Historical Geology Exam II Spring, 2008
|
|
|
- Carmella Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Historical Geology Exam II Spring, What are early Paleozoic (Cambrian-Ordovician) biotas essentially the story of? a) The story of life b) The story of trilobites c) The story of plants d) The story of life in the sea 2. What was the difference between the bodies of animals in the Neoproterozoic and the Cambrian? a) Bodies were bigger in the Cambrian b) Bodies were soft in the Neoproterozoic but had hard shells or skeletons in the Cambrian c) Bodies were more streamlined in the Cambrian d) Bodies were symmetric in the Cambrian 3. What did most terrestrial environments (other than lakes and wetlands) look like before the Silurian? a. Moss covered b. Filled with stromatolites c. Barren rock and soil d. Forest covered 4. What is vascular about vascular plants? a. They vacillate between wet and dry environments b. They vacillate between photosynthesis and respiration c. They could also live off of dead tissue like fungi and mushrooms d. They have tubes to transport water and food 5. What is the evolutionary advantage for a plant in having a seed? a. It lets the plant survive in drier habitats b. It lets a plant survive in wetter habitats c. It lets a plant survive in colder habitats d. It lets a plant be pollinated by an insect 6. When did invertebrate animals (insects) first begin to inhabit the land? a. Late Cambrian-Early Ordovician b. Late Ordovician-Early Silurian c. Late Silurian-Early Devonian d. Late Permian-Early Cretaceous 7. Of plants, herbivores and carnivores, what is the order in which they first inhabit the land? a. First herbivores, then plants, then carnivores b. First plants, then herbivores, then carnivores c. First carnivores, then herbivores, then plants d. They all came at about the same time 1
2 8. When did vertebrate animals start to inhabit the land? a. Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) b. Late Permian c. Early Ordovician d. The Cretaceous 9. The Carboniferous, Silurian and Devonian Systems were all identified separately. What caused scientists to decide that the temporal order was Silurian first, Devonian second and Carboniferous last? a. That is the way they appeared in outcrops: Silurian on the bottom, Devonian in between and Carboniferous on top b. Fossils from the Devonian appeared to be transitional between those of the Silurian and Carboniferous c. The Silurian had lots of fish, the Carboniferous had a lot of coal, and Devonian had both d. Because you couldn't have fish before you had coal 10. What happened to marine taxa organisms after the massive extinction at the end of the Ordovician? a. The marine Reptiles expanded to fill opened the ecological niches b. They never quite recovered c. There was another great evolutionary radiation in the marine realm shortly thereafter d. Marine organisms moved to the land 11. What changes occurred to land plants in the interval from the mid-silurian to the end of the Devonian? a. They went from the first appearing on land to forming upland forests b. They went from oceans to the swamps c. They went from stromatolites to club mosses d. Both B and C are true 12. What type of fish first appeared in the Early Silurian? a. The Placoderms b The Lobe-finned fishes c. The Acanthodians d. The earliest jawed fishes 13. When did the first ammonoids appear? a. In the Early Cambrian b. In the Early Ordovician c. In the Early Devonian d. In the Early Permian 14. When did the first spiders, centipedes and flightless insects first appear? a. In the Middle Cambrian b. In the Middle Ordovician c. In the Middle Devonian d. In the Middle Permian 2
3 15. What animals directly evolved from the acanthodians? a. The Mammals b. The Reptiles c. The Fishes d. The Cephalopods 16. When did the first Ray-finned fishes, Lobe-finned fishes, Placoderms and Amphibians appear? a. Middle to Late Cambrian b. Middle to Late Ordovician c. Middle to Late Devonian d. Middle to Late Permian 17. What bony parts of jawless fishes evolved into jaws? a. Jaws evolved from mouths b. Jaws evolved from denticles c. Jaws evolved from gills d. Jaws evolved from the gillbars closest to the mouth 18. What were the placoderms? a. The Bony-skinned fishes b. The cartilaginous fishes c. The bony fishes d. Heavily armored fishes with jaws, e.g. Dunkleostus 19. What are the two main groups of bony fishes? a. Ray-finned and Lobe-finned b. Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes c. Teleost and Paleost d. Endothermic and Ectothermic 20. What sedimentary deposit is characteristic of the Carboniferous Period? a. Red Beds b. Carbonates c. Coal d. Shales 21. What happened to climates during the Permian? a. They became colder b. They became drier c. They became wetter d. Both A and C 22. What 'devastating event brought the Paleozoic Era to an end? a. The greatest glacial epoch ever b. The end of the Dinosaurs c. The failure of the Midcontinent Rift d. The greatest mass extinction ever 3
4 23. What caused sea level to drop at the end of the Mississippian? a. Global tectonism b. High rates of crustal formation c. The dramatic expansion of glaciers on Gondwanaland d. Global warming 24. When did extensive coal swamps appear on land? a. Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) b. Late Permian c. Early Ordovician d. The Cretaceous 25. When did Amphibians first appear on land? a. Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) b. Late Permian c. Early Ordovician d. The Cretaceous 26. When did the first Reptiles appear on land? a. Early Carboniferous (Mississippian) b. Early Permian c. Early Ordovician d. Early Cretaceous 27. What type of swimming animal replaced the heavily armored Placoderms? a. More mobile types b. Bigger types c. Shelled types d. Ammonites 28. To what type of environment are spore plants typically confined? a. Cold environments b. Hot environments c. Dry environments d. Wet environments 29. What large plant group dominated terrestrial environments during the Permian? a. Gymnosperms b. Angiosperms c. Lycopods d. Mosses 30. What is the general impact of seeds and the amniote egg? a. They provide a food source for scavenging animals b. They increase the rate of genetic mutations c. They allowed for cross breeding d. They allow plants and animals to live and reproduce in drier habitats 4
5 31. What happened to Amphibians during the Permian as Reptiles expanded? a. They became extinct b. Amphibians were replaced by reptiles in various ecological roles c. They flourished under the competition because of inherent advantages d. They expanded as well as a result of Coevolution 32. When referring to animals, what do endothermic and ectothermic mean? a. Animals that prefer hot and cold climates, respectively b. Chemical reactions that require input of heat or those that give off heat, respectively c. Herbivore and Carnivore, respectively d. Warm-blooded and Cold-blooded, respectively 33. What major geologic features of the Earth are outlined by earthquakes? a. Hot spots b. The boundaries of mountain ranges c. The boundaries of subduction zones d. The boundaries of the crustal plates 34. Which are the differences between continental and oceanic crust? a. continental crust is thicker, denser and more felsic b. continental crust is thicker, less dense and more felsic c. continental crust is thinner, more dense and less felsic d. continental crust is thicker, denser and less felsic 35. What happens at convergent boundaries? a. Oceanic crust is formed b. Crust is subducted and/or mountains are created c. Reefs forms on Guyots d. Hot spots are created 36. What is a hot spot? a. Any warm place on the surface of the Earth b. Any volcano c. Any hydrothermal system d. A plume of magma rising from deep in the mantle 37. What does the deposition of Banded Iron Formations (BIFs) 2 billion years ago say about the composition of the atmosphere? a. That oxygen concentrations rose around that time b. That carbon dioxide concentrations rose around that time c. That carbon dioxide concentrations declined around that time d. That nitrogen concentrations rose around that time 38. What was unique about the major ice age of the Neoproterozoic? a. It lasted more 100 million years b. It only affected the Tropics c. It only affected the High Latitudes d. It was global 5
6 39. When did life first appear on the Earth? a. About 4.6 Billion years ago b. About 3.8 Billion years ago c. About 2.0 Billion years ago d. About 800 Million years ago e. About 545 Million years ago 40. When did metazoans first appear? a. About 4.6 Billion years ago b. About 3.8 Billion years ago c. About 2.0 Billion years ago d. About 800 Million years ago e. About 545 Million years ago 41. What are metazoans? a. Single celled organisms b. Prokaryotes c. Soft-bodied organisms d. Multicellular organisms 42. What is the difference between a Colonial Organism and a true Multicellular Organism? a. Colonials are much larger and more complex b. Colonial Organisms are prokaryotes, Multicellular Organisms are eukaryotes c. Colonial Organisms are heterotrophic, Multicellular Organisms are photosynthetic d. Colonial Organisms are individual cells living together; Multicellular Organisms are differentiated cells living cooperatively 43. What is the theory of endosymbiosis? a. That atmospheric oxygen rose because of photosynthesis b. That cells evolved homologous living systems c. That the eukaryotic cell s organelles were once free living prokaryotes d. That cells evolved into convergent life forms 44. What fundamental biologic process takes place in a chloroplast? a. Photosynthesis b. Respiration c. Biosynthesis d. Catabolism 45. What fundamental biologic process takes place in mitochondria? a. Photosynthesis b. Respiration c. Biosynthesis d. Catabolism 6
