A synopsis of the channel iron deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia
|
|
|
- Veronica Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A synopsis of the channel iron deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia E. R. Ramanaidou and R. C. Morris Erick Raymond Ramanaidou Minerals Down Under Flagship CSIRO ARRC PO Box 1130 Bentley WA 6102 Australia Richard Cecil Morris CSIRO Earth Science & Resource Engineering CSIRO ARRC PO Box 1130 Bentley WA 6102 Australia
2 A synopsis of the channel iron deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia E. R. Ramanaidou and R. C. Morris ABSTRACT The channel iron deposit type or CID is one of the two major iron ore types mined in the Hamersley Province (Ramanaidou et al., 2003; Macphail and Stone, 2004; Heim et al., 2007; Morris et al., 2007; Vasconcelos et al., 2007). CID provided around 40% of the total of 394 Mt of iron ore mined from the Hamersley Province in 2009, and the current CID resource is around 7 billion tonnes. CID deposits occupy numerous meandering palaeochannels in a mature surface that includes Precambrian rocks and ferruginous Palaeogene valley fill. These palaeochannels are generally less than a kilometre but can range to several kilometres in width and from one metre to more than 100 m thick. There are two currently mined CID areas the first in the western Hamersley Province in the Robe palaeochannel, and the second in the eastern Yandi palaeochannel. These two major CID channels extend over 100 km to 150 km, with the Robe system up to 5 km wide. The granular ore facies typically contains ooids and lesser pisoids with hematite nuclei and goethite cortices, with abundant goethitised wood/charcoal fragments and goethitic peloids, minor clay, and generally minimal porous goethitic matrix. Post deposition weathering is common and produced secondary facies. Ooids and pisoids were mostly derived from the stripping of a well-vegetated, deep ferruginous surface. The peloids were derived intra-formationally from both fragmentation and reworking of desiccated goethite-rich mud. Minute wood/charcoal fragments in the soil were initially replaced by goethite and then dehydrated to hematite, forming nuclei for many ooids and pisoids. In addition, abundant, generally small ( 10 mm) fragments of wood/charcoal were replaced in situ by goethite within the consolidating CID. This profusion of fossil wood, both as ooids and pisoids nuclei and as discrete fragments, as well as the local presence of kenomagnetite suggests major episodic wild fires in heavily vegetated catchments. The goethitic matrix was the result of chemically precipitated iron hydroxyoxides, resulting from leaching of iron-rich soils in an organic environment.
3 INTRODUCTION Iron ore production in Western Australia has been increasing strongly from 2005 to 2010 (Figure 1) and relies on two different types of iron ore: the bedded iron deposits and the channel iron deposits. There are three main iron ore types in the Pilbara craton and Hamersley province: the banded ironformation - hosted hematite and hematite goethite bedded iron deposits; the goethite-hematite channel iron deposits or CID, and the minor hematite goethite detrital iron deposits. The current production of CID from the three mines (Mesa J, Yandicoogina and Yandi) represents approximately 40% of the total iron ore production from Western Australia. The general term CID includes the Robe Formation (previously known as the Robe Pisolite, including the Mesa J deposit), the Marillana Formation, (including the Yandi deposits), the Poondano Formation of the northern Pilbara and the minor deposits of the Yilgarn Craton, all in Western Australia, and the lesser known fluvial to lacustrine deposits of Kazakhstan. CHANNEL IRON DEPOSIT DISTRIBUTION CID occupy meandering palaeochannels on a mature surface that includes Precambrian rocks and ferruginous Palaeogene valley fill. CID are generally less than one km wide (up to five km) with a preserved thickness now ranging from one to rarely over 100 m. The Robe palaeochannel is the longest with CID partly preserved over a distance of 150 km (Figure 2). In the Robe Valley, CID are often preserved in an inverted topography as remnant mesas in the centre of the palaeochannels (Figure 3). In other cases, CID abut the margin of the palaeochannels. A variety of facies can be found within the CID - granular with local intra-formational conglomerate, bedded and altered types: conchoidal, leached, and surface types. The granular facies is the only type which typically meets the specification to be considered as ore.
