Determination of Natural Radioactivity and Hazard in Soil and Rock Samples in a Mining Area in Ghana
|
|
|
- Job Cummings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Determination of Natural Radioactivity and Hazard in Soil and Rock Samples in a Mining Area in Ghana 1* 1 2 A. Faanu,E. O. Darko and J. H. Ephraim 1 Radiation Protection Institute, Ghana Atomic Energy Commission, P. O. Box LG 80, Legon, Accra, Ghana 2 Department of Chemistry, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi Corresponding author; afaanu@yahoo.co.uk. Abstract The activity concentrations of natural radionuclides Ra, Th and K in soil, rock, waste and tailing samples were measured by gamma spectrometry using high-purity germanium detector. In addition, radiological hazard 232 assessments due to these natural radionuclides were carried out. The average activity concentrations of Ra, Th 40 and K determined were Bq/kg, Bq/kg and Bq/kg, respectively. The average annual effective dose was msv. The average radium equivalent activity concentration in the sample was Bq/kg. The calculated external and internal hazard indices were less than unity with average 222 values of 0.16 and 0.20, respectively. The result of the Rn emanation fraction varied in a range of The results obtained show that soil, rock and waste materials that may be used for construction of buildings may not pose any significant radiological hazards to the inhabitants in the study area. Introduction Natural sources of radiation are known to be the most significant means by which the public are exposed to radiation. These are mainly due to the primordial radionuclides, such as K and radionuclides from the U 232 and Th decay series. Uranium and thorium occur at trace levels in the earth crust, and 0.018% of the total amount is potassium is 40 K (Mujahid et al., 2008). Also most minerals in the earth s crust contain small, but measurable concentrations of naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM). Geochemical properties associated with mining and mineral processing may result in elevated concentrations of U and Th (White & Rood, 2001). The health concern from NORM is associated primarily with the 222 generation and release of Rn gas, produced through the radioactive decay of Ra (a 238 member of U decay series). The inhalation 222 of Rn has been associated with increased risk of lung cancer (NAS, 1988). Even though the concentrations of these radionuclides are widely distributed, the levels have been found to depend on the local geological conditions, and as a result vary from place to place (Xinwei et al., 2006). The specific levels in soil are related to the types of rock from which the soil originates. Higher radioactivity levels are associated with igneous rocks such as granite and lower levels with sedimentary rocks. The content of U and Th generally increases with SiO 2 content during differentiation, fractional crystallisation, partial melting, etc. in the final stage of magmatic procedures (Mason & Moore, 1982). The increase of U with both SiO and alkali 2 content is usually more marked than the increase of Th. Uranium and thorium are enhanced mainly in accessory minerals such
2 78 West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, 2011 as orthite or allanite, monazite, zircon, appetite and shene which are constituents of granitic rocks (Mason & Moore, 1982). There are exceptions, however, as some shale, and phosphate rocks have relatively high content of radionuclides (Uosif, 2007). If these materials contain significant levels of naturally occurring radioactive materials and are used for building purposes, it may lead to exposure of the inhabitants of the study area (UNSCEAR, 2000). Mining has been identified as one of the potential sources of exposure to NORM (UNSCEAR, 2000). In Ghana there are more than 200 mining companies operating from small, medium to large scale mining. There is limited data on the levels of environmental radioactivity concentrations and public exposure due to mining and mineral processing activities of mines in Ghana (Darko et al., 2005; Darko et al., 2010). Consequently, there is general lack of awareness and knowledge of the radiological hazards and exposure levels by legislators, regulators and operators. As a result measurement of radioactivity to determine the presence and concentrations of these radionuclides in soils, which could be used as building materials by communities in and around the mines is important for developing guidelines. Soil and rocks in the study area require investigation to quantify the activity concentrations of uranium, thorium and potassium in the materials. Knowledge of radon emanation fraction would also play an important role in characterisation of radon source strengths in soil which could be used as building materials. Radon emanation fraction is defined as the fraction of radon atoms formed in a solid that escapes from the solid and is free to migrate (White & Rood, 2001). The physical properties of the Ra-bearing material determine the radon emanation fraction of the material (Tanner, 1980). The objective of this present study was to measure the activity concentrations of Ra, Th and K in soils, wastes, rocks and tailings in Tarkwa Gold Mine and its surrounding communities to assess the radiological hazards and risk associated with exposure of the public. The results from the study will serve as a baseline data in data bank for the Radiation Protection Board of Ghana, as part of a national programme to establish data on environmental radioactivity in Ghana. Materials and methods Study area The study area is Tarkwa Goldmine and its surrounding communities in the mines area of concession. The Tarkwa Goldmine is located in the Wassa West District in the Western Region of Ghana. The Tarkwa o township is located at latitude 5 15 N and o longitude 2 00 W. The mine is about 4 km from Tarkwa township. Fig. 1 shows the concession of the mine and the surrounding communities where sampling was carried out. The concession of the mine covers an 2 area of km. Table 1 shows the communities and the population distribution around the mines. Tarkwa township lies within the main gold belt of Ghana that stretches from Axim in the southwest to Konongo in the northeast (Kortasi, 2004). The total population of the Tarkwa township is about 80,000 (Kuma, 2007), with an estimated population of the District being 236,000 (IFC, 2003; Darko et al., 2010). In
3 Faanuet al..: Determination of natural radioactivity in soil and rock samples in a gold mining area 79 Fig. 1. Location map of the study area.
4 West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, TABLE 1 Communities and the population distribution around the mines [GFGL, 2007] # Community Location coordinates Population (2004 estimates) Abekoase Brahabebom Huniso New Atuabo Pepesa Samahu Tarkwa township N " W " N " W " N " W " N " W " N " W " N " W " N " W " ,000 Gold ore is the alluvial type and nonaddition there are eight communities dotted sulphidic associated with the conglome-rates around the mine. of the Tarkwaian formations. Two main methods are used by the Tarkwa Goldmine to Geology of the mining area Geologically, the gold ore is located recover gold from the ore. The carbon in leach within the Tarkwaian system, which forms a (CIL) and the heap leach (HL) methods are significant portion of the stratigraphy of the being employed. The geological map of the Ashanti Belt in south-western Ghana. study area is shown in Fig. 2. Intrusive igneous rocks contribute to about 20% of the total thickness of the Tarkwaian Hydrogeology and climatology of the study system in the Tarkwa area. The ore body area Hydrogeologically, most of the major consist of a series of sedimentary banket quartz reef units similar to those mined in towns and villages except Tarkwa township the Witwatersrand area of South Africa, in the Wassa West District depend on where the gold ore is associated with groundwater as the main source of water uranium in commercial quantities. The supply through boreholes and hand-dug wells local geology is dominated by sedimentary (Kortasi, 2004). The groundwater occurrence Banket series, which consists of a well- is associated with the development of sorted conglomerates and pebbly quartzite secondary porosity through fissuring and with clasts generally considered to be weathering since the area lacks primary Birimian in origin and containing porosity due to the consolidated nature of the significant gold mineralization, hosting the rocks. Two types of soils exist in the TarkwaTarkwa ore body. The rocks of the Prestea area, and these are forest oxysol in the Tarkwaian system consist of the Kawere south, and forest ochrosol-oxysol integrates Group, the Banket series, the Tarkwa in the north [Kortasi, 2004]. The Phyllite and the Huni Sandstone. Most of characteristics of the soils in the area are the rocks that resemble sandstone at the shown in Table 2 (Kuma & Younger, 2001). The climate of Tarkwa is the tropical type surface are weathered equivalents of parent quartzite (Kuma & Younger, 2001). characterised by two wet seasons;
5 Faanuet al..: Determination of natural radioactivity in soil and rock samples in a gold mining area 81 Fig. 2.Geological map of the study area.
