Chapter 6. Weathering, Erosion, and Soil
|
|
|
- Rudolph Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil
2 Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material reacts with its new physical and chemical environment transforming it into a new equilibrium state. Fig. 6.1, p. 136
3 Introduction How does weathering differ from erosion? Weathering is the mechanical and chemical alteration of Earth materials at or near the surface. Erosion involves removing weathered materials from their place of origin-by running water or wind, for example.
4 Alteration of Minerals and Rocks The products of weathering include soluble salts, ions in solution, and solid particles. These products of weathering can be eroded and become sedimentary rock at another location or be modified in place to become soils. Fig. 6.1, p. 136
5 Alteration of Minerals and Rocks Weathering and erosion take place at different rates Rocks are not compositionally and structurally homogenous Different parts of a rock will weather at different rates producing differential weathering Geo-inSight 9., p. 151
6 Mechanical Weathering - Disaggregation of Earth Materials Mechanical processes (Physical Weathering) Frost action Pressure release Thermal expansion and contraction Crystal growth Activities of organisms The products of mechanical (physical) weathering are chemically the same as their parent materials. Fig. 6.9d, p. 143
7 Mechanical Weathering - Disaggregation of Earth Materials Frost Action When water freezes in cracks in rocks it expands and contracts when it thaws, thus exerting pressure and opening the cracks wider. Repeated freezing and thawing disaggregates rocks into angular pieces that may tumble downslope and accumulate as talus. Fig. 6.2a, p. 137
8 Fig. 6.3 a, p. 138 Fig. 6.4, p. 138 Mechanical Weathering - Disaggregation of Earth Materials Pressure Release and Sheet Joints Sheet joints are fractures more or less parallel to exposed rock surfaces, especially rocks now at the surface that formed under great pressure at depth.
9 Fig. 6.3 a, p. 138 Fig. 6.4, p. 138 Mechanical Weathering - Disaggregation of Earth Materials Pressure Release and Sheet Joints These joints form in response to pressure release; that is, when the rocks formed deep with the Earth, they contained energy that is released by outward expansion at the surface.
10 Mechanical Weathering - Disaggregation of Earth Materials Thermal Expansion and Contraction Extreme heating and cooling in deserts, or forest fires, might crack rocks Dark minerals absorb heat better than surrounding light-colored minerals, so differential expansion and cracking can occur Lab experiments indicate that this process is probably minor
11 Mechanical Weathering - Disaggregation of Earth Materials Growth of Salt Crystals Growth and expansion of salt crystals in cracks in rocks can widen the cracks Most common in hot deserts and along rocky marine coasts where breaking waves create salt spray
12 Mechanical Weathering - Disaggregation of Earth Materials How do organisms contribute to mechanical and chemical weathering? Any organic activity, such as tree roots growing in cracks, contributes to mechanical weathering. Organic acids, and the tendrils of mosses and lichens, aid in the chemical alteration of parent material. Fig. 6.5b, p. 139
13 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Chemical weathering: Decomposes rocks and minerals by chemical alteration Unlike mechanical weathering, the chemistry and mineralogy changes during weathering Hot and wet environments accelerate chemical weathering Chemical weathering occurs in all environments, except, possibly, permanently frozen polar regions
14 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Chemical processes Solution Oxidation Hydrolysis Fig. 6.7, p. 141
15 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials The parent material is transformed into weathering products, including: ions in solution, water-soluble salts and insoluble solids, such as clay mineral Fig. 6.6, p. 140
16 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Important agents of chemical weathering Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Acids Organisms Fig. 6.6, p. 140
17 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Solution rocks dissolve Carbonate Rocks Calcite (CaCO ³ ) in limestone is nearly insoluble in neutral or alkaline solutions, but it rapidly dissolves in acidic solutions. The atoms making up the minerals dissociate, that is, they separate and the rock dissolves.
18 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Solution rocks dissolve Important acids in nature Carbonic acid forms from CO 2 interacting with water Organic acids from organisms Nitric acid from acid rain Sulfuric acid from acid rain and the weathering of sulfide minerals
19 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Oxidation rocks rust Rocks such as sandstone may contain iron minerals that will breakdown when exposed to oxygen. The atoms making up the minerals dissociate; that is, they separate as the rock rusts away. Geo-InSight 4, p. 150
20 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Hydrolysis breakdown to clays Potassium Feldspar During hydrolysis hydrogen ions react with and replace positive ions in potassium feldspar. The result is clay minerals and substances in solution such as potassium and silica.