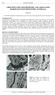
4 A section of Marillana Formation typically comprises from bottom to top: a basal conglomerate and a basal clay zone (Munjina Member); lower or basal CID and higher or main CID (Barimunya Member, Kneeshaw in Ramanaidou et al., 2003). The Robe Formation shows similar general features. GENERAL GEOLOGY CID consist of the Miocene (Ramanaidou et al., 2003; Macphail and Stone, 2004; Heim et al., 2007; Morris et al., 2007; Vasconcelos et al., 2007) iron-rich detrital horizons of the channels. Their granular components include very rare lithic fragments, but contain abundant diagnostic ferruginised wood fragments. The granular material ranges from coarse sand to fine gravel (typically 1 10 mm) and includes varying proportions of peloids [fragments of fine-grained to silty a structural goethite], pelletoids [ooids (<2 mm) and pisoids (2-10 mm) - rounded ferruginous particles consisting of a nucleus surrounded by a goethitic cortex], and fossil wood fragments (Figures 4 and 5). The nuclei vary widely between almost perfect spheres and irregular shapes. Nuclei are either simple or complex. A typical nucleus has a primary centre (core) with a series of layers that now form a single coherent particle. Kenomagnetite - maghemite is randomly disseminated within the peloids, occasionally in the nuclei and frequently along layer boundaries and cracks. A porous, ramifying goethitic matrix with minor secondary goethite and silica infill, encloses and cements the granules. Numerous electron microprobe analyses of CID showed that aluminium (Al) and silicon (Si) increase from the hematitic nuclei to the matrix, and then the cortex. In the Robe Valley deposits, Al content in the nuclei ranges from 0.5 to 2.8% whereas in the Yandi deposits, Al ranges from 0.2 to 0.7%. The Al content in cortex is either twice as high (Robe CID) or three times (Yandi CID) as the Al content of the nucleus. GENESIS OF WESTERN AUSTRALIAN CHANNEL IRON DEPOSITS
5 A detailed account of the genesis of Western Australia CID has been presented in Morris and Ramanaidou (2007). Large terrestrial iron-rich ooidal/pisoidal deposits are rare. Apart from WA and Kazakhstan, only minor concentrations have been reported elsewhere. Relic rock textures are extremely rare in the Australian CID components in contrast with abundant martite and hematite/goethite-pseudomorphed banded iron formation textures found in the underlying and overlying detrital iron deposits that occur stratigraphically above and below CID. The huge volume of CID pelletoids contrasting with the small amount of comparable pelletoids in the underlying and overlying detrital iron deposits implies very specific climatic conditions during the forming and stripping of the mid-miocene surface. Although highly resistant lithic material is rare, CID are notable for the abundance of preserved ferruginised wood/charcoal fragments. The accretionary coatings on the pelletoids (Figure 8) with their evidence of multiple cycles of burial, ferruginisation, and reexposure suggest rapid and recurring changes from pluvial to arid conditions. The presence of a heath-like surface is suggested by the time the CID horizons began to accumulate. We suggest that unlike the current cuirass style, the mid-miocene Hamersley surface was a relatively easily eroded ferruginised soil produced by a prolonged warm non-seasonal climate of moderate rainfall - the Miocene climatic optimum. The ferruginised soil was probably dominated by poorly -structured goethite, with abundant minute fragments of ferruginised wood/charcoal and root material. The stripping phase culminated at around 12 Ma, with increasing cold arid conditions indicated by the overlying calcretised limestone of the Oakover Formation, before the onset of the Pliocene warming reversal. Fires played a significant role by dehydrating surface goethite to hematite (or kenomagnetite-maghemite) with consequent fracturing along cracks. Consolidation of the irondominated colluvium occurred at breaks in the slopes, as today, where conditions were favourable for ferruginisation to form soil hardgrounds. The combination of chemical and physical weathering reexposed and released the goethite-coated fragments, typically dehydrated to hematite with time. This process repeated itself further downslope through many cycles before final deposition as pelletoidal CID in the channels. The general lack of chert and clay in the ore CID suggests that the shed from this weathering surface was largely iron oxide.
