Law of Superposition Law of Superposition
|
|
|
- Felix Warren Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 History of Earth
2 Relative Dating In the same way that a history book shows an order of events, layers of rock (called strata) show the sequence of events that took place in the past. Using a few basic principles, scientists can determine the order in which rock layers formed. Once they can know the order, a relative age can be determined for each rock layer. *Relative age indicates that one layer is older or younger than another layer, but does not indicate the rock s age in years (absolute age).
3 Sedimentary rocks form when new sediments are deposited on top of old layers of sediment. As the sediments accumulate, they are compressed and harden into sedimentary rock layers. Scientists use a basic principle called the Law of Superposition to determine the relative age of a layer of sedimentary rock. *The Law of Superposition is that an undeformed sedimentary rock layer is older than the layers above it and younger than the layers below it. According to the Law of Superposition, layer 1 was the first layer deposited, and thus the oldest layer. The last layer deposited was layer 12, and thus it is the youngest layer. Law of Superposition
4 *Principle of Original Horizontality Scientists also know that sedimentary rock generally forms in horizontal layers. The Principle of Original Horizontality is that sedimentary rocks left undisturbed will remain in horizontal layers. Therefore, scientists can assume that sedimentary rock layers that are not horizontal have been tilted or deformed by crustal movements that happened after the layers formed.
5 Unconformities Movements of Earth s crust can lift up rock layers that were buried and expose them to erosion. Then, if sediments are deposited, new rock layers form in place of the eroded layers. The missing rock layers create a break in the geologic record in the same way that pages missing from a book create a break in a story. *A break in the geologic record is called an unconformity. An unconformity shows that deposition stopped for a period of time, and rock may have been removed by erosion before deposition resumed.
6 *Unconformities There are three types of unconformities. 1. An unconformity in which stratified (layers) of rock rests upon unstratified rock is called a nonconformity. 2. The boundary between a set of tilted layers and a set of horizontal layers is called an angular unconformity. 3. The boundary between horizontal layers of old sedimentary rock and younger, overlying layers that are deposited on an eroded surface is called a disconformity. According to the Law of Superposition, all rocks beneath an unconformity are older than the rocks above the unconformity.
7 Crosscutting Relationships When rock layers have been disturbed by faults (a break or crack in Earth s crust) or intrusions (a mass of igneous rock that forms when magma is injected into rock and then cools and solidifies), determining relative age may be difficult. In such cases, scientists may apply the Law of Crosscutting Relationships. *The Law of Crosscutting Relationships is that a fault or intrusion is always younger than all the rocks it cuts through above and below the unconformity.
8 Relative Age Based on what you now know about the Law of Superposition, the Principle of Original Horizontality, unconformities, and the Law of Crosscutting Relationships can you place the layers indicated in the diagram in the correct order, starting from the oldest layer? The oldest layer is Q, followed by O, then N, then M, then L. P cuts across layers L-Q, so it is the next layer since it does not cut into layer H. Above the unconformity we then have layer H, followed by I, then J, with K being the youngest layer.
9 *Index Fossils Paleontologists can use fossils to determine the relative ages of the rock layers in which the fossils are located. Fossils that occur only in rock layers of a particular geologic age are called index fossils. To be an index fossil, a fossil must meet certain requirements: 1. It must be present in rocks scattered over a large region. 2. It must have features that clearly distinguish it from other fossils. 3. Organisms from which the fossil formed must have lived during a short span of geologic time. 4. The fossil must occur in fairly large numbers within the rock layers.
Directed Reading page
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading page 185-190 Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading page 185-190 Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the
State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks.
 Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
Objectives State the principle of uniformitarianism. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting
Directed Reading A. Section: Relative Dating: Which Came First?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Relative Dating: Which Came First? Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Determining the age of objects or events in relation to
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Relative Dating: Which Came First? Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Determining the age of objects or events in relation to
Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with
 Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with complete sentences. How old is the Earth? The Earth is
Notepack 18 AiM: How can we tell the age of rock layers? Do now: Which Jenga piece was placed first to build this tower? Support your answer with complete sentences. How old is the Earth? The Earth is
UNCONFORMITY. Commonly four types of unconformities are distinguished by geologists: a) Disconformity (Parallel Unconformity)
 UNCONFORMITY Unconformities are gaps in the geologic record that may indicate episodes of crustal deformation, erosion, and sea level variations. They are a feature of stratified rocks, and are therefore
UNCONFORMITY Unconformities are gaps in the geologic record that may indicate episodes of crustal deformation, erosion, and sea level variations. They are a feature of stratified rocks, and are therefore
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz
 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz TEST NO A Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUIZ! Relative Dating and Stratigraphic Principles Quiz TEST NO A Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Relative Dating. The Rock Cycle. Key Concept Scientists can interpret the sequence of events in Earth s history by studying rock layers.
 2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
2 What You Will Learn The rock cycle includes the formation and recycling of rock. Relative dating establishes the order in which rocks formed or events took place. The principle of superposition states
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
CHAPTER 8 DETERMINING EARTH S AGE RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE ROCK AGES. Loulousis
 CHAPTER 8 DETERMINING EARTH S AGE RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE ROCK AGES Loulousis Bellringer What are 5 visual clues that help you determine if someone is older or younger than you? Color of hair Wrinkles in
CHAPTER 8 DETERMINING EARTH S AGE RELATIVE AND ABSOLUTE ROCK AGES Loulousis Bellringer What are 5 visual clues that help you determine if someone is older or younger than you? Color of hair Wrinkles in
Clues to Earth s Past
 chapter 13 3 Clues to Earth s Past section 2 Relative Ages of Rocks Before You Read Think of two friends. You want to know who is older. What information do you need to figure out who s older? What You
chapter 13 3 Clues to Earth s Past section 2 Relative Ages of Rocks Before You Read Think of two friends. You want to know who is older. What information do you need to figure out who s older? What You
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Unit
 Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Unit Text: Chapters 8 Lab: Exercise 6 Name Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Page 1 Geology 12: Geologic Time 8.1: The Geologic Time Scale Today, we know that Earth is approximately
Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Unit Text: Chapters 8 Lab: Exercise 6 Name Earth Science 11: Geologic Time Page 1 Geology 12: Geologic Time 8.1: The Geologic Time Scale Today, we know that Earth is approximately
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references.
 Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Name: Date: Class: This is a printable assignment.
 Name: Date: Class: Tell the Story of Rock Sequences Earth Science Exercise Parts 1 and 2: Look at the illustrations below which show several horizontally layered sedimentary rock layers, unconsolidated
Name: Date: Class: Tell the Story of Rock Sequences Earth Science Exercise Parts 1 and 2: Look at the illustrations below which show several horizontally layered sedimentary rock layers, unconsolidated
FOSSILS. Book G Chapter 4 Section 1
 FOSSILS Book G Chapter 4 Section 1 OVERVIEW Explain what fossils are and how most fossils form. Describe what fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time. Identify and describe different types
FOSSILS Book G Chapter 4 Section 1 OVERVIEW Explain what fossils are and how most fossils form. Describe what fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time. Identify and describe different types
Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores
 Earths History Reu2.notebook November 14, 2013 Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores One goal of geology is to develop a timeline of Earth's past, including both geological and biological events.
Earths History Reu2.notebook November 14, 2013 Determining Earth's History Rocks and Ice Cores One goal of geology is to develop a timeline of Earth's past, including both geological and biological events.
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references.
 Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Before the 1700 s, scientists thought that the Earth was only 6,000 years old. This mindset was based on biblical references. However, as scientists began to better understand the processes that shape
Determining geological ages
 Determining geological ages Relative ages placing rocks and geologic events in their proper sequence, oldest to youngest. Absolute dates define the actual numerical age of a particular geologic event.
Determining geological ages Relative ages placing rocks and geologic events in their proper sequence, oldest to youngest. Absolute dates define the actual numerical age of a particular geologic event.
Chapter 09 Geologic Time
 Physical Geology 1330 116-S&R 1 Chapter 09 Geologic Time Lectures 12 & 13 Dr. Mike Murphy mmurphy@mail.uh.edu 333-S&R-1 www.uh.edu/~mamurph2/homepage.html Two Ways to Date Geologic Events 1. Relative Dating
Physical Geology 1330 116-S&R 1 Chapter 09 Geologic Time Lectures 12 & 13 Dr. Mike Murphy mmurphy@mail.uh.edu 333-S&R-1 www.uh.edu/~mamurph2/homepage.html Two Ways to Date Geologic Events 1. Relative Dating
9. RELATIVE AND RADIOMETRIC AGES
 LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. RELATIVE AND RADIOMETRIC AGES Your work will be graded on the basis of its accuracy, completion, clarity, neatness, legibility, and correct spelling of
LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. RELATIVE AND RADIOMETRIC AGES Your work will be graded on the basis of its accuracy, completion, clarity, neatness, legibility, and correct spelling of
Directed Reading. Section: Determining Relative Age. conclusions? UNIFORMITARIANISM. geology? of Earth? Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the 18th-century
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the 18th-century
Principles of Geology
 Principles of Geology Essential Questions What is Uniformitarianism? What is Catastrophism? What is Steno s s Law? What are the other geologic principles? How is relative age determined using these principles?
Principles of Geology Essential Questions What is Uniformitarianism? What is Catastrophism? What is Steno s s Law? What are the other geologic principles? How is relative age determined using these principles?
Learning Target: I can create a foldable about the geologic principles that are used to relatively date rock sequences.
 Geologic Principles Learning Target: I can create a foldable about the geologic principles that are used to relatively date rock sequences. 1 Geologic Principles Foldable You will need 3 pieces of paper
Geologic Principles Learning Target: I can create a foldable about the geologic principles that are used to relatively date rock sequences. 1 Geologic Principles Foldable You will need 3 pieces of paper
9. DATING OF ROCKS, FOSSILS, AND GEOLOGIC EVENTS
 LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. DATING OF ROCKS, FOSSILS, AND GEOLOGIC EVENTS Refer to Laboratory 8 in your Lab Manual on pages 207-226 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your
LAST NAME (IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions: 9. DATING OF ROCKS, FOSSILS, AND GEOLOGIC EVENTS Refer to Laboratory 8 in your Lab Manual on pages 207-226 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 12 Geologic Time 12.1 Discovering Earth s History Rocks Record Earth History Rocks record geological events and changing life forms of the past. We have
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 12 Geologic Time 12.1 Discovering Earth s History Rocks Record Earth History Rocks record geological events and changing life forms of the past. We have
Name Geo 4 Practice Match the principle on the left (column A) with the definition (or part of the definition) on the right (column B).
 Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
Name Geo 4 Practice 1 Target 1 2 3 4 Geo 4 I can define the create, alter and/or destroy the rock record. I can interpret a diagram to determine the sequence of events (relative age) in Earth s history
3. Bedrock from which entire geologic time period is missing between rock units 5 and 6? The fault most likely occurred after
 Homework # 4 Relative Dating Name: Section: Date: 1. The cross section below represents a portion of Earth s crust. Letters through D are locations within the rock units. 5. The sequence of rock types
Homework # 4 Relative Dating Name: Section: Date: 1. The cross section below represents a portion of Earth s crust. Letters through D are locations within the rock units. 5. The sequence of rock types
Unconformities, Geologic Time Scale, and Uniformitarianism. Ms. P Science 2016
 Unconformities, Geologic Time Scale, and Uniformitarianism Ms. P Science 2016 Do Now due tomorrow! 1. Compare and contrast relative dating to absolute dating. 2. The Law of Superposition states that younger
Unconformities, Geologic Time Scale, and Uniformitarianism Ms. P Science 2016 Do Now due tomorrow! 1. Compare and contrast relative dating to absolute dating. 2. The Law of Superposition states that younger
8. GEOLOGIC TIME LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating
 General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
Geologic Time. Kentucky Geological Survey Modified McCann
 Geologic Time Kentucky Geological Survey Modified McCann Procedure Plate tectonics Classroom activity #1 What is geologic time? Relative age dating Absolute age dating Classroom activity #2 T C What is
Geologic Time Kentucky Geological Survey Modified McCann Procedure Plate tectonics Classroom activity #1 What is geologic time? Relative age dating Absolute age dating Classroom activity #2 T C What is
GEOLOGIC EVENTS SEDIMENTARY ROCKS FAULTING FOLDING TILTING
 RELATIVE TIME (DATING) ABSOLUTE TIME (DATING) GEOLOGIC TIME List the order in which events occurred, without regard to the amount of time separating them. Refers to the age of a rock in relation to other
RELATIVE TIME (DATING) ABSOLUTE TIME (DATING) GEOLOGIC TIME List the order in which events occurred, without regard to the amount of time separating them. Refers to the age of a rock in relation to other
Today you will be able to: Utilize the SEVEN rules of rock age identification to describe the geologic age of this rock sequence!
 Mr. Sandomenico Welcome!!!! Today we will begin a new unit! The Earth s History!!!!! Today you will be able to: Utilize the SEVEN rules of rock age identification to describe the geologic age of this rock
Mr. Sandomenico Welcome!!!! Today we will begin a new unit! The Earth s History!!!!! Today you will be able to: Utilize the SEVEN rules of rock age identification to describe the geologic age of this rock
Earth Science - Lab #11 Geologic Time
 Earth Science - Lab #11 Geologic Time Page # Below are standard geologic symbols for the 3 main categories of rocks. Although these symbols are not universal, they are generally accepted by most geologists
Earth Science - Lab #11 Geologic Time Page # Below are standard geologic symbols for the 3 main categories of rocks. Although these symbols are not universal, they are generally accepted by most geologists
11/5/2015. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. The Geologic Time Scale
 GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
ENVI.2030L Geologic Time
 Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years
 Geologic Time Geologic Time geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years Geologic Time very difficult to appreciate from our human perspective necessary to understand history of Earth two basic ways
Geologic Time Geologic Time geologic age of Earth - about 4.6 billion years Geologic Time very difficult to appreciate from our human perspective necessary to understand history of Earth two basic ways
Principle of Uniformitarianism: Laws of nature don t change with time
 G e o l o g i c T i m e Principle of Uniformitarianism: Laws of nature don t change with time Radical idea proposed by Hutton in 1780 s Proposed that past events could be explained by modern processes
G e o l o g i c T i m e Principle of Uniformitarianism: Laws of nature don t change with time Radical idea proposed by Hutton in 1780 s Proposed that past events could be explained by modern processes
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8 Clocks in Rocks Timing the Geologic Record 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Stratigraphy and fossils Figure 8.4 (page 172)
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 8 Clocks in Rocks Timing the Geologic Record 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Stratigraphy and fossils Figure 8.4 (page 172)
Deep Time: How Old Is Old?
 Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Deep Time: How Old Is Old? Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior Geologist
Geohistory Review. Things you need to know:
 Geohistory Review Things you need to know: a) The earth and the solar system are 4.5 billion years old (4.5 X 10 9 ) b) Law of original horizontality: Sedimentary rock layers are always deposited as horizontal
Geohistory Review Things you need to know: a) The earth and the solar system are 4.5 billion years old (4.5 X 10 9 ) b) Law of original horizontality: Sedimentary rock layers are always deposited as horizontal
2. How do igneous rocks form? 3. How do sedimentary rocks form? 4. How do metamorphic rocks form?
 Name: Class: Earth s History Test Review Packet Test: Monday, February 13, 2017 The Rock Cycle 1. Explain why it is called the rock CYCLE. Does it truly have a starting point or end point? 2. How do igneous
Name: Class: Earth s History Test Review Packet Test: Monday, February 13, 2017 The Rock Cycle 1. Explain why it is called the rock CYCLE. Does it truly have a starting point or end point? 2. How do igneous
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
Stratigraphy. Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their
 Stratigraphy Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their composition origin age relationships geographic extent Stratified Sedimentary
Stratigraphy Stratigraphy deals with the study of any layered (stratified) rock, but primarily with sedimentary rocks and their composition origin age relationships geographic extent Stratified Sedimentary
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Your quiz will have some multiple-choice questions, matching, fill-in-the-blank questions, and short answer. To review, study DQs, notes from class,
 Review for Strata & Fossil Quiz Name: Quiz Date: Your quiz will have some multiple-choice questions, matching, fill-in-the-blank questions, and short answer. To review, study DQs, notes from class, labs,
Review for Strata & Fossil Quiz Name: Quiz Date: Your quiz will have some multiple-choice questions, matching, fill-in-the-blank questions, and short answer. To review, study DQs, notes from class, labs,
Vocabulary and Section Summary B
 The Study of Earth s History After you finish reading the section, try this puzzle! Use the clues given to fill in the blanks below. Then, copy the numbered letters into the corresponding boxes below to
The Study of Earth s History After you finish reading the section, try this puzzle! Use the clues given to fill in the blanks below. Then, copy the numbered letters into the corresponding boxes below to
Geologic Time. Earth s History
 Geologic Time Chapter 12 Earth s History Earth s history is recorded in rocks Rocks record geological events and changing life forms of the past. We have learned that Earth is much older than anyone had
Geologic Time Chapter 12 Earth s History Earth s history is recorded in rocks Rocks record geological events and changing life forms of the past. We have learned that Earth is much older than anyone had
6. Relative and Absolute Dating
 6. Relative and Absolute Dating Adapted by Sean W. Lacey & Joyce M. McBeth (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R, & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
6. Relative and Absolute Dating Adapted by Sean W. Lacey & Joyce M. McBeth (2018) University of Saskatchewan from Deline B, Harris R, & Tefend K. (2015) "Laboratory Manual for Introductory Geology". First
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Let s Rock! What is rock? Rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals that may also include organic matter. Most rock is made of minerals, but some rock is made of nonmineral material
Let s Rock! What is rock? Rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals that may also include organic matter. Most rock is made of minerals, but some rock is made of nonmineral material
3 Absolute Dating: A Measure of Time
 CHAPTER 3 3 Absolute Dating: A Measure of Time SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can geologists learn the
CHAPTER 3 3 Absolute Dating: A Measure of Time SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can geologists learn the
Earth History 870:035
 Earth History 870:035 Course goal: To describe the history of Earth and its inhabitants Most of Earth s history predates humanity, so it has not been observed Therefore, we will emphasize how scientists
Earth History 870:035 Course goal: To describe the history of Earth and its inhabitants Most of Earth s history predates humanity, so it has not been observed Therefore, we will emphasize how scientists
Station Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus
 Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically
 Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
Today: 1) Quiz- Vocabulary Chapter 8 2) Lecture on Telling Time Geologically Next Class: 1) Go over Exam 2 2) Continue: Telling Time Geologically 3) In Class Exercise: Radiometric dating Introduction to
GEOLOGY 1--Physical Geology Lecture #2, 2/9/2006
