(3,2),(4,5)} {(,2),(3,3),(4,5)} If a function is not one-to-one, restrict the domain in order to define an inverse function. (Recall intro to Obj 2.) Objective 2d Given a function, find the function rule for f. *************** Plan of Attack. Write for f() (to simplif the notation). 2. Solve for. For applied mathematicians, when units are usuall associated with the variables, ou have the inverse function. 3. For our College Algebra course, we will interchange and to write the inverse as a function of. 4. Write f () for (to return to function notation). *************** Find the function rule for f for each of the following. f() = 3 5 f() = (4 )
4 f() = f() = + 3 f() = Objective 22 Eponential Functions. f() = a, a > 0, a Does this define a function? Don t allow base to be negative because could be Don t allow base to be because for some. i.e., graph would be linear, not eponential. What s the domain? All reals? If so, we have to define what s meant b irrational eponents. For eample: 4 2 or 4 π We haven t worked with irrational eponents. Good News: The limiting processes of calculus guarantee that irrational eponents are defined, and line up as we want. That means, since 3 < π < 4, then a 3 < a π < a 4. That means, since < 2 < 2, then a < a 2 < a 2. 80
5 The eponential functions are classified into 2 groups, depending on the base. f() = a, a > f() = a, 0 < a < We will consider two specific cases to develop the concept. This is not an egrade eample; ou will not be making tables of values - ou will not be plotting points. ( Consider f() = 4 Consider f() = 4) for an eample of a > for an eample of 0 < a < Objective 22a Properties and Graphs of Eponential Functions f() = a, a > f() = a, 0 < a < 8
6 Objective 22b Graphing Eponential Functions with Reflections or Translations Don t. Don t. Use Obj 4! Select the graph that best represents the graph of each of the following. ( f() = 5 f() = 4) Which function best describes the graph shown? Which function best describes the graph shown? f() = (2.5) f() = (2.5) f() = (2.5) f() = (2.5) f() = (0.4) f() = (0.4) f() = (0.4) f() = (0.4) More Objective 22b Graphing Eponential Functions with Translations Don t. Don t. Use Obj 4! 82
7 Select the graph that best represents the graph of each of the following. f() = 4 3 f() = ( ) +2 5 Which function best describes the graph shown? Which function best describes the graph shown? f() = 6 +3 f() = 6 +3 f() = ( ) +2 5 f() = ( ) f() = (0.6) +3 f() = (0.6) +3 f() = ( ) 2 2 f() = ( )
8 Objective 22c The eponential function is f() = e because of so man areas of application. ( e e = lim n + ) n n Graph f() = e Evaluate e on a scientific calculator (the Mac calculator in lab class). Strontium 90 is a radioactive material that decas over time. The amount, A, in grams of Strontium 90 remaining in a certain sample can be approimated with the function A(t) = 225e 0.037t, where t is the number of ears from now. How man grams of Strontium 90 will be remaining in this sample after 7 ears? $8,000 is invested in a bond trust that earns 5.9% interest compounded continuousl. The account balance t ears later can be found with the function A = 8000e 0.059t. How much mone will be in the account after 6 ears? 84
9 Objective 22d Solving eponential equations when we can obtain the same base. Eponential functions are one-to-one; that means: if and onl if Rewrite each side (if needed) in terms of a common base; use the smallest base possible. Be sure to replace equals. Solve 5 2+ = 25 3 ( ) 4 4 Solve = 9 ( ) Solve ( ) 4 25 =
10 Objective 23 Logarithmic Functions Consider an eponential function = a What s the inverse function? There is no algebraic operation to solve for. We must define a new function. = log a Objective 23a Evaluate Logarithmic Functions log 2 8 = log 25 5 = log /6 2 = log 2 2 = log 2 = Which are defined? (Be careful, sometimes ask Which are undefined? ) log /2 log /4 4 log /2 ( 4) log /2 0 86
11 Objective 23b Properties and Graphs of Logarithmic Functions f() = log b, b > 0, b The logarithmic functions are classified into two groups comparable to the eponential functions. Recall Obj 22a = a, a > = a, 0 < a < = log b, b > = log b, 0 < b < Consider f() = log 4 Consider f() = log /4 for an eample of b > for an eample of 0 < b < Pick the -values, find the -values. Pick the -values, find the -values
12 Objective 23c Graphing Logarithmic Functions with Reflections or Translations Don t. Don t. Use Obj 4! Select the graph that best represents the graph of each of the following. f() = log 4 f() = log /4 ( ) Which function best describes the graph shown? Which function best describes the graph shown? f() = log (5/2) () f() = log (5/2) ( ) f() = log (2/5) () f() = log (2/5) ( ) f() = log (5/2) () f() = log (5/2) ( ) f() = log (2/5) () f() = log (2/5) ( ) More Objective 23c Graphing Logarithmic Functions with Translations Don t. Don t. Use Obj 4! 88
13 Select the graph that best represents the graph of each of the following. f() = log 3 ()+2 f() = log /3 (+2) Which function best describes the graph shown? Which function best describes the graph shown? f() = log (5/2) ()+2 f() = log (5/2) () 2 f() = log (2/5) ()+2 f() = log (2/5) () 2 f() = log (5/2) (+2) f() = log (5/2) ( 2) f() = log (2/5) (+2) f() = log (2/5) ( 2) 89
14 Objective 23d Domain of Logarithmic Functions (not b graphing) Give the domain. f() = log b (4 5) f() = 5 log b (3) ( ) + f() = log b 3 f() = log 3 (4 2 ) f() = log 3 ( 2 +4) 90