7 46. What are the three major domains of life? a. Animal, Vegetable and Mineral b. Animal, Plant and Fungi c. Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya d. Photosynthesis, Chemosynthesis and Respiration 47. In what environments are Archaea typically found? a. Marine habitats b. In moist environments c. In extreme environments, e.g. hot springs, acidic or hypersaline water d. Everywhere 48. What does Photosynthesis do? a. It uses light energy to biochemically combine inorganic CO2 and H2O to form organic compounds b. It uses chemical energy to biochemically combine inorganic CO2 and H2O to form organic compounds c. It uses light energy to break down organic molecules d. It collects chemical energy from the biochemical breakdown of organic molecules 49. What does Respiration do? a. It uses light energy to biochemically combine inorganic CO2 and H2O to form organic compounds b. It uses chemical energy to biochemically combine inorganic CO2 and H2O to form organic compounds c. It uses light energy to break down organic molecules d. It collects chemical energy from the biochemical breakdown of organic molecules 50. What is a stromatolite? a. The largest of the Ediacaran fauna b. The first eukaryote c. Layered algal mats formed in tidal pools d. The first metazoan 51. What is meant by convergent evolution? a. Symbiotic organisms evolving together b. Organisms that evolved from a common ancestor c. The same animal filling a different ecological role in a different habitat d. Different types of animals performing the same ecological role, e.g. marine reptiles and sharks as ocean predators 52. What is meant by coevolution? a. Symbiotic organisms evolving together b. Organisms that evolved from a common ancestor c. The same animal filling a different ecological role in a different habitat d. Different types of animals performing the same ecological role, 7
8 53. What is continental shield? a. Precambrian crystalline basement rock that is exposed at the Earth s surface b. Margins of ancient continents that filled in with sands, limestones and shales c. Margins of ancient continents that repeatedly experienced crustal collision and separation d. Any crystalline basement rock 54. What are mobile belts? a. Precambrian crystalline basement rock that is exposed at the Earth s surface b. Margins of ancient continents that filled in with sands, limestones and shales c. Margins of ancient continents that repeatedly experienced crustal collision and separation d. Any crystalline basement rock 55. How old are the rocks of the Beartooth uplift? a. About 1.9 Billion years old b. About 545 Million years old c. About 65 Million years old d. About 12,000 years old 56. When was the Beartooth plateau lifted up? a. About 1.9 Billion years old b. About 545 Million years old c. About 65 Million years old d. About 12,000 years old 57. When were the Beartooth Mountains last shaped by glaciers? a. 1.9 Billion years old b. 545 Million years old c. About 65 Million years old d. About 12,000 years old 58. What is the closest hot spot to Billings? a. Hawaii b. Mt. St. Helens c. Glacial National Park d. Yellowstone 59. What are analogous structures in evolution? a. The same physical structures, e.g. bones, in different animals performing different tasks b. Different physical structures, e.g. bones, in different animals performing the same tasks c. Physical structures in animals that are evolutionary improvements d. Physical structures in animals that lead to the evolution of Homo sapiens 60. What are homologous structures in evolution? a. The same physical structures, e.g. bones, in different animals performing different tasks b. Different physical structures, e.g. bones, in different animals performing the same tasks c. Physical structures in animals that are evolutionary improvements d. Physical structures in animals that lead to the evolution of Homo sapiens 8
Chapter 19. History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Spring th Grade
 Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Outline. Origin and History of Life
 Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
Directed Reading. Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era EVOLUTION. beginning of life is called. to. PRECAMBRIAN TIME.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale
 CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6
 Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Module 9: Earth's History Topic 3 Content: A Tour of Geologic Time Notes
 The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
Earth s Evolution Through Time
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth s Evolution Through Time Earth 9 th edition Chapter 22 Earth s evolution: summary in haiku form Super-continents have come and gone many times: giant bumper cars.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth s Evolution Through Time Earth 9 th edition Chapter 22 Earth s evolution: summary in haiku form Super-continents have come and gone many times: giant bumper cars.
Page 143: Geologic Time
 Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
Name Class Date. Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle.
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Cycles in the Phanerozoic
 Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth History. What is the Earth s time scale? Geological time Scale. Pre-Cambrian. FOUR Eras
 The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
Evolution and diversity of organisms
 Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth.
 Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
Geologic Time. Early Earth History
 chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. The Ever-Changing Earth. Early Life. Evolution and the Fossil Record. Life in the Phanerozoic Eon
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
A brief history of the Earth!
 A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Earth s s Geologic History
 The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
EARTH S HISTORY. What is Geology? logy: science. Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its:
 EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
3. Evolutionary change is random because gene mutations are random. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 9, 2015, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D. Survival
Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 9, 2015, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D. Survival
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide
 Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
Geosphere Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 Intro to Earth Systems 1. Name and describe Earth s 4 major spheres Geosphere-- nonliving, mostly solid rock divided into crust, mantle, and core Atmosphere a
I. History of Life on Earth
 Evolution I. History of Life on Earth I. History of Life A. Early History of Earth I. Early earth was inhospitable hot, with many volcanoes little free oxygen and lots of carbon dioxide other gases present:
Evolution I. History of Life on Earth I. History of Life A. Early History of Earth I. Early earth was inhospitable hot, with many volcanoes little free oxygen and lots of carbon dioxide other gases present:
Adjustments to Life in Air
 1 Adjustments to Life in Air Plants and Animals no buoyancy, need skeletal support desiccation physical-chemical environmental extremes (temperature, humidity, salinity) no nutrients in air reproductive
1 Adjustments to Life in Air Plants and Animals no buoyancy, need skeletal support desiccation physical-chemical environmental extremes (temperature, humidity, salinity) no nutrients in air reproductive
Fossils Biology 2 Thursday, January 31, 2013
 Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Calculating extra credit from clicker points. Total points through last week: Participation: 6 x 2 = 12 Performance: = 26
 Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 10, 2016, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D.
Clicker Questions, Test 2 February 10, 2016, Outline 7 1. Darwin coined the term Natural Selection to contrast with what other term? A. Evolutionary Selection B. Competition C. Artificial Selection D.
Unit 5: Earth s History Practice Problems
 Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock would be most likely to contain fossils? A. Precambrian granite B. Cambrian shale C. Pleistocene basalt D. Middle-Proterozoic quartzite 6. Base your answer(s) to the following
1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B.
 Name Roy G Biv 1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B. Which numbered position best represents the time when humans first appeared in the
Name Roy G Biv 1. The timeline below represents time on Earth from the beginning of the Paleozoic Era Ato the present B. Which numbered position best represents the time when humans first appeared in the
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions.
 History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
Chapter 15. The Late Paleozoic World
 Chapter 15 The Late Paleozoic World Guiding Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did terrestrial floras change on a global scale in late Paleozoic
Chapter 15 The Late Paleozoic World Guiding Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did terrestrial floras change on a global scale in late Paleozoic
5 Time Marches On. TAKE A LOOK 1. Identify What kinds of organisms formed the fossils in the picture?
 CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
GO ON. Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1.
 d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity
 UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity CHAPTER 14: The History of Life PAST NOW FUTURE? What is this? Earth s Early history Approximately 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth was formed when many pieces of
UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity CHAPTER 14: The History of Life PAST NOW FUTURE? What is this? Earth s Early history Approximately 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth was formed when many pieces of
Geologic time. 8 th Grade
 + Geologic time 8 th Grade + Trilobites n Trilobites are small, hard-shelled animals that lived in ancient seas. Trilobites are considered to be index fossils. n Index fossils lived over vast regions of
+ Geologic time 8 th Grade + Trilobites n Trilobites are small, hard-shelled animals that lived in ancient seas. Trilobites are considered to be index fossils. n Index fossils lived over vast regions of
What is the Earth s time scale?
 Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
The Paleozoic Era. The Beginning Of An Explosion Of Life Forms
 The Paleozoic Era The Beginning Of An Explosion Of Life Forms The Paleozoic Era is the beginning of an explosion of life forms. The CambrianExplosion marks the era with thousands of new life forms in the
The Paleozoic Era The Beginning Of An Explosion Of Life Forms The Paleozoic Era is the beginning of an explosion of life forms. The CambrianExplosion marks the era with thousands of new life forms in the
The History of Life. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE
 Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale
 History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 WS #3 GEOLOGIC TIME & THE FOSSIL RECORD
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 WS #3 GEOLOGIC TIME & THE FOSSIL RECORD NAME Multiple Choice 1. Fossils are most commonly found in A. sedimentary rocks. B. metamorphic rocks. C. igneous rocks. D. all kinds of rocks.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 WS #3 GEOLOGIC TIME & THE FOSSIL RECORD NAME Multiple Choice 1. Fossils are most commonly found in A. sedimentary rocks. B. metamorphic rocks. C. igneous rocks. D. all kinds of rocks.
251 Million years. 299 Million years. 318 Million years. 359 Million years
 The Late Paleozoic 251 Million years 299 Million years 318 Million years 359 Million years Major Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did
The Late Paleozoic 251 Million years 299 Million years 318 Million years 359 Million years Major Questions How did marine life of late Paleozoic time differ from that of middle Paleozoic time? How did
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20)
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME
 Name: Date: Period: UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME The earth is 4.6 billion years old. That s a long time! The scale of geologic time is so different from what human beings experience that it s often quite
Name: Date: Period: UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME The earth is 4.6 billion years old. That s a long time! The scale of geologic time is so different from what human beings experience that it s often quite
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE. Dr. Bertolotti
 CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Fossils. Name Date Class. A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary
 Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils
 Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
~22.5 MYA ~2500 MYA ~3000MYA ~3500 MYA ~1000 MYA ~2100 MYA. Early apes are found. Savannas expand
 Early apes are found. Savannas expand ~22.5 MYA Photosynthesis by blue-green bacteria. Oxygen forms in the atmosphere but immediately reacts with molecules in the ocean and crust of the Earth. The actual
Early apes are found. Savannas expand ~22.5 MYA Photosynthesis by blue-green bacteria. Oxygen forms in the atmosphere but immediately reacts with molecules in the ocean and crust of the Earth. The actual
The history of Life Section 19.1: The fossil record
 The history of Life Section 19.1: The fossil record Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils provide information about extinct species Fossils can vary greatly Different sizes, types and degrees of preservation
The history of Life Section 19.1: The fossil record Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils provide information about extinct species Fossils can vary greatly Different sizes, types and degrees of preservation
The Phanerozoic Eon. 542 mya Present. Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras
 542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
The Geological Time Scale. Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of Canada.
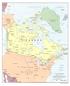 Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
Origins of Life. Fundamental Properties of Life. The Tree of Life. Chapter 26
 Origins of Life The Tree of Life Cell is the basic unit of life Today all cells come from pre-existing cells Earth formed ~4.5 billion years ago (BYA) Chapter 26 As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were
Origins of Life The Tree of Life Cell is the basic unit of life Today all cells come from pre-existing cells Earth formed ~4.5 billion years ago (BYA) Chapter 26 As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were
2/13/17. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination. Geologic Time - Relative Age Determination
 A) Principle of Uniformitarianism = For natural disasters, uniformitarianism used to predict future events. Examples? Which rock layer is oldest (bottom, middle or top)? B) Principle of Superposition =
A) Principle of Uniformitarianism = For natural disasters, uniformitarianism used to predict future events. Examples? Which rock layer is oldest (bottom, middle or top)? B) Principle of Superposition =
Geologic History. A. Basic Geologic Principles The relative age of rock formations relies on the following basic geologic principles:
 Geologic History I. Relative Age Dating of Rocks Relative age of rocks does not rely on an exact date of a rock, but relates its age relative to other rock formations or layers. A. Basic Geologic Principles
Geologic History I. Relative Age Dating of Rocks Relative age of rocks does not rely on an exact date of a rock, but relates its age relative to other rock formations or layers. A. Basic Geologic Principles
Name: Date: Period: Page 1
 Name: Date: Period: Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the three bedrock outcrops below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The outcrops, labeled I, II, and III, are located within 15 kilometers
Name: Date: Period: Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the three bedrock outcrops below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The outcrops, labeled I, II, and III, are located within 15 kilometers
The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom
 The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Many questions regarding the origins and evolutionary history of the animal kingdom continue to be researched and debated, as new fossil
The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Many questions regarding the origins and evolutionary history of the animal kingdom continue to be researched and debated, as new fossil
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name:
 Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time.
 Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time. What is geologic time?
 Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time What is geologic time? The division of Earth s history into time units back to 4.6 b.y.a. Usually based on the life-forms that lived during certain periods May be based
Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time What is geologic time? The division of Earth s history into time units back to 4.6 b.y.a. Usually based on the life-forms that lived during certain periods May be based
The Origin of Life. Lab Exercise 18. Contents. Introduction. Objectives
 Lab Exercise The Origin of Life Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Geologic Time 2 Activity.2 Time Periods 2 Resutls Section 6 Introduction The history of the earth is recorded in the rocks
Lab Exercise The Origin of Life Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Geologic Time 2 Activity.2 Time Periods 2 Resutls Section 6 Introduction The history of the earth is recorded in the rocks
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
.Biology Chapter 14 Test: The History of Life
 Class: Date:.Biology Chapter 14 Test: The History of Life True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. On the geologic time scale, an eon is longer than an era. 2. The oblong shape of
Class: Date:.Biology Chapter 14 Test: The History of Life True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. On the geologic time scale, an eon is longer than an era. 2. The oblong shape of
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Biogeography. Lecture 5
 Biogeography. Lecture 5 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 25, 2016 Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 5 January 25, 2016 1 / 34 Outline Palaeogeography Plate tectonics Cryogenian period
Biogeography. Lecture 5 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 25, 2016 Shipunov (MSU) Biogeography. Lecture 5 January 25, 2016 1 / 34 Outline Palaeogeography Plate tectonics Cryogenian period
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale
 Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
Major geological events fit into a timeline, beginning with the formation of the Earth
 Chapter 4 Major geological events fit into a timeline, beginning with the formation of the Earth 4.1 The origin and development of life William Smith was a canal engineer who supervised the excavation
Chapter 4 Major geological events fit into a timeline, beginning with the formation of the Earth 4.1 The origin and development of life William Smith was a canal engineer who supervised the excavation
Name: Class: Date: 7. The prebiotic soup hypothesis proposes that organic molecules formed from cracks in the ocean floor.
 Match the period with the corresponding biological events. a. Cambrian 542mya b. Carboniferous 359 mya c. Devonian 488 mya d. Jurassic 200mya e. Quaternary 2.6 mya 1. Gymnosperms common, large dinosaurs
Match the period with the corresponding biological events. a. Cambrian 542mya b. Carboniferous 359 mya c. Devonian 488 mya d. Jurassic 200mya e. Quaternary 2.6 mya 1. Gymnosperms common, large dinosaurs
Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY
 Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY Use Figure 2 to answer the following two questions. 10. Interpreting Graphics Which is older the sandstone layer or Dike A? Explain your answer. Conglomerate Sandstone
Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY Use Figure 2 to answer the following two questions. 10. Interpreting Graphics Which is older the sandstone layer or Dike A? Explain your answer. Conglomerate Sandstone
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 Date Class _ A Trip Through Geologic Time Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Late in the Paleozoic Era, the supercontinent Pangaea formed.
Date Class _ A Trip Through Geologic Time Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Late in the Paleozoic Era, the supercontinent Pangaea formed.
Diversity, Change and Continuity. History of Life
 Diversity, Change and Continuity History of Life Change throughout the history of Life. A summary of content covered 1 2 3 4 Changes in the atmosphere Changes in climate Geological events Biogeography
Diversity, Change and Continuity History of Life Change throughout the history of Life. A summary of content covered 1 2 3 4 Changes in the atmosphere Changes in climate Geological events Biogeography
» The elements on our planet all originated from the sun or other stars
 Chapter 18 » We ve identified over 300 characteristics that a planet needs to support life. Lose one, and the planet is barren» The earth formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago (bya). The growing gravitational
Chapter 18 » We ve identified over 300 characteristics that a planet needs to support life. Lose one, and the planet is barren» The earth formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago (bya). The growing gravitational
Chapter 1: Life on Earth R E V I E W Q U E S T I O N S
 Chapter 1: Life on Earth R E V I E W Q U E S T I O N S Chapter 1: Review Name three characteristics that define something as Alive. Chapter 1: Review Name three characteristics that define something as
Chapter 1: Life on Earth R E V I E W Q U E S T I O N S Chapter 1: Review Name three characteristics that define something as Alive. Chapter 1: Review Name three characteristics that define something as
Earth Science. Name Block. Unit 3 Review Worksheet. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Earth Science Unit 3 Review Worksheet Name Block Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1. Which geologic principle is used when a geologist observes an outcrop or rocks and determines
Question #1: What are some ways that you think the climate may have changed in the area where you live over the past million years?
 Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma)
 The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
The Proterozoic Eon (2500 ma to 540 ma) December November October September August July June May April March February January 0 Ma Phanerozoic C M P 540 Ma oldest shelly fossils Proterozoic 2500 Ma first
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life
 Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
Phanerozoic (last 0.54 by) Tectonics Climate Life Tools for Locating Past Continent Positions Fossils depending on climate Alignment of geological features Geometrical fit of continental margins Similarity
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
Plate Tectonics. Alfred Lothar Wegener. Relatively new theory - introduced about 30 years ago Unifies several branches of the Earth Sciences
 Plate Tectonics Relatively new theory - introduced about 30 years ago Unifies several branches of the Earth Sciences http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/dynamic.html Alfred Lothar Wegener In 1858, geographer
Plate Tectonics Relatively new theory - introduced about 30 years ago Unifies several branches of the Earth Sciences http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/dynamic.html Alfred Lothar Wegener In 1858, geographer
Unit 10 Lesson 2 What Was Ancient Earth Like? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 How Rocks and Fossils Tell a Story Sedimentary rock forms in layers. Many sedimentary rocks contain fossils. The oldest rock layers are at the bottom, and the youngest rock layers are at the top. The relative
How Rocks and Fossils Tell a Story Sedimentary rock forms in layers. Many sedimentary rocks contain fossils. The oldest rock layers are at the bottom, and the youngest rock layers are at the top. The relative
Summary The Fossil Record Earth s Early History. Name Class Date
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 Summary The History of Life 17 1 The Fossil Record Fossils are preserved traces and remains of ancient life. Scientists who study fossils are called paleontologists. They use
Name Class Date Chapter 17 Summary The History of Life 17 1 The Fossil Record Fossils are preserved traces and remains of ancient life. Scientists who study fossils are called paleontologists. They use
HISTORICAL GEOLOGY. Relative & Absolute age, fossils and geologic time
 HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Relative & Absolute age, fossils and geologic time Historical Geology A. Measuring Time 1. Relative Time (Relative Age) Measurement of time using comparison. No numbers used; uses words
HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Relative & Absolute age, fossils and geologic time Historical Geology A. Measuring Time 1. Relative Time (Relative Age) Measurement of time using comparison. No numbers used; uses words
Chapter 14 The History of Life
 Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change Section 2: The Origin of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 14.1 Fossil Evidence of Change Land Environments Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Gravity pulled
Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change Section 2: The Origin of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 14.1 Fossil Evidence of Change Land Environments Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Gravity pulled
Laboratory 7 Geologic Time
 (Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
(Name) Laboratory 7 Geologic Time We will be exploring ideas behind the development of the geological column. The geological column is a general term that is used to describe the template behind which
Chapter 12. Life of the Paleozoic
 Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Chapter 12 Life of the Paleozoic Paleozoic Invertebrates Representatives of most major invertebrate phyla were present during Paleozoic, including sponges, corals, bryozoans, brachiopods, mollusks, arthropods,
Station Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus
 Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
 The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
12.1. KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. 68 Reinforcement Unit 4 Resource Book
 12.1 THE FOSSIL RECORD KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. Fossils can form in several different ways: Permineralization occurs when water surrounds a hard structure such
12.1 THE FOSSIL RECORD KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. Fossils can form in several different ways: Permineralization occurs when water surrounds a hard structure such
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck)
 The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