6 CONCLUSIONS The CID is one of the two major mineable iron ore types in the Hamersley Province and accounts for 40% of current production. CID include the Robe Formation, the Marillana Formation, the Poondano Formation, and minor deposits of the Yilgarn, as well as the large deposits of Kazakhstan. CID occur in palaeochannels one to five km wide and one to 100 m thick with the Robe paleochannel being the longest. CID are iron-rich detrital accumulations comprising coarse sand to fine gravel size granules that include: pelletoids (ooids and pisoids); peloids, ferruginised wood (goethitic wood in the matrix and hematitic wood in the nucleus) and a porous matrix that envelops the granules. Al and Si increase from the hematitic nuclei to the matrix, and then the cortex. The proposed genetic model starts with a well vegetated surface growing on deeply ferruginised rock. The stripping of the ferruginous surface generates pelletoids often with hematitised wood as nuclei. The abundant presence of ferruginised wood/charcoal and kenomagnetite-maghemite suggests extensive fires. The goethitic matrix is dominantly chemically precipitated within the channels, and the goethitised wood was probably ferruginised within the consolidating CID. This paper has been reproduced with the kind permission of the Australasian Institute for Mining and Metallurgy from Iron Ore 2007, August 2007, Perth, Western Australia. REFERENCES Heim, J A, Vasconcelos, P M, Schuster, D L, Farley, K A and Broadbent, G, Dating paleochannel iron ore by (U/Th)/He analysis of supergene goethite, Hamersley Province, Australia, Geology, 34:
7 Macphail, M K and Stone, M S, Age and palaeoenvironmental constraints on the genesis of the Yandi channel iron deposits, Marillana Formation, Pilbara, northwestern Australia, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 51: Morris, R C, Kneeshaw, M and Ramanaidou, E R, Dating paleochannel iron ore by (U-Th)/He analysis of supergene goethite, Hamersley Province, Australia, Geology, comment page e118 [online], April 2007, DOI /G22891C.1. Morris, R C and Ramanaidou, E R, Genesis of the channel iron deposits (CID) of the Pilbara of Western Australia, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 54: Ramanaidou, E R, Morris, R C and Horwitz, R C, Channel iron deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 50: Vasconcelos, P M, Heim, J A, Schuster, D L, Farley, K A and Broadbent, G, Dating paleochannel iron ore by (U/Th)/He analysis of supergene goethite, Hamersley Province, Australia, Geology, reply page e119 [online], April 2007, DOI: /G23755Y.1.
8 Figures Figure 1. Iron Ore Production in Kt (ABARE, 2007) Figure 2. CID distribution in the Hamersley Province with the Robe and Marillana palaeochannels. Figure 3. A CID mesa in the Robe Valley. Figure 4. CID ooidal texture: a polished thin section of the Robe Valley area. Figure 5. Polished thin section of CID under reflected light, showing irregular to spheroidal pelletoids with ferruginised wood in a ramifying porous matrix of goethite. [H = hematite] Figure 6. Polished thin section showing accretionary growths of goethite on the hematite nucleus of a pelletoid showing variable levels of dehydration to hematite. The outermost layer is essentially partly ferruginised soil of the current cycle.
9 Figure 1. Australian Iron Ore Production in 1000 tonnes (ABARE, 2010).
10 Figure 2. CID distribution in the Hamersley Province with the Robe and Marillana palaeochannels.
11 Figure 3. A CID mesa in the Robe Valley. 2 mm Figure 4. CID ooidal texture: a polished thin section of the Robe Valley.
12 Figure 5. CID under reflected light, showing irregular to spheroidal pelletoids with ferruginised wood in a ramifying porous matrix of goethite.
13 Figure 6. Accretionary growths of goethite on the hematite nucleus of a pelletoid showing variable levels of dehydration to hematite. The outermost layer is essentially partly ferruginised soil of the current cycle.
Weathering, Landscape Evolution, Supergene Enrichment, and Ore Genesis: Implications to Mineral Exploration. Paulo Vasconcelos
 Weathering, Landscape Evolution, Supergene Enrichment, and Ore Genesis: Implications to Mineral Exploration Paulo Vasconcelos 1 Lateritic/Oxide Au, Fe, Mn, Al, Ni, Cu, Zn, 2 Lateritic/Oxide Au, Fe, Mn,
Weathering, Landscape Evolution, Supergene Enrichment, and Ore Genesis: Implications to Mineral Exploration Paulo Vasconcelos 1 Lateritic/Oxide Au, Fe, Mn, Al, Ni, Cu, Zn, 2 Lateritic/Oxide Au, Fe, Mn,
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Geology 252, Historical Geology, California State University, Los Angeles - professor: Dr. Alessandro Grippo
 LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
WEATHERING-CONTROLLED FRACTIONATION OF ORE AND PATHFINDER ELEMENTS AT COBAR, NSW
 296 WEATHERING-CONTROLLED FRACTIONATION OF ORE AND PATHFINDER ELEMENTS AT COBAR, NSW Kenneth G. McQueen 1,2 & Dougal C. Munro 1 1 CRC LEME, Department of Geology, Australian National University, ACT, 0200
296 WEATHERING-CONTROLLED FRACTIONATION OF ORE AND PATHFINDER ELEMENTS AT COBAR, NSW Kenneth G. McQueen 1,2 & Dougal C. Munro 1 1 CRC LEME, Department of Geology, Australian National University, ACT, 0200
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 100. Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Mechanical Weathering
 Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Mechanical & Chemical Weathering. Sediments. Lithification. Deposition. Transport. Erosion.
 Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Figure 1. Location map for part of the Hamersley Iron Province, Western Australia.
 HAMERSLEY IRON PROVINCE, WESTERN AUSTRALIA M.F. Killick 1, H.M. Churchward 2 and R.R. Anand 3 1. 92 Lockwood Street, Yokine, WA 6060 2. PO Box 159, Balingup, WA 6153 3. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and
HAMERSLEY IRON PROVINCE, WESTERN AUSTRALIA M.F. Killick 1, H.M. Churchward 2 and R.R. Anand 3 1. 92 Lockwood Street, Yokine, WA 6060 2. PO Box 159, Balingup, WA 6153 3. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface.
 The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA
 254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
Sediment. Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface
 Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Concretions are accumulation of one or more minerals within the body of a sedimentary rock, or within
 Tibooburra concretions Page 1 Concretions are accumulation of one or more minerals within the body of a sedimentary rock, or within cracks and cavities in a rock. They form when minerals such as quartz,
Tibooburra concretions Page 1 Concretions are accumulation of one or more minerals within the body of a sedimentary rock, or within cracks and cavities in a rock. They form when minerals such as quartz,
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
DISCOVERY OF MINERALISED PORPHYRY & MAGNETITE-COPPER-GOLD AT KAMARANGAN
 MEDUSA MINING LIMITED ABN: 60 099 377 849 Unit 7, 11 Preston Street Como WA 6152 PO Box 860 Canning Bridge WA 6153 Telephone: +618-9367 0601 Facsimile: +618-9367 0602 Email: admin@medusamining.com.au Internet:
MEDUSA MINING LIMITED ABN: 60 099 377 849 Unit 7, 11 Preston Street Como WA 6152 PO Box 860 Canning Bridge WA 6153 Telephone: +618-9367 0601 Facsimile: +618-9367 0602 Email: admin@medusamining.com.au Internet:
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks
 GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p )
 13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
 UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
Sedimentary Rocks. All sedimentary rocks begin to form when existing rocks are broken down into sediments Sediments are mainly weathered debris
 Rocks! Objectives Describe the major processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rock Distinguish between clastic sedimentary rocks and chemical sedimentary rocks Identify the features that are
Rocks! Objectives Describe the major processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rock Distinguish between clastic sedimentary rocks and chemical sedimentary rocks Identify the features that are
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 56 Structure of Sedimentary Rocks Frequently Asked Questions FAQ s Que 01. What
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 56 Structure of Sedimentary Rocks Frequently Asked Questions FAQ s Que 01. What
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Classification of sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks are products of weathered, fragmented or dissolved,
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Classification of sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks are products of weathered, fragmented or dissolved,
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks
 Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
GEOL Lab 9 (Carbonate Sedimentary Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section)
 GEOL 333 - Lab 9 (Carbonate Sedimentary Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section) Sedimentary Rock Classification - As we learned last week, sedimentary rock, which forms by accumulation and lithification
GEOL 333 - Lab 9 (Carbonate Sedimentary Rocks in Hand Sample and Thin Section) Sedimentary Rock Classification - As we learned last week, sedimentary rock, which forms by accumulation and lithification
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL DESCRIPTIONS OF OTHER STRATIGRAPHIC SECTIONS Cherry Creek In its middle reaches, Cherry Creek meanders between three paired terraces within a narrow bedrock valley. The highest is
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL DESCRIPTIONS OF OTHER STRATIGRAPHIC SECTIONS Cherry Creek In its middle reaches, Cherry Creek meanders between three paired terraces within a narrow bedrock valley. The highest is
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
Chemical Weathering and Soils
 Chemical Weathering and Soils Fresh rocks and minerals that once occupied the outermost position reached their present condition of decay through a complex of interacting physical, chemical, and biological
Chemical Weathering and Soils Fresh rocks and minerals that once occupied the outermost position reached their present condition of decay through a complex of interacting physical, chemical, and biological
1/31/2013. Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes. Weathering Mechanisms. Wind abrasion forming Ventifacts
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
10 BILLION TONNES TOTAL RESOURCES ACHIEVED FROM MAJOR MAIDEN RESOURCE ESTIMATE FOR WESTERN HUB
 23 March 2011 The Companies Officer ASX Limited 2 The Esplanade Perth WA 6000 Dear Sir 10 BILLION TONNES TOTAL RESOURCES ACHIEVED FROM MAJOR MAIDEN RESOURCE ESTIMATE FOR WESTERN HUB A substantial increase
23 March 2011 The Companies Officer ASX Limited 2 The Esplanade Perth WA 6000 Dear Sir 10 BILLION TONNES TOTAL RESOURCES ACHIEVED FROM MAJOR MAIDEN RESOURCE ESTIMATE FOR WESTERN HUB A substantial increase
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Sand. Sand is any eroded material (igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary) that has a grain size from 1/16 th to 2 millimeters in size.
 Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Mud Sand Gravel. Clastic Textures
 Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Please see the questions online before you begin. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Please see the questions online before you begin. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Mud Sand Gravel. Clastic Textures
 Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Read the sedimentary rocks chapter before you start. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Sed Rocks Self-Instruction Lab Name Geology 100 Harbor Section Read the sedimentary rocks chapter before you start. Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering,
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8
 Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
GOLD DISTRIBUTION THROUGH THE REGOLITH PROFILE: EXAMPLES FROM THE WHITE DAM PROSPECT, OLARY, SOUTH AUSTRALIA
 GOLD DISTRIBUTION THROUGH THE REGOLITH PROFILE: EXAMPLES FROM THE WHITE DAM PROSPECT, OLARY, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Robert C. Dart, David J. Chittleborough and Karin M. Barovich CRC LEME, School of Earth and
GOLD DISTRIBUTION THROUGH THE REGOLITH PROFILE: EXAMPLES FROM THE WHITE DAM PROSPECT, OLARY, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Robert C. Dart, David J. Chittleborough and Karin M. Barovich CRC LEME, School of Earth and
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS
 LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
LAB 2 IDENTIFYING MATERIALS FOR MAKING SOILS: ROCK AND PARENT MATERIALS Learning outcomes The student is able to: 1. understand and identify rocks 2. understand and identify parent materials 3. recognize
Bowen s Chemical Stability Series
 Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
For personal use only
 The Company Announcements Office ASX Limited Via E Lodgement 31 January 2012 QUARTERLY ACTIVITIES REPORT TO 31 DECEMBER 2012 PROJECT ACQUISITION During the quarter, Coziron Resources Limited ( Coziron
The Company Announcements Office ASX Limited Via E Lodgement 31 January 2012 QUARTERLY ACTIVITIES REPORT TO 31 DECEMBER 2012 PROJECT ACQUISITION During the quarter, Coziron Resources Limited ( Coziron
A Classification Oncoidal wackestone. Interpretation Shallow tail or channel environment.
 A132 Photo 1: Matrix of micrite/ carbonaceous mud with high percentage of siliciclastic sand and silt. Shrinkage fractures partially filled with microcrystalline carbonate cement. Other small voids contain
A132 Photo 1: Matrix of micrite/ carbonaceous mud with high percentage of siliciclastic sand and silt. Shrinkage fractures partially filled with microcrystalline carbonate cement. Other small voids contain
Clastic Textures. I. What is the sorting of sample numbers 60, 61, and 62? Answers on last page.
 Sed Rock s Sel f-instruction N ame Geology 100 Harbor Secti on Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering, which originates by the successive deposition of
Sed Rock s Sel f-instruction N ame Geology 100 Harbor Secti on Sedimentary rocks are usually identified in the field by their stratification or layering, which originates by the successive deposition of
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
AGM Geology Presentation. 30th November 2016
 AGM Geology Presentation 30th November 2016 2 Disclaimer Disclaimer This presentation contains forward looking statements that are subject to risk factors associated with the exploration and mining industry.
AGM Geology Presentation 30th November 2016 2 Disclaimer Disclaimer This presentation contains forward looking statements that are subject to risk factors associated with the exploration and mining industry.
Exploration Significance of Unconformity Structure on Subtle Pools. 1 Vertical structure characteristics of unconformity
 Exploration Significance of Unconformity Structure on Subtle Pools Wu Kongyou (China University of Petroleum,College of Geo-Resources and Information,Shandong Qingdao 266555) Abstract: Vertical structure
Exploration Significance of Unconformity Structure on Subtle Pools Wu Kongyou (China University of Petroleum,College of Geo-Resources and Information,Shandong Qingdao 266555) Abstract: Vertical structure
GEOL And a Quick Review of Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 GEOL 3000 And a Quick Review of Sedimentary Rocks and Processes North American Stratigraphic Code A formulation of current views on stratigraphic principles and procedures designed to promote standardized
GEOL 3000 And a Quick Review of Sedimentary Rocks and Processes North American Stratigraphic Code A formulation of current views on stratigraphic principles and procedures designed to promote standardized
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT Date: 03 October 2018 Number: 604/031018
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT Date: 03 October 2018 Number: 604/031018 TRIAL BULK SAMPLING PROGRAMME COMPLETED AT BLACKRIDGE CONGLOMERATE-HOSTED GOLD PROJECT QUEENSLAND Approx 8.5 tonnes of samples collected covering
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT Date: 03 October 2018 Number: 604/031018 TRIAL BULK SAMPLING PROGRAMME COMPLETED AT BLACKRIDGE CONGLOMERATE-HOSTED GOLD PROJECT QUEENSLAND Approx 8.5 tonnes of samples collected covering
Beneath the sand of the Tanami Desert
 Beneath the sand of the Tanami Desert ARGA 2018, Wallaroo, SA Nadir de Souza Kovacs Ngururrpa program The program area covers the traditional land of the Parna Ngururrpa People in a remote part of the
Beneath the sand of the Tanami Desert ARGA 2018, Wallaroo, SA Nadir de Souza Kovacs Ngururrpa program The program area covers the traditional land of the Parna Ngururrpa People in a remote part of the
Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
 Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20
 Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 3302
 Engineering Geology ECIV 3302 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2019-2018 Chapter (5) Weathering & Soil Chapter 5: Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting External processes include : (1) Weathering (2) Mass wasting
Engineering Geology ECIV 3302 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2019-2018 Chapter (5) Weathering & Soil Chapter 5: Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting External processes include : (1) Weathering (2) Mass wasting
Lecture # 02 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SWEDISH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY, WAH CANTT. 14th December,
 Lecture # 02 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SWEDISH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY, WAH CANTT Instructor: Date: Engr. Imran Mehmood 14th December, 2011 1 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS SEDIMENTARY ROCKS The rocks
Lecture # 02 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SWEDISH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY, WAH CANTT Instructor: Date: Engr. Imran Mehmood 14th December, 2011 1 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS SEDIMENTARY ROCKS The rocks
Emily and Megan. Earth System Science. Elements of Earth by weight. Crust Elements, by weight. Minerals. Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight
 Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e and s Chapter 5 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer Cole Northeastern University Earth
Essentials of Geology, 11e and s Chapter 5 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer Cole Northeastern University Earth
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Mechanisms
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs. LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes Last week we covered the basic types of rocks and the rock cycle. This lab concentrates on sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks have special
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes Last week we covered the basic types of rocks and the rock cycle. This lab concentrates on sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks have special
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks
 The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
Earth Science, 10e. Edward J. Tarbuck & Frederick K. Lutgens
 Earth Science, 10e Edward J. Tarbuck & Frederick K. Lutgens Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting Chapter 3 Earth Science, 10e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College Earth's external processes
Earth Science, 10e Edward J. Tarbuck & Frederick K. Lutgens Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting Chapter 3 Earth Science, 10e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College Earth's external processes
What is a sedimentary rock?
 Sedimentary Rocks What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of mechanical and chemical weathering They account for only 5% of the top 10 miles of the outer crust, yet most of the earth
Sedimentary Rocks What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of mechanical and chemical weathering They account for only 5% of the top 10 miles of the outer crust, yet most of the earth
THE MULLAQUANA URANIUM PROJECT
 THE MULLAQUANA URANIUM PROJECT South Australian Explorers Conference 26 November 2010 Russel Bluck - Managing Director DISCLAIMER This presentation has been prepared by UraniumSA Limited in summary form
THE MULLAQUANA URANIUM PROJECT South Australian Explorers Conference 26 November 2010 Russel Bluck - Managing Director DISCLAIMER This presentation has been prepared by UraniumSA Limited in summary form
STUDENT SOIL PRESENTATIONS
 STUDENT SOIL PRESENTATIONS Soil Order (and informal name) Student Name(s) Alfisol = deciduous forest soil Andisol = formed on volcanic ash Aridisol = desert soil Entisol = alluvium soil Gelisol = tundra
STUDENT SOIL PRESENTATIONS Soil Order (and informal name) Student Name(s) Alfisol = deciduous forest soil Andisol = formed on volcanic ash Aridisol = desert soil Entisol = alluvium soil Gelisol = tundra
Mineral Resource for Pilbara Iron Ore Project increased to more than 900 Mt Pilbara Iron Ore Project (PIOP), Western Australia
 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 14 November 2011 Mineral Resource for Pilbara Iron Ore Project increased to more than 900 Mt Pilbara Iron Ore Project (PIOP), Western Australia highlights Further 23% increase to 917 Mt
ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 14 November 2011 Mineral Resource for Pilbara Iron Ore Project increased to more than 900 Mt Pilbara Iron Ore Project (PIOP), Western Australia highlights Further 23% increase to 917 Mt
The Kingfisher Field, Uganda - A Bird in the Hand! S R Curd, R Downie, P C Logan, P Holley Heritage Oil plc *
 A Bird in the Hand! EXTENDED ABSTRACT The Kingfisher Field, Uganda - A Bird in the Hand! Heritage Oil plc * The Kingfisher Field lies on Uganda s western border beneath Lake Albert, situated in the western
A Bird in the Hand! EXTENDED ABSTRACT The Kingfisher Field, Uganda - A Bird in the Hand! Heritage Oil plc * The Kingfisher Field lies on Uganda s western border beneath Lake Albert, situated in the western
GOURDIS AND EMPIRE LATERITIC GOLD DEPOSITS, WESTERN AUSTRALIA
 GOURDIS AND EMPIRE LATERITIC GOLD DEPOSITS, WESTERN AUSTRALIA INTRODUCTION M.D. Paine1 and M.F.P. Foo2 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. 20 Hibbertia Court, Forrest
GOURDIS AND EMPIRE LATERITIC GOLD DEPOSITS, WESTERN AUSTRALIA INTRODUCTION M.D. Paine1 and M.F.P. Foo2 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. 20 Hibbertia Court, Forrest
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
 Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 13: Immature Siliciclastic Sedimentary Environments Alluvial Fans, Braided Streams Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Immature
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 402: Sedimentary Petrology Lecture 13: Immature Siliciclastic Sedimentary Environments Alluvial Fans, Braided Streams Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Immature
Soil Formation. Parent Material. Time. Climate
 Soil Formation Parent Material Time Climate Topography Biota Main Objectives 1. Gain a general understanding of soil formation processes 2. Understand the importance of mineral weathering in soil formation
Soil Formation Parent Material Time Climate Topography Biota Main Objectives 1. Gain a general understanding of soil formation processes 2. Understand the importance of mineral weathering in soil formation
EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Feet. SAND; clayey, fine grained; shells are common; rounded quartz grains. SHELLS; muddy; almost no sand, shells and fragments common
 SAND; clayey, fine grained; shells are common; rounded quartz grains SHELLS; muddy; almost no sand, shells and fragments common SAND; back to medium to fine; has a mottled appearance and looks burrowed;
SAND; clayey, fine grained; shells are common; rounded quartz grains SHELLS; muddy; almost no sand, shells and fragments common SAND; back to medium to fine; has a mottled appearance and looks burrowed;
Earth and Space Science. Semester 2 Review, Part 2
 Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
8(b). Disruption of mats by seismic events
 1 8(b). Disruption of mats by seismic events J.A. Donaldson and J.R. Chiarenzelli This series of photographs documents structures in quartz arenites of the Nepean Formation (Cambro-Ordovician) in Ottawa,
1 8(b). Disruption of mats by seismic events J.A. Donaldson and J.R. Chiarenzelli This series of photographs documents structures in quartz arenites of the Nepean Formation (Cambro-Ordovician) in Ottawa,
Sedimentary Geology. Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1
 Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Explain how rock composition affects the rate of weathering. Discuss how surface area affects the rate at which rock weathers.
 Objectives Explain how rock composition affects the rate of weathering. Discuss how surface area affects the rate at which rock weathers. Describe the effects of climate and topography on the rate of weathering.
Objectives Explain how rock composition affects the rate of weathering. Discuss how surface area affects the rate at which rock weathers. Describe the effects of climate and topography on the rate of weathering.
Your teacher will show you a sample or diagram of each, and show you a settling column. Draw these, and label your diagrams (8 pts) Ungraded:
 From Sand to Stone: How do we recognize and interpret sedimentary rocks in the rock record? (Based closely on the University of Washington ESS 101 Lab 5: Sedimentary Rocks) Introduction: This lab consists
From Sand to Stone: How do we recognize and interpret sedimentary rocks in the rock record? (Based closely on the University of Washington ESS 101 Lab 5: Sedimentary Rocks) Introduction: This lab consists
Chapter 8 Earth Systems and Resources
 Chapter 8 Earth Systems and Resources Earth s resources were determined when the planet formed. The Earth s Crust Layers Core: innermost zone of the planet, largely nickel and iron. Mantle: above the core,
Chapter 8 Earth Systems and Resources Earth s resources were determined when the planet formed. The Earth s Crust Layers Core: innermost zone of the planet, largely nickel and iron. Mantle: above the core,
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Crust Elements. Elements of Earth. Minerals. Crystals. Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air
 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Objectives. Introduction to Soils. Terms to know: What is soil? Study of Soils. The Soil Body 11/9/2012
 Objectives Explain what soil is and where it comes from Define a soil body List examples of the five soil-forming factors Explain how soils develop Introduction to Soils Terms to know: What is soil? Alluvial
