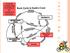
Volcano Unit Pre Assessment. Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two.
|
|
|
- Joshua Hudson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volcano Unit Pre Assessment Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select the best answer and write the letter on the line. 1. Where are most volcanoes found? a. On mountains b. Europe c. Along plate boundaries d. South America 2. A major volcanic belt formed by many volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean is called a. The Ring of Fire b. The Volcanic Belt c. Explosivo d. Rim of Volcanoes 1
2 3. A volcano that is erupting, or has erupted recently is classified as a. Active b. Dormant c. Extinct d. Awake 4. A volcano that hasn t erupted in recent history, but could erupt is classified as a. Active b. Extinct c. Dormant d. Sleeping 5. A volcano that will never erupt again is considered a a. Dormant b. Extinct c. Active d. Dead 6. An area where material from deep within the mantle rises and then melts, forming magma is called a a. Magma pool b. Hot Spring c. Chamber d. Hot Spot 7. When groundwater is heated in hot rock near shallow magma bodies a can form a. Batholith b. Dike c. Geyser d. Volcano 8. When magma heats underground water, the result may be a a. lava flow b. hot spring c. hot spot d. bath 2
3 9. The tendency of a fluid to resist flowing is called a. Static b. Resistance c. Friction d. Viscosity 10. The major ingredient in Magma is a. silica b. basalt c. Carbon Dioxide d. granite 11. As a volcano erupts, what force pushes magma out of a volcano onto the surface? a. Flowing water b. The Jedi Force c. Dynamite d. The force of expanding gases True or False. Circle whether the state is true or false. 12. True or False. A volcano is a weak spot in the Earth s crust where molten material comes to the surface 13. True or False. Yellowstone National Park marks a hot spot under the North American plate. 14. True or False. How fast lava flows depends on the properties of the magma from which it formed including its silica content and temperature. 15. True or False. Dormant volcanoes can become active at any time. 3
4 Label Label the parts of the volcano listed below on the diagram. Magma Chamber Vent Crater 4
5 Volcano Unit Pre Assessment - Modified Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select the best answer and write the letter on the line. 1. Where are most volcanoes found? a. On mountains b. Europe c. Along plate boundaries 2. A major volcanic belt formed by many volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean is called a. The Ring of Fire b. The Volcanic Belt c. Explosivo 5
6 3. A volcano that is erupting, or has erupted recently is classified as a. Active b. Dormant c. Extinct 4. A volcano that hasn t erupted in recent history, but could erupt is classified as a. Active b. Extinct c. Dormant 5. A volcano that will never erupt again is considered a a. Dormant b. Extinct c. Active 6. An area where material from deep within the mantle rises and then melts, forming magma is called a a. Hot Spring b. Chamber c. Hot Spot 7. When groundwater is heated in hot rock near shallow magma bodies a can form a. Batholith b. Dike c. Geyser 8. When magma heats underground water, the result may be a a. lava flow b. hot spring c. hot spot 9. The tendency of a fluid to resist flowing is called a. Resistance b. Friction c. Viscosity 6
7 10. The major ingredient in Magma is a. silica b. basalt c. Carbon Dioxide 11. As a volcano erupts, what force pushes magma out of a volcano onto the surface? a. Flowing water b. The Jedi Force c. The force of expanding gases True or False. Circle whether the state is true or false. 12. True or False. A volcano is a weak spot in the Earth s crust where molten material comes to the surface 13. True or False. Yellowstone National Park marks a hot spot under the North American plate. Label Label the parts of the volcano listed below on the diagram. Magma Chamber Vent Crater 7
8 Volcano Unit Post Assessment Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select the best answer and write the letter on the line. 1. Where are most volcanoes found? a. On mountains b. Europe c. Along plate boundaries d. South America 2. A major volcanic belt formed by many volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean is called a. The Ring of Fire b. The Volcanic Belt c. Explosivo d. Rim of Volcanoes 8
9 3. A volcano that is erupting, or has erupted recently is classified as a. Active b. Dormant c. Extinct d. Awake 4. A volcano that hasn t erupted in recent history, but could erupt is classified as a. Active b. Extinct c. Dormant d. Sleeping 5. A volcano that will never erupt again is considered a a. Dormant b. Extinct c. Active d. Dead 6. An area where material from deep within the mantle rises and then melts, forming magma is called a d. Magma pool e. Hot Spring f. Chamber g. Hot Spot 7. When groundwater is heated in hot rock near shallow magma bodies a can form a. Batholith b. Dike c. Geyser d. Volcano 8. When magma heats underground water, the result may be a a. lava flow b. hot spring c. hot spot d. bath 9