6 82 West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, 2011 TABLE 2 Characteristics of soils in the study area (Kuma and Younger, 2001) Soil type Texture Percentage Gravel Sand Silt Clay Banket series Silty-sand Laterite Huni Silty-sand Kawere Silt sand Tarkwa phyllite laterite Weathered dyke Silt March July and September-November. D a t a o b t a i n e d f r o m t h e m i n e s Environmental Department shows that the total annual rainfall figures measured for the year 2008 was 1744 mm with an average of 145 mm. The average rainfall figure from January to July 2009 was mm in a range of 2.2 mm in January to 283 mm in June. The relative humidity for the area measured was in the range of 73 98% with an average of 86%. The average atmospheric pressure was about 1002 mbar in the range of mbar, and outdoor temperature in o the range of C with an average value o of 34 C. Sampling and sample preparation Thirty-eight soil/rock samples were collected randomly within selected areas of the mine concession and also in the communities, and analysed by gamma spectrometry to determine the activity concentration of radionuclides. The sample types included soil, rock, waste and tailings. Fig. 1 shows the sampling locations. At the laboratory, each of the soil/rock samples were air-dried in trays for 7 days and then o oven-dried at a temperature of 105 C until all moisture was completely lost. The samples were then grinded into a fine powder using a ball mill, and sieved through a 2-mm pore size mesh into 1-litre Marinelli beaker. The Marinelli beakers with the samples were hermetically sealed and stored for 4 weeks for the short-lived daughters of Ra (in the U decay series) and Th decay series to attain secular equilibrium with their longlived parent radionuclides. Instrument calibration and measurements The activity concentrations of the radionuclides in the samples were measured using a High Purity Germanium Detector (HPGD). The gamma spectrometry system consists of an n-type HPGD (ORTEC) coupled to a computer based multi-channel analyser (MCA) mounted in a cylindrical lead shield (100 mm thick) and cooled in liquid nitrogen. The relative efficiency of the detector was 20% with energy resolution of 1.8 kev at gamma ray energy of 1332 kev of 60 Co. The radionuclides were identified using gamma ray spectrum analysis software, ORTEC MAESTRO-32. The background radiation distribution in the environment around the detector was determined using 1 litre Marinelli beaker which was thoroughly cleaned and filled with
7 Faanuet al..: Determination of natural radioactivity in soil and rock samples in a gold mining area 83 distilled water and counted for s and in the same geometry as the samples. The background spectra were used to correct the net peak area of gamma rays of measured isotopes. The minimum detectable activity ( Th was 0.11 Bq/kg and K was 0.15 Bq/kg. The energy and efficiency calibration 238 of Ra U decay series) was 0.12 Bq/kg, were performed using multi gamma solid water standard in a 1-litre Marinelli beaker in the energy range of 60 kev to ~2000 kev. The standard radionuclides are uniformly distributed in solid water with volume and 3 density of 1000 ml and 1.0 g/m, respectively (source number, NW146) and manufactured by QSA Global GmbH, Germany. The gamma emitting radionuclides used for the calibration in the Marinelli beaker geometry were Co (122 kev), Cs (662 kev), Co 88 (1173 and 1333 kev) and Y (1838 kev) with certified uncertainties < 3%. Calculation of activity concentration and estimation of doses The activity concentration of Ra was calculated from the average energies of of Pb and of Bi, respectively. Similarly, the activity 232 concentration of Th was determined from 208 the average energies of of Tl and kev of Ac. This was based on the assumption that secular equilibrium has been established between the long-lived parent radionuclides R and Th, and their short lived daughter radionuclides. The 40 activity concentration of K was determined from the energy of kev. The analytical expression used in the calculation of the activity concentrations is given by Equation (1) in Bq/kg. A sp P td N De p. T. ( E). M c (1) where N is the net counts of the radionuclide D in the samples, t is the delay time between d sampling and counting, P is the gamma emission probability (gamma yield), (E) is the absolute counting efficiency of the detector system, T c is the sample counting, M ( ptd) is the mass of the sample (kg), e is the decay correction factor for delay between time of sampling and counting, and is p the decay constant of the parent radionuclide. Radiation hazard indices In the determination of radon emanation fractions (EF), the soil and rock samples were air-dried for 1 week and finally oven-dried to remove any additional moisture from the samples. The dried samples were each transferred into a 1-litre Marinelli beaker without any treatment (i.e. coarse and bulky samples were not broken down before measurement) hermetically sealed and counted for 2 h, and then allowed to stay for 4 weeks for secular equilibrium to be established between Ra and its short-lived daughter nuclides of Pb and Bi. The net peak area of Ra was determined from average peak areas of Pb and Bi. The samples were categorised as follows: granular samples of soil and gravel (GS); mixed granular and massive samples of soil and rock (M); massive rock samples (MS) and fine particle samples of tailings (F). The radon emanation fraction was determined using the following method described by White & Rood (2001). In this method, the emanation fraction is determined from the net count rates after sealing the sample container (C 1) and the net count rate at secular
8 84 West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, 2011 equilibrium (C ). The EF determination is based on the increase of Rn concentration during the time interval between sealing (t ) 1 and after 30 days (t 2), and expressed mathematically as follows; t1 C 1 = A 0 + N (1 e ) (2) t2 C 2 = A 0 + N (1 e ) (3) A o and N are determined by solving equations (2) and (3) as follows: Equations (2) and (3) were simplified by substituting x ët -ët for 1-e 1 -ët1 and y for 1-e 2. The results for N, A o and EF are given in equations (4), (5) and (6), respectively. C C N 1 2 x y xc yc A o 2 1 x y N EF A N o (4) (5) (6) 222 where A o is the count rate of Rn present in a sample at sealing time t 1, N is the net count rate of Rn emanated after time t, is Rn 2-1 decay constant (s ). The emanation fraction (EF) was calculated from Equation (6). The radiological hazard of the NORM was determined by calculating the radium equivalent concentration (Ra ), the external eq and internal hazard indices. The term radium equivalent activity (Ra ) in Bq/kg is eq normally used to compare the uniformity in radiation of material containing different amounts of Ra, Th and K. It is based on the estimation that 370 Bq/kg of Ra, Bq/kg of Th and 4810 Bq/kg of K produce the same gamma ray dose rate (Xinwei et al., 2006). Raeq is a widely used hazard index and was determined using Equation (7) (Beretka & Mathew, 1985). Ra eq = C Ra C Th CK (7) where C, C and C are the activity Ra Th K concentrations for Ra, Th and K, respectively. The values of the external and internal hazard indices must be less than one for the radiation hazard to be considered negligible i.e. the radiation exposure due to the radioactivity from the construction material is limited to 1.5 msv/y (Beretka & Mathew, 1985). Also, radon and its short-lived products are hazardous to the respiratory organs and as a result, the internal exposure to radon and its daughter products is quantified using the internal hazard index. The external hazard index (H ) was ex calculated from Equation (8) and the internal hazard index (H ) from Equation (9). in H H ex in C C C Ra Th K 1 (8) C C C Ra Th K 1 (9) where C Ra, C Th and C K are the activity concentrations of Ra, Th and K, respectively. The external gamma dose rate from the soil/rock samples in outdoor air at 1 m above the ground was calculated from the activity concentrations using Equation (10) (Uosif, 2007). 1 D(nGyh ) = A k A U A Th (10) where A, A and A are the activity K Ra Th concentrations of K, Ra and Th, respectively. The effective dose was calculated from the absorbed dose rate by applying the dose conversion factor of 0.7 Sv/Gy and an outdoor occupancy factor of 0.2 (UNSCEAR, 2000).
9 Faanuet al..: Determination of natural radioactivity in soil and rock samples in a gold mining area 85 In addition, the cancer and hereditary risks due to low doses were estimated using the ICRP cancer risk assessment methodology (ICRP, 1991; 2007). The lifetime risks coefficient of fatal cancer recommended in the 1990 recommendations -2-1 by the ICRP are 5 10 Sv for the members -2-1 of the public and 4 10 Sv for occupationally exposed workers (ICRP, 1991; 2007). The risk of exposure of low doses and dose rates of radiation to members of the public in Tarkwa and surroundings as a result of the mining and mineral processing of the mine was estimated using the 2007 recommended risk coefficients (ICRP, 2007) and an assumed 70 years lifetime of continuous exposure of the population to low level radiation. According to the ICRP methodology: Fatality cancer risk = total annual effective dose (Sv) cancer nominal risk factor. Hereditary effect = total annual effective dose (Sv) hereditary nominal effect factor. Results and discussion Table 1 shows the communities around the mine and the population distribution of the study area. The estimated population of the study area was 93,500 people. Table 2 shows the soil characteristics of the study area. There are two types soil in the study area, namely forest oxysol in the south which is porous and highly leached, and forest ochrosol-oxysol integrates in north which is less leached. The soil types of the Goldmine is more of the Banket series with mixed soil texture of silt-sand with patches of laterite and are generally considered as clayed soiltypes (Kortasi, 2004). The results of the activity concentrations, absorbed dose rates, annual effective dose, radium equivalent activity and hazards indices are shown in Table 3. The average activity concentration of Ra was 13.61±5.39 Bq/kg in a range of 2.26 Bq/kg from a waste rock sample taken at Makulu waste dump (SS 12) to Bq/kg from a soil sample in a cocoyam/cassava farm near the Agricultural Hill closed to Teberebie pit of the mine. The average activity concentration 232 of Th was 24.22±17.15 Bq/kg in the range of 6.00 Bq/kg from soil sample taken at Huniso community to Bq/kg from a soil sample in the cassava/ cocoyam farm at 40 Agricultural Hill. For K, the average activity concentration was ±63.69 in a range of Bq/kg in a waste dump in the mine to Bq/kg in the same soil sample at Agricultural Hill. The reported total uncertainties are based on random (counting statistics) and systematic errors (uncertainty in efficiency, calibration source uncertainty) involved in producing the final nuclide activity concentration. In general, the activity concentrations of radionuclides in the different types of samples are variable and do not show any particular pattern. The reasons for the variations in the activity concentrations could be due to differences in soil characteristics and geological properties from one location to another as shown in Table 2. The average activity concentrations Ra, Th and K in this study are lower than the worldwide average values of 32, 45 and 420 Bq/kg, respectively (UNSCEAR, 2000). It is also worth noting that the Ra activity concentrations, in all the 38 composite samples had values less than the worldwide 232 average. For Th the values in all the
10 ngy/h dose, msv (H ex) (H in) Range Average±Stdev ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, 2011 TABLE Results of the average activity concentration of Ra, Th and K together with their total uncertainties, total absorbed dose, annual effective dose, radium equivalent activity and hazard indices of the samples in the study area Community Activity concentration, Bq/kg Absorbed Annual Ra eq, Bq/kg Hazard External Ra Th K dose rate, effective index internal Abekoase ± ± ± Brahabebom ± ± ± Huniso 5.22 ± ± ± New Atuabo ± ± ± Pepesa ± ± ± Samahu ± ± ± Tarkwa ± ± ± Mine (rock) 8.56 ± ± ± Mine (tailings) 7.18 ± ± ± Mine (soil) ± ± ±