15 Objective 24 Properties of Logarithmic Functions As used below: a > 0, a, b > 0, b, M > 0, N > 0, > 0, and r represent an real number Definition - Obj 24a means Common Logarithms are logarithms base 0; we write instead of. Natural Logarithms are logarithms base e; we write instead of. Objective 24a Eample Which of the following is equivalent to ln5 =? A) 5 e = B) e = 5 C) 5 = e Properties of Logarithms - Obj 24b Product Rule log b (MN) = Must Note: log b (MN) Must Note: log b (M +N) Quotient Rule ( ) M log b = N ( ) M Must Note: log b N Must Note: log b (M N) Power Rule log b M r = Change-of-Base Formula log b M = log b M = When Base and Result Match log b b = When Result is log b = 9
16 Inverse Function Properties - Obj 24c Recall Obj 2: (f f )() = and (f f)() = a log a M = log a a r = Objective 24c Eamples Solve for if 5 log 5 (3) = 5 Solve for if lne 5 = 3 Objective 24b Eample Which of the following is equivalent to log b ( )? ( ) A) log b C) both A and B B) log b log b D) none is equivalent Objective 24e Eamples Evaluating e or ln on a scientific calculator and rounding the result to 3 decimal places. When rounding a number to 3 decimal places, look at the 4th digit of the decimal. If that number is less than 5, then keep the 3rd digit as it is and drop the remaining decimal digits. If that number is greater than, or equal to 5, then round the 3rd digit up (add to the 3rd digit) and drop the remaining decimal digits. Evaluate, round to 3 decimal places. e 5 ln50 Objective 24be Eample Select all that are correct for log 3 8. Choice: = log8 log3 Choice: = ln3 ln8 Choice:.983 Choice: Objective 24abc Eample Select ALL the correct formulas/statements if b > 0,b, > 0, > 0. (egrade does not warn when a multiple selection problem is left blank.) log(+) = log+log log( ) = log log log = means 0 = log 5 = 0 If log0 4 = 2, then = 3 92
17 Appling Log Properties - Objective ( ) 24d 2 Epand using log properties. log b z ( 2 ) Epand using log properties. log b z(w +3) Which of the following is equivalent to A) 2log b +log b log b z +log b (w+3) B) 2log b +log b log b z log b (w+3) C) A and B are the same log b ( 2 ) log b (z(w +3)) another Objective 24d Eample Write as a single logarithm 2log b log b + log 2 bz A) log b 2 z B) log b 2 z 93
18 another Objective 24d Eample Write as a single logarithm. 2log b (z w) log b w +3log b z +log b log b (+w) another Objective 24d Eample If log b 2 = l and log b 5 = m, epress log b 00 in terms of l and m. another Objective 24d Eample If log b 2 = l and log b 5 = m, epress (log b 4) (log b 25) in terms of l and m. Objective 25 Solving Eponential Equations when we can t obtain the same base. Logarithmic functions are one-to-one. That means: if and onl if Objective 25a Solve. 6 2 = 4 3 Solve = 2 94
19 Objective 25b Round solution to 3 decimal places. Solve. 400e 3+ = Solve. 40e 2 = 20 Solve = Solve = 20 Objective 26 Solving Logarithmic Equations Objective 26a All terms in the equation involve log functions. Solve. log+log( 2) = log(+4) Solve. log 3 (+) log 3 (+7) = log 3 (+5) 95
20 Solve. log 7 ( 8)+log 7 ( 9) = log 7 (23 3) Solve. log 5 (+4) = log 5 (3+8) log 5 (+3) Objective 26b Use the Definition of logarithmic notation. Solve. 5 7log /3 = 5 Solve. log( 2 +2+) = Solve. 6log 4 ( 5) = 3 Solve. log 2 ( 2 +7) = 4 96
21 Objective 27 Solving Equations that involve eponential functions. Solve. e e 2 2 e 4 = 0 Solve. e 3 ( 3 ) + e 3 4 e 6 = 0 Solve. ( 2 ) e e 4 e 2 = 0 Solve. 2e 2 (4+5) 3 e 2 3 (4+5) 2 4 (4+5) 6 = 0 Solve. (3+7) 4 e 4 4 e 4 4(3+7) 3 3 (3+7) 8 = 0 97
22 Solve. (+2) 6 e 3 2 5(+2) 4 2 e 3 = 0 (+2) 8 Solve. 2 ( 3) 5 e 4 2 e 4 ( 3) 3 4 ( 3) 6 = 0 Objective 28 Solving Equations that involve natural logarithmic functions. Solve. 22 ( ( 2ln+2 7 = 0 )) Solve. 44 ( ( ) 8 +8ln = 0 ) Solve. ( 2 2ln ) 2 = 0 Solve. 4 3 (3ln)(43 ) 8 = 0 98
23 Solve. ( 4 3 ln 6ln ) = 0 Solve. (ln) 2 ( ) 3 3 ln 3 4 ln 3 = 0 6 Objective 30 Solve 2 linear equations in 2 unknowns There are 3 possible situations. To solve algebraicall we will use the Multipl one, or both equation if needed, b non-zero numbers so that when the equations are added, one variable is eliminated. 99
24 Solve. 2+5 = 0 Solve. 7 4 = = = 4 Solve. 9 2 = = 2 Solve. 6+0 = = 4 Objective 3 Solve 2 equations in 2 unknowns First tpe: Quadratic and Linear - Algebraic solution To solve algebraicall we will use the Substitute the into the. Solve. = 2 +2 Solve. = = 5 3 = 5 Give the -coordinate(s) onl of an solution(s). If multiple solutions, then enter the values in an order, separated b a semicolon. If there is no solution, then enter: no solution (When there is no solution, do not use an capital letters; do not use an punctuation marks.) 00
25 Second tpe: 2 Various equations - Solve b GRAPHING We will ask: solutions are there? Must know all the basic functions and equations we have graphed and we must know Obj 4 - and r (,) ( h,k) 0
26 Solve the sstem of equations b graphing. How man real solutions are there? = + = 2 Solve the sstem of equations b graphing. How man real solutions are there? = e = 3 Solve the sstem of equations b graphing. How man real solutions are there? = ln ( ) = 4 Copright c 200-present, Annette Blackwelder, all rights are reserved. Reproduction or distribution of these notes is strictl forbidden. 02
is on the graph of y = f 1 (x).
 Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
Objective 2 Inverse Functions Illustrate the idea of inverse functions. f() = 2 + f() = Two one-to-one functions are inverses of each other if (f g)() = of g, and (g f)() = for all in the domain of f.
a > 0 parabola opens a < 0 parabola opens
 Objective 8 Quadratic Functions The simplest quadratic function is f() = 2. Objective 8b Quadratic Functions in (h, k) form Appling all of Obj 4 (reflections and translations) to the function. f() = a(
Objective 8 Quadratic Functions The simplest quadratic function is f() = 2. Objective 8b Quadratic Functions in (h, k) form Appling all of Obj 4 (reflections and translations) to the function. f() = a(
3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs
 .1 Eponential Functions and Their Graphs Sllabus Objective: 9.1 The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential or logarithmic
.1 Eponential Functions and Their Graphs Sllabus Objective: 9.1 The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential or logarithmic
f 0 ab a b: base f
 Precalculus Notes: Unit Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllabus Objective: 9. The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential
Precalculus Notes: Unit Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllabus Objective: 9. The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential
Math RE - Calculus I Exponential & Logarithmic Functions Page 1 of 9. y = f(x) = 2 x. y = f(x)
 Math 20-0-RE - Calculus I Eponential & Logarithmic Functions Page of 9 Eponential Function The general form of the eponential function equation is = f) = a where a is a real number called the base of the
Math 20-0-RE - Calculus I Eponential & Logarithmic Functions Page of 9 Eponential Function The general form of the eponential function equation is = f) = a where a is a real number called the base of the
First Semester Final Review NON-Graphing Calculator
 Algebra First Semester Final Review NON-Graphing Calculator Name:. 1. Find the slope of the line passing through the points ( 5, ) and ( 3, 7).. Find the slope-intercept equation of the line passing through
Algebra First Semester Final Review NON-Graphing Calculator Name:. 1. Find the slope of the line passing through the points ( 5, ) and ( 3, 7).. Find the slope-intercept equation of the line passing through
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8
 Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
Chapter 8 Notes SN AA U2C8 Name Period Section 8-: Eploring Eponential Models Section 8-2: Properties of Eponential Functions In Chapter 7, we used properties of eponents to determine roots and some of
MTH 112 Practice Test 3 Sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 1.9, 7.4, 7.5, 8.1, 8.2
 MTH 112 Practice Test 3 Sections 3.3, 3., 3., 1.9, 7., 7., 8.1, 8.2 Use properties of logarithms to epand the logarithmic epression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic epressions
MTH 112 Practice Test 3 Sections 3.3, 3., 3., 1.9, 7., 7., 8.1, 8.2 Use properties of logarithms to epand the logarithmic epression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic epressions
Practice A ( 1, 3 ( 0, 1. Match the function with its graph. 3 x. Explain how the graph of g can be obtained from the graph of f. 5 x.
 8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
8. Practice A For use with pages 65 7 Match the function with its graph.. f. f.. f 5. f 6. f f Lesson 8. A. B. C. (, 6) (0, ) (, ) (0, ) ( 0, ) (, ) D. E. F. (0, ) (, 6) ( 0, ) (, ) (, ) (0, ) Eplain how
Logarithms. Bacteria like Staph aureus are very common.
 UNIT 10 Eponentials and Logarithms Bacteria like Staph aureus are ver common. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
UNIT 10 Eponentials and Logarithms Bacteria like Staph aureus are ver common. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including illustrations,
f 0 ab a b: base f
 Precalculus Notes: Unit Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllaus Ojective: 9. The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential
Precalculus Notes: Unit Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllaus Ojective: 9. The student will sketch the graph of a eponential, logistic, or logarithmic function. 9. The student will evaluate eponential
MAC 1105 Review for Exam 4. Name
 MAC 1105 Review for Eam Name For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f() = +, g() = 8-7; Find (f g)(). 1) Find the domain of the composite function f g. 9 ) f() = + 9;
MAC 1105 Review for Eam Name For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f() = +, g() = 8-7; Find (f g)(). 1) Find the domain of the composite function f g. 9 ) f() = + 9;
5A Exponential functions
 Chapter 5 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions bjectives To graph eponential and logarithmic functions and transformations of these functions. To introduce Euler s number e. To revise the inde and logarithm
Chapter 5 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions bjectives To graph eponential and logarithmic functions and transformations of these functions. To introduce Euler s number e. To revise the inde and logarithm
Name Period Date. Practice FINAL EXAM Intro to Calculus (50 points) Show all work on separate sheet of paper for full credit!
 Name Period Date Practice FINAL EXAM Intro to Calculus (0 points) Show all work on separate sheet of paper for full credit! ) Evaluate the algebraic epression for the given value or values of the variable(s).
Name Period Date Practice FINAL EXAM Intro to Calculus (0 points) Show all work on separate sheet of paper for full credit! ) Evaluate the algebraic epression for the given value or values of the variable(s).
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions In this chapter ou will stud two tpes of nonalgebraic functions eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eponential and logarithmic functions are widel used
7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions In this chapter ou will stud two tpes of nonalgebraic functions eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eponential and logarithmic functions are widel used
where a 0 and the base b is a positive number other
 7. Graph Eponential growth functions No graphing calculators!!!! EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION A function of the form than one. a b where a 0 and the base b is a positive number other a = b = HA = Horizontal Asmptote:
7. Graph Eponential growth functions No graphing calculators!!!! EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION A function of the form than one. a b where a 0 and the base b is a positive number other a = b = HA = Horizontal Asmptote:
lim a, where and x is any real number. Exponential Function: Has the form y Graph y = 2 x Graph y = -2 x Graph y = Graph y = 2
 Precalculus Notes Da 1 Eponents and Logarithms Eponential Function: Has the form a, where and is an real number. Graph = 2 Graph = -2 +2 + 1 1 1 Graph = 2 Graph = 3 1 2 2 2 The Natural Base e (Euler s
Precalculus Notes Da 1 Eponents and Logarithms Eponential Function: Has the form a, where and is an real number. Graph = 2 Graph = -2 +2 + 1 1 1 Graph = 2 Graph = 3 1 2 2 2 The Natural Base e (Euler s
 Test #4 33 QUESTIONS MATH1314 09281700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm1314bli28 www.alvarezmathhelp.com website SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
Test #4 33 QUESTIONS MATH1314 09281700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm1314bli28 www.alvarezmathhelp.com website SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Test # 33 QUESTIONS MATH131 091700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm131bli www.alvarezmathhelp.com website MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Test # 33 QUESTIONS MATH131 091700 COLLEGE ALGEBRA Name atfm131bli www.alvarezmathhelp.com website MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions
 Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions We have studied inverse functions, learning when they eist and how to find them. If we look at the graph of the eponential function, f ( ) = a, where
Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions We have studied inverse functions, learning when they eist and how to find them. If we look at the graph of the eponential function, f ( ) = a, where
6.4 graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
Final Exam Review. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Final Eam Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether or not the relationship shown in the table is a function.