21 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Hydrolysis breakdown of orthoclase (K-feldspar) to kaolinite clay 2KAlSi 3 O 8 + 2H + + 2HCO H 2 O orthoclase hydrogen bicarbonate ion water Al 2 Si 2 O 5 (OH) 4 + 2K + + 2HCO SiO 2 clay (kaolinite) potassium ion bicarbonate ion silica Equation, p. 141
22 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Factors That Control the Rate of Chemical Weathering Mechanical weathering enhances chemical weathering by breaking material into smaller pieces, thereby increasing the surface area for chemical reactions. Because chemical weathering is a surface process, the more surface exposed, the faster the weathering Fig. 6.8, p. 142
23 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Factors That Control the Rate of Chemical Weathering The stability of igneous minerals during chemical weathering is the inverse of Bowen's Reaction Series (Chapter 4). Quartz is most stable and less susceptible to chemical weathering, whereas olivine is the least stable. Table 6.1, p. 142
24 Chemical Weathering - Decomposition of Earth Materials Spheroidal Weathering Angular rocks tend to round during chemical weathering. Chemical weathering preferentially attacks the sharp corners of fractured rocks rather than the center. Fig. 6.9, p. 143
25 Soil and Its Origin Regolith Layers of weathering products on the Earth's surface, includes: Sediment - weathered materials brought in by erosion Soil - organic-bearing regolith that supports plant life Materials largely weather in place, but some soils may contain sediments brought in from other locations
26 Soil and Its Origin Soils Supports plant life Contains humus - organic debris from decayed organisms, resistant to weathering, important plant nutrient Contains clays, sands, and/or other mineral matter Residual or transported Has layers or soil horizons
27 Soil and Its Origin Soils Soils consist of weathered materials, air, water, humus and also the plants which they support. Fig. 6.10a, p. 146
28 Soil and Its Origin Soil Profiles Soil formation produces horizons. The most common horizons in descending order are O, A, B, and C. These horizons differ from one another in texture, structure, composition and color. Fig. 6.10b, p. 146
29 Soil and Its Origin Soil Profiles O horizon Thin layer of humus and partially decayed plants Fig. 6.10b, p. 146
30 Soil and Its Origin Soil Profiles A horizon Top soil, thick in fertile soils More organically rich than underlying horizons Most important layer for plant growth, including crops Fig. 6.10b, p. 146
31 Soil and Its Origin Soil Profiles B horizon Subsoil Zone of accumulation, especially of clays Fig. 6.10b, p. 146
32 Soil and Its Origin Soil Profiles C horizon Partially weathered inplace bedrock Other horizons, such as the E, are less common Fig. 6.10b, p. 146
33 O A E Loose leaves and organic debris Partly decomposed organic debris Topsoil; dark in color; rich in organic matter Zone of intense leaching or eluviation B Subsoil, zone of accumulation Transition to C C Partly weathered parent material Parent material Stepped Art Fig. 6-10b, p. 146
34 Soil and Its Origin Factors That Control Soil Formation Climate - the most important factor in soil formation because chemical processes operate faster where it is warm and wet Fig. 6.11, p. 146
35 Fig. 6.11, p. 146
36 Soil and Its Origin Factors That Control Soil Formation Types of soils: Humid Forest Forest soils develop in humid climates such as the eastern United States and much of Canada. Well-developed A horizon Iron- and aluminum-rich B horizon Fig. 6.12c,d, p. 147
37 Soil and Its Origin Factors That Control Soil Formation Types of soils: Hot desert Hot desert soils have thin O and A horizons because of the lack of plant growth B horizon often contains irregular masses of calcite, called caliche Desert soils are often alkaline Fig. 6.12a, p. 147
38 Soil and Its Origin Factors That Control Soil Formation Types of soils: Hot desert Fig. 6.13, p. 148
39 Soil and Its Origin Factors that Control Soil Formation Types of Soils: Laterites Red tropical soils Severe chemical weathering Fig. 6.14a, p. 149
40 Soil and Its Origin Factors that Control Soil Formation Types of Soils: Laterites Thin and infertile A horizons. Rapid decomposition prevents the formation of fertile A horizons Not a good soil for agriculture. Fig. 6.12c, p. 147
41 Soil and Its Origin Factors that Control Soil Formation Types of Soils: Laterites Thick B horizon rich in insoluble clays, aluminum oxides and iron oxides B horizon may be mined as an aluminum ore (bauxite) Fig. 6.12c, p. 147
42 Fig. 6.12, p. 147
43 Soil and Its Origin Other Factors That Control Soil Formation Parent material Organic activity Relief and slope Time Fig. 6.7, p. 141
44 Expansive Soils and Soil Degradation Expansive Soils Some soils contain clays that considerably expand when wet and contract when dry. With expansive soils, the change in volume is 6% or more. Expansive soils destroy the foundations of buildings, roadways, and other structures. Construction projects should avoid these soils. If alternative sites cannot be found, the soils may need to be removed, which can be expensive.
45 Expansive Soils and Soil Degradation Soil Degradation - Any process that leads to loss in soil fertility, including: erosion, contamination with pollutants, and the destruction of soils nutrients Fig. 6.17, p. 153
46 Expansive Soils and Soil Degradation Soil Degradation Soil erosion is caused mostly by sheet and rill erosion. Erosion is often accelerated by human activities, such as construction, agriculture, ranching, and deforestation. Fig. 6.16, p. 153
47 Expansive Soils and Soil Degradation Soil Degradation Depletion of soil nutrients by extensive farming Salinization: Accumulation of salts in soils from excessive irrigation Other pollutants: Improper disposal of wastes, excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers, and oil and chemical spills Compaction of soils by livestock and heavy equipment, which makes the soils too hard for plant growth
48 The Dust Bowl An American Tragedy Overgrazing, deforestation, and excessive plowing in the Midwest led to wind erosion, destroying valuable top soils during the drought of the 1930s. Fig. 6.15a,c, p. 152
49 Expansive Soils and Soil Degradation Protecting soils Crop rotation to maintain soil nutrients Contour plowing Terracing No-till planting Fig. 6.17, p. 153
50 Weathering and Resources Intense chemical weathering may concentrate valuable mineral resources Residual concentrations bauxite and other valuable ore deposits are concentrated by selective removal of soluble substances during chemical weathering
51 Weathering and Resources Residual concentrations Bauxite forms in laterite soils in the tropics. Bauxite is a valuable aluminum ore. Bauxite occurs in areas where chemical weathering is so intense that only aluminum oxides and other very insoluble compounds accumulate in soils.
52 Weathering and Resources Residual concentrations Gossans - hydrated iron oxides formed on the surface by oxidation of iron Sulfide minerals oxidize, leach and the metals concentrate as ore deposits of iron, copper, lead, and zinc beneath the gossan
53 End of Chapter 6
Chapter 6 9/25/2012. Weathering, Erosion and Soils. Introduction. How Are Earth Materials Altered? Introduction. How Are Earth Materials Altered?