 Topics: GEOLOGY 1--Physical Geology Lecture #2, 2/9/2006 Lithospheric plates and their motions Types of plate boundaries or margins The present is the key to the past Relative Time Numerical Age Age of
Topics: GEOLOGY 1--Physical Geology Lecture #2, 2/9/2006 Lithospheric plates and their motions Types of plate boundaries or margins The present is the key to the past Relative Time Numerical Age Age of
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale
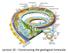 Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Page 1. Name:
 Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
Name: Questions 1 through 3 refer to the following: The diagrams below represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock
Rock cycle diagram. Relative dating. Placing rocks and events in proper sequence of formation Deciphering Earth s history from clues in the rocks
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Clues to Earth s Past. Fossils and Geologic Time
 Clues to Earth s Past Fossils and Geologic Time Fossils A. Paleontologists study fossils and reconstruct the appearance of animals. Fossils B. Fossils remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms
Clues to Earth s Past Fossils and Geologic Time Fossils A. Paleontologists study fossils and reconstruct the appearance of animals. Fossils B. Fossils remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms
Geologic History Unit Notes. Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent
 Geologic History Unit Notes Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent Absolute age - specific age like 4,600 million years old Fundamental Principles of Relative Dating 1. Uniformitarianism
Geologic History Unit Notes Relative age - general age statement like older, younger more recent Absolute age - specific age like 4,600 million years old Fundamental Principles of Relative Dating 1. Uniformitarianism
GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES
 DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
Geologic Time: Hutton s Outcrop at Siccar Point
 Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? Hutton s Outcrop at Siccar Point Hutton looked at this outcrop and reasoned that the Earth was
Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? Hutton s Outcrop at Siccar Point Hutton looked at this outcrop and reasoned that the Earth was
Fossils: evidence of past life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
GEOLOGIC TIME. Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS
 GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
HISTORICAL NOTES. Catastrophism. James Usher, mid-1600s, concluded Earth was only a few thousand years old
 1 GEOLOGIC TIME HISTORICAL NOTES Catastrophism James Usher, mid-1600s, concluded Earth was only a few thousand years old Uniformitarianism Charles Lyell published Principles of Geology 1830. 3 HOW DO WE
1 GEOLOGIC TIME HISTORICAL NOTES Catastrophism James Usher, mid-1600s, concluded Earth was only a few thousand years old Uniformitarianism Charles Lyell published Principles of Geology 1830. 3 HOW DO WE
Geologic Time: Hutton s Outcrop at Siccar Point. How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know?
 Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D.
Geologic Time: How do we determine age (relative & absolute) What is the age of the earth? How do we know? What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D.
Geologic Time Test Study Guide
 Geologic Time Test Study Guide Chapter 12 Section 1 The Earth s Story and Those Who First Listened 1. What is the difference between uniformitarianism and catastrophism? Uniformitarianism: the same geologic
Geologic Time Test Study Guide Chapter 12 Section 1 The Earth s Story and Those Who First Listened 1. What is the difference between uniformitarianism and catastrophism? Uniformitarianism: the same geologic
Interpreting Rock Layers
 Science Concept: Sedimentary rocks can be aged using the law of superposition. Unconformities can create exceptions to this law. Objectives: The student will: explain how rocks are dated by relative position
Science Concept: Sedimentary rocks can be aged using the law of superposition. Unconformities can create exceptions to this law. Objectives: The student will: explain how rocks are dated by relative position
GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS
 NAME GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence.
NAME GEOLOGIC TIME AND GEOLOGIC MAPS I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence.
2) What type of motion of the plates created the mountain range in the picture below?
 Name Geo 4&5 Practice 5 Target 1 2 (all of 1 plus) 3 (all of 2 plus) 4 (all of 3 plus) LE 5.7 Preparedness Does not complete formative or summative in an effortful and timely manner, is not engaged, does
Name Geo 4&5 Practice 5 Target 1 2 (all of 1 plus) 3 (all of 2 plus) 4 (all of 3 plus) LE 5.7 Preparedness Does not complete formative or summative in an effortful and timely manner, is not engaged, does
The Earth s Structure
 Planet Earth The Earth s Structure Crust the outermost and thinnest layer of Earth Mantle the layer of rock between the Earth s crust and its core - rocks are plastic soft and easily deformed The Earth
Planet Earth The Earth s Structure Crust the outermost and thinnest layer of Earth Mantle the layer of rock between the Earth s crust and its core - rocks are plastic soft and easily deformed The Earth
Remains or traces of prehistoric life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Writing Earth s History
 Earths History Writing Earth s History How is Earths History like writing in your Journal? Everyday, something happens and, with a pen, it is written down in the pages of your journal. As you continue,
Earths History Writing Earth s History How is Earths History like writing in your Journal? Everyday, something happens and, with a pen, it is written down in the pages of your journal. As you continue,
Geology Test Review Answers
 Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
Name: Geology Test Review Answers Core: Fill in the blanks: 1. Sediments get compacted and cemented into sedimentary rock. 2. Igneous rocks can be intrusive or extrusive from a volcano. 3. Adding heat
GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES
 DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
DATE DUE: INSTRUCTOR: TERRY J. BOROUGHS Geology 305 NAME: SECTION: GEOLOGICAL TIME / DATING TECHNIQUES Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Provide specific and
Geologic Time. Geologic Events
 Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
Geologic Time Much of geology is focused on understanding Earth's history. The physical characteristics of rocks and minerals offer clues to the processes and conditions on and within Earth in the past.
Earth Science Unit 1 Review
 Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows a model of the rock cycle. 2. rock cycle diagram is shown below. During which part of the rock cycle does water break rocks apart?. part 1 B. part 2. part 3 D. part
Name: Date: 1. The picture below shows a model of the rock cycle. 2. rock cycle diagram is shown below. During which part of the rock cycle does water break rocks apart?. part 1 B. part 2. part 3 D. part
Objectives. Vocabulary. Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch.
 The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle What are minerals? A mineral is a naturally occurring, usually inorganic solid that has a defininite crystalline structure and chemical composition. Naturally occuring =
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Rock Cycle What are minerals? A mineral is a naturally occurring, usually inorganic solid that has a defininite crystalline structure and chemical composition. Naturally occuring =
The Geology of Pacific Northwest Rocks & Minerals Activity 1: Geologic Time
 Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
Name: Age: I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt is made to determine
B) color B) Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to sedimentary rock. D) igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
 1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
2. Can you name earth s three eras and explain why they are divided that way?
 Unit: 3 Earth s History LT 3.1 Earth s History: I can map out a basic history of the earth, including key events. 1. Can you place the key events of earth s history in order? #1 Yes I can: 2. Can you name
Unit: 3 Earth s History LT 3.1 Earth s History: I can map out a basic history of the earth, including key events. 1. Can you place the key events of earth s history in order? #1 Yes I can: 2. Can you name
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP
 L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
L.O: HOW GEOLOGISTS SEQUENCE EVENTS IN EARTH'S GEOLOGIC HISTORY IF NOT OVERTURNED, OLDEST ON BOTTOM, YOUNGEST ON TOP 1. Unless a series of sedimentary rock layers has been overturned, the bottom rock layer
TOPIC 1: RELATIVE DATING ESSENTIAL QUESTION: HOW DO WE DETERMINE A ROCK S AGE BY THE SURROUNDING ROCKS?
 TOPIC 1: RELATIVE DATING ESSENTIAL QUESTION: HOW DO WE DETERMINE A ROCK S AGE BY THE SURROUNDING ROCKS? TOPIC 1: RELATIVE DATING UNIFORMITARIANISM: THE IDEA THAT THE SAME FORCES HAVE BEEN AND CONTINUE
TOPIC 1: RELATIVE DATING ESSENTIAL QUESTION: HOW DO WE DETERMINE A ROCK S AGE BY THE SURROUNDING ROCKS? TOPIC 1: RELATIVE DATING UNIFORMITARIANISM: THE IDEA THAT THE SAME FORCES HAVE BEEN AND CONTINUE
Rock cycle diagram. Principle of Original Horizontality. Sediment is deposited horizontally
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Dating the age of the Earth
 Dating the age of the Earth What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D. 10000 years Discuss this with your neighbor: How do we know the age of the Earth?
Dating the age of the Earth What is the age of the Earth? A. 4.44 million years B. 1 million years C. 4.55 billion years D. 10000 years Discuss this with your neighbor: How do we know the age of the Earth?
You must take the exam in the lecture section for which you are registered. Any exceptions must be cleared with the instructor in advance.
 Geo 101, Fall 2000 Review Questions for Final Exam GEOLOGIC TIME AND FOLDING AND FAULTING THE FINAL EXAM FOR MWF CLASS WILL BE TUESDAY 1400 THE FINAL EXAM FOR TR CLASS WILL BE FRIDAY 930 These questions
Geo 101, Fall 2000 Review Questions for Final Exam GEOLOGIC TIME AND FOLDING AND FAULTING THE FINAL EXAM FOR MWF CLASS WILL BE TUESDAY 1400 THE FINAL EXAM FOR TR CLASS WILL BE FRIDAY 930 These questions
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities
 Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities The Geologic Cycle 3 key events: deposition, uplift, erosion Sedimentation of beds A-D beneath the sea Uplift above sea level and exposure of D to erosion
Geologic and Rock Cycles, Fossils and Unconformities The Geologic Cycle 3 key events: deposition, uplift, erosion Sedimentation of beds A-D beneath the sea Uplift above sea level and exposure of D to erosion
Faults, Fossils, Rocks and Minerals Review:
 Faults, Fossils, Rocks and Minerals Review: 1. The preserved remains or traces of organisms that lived in the past are. - Fossils 2. How do Fossils form? - A dead organism becomes buried in sediment 3.
Faults, Fossils, Rocks and Minerals Review: 1. The preserved remains or traces of organisms that lived in the past are. - Fossils 2. How do Fossils form? - A dead organism becomes buried in sediment 3.
Geologic Time Essentials of Geology, 11th edition, Chapter 18 Geologic Time: summary in haiku form Key Concepts Determining geological ages
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Geologic Time Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition, Chapter 18 Geologic Time: summary in haiku form Superposition and horizontality tell stories in rocks. Key
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Geologic Time Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition, Chapter 18 Geologic Time: summary in haiku form Superposition and horizontality tell stories in rocks. Key
City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012
 1 City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012 Levels of Analysis Descriptive (What do you see, feel, hear, etc..) This rock is made of round grains of quartz. Interpretive-- (The detective
1 City of Fort Collins: Geology Staff Training, June 2012 Levels of Analysis Descriptive (What do you see, feel, hear, etc..) This rock is made of round grains of quartz. Interpretive-- (The detective
Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles
 Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction - An appreciation for the immensity of geologic time is essential for understanding the history of our planet - Geologists use two references for time
Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction - An appreciation for the immensity of geologic time is essential for understanding the history of our planet - Geologists use two references for time
Geological Time How old is the Earth
 Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 2.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following statements regarding the scientific method is false? A) A hypothesis must be agreed upon by more than one scientist. B) A theory is a hypothesis that has withstood
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following statements regarding the scientific method is false? A) A hypothesis must be agreed upon by more than one scientist. B) A theory is a hypothesis that has withstood
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History
 Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Exploring Geology Chapter 9 Geologic Time
 Exploring Geology Chapter 9 Geologic Time Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9: Geologic Time Stratigraphic Principles Relative Age Dating
Exploring Geology Chapter 9 Geologic Time Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9: Geologic Time Stratigraphic Principles Relative Age Dating
Age of Earth/Geologic Time. Vocabulary
 Age of Earth/Geologic Time Vocabulary Big Ideas Geologic Time Earth Structures Identify current methods for measuring the age of Earth and its parts, including the law of superposition and radioactive
Age of Earth/Geologic Time Vocabulary Big Ideas Geologic Time Earth Structures Identify current methods for measuring the age of Earth and its parts, including the law of superposition and radioactive