Final Eam Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether or not the relationship shown in the table is a function.
Example 1: What do you know about the graph of the function
 Section 1.5 Analyzing of Functions In this section, we ll look briefly at four types of functions: polynomial functions, rational functions, eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eample 1: What
Section 1.5 Analyzing of Functions In this section, we ll look briefly at four types of functions: polynomial functions, rational functions, eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eample 1: What
Chapter 9 Vocabulary Check
 9 CHAPTER 9 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Find the inverse function of each one-to-one function. See Section 9.. 67. f = + 68. f = - CONCEPT EXTENSIONS The formula = 0 e kt gives the population
9 CHAPTER 9 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Find the inverse function of each one-to-one function. See Section 9.. 67. f = + 68. f = - CONCEPT EXTENSIONS The formula = 0 e kt gives the population
Math 121. Practice Problems from Chapter 4 Fall 2016
 Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 1 Inverse Functions 1. The graph of a function f is given below. On same graph sketch the inverse function of f; notice that f goes through the points (0,
Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 1 Inverse Functions 1. The graph of a function f is given below. On same graph sketch the inverse function of f; notice that f goes through the points (0,
7-1. Exploring Exponential Models. Vocabulary. Review. Vocabulary Builder. Use Your Vocabulary. 1. Cross out the expressions that are NOT powers.
 7-1 Eploring Eponential Models Vocabular Review 1. Cross out the epressions that are NOT powers. 16 6a 1 7. Circle the eponents in the epressions below. 5 6 5a z Vocabular Builder eponential deca (noun)
7-1 Eploring Eponential Models Vocabular Review 1. Cross out the epressions that are NOT powers. 16 6a 1 7. Circle the eponents in the epressions below. 5 6 5a z Vocabular Builder eponential deca (noun)
3.2 LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
Section. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 7. LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Ariel Skelle/Corbis What ou should learn Recognize and evaluate logarithmic functions with base a. Graph logarithmic
The Natural Base e. ( 1, e 1 ) 220 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Example 6 Evaluating the Natural Exponential Function.
 0 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions (, e) f() = e (, e ) (0, ) (, e ) FIGURE.9 The Natural Base e In man applications, the most convenient choice for a base is the irrational number e.78888....
0 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions (, e) f() = e (, e ) (0, ) (, e ) FIGURE.9 The Natural Base e In man applications, the most convenient choice for a base is the irrational number e.78888....
Ch. 4 Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Ch. Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the functions are inverses of each other. 3 5 +
Ch. Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the functions are inverses of each other. 3 5 +
Math 121. Practice Problems from Chapter 4 Fall 2016
 Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 Section 1. Inverse Functions 1. Graph an inverse function using the graph of the original function. For practice see Eercises 1,.. Use information about
Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 Section 1. Inverse Functions 1. Graph an inverse function using the graph of the original function. For practice see Eercises 1,.. Use information about
( 3x. Chapter Review. Review Key Vocabulary. Review Examples and Exercises 6.1 Properties of Square Roots (pp )
 6 Chapter Review Review Ke Vocabular closed, p. 266 nth root, p. 278 eponential function, p. 286 eponential growth, p. 296 eponential growth function, p. 296 compound interest, p. 297 Vocabular Help eponential
6 Chapter Review Review Ke Vocabular closed, p. 266 nth root, p. 278 eponential function, p. 286 eponential growth, p. 296 eponential growth function, p. 296 compound interest, p. 297 Vocabular Help eponential
ab is shifted horizontally by h units. ab is shifted vertically by k units.
 Algera II Notes Unit Eight: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllaus Ojective: 8. The student will graph logarithmic and eponential functions including ase e. Eponential Function: a, 0, Graph of an
Algera II Notes Unit Eight: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Sllaus Ojective: 8. The student will graph logarithmic and eponential functions including ase e. Eponential Function: a, 0, Graph of an
Math125 Exam 5 Review Name. Do the following as indicated.
 Math Eam Review Name Do the following as indicated. For the given functions f and g, find the requested function. ) f() = - 6; g() = 9 Find (f - g)(). ) ) f() = 33 + ; g() = - Find (f g)(). 3) f() = ;
Math Eam Review Name Do the following as indicated. For the given functions f and g, find the requested function. ) f() = - 6; g() = 9 Find (f - g)(). ) ) f() = 33 + ; g() = - Find (f g)(). 3) f() = ;
) approaches e
 COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSF-IF.C.7e HSF-LE.B.5. USING TOOLS STRATEGICALLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use technological tools to eplore and deepen our understanding of concepts. The Natural
COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSF-IF.C.7e HSF-LE.B.5. USING TOOLS STRATEGICALLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use technological tools to eplore and deepen our understanding of concepts. The Natural
8-1 Exploring Exponential Models
 8- Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function A function with the general form, where is a real number, a 0, b > 0 and b. Eample: y = 4() Growth Factor When b >, b is the growth factor Eample: y =
8- Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function A function with the general form, where is a real number, a 0, b > 0 and b. Eample: y = 4() Growth Factor When b >, b is the growth factor Eample: y =
Unit 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 71 Rational eponents Unit 5: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions If b is a real number and n and m are positive and have no common factors, then n m m b = b ( b ) m n n Laws of eponents a) b) c) d) e)
71 Rational eponents Unit 5: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions If b is a real number and n and m are positive and have no common factors, then n m m b = b ( b ) m n n Laws of eponents a) b) c) d) e)
2. Tell whether the equation or graph represents an exponential growth or exponential decay function.
 Name: Date: Period: ID: 1 Unit 9 Review Eponents & Logarithms NO GRAPHING CALCULATOR 1. Under each function, write es if it is an eponential function. If the answer is no, write an eplanation wh not. a)
Name: Date: Period: ID: 1 Unit 9 Review Eponents & Logarithms NO GRAPHING CALCULATOR 1. Under each function, write es if it is an eponential function. If the answer is no, write an eplanation wh not. a)
MAC 1105 Lecture Outlines for Ms. Blackwelder s lecture classes
 MAC 1105 Lecture Outlines for Ms. Blackwelder s lecture classes These notes are prepared using software that is designed for typing mathematics; it produces a pdf output. Alternative format is not available.