 Chapter 6 Introduction Rocks and minerals are disintegrated and decomposed by the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering. Weathering, Erosion and Soils This breakdown occurs because the parent
Chapter 6 Introduction Rocks and minerals are disintegrated and decomposed by the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering. Weathering, Erosion and Soils This breakdown occurs because the parent
Weathering, Soil, and Mass Movements
 Tarbuck Lutgens Weathering, Soil, and Mass Movements 5.1 Weathering Mechanical Weathering Mechanical weathering occurs when physical forces break rock into smaller and smaller pieces without changing the
Tarbuck Lutgens Weathering, Soil, and Mass Movements 5.1 Weathering Mechanical Weathering Mechanical weathering occurs when physical forces break rock into smaller and smaller pieces without changing the
Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Weathering and Soil
 Chapter 6 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Weathering and Soil Tarbuck and Lutgens Weathering Weathering involves the physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock
Chapter 6 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Weathering and Soil Tarbuck and Lutgens Weathering Weathering involves the physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e and s Chapter 5 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer Cole Northeastern University Earth
Essentials of Geology, 11e and s Chapter 5 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Jennifer Cole Northeastern University Earth
Mechanical Weathering
 Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
WEATHERING. Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions 10/22/2012
 WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
Rocks and Weathering
 Rocks and Weathering The Effects of Weathering The process of mountain building thrusts rock up to Earth s surface. Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth s surface.
Rocks and Weathering The Effects of Weathering The process of mountain building thrusts rock up to Earth s surface. Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth s surface.
Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200
 Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200 Use these questions to test your knowledge of Lecture5. The exams will be similar in format, except that they will deal with more than one chapter, and will
Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200 Use these questions to test your knowledge of Lecture5. The exams will be similar in format, except that they will deal with more than one chapter, and will
Earth Science, 10e. Edward J. Tarbuck & Frederick K. Lutgens
 Earth Science, 10e Edward J. Tarbuck & Frederick K. Lutgens Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting Chapter 3 Earth Science, 10e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College Earth's external processes
Earth Science, 10e Edward J. Tarbuck & Frederick K. Lutgens Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting Chapter 3 Earth Science, 10e Stan Hatfield and Ken Pinzke Southwestern Illinois College Earth's external processes
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Mechanisms
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface.
 The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
The physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rocks and minerals at or near Earth s surface. The material that is chemically and mechanically weathered to yield sediment and soil. Regolith consisting
Limestone dissolved by naturally acidic rainwater. Weathering and Soils Lecture 5
 Last time Viscosity determines the ability of a melt to releases gasses coming out of solution Viscosity depends on silica content and TEMPERATURE Mafic (Basaltic) melts are extremely hot and have low
Last time Viscosity determines the ability of a melt to releases gasses coming out of solution Viscosity depends on silica content and TEMPERATURE Mafic (Basaltic) melts are extremely hot and have low
Chapter: Weathering and Erosion
 Chapter: Weathering and Erosion Section 1: Weathering and Soil Formation Minerals form rocks Rocks form soil Weathering Weathering is a mechanical or chemical surface process that breaks rocks into smaller
Chapter: Weathering and Erosion Section 1: Weathering and Soil Formation Minerals form rocks Rocks form soil Weathering Weathering is a mechanical or chemical surface process that breaks rocks into smaller
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Weathering and Soil Earth - Chapter 6 Earth s External Processes Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the transfer of rock and soil downslope under the influence
Weathering and Soil Earth - Chapter 6 Earth s External Processes Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the transfer of rock and soil downslope under the influence
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Weathering and Soil Earth - Chapter 6 Earth s External Processes Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the transfer of rock and soil downslope under the influence
Weathering and Soil Earth - Chapter 6 Earth s External Processes Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the transfer of rock and soil downslope under the influence
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils. Fig. 5.14
 Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils Fig. 5.14 OBJECTIVES Recognize that weathering breaks down minerals and rocks and occurs as a result of both mechanical and chemical processes. Explain the processes that
Chapter 5: Weathering and Soils Fig. 5.14 OBJECTIVES Recognize that weathering breaks down minerals and rocks and occurs as a result of both mechanical and chemical processes. Explain the processes that
Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth s surface
 Chapter 8 Notes Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth s surface Factors that contribute to weathering Heat Cold Water Ice O 2 & CO 2 in the atmosphere Examples of
Chapter 8 Notes Weathering is the process that breaks down rock and other substances at Earth s surface Factors that contribute to weathering Heat Cold Water Ice O 2 & CO 2 in the atmosphere Examples of
Weathering is the process by which rocks on or near Earth s surface break down and change. Spherical weathering near Paris, NC
 Weathering Weathering is the process by which rocks on or near Earth s surface break down and change. Spherical weathering near Paris, NC The two types of weathering are Chemical and. Mechanical Mechanical
Weathering Weathering is the process by which rocks on or near Earth s surface break down and change. Spherical weathering near Paris, NC The two types of weathering are Chemical and. Mechanical Mechanical
Physical Geology, 15/e
 Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Weathering and Soil Physical Geology 15/e, Chapter 5 Weathering, Erosion and Transportation Rocks exposed at Earth s surface are constantly
Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Weathering and Soil Physical Geology 15/e, Chapter 5 Weathering, Erosion and Transportation Rocks exposed at Earth s surface are constantly
How does Rock become Exposed to the Surface?