10 9. The tendency of a fluid to resist flowing is called a. Static b. Resistance c. Friction d. Viscosity 10. The major ingredient in Magma is a. silica b. basalt c. Carbon Dioxide d. granite 11. As a volcano erupts, what force pushes magma out of a volcano onto the surface? a. Flowing water b. The Jedi Force c. Dynamite d. The force of expanding gases 12. What are two main factors that affect the viscosity of magma? a. Altitude and season b. Location and Temperature c. Temperature and Silica content d. Viscosity of all magma is the same 13. As temperature of magma increases, its viscosity a. Increases b. Decreases c. Stays the same d. Hardens 14. The collapse of a volcano s magma chamber may produce a a. crater b. island arc c. still d. caldera 15. Volcanic ash is a. smoke and fire b. small pieces of cooled lava c. burned substance d. dirt 10
11 True or False. Circle whether the state is true or false. 16. True or False. A volcano is a weak spot in the Earth s crust where molten material comes to the surface 17. True or False. Yellowstone National Park marks a hot spot under the North American plate. 18. True or False. How fast lava flows depends on the properties of the magma from which it formed including its silica content and temperature. 19. True or False. Dormant volcanoes can become active at any time. Short Answer Please answer in complete sentences. What is more likely to be more hazardous a volcano that erupts frequently, or a volcano that has been inactive for hundreds of years? Why? 11
12 Label Label the parts of the volcano listed below on the diagram. Magma Chamber Vent Crater 12
13 Volcano Unit Post Assessment - Modified Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano Shield Volcano Cinder Cone Volcano Multiple Choice Select the best answer and write the letter on the line. 1. Where are most volcanoes found? a. On mountains b. Europe c. Along plate boundaries 2. A major volcanic belt formed by many volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean is called a. The Ring of Fire b. The Volcanic Belt c. Explosivo 13
14 3. A volcano that is erupting, or has erupted recently is classified as a. Active b. Dormant c. Extinct 4. A volcano that hasn t erupted in recent history, but could erupt is classified as a. Active b. Extinct c. Dormant 5. A volcano that will never erupt again is considered a a. Dormant b. Extinct c. Active 6. An area where material from deep within the mantle rises and then melts, forming magma is called a a. Hot Spring b. Chamber c. Hot Spot 7. When groundwater is heated in hot rock near shallow magma bodies a can form a. Batholith b. Dike c. Geyser 8. When magma heats underground water, the result may be a a. lava flow b. hot spring c. hot spot 9. The tendency of a fluid to resist flowing is called a. Resistance b. Friction c. Viscosity 14
15 10. The major ingredient in Magma is a. silica b. basalt c. Carbon Dioxide 11. As a volcano erupts, what force pushes magma out of a volcano onto the surface? a. Flowing water b. The Jedi Force c. The force of expanding gases 12. What are two main factors that affect the viscosity of magma? a. Altitude and season b. Location and Temperature c. Temperature and Silica content 13. As temperature of magma increases, its viscosity a. Increases b. Decreases c. Stays the same 14. The collapse of a volcano s magma chamber may produce a a. crater b. island arc c. caldera 15. Volcanic ash is a. smoke and fire b. small pieces of cooled lava c. burned substance True or False. Circle whether the state is true or false. 16. True or False. A volcano is a weak spot in the Earth s crust where molten material comes to the surface 17. True or False. Yellowstone National Park marks a hot spot under the North American plate. 15
16 Label Label the parts of the volcano listed below on the diagram. Magma Chamber Vent Crater Bonus You may draw pictures with your answer to help you with an explanation if you wish. What is more likely to be more hazardous a volcano that erupts frequently, or a volcano that has been inactive for hundreds of years? Why? 16
17 Lesson 1 Assessment A volcano discovery Web Quest Name: Instructions: Follow each link provided (find the links in your google classroom), and answer the questions accommodating each link in complete sentences. All answers are found using these links. Be sure to click on every link provided within the simulation, and read carefully! Link 1: Introduction to Volcanism index.htm 1. Draw and label a diagram of a volcano. Provide a short description for each part. 17
18 2. The that forms from layers of and is called a. 3. Volcanoes are classified as active, dormant, or extinct. Describe what those classifications mean. 4. There are 4 main types of volcanoes. How are they classified? 5. What are the two primary types of volcanoes? What are the two secondary types? Why are they secondary? 6. List one fact about each type of volcano. Draw the basic shape of each type. 18
19 7. What are the three places that volcanoes commonly occur? 8. How many hot spots have been identified around the world? 9. What is Hawaii? 10. What kind of volcanoes are associated with hot spots? What other features are associated with hot spots? 11. are places where tectonic plates are moving away from one another. 12. What is much of the oceanic crust made of? 13. is the word used to describe melted or molten rock inside Earth. 14. What is magma made of? 19
20 15. What determines the eruption style, rock type, and volcano shape? 16. List the three types of magma and what type of volcano each type comes out of. 17. rocks are formed when molten rock cools and hardens. 18. What are the two classes of igneous rocks? Where are they found? (Below or on top of Earth s surface?) Link 2: Volcanic Eruptions and Hazards ess05_int_volcanerupt/02_effusive.htm 19. eruptions are generally considered to be gentler than explosive eruptions. What types of hazards can result from this type of eruption? List 3. 20