MAC 1105 Lecture Outlines for Ms. Blackwelder s lecture classes These notes are prepared using software that is designed for typing mathematics; it produces a pdf output. Alternative format is not available.
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
Chapters 8 & 9 Review for Final
 Math 203 - Intermediate Algebra Professor Valdez Chapters 8 & 9 Review for Final SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the formula for
Math 203 - Intermediate Algebra Professor Valdez Chapters 8 & 9 Review for Final SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the formula for
Math125 Exam 5 (Final) Review Name. Do the following as indicated. 17) log 17x = 1.2 (Round answer to four decimal places.)
 Math12 Eam (Final) Review Name Do the following as indicated. For the given functions f and g, find the requested function. 1) f() = - 6; g() = 92 Find (f - g)(). 2) f() = 33 + 1; g() = 2-2 Find (f g)().
Math12 Eam (Final) Review Name Do the following as indicated. For the given functions f and g, find the requested function. 1) f() = - 6; g() = 92 Find (f - g)(). 2) f() = 33 + 1; g() = 2-2 Find (f g)().
3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions. Quadratic functions are of the form.
 3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Quadratic Functions Completing the Square Quadratic functions are of the form. 3. It is easiest to graph quadratic functions when the are in the form using transformations.
3.1 Graphing Quadratic Functions A. Quadratic Functions Completing the Square Quadratic functions are of the form. 3. It is easiest to graph quadratic functions when the are in the form using transformations.
SAMPLE. Exponential and logarithmic functions
 Objectives C H A P T E R 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions To graph eponential and logarithmic functions. To graph transformations of the graphs of eponential and logarithmic functions. To introduce
Objectives C H A P T E R 5 Eponential and logarithmic functions To graph eponential and logarithmic functions. To graph transformations of the graphs of eponential and logarithmic functions. To introduce
Lesson 5.1 Exponential Functions
 Lesson.1 Eponential Functions 1. Evaluate each function at the given value. Round to four decimal places if necessar. a. r (t) 2(1 0.0) t, t 8 b. j() 9.(1 0.09), 10 2. Record the net three terms for each
Lesson.1 Eponential Functions 1. Evaluate each function at the given value. Round to four decimal places if necessar. a. r (t) 2(1 0.0) t, t 8 b. j() 9.(1 0.09), 10 2. Record the net three terms for each
6. The braking distance (in feet) for a car traveling 50 miles per hour on a wet uphill road is given by
 MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test 3 Section 4.6. Let f ( ) = 3 5 + 4. (a) What is the domain? (b) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (c) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (d) Give the equation(s) of the
MATH 34 - College Algebra Review for Test 3 Section 4.6. Let f ( ) = 3 5 + 4. (a) What is the domain? (b) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (c) Give the -intercept(s), if an. (d) Give the equation(s) of the
Pre-Calculus B Semester 1 Review Packet December 2015
 Pre-Calculus B Semester Review Packet December 05 Name DISCLAIMER The memor on all calculators will be cleared the da of the final. If ou have programs on our calculator that ou would like to keep, please
Pre-Calculus B Semester Review Packet December 05 Name DISCLAIMER The memor on all calculators will be cleared the da of the final. If ou have programs on our calculator that ou would like to keep, please
Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus
 Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus 01 017 Assignment: Summer Homework for those who will be taking FOCA 017 01 onl available until Sept. 15 1. Write the epression
Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus 01 017 Assignment: Summer Homework for those who will be taking FOCA 017 01 onl available until Sept. 15 1. Write the epression
MA Lesson 14 Notes Summer 2016 Exponential Functions
 Solving Eponential Equations: There are two strategies used for solving an eponential equation. The first strategy, if possible, is to write each side of the equation using the same base. 3 E : Solve:
Solving Eponential Equations: There are two strategies used for solving an eponential equation. The first strategy, if possible, is to write each side of the equation using the same base. 3 E : Solve:
Log Test Review - Graphing Problems
 Algebra Honors - Mr. Allen-Black d^0id7i wkpuftza SSqoffLtrw`aerZef CLOLACq.m H LAwlrl` _raidgqhvtssb reisaenrdvqekdr. Log Test Review - Graphing Problems ) = 3 Name ID: ) = ( Date Period - - - - - - -
Algebra Honors - Mr. Allen-Black d^0id7i wkpuftza SSqoffLtrw`aerZef CLOLACq.m H LAwlrl` _raidgqhvtssb reisaenrdvqekdr. Log Test Review - Graphing Problems ) = 3 Name ID: ) = ( Date Period - - - - - - -
Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents
 Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
Math 1400 - Mano Table of Contents - Review - page 1 of 2 Review Topics for MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus Table of Contents MATH 1400 Elements of Calculus is one of the Marquette Core Courses for Mathematical
Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16. Lecture Guide. Math College Algebra Chapter 4. to accompany. College Algebra by Julie Miller
 Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 4 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 4 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 4 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
LESSON 12.2 LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
 LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 OVERVIEW Here's what ou'll learn in this lesson: The Logarithm Function a. Converting from eponents to logarithms and from logarithms
LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES LESSON. LOGS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 OVERVIEW Here's what ou'll learn in this lesson: The Logarithm Function a. Converting from eponents to logarithms and from logarithms
where is a constant other than ( and ) and
 Section 12.1: EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS When you are done with your homework you should be able to Evaluate eponential functions Graph eponential functions Evaluate functions with base e Use compound interest