 Weathering How does Rock become Exposed to the Surface? Most rocks, like granite, form under earth s surface. The rocks uplift and eventually make their way to earth s surface. Conditions on the surface
Weathering How does Rock become Exposed to the Surface? Most rocks, like granite, form under earth s surface. The rocks uplift and eventually make their way to earth s surface. Conditions on the surface
Weathering. Weathering: is the process which breaks rocks into smaller bits. A. Physical or mechanical weathering
 Weathering Weathering: is the process which breaks rocks into smaller bits. Types of Weathering: A. Physical or mechanical weathering B. Chemical weathering C. Biological weathering 1 Mechanical or Physical
Weathering Weathering: is the process which breaks rocks into smaller bits. Types of Weathering: A. Physical or mechanical weathering B. Chemical weathering C. Biological weathering 1 Mechanical or Physical
Introduction to Weathering
 Name: Date: Period: Unit 9: Earth s Destructive Forces A. Kinds of Weathering Introduction to Weathering Distinguish between two major processes that change the Earth surface. Identify two types of weathering.
Name: Date: Period: Unit 9: Earth s Destructive Forces A. Kinds of Weathering Introduction to Weathering Distinguish between two major processes that change the Earth surface. Identify two types of weathering.
Weathering and Erosion
 Weathering and Erosion Weathering the disintegration and decomposition of material at the surface Erosion the transportation of weathered material by water, wind, or ice Weathering Two kinds of weathering
Weathering and Erosion Weathering the disintegration and decomposition of material at the surface Erosion the transportation of weathered material by water, wind, or ice Weathering Two kinds of weathering
Weathering. weathering involves breaking rocks without changing. As their roots grow and put pressure on rocks,
 Text Pages 148 155 STUDY GUIDE Use the words to fill in the blanks of the paragraphs. Weathering plants pieces moisture ice wedging acids carbonic acid freezing chemical oxidation temperatures minerals
Text Pages 148 155 STUDY GUIDE Use the words to fill in the blanks of the paragraphs. Weathering plants pieces moisture ice wedging acids carbonic acid freezing chemical oxidation temperatures minerals
1/31/2013. Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes. Weathering Mechanisms. Wind abrasion forming Ventifacts
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes Weathering Mechanisms Physical
Why study Weathering?
 Why study Weathering? Weathering process of disintegrating solid rock & producing loose debris To understand geol process (like hydrologic systems) and how landscapes evolve (topo maps, landforms) Weathering
Why study Weathering? Weathering process of disintegrating solid rock & producing loose debris To understand geol process (like hydrologic systems) and how landscapes evolve (topo maps, landforms) Weathering
Sedimentary Geology. Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1
 Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Section 7.1. Weathering. SES3a. Objectives
 SES3a. Objectives Distinguish between mechanical and chemical weathering. Describe the different factors that affect mechanical and chemical weathering. Identify variables that affect the rate of weathering.
SES3a. Objectives Distinguish between mechanical and chemical weathering. Describe the different factors that affect mechanical and chemical weathering. Identify variables that affect the rate of weathering.
Weathering and Soil Formation. Chapter 10
 Weathering and Soil Formation Chapter 10 Old and New Mountains The Appalachian Mountains appear very different from the Sierra Mountains. The Appalachians are smaller, rounded, gently sloping, and covered
Weathering and Soil Formation Chapter 10 Old and New Mountains The Appalachian Mountains appear very different from the Sierra Mountains. The Appalachians are smaller, rounded, gently sloping, and covered
Wearing Down Landforms
 Wearing Down Landforms Denudation Denudation has also been called gradation. It is the Natural loss of soil and rock debris, blown away by wind or washed away by running water, laying bare the rock below.
Wearing Down Landforms Denudation Denudation has also been called gradation. It is the Natural loss of soil and rock debris, blown away by wind or washed away by running water, laying bare the rock below.
Weathering & Soil. Chpt 6
 Weathering & Soil Chpt 6 Some important processes that break-down and transport solid material at the Earth s surface Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the
Weathering & Soil Chpt 6 Some important processes that break-down and transport solid material at the Earth s surface Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the
Engineering Geology ECIV 3302
 Engineering Geology ECIV 3302 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2019-2018 Chapter (5) Weathering & Soil Chapter 5: Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting External processes include : (1) Weathering (2) Mass wasting
Engineering Geology ECIV 3302 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2019-2018 Chapter (5) Weathering & Soil Chapter 5: Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting External processes include : (1) Weathering (2) Mass wasting
Wednesday, October 10 th
 Wednesday, October 10 th Page 13a (left side) / Place Lab on table Objective: We will describe the different types of weathering and erosion and identify evidence of each type. Warm-up: 1. What is weathering?
Wednesday, October 10 th Page 13a (left side) / Place Lab on table Objective: We will describe the different types of weathering and erosion and identify evidence of each type. Warm-up: 1. What is weathering?
D. Ask questions to identify types of weathering, agents of erosion and transportation, and environments of deposition.
 Weathering, Soil, Erosion, and Deposition S6E5: Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to show how Earth s surface is formed. C. Construct an explanation of how to classify rocks by their formation
Weathering, Soil, Erosion, and Deposition S6E5: Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to show how Earth s surface is formed. C. Construct an explanation of how to classify rocks by their formation
Weathering The effects of the physical and chemical environment on the decomposition of rocks
 Weathering The effects of the physical and chemical environment on the decomposition of rocks - Igneous rocks form at high temperatures and the constituent minerals reflect the conditions of formation.
Weathering The effects of the physical and chemical environment on the decomposition of rocks - Igneous rocks form at high temperatures and the constituent minerals reflect the conditions of formation.