11 Faanuet al..: Determination of natural radioactivity in soil and rock samples in a gold mining area 87 TABLE 4 Radon emanation coefficient of the soil, tailings and rock samples Location Number of samples Ra, Bq/kg average ±SD EF ± SD Mine soil Tarkwa (GS) ± ± 0.03 Mine rock Tarkwa (MS) ± ± 0.03 Mine north Heap Leach (M) ± ± 0.03 Mine south Heap Leach (M) ± ± 0.03 Mine Tailing (F) ± ± 0.03 Mine Waste (Rock) (MS) ± ± 0.03 Mine Pit (Teberebie) (M) ± ± 0.04 Mine Pit (Pepe) (M) ± ± 0.03 Mine Pit (Kontraverchy) (M) ± ± 0.03 Mine Pit (Akontansi) (M) ± ± 0.05 Ore Stockpile (MS) ± ± 0.03 Plant Site (M) ± ± 0.03 New Atuabo community (GS) ± ± 0.03 Goldfields Clubhouse (GS) ± ± 0.03 Brahabebom community (GS) ± ± 0.05 Samahu community (GS) ± ± 0.04 Boboobo community (GS) ± ± 0.03 Abekoase community (GS) ± ± 0.03 Huniso community (GS) ± ± 0.03 Pepesa community (GS) ± ± 0.03 UMAT/Agric Hill (GS) ± ± 0.03 Legend: GS- granular samples; M- mixed samples (granular and massive); MS- massive samples; F-fine particles samples, UMAT- University of Mines and Technology; EF-emanation fraction and SD-standard deviation. samples are lower than the world average except values in soil samples in farms at Agricultural Hill and University of Mines 40 and Technology in Tarkwa. The K activity concentrations in all soil/rock samples have values less than the worldwide average value except soil sample at Teberebie pit of the mine. The results of the activity concentrations in this study compared quite well with similar studies that have been carried out in other countries as shown in Table 5. This implies that the rock of the area which is sedimentary have low levels of radioactivity. The results of the calculated absorbed dose rate in the soil/rock samples varied in a range of ngy/h with an average value of ngy/h. The average absorbed dose rate in this study is lower than the worldwide average value of 60 ngy/h estimated from soil concentrations (UNSCEAR, 2000). The corresponding estimated annual effective dose was 0.17 msv/year. The natural radioactivity in building materials is usually determined 232 from the activity concentrations of Ra, Th 40 and K. In order to assess if the soil/rock in the study area could be a source of public radiation exposure if used for building purposes the following hazard assessments
12 88 West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, 2011 TABLE 5 Comparison of the average activity concentrations, the radium equivalent activities (Ra eq ) of soil, rocks, waste and tailings of the study area with published data. Country N Specific activity concentration, Bq/kg Ra eq, Reference Ra Th K Bq/kg Australia Beretka and Mathew (1985) Austria Sorantin and Steger (1984) Algeria Amrani and Tahtat (2001) Brazil Malanca et al. (1993) China Zinwei (2005) Egypt El Afifi et al. (2006) India Kumar et al. (1999) Japan Suzuki et al. (2000) Netherlands Ackers et al. (1985) Tunisia Hizem et al. (2005) Turkey Turhan and Gurbuz (2008) Ghana This work Legend: N- number of samples were used; radium equivalent (Ra ) activity eq in Bq/kg, external (H ) and the internal ex hazard (H ). The radium equivalent activity in is related to the external gamma dose from the terrestrial radionuclides and the internal dose due to radon and its decay products of Pb and Po. In this study, the average radium equivalent activity in the samples was Bq/kg in a range of Bq/kg. The average external and internal indices were 0.16 and 0.20, respectively. The maximum acceptable value of Ra in building materials eq must be less than 370 Bq/kg for the material to be considered safe for use. The values of the Ra, H and H are below the acceptable eq ex in values. This indicates that soil and other materials in the study area that might be used for building purposes for shelter may not pose any significant radiological radiation hazard and, thus, regarded safe. 222 The results of Rn emanation fraction (EF) in the samples and the average activity concentration of Ra are shown in Table 6. The result of the EF varied in a range of 0.51 in mine tailings (fine particles) to 0.80 in a mine pit samples containing granular and massive particles. The result from the study has also confirm previous studies which indicates that the variation of EF is independent of the Ra content in the sample, and is strongly correlated with the grain surface density (White & Rood, 2001). The results in this study for both granular and massive samples also showed that the EF of the different types of samples are almost the same contrary to what has been reported in earlier EF studie,s where the smaller the grain size the higher the EF as follows EF(GS)>EF(M)>EF(MS). Generally, the 222 Rn EF of different Te-NORM wastes can be ordered as follows: mining > gypsum > oil
13 Faanuet al..: Determination of natural radioactivity in soil and rock samples in a gold mining area 89 and gas > coal power plant (Afifi et al., 2004). The EF values in this study are compared with similar studies as shown in Table 6. The radiological fatality cancer risks for the population and severe hereditary effects b a s e d o n I C R P r i s k a s s e s s m e n t methodologies (ICRP, 1991; 2007) were carried out and the results shown in Table 7. The estimated lifetime fatality cancer risk and the lifetime hereditary effect were and , respectively. This means that approximately seven persons out of 10,000 people are likely to suffer from cancer related diseases from irradiation due to low background radiation exposure. In the case of lifetime hereditary effect, approximately two people out of 100, 000 are likely to suffer from some form of hereditary diseases. This means that the lifetime fatality cancer risk is slightly above the USEPA acceptable range -6-4 of risks of 1 10 to 1 10 values for the population of the study area. TABLE Comparison of activity concentration of Ra and Rn emanation fraction (EF) of the study with different NORM waste from various industrial activities Industrial activity 222 Ra activity Rn EF Reference concentration, kbq/kg Oil and gas production Oklahoma USEPA (1993) Michigan USEPA (1993) Phosphate industry Gypsum USEPA (1993), Egidi and Hull (1997) Slag USEPA (1993), Egidi and Hull (1997) Power plants generation Coal ash USEPA (1993), Egidi and Hull (1997) Metallurgical processing Uranium mining White & Rood (2001) Rare earth s White & Rood (2001) Gold mining This work TABLE 7 Estimated risk due to radionuclides in soil and rock samples Mode of exposure Average annual Fatality cancer Lifetime fatality Severe Estimated effective dose, risk to population cancer risk hereditary lifetime msv/year per year to population efects per hereditary year effects External irradiation x x x x due to U, Th and K in soil/rock samples
14 90 West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, 2011 Conclusion The activity concentrations of the naturally 232 occurring radionuclides of Ra, Th and 40 K in soil, rock, wastes and tailing samples were determined by gamma spectrometry. The average activity concentrations of Ra, Th and K in the samples were estimated to be Bq/kg, Bq/kg and Bq/kg, respectively. The average radium equivalent activity in the samples was Bq/kg. The absorbed dose rate due the radionuclides in the samples was calculated to be in a range of 9.05 to ngy/h with an average value of ngy/h. The corresponding annual effective dose was calculated to be 0.17 msv/year. The external and the internal hazard indices in all the samples were less than unity with average values of 0.16 and 0.20, respectively. The values of the radon emanation fraction of the samples were less than unity with values ranging from 0.51 to On the basis of the radium equivalent activity, radon emanation fractions, hazard indices, the absorbed dose rate and annual effective dose of all the samples studied, it can be concluded that these materials if used for construction of dwellings by the inhabitants of the study area might not pose any significant radiation hazard. The results in this study compare well with some studies in other countries and show some variations in other countries. Any variation could be attributed to differences in geological formations. Acknowledgement The authors would like to thank the Radiation Protection Institute of Ghana Atomic Energy Commission and the Goldfields Ghana Ltd, who provided financial support to carry out the study. The authors are also grateful to the staff of the Environmental Department of Goldfields Ghana Ltd and to Mr. David Kpeglo, Oscar Adukpo, Rita Kpordzro, Henry Lawluvi, Bernice Agyeman, Ali Ibrahim, all of the Radiation Protection Institute, for their assistance in carrying out the study. This research work was financed by the Radiation Protection Institute of the Ghana Atomic Energy Commission and the Tarkwa Goldmine Ltd. The two institutions are gratefully acknowledged for their support. References Ackers J. G., Den Boer J. F., De Jong P. and Wolschrijn R. A. (1985). Radioactivity and exhalation rates of building materials in the Netherlands. Sci. Tot. Envir. 45: Afifi E. M., Khalifa S. M. and Aly H. F. (2004). 222 Assessment of the Ra content and the Rn emanation fraction of TE-NORM wastes at certain sites of petroleum and gas production in Egypt. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 260(1): Amrani D. and Tahtat M. (2001). Natural radioactivity in Algeria building materials. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 54: ASTM (1983). Standard Method for sampling surface soils for radionuclides. American Society for Testing Materials, Report No. C (PA: ASTM) ASTM (1986). Recommended practice for investigation and sampling soil and rock for engineering purposes, In Annal Book of ASTM Standards; (04/08). American Society for Testing Materials, Report No. D, 420 (PA: ASTM) Beretka J. and Mathew P. J. (1985). Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrial wastes and by-products. Hlth Phys. 48: Cember H. (1996). Introduction to Health Physics. 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York. Darko E. O., Tetteh G. K. and Akaho E. H. K. (2005). Occupational radiation exposure to norms in a gold mine. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 114(4): Darko E. O. and Faanu A. (2007). Baseline radioactivity measurements in the vicinity of a Gold
15 Faanuet al..: Determination of natural radioactivity in soil and rock samples in a gold mining area 91 Treatment Plant. J. appl. Sci.Tech. 10(1 & 2): Darko E. O., Faanu A., Razak A., Emi-Reynolds G., Yeboah J., Oppon O. C. and Akaho E. H. K. (2010). Public exposure hazards associated with natural radioactivity in open-pit mining in Ghana. Rad. Prot, Dosim. 138(1): Egidi P. and Hull C. (1999). NORM and TE-NORM: procedures, users and regulations. 32rd Midyear Topical Meeting of the Health Physics Society. Albuquerque, NM, USA, Jun El Afifi E. M., Hilal M. A., Khalifa S. M. and Aly H. F. (2006). Evaluation of U, Th, K and emanated radon in some NORM and TENORM samples. Radiat. Meas. 41: Gold fields Ghana Ltd (2007). Securing the future: mineral resource and ore reserve statement. Tarkwa Goldmine Ltd, Tarkwa, Ghana. Hizem N., Fredj A. B. and Ghedira L. (2005). Determination of natural radioactivity in building materials used in Tunisia dwellings by gamma ray spectrometry. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. (114): IAEA (2005). Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials (IV), proceedings of an international c o n f e re n c e h e l d i n S z c z y r k. I A E A - TECDOC 1472, Poland. ICRP (1991) Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 60, Pergamon Press, Oxford. ICRP (2007) Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 103, Pergamon Press, Oxford IFC (2003). Socio-Economic Baseline and Impact Assessment Report. Community Development Plan, Iduapriem and Teberebie Goldmines, GAGL, International Finance Corporation, Ghana. Kortasi B. K. (2004). Hydrochemistry of groundwater in the mining area of Tarkwa-Prestea, Ghana. (PhD Thesis.) University of Ghana, Legon-Accra, Ghana. Kuma J. S and Younger P. L. (2001). Pedological characteristics related to groundwater occurrence in the Tarkwa area, Ghana. J. Afri. Earth Sci. 33(2): Kuma J. S. (2007). Hydrogeological Studies on the Tarkwa Gold Mining District, Ghana. Bull Eng Geol Envir. 66(1): Kumar V., Ramachandran T. V. and Prasad R. (1999). Natural radioactivity of Indian building materials and by products. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 51: Malanca A., Pessina V. and Dallara G. (1993). Radionuclide content of building materials and gamma-ray dose rates in dwellings of Rio-Grande Do-Norte Brazil. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 48: Mason B. and Moore C. B. (1982). Principles of Geochemistry, 4th edn. Wiley, New York. Mujahid S. A., Rahim A., Hussain S. and Farooq (2008). Measurements of natural radioactivity and radon exhalation rates from different brands of cement used in Pakistan. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 130(2): NAS (1988). Health risks of radon and other internally deposited alpha emitters. BEIR IV, National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council. Academy Press, Washington DC. OECD/NEA (1979). Exposure to radiation from natural radioactivity in building materials. Report by Nuclear Energy Agency Group of Experts, OECD, Paris. Rogers J. J. W. and Adams J. A. S. (1969). Uranium and thorium. In Handbook of Geochemistry. (K. H. Wedepohl, ed.), 11 (13). Springer, Berlin. Sorantin P. and Steger F. (1984). Natural radioactivity of building materials in Austria. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 7: Suzuki A., Iida T., Moriizumi J. and Sakuma Y. (2000). The effects of different types of concrete on population doses. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 90: Tanner A. B. (1980). Radon migration in the ground: A supplementary review, In Natural radiation environment III. (T. F. Gesell and W. M. Lowder, eds), Vol. 1, pp US Department of Energy Report CONF Turhan S. and Gurbuz G. (2008). Radiological significance of cement used in building construction in Turkey. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 129(4): Uosif M. A. M. (2007). Gamma ray spectroscopic analysis of selected samples from the Nile river sediments in Upper Egypt. 123(2): Rad. Prot. Dosim.
16 92 West African Journal of Applied Ecology, vol. 19, 2011 U S E PA ( ). D i f f u s e N O R M w a s t e characterisation and preliminary risk assessment. S. Cohen and Associates, Inc. Rogers & Associates Engineering Corp., US Environmental Protection Agency. Office of Radiation and Indoor Air. USGAO (1994). United States General Accounting Office, Nuclear Health and Safety: Consensus on Acceptable Radiation Risk to the Public is lacking. United States General Accounting Office, GAO/RCED , Washington DC. UNSCEAR (2000). Exposures from Natural Sources Report to General Assembly. Annex B, New York. White G. J. and Rood A. S. (2001). Radon emanation from NORM-contaminated pipe scale and soil at petroleum industry site. J. Envir. Radioact. 54: Xinwei L. (2005). Radioactive analysis of cement and its products collected from Shaanxi, China. Hlth Phys. 88: Xinwei L., Lingquig W., Xiaodan J., Leipeng Y. and Gelian D. (2006). Specific activity and hazards of Archeozoic-Cambrian rock samples collected from the Weibei area of Xhaanxi, China. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 118(3):
Estimating the natural and artificial radioactivity in soil samples from some oil sites in Kirkuk-Iraq using high resolution gamma rays spectrometry
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, September 2017, pp. 674-682 Estimating the natural and artificial radioactivity in soil samples from some oil sites in Kirkuk-Iraq using high resolution
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 55, September 2017, pp. 674-682 Estimating the natural and artificial radioactivity in soil samples from some oil sites in Kirkuk-Iraq using high resolution
Radioactivity measurements and risk assessments in soil samples at south and middle of Qatar
 Radioactivity measurements and risk assessments in soil samples at south and middle of Qatar A. T. Al-Kinani*, M. A. Amr**, K. A. Al-Saad**, A. I. Helal***, and M. M. Al Dosari* *Radiation and Chemical
Radioactivity measurements and risk assessments in soil samples at south and middle of Qatar A. T. Al-Kinani*, M. A. Amr**, K. A. Al-Saad**, A. I. Helal***, and M. M. Al Dosari* *Radiation and Chemical
Natural Radioactivity and its Associated Radiological Hazards in Ghanaian Cement
 Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences 3(2): 160-166, 2011 ISSN: 2041-0492 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2011 Received: November 27, 2010 Accepted: December 25, 2010 Published: March 05,
Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences 3(2): 160-166, 2011 ISSN: 2041-0492 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2011 Received: November 27, 2010 Accepted: December 25, 2010 Published: March 05,
Radiological significance of Egyptian limestone and alabaster used for construction of dwellings
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 49, March 011, pp. 157-161 Radiological significance of Egyptian limestone and alabaster used for construction of dwellings A El-Taher 1, * & S Makhluf 1 1
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 49, March 011, pp. 157-161 Radiological significance of Egyptian limestone and alabaster used for construction of dwellings A El-Taher 1, * & S Makhluf 1 1
Natural Radiation Map of the Sudan
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Natural Radiation Map of the Sudan * Magdi Hassan Saad 1, 2 1 - Department
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org Natural Radiation Map of the Sudan * Magdi Hassan Saad 1, 2 1 - Department
The Pharmaceutical and Chemical Journal, 2017, 4(6): Research Article
 , 217, 4(6):53-6 Available online www.tpcj.org Research Article ISSN: 2349-792 CODEN(USA): PCJHBA Determination of Natural Radioactivity Concentration Levels in Soil Samples in Odigbo Local Government
, 217, 4(6):53-6 Available online www.tpcj.org Research Article ISSN: 2349-792 CODEN(USA): PCJHBA Determination of Natural Radioactivity Concentration Levels in Soil Samples in Odigbo Local Government
Assessment of Natural Radioactivity Levels and Radiological Hazards of Cement in Iraq
 Nuclear Science 2018; 3(2): 23-27 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ns doi: 10.11648/j.ns.20180302.11 Assessment of Natural Radioactivity Levels and Radiological Hazards of Cement in Iraq Zaki A.
Nuclear Science 2018; 3(2): 23-27 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ns doi: 10.11648/j.ns.20180302.11 Assessment of Natural Radioactivity Levels and Radiological Hazards of Cement in Iraq Zaki A.
Radiometric assessment of natural radioactivity levels around Mrima Hill, Kenya
 International Journal of the Physical Sciences Vol. 6(13), pp. 3105 3110, 4 July, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ijps DOI: 10.5897/IJPS11.052 ISSN 1992-1950 2011 Academic Journals
International Journal of the Physical Sciences Vol. 6(13), pp. 3105 3110, 4 July, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ijps DOI: 10.5897/IJPS11.052 ISSN 1992-1950 2011 Academic Journals
Assessment of the natural radioactivity and its radiological hazards in some Egyptian rock phosphates
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 43, July 2005, pp. 489-493 Assessment of the natural radioactivity and its radiological hazards in some Egyptian rock phosphates A Abbady Physics Department,
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 43, July 2005, pp. 489-493 Assessment of the natural radioactivity and its radiological hazards in some Egyptian rock phosphates A Abbady Physics Department,
Gamma Ray Spectrometric Analysis of Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials (NORMS) in Gold Bearing Soil using NaI (Tl) Technique
 Gamma Ray Spectrometric Analysis of Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials (NORMS) in Gold Bearing Soil using NaI (Tl) Technique M.A. Abdullahi S. O. Aliu M. S. Abdulkarim Department of Applied Science,
Gamma Ray Spectrometric Analysis of Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials (NORMS) in Gold Bearing Soil using NaI (Tl) Technique M.A. Abdullahi S. O. Aliu M. S. Abdulkarim Department of Applied Science,
Evaluation of Natural Radioactivity and its Radiation Hazards in Some Building and Decorative Materials in Iraq
 The Egyptian Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and Applications Society of Nuclear Vol 51, 1, (39-45) 2018 Sciences and Applications ISSN 1110-0451 Web site: esnsa-eg.com (ESNSA) Evaluation of Natural Radioactivity
The Egyptian Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and Applications Society of Nuclear Vol 51, 1, (39-45) 2018 Sciences and Applications ISSN 1110-0451 Web site: esnsa-eg.com (ESNSA) Evaluation of Natural Radioactivity
Analysis of natural radioactivity and artificial radionuclides in soil samples in the Najran region of Saudi Arabia
 Safety and Security Engineering V 675 Analysis of natural radioactivity and artificial radionuclides in soil samples in the Najran region of Saudi Arabia A. Al-Zahrany & K. S. Al-Mogabes Institute of Atomic
Safety and Security Engineering V 675 Analysis of natural radioactivity and artificial radionuclides in soil samples in the Najran region of Saudi Arabia A. Al-Zahrany & K. S. Al-Mogabes Institute of Atomic
NATURAL RADIOACTIVITY AND ASSOCIATED RADIATION HAZARDS IN LOCAL PORTLAND AND POZZOLANIC CEMENTS USED IN JORDAN
 NATURAL RADIOACTIVITY AND ASSOCIATED RADIATION HAZARDS IN LOCAL PORTLAND AND POZZOLANIC CEMENTS USED IN JORDAN Mefleh S. Hamideen Department of Physics and Applied Sciences, Faculty of Engineering Technology,
NATURAL RADIOACTIVITY AND ASSOCIATED RADIATION HAZARDS IN LOCAL PORTLAND AND POZZOLANIC CEMENTS USED IN JORDAN Mefleh S. Hamideen Department of Physics and Applied Sciences, Faculty of Engineering Technology,
Radon escape from mine tailings dams. Robbie Lindsay + Joash Ongori (PhD student) Co-authors Prof Richard Newman/Dr Peane Maleka
 Radon escape from mine tailings dams Robbie Lindsay + Joash Ongori (PhD student) (rlindsay@uwc.ac.za) Co-authors Prof Richard Newman/Dr Peane Maleka What is the radon problem in South Africa? Not in houses
Radon escape from mine tailings dams Robbie Lindsay + Joash Ongori (PhD student) (rlindsay@uwc.ac.za) Co-authors Prof Richard Newman/Dr Peane Maleka What is the radon problem in South Africa? Not in houses
Full length Research Article Natural Radioactivity and Hazard Assessment of Imported Ceramic Tiles in Nigeria Ademola J. A.
 www.ajbrui.net Full length Research Article Natural Radioactivity and Hazard Assessment of Imported eramic Tiles in Nigeria Ademola J. A. Department of Physics, University of Ibadan Ibadan, Nigeria ABSTRAT:
www.ajbrui.net Full length Research Article Natural Radioactivity and Hazard Assessment of Imported eramic Tiles in Nigeria Ademola J. A. Department of Physics, University of Ibadan Ibadan, Nigeria ABSTRAT:
A. Faanu *, G. Emi-Reynolds, E. O. Darko, R. Awudu, E.T. Glover, O. K. Adukpo, F. 1
 Calibration and Performance Testing of Sodium Iodide, NaI (Tl), Detector at the Food and Environmental Laboratory of the Radiation Protection Institute of the Ghana Atomic Energy Commission 1 1 1 1 2 1
Calibration and Performance Testing of Sodium Iodide, NaI (Tl), Detector at the Food and Environmental Laboratory of the Radiation Protection Institute of the Ghana Atomic Energy Commission 1 1 1 1 2 1
Radioactivity Measurement in Different Types of Fabricated Building Materials Used in Palestine
 Radioactivity Measurement in Different Types of Fabricated Building Materials Used in Khalil M. Dabayneh* * Faculty of Science and Technology, Hebron University, P.O. Box 4, Hebron,, kaleel5@hotmail.com
Radioactivity Measurement in Different Types of Fabricated Building Materials Used in Khalil M. Dabayneh* * Faculty of Science and Technology, Hebron University, P.O. Box 4, Hebron,, kaleel5@hotmail.com
RADIOACTIVITY IN CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS
 RADIOACTIVITY IN CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS Milica M. Rajačić, Nataša B. Sarap, Marija M. Janković, Jelena D. Nikolić, Dragana J. Todorović and Gordana. Pantelić Institute for Nuclear Sciences "Vinča", University
RADIOACTIVITY IN CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS Milica M. Rajačić, Nataša B. Sarap, Marija M. Janković, Jelena D. Nikolić, Dragana J. Todorović and Gordana. Pantelić Institute for Nuclear Sciences "Vinča", University
Journal of American Science 2013;9(12)
 Journal of American Science 213;9(12) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Estimation of the Radiation Dose for Some Individuals Working With Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials Tarek Mahmoud Morsi,
Journal of American Science 213;9(12) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Estimation of the Radiation Dose for Some Individuals Working With Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials Tarek Mahmoud Morsi,
Jordan Journal of Physics
 Volume 11, Number 3, 2018. pp. 173-179 ARTICLE Jordan Journal of Physics Natural Radioactivity and Associated Radiation Hazards in Local Portland and Pozzolanic Cements Used in Jordan Mefleh S. Hamideen
Volume 11, Number 3, 2018. pp. 173-179 ARTICLE Jordan Journal of Physics Natural Radioactivity and Associated Radiation Hazards in Local Portland and Pozzolanic Cements Used in Jordan Mefleh S. Hamideen
Natural radioactivity levels in soils, rocks and water at a mining concession of Perseus gold mine and surrounding towns in Central Region of Ghana
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1716-5 RESEARCH Open Access Natural radioactivity levels in soils, rocks and water at a mining concession of Perseus gold mine and surrounding towns in Central Region of Ghana A.
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1716-5 RESEARCH Open Access Natural radioactivity levels in soils, rocks and water at a mining concession of Perseus gold mine and surrounding towns in Central Region of Ghana A.
Measurement of Gamma Emitting Radionuclides in Environmental Samples of Talagang Tehsil-District Chakwal
 Nuclear Science 2017; 2(2): 54-58 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ns doi: 10.11648/j.ns.20170202.14 Measurement of Gamma Emitting Radionuclides in Environmental Samples of Talagang Tehsil-District
Nuclear Science 2017; 2(2): 54-58 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ns doi: 10.11648/j.ns.20170202.14 Measurement of Gamma Emitting Radionuclides in Environmental Samples of Talagang Tehsil-District
ASSESSMENT OF RADIOACTIVITY CONCENTRATION IN SOIL OF SOME MINING AREAS IN CENTRAL NASARAWA STATE, NIGERIA
 ASSESSMENT OF RADIOACTIVITY CONCENTRATION IN SOIL OF SOME MINING AREAS IN CENTRAL NASARAWA STATE, NIGERIA Full Length Research Article 1 Ibrahim, U, 2 Akpa, T.C., and 3 Daniel, I.H. 1,2 Nasarawa State
ASSESSMENT OF RADIOACTIVITY CONCENTRATION IN SOIL OF SOME MINING AREAS IN CENTRAL NASARAWA STATE, NIGERIA Full Length Research Article 1 Ibrahim, U, 2 Akpa, T.C., and 3 Daniel, I.H. 1,2 Nasarawa State
RADIOLOGICAL HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF CEMENT AND SAND USED FOR CONSTRUCTION OF DWELLINGS IN DINGXI, CHINA
 RADIOLOGICAL HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF CEMENT AND SAND USED FOR CONSTRUCTION OF DWELLINGS IN DINGXI, CHINA YUXIN LI 1, XINWEI LU 1, XIAOLAN ZHANG 2 1 School of Tourism and Environment, Shaanxi Normal University,
RADIOLOGICAL HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF CEMENT AND SAND USED FOR CONSTRUCTION OF DWELLINGS IN DINGXI, CHINA YUXIN LI 1, XINWEI LU 1, XIAOLAN ZHANG 2 1 School of Tourism and Environment, Shaanxi Normal University,
Te-Norm in Phosphogypsum; Characterization and Treatment
 Te-Norm in Phosphogypsum; Characterization and Treatment S.A. El-Reefy, M.F. AttaAllah, M.A. Hilal, E.M. EL Afifi Hot Laboratories and Waste Management Center, Atomic Energy Authority, 13759, Egypt ABSTRACT
Te-Norm in Phosphogypsum; Characterization and Treatment S.A. El-Reefy, M.F. AttaAllah, M.A. Hilal, E.M. EL Afifi Hot Laboratories and Waste Management Center, Atomic Energy Authority, 13759, Egypt ABSTRACT
Evaluation and analysis of 226 Ra, 232 Th, 40 K and radon exhalation rate in various grey cements
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 48, July 2010, pp. 473-477 Evaluation and analysis of 226 Ra, 232 Th, 40 K and radon exhalation rate in various grey cements Rati Varshney a, A K Mahur c,
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 48, July 2010, pp. 473-477 Evaluation and analysis of 226 Ra, 232 Th, 40 K and radon exhalation rate in various grey cements Rati Varshney a, A K Mahur c,
Occupational Exposures during the U-Exploration Activities at Seila Area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt
 Arab Journal of Nuclear Science and Applications, 50 (2), (-29) 207 Occupational Exposures during the U-Exploration Activities at Seila Area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt Y.A. Abdel-Razek a, M.S. Masoud
Arab Journal of Nuclear Science and Applications, 50 (2), (-29) 207 Occupational Exposures during the U-Exploration Activities at Seila Area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt Y.A. Abdel-Razek a, M.S. Masoud
ASSESSMENT OF PUBLIC EXPOSURE TO NATURALLY OCCURRING RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS FROM MINING AND MINERAL PROCESSING ACTIVITIES OF TARKWA GOLDMINE IN GHANA
 ASSESSMENT OF PUBLIC EXPOSURE TO NATURALLY OCCURRING RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS FROM MINING AND MINERAL PROCESSING ACTIVITIES OF TARKWA GOLDMINE IN GHANA A thesis submitted to the Department of Chemistry, College
ASSESSMENT OF PUBLIC EXPOSURE TO NATURALLY OCCURRING RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS FROM MINING AND MINERAL PROCESSING ACTIVITIES OF TARKWA GOLDMINE IN GHANA A thesis submitted to the Department of Chemistry, College
Earth & Environmental Science Research & Reviews
 Research Article Natural Radioactivity Levels in Soil s of AL- Sadr and AL-Forat AL-Aosat Hospitals in Najaf Hussein H Al-Gazaly*, and Zuhier H AL-Thbhawy Earth & Environmental Science Research & Reviews
Research Article Natural Radioactivity Levels in Soil s of AL- Sadr and AL-Forat AL-Aosat Hospitals in Najaf Hussein H Al-Gazaly*, and Zuhier H AL-Thbhawy Earth & Environmental Science Research & Reviews
Natural radioactivity levels in phosphate fertilizer and its environmental implications in Assuit governorate, Upper Egypt
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 48, October 2010, pp. 697-702 Natural radioactivity levels in phosphate fertilizer and its environmental implications in Assuit governorate, Upper Egypt A
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 48, October 2010, pp. 697-702 Natural radioactivity levels in phosphate fertilizer and its environmental implications in Assuit governorate, Upper Egypt A
Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh , India. INTRODUCTION
 Assessment of natural radioactivity in soil collected from Jaduguda U-mines area East Singhbhum shear zone, Jharkhand India and radiological implications A. K. Mahur 1*, Rajesh Kumar 1, M. Mishra 1, S.
Assessment of natural radioactivity in soil collected from Jaduguda U-mines area East Singhbhum shear zone, Jharkhand India and radiological implications A. K. Mahur 1*, Rajesh Kumar 1, M. Mishra 1, S.