Section 12.1: EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS When you are done with your homework you should be able to Evaluate eponential functions Graph eponential functions Evaluate functions with base e Use compound interest
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Exponential Functions, Growth, and Decay
 7A Find these vocabular words in Lesson 7-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Eponential Functions, Growth, and Deca eponential growth eponential deca asmptote
7A Find these vocabular words in Lesson 7-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Eponential Functions, Growth, and Deca eponential growth eponential deca asmptote
REVIEW. log e. log. 3 k. x 4. log ( x+ 3) log x= ,if x 2 y. . h
 Math REVIEW Part I: Problems Simplif (without the use of calculators) ln log 000 e 0 k = k = k 7 log ( ) 8 lo g (log ) Solve the following equations/inequalities Check when necessar 8 =0 9 0 + = log (
Math REVIEW Part I: Problems Simplif (without the use of calculators) ln log 000 e 0 k = k = k 7 log ( ) 8 lo g (log ) Solve the following equations/inequalities Check when necessar 8 =0 9 0 + = log (
Learning Goals. College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 101: College Algebra Final Exam Review Problems 1
 College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Lesson 6 Eponential and Logarithmic Fu tions Lesson 6 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential functions are of the form y = a where a is a constant greater than zero and not equal to one and is
Lesson 6 Eponential and Logarithmic Fu tions Lesson 6 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential functions are of the form y = a where a is a constant greater than zero and not equal to one and is
We have examined power functions like f (x) = x 2. Interchanging x
 CHAPTER 5 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions We have eamined power functions like f =. Interchanging and ields a different function f =. This new function is radicall different from a power function
CHAPTER 5 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions We have eamined power functions like f =. Interchanging and ields a different function f =. This new function is radicall different from a power function
7-3 Skills Practice. Square Root Functions and Inequalities. Lesson 7-3. Graph each function. State the domain and range of each function.
 NAME DATE PERID 7- Skills Practice Square Root Functions and Inequalities Graph each function. State the domain and range of each function...... 6. Copright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill
NAME DATE PERID 7- Skills Practice Square Root Functions and Inequalities Graph each function. State the domain and range of each function...... 6. Copright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill
Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part 2) Notes
 SCIE 0, Spring 0 Miller Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part ) Notes Quadratic Functions (cont.) So far, we have onl looked at quadratic functions in which the term is squared. A more general form of
SCIE 0, Spring 0 Miller Math Review Packet #5 Algebra II (Part ) Notes Quadratic Functions (cont.) So far, we have onl looked at quadratic functions in which the term is squared. A more general form of
Section 11.1 Rational Exponents Goals: 1. To use the properties of exponents. 2. To evaluate and simplify expressions containing rational exponents.
 Section 11.1 Rational Eponents Goals: 1. To use the properties of eponents.. To evaluate and simplif epressions containing rational eponents. I. Properties to Review m n A. a a = m B. ( a ) n = C. n a
Section 11.1 Rational Eponents Goals: 1. To use the properties of eponents.. To evaluate and simplif epressions containing rational eponents. I. Properties to Review m n A. a a = m B. ( a ) n = C. n a
9) A) f-1(x) = 8 - x B) f-1(x) = x - 8 C)f-1(x) = x + 8 D) f-1(x) = x 8
 Review for Final Eam Name Algebra- Trigonometr MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor the polnomial completel. If a polnomial cannot
Review for Final Eam Name Algebra- Trigonometr MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor the polnomial completel. If a polnomial cannot
( ) ( ) x. The exponential function f(x) with base b is denoted by x
 Page of 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions and Their Graphs: Section Objectives: Students will know how to recognize, graph, and evaluate eponential functions. The eponential function
Page of 7 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions and Their Graphs: Section Objectives: Students will know how to recognize, graph, and evaluate eponential functions. The eponential function
The speed the speed of light is 30,000,000,000 m/s. Write this number in scientific notation.
 Chapter 1 Section 1.1 Scientific Notation Powers of Ten 1 1 1.1.1.1.1 Standard Scientific Notation N n where 1 N and n is an integers Eamples of numbers in scientific notation. 8.17 11 Using Scientific
Chapter 1 Section 1.1 Scientific Notation Powers of Ten 1 1 1.1.1.1.1 Standard Scientific Notation N n where 1 N and n is an integers Eamples of numbers in scientific notation. 8.17 11 Using Scientific
Sections 4.1 & 4.2 Exponential Growth and Exponential Decay
 8 Sections 4. & 4.2 Eponential Growth and Eponential Deca What You Will Learn:. How to graph eponential growth functions. 2. How to graph eponential deca functions. Eponential Growth This is demonstrated
8 Sections 4. & 4.2 Eponential Growth and Eponential Deca What You Will Learn:. How to graph eponential growth functions. 2. How to graph eponential deca functions. Eponential Growth This is demonstrated
Math 0210 Common Final Review Questions (2 5 i)(2 5 i )
 Math 0 Common Final Review Questions In problems 1 6, perform the indicated operations and simplif if necessar. 1. ( 8)(4) ( )(9) 4 7 4 6( ). 18 6 8. ( i) ( 1 4 i ) 4. (8 i ). ( 9 i)( 7 i) 6. ( i)( i )
Math 0 Common Final Review Questions In problems 1 6, perform the indicated operations and simplif if necessar. 1. ( 8)(4) ( )(9) 4 7 4 6( ). 18 6 8. ( i) ( 1 4 i ) 4. (8 i ). ( 9 i)( 7 i) 6. ( i)( i )
Sec 5.1 Exponential & Logarithmic Functions (Exponential Models)
 Sec 5.1 Eponential & Logarithmic Functions (Eponential Models) 1. The population of the cit Suwanee, GA has consistentl grown b 4% for the last several ears. In the ear 000, the population was 9,500 people.
Sec 5.1 Eponential & Logarithmic Functions (Eponential Models) 1. The population of the cit Suwanee, GA has consistentl grown b 4% for the last several ears. In the ear 000, the population was 9,500 people.