Weathering, Erosion & Soils Quiz
 Weathering, Erosion & Soils Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below shows a cross-section of a rock layer. Erosion is the
Weathering, Erosion & Soils Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below shows a cross-section of a rock layer. Erosion is the
EARTH SCIENCE KESSEL
 EARTH SCIENCE KESSEL Bell Ringer Explain the concept of matter.? s to answer that might help you in your explanation: 1. What is it? 2. What is it made of? 3. Does it have a shape? 4. How would you know
EARTH SCIENCE KESSEL Bell Ringer Explain the concept of matter.? s to answer that might help you in your explanation: 1. What is it? 2. What is it made of? 3. Does it have a shape? 4. How would you know
Chapter 12 Weathering and Erosion
 Chapter 12 Weathering and Erosion Multiple Choice Select the definition that most nearly defines the given word. 1. Landform A. chemical combination of metallic elements with oxygen B. layer of weathered
Chapter 12 Weathering and Erosion Multiple Choice Select the definition that most nearly defines the given word. 1. Landform A. chemical combination of metallic elements with oxygen B. layer of weathered
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material
 Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
Weathering, Soil, & Mass Movements. Chapter 5
 Weathering, Soil, & Mass Movements Chapter 5 5.1 Weathering Weathering: the breaking down and changing of rocks at or near the Earth s surface. Basic part of the rock cycle. 2 main types: 1. Mechanical
Weathering, Soil, & Mass Movements Chapter 5 5.1 Weathering Weathering: the breaking down and changing of rocks at or near the Earth s surface. Basic part of the rock cycle. 2 main types: 1. Mechanical
Ecoregions Glossary. 7.8B: Changes To Texas Land Earth and Space
 Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Rock Weathering (West, Ch. 8)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 23 Rock Weathering (West, Ch. 8) Outline Introduction of weathering Mechanical weathering Chemical weathering Comparison of surface and subsurface conditions Subsurface
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 23 Rock Weathering (West, Ch. 8) Outline Introduction of weathering Mechanical weathering Chemical weathering Comparison of surface and subsurface conditions Subsurface
EARTH S CHANGING SURFACE
 EARTH S CHANGING SURFACE Weathering Together, weathering and erosion work continuously to wear down the material on Earth s surface. weathering process that breaks down rock and other substances of Earth
EARTH S CHANGING SURFACE Weathering Together, weathering and erosion work continuously to wear down the material on Earth s surface. weathering process that breaks down rock and other substances of Earth
What factors affect the angle of a slope?
 Climate Rock type and Structure What factors affect the angle of a slope? Aspect Fast mass movements Slides: Slides are movements along the SLIP PLANE, i.e. a line of weakness in the rock or soil structure.
Climate Rock type and Structure What factors affect the angle of a slope? Aspect Fast mass movements Slides: Slides are movements along the SLIP PLANE, i.e. a line of weakness in the rock or soil structure.
Surface Processes on the Earth. Rocks, Weathering, Erosion and Soil
 Surface Processes on the Earth Rocks, Weathering, Erosion and Soil ROCKS AND ROCK CYCLE Rock types Three main types of rock Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary Igneous Form when magma or lava cools and hardens
Surface Processes on the Earth Rocks, Weathering, Erosion and Soil ROCKS AND ROCK CYCLE Rock types Three main types of rock Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary Igneous Form when magma or lava cools and hardens
Bill Nye: Rocks and Soil
 Bell Ringer 1.What kind of rock is formed by applying heat and pressure to existing rock? 2.What would be required to turn a sedimentary rock into an igneous rock? 3.How are sedimentary rocks classified?
Bell Ringer 1.What kind of rock is formed by applying heat and pressure to existing rock? 2.What would be required to turn a sedimentary rock into an igneous rock? 3.How are sedimentary rocks classified?
Chapter 5: Weathering and soils! Monument Valley, Utah!
 Chapter 5: Weathering and soils! Monument Valley, Utah! weathering, erosion, and transportation! rocks on Earth s surface are constantly changed by "water, air, temperature changes and other factors! weathering
Chapter 5: Weathering and soils! Monument Valley, Utah! weathering, erosion, and transportation! rocks on Earth s surface are constantly changed by "water, air, temperature changes and other factors! weathering
The Production of Sediment. Contents. Weathering. Chapters 1, 3
 The Production of Sediment Chapters 1, 3 Contents Weathering Physical, chemical, biogeochemical processes Rates Products Carbon cycle and global change Erosion/Soils Sediment Texture Weathering General
The Production of Sediment Chapters 1, 3 Contents Weathering Physical, chemical, biogeochemical processes Rates Products Carbon cycle and global change Erosion/Soils Sediment Texture Weathering General
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
 Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
Section 1: Weathering and Soil Formation. We will study some of the processes that contribute to soil formation
 Section 1: Weathering and Soil Formation We will study some of the processes that contribute to soil formation ***Minerals form rocks. The decomposition of rocks and minerals will form soil. Minerals are
Section 1: Weathering and Soil Formation We will study some of the processes that contribute to soil formation ***Minerals form rocks. The decomposition of rocks and minerals will form soil. Minerals are
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Geology 101. Reading Guides for Chapters 6 and 12
 Geology 101 Name Chapter 6: Weathering and Soils (p. 160): Reading Guides for Chapters 6 and 12 This chapter is about the processes involved in the disintegration of rock. Weathering is often mistaken