Objectives Explain what soil is and where it comes from Define a soil body List examples of the five soil-forming factors Explain how soils develop Introduction to Soils Terms to know: What is soil? Alluvial
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69
 EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
Earth Materials Unit: Sedimen ntary Rocks and Processes Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Five and Six Lab: Laboratorry Six Name
 Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time
 Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time A rock is any naturally formed, nonliving, coherent aggregate mass of solid matter that constitutes part of a planet, asteroid, moon, or other planetary
Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time A rock is any naturally formed, nonliving, coherent aggregate mass of solid matter that constitutes part of a planet, asteroid, moon, or other planetary
GEOLOGIC LOG. sandy. coarse-grained, dark-green autochthonous glauconite; minor amount of sand-grade shell debris, foraminifers rare
 OWNER: William E. Hackney o (Rivercliff Subdivision) DRILLER: Pittman wood & Metal Products Co. COUNTY: Nansemond (Driver) VDMR: WWCR: TOTAL DEPTH: 2092 173 607' GEOLOGIC LOG Depth in feet COLUMBIA GROUP
OWNER: William E. Hackney o (Rivercliff Subdivision) DRILLER: Pittman wood & Metal Products Co. COUNTY: Nansemond (Driver) VDMR: WWCR: TOTAL DEPTH: 2092 173 607' GEOLOGIC LOG Depth in feet COLUMBIA GROUP
Tim Carr - West Virginia University
 Tim Carr - West Virginia University Exploration s Ultimate Goal is to Answer Four Questions: Where to Drill? What to Expect? How Certain? How Profitable? Location & Depth HC Volumes Chance of Success
Tim Carr - West Virginia University Exploration s Ultimate Goal is to Answer Four Questions: Where to Drill? What to Expect? How Certain? How Profitable? Location & Depth HC Volumes Chance of Success
ES120 Sedimentology/Stratigraphy
 Midterm Exam 5/05/08 NAME: 1. List or describe 3 physical processes that contribute to the weathering of rocks (3pts). exfoliation frost wedging many others. roots, thermal expansion/contraction also credit
Midterm Exam 5/05/08 NAME: 1. List or describe 3 physical processes that contribute to the weathering of rocks (3pts). exfoliation frost wedging many others. roots, thermal expansion/contraction also credit
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6
 Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
Ecoregions Glossary. 7.8B: Changes To Texas Land Earth and Space
 Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
The Earth s Layers. Convection and Hot Spots. The Earth s Layers. The Earth s resources were determined when the planet formed.
 The Earth s resources were determined when the planet formed. Chapter 8 Earth Systems and Resources The Earth s Layers Core- the innermost zone of the planet made of nickel and iron. Mantle- above the
The Earth s resources were determined when the planet formed. Chapter 8 Earth Systems and Resources The Earth s Layers Core- the innermost zone of the planet made of nickel and iron. Mantle- above the
The Production of Sediment. Contents. Weathering. Chapters 1, 3
 The Production of Sediment Chapters 1, 3 Contents Weathering Physical, chemical, biogeochemical processes Rates Products Carbon cycle and global change Erosion/Soils Sediment Texture Weathering General
The Production of Sediment Chapters 1, 3 Contents Weathering Physical, chemical, biogeochemical processes Rates Products Carbon cycle and global change Erosion/Soils Sediment Texture Weathering General
SEDIMENTARY TEXTURES:
 SEDIMENTARY TEXTURES: What are they? Grain size Grain shape Particle Surface texture Grain fabric Grain Size Depositional environment - subaerial, water depth, energy Sediment maturity - source, weathering
SEDIMENTARY TEXTURES: What are they? Grain size Grain shape Particle Surface texture Grain fabric Grain Size Depositional environment - subaerial, water depth, energy Sediment maturity - source, weathering
Maggie Payne Jim Turenne
 Maggie Payne Jim Turenne USDA-NRCS 60 Quaker Lane, Suite 46 Warwick, RI. 02886 401-822-8832 maggie.payne@ri.usda.gov U.S. Department of Agriculture 1935: Soil Conservation Service (SCS) Natural Resources
Maggie Payne Jim Turenne USDA-NRCS 60 Quaker Lane, Suite 46 Warwick, RI. 02886 401-822-8832 maggie.payne@ri.usda.gov U.S. Department of Agriculture 1935: Soil Conservation Service (SCS) Natural Resources
ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION
 Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
GEL 109 Midterm W01, Page points total (1 point per minute is a good pace, but it is good to have time to recheck your answers!
 GEL 109 Midterm W01, Page 1 50 points total (1 point per minute is a good pace, but it is good to have time to recheck your answers!) 1. Where in a water flow is there usually a zone of laminar flow even
GEL 109 Midterm W01, Page 1 50 points total (1 point per minute is a good pace, but it is good to have time to recheck your answers!) 1. Where in a water flow is there usually a zone of laminar flow even
Components of a Carbonate rock
 Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix (
Components of a Carbonate rock Skeletal grains Pores Matrix (
Chapter 6. Weathering, Erosion, and Soil
 Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