Lesson Goals. Unit 5 Exponential/Logarithmic Functions Exponential Functions (Unit 5.1) Exponential Functions. Exponential Growth: f (x) = ab x, b > 1
 Unit 5 Eponential/Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions Unit 5.1) William Bill) Finch Mathematics Department Denton High School Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Recognize and
Unit 5 Eponential/Logarithmic Functions Eponential Functions Unit 5.1) William Bill) Finch Mathematics Department Denton High School Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Recognize and
Glossary. Also available at BigIdeasMath.com: multi-language glossary vocabulary flash cards. An equation that contains an absolute value expression
 Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Glossar This student friendl glossar is designed to be a reference for ke vocabular, properties, and mathematical terms. Several of the entries include a short eample to aid our understanding of important
Algebra II. Chapter 8 Notes. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Name
 Algebra II Chapter 8 Notes Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Name Algebra II 8.1 Eponential Growth Toda I am graphing eponential growth functions. I am successful toda when I can graph eponential growth
Algebra II Chapter 8 Notes Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Name Algebra II 8.1 Eponential Growth Toda I am graphing eponential growth functions. I am successful toda when I can graph eponential growth
Math098 Practice Final Test
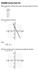 Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Self- assessment 1010 (Intermediate Algebra)
 Self- assessment (Intermediate Algebra) If ou can work these problems using a scientific calculator, ou should have sufficient knowledge to demonstrate master of Intermediate Algebra and to succeed in
Self- assessment (Intermediate Algebra) If ou can work these problems using a scientific calculator, ou should have sufficient knowledge to demonstrate master of Intermediate Algebra and to succeed in
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions, Applications, and Models
 86 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions, Applications, and Models Eponential Functions In this section we introduce two new tpes of functions The first of these is the eponential function Eponential Function
86 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions, Applications, and Models Eponential Functions In this section we introduce two new tpes of functions The first of these is the eponential function Eponential Function
Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods
 Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods Foundational Knowledge Created b Triumph Tutoring Copright info Copright Triumph Tutoring 07 Triumph Tutoring Pt Ltd ABN 60 607 0 507 First published in 07 All rights
Unit 3 Notes Mathematical Methods Foundational Knowledge Created b Triumph Tutoring Copright info Copright Triumph Tutoring 07 Triumph Tutoring Pt Ltd ABN 60 607 0 507 First published in 07 All rights
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions. Eponential Functions and Their Graphs. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs. Properties of Logarithms. Eponential and Logarithmic Equations.5 Eponential and Logarithmic
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, it is my epectation that you will have this packet completed. You will be way behind at the beginning of the year if you haven t attempted
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, it is my epectation that you will have this packet completed. You will be way behind at the beginning of the year if you haven t attempted
Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions
 CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.1 Eponential and Logistic Functions 3.2 Eponential and Logistic Modeling 3.3 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic
CHAPTER 3 Eponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions 3.1 Eponential and Logistic Functions 3.2 Eponential and Logistic Modeling 3.3 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic
17 Exponential Functions
 Eponential Functions Concepts: Eponential Functions Graphing Eponential Functions Eponential Growth and Eponential Deca The Irrational Number e and Continuousl Compounded Interest (Section. &.A). Sketch
Eponential Functions Concepts: Eponential Functions Graphing Eponential Functions Eponential Growth and Eponential Deca The Irrational Number e and Continuousl Compounded Interest (Section. &.A). Sketch
Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 10
 Math M: Lecture Notes For Chapter 0 Sections 0.: Inverse Function Inverse function (interchange and y): Find the equation of the inverses for: y = + 5 ; y = + 4 3 Function (from section 3.5): (Vertical
Math M: Lecture Notes For Chapter 0 Sections 0.: Inverse Function Inverse function (interchange and y): Find the equation of the inverses for: y = + 5 ; y = + 4 3 Function (from section 3.5): (Vertical
Honors Algebra 2: Semester 1 Review
 Name Block Date Honors Algebra : Semester 1 Review NON-CALCULATOR 6-5 1. Given the functions f ( ) 5 11 1, g( ) 6 ( f h)( ) b) ( g f )( ), and h ( ) 4, find each function. g c) (g h)( ) d) ( ) f -1, 4-7,
Name Block Date Honors Algebra : Semester 1 Review NON-CALCULATOR 6-5 1. Given the functions f ( ) 5 11 1, g( ) 6 ( f h)( ) b) ( g f )( ), and h ( ) 4, find each function. g c) (g h)( ) d) ( ) f -1, 4-7,
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions 6 Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE 6. Eponential Functions 6. Logarithmic Properties 6. Graphs
Eponential and Logarithmic Functions 6 Figure Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE 6. Eponential Functions 6. Logarithmic Properties 6. Graphs
Name: Math Analysis Chapter 3 Notes: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Name: Math Analysis Chapter 3 Notes: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Day : Section 3-1 Eponential Functions 3-1: Eponential Functions After completing section 3-1 you should be able to do the following:
Name: Math Analysis Chapter 3 Notes: Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Day : Section 3-1 Eponential Functions 3-1: Eponential Functions After completing section 3-1 you should be able to do the following:
7-1 Practice. Graphing Exponential Functions. Graph each function. State the domain and range. 1. y = 1.5(2) x 2. y = 4(3) x 3. y = 3(0.
 7-1 Practice Graphing Eponential Functions Graph each function. State the domain and range. 1. = 1.5(2) 2. = 4(3) 3. = 3(0.5) 4. = 5 ( 1 2) - 8 5. = - 2 ( 1 4) - 3 6. = 1 2 (3) + 4-5 7. BILGY The initial
7-1 Practice Graphing Eponential Functions Graph each function. State the domain and range. 1. = 1.5(2) 2. = 4(3) 3. = 3(0.5) 4. = 5 ( 1 2) - 8 5. = - 2 ( 1 4) - 3 6. = 1 2 (3) + 4-5 7. BILGY The initial
Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions
 TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
TEKS 7.4 2A.4.C, 2A..A, 2A..B, 2A..C Before Now Evaluate Logarithms and Graph Logarithmic Functions You evaluated and graphed eponential functions. You will evaluate logarithms and graph logarithmic functions.