Geology 101 Name Chapter 6: Weathering and Soils (p. 160): Reading Guides for Chapters 6 and 12 This chapter is about the processes involved in the disintegration of rock. Weathering is often mistaken
WEATHERING. Weathering breakdown of rock materials Erosion transport of broken-down materials
 WEATHERING the interacting physical, chemical & biological processes that progressively alter the original lithologic character of rocks to produce secondary minerals (e.g. clays) & unconsolidated regolith
WEATHERING the interacting physical, chemical & biological processes that progressively alter the original lithologic character of rocks to produce secondary minerals (e.g. clays) & unconsolidated regolith
- Take a notes packet from trapezoid table. - Start vocab on notes packet
 - Take a notes packet from trapezoid table. - Start vocab on notes packet Objectives: You will learn about weathering and its effects. You will learn to explain what mechanical weathering is and how it
- Take a notes packet from trapezoid table. - Start vocab on notes packet Objectives: You will learn about weathering and its effects. You will learn to explain what mechanical weathering is and how it
Earth systems the big idea guiding questions Chapter 1 & 2 Earth and Earth Systems review notes are in purple
 Earth systems the big idea guiding questions Chapter 1 & 2 Earth and Earth Systems review notes are in purple How can you describe Earth? What are the composition and the structure of the atmosphere? How
Earth systems the big idea guiding questions Chapter 1 & 2 Earth and Earth Systems review notes are in purple How can you describe Earth? What are the composition and the structure of the atmosphere? How
CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 2. Rock Cycle, and Origin of Soil (Das, Ch. 2)
 CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 2 Rock Cycle, and Origin of Soil (Das, Ch. 2) Outline of this Lecture 1.Rock types and rock cycle 2.Basic Mineralogy 3.Weathering of rocks 1. mechanical weathering
CE 240 Soil Mechanics & Foundations Lecture 2 Rock Cycle, and Origin of Soil (Das, Ch. 2) Outline of this Lecture 1.Rock types and rock cycle 2.Basic Mineralogy 3.Weathering of rocks 1. mechanical weathering
Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces. & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry
 Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry 3. charge transfer (e.g., ligand/donor sorption): Sorption involves a number of related processes that all
Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry 3. charge transfer (e.g., ligand/donor sorption): Sorption involves a number of related processes that all
Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p ) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 WEATHERING
 Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p. 95-125) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 THE BIG PICTURE: Weathering, erosion and deposition are processes that cause changes to rock material
Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p. 95-125) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 THE BIG PICTURE: Weathering, erosion and deposition are processes that cause changes to rock material
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 16: WEATHERING, EROSION, AND MASS WASTING Interface Between Climate and Tectonics Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors,
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 16: WEATHERING, EROSION, AND MASS WASTING Interface Between Climate and Tectonics Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors,
Mechanical and Chemical
 Mechanical and Chemical http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:toad_rock_-_geograph.org.uk_- _767454.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:kharazaarch.jpg The mechanical or chemical processes that break
Mechanical and Chemical http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:toad_rock_-_geograph.org.uk_- _767454.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:kharazaarch.jpg The mechanical or chemical processes that break
Weathering, Mass Wasting and Karst
 Weathering, Mass Wasting and Karst Capable of wearing down anything that the internal processes can build. Gravity, water, wind and ice Denudation - the overall effect of disintegration, wearing away and
Weathering, Mass Wasting and Karst Capable of wearing down anything that the internal processes can build. Gravity, water, wind and ice Denudation - the overall effect of disintegration, wearing away and
Biosphere. All living things, plants, animals, (even you!) are part of the zone of the earth called the biosphere.
 Unit 1 Study Guide Earth s Spheres Biosphere All living things, plants, animals, (even you!) are part of the zone of the earth called the biosphere. Hydrosphere Water covers ¾ of the earth, made up mostly
Unit 1 Study Guide Earth s Spheres Biosphere All living things, plants, animals, (even you!) are part of the zone of the earth called the biosphere. Hydrosphere Water covers ¾ of the earth, made up mostly
Identify three agents of mechanical weathering. Compare mechanical and chemical weathering processes.
 Objectives Identify three agents of mechanical weathering. Compare mechanical and chemical weathering processes. Describe four chemical reactions that decompose rock. #1 Weathering Processes weathering
Objectives Identify three agents of mechanical weathering. Compare mechanical and chemical weathering processes. Describe four chemical reactions that decompose rock. #1 Weathering Processes weathering
Surface Processes. Water Cycle. Evaporation Transpiration Condenstation Precipitation Infiltration Runoff
 s e s s roce S P e c urfa s e s s e c o r P e s c d r a a f C r Su iew Note v e R Water Cycle Evaporation Transpiration Condenstation Precipitation Infiltration Runoff Runoff The moving of water along
s e s s roce S P e c urfa s e s s e c o r P e s c d r a a f C r Su iew Note v e R Water Cycle Evaporation Transpiration Condenstation Precipitation Infiltration Runoff Runoff The moving of water along
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
CLASS EXERCISE 5.1 List processes occurring in soils that cause changes in the levels of ions.
 5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
Anticipation Guide #4 Ice wedging is a form of chemical weathering Erosion is the process where rocks are broken down The most active erosion agent
 Weathering Anticipation Guide #4 Ice wedging is a form of chemical weathering Erosion is the process where rocks are broken down The most active erosion agent on the planet is running water Gravity plays
Weathering Anticipation Guide #4 Ice wedging is a form of chemical weathering Erosion is the process where rocks are broken down The most active erosion agent on the planet is running water Gravity plays
UNIT SEVEN: Earth s Water. Chapter 21 Water and Solutions. Chapter 22 Water Systems. Chapter 23 How Water Shapes the Land
 UNIT SEVEN: Earth s Water Chapter 21 Water and Solutions Chapter 22 Water Systems Chapter 23 How Water Shapes the Land Chapter Twenty-Three: How Water Shapes the Land 23.1 Weathering and Erosion 23.2
UNIT SEVEN: Earth s Water Chapter 21 Water and Solutions Chapter 22 Water Systems Chapter 23 How Water Shapes the Land Chapter Twenty-Three: How Water Shapes the Land 23.1 Weathering and Erosion 23.2
Earth and Space Science. Semester 2 Review, Part 2
 Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Review, Part 2 2015 Chemical Weathering -The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. Examples that cause chemical weathering include the action of water
Unit 3 Rocks, Minerals, Soil Twitter Review Questions
 Unit 3 Rocks, Minerals, Soil Twitter Review Questions U3-1: Which type of rock is most representative of a slow cooling process of molten material? (Be specific) - Answer: Intrusive Igneous Rock U3-2:
Unit 3 Rocks, Minerals, Soil Twitter Review Questions U3-1: Which type of rock is most representative of a slow cooling process of molten material? (Be specific) - Answer: Intrusive Igneous Rock U3-2:
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Weathering and Erosion
 Weathering and Erosion OBJECTIVE: Explain how erosion and deposition shape Earth s surface by matching and using models How do erosion and deposition shape Earth s surface? Deposition Formation Transported
Weathering and Erosion OBJECTIVE: Explain how erosion and deposition shape Earth s surface by matching and using models How do erosion and deposition shape Earth s surface? Deposition Formation Transported
Overview. Rock weathering Functions of soil Soil forming factors Soil properties
 UN-FAO A. Healthy soils are the basis for healthy food production. B. A tablespoon of normal topsoil has more microorganisms than the entire human population on Earth. C. It can take up to 1,000 years
UN-FAO A. Healthy soils are the basis for healthy food production. B. A tablespoon of normal topsoil has more microorganisms than the entire human population on Earth. C. It can take up to 1,000 years
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science. Lesson 2: Understanding Soil Formation
 Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 2: Understanding Soil Formation Important Terms Alluvium Bedrock Chemical weathering Climate Glacial till Loess Native vegetation Organic matter Outwash
Unit E: Basic Principles of Soil Science Lesson 2: Understanding Soil Formation Important Terms Alluvium Bedrock Chemical weathering Climate Glacial till Loess Native vegetation Organic matter Outwash
The Lithosphere. Definition
 10/14/2014 www.komar.de The Lithosphere Ben Sullivan, Assistant Professor NRES 765, Biogeochemistry October 14th, 2014 Contact: bsullivan@cabnr.unr.edu Definition io9.com tedquarters.net Lithos = rocky;
10/14/2014 www.komar.de The Lithosphere Ben Sullivan, Assistant Professor NRES 765, Biogeochemistry October 14th, 2014 Contact: bsullivan@cabnr.unr.edu Definition io9.com tedquarters.net Lithos = rocky;
Glaciers. 1. The photograph below shows the results of a landslide.
 Name: Date: 1. The photograph below shows the results of a landslide. This landslide is an example of A) wind abrasion B) glacial deposition C) wave action D) mass movement 2. Which agent of erosion is
Name: Date: 1. The photograph below shows the results of a landslide. This landslide is an example of A) wind abrasion B) glacial deposition C) wave action D) mass movement 2. Which agent of erosion is
Weathering. Transportation. Uplift & exposure. Deposition. Igneous rocks. (extrusive) Sediments. Lithification (Compaction and Cementation)
 Weathering Transportation Uplift & exposure Deposition Lithification (Compaction and Cementation) Sedimantary rocks Sediments Pyroclastic material Consolidation Igneous rocks (extrusive) Metamorphic rocks
Weathering Transportation Uplift & exposure Deposition Lithification (Compaction and Cementation) Sedimantary rocks Sediments Pyroclastic material Consolidation Igneous rocks (extrusive) Metamorphic rocks
SOIL: DEFINITION, FORMATION! & LAYERS"
 SOIL: DEFINITION, FORMATION & LAYERS" What Is Soil? soil - upper-most (relatively thin) layer of Earth s crust, which supports terrestrial plants, animals, & microorganisms basic natural resource that
SOIL: DEFINITION, FORMATION & LAYERS" What Is Soil? soil - upper-most (relatively thin) layer of Earth s crust, which supports terrestrial plants, animals, & microorganisms basic natural resource that
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas WEATHERING & MASS WASTING Denudation Disintegration, wearing away, and removal of rock material Involves three activities: Weathering is the break down of rocks into smaller
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas WEATHERING & MASS WASTING Denudation Disintegration, wearing away, and removal of rock material Involves three activities: Weathering is the break down of rocks into smaller
WEATHERING AND MASS MOVEMENTS. 1. Introduction 2. Physical/mechanical weathering 3. Chemical weathering 4. Mass movement processes
 WEATHERING AND MASS MOVEMENTS 1. Introduction 2. Physical/mechanical weathering 3. Chemical weathering 4. Mass movement processes Mean annual temperature ( C) Hot Cold TEMP. -10 0 10 20 Strong chemical
WEATHERING AND MASS MOVEMENTS 1. Introduction 2. Physical/mechanical weathering 3. Chemical weathering 4. Mass movement processes Mean annual temperature ( C) Hot Cold TEMP. -10 0 10 20 Strong chemical
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development
 Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
Chapter 5 Weathering Soil And Mass Movement
 CHAPTER 5 WEATHERING SOIL AND MASS MOVEMENT PDF - Are you looking for chapter 5 weathering soil and mass movement Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 5 weathering soil and mass movement
CHAPTER 5 WEATHERING SOIL AND MASS MOVEMENT PDF - Are you looking for chapter 5 weathering soil and mass movement Books? Now, you will be happy that at this time chapter 5 weathering soil and mass movement
2 Rates of Weathering
 Name CHAPTER 10 Class Date Weathering and Soil Formation SECTION 2 Rates of Weathering National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Name CHAPTER 10 Class Date Weathering and Soil Formation SECTION 2 Rates of Weathering National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Weathering Cycle Teacher Notes
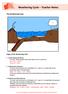 The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
Weathering of Rocks. Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks
 Weathering of Rocks Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks Mechanical weathering requires physical forces to break rocks into smaller pieces. Chemical
Weathering of Rocks Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks Mechanical weathering requires physical forces to break rocks into smaller pieces. Chemical
Explain how rock composition affects the rate of weathering. Discuss how surface area affects the rate at which rock weathers.
 Objectives Explain how rock composition affects the rate of weathering. Discuss how surface area affects the rate at which rock weathers. Describe the effects of climate and topography on the rate of weathering.
Objectives Explain how rock composition affects the rate of weathering. Discuss how surface area affects the rate at which rock weathers. Describe the effects of climate and topography on the rate of weathering.
Lithosphere. Solid shell of the Earth, consists of crust and upper mantle The lithosphere includes things like:
 Lithosphere Lithosphere Solid shell of the Earth, consists of crust and upper mantle The lithosphere includes things like: Rocks, minerals, soil Mountains Plains Volcanoes Essential to Life The lithosphere
Lithosphere Lithosphere Solid shell of the Earth, consists of crust and upper mantle The lithosphere includes things like: Rocks, minerals, soil Mountains Plains Volcanoes Essential to Life The lithosphere
Watch the next few slides. When the slides stop transitioning get with an elbow partner to discuss the events that caused the formation of the
 Watch the next few slides. When the slides stop transitioning get with an elbow partner to discuss the events that caused the formation of the beautiful features. Be as specific as possible. Discuss
Watch the next few slides. When the slides stop transitioning get with an elbow partner to discuss the events that caused the formation of the beautiful features. Be as specific as possible. Discuss
Monday, Oct Field trip A1 & A2 signups: make sure you are where you think you should be
 Monday, Oct. 4 1. Field trip A1 & A2 signups: make sure you are where you think you should be 2. 5 credit people, field trip introduction in lab today 1. If you are unable to attend THIS SATURDAY, let
Monday, Oct. 4 1. Field trip A1 & A2 signups: make sure you are where you think you should be 2. 5 credit people, field trip introduction in lab today 1. If you are unable to attend THIS SATURDAY, let
ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
 Advanced Placement ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Geologic Processes & Soil Student 2014 Geologic Processes and Soil Geologic Processes The age of Earth is best measured by the geologic time scale. The idea that
Advanced Placement ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Geologic Processes & Soil Student 2014 Geologic Processes and Soil Geologic Processes The age of Earth is best measured by the geologic time scale. The idea that
Chemical Weathering and Soils
 Chemical Weathering and Soils Fresh rocks and minerals that once occupied the outermost position reached their present condition of decay through a complex of interacting physical, chemical, and biological
Chemical Weathering and Soils Fresh rocks and minerals that once occupied the outermost position reached their present condition of decay through a complex of interacting physical, chemical, and biological
Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth?
 Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth? IT GETS HOTTER. 2. What happens to the density as you travel to the
Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth? IT GETS HOTTER. 2. What happens to the density as you travel to the
3/22/2014. Earth s subsystems or cycles. Outline for next couple weeks. Weathering (breakdown of rock) Erosion
 and Erosion Earth s subsystems or cycles Outline for next couple weeks 1. and Erosion 2. Surface water systems (rivers) 3. Groundwater systems 4. Groundwater in-class activity (grade) (breakdown of rock)
and Erosion Earth s subsystems or cycles Outline for next couple weeks 1. and Erosion 2. Surface water systems (rivers) 3. Groundwater systems 4. Groundwater in-class activity (grade) (breakdown of rock)
Soil. Soil in Our Environment
 Soil Soil in Our Environment What is soil? Or is it Dirt? Gold s father is dirt, yet it regards itself as noble. Yiddish Proverb Is it alive? Is it fragile? Formations of Soils How much time does it take
Soil Soil in Our Environment What is soil? Or is it Dirt? Gold s father is dirt, yet it regards itself as noble. Yiddish Proverb Is it alive? Is it fragile? Formations of Soils How much time does it take
Lecture # 7. Weathering and Erosion
 1 Lecture # 7 Weathering and Erosion Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 Weathering is the process that produces changes
1 Lecture # 7 Weathering and Erosion Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 Weathering is the process that produces changes
Weathering/ Erosion/ Deposition in the Texas Ecoregions
 Practice Test Study these answers Weathering/ Erosion/ Deposition in the Texas Ecoregions 1. In the Texas Panhandle, physical weathering by abrasion is usually caused by wind, water and gravity 2. Two
Practice Test Study these answers Weathering/ Erosion/ Deposition in the Texas Ecoregions 1. In the Texas Panhandle, physical weathering by abrasion is usually caused by wind, water and gravity 2. Two
THE SCIENCE OF MAPS. ATL Skill: Critical thinking - Use models and simulations to explore complex systems and issues
 THE SCIENCE OF MAPS 8.9C interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering ATL Skill: Critical thinking
THE SCIENCE OF MAPS 8.9C interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering ATL Skill: Critical thinking
Soil Formation. Lesson Plan: NRES B2-4
 Soil Formation Lesson Plan: NRES B2-4 1 Anticipated Problems 1. What are five different factors that affect soil formation? 2. What are some different types of parent material that affect soils? 3. What
Soil Formation Lesson Plan: NRES B2-4 1 Anticipated Problems 1. What are five different factors that affect soil formation? 2. What are some different types of parent material that affect soils? 3. What