21 20. eruptions are the most hazardous, involving large volumes of tephra and gases emitted from the volcano. What types of hazards can result from this type of eruption? List 3. Extra Credit (Extension for advanced students) Follow this link to a third simulation: Volcanic Features. ess05_int_volcanfeatr/03_caldera.htm 21. How do we know that Yellowstone is actually a volcano? Provide details. 22. What is Devils Tower? 21
22 What you need: * 4 small plastic cups Fill 1 cup ½ full of Nacho cheese Fill 1 cup ½ full of vegetable oil * 1 straw per person, cut in half * 1 lab tray * 1 ruler * 1 timer: phone or stopwatch Lesson 2 Assessment Viscosity Lab Investigation Name: Part 1 Instructions: * Each person will grab ½ of a straw. * One person at a time, place the straw into the cup of oil. * Blow bubbles like you would do with a soda. * Observe how hard you have to blow, and the force and size of the bubbles once the air gets through. * Do the same with the Nacho Cheese using your other 1/2 of the straw. Record your observations below. All group members will do this. a. Blowing in the oil: b. Blowing in the nacho cheese: 22
23 Part 2 Instructions: * One team member will be the pourer, while another is the timer. * The pourer will first grab the cup with vegetable oil. Holding the ruler vertically (either person can hold the ruler), the pourer will hold the cup approximately 12 inches above an empty cup. * The timer will begin the timing as soon and the pourer begins to pour the oil into one of the empty cups. * The timer will stop the stopwatch as soon as the cup of oil is empty. Record this time in the table below. * Repeat steps 3-5 with the nacho cheese and the other empty cup. * Get some chips and eat your cheese if you want! Liquid Time in Seconds Oil Nacho Cheese Answer the questions below. 1. Describe your flow-test results. Why did you get the results you did? 2. Is the viscosity of the oil higher or lower than the nacho cheese? How do you know? 3. One way to decrease the viscosity of a liquid is to (heat/cool) the fluid? 4. What factors affect the viscosity of a substance? 23
24 5. What would happen to the viscosity of the oil and the nacho cheese if you heated it up? What if you cooled it down? 6. Can magma have different viscosities? What influences the viscosity of magma? (conduct research if you need to) 7. If magma in a volcano has a high viscosity, would the eruption be quiet or explosive? Why? (Think of how the fluids reacted to you blowing air into them) 8. Could viscosity affect how often a volcano erupts? Why? 9. What are some dangers of a volcanic eruption with high viscosity magma? 10. What are some dangers of a volcanic eruption with low viscosity magma? Bonus: Do you prefer mashed potatoes with low or high viscosity? Explain. 24
25 Answer Key (Answers in Green) Volcano Unit Pre Assessment Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano: Middle Shield Volcano: Bottom Cinder Cone Volcano: Top Multiple Choice Select the best answer and write the letter on the line. 1. Where are most volcanoes found? a. On mountains b. Europe c. Along plate boundaries d. South America 2. A major volcanic belt formed by many volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean is called a. The Ring of Fire b. The Volcanic Belt c. Explosivo 25
26 d. Rim of Volcanoes 3. A volcano that is erupting, or has erupted recently is classified as a. Active b. Dormant c. Extinct d. Awake 4. A volcano that hasn t erupted in recent history, but could erupt is classified as a. Active b. Extinct c. Dormant d. Sleeping 5. A volcano that will never erupt again is considered a a. Dormant b. Extinct c. Active d. Dead 6. An area where material from deep within the mantle rises and then melts, forming magma is called a d. Magma pool e. Hot Spring f. Chamber g. Hot Spot 7. When groundwater is heated in hot rock near shallow magma bodies a can form a. Batholith b. Dike c. Geyser d. Volcano 8. When magma heats underground water, the result may be a a. lava flow b. hot spring c. hot spot 26
27 d. bath 9. The tendency of a fluid to resist flowing is called a. Static b. Resistance c. Friction d. Viscosity 10. The major ingredient in Magma is a. silica b. basalt c. Carbon Dioxide d. granite 11. As a volcano erupts, what force pushes magma out of a volcano onto the surface? a. Flowing water b. The Jedi Force c. Dynamite d. The force of expanding gases True or False. Circle whether the state is true or false. 12. True or False. A volcano is a weak spot in the Earth s crust where molten material comes to the surface 13. True or False. Yellowstone National Park marks a hot spot under the North American plate. 14. True or False. How fast lava flows depends on the properties of the magma from which it formed including its silica content and temperature. 15. True or False. Dormant volcanoes can become active at any time. 27
28 Label Label the parts of the volcano listed below on the diagram. Magma Chamber Vent Crater Crater Vent Magma Chamber 28
29 Volcano Unit Post Assessment: Answer Key Name Matching Match the type of volcano to the correct picture by drawing a line to connect the two. Composite Volcano: Middle Shield Volcano: Bottom Cinder Cone Volcano: Top Multiple Choice Select the best answer and write the letter on the line. 1. Where are most volcanoes found? a. On mountains b. Europe c. Along plate boundaries d. South America 2. A major volcanic belt formed by many volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean is called a. The Ring of Fire b. The Volcanic Belt c. Explosivo d. Rim of Volcanoes 29
30 3. A volcano that is erupting, or has erupted recently is classified as a. Active b. Dormant c. Extinct d. Awake 4. A volcano that hasn t erupted in recent history, but could erupt is classified as a. Active b. Extinct c. Dormant d. Sleeping 5. A volcano that will never erupt again is considered a a. Dormant b. Extinct c. Active d. Dead 6. An area where material from deep within the mantle rises and then melts, forming magma is called a e. Magma pool f. Hot Spring g. Chamber h. Hot Spot 7. When groundwater is heated in hot rock near shallow magma bodies a can form a. Batholith b. Dike c. Geyser d. Volcano 8. When magma heats underground water, the result may be a a. lava flow b. hot spring c. hot spot d. bath 30
31 9. The tendency of a fluid to resist flowing is called a. Static b. Resistance c. Friction d. Viscosity 10. The major ingredient in Magma is a. silica b. basalt c. Carbon Dioxide d. granite 11. As a volcano erupts, what force pushes magma out of a volcano onto the surface? a. Flowing water b. The Jedi Force c. Dynamite d. The force of expanding gases 12. What are two main factors that affect the viscosity of magma? a. Altitude and season b. Location and Temperature c. Temperature and Silica content d. Viscosity of all magma is the same 13. As temperature of magma increases, its viscosity a. Increases b. Decreases c. Stays the same d. Hardens 14. The collapse of a volcano s magma chamber may produce a a. crater b. island arc c. still d. caldera 15. Volcanic ash is a. smoke and fire b. small pieces of cooled lava c. burned substance d. dirt 31
32 True or False. Circle whether the state is true or false. 16. True or False. A volcano is a weak spot in the Earth s crust where molten material comes to the surface 17. True or False. Yellowstone National Park marks a hot spot under the North American plate. 18. True or False. How fast lava flows depends on the properties of the magma from which it formed including its silica content and temperature. 19. True or False. Dormant volcanoes can become active at any time. Short Answer Please answer in complete sentences. What is more likely to be more hazardous a volcano that erupts frequently, or a volcano that has been inactive for hundreds of years? Why? 32
33 Label Label the parts of the volcano listed below on the diagram. Magma Chamber Vent Crater Crater Vent Magma Chamber 33
34 Lesson 1 Assessment: Answer Key A volcano discovery Web Quest Name: Instructions: Follow each link provided (find the links in your google classroom), and answer the questions accommodating each link in complete sentences. All answers are found using these links. Be sure to click on every link provided within the simulation, and read carefully! Link 1: Introduction to Volcanism index.htm 1. Draw and label a diagram of a volcano. Provide a short description for each part. 34
35 2. The mountain that forms from layers of lava and tephra is called a volcano. 3. Volcanoes are classified as active, dormant, or extinct. Describe what those classifications mean. Active: the volcano is currently erupting or has erupted recently Dormant: The volcano hasn t recently erupted but still can erupt Extinct: The volcano is unlikely to ever erupt again 4. There are 4 main types of volcanoes. How are they classified? Cinder Cone Composite Shield Lava Dome 5. What are the two primary types of volcanoes? What are the two secondary types? Why are they secondary? Two primary types are composite and shield volcanoes. Lava domes and cinder cones are secondary because they tend to form on or near primary volcanoes. 6. List one fact about each type of volcano. Draw the basic shape of each type. 7. What are the three places that volcanoes commonly occur? Hot spots, spreading centers, subduction zones 35
36 8. How many hot spots have been identified around the world? What is Hawaii? A hot spot 10. What kind of volcanoes are associated with hot spots? What other features are associated with hot spots? Shield volcanoes and geothermal features 11. Spreading centers are places where tectonic plates are moving away from one another. 12. What is much of the oceanic crust made of? Basalt 13. Magma is the word used to describe melted or molten rock inside Earth. 14. What is magma made of? Elements, minerals, gases 15. What determines the eruption style, rock type, and volcano shape? The composition of the magma 16. List the three types of magma and what type of volcano each type comes out of. Felsic, mafic, intermediate 36
37 17. Igneous rocks are formed when molten rock cools and hardens. 18. What are the two classes of igneous rocks? Where are they found? (Below or on top of Earth s surface?) Intrusive: Below the surface. Extrusive: Above the surface Link 2: Volcanic Eruptions and Hazards ess05_int_volcanerupt/02_effusive.htm 19. Effusive eruptions are generally considered to be gentler than explosive eruptions. What types of hazards can result from this type of eruption? List 3. Lava flows, tsunamis, volcanic gases 20. Explosive eruptions are the most hazardous, involving large volumes of tephra and gases emitted from the volcano. What types of hazards can result from this type of eruption? List 3. Blow downs, lahars, pyroclastic flows, lava flows, volcanic gases, tephra Extra Credit (Extension for advanced students) Follow this link to a third simulation: Volcanic Features. ess05_int_volcanfeatr/03_caldera.htm 21. How do we know that Yellowstone is actually a volcano? Provide details. 37
38 Geothermal activity is common around hot spots. 22. What is Devils Tower? Volcanic neck: Ancient intrusive igneous rock 38
39 What you need: * 4 small plastic cups Fill 1 cup ½ full of Nacho cheese Fill 1 cup ½ full of vegetable oil * 1 straw per person, cut in half * 1 lab tray * 1 ruler * 1 timer: phone or stopwatch Lesson 2 Assessment: Key Viscosity Lab Investigation Name: Part 1 Instructions: * Each person will grab ½ of a straw. * One person at a time, place the straw into the cup of oil. * Blow bubbles like you would do with a soda. * Observe how hard you have to blow, and the force and size of the bubbles once the air gets through. * Do the same with the Nacho Cheese using your other 1/2 of the straw. Record your observations below. All group members will do this. a. Blowing in the oil: Students should note the oil was easier to blow in and it produced many bubbles. It was like blowing in water, or milk, or soda etc. b. Blowing in the nacho cheese: Due to the thickness of nacho cheese, it took more effort to blow in it. It produced only one big hole. 39
40 Part 2 Instructions: * One team member will be the pourer, while another is the timer. * The pourer will first grab the cup with vegetable oil. Holding the ruler vertically (either person can hold the ruler), the pourer will hold the cup approximately 12 inches above an empty cup. * The timer will begin the timing as soon and the pourer begins to pour the oil into one of the empty cups. * The timer will stop the stopwatch as soon as the cup of oil is empty. Record this time in the table below. * Repeat steps 3-5 with the nacho cheese and the other empty cup. * Get some chips and eat your cheese if you want! Liquid Time in Seconds Oil Nacho Cheese Answer the questions below. 1. Describe your flow-test results. Why did you get the results you did? The oil flowed much quicker than the nacho cheese. This is because the nacho cheese is thicker than the oil. 2. Is the viscosity of the oil higher or lower than the nacho cheese? How do you know? The oil has a lower viscosity because it flows faster and is less sticky. 3. One way to decrease the viscosity of a liquid is to Heat (heat/cool) the fluid? 4. What factors affect the viscosity of a substance? Temperature and chemical structure 40
41 5. What would happen to the viscosity of the oil and the nacho cheese if you heated it up? What if you cooled it down? The viscosity of both the oil and nacho cheese would be lower if heated, and higher if cooled down. 6. Can magma have different viscosities? What influences the viscosity of magma? (conduct research if you need to) Yes, magma can have different viscosities. The temperature of the magma, and the chemical structure, including the silica content, influences the viscosity of magma. 7. If magma in a volcano has a high viscosity, would the eruption be quiet or explosive? Why? (Think of how the fluids reacted to you blowing air into them) The eruption would be explosive. This is because it is thicker, which makes it more difficult for the gases to escape. The gases build up, and when they finally break through it is more explosive. 8. Could viscosity affect how often a volcano erupts? Why? Yes. When magma has a higher viscosity, the gas and pressure need to build up over time before there is enough force to break through. 9. What are some dangers of a volcanic eruption with high viscosity magma? High viscosity magma means the eruption will be more explosive. This could cause pyroclastic flows, falling rock, landslides etc. 10. What are some dangers of a volcanic eruption with low viscosity magma? This magma is thinner and less sticky. An eruption could cause a faster lava flow and can cover a lot of area in a short amount of time. Bonus: Do you prefer mashed potatoes with low or high viscosity? Explain. 41
Lesson 1 Handout. A volcano discovery Web Quest
 Lesson 1 Handout A volcano discovery Web Quest Name: Instructions: Follow each link provided (find the links in your google classroom), and answer the questions accommodating each link in complete sentences.
Lesson 1 Handout A volcano discovery Web Quest Name: Instructions: Follow each link provided (find the links in your google classroom), and answer the questions accommodating each link in complete sentences.
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!!
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep Cone-shaped hill/ mountain Composite Volcano Tall,
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth
 Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Volcano. Magma. Lava. weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up. molten mixture of rockforming
 Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
Volcanoes Volcano weak spot in crust where magma and gases come up Magma Lava molten mixture of rockforming substance, gases, water from the mantle Magma that flows onto earth surface forms solid rock
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES
 Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! VOLCANOES VOLCANOS Three Types of Volcanos Shield Cinder Cone Composite LAND FORMATIONS FROM LAVA & ASH Shield Volcano Created by hot spots Gently sloping Cinder Volcano Steep
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Effects of Eruptions. Most active in the world Kilauea, Hawaii.
 Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Name Date Class. Answer the following questions. Use your textbook and the ideas above. 1. If a volcano collapses, it leaves a huge hole called a(an).
 Volcanic Landforms (pages 217 223) Landforms From Lava and Ash (pages 218 220) Key Concept: Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes,
Volcanic Landforms (pages 217 223) Landforms From Lava and Ash (pages 218 220) Key Concept: Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes,
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
Volcanoes. Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms
 Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Volcanology. The study of volcanoes
 Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Critical Thinking 1. Contrast How could you tell the difference between a mafic rock and a felsic rock by looking at them?
 CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted.
 What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts
 3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out.
 Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out." ~Anonymous Sep 26 10:30 AM 1 Copy Directly into your notebook... 1. Pyro Latin
Bellringer: What materials are ejected from volcanoes? Quote of the Day: "Science is not belief, but the will to find out." ~Anonymous Sep 26 10:30 AM 1 Copy Directly into your notebook... 1. Pyro Latin
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
Volcanic Eruptions (pp )
 Name Date Class Volcanic Eruptions (pp. 221 228) This section explains how volcanoes erupt and describes types of volcanic eruptions as well as other types of volcanic activity. The section also describes
Name Date Class Volcanic Eruptions (pp. 221 228) This section explains how volcanoes erupt and describes types of volcanic eruptions as well as other types of volcanic activity. The section also describes
A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through
 Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Study guide chapter 9
 Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure. Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages )
 Name Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages 676 683) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth s plates move about quickly on top of
Name Earth s Interior HW Packet HW #1 Plate Tectonics (pages 676 683) 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth s plates move about quickly on top of
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
Week: Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 19 E 20 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Volcano Notes *Bill Nye Notes 21 E 22
clementaged.weebly.com Name: ODD Period: Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/19 10/30 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 19 E 20 O *Vocabulary *Frayer Vocab *Volcano Notes *Bill Nye Notes 21 E 22
Volcanic Eruptions (pages )
 Volcanic Eruptions (pages 209 216) Magma Reaches Earth s Surface (pages 210 211) Key Concept: When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe
Volcanic Eruptions (pages 209 216) Magma Reaches Earth s Surface (pages 210 211) Key Concept: When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe
Week: Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos
 clementaged.weebly.com Name: Period: 7 Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 No School 14 O *Greenhand Conference *Vocabulary *Volcano Movie 15 E *Volcano
clementaged.weebly.com Name: Period: 7 Week: 10 11 Dates: 10/13 10/24 Unit: Volcanos Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 13 No School 14 O *Greenhand Conference *Vocabulary *Volcano Movie 15 E *Volcano
Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT
 1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only a single (one) type of compound
 Science Name: Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly KEY Date: Study Guide - Lessons 5 and 6 Test Define the following terms: 1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only
Science Name: Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly KEY Date: Study Guide - Lessons 5 and 6 Test Define the following terms: 1. minerals - A naturally occurring substance that takes a solid Crystal form and is made of only
Apr 20 2:26 PM. the opening in Earth's crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. the landform that develops around this opening
 Volcanoes Cleveland Volcano, Alaska, May 2006 Taken from the ISS Apr 20 2:26 PM The term volcano can refer to two things: 1. the opening in Earth's crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt
Volcanoes Cleveland Volcano, Alaska, May 2006 Taken from the ISS Apr 20 2:26 PM The term volcano can refer to two things: 1. the opening in Earth's crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES.
 Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes KEY CONCEPT: TECTONIC PLATE MOTIONS CAN RESULT IN VOLCANIC ACTIVITY AT PLATE BOUNDARIES. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes. Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries.
 Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
A. What is a volcano?
 VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
VOLCANISM THE ROCK CYCLE I. Introduction From: Roman god of fire, Vulcan A. What is a volcano? A conical mountain formed around a vent where lava, pyroclastic materials, and gases are erupted. I. Introduction
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes. An active volcano is one that has erupted within recorded history.
 Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes
 The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
A R O U N D W E G O COLOR CODE THE PATHWAY TO IGNEOUS ROCKS!
 COLOR CODE THE PATHWAY TO IGNEOUS ROCKS! A R O U N D W E G O VOCABULARY FOR IGNEOUS ROCKS IGNEOUS ORIGINS volcanoes active volcano dormant volcano magma plutonic rocks intrusives lava volcanic rocks extrusives
COLOR CODE THE PATHWAY TO IGNEOUS ROCKS! A R O U N D W E G O VOCABULARY FOR IGNEOUS ROCKS IGNEOUS ORIGINS volcanoes active volcano dormant volcano magma plutonic rocks intrusives lava volcanic rocks extrusives
Physical Geology, 15/e
 Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Lecture Outlines Physical Geology, 15/e Plummer, Carlson & Hammersley Copyright McGraw-Hill Education, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Volcanism and Extrusive Rocks Physical Geology
Magma vs. Lava. Molten rock below Earth s surface is called magma. The magma that reaches the surface and erupts out of a volcano is called lava.
 CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
Introduction to volcanoes. Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt
 Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features
 Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
Convergent Plate Boundary Geologic Features Ocean Trench Mtn / Volcano New Ocean Crust Old Continenta l Crust Beadle, 2009 Convection cells provide the force to move the continents. The crust is carried
L wave Lahar Lava Magma
 Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Volcanoes What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Earthquakes and Volcanoes Volcanoes What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions. light in color is called a. felsic. b. oceanic. c. mantle. d. mafic. dark in color is called
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
12.2 Volcanoes Looking inside a volcano What is a volcano? volcano magma magma chamber lava
 12.2 Volcanoes Early explorers noticed that many volcanoes were located near coastlines, but they didn t know why. One volcano that is near a coastline is Mount St. Helens in Washington state. This famous
12.2 Volcanoes Early explorers noticed that many volcanoes were located near coastlines, but they didn t know why. One volcano that is near a coastline is Mount St. Helens in Washington state. This famous
Name: Earth Science Date:
 Name: Earth Science Date: Lab Report: Plate Tectonics Data: Submit the Mid- Atlantic Seafloor Profile Maps (from Divergent Plate Boundary Lab) on and the Convergent Plate Boundary Data Page. (6 points)
Name: Earth Science Date: Lab Report: Plate Tectonics Data: Submit the Mid- Atlantic Seafloor Profile Maps (from Divergent Plate Boundary Lab) on and the Convergent Plate Boundary Data Page. (6 points)
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter 18. Volcanism
 Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Volcanoes. Presented by Kesler Science
 Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are the parts of a volcano? 2. What are the four types? 3. What processes form volcanoes? 4. Where are volcanoes located on earth? What is a Volcano?
Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are the parts of a volcano? 2. What are the four types? 3. What processes form volcanoes? 4. Where are volcanoes located on earth? What is a Volcano?
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Study Guide: Unit 1. 1) Take careful notes in class during the lectures as well as the information given in the slides presented during class
 Geology 101 Study Guide: Unit 1 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the first unit exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. You will not be asked to
Geology 101 Study Guide: Unit 1 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the first unit exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. You will not be asked to
Earthquakes. Written by Rebecca Stark Educational Books n Bingo
 Earthquakes Create-A-Center Written by Rebecca Stark Educational Books n Bingo DIRECTIONS FOR CREATING A LEARNING CENTER MATERIALS: 4 pieces of oak tag or heavy poster board, 28 x 22 Scissors Plastic or
Earthquakes Create-A-Center Written by Rebecca Stark Educational Books n Bingo DIRECTIONS FOR CREATING A LEARNING CENTER MATERIALS: 4 pieces of oak tag or heavy poster board, 28 x 22 Scissors Plastic or
Lab Report: Plate Tectonics Data: Submit the Convergent Plate Boundary Data Page. (6 points)
 Name: Earth Science Date: Lab Report: Plate Tectonics Data: Submit the Convergent Plate Boundary Data Page. (6 points) Conclusion: 1. The diagram below shows both a spreading zone and a subduction zone
Name: Earth Science Date: Lab Report: Plate Tectonics Data: Submit the Convergent Plate Boundary Data Page. (6 points) Conclusion: 1. The diagram below shows both a spreading zone and a subduction zone
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 4 22 January 2004 Turn in Homework #1 Any Questions? IMPORTANT Big Island Field Trip We need a $162 payment for airfare BEFORE January 29 th Description of logistics,
VOLCANOES. {Singing} I don t know, I don t know, I don t know where I am-a gonna go when the volcano blows!
 Name: Tymesha B, Manny U, Malaika R VOLCANOES {Singing} I don t know, I don t know, I don t know where I am-a gonna go when the volcano blows! --Jimmy Buffett Part 1 Volcanic History of New Jersey Use
Name: Tymesha B, Manny U, Malaika R VOLCANOES {Singing} I don t know, I don t know, I don t know where I am-a gonna go when the volcano blows! --Jimmy Buffett Part 1 Volcanic History of New Jersey Use
Volcanoes. Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman
 Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Volcanoes Environmental Geology, Mr. Paul Lowrey Stacey Singleton, Cassandra Combs, Dwight Stephenson, Matt Smithyman EMPACTS Project, Spring 2017 Northwest Arkansas Community College, Bentonville, AR
Earth s Changing Surface
 Earth s Changing Surface Earthquakes and Volcanoes Key Concepts What causes earthquakes? What causes volcanoes to form? How do earthquakes and volcanoes change Earth s surface? What do you think? Read
Earth s Changing Surface Earthquakes and Volcanoes Key Concepts What causes earthquakes? What causes volcanoes to form? How do earthquakes and volcanoes change Earth s surface? What do you think? Read
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2
 FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
FOUNDATIONS OF GEOLOGY CHAPTER 2 2.3A- VOLCANOES Volcanoes all share common characteristics. Vent- a central channel through which gases, ash and rock are ejected. Magma- molten rock which lies several
Constructive & Destructive Forces
 Constructive & Destructive Forces Intro: Constructive Forces Processes that create landforms. Destructive Forces Processes that destroy landforms. Intro: Constructive Forces Volcanoes Deposition Landslides
Constructive & Destructive Forces Intro: Constructive Forces Processes that create landforms. Destructive Forces Processes that destroy landforms. Intro: Constructive Forces Volcanoes Deposition Landslides
Dynamic Planet PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. c) low temperature d) high volatile content
 School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
School Name: Team #: Students Names: Dynamic Planet 2016 Science Olympiad Invitational University of Texas at Austin PUT ALL YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ANSWER SHEET 1) Low viscosity magmas have: a) high silica
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 CHAPTER 13 SECTION Volcanoes 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What three conditions can cause magma to form? What is volcanism? What are
CHAPTER 13 SECTION Volcanoes 1 Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What three conditions can cause magma to form? What is volcanism? What are
Ch12&13 Test. 3. Where does the first motion of an earthquake occur? a. fault c. epicenter b. focus d. locus
 Ch12&13 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the epicenter of an earthquake? a. the location along a fault where the first motion
Ch12&13 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the epicenter of an earthquake? a. the location along a fault where the first motion
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
ANSWER KEY. Chapter Project. Volcanoes. Worksheet 1. Worksheet 2. Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Guided Reading and Study
 Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. Ethiopia, Tanzania, Zaire. 2. Guadeloupe, Iceland, Indonesia, Japan, Martinique, Montserrat, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, St. Vincent, USA (Hawaii). 3. USA
Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. Ethiopia, Tanzania, Zaire. 2. Guadeloupe, Iceland, Indonesia, Japan, Martinique, Montserrat, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, St. Vincent, USA (Hawaii). 3. USA
Magma Why don t all volcanoes look and act the same?
 Lesson Plan 7 Discuss What shapes can volcanoes be? (revisit photos if necessary) --Cone shaped -Ruapehu, Taranaki, Rangitoto, White Island, Ngauruhoe --Crater (caldera) shaped-taupo & Rotorua --Fissures-
Lesson Plan 7 Discuss What shapes can volcanoes be? (revisit photos if necessary) --Cone shaped -Ruapehu, Taranaki, Rangitoto, White Island, Ngauruhoe --Crater (caldera) shaped-taupo & Rotorua --Fissures-
Study Guide: Unit 3. Density and Pressure: You should be able to answer the types of questions given in the end of module questions.
 IDS 102 Study Guide: Unit 3 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the third exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. In the Focus On section you will find
IDS 102 Study Guide: Unit 3 The purpose of this study guide is to help you prepare for the third exam by focusing your studying and providing example essay questions. In the Focus On section you will find
3/24/2016. Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016
 Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
20.2 Volcanoes. Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES. Where you find volcanoes 508 UNIT 6 EARTH S STRUCTURE
 Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.2 Volcanoes Have you ever heard of the Ring of Fire? About half of the active volcanoes on Earth are present along the shores of the Pacific Ocean in this region.
Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.2 Volcanoes Have you ever heard of the Ring of Fire? About half of the active volcanoes on Earth are present along the shores of the Pacific Ocean in this region.
! Profile of Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Mauna Loa is one of five huge shield volcanoes that make up the island of Hawaii.
 - Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
- Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
Back to the Big Question
 5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
5.1 Understand the 5.4 Question Explore Learning Set 5 Back to the Big Question What processes within Earth cause geologic activity? You now know a lot about patterns of volcanoes in your region and around
lava magma pyroclastic materials lava flow igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma
 magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
Module 7: Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure Topic 3 Content: Volcanoes - The Basics Notes. Volcanoes The Basics
 Volcanoes The Basics 1 Hello, my name is Dr. Simpson, and I am a volcanologist. I am here to explain some basic information about volcanoes to you. 3 I think we should get started by taking a look at the
Volcanoes The Basics 1 Hello, my name is Dr. Simpson, and I am a volcanologist. I am here to explain some basic information about volcanoes to you. 3 I think we should get started by taking a look at the
THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW
 THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases
THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Physical Geography. Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Volcanism. Chapter 12 GEOGRAPHY Earthquakes and Volcanoes. What are Earthquakes?
 Physical Geography GEOGRAPHY 1710 DAVID R. SALLEE Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Chapter 12 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes? The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy Usually associated
Physical Geography GEOGRAPHY 1710 DAVID R. SALLEE Tectonics, Earthquakes, and Chapter 12 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes? The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy Usually associated
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
When magma is ejected by a volcano or other vent, the material is called lava. Magma that has cooled into a solid is called igneous rock.
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
Errata for Earth Science: God s World, Our Home
 Errata for Earth Science: God s World, Our Home Page 1 Updated December 21, 2017 Chapter 1, Learning Check 1.5 2. The answer key on the Resource CD repeats question 1 but gives the correct answer for question
Errata for Earth Science: God s World, Our Home Page 1 Updated December 21, 2017 Chapter 1, Learning Check 1.5 2. The answer key on the Resource CD repeats question 1 but gives the correct answer for question
Thanks. You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction and save time prepping.
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