Measurement of Radioactivity Levels and Assessment of Radiation Hazards for Plants Species Grown at Scrap Yard (B) at Al-Tuwaitha Nuclear Site (Iraq)
 Nuclear Science 2017; 2(4): 94-98 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ns doi: 10.11648/j.ns.20170204.11 Measurement of Radioactivity Levels and Assessment of Radiation Hazards for Plants Species Grown
Nuclear Science 2017; 2(4): 94-98 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ns doi: 10.11648/j.ns.20170204.11 Measurement of Radioactivity Levels and Assessment of Radiation Hazards for Plants Species Grown
J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 2, No. 1, (2017) 17 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal
 J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 2, No. 1, 17-21 (2017) 17 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.18576/jrna/020103 Radiological Assay of Technologically Enhanced
J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 2, No. 1, 17-21 (2017) 17 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.18576/jrna/020103 Radiological Assay of Technologically Enhanced
Canadian Journal of Physics. Determination of Radioactivity Levels of Salt Minerals on the Market
 Determination of Radioactivity Levels of Salt Minerals on the Market Journal: Canadian Journal of Physics Manuscript ID cjp-2017-0775.r1 Manuscript Type: Article Date Submitted by the Author: 29-Nov-2017
Determination of Radioactivity Levels of Salt Minerals on the Market Journal: Canadian Journal of Physics Manuscript ID cjp-2017-0775.r1 Manuscript Type: Article Date Submitted by the Author: 29-Nov-2017
Identification of Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material in Sand
 Identification of Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material in Sand Michael Pope 2012 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisors: Dr. Ed Stech, Dr. Michael Wiescher Abstract Radionuclides
Identification of Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material in Sand Michael Pope 2012 NSF/REU Program Physics Department, University of Notre Dame Advisors: Dr. Ed Stech, Dr. Michael Wiescher Abstract Radionuclides
Norm in soil and sludge samples in Dukhan oil Field, Qatar state
 BJRS BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF RADIATION SCIENCES 3-1 (215) 1-15 Norm in soil and sludge samples in Dukhan oil Field, Qatar state A.T. Al-Kinani a, M. Hushari a, Huda Al-Sulaiti a and I.A. Alsadig a a Radiation
BJRS BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF RADIATION SCIENCES 3-1 (215) 1-15 Norm in soil and sludge samples in Dukhan oil Field, Qatar state A.T. Al-Kinani a, M. Hushari a, Huda Al-Sulaiti a and I.A. Alsadig a a Radiation
Natural radioactivity in soil at regions around the uranium mine in Abu-Skhair Najaf Province, Iraq
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):13-17 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Natural radioactivity in soil at regions around the uranium
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2014, 5(1):13-17 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Natural radioactivity in soil at regions around the uranium
Evaluation of natural radioactivity in Selected Soil Samples from the Archaeological of Ur City by using HPGe detector
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 62 (2017) 79-92 EISSN 2392-2192 Evaluation of natural radioactivity in Selected Soil Samples from the Archaeological of Ur City by using HPGe detector
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 62 (2017) 79-92 EISSN 2392-2192 Evaluation of natural radioactivity in Selected Soil Samples from the Archaeological of Ur City by using HPGe detector
Natural Radioactivity in Soil Samples For Selected Regions in Baghdad Governorate
 International Journal of Recent Research and Review, Vol. VIII, Issue 1, March 2015 ISSN 2277 8322 Natural Radioactivity in Soil Samples For Selected Regions in Baghdad Governorate Nada Fathil Tawfiq 1*,
International Journal of Recent Research and Review, Vol. VIII, Issue 1, March 2015 ISSN 2277 8322 Natural Radioactivity in Soil Samples For Selected Regions in Baghdad Governorate Nada Fathil Tawfiq 1*,
Natural Radioactivity in Dust Storm Samples from Al-Najaf, Iraq
 Natural Radioactivity in Dust Storm Samples from Al-Najaf, Iraq Ali Abid Abojassim Al-Hamidawi Department of Physics University of Kufa Al-Najaf/ Kufa, box (221) Najaf, Iraq ali.alhameedawi@uokufa.edu.iq,
Natural Radioactivity in Dust Storm Samples from Al-Najaf, Iraq Ali Abid Abojassim Al-Hamidawi Department of Physics University of Kufa Al-Najaf/ Kufa, box (221) Najaf, Iraq ali.alhameedawi@uokufa.edu.iq,
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Available online at ScienceDirect. Journal of Taibah University for Science xxx (2015) xxx xxx
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Taibah University for Science xxx (2015) xxx xxx Effective radiation doses from natural sources at Seila area South Eastern Desert, Egypt
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Taibah University for Science xxx (2015) xxx xxx Effective radiation doses from natural sources at Seila area South Eastern Desert, Egypt
Jordan Journal of Physics
 Volume 10, Number 3, 2017. pp. 117-125 ARTICLE Jordan Journal of Physics Estimation of Natural and Anthropogenic Exposures to Gamma Ray from a High Agricultural Area in Jordan "Bani-Kananah District" Hamed
Volume 10, Number 3, 2017. pp. 117-125 ARTICLE Jordan Journal of Physics Estimation of Natural and Anthropogenic Exposures to Gamma Ray from a High Agricultural Area in Jordan "Bani-Kananah District" Hamed
Natural radioactivity in building materials in Iran
 NUKLEONIKA 2011;56(4):363 368 ORIGINAL PAPER Natural radioactivity in building materials in Iran Simin Mehdizadeh, Reza Faghihi, Sedigheh Sina Abstract. This work presents a comprehensive study of natural
NUKLEONIKA 2011;56(4):363 368 ORIGINAL PAPER Natural radioactivity in building materials in Iran Simin Mehdizadeh, Reza Faghihi, Sedigheh Sina Abstract. This work presents a comprehensive study of natural
Natural Radioactivity Study in The Coastal Villages of Northern Chennai
 Natural Radioactivity Study in The Coastal Villages of Northern Chennai I. Inigo Valan 1, V. Narayanan 2, A. Stephen 1* 1 Department of Nuclear Physics, Guindy Campus, University of Madras, Chennai 600025,
Natural Radioactivity Study in The Coastal Villages of Northern Chennai I. Inigo Valan 1, V. Narayanan 2, A. Stephen 1* 1 Department of Nuclear Physics, Guindy Campus, University of Madras, Chennai 600025,
Evaluation of Radiological Hazard Indices Due to Radioactivity in Quarry Sites in Itu, Akwa Ibom State, Nigeria
 International Journal of Scientific Research in Environmental Sciences, 4(3), pp. 0071-0077, 2016 Available online at http://www.ijsrpub.com/ijsres ISSN: 2322-4983; 2016; Author(s) retain the copyright
International Journal of Scientific Research in Environmental Sciences, 4(3), pp. 0071-0077, 2016 Available online at http://www.ijsrpub.com/ijsres ISSN: 2322-4983; 2016; Author(s) retain the copyright
Nserdin A. Ragab 4. 2 Physics Department, Faculty of Sciences, Sudan University of Sciences and Technology, Sudan
 International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 219 1414 Assessment of Natural Radio activity in Rock Samples around South Kordofan State, Sudan Amna M. Hassan 1,2, Abdelrahman E. Mohamed
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 219 1414 Assessment of Natural Radio activity in Rock Samples around South Kordofan State, Sudan Amna M. Hassan 1,2, Abdelrahman E. Mohamed
Radioactive Waste Management
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 4 Issue 6 ǁ June. 2016 ǁ PP.67-71 Asma Osman Ibrahim Osman 1, Hamid Mohamed
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 4 Issue 6 ǁ June. 2016 ǁ PP.67-71 Asma Osman Ibrahim Osman 1, Hamid Mohamed
Assessment of Natural Radioactivity Levels and Radiological Significance of Bottled Drinking Water in Bangladesh
 American Journal of Physics and Applications 2015; 3(6): 203-207 Published online December 3, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajpa) doi: 10.11648/j.ajpa.20150306.13 ISSN: 2330-4286 (Print);
American Journal of Physics and Applications 2015; 3(6): 203-207 Published online December 3, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajpa) doi: 10.11648/j.ajpa.20150306.13 ISSN: 2330-4286 (Print);
THE ANNUAL EFFECTIVE DOSE FROM NATURAL RADIONUCLIDES SOIL SURFACES OF UZHGOROD AREA
 THE ANNUAL EFFECTIVE DOSE FROM NATURAL RADIONUCLIDES SOIL SURFACES OF UZHGOROD AREA I. Pataki, O. Parlag, V. Maslyuk, A. Lengyel, Z. Torich Institute of Electron Physics Ukrainian National Academy of Sciences,
THE ANNUAL EFFECTIVE DOSE FROM NATURAL RADIONUCLIDES SOIL SURFACES OF UZHGOROD AREA I. Pataki, O. Parlag, V. Maslyuk, A. Lengyel, Z. Torich Institute of Electron Physics Ukrainian National Academy of Sciences,
EVALUATION OF Ra, Th, K AND RADIUM EQUIVALENT ACTIVITY IN SAND SAMPLES FROM CAMBURI BEACH, VITÓRIA, ESPÍRITO SANTO, BRAZIL.
 IX Latin American IRPA Regional Congress on Radiation Protection and Safety - IRPA 2013 Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, April 15-19, 2013 SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE PROTEÇÃO RADIOLÓGICA - SBPR EVALUATION OF Ra,
IX Latin American IRPA Regional Congress on Radiation Protection and Safety - IRPA 2013 Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, April 15-19, 2013 SOCIEDADE BRASILEIRA DE PROTEÇÃO RADIOLÓGICA - SBPR EVALUATION OF Ra,
Radon Activity And Exhalation Rate In Building Materials From Crushing Zone Of Shivalik Foothills In India
 Radon Activity And Exhalation Rate In Building Materials From Crushing Zone Of Shivalik Foothills In India Sunil Kamboj, Vakul Bansal, Anil Pundir, R.P. Chauhan Sunil Kamboj & Vakul Bansal Department of
Radon Activity And Exhalation Rate In Building Materials From Crushing Zone Of Shivalik Foothills In India Sunil Kamboj, Vakul Bansal, Anil Pundir, R.P. Chauhan Sunil Kamboj & Vakul Bansal Department of
GAMMA DOSE RATE, ANNUAL EFFECTIVE DOSE AND COLLECTIVE EFFECTIVE DOSE OF FOOD CROP PRODUCING REGION OF ONDO STATE, NIGERIA
 GAMMA DOSE RATE, ANNUAL EFFECTIVE DOSE A COLLECTIVE EFFECTIVE DOSE OF FOOD CROP PRODUCING REGION OF OO STATE, NIGERIA T.J Ojo 1 * K.A.J Gbadegesin 1 1. Physics Unit of Science Technology Department, Federal
GAMMA DOSE RATE, ANNUAL EFFECTIVE DOSE A COLLECTIVE EFFECTIVE DOSE OF FOOD CROP PRODUCING REGION OF OO STATE, NIGERIA T.J Ojo 1 * K.A.J Gbadegesin 1 1. Physics Unit of Science Technology Department, Federal
Evaluation of natural radioactivity and radiological hazards caused by different marbles of India
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 3, November 200, pp. 81-820 Evaluation of natural radioactivity and radiological hazards caused by different marbles of India V Ramasamy a, V Ponnusamy a,
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 3, November 200, pp. 81-820 Evaluation of natural radioactivity and radiological hazards caused by different marbles of India V Ramasamy a, V Ponnusamy a,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 80 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 80 (2015 ) 135 139 26th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids, 26ICNTS Measurement of natural radioactivity, radon
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 80 (2015 ) 135 139 26th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids, 26ICNTS Measurement of natural radioactivity, radon
Radiological Protection Principles concerning the Natural Radioactivity of Building Materials
 European Commission Radiation protection 112 Radiological Protection Principles concerning the Natural Radioactivity of Building Materials 1999 Directorate-General Environment, Nuclear Safety and Civil
European Commission Radiation protection 112 Radiological Protection Principles concerning the Natural Radioactivity of Building Materials 1999 Directorate-General Environment, Nuclear Safety and Civil
Measurement of Radioactivity in Soil Samples for Selected Regions in Thi-Qar Governorate-Iraq
 J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 1, No. 1, 25-30 (2016) 25 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.18576/jrna/010104 Measurement of Radioactivity in Soil Samples
J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 1, No. 1, 25-30 (2016) 25 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.18576/jrna/010104 Measurement of Radioactivity in Soil Samples
Determination of natural radiation contamination for some types of legumes available in the Iraqi markets
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2013, 4(5):245-250 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Determination of natural radiation contamination for some
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2013, 4(5):245-250 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Determination of natural radiation contamination for some
International Atomic Energy Agency. Department of Nuclear Sciences and Applications. IAEA Environment Laboratories
 International Atomic Energy Agency Department of Nuclear Sciences and Applications IAEA Environment Laboratories Vienna International Centre, P.O. Box 100, 1400 Vienna, Austria REFERENCE SHEET CERTIFIED
International Atomic Energy Agency Department of Nuclear Sciences and Applications IAEA Environment Laboratories Vienna International Centre, P.O. Box 100, 1400 Vienna, Austria REFERENCE SHEET CERTIFIED
Assessment of Natural Radioactivity Levels of Cements and Cement Composites in the Slovak Republic
 Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 7165-7179; doi:10.3390/ijerph10127165 Article International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health ISSN 1660-4601 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 7165-7179; doi:10.3390/ijerph10127165 Article International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health ISSN 1660-4601 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijerph
Natural Radioactivity of Building Rocks in quarries South-west part of Yemen.
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov.-Dec. 2014), PP 76-89 Natural Radioactivity of Building Rocks in quarries South-west part of Yemen. Geologist/
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov.-Dec. 2014), PP 76-89 Natural Radioactivity of Building Rocks in quarries South-west part of Yemen. Geologist/
Radon exhalation rates from zircon sands and ceramic tiles in Italy
 Radioprotection, vol.44, n 5 (2009) 445 451 C EDP Sciences, 2009 DOI: 10.1051/radiopro/20095083 Radon exhalation rates from zircon sands and ceramic tiles in Italy S. Verità 1,2,S.Righi 1,2, R. Guerra
Radioprotection, vol.44, n 5 (2009) 445 451 C EDP Sciences, 2009 DOI: 10.1051/radiopro/20095083 Radon exhalation rates from zircon sands and ceramic tiles in Italy S. Verità 1,2,S.Righi 1,2, R. Guerra
Determination of Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material in the Egyptian Oil
 S.U.EL-Kameesy, et al. Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl, Vol 50, The 4, 55-62 Egyptian (2017) Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and Applications Society of Nuclear Vol 50, 4, (55-62) 2017 Sciences and Applications
S.U.EL-Kameesy, et al. Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl, Vol 50, The 4, 55-62 Egyptian (2017) Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and Applications Society of Nuclear Vol 50, 4, (55-62) 2017 Sciences and Applications
Multilayer Nuclear Track Detectors for Retrospective Radon Dosimetry
 Multilayer Nuclear Track Detectors for Retrospective Radon Dosimetry V. V. Bastrikov 1, M. V. Zhukovsky 2 1 Experimental Physics Department, Ural State Technical University, Mira St., 19/5, 620002, Ekaterinburg,
Multilayer Nuclear Track Detectors for Retrospective Radon Dosimetry V. V. Bastrikov 1, M. V. Zhukovsky 2 1 Experimental Physics Department, Ural State Technical University, Mira St., 19/5, 620002, Ekaterinburg,
Journal of American Science 2014;10(2) Evaluation of Natural Radioactivity in Different Regions in Sudan
 Journal of American Science 214;1(2) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Evaluation of Natural Radioactivity in Different Regions in Sudan Magdi. Hasan. Saad 1,3, Jumaa. Yousif. Tamboul 2,4, Mohamed Yousef
Journal of American Science 214;1(2) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Evaluation of Natural Radioactivity in Different Regions in Sudan Magdi. Hasan. Saad 1,3, Jumaa. Yousif. Tamboul 2,4, Mohamed Yousef
Assessment of dose due to natural radio-nuclides in vegetables of high background radiation area in south-eastern part of Bangladesh
 Volume 12, No 3 International Journal of Radiation Research, July 2014 Assessment of dose due to natural radio-nuclides in vegetables of high background radiation area in south-eastern part of Bangladesh
Volume 12, No 3 International Journal of Radiation Research, July 2014 Assessment of dose due to natural radio-nuclides in vegetables of high background radiation area in south-eastern part of Bangladesh
Determination of Absorbed and Effective Dose from Natural Background Radiation around a Nuclear Research Facility
 American Journal of Environmental Sciences 7 (2): 173-177, 2011 ISSN 1553-345X 2010 Science Publications Determination of Absorbed and Effective Dose from Natural Background Radiation around a Nuclear
American Journal of Environmental Sciences 7 (2): 173-177, 2011 ISSN 1553-345X 2010 Science Publications Determination of Absorbed and Effective Dose from Natural Background Radiation around a Nuclear
Absorbed Gamma Ray Doses due to Natural Radionuclides in Building Materials
 Absorbed Gamma Ray Doses due to Natural Radionuclides in Building Materials Vitor A.P. Aguiar a, Nilberto H. Medina a, Ramon H. Moreira b, Marcilei A.G. Silveira b and José R.B. Oliveira a a Instituto
Absorbed Gamma Ray Doses due to Natural Radionuclides in Building Materials Vitor A.P. Aguiar a, Nilberto H. Medina a, Ramon H. Moreira b, Marcilei A.G. Silveira b and José R.B. Oliveira a a Instituto
RADON EQUILIBRIUM MEASUREMENT IN THE AIR *
 RADON EQUILIBRIUM MEASUREMENT IN THE AIR * SOFIJA FORKAPIĆ, DUŠAN MRĐA, MIROSLAV VESKOVIĆ, NATAŠA TODOROVIĆ, KRISTINA BIKIT, JOVANA NIKOLOV, JAN HANSMAN University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Sciences, Department
RADON EQUILIBRIUM MEASUREMENT IN THE AIR * SOFIJA FORKAPIĆ, DUŠAN MRĐA, MIROSLAV VESKOVIĆ, NATAŠA TODOROVIĆ, KRISTINA BIKIT, JOVANA NIKOLOV, JAN HANSMAN University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Sciences, Department
The Influence of Mount Sinabung Volcanic Ash and Phoshate Fertilizers on Natural Radionuclide Content in Agricultural Soils
 Research Article The Influence of Mount Sinabung Volcanic Ash and Phoshate Fertilizers on Natural Radionuclide Content in Agricultural Soils Reh Malem Karo 1*, Harlem Marpaung 1, Jamahir Gultom 1, Eko
Research Article The Influence of Mount Sinabung Volcanic Ash and Phoshate Fertilizers on Natural Radionuclide Content in Agricultural Soils Reh Malem Karo 1*, Harlem Marpaung 1, Jamahir Gultom 1, Eko
Assessment of Radioactivity and the Exposure Doses from Local Cement Types in Saudi Arabia
 Assessment of Radioactivity and the Exposure Doses from Local Cement Types in Saudi Arabia J. H. AlZahrani Physics Department, Faculty science Faculty for Girls, king AbdulAziz University, Jeddah, Saudi
Assessment of Radioactivity and the Exposure Doses from Local Cement Types in Saudi Arabia J. H. AlZahrani Physics Department, Faculty science Faculty for Girls, king AbdulAziz University, Jeddah, Saudi
Activity Concentrations and Associated Gamma Doses of 238 U and 235 U in Jordan
 Journal of Physical Science and Application 5 (5) (2015) 367-372 doi: 10.17265/2159-5348/2015.05.007 D DAVID PUBLISHING Activity Concentrations and Associated Gamma Doses of 238 U and 235 U in Jordan ABDUL-WALI
Journal of Physical Science and Application 5 (5) (2015) 367-372 doi: 10.17265/2159-5348/2015.05.007 D DAVID PUBLISHING Activity Concentrations and Associated Gamma Doses of 238 U and 235 U in Jordan ABDUL-WALI
Determination of Natural Radioactivity Levels due to Mine Tailings from Selected Mines in Southwestern Uganda
 Determination of Natural Radioactivity Levels due to Mine Tailings from Selected Mines in Southwestern Uganda Silver Turyahabwa E.R. 1*, Edward Jurua 1,2, Richard Oriada 1, Aron Mugaiga 1, Ben Enjiku D.D.
Determination of Natural Radioactivity Levels due to Mine Tailings from Selected Mines in Southwestern Uganda Silver Turyahabwa E.R. 1*, Edward Jurua 1,2, Richard Oriada 1, Aron Mugaiga 1, Ben Enjiku D.D.
Radionuclides in hot mineral spring waters in Jordan
 Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 52 (2001) 99}107 Technical note Radionuclides in hot mineral spring waters in Jordan S. A. Saqan, M. K. Kullab *, A. M. Ismail Physics Department, Jordan University
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 52 (2001) 99}107 Technical note Radionuclides in hot mineral spring waters in Jordan S. A. Saqan, M. K. Kullab *, A. M. Ismail Physics Department, Jordan University
Natural Radioactivity Concentration and Estimation of Radiation Exposure in Environmental Soil Samples from Al-Sader City/Iraq
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Natural
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Natural
Study of Natural and Artificial Radioactivity in some Food Grains
 SCIREA Journal of Food http://www.scirea.org/journal/food November 21, 2016 Volume 1, Issue1, October 2016 Study of Natural and Artificial Radioactivity in some Food Grains Jannatul Ferdous 1*, Projit
SCIREA Journal of Food http://www.scirea.org/journal/food November 21, 2016 Volume 1, Issue1, October 2016 Study of Natural and Artificial Radioactivity in some Food Grains Jannatul Ferdous 1*, Projit
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 216e220. Available online at ScienceDirect
 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage: http://www.elsevier.com/locate/jrras Radioactivity concentration variation
HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage: http://www.elsevier.com/locate/jrras Radioactivity concentration variation
Investigation the Natural Radioactivity in Local and Imported Chemical Fertilizers
 777 Vol.54, n. 4: pp. 777-782, July-August 2011 ISSN 1516-8913 Printed in Brazil BRAZILIAN ARCHIVES OF BIOLOGY AND TECHNOLOGY A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L J O U R N A L Investigation the Natural Radioactivity
777 Vol.54, n. 4: pp. 777-782, July-August 2011 ISSN 1516-8913 Printed in Brazil BRAZILIAN ARCHIVES OF BIOLOGY AND TECHNOLOGY A N I N T E R N A T I O N A L J O U R N A L Investigation the Natural Radioactivity
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: Volume 8, Issue 5 Ver. III (Sep - Oct. 2016), PP
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 8, Issue 5 Ver. III (Sep - Oct. 2016), PP 89-95 www.iosrjournals.org Measurement of Activity Concentration, Absorbed Dose Rate and Annual
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 8, Issue 5 Ver. III (Sep - Oct. 2016), PP 89-95 www.iosrjournals.org Measurement of Activity Concentration, Absorbed Dose Rate and Annual
Radioactivity Levels and dose evaluation in Some Environmental Rock Samples from Taiz, Yemen
 Radioactivity Levels and dose evaluation in Some Environmental Rock Samples from Taiz, Yemen M. Al-Abyad 1, S. U. El-Kameesy, S.A. El-Fiki, M. N. Dahesh,3 1 Physics department (Cyclotron Facility), Nuclear
Radioactivity Levels and dose evaluation in Some Environmental Rock Samples from Taiz, Yemen M. Al-Abyad 1, S. U. El-Kameesy, S.A. El-Fiki, M. N. Dahesh,3 1 Physics department (Cyclotron Facility), Nuclear
Measurement of 226 Ra, 232 Th and 40 K in Arum Grown on the Bank of Rupsha River, Khulna, Bangladesh Using HPGe Detector
 ISSN 1022-8594 JUJS 2018 Jahangirnagar University Journal of Science Vol. 41, No.1, pp.57-66 Measurement of 226 Ra, 232 Th and 40 K in Arum Grown on the Bank of Rupsha River, Khulna, Using HPGe Detector
ISSN 1022-8594 JUJS 2018 Jahangirnagar University Journal of Science Vol. 41, No.1, pp.57-66 Measurement of 226 Ra, 232 Th and 40 K in Arum Grown on the Bank of Rupsha River, Khulna, Using HPGe Detector
MEASUREMENTS OF NATURAL RADIONUCLIDES AND RADIOLOGICAL HAZARDS IN EGYPTIAN CEMENT AND GYPSUM
 Journal of Nuclear and Radiation Physics, Vo.10 (2015), No. 1&2, pp. 59-69 MEASUREMENTS OF NATURAL RADIONUCLIDES AND RADIOLOGICAL HAZARDS IN EGYPTIAN CEMENT AND GYPSUM S. Harb Physics Department, Faculty
Journal of Nuclear and Radiation Physics, Vo.10 (2015), No. 1&2, pp. 59-69 MEASUREMENTS OF NATURAL RADIONUCLIDES AND RADIOLOGICAL HAZARDS IN EGYPTIAN CEMENT AND GYPSUM S. Harb Physics Department, Faculty
J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 2, No. 1, (2017) 11 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal
 J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 2, No. 1, 11-15 (2017) 11 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.18576/jrna/020102 Measurement of Radium Concentration and Radon
J. Rad. Nucl. Appl. 2, No. 1, 11-15 (2017) 11 Journal of Radiation and Nuclear Applications An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.18576/jrna/020102 Measurement of Radium Concentration and Radon
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 17e25. Available online at ScienceDirect
 Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 17e25 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage:
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 17e25 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage:
Pelagia Research Library. Advances in Applied Science Research, 2017, 8(1):36-41
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2017, 8(1):36-41 ISSN : 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Determination of Activity Concentration and Radiological Parameters
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2017, 8(1):36-41 ISSN : 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Determination of Activity Concentration and Radiological Parameters
Determination of natural radionuclides 40K, eu and eth in environmental samples from the vicinity of Aramar Experimental Center, Brazil
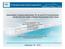 Determination of natural radionuclides 40K, eu and eth in environmental samples from the vicinity of Aramar Experimental Center, Brazil André Luis Lima de Araújo Marco Antônio Proença de Moraes Bruno Robles
Determination of natural radionuclides 40K, eu and eth in environmental samples from the vicinity of Aramar Experimental Center, Brazil André Luis Lima de Araújo Marco Antônio Proença de Moraes Bruno Robles
Accurate prediction of radiation exposures of workers involved in the transport of NORM
 Accurate prediction of radiation exposures of workers involved in the transport of NORM N. Tsurikov Calytrix Consulting Pty Ltd, Perth, Australia Abstract. The study of actual radiation exposures encountered
Accurate prediction of radiation exposures of workers involved in the transport of NORM N. Tsurikov Calytrix Consulting Pty Ltd, Perth, Australia Abstract. The study of actual radiation exposures encountered
Natural environmental radioactivity and estimation of radiation exposure from saline soils
 International N. Akhtar, et Journal al. of Environmental Science & Technology Natural environmental radioactivity... Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 279-285, Winter 2005 Natural environmental radioactivity and estimation
International N. Akhtar, et Journal al. of Environmental Science & Technology Natural environmental radioactivity... Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 279-285, Winter 2005 Natural environmental radioactivity and estimation
Determining the Need For External Radiation Monitoring at FUSRAP Projects Using Soil Characterization Data. Todd Davidson
 Determining the Need For External Radiation Monitoring at FUSRAP Projects Using Soil Characterization Data Todd Davidson Introduction According to Regulatory Guide 8.34 Monitoring Criteria and Methods
Determining the Need For External Radiation Monitoring at FUSRAP Projects Using Soil Characterization Data Todd Davidson Introduction According to Regulatory Guide 8.34 Monitoring Criteria and Methods
North-West University, Private Bag X2046, Mmabatho 2735, South Africa. 2. *Corresponding author:
 Re-mobilization of uranium and thorium from sediments contaminated by naturally occurring radioactive material (NORM) through leaching by acid mine drainage (AMD). Faanhof A 1, Shongwe NS 2 and Connell,
Re-mobilization of uranium and thorium from sediments contaminated by naturally occurring radioactive material (NORM) through leaching by acid mine drainage (AMD). Faanhof A 1, Shongwe NS 2 and Connell,
An Analysis for Distribution of Natural Radionuclides in Soil, Sand and Sediment of Potenga Sea Beach Area of Chittagong, Bangladesh
 Journal of Environmental Protection, 2014, 5, 1553-1563 Published Online December 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jep http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jep.2014.517147 An Analysis for Distribution
Journal of Environmental Protection, 2014, 5, 1553-1563 Published Online December 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jep http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jep.2014.517147 An Analysis for Distribution
Radioactivity measurements and radiation dose assessments in soil of Al-Qassim region, Saudi Arabia
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 52, March 2014, pp. 147-154 Radioactivity measurements and radiation dose assessments in soil of Al-Qassim region, Saudi Arabia A El-Taher* 2,3 & J H Al-Zahrani
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 52, March 2014, pp. 147-154 Radioactivity measurements and radiation dose assessments in soil of Al-Qassim region, Saudi Arabia A El-Taher* 2,3 & J H Al-Zahrani
RADIOACTIVITY MEASUREMENTS CAMPAIGN ON CERAMIC INDUSTRIES: RESULTS AND COMMENTS
 RADIOACTIVITY MEASUREMENTS CAMPAIGN ON CERAMIC INDUSTRIES: RESULTS AND COMMENTS V. Serradell, J. Ortiz, L. Ballesteros, I. Zarza Laboratorio de Radioactividad Ambiental, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia,
RADIOACTIVITY MEASUREMENTS CAMPAIGN ON CERAMIC INDUSTRIES: RESULTS AND COMMENTS V. Serradell, J. Ortiz, L. Ballesteros, I. Zarza Laboratorio de Radioactividad Ambiental, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia,
Terrestrial gamma dose rates along one of the coastal highways in Sri Lanka
 Sri Lankan Journal of Physics, Vol. 2 (21) 1-6 Institute of Physics - Sri Lanka Terrestrial gamma dose rates along one of the coastal highways in Sri Lanka C.S. Sumithrarachchi and R. Hewamanna * Department
Sri Lankan Journal of Physics, Vol. 2 (21) 1-6 Institute of Physics - Sri Lanka Terrestrial gamma dose rates along one of the coastal highways in Sri Lanka C.S. Sumithrarachchi and R. Hewamanna * Department
Radiological Characterization of Buildings at the Ranstad Uranium Works
 Radiological Characterization of Buildings at the Ranstad Uranium Works Report presented at the Workshop on Radiological Characterization for Decommissioning Studsvik, Nyköping, Sweden 17 19 April 2012
Radiological Characterization of Buildings at the Ranstad Uranium Works Report presented at the Workshop on Radiological Characterization for Decommissioning Studsvik, Nyköping, Sweden 17 19 April 2012
Measurement of Specific Activities of Some Biological Samples for Some Iraq Governorates
 International Journal of Recent Research and Review, Vol. IX, Issue 3, September 2016 ISSN 2277 8322 Measurement of Specific Activities of Some Biological s for Some Iraq Governorates Mahmood S. Karim
International Journal of Recent Research and Review, Vol. IX, Issue 3, September 2016 ISSN 2277 8322 Measurement of Specific Activities of Some Biological s for Some Iraq Governorates Mahmood S. Karim
S. Harb Physics Department, Faculty of science, South Valley university, Qena, Egypt
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 8, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep - Oct. 2016), PP 117-125 www.iosrjournals.org Estimation of annual external exposure and internal exposure dose
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 8, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep - Oct. 2016), PP 117-125 www.iosrjournals.org Estimation of annual external exposure and internal exposure dose
Journal of Natural Sciences Research ISSN (Paper) ISSN (Online) Vol.4, No.12, 2014
 Determination of External and Internal Hazard Indices from Naturally Occurring Radionuclide in Rock, Sediment and Building s collected from Sikiti, Southwestern Nigeria. Abstract Ibrahim Ayodeji Bello
Determination of External and Internal Hazard Indices from Naturally Occurring Radionuclide in Rock, Sediment and Building s collected from Sikiti, Southwestern Nigeria. Abstract Ibrahim Ayodeji Bello
Abstract The concentrations of the natural radionuclides: 226 Ra, 232 Th, 40 K, have been determined in
 Assessment of population doses and radiation hazards from rock samples collected in the South West of Cameroon Abiama Ele P 1,3., Owono Ateba P 3., Ekobena F. H. P 3., Ben-Bolie G. H* 3. and El Khoukhi
Assessment of population doses and radiation hazards from rock samples collected in the South West of Cameroon Abiama Ele P 1,3., Owono Ateba P 3., Ekobena F. H. P 3., Ben-Bolie G. H* 3. and El Khoukhi
Gamma spectrometric analysis of ore samples from Sandur of Bellary, Karnataka, India
 J Radioanal Nucl Chem DOI 10.1007/s10967-011-1599-4 Gamma spectrometric analysis of ore samples from Sandur of Bellary, Karnataka, India B. R. Kerur T. Rajeshwari S. Anilkumar K. Narayani A. K. Rekha Received:
J Radioanal Nucl Chem DOI 10.1007/s10967-011-1599-4 Gamma spectrometric analysis of ore samples from Sandur of Bellary, Karnataka, India B. R. Kerur T. Rajeshwari S. Anilkumar K. Narayani A. K. Rekha Received:
Assessment of radon-222 concentrations and exhalation rates of rocks and building materials
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 44, April 2006, pp. 287-291 Assessment of radon-222 concentrations and exhalation rates of rocks and building materials A M El-Arabi, A Abbady, N K Ahmed,
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 44, April 2006, pp. 287-291 Assessment of radon-222 concentrations and exhalation rates of rocks and building materials A M El-Arabi, A Abbady, N K Ahmed,