(2.5) 1. Solve the following compound inequality and graph the solution set.
 Intermediate Algebra Practice Final Math 0 (7 th ed.) (Ch. -) (.5). Solve the following compound inequalit and graph the solution set. 0 and and > or or (.7). Solve the following absolute value inequalities.
Intermediate Algebra Practice Final Math 0 (7 th ed.) (Ch. -) (.5). Solve the following compound inequalit and graph the solution set. 0 and and > or or (.7). Solve the following absolute value inequalities.
You studied exponential growth and decay functions.
 TEKS 7. 2A.4.B, 2A..B, 2A..C, 2A..F Before Use Functions Involving e You studied eponential growth and deca functions. Now You will stud functions involving the natural base e. Wh? So ou can model visibilit
TEKS 7. 2A.4.B, 2A..B, 2A..C, 2A..F Before Use Functions Involving e You studied eponential growth and deca functions. Now You will stud functions involving the natural base e. Wh? So ou can model visibilit
LESSON #48 - INTEGER EXPONENTS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON #8 - INTEGER EXPONENTS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II We just finished our review of linear functions. Linear functions are those that grow b equal differences for equal intervals. In this unit we will
LESSON #8 - INTEGER EXPONENTS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II We just finished our review of linear functions. Linear functions are those that grow b equal differences for equal intervals. In this unit we will
Chapter 8. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 8 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Lesson 8-1 Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function The general form of an eponential function is y = ab. Growth Factor When the value of b is greater
Chapter 8 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Lesson 8-1 Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function The general form of an eponential function is y = ab. Growth Factor When the value of b is greater
7Exponential and. Logarithmic Functions
 7Eponential and Logarithmic Functions A band of green light occasionall appears above the rising or setting sun. This phenomenon is known as a green flash because it lasts for a ver brief period of time.
7Eponential and Logarithmic Functions A band of green light occasionall appears above the rising or setting sun. This phenomenon is known as a green flash because it lasts for a ver brief period of time.
OBJECTIVE 4 EXPONENTIAL FORM SHAPE OF 5/19/2016. An exponential function is a function of the form. where b > 0 and b 1. Exponential & Log Functions
 OBJECTIVE 4 Eponential & Log Functions EXPONENTIAL FORM An eponential function is a function of the form where > 0 and. f ( ) SHAPE OF > increasing 0 < < decreasing PROPERTIES OF THE BASIC EXPONENTIAL
OBJECTIVE 4 Eponential & Log Functions EXPONENTIAL FORM An eponential function is a function of the form where > 0 and. f ( ) SHAPE OF > increasing 0 < < decreasing PROPERTIES OF THE BASIC EXPONENTIAL
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, you will be epected to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that you will pull out of your toolbo this
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: When you come back to school, you will be epected to have attempted every problem. These skills are all different tools that you will pull out of your toolbo this
Math Review Part C Advanced Level (Up to end of MAT 053)
 Math Review Part C Advanced Level (Up to end of MAT 05) A scientific calculator is allowed. Answers provided in the final section. Math Review Part C Advanced Level Advanced Level Algebra ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
Math Review Part C Advanced Level (Up to end of MAT 05) A scientific calculator is allowed. Answers provided in the final section. Math Review Part C Advanced Level Advanced Level Algebra ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
Unit 8: Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
 Date Period Unit 8: Eponential & Logarithmic Functions DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 8.1 Eponential Growth Pg 47 48 #1 15 odd; 6, 54, 55 8.1 Eponential Decay Pg 47 48 #16 all; 5 1 odd; 5, 7 4 all; 45 5 all 4
Date Period Unit 8: Eponential & Logarithmic Functions DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 8.1 Eponential Growth Pg 47 48 #1 15 odd; 6, 54, 55 8.1 Eponential Decay Pg 47 48 #16 all; 5 1 odd; 5, 7 4 all; 45 5 all 4
PRACTICE FINAL EXAM. 3. Solve: 3x 8 < 7. Write your answer using interval notation. Graph your solution on the number line.
 MAC 1105 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM College Algebra *Note: this eam is provided as practice onl. It was based on a book previousl used for this course. You should not onl stud these problems in preparing for
MAC 1105 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM College Algebra *Note: this eam is provided as practice onl. It was based on a book previousl used for this course. You should not onl stud these problems in preparing for
Name Please print your name as it appears on the class roster.
 Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
, Range: [ 4, ) c. Domain: [ 0 ) Range: (, ) d. Domain: [ 8 ) Range: [ 0, )
 Honors Pre-Calculus Semester Review 0 Chapters to. (GC Selected Problems Onl!). Model the following situation with a linear equation in slope-intercept form. The gas tank in a truck holds gallons. The
Honors Pre-Calculus Semester Review 0 Chapters to. (GC Selected Problems Onl!). Model the following situation with a linear equation in slope-intercept form. The gas tank in a truck holds gallons. The
Honors Pre-Calculus. Multiple Choice 1. An expression is given. Evaluate it at the given value
 Honors Pre-Calculus Multiple Choice. An epression is given. Evaluate it at the given value, (A) (B) 9 (C) 9 (D) (E). Simplif the epression. (A) + (B) (C) (D) (E) 7. Simplif the epression. (A) (B) (C) (D)
Honors Pre-Calculus Multiple Choice. An epression is given. Evaluate it at the given value, (A) (B) 9 (C) 9 (D) (E). Simplif the epression. (A) + (B) (C) (D) (E) 7. Simplif the epression. (A) (B) (C) (D)
C)not a function. B) function domain: {-3, 2, 4, 6} range: {-7, 4, 2, -1}
 Name Spring Semester Final Review (Dual) Precalculus MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the relation represents a function.
Name Spring Semester Final Review (Dual) Precalculus MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the relation represents a function.
Algebra II Notes Unit Six: Polynomials Syllabus Objectives: 6.2 The student will simplify polynomial expressions.
 Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MAC 0 Module Test 8 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the function value. ) Let f() = -. Find f(). -8 6 C) 8 6 Objective:
MAC 0 Module Test 8 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the function value. ) Let f() = -. Find f(). -8 6 C) 8 6 Objective:
