Please take out your fill-in notes again, and we will continue learning about extinct creatures.
|
|
|
- Holly Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Today s Topic Evolution: Extinction Learning Goal: SWBAT explain why creatures go extinct from Earth, and why some recently-extinct creatures have gone extinct. Please take out your fill-in notes again, and we will continue learning about extinct creatures.
2 Homework Complete the Simulating Adaptations Lab (Due Monday, 4/13) Complete the Conditions of Natural Selection homework and History of Evolution Research Assignment. (Five Days Late) Complete cattle, cows, and dogs articles. (Two Days Late)
3 Upcoming Test Our next test will take place on Wednesday, 4/15. It will cover all of Evolution: Biological Evolution Natural Selection Artificial Selection Adaptations Extinction Succession
4 Five Extinct Creatures: Pyrenean Ibex Was once numerous across Spain and France. However, by the early 1900s, fewer than 100 remained.
5 Five Extinct Creatures: Pyrenean Ibex The last was seen on January 6, 2000, when it was found dead under a fallen tree. Their populations dwindled due to interspecific competition and poaching.
6 Five Extinct Creatures: Pyrenean Ibex In 2009, the ibex was unextinct when scientists cloned an ibex. However, this clone died 7 minutes after being birthed due to lung defects.
7 Five Extinct Creatures: Spix s Macaw Lived in northern Brazil. 71 exist in captivity, but the last wild macaw disappeared in 2000, and there are no other wild macaws known to remain.
8 In 1990, a single male was paired with a female in captivity to reproduce in the wild. Seven weeks later after the female s release, she collided with a power line and died.
9 Five Extinct Creatures: Spix s Macaw Their decline in population is attributed to hunting and trapping, habitat destruction, and introduction of Africanized bees, which compete for nesting sites with macaw.
10 Today s Fill-In Notes We re next going to work through the five mass-extinction events that took place on Earth. After that, we are going to watch the beginning of an episode of Cosmos regarding one of the extinction events.
11 The Five Mass-Extinction Events Throughout Earth s history there have been many extinction events. However, there has been five massextinction events that occurred in Earth s history. In a mass-extinction event, over 50% of all plant and animal life go extinct.
12 The Five Mass-Extinction Events The Five Mass-Extinction Events that occurred are: a. The Ordovician-Silurian ( Mya) b. The Late Devonian ( Mya) c. Permian-Triassic (252 Mya) (Cosmos) d. Triassic-Jurassic (201.3 Mya) e. Cretaceous-Plaeogene (66 Mya)
13 The Ordovician-Silurian The Ordovician-Silurian mass-extinction occurred approximately Mya at the end of the Ordovician Period. Typically large scale events, such as mass-extinctions, mark the end of a geologic time period. During this time, 70% of all species on Earth were killed.
14 The Ordovician-Silurian During this period of time, all life existed in the oceans.
15 The Ordovician-Silurian However, two events occurred, an estimated four million years apart, that set off this mass-extinction event.
16 The Ordovician-Silurian First was the movement of the supercontinent of Gondwana. Gondwana, through tectonic plate movement, shifted towards the south. This in turn led to global cooling.
17 The Ordovician-Silurian As a result of this global cooling, glaciers began to form all over the planet. This caused a drop in sea levels, which further killed off many creatures.
18 The Late Devonian The Late Devonian mass-extinction occurred approximately Mya at the transition from the Devonian Period to the Carboniferous Period. This extinction event caused 70% of all creatures on Earth to perish.
19 The Late Devonian It is unclear what caused the massextinction, but evidence suggests that it was not one singular event that triggered the extinction. It is thought that several small events occurred over the span of 20 million years.
20 The Late Devonian This extinction event only appeared to affected marine life. Some theories as to what caused the extinction event are changed to ocean levels, or depletion of oxygen in oceans. This would have been caused by volcanic activity in the ocean.
21 The Triassic-Jurassic The Triassic-Jurassic mass-extinction occurred approximately Mya at the end of the Triassic Period. This extinction event caused 70% - 75% of all creatures on Earth to go extinct.
22 The Triassic-Jurassic Land and air-dwelling dinosaurs survived perfectly well through this extinction event.
23 The Triassic-Jurassic However, non-dinosaur aquatic creatures in the oceans continued to dominate the oceans.
24 The Triassic-Jurassic There are many theories as to what caused the extinction event: Gradual climate change Sea-level fluctuations Ocean acidification
25 The Triassic-Jurassic One theory suggests the possibility of an asteroid impact. However, none of these hypotheses have any significant evidence to support them.
26 The Cretaceous-Paleogene The Cretaceous-Paleogene massextinction occurred approximately 66 Mya at the end of the Cretaceous Period. This extinction event caused 75% of all creatures on Earth to go extinct.
27 The Cretaceous-Paleogene This extinction event killed all non-avian (non-flying) dinosaurs.
28 The Cretaceous-Paleogene This extinction event was believed to have been caused by a massive comet/asteroid impact.
29 The Cretaceous-Paleogene The impact had dire effects on the entire globe s environment.
30 The Cretaceous-Paleogene The dark line in the rock marks this event
31 The Cretaceous-Paleogene Sampling shows higher concentrations (30x higher than naturally found on Earth) of iridium in this region, which is prevalent in meteors and comets. It also corresponds to ash and carbon, as the impact triggered many fires (high O 2 levels)
32 The Cretaceous-Paleogene The impact caused an impact-winter, which is caused by an ejection of dust and dirt into Earth s atmosphere. This dust and dirt blocks sunlight from entering, which prevents photosynthesis from occurring in plants and plankton.
33 The Permian-Triassic To learn about the Permian-Triassic extinction event, we turn to our friend Neil degrasse Tyson.
Causes of Extinction
 Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
Earth History. What is the Earth s time scale? Geological time Scale. Pre-Cambrian. FOUR Eras
 The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions.
 History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
The History of Life on Earth
 8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
8 The History of Life on Earth lesson 1 Geologic Time and Mass Extinctions Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.b. Students know the history of life on Earth has been disrupted by major catastrophic
Directed Reading. Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era EVOLUTION. beginning of life is called. to. PRECAMBRIAN TIME.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
(continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037
 Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
What Happened to the Dinosaurs?
 A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
The Phanerozoic Eon. 542 mya Present. Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras
 542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
What is the Earth s time scale?
 Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
ESA's Rosetta spacecraft What are habitable exoplanets? Is there an Earth 2.0?
 ESA's Rosetta spacecraft - 2009 What are habitable exoplanets? Is there an Earth 2.0? Christina Hedges (Institute of Astronomy) For the past 20 years, since the discovery of planets outside our solar system,
ESA's Rosetta spacecraft - 2009 What are habitable exoplanets? Is there an Earth 2.0? Christina Hedges (Institute of Astronomy) For the past 20 years, since the discovery of planets outside our solar system,
2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale
 CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6
 Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Grade 1.) 2.) 3.) 3.7 (EVOLUTION & EXTINCTION) HISTORY OF THE EARTH CATALYST
 SCIENCE Grade / Name: Date: Cohort: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) OBJECTIVE SWBAT define extinction and describe how meteorite impacts can cause mass extinction events and have altered the evolutionary history
SCIENCE Grade / Name: Date: Cohort: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) OBJECTIVE SWBAT define extinction and describe how meteorite impacts can cause mass extinction events and have altered the evolutionary history
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
The Fossil Record. CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163
 The Fossil Record CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163 Objectives 1. Describe how most fossils form. 2. Explain how scientists can determine a fossil s age. 3. Identify some unanswered
The Fossil Record CELLS and HEREDITY, CHAPTER 5, SECTION 3, PAGES 155 to 163 Objectives 1. Describe how most fossils form. 2. Explain how scientists can determine a fossil s age. 3. Identify some unanswered
Geologic Time. Mr. Skirbst
 Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life
 Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
5 Time Marches On. TAKE A LOOK 1. Identify What kinds of organisms formed the fossils in the picture?
 CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
Life on a Sterile Planet Results From a Pilot Study on Misconceptions of Mass Extinctions
 Life on a Sterile Planet Results From a Pilot Study on Misconceptions of Mass Extinctions Kyle Gray & Alexa Sedlacek Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences University of Northern Iowa Mass Extinctions
Life on a Sterile Planet Results From a Pilot Study on Misconceptions of Mass Extinctions Kyle Gray & Alexa Sedlacek Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences University of Northern Iowa Mass Extinctions
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale
 Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
4 Changes in Climate. TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why is more land exposed during glacial periods than at other times?
 Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families end Ord.
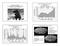 Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE
 Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
Risk of extinction and bottleneck effect in Penna model
 Risk of extinction and bottleneck effect in Penna model K. Malarz Faculty of Physics & Applied Computer Science AGH University of Science & Technology Kraków, Poland ZIS, 2007/06/18 1 Introduction A species
Risk of extinction and bottleneck effect in Penna model K. Malarz Faculty of Physics & Applied Computer Science AGH University of Science & Technology Kraków, Poland ZIS, 2007/06/18 1 Introduction A species
What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
5/3/17. Extinction of the Dinosaurs. Extinction of Dinosaurs - Causes. #40 Meteorite Impacts III - Dinosaur Extinction, Future Risk, Mitigation
 Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
Unit 10 Lesson 2 What Was Ancient Earth Like? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 How Rocks and Fossils Tell a Story Sedimentary rock forms in layers. Many sedimentary rocks contain fossils. The oldest rock layers are at the bottom, and the youngest rock layers are at the top. The relative
How Rocks and Fossils Tell a Story Sedimentary rock forms in layers. Many sedimentary rocks contain fossils. The oldest rock layers are at the bottom, and the youngest rock layers are at the top. The relative
Extinctions & Climate Change Student Activity. Diagram interpretation and using research data
 Diagram interpretation and using research data Biodiversity relates to the variety of life found in an area. The number and variety of species is a simple measure of its health i.e. its ability to respond
Diagram interpretation and using research data Biodiversity relates to the variety of life found in an area. The number and variety of species is a simple measure of its health i.e. its ability to respond
Question #1: What are some ways that you think the climate may have changed in the area where you live over the past million years?
 Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Spring th Grade
 Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
How the Earth was formed
 How the Earth was formed Short Answer: (2 points a piece) 1) Who was the man that stated the Earth was 6000 yrs old? 2) Hutton determined that this age was incorrect, what lead him to a much later date?
How the Earth was formed Short Answer: (2 points a piece) 1) Who was the man that stated the Earth was 6000 yrs old? 2) Hutton determined that this age was incorrect, what lead him to a much later date?
IX Life on Earth.
 IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Select the term or terms that best complete the statement. A. algae and bacteria B. Cretaceous Extinction C. fossil record D. mass extinction E. multicellular organism F. Permian Extinction
Name: Key Concepts Select the term or terms that best complete the statement. A. algae and bacteria B. Cretaceous Extinction C. fossil record D. mass extinction E. multicellular organism F. Permian Extinction
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
A brief history of the Earth!
 A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
A brief history of the Earth! The Geologic Time Scale Age of the Earth Hadean Eon Hadean Eon (4.57-3.85 Gyrs) Hell on Earth: 4.527 Gyrs formation of Moon 4.5 Gyrs - magma ocean, differentiation of core,
Geological Time How old is the Earth
 Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Station Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus
 Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
Station 1 1. Look at the fossil labeled # 16. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum c. Class d. Genus 2. Look at the fossil labeled #7. Identify each of the following: a. Kingdom b. Phylum
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION. 444 million years ago
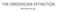 THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
THE ORDOVICIAN EXTINCTION 444 million years ago TOTAL GENERA THROUGH THE PHANEROZOIC ERA The Cambrian to the Present PERMIAN TRIASSIC CRETACEOUS Holocene The Present Miocene DEVONIAN ORDOVICIAN Mississippian
Module 9: Earth's History Topic 3 Content: A Tour of Geologic Time Notes
 The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
EARTH S HISTORY. What is Geology? logy: science. Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its:
 EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time.
 Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
Section 1: Fossils provide evidence of the change in organisms over time. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the similarities and differences between
Past Mass Extinctions
 Past Mass Extinctions Past Extinction/Causes Effects, future implications Major Events Pleistocene events Ordovician-Silurian extinction,, about 439 million years ago, caused by a drop in sea levels as
Past Mass Extinctions Past Extinction/Causes Effects, future implications Major Events Pleistocene events Ordovician-Silurian extinction,, about 439 million years ago, caused by a drop in sea levels as
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name:
 Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
Notes on Life & Geologic Time Name: S.W.B.A.T Explain how time can be divided into units Relate changes of Earth s to divisions on the geologic time scale Describe how plate tectonics affects Geologic
The light at the end of the tunnel is the oncoming 6 th Mass Extinction YOURS! And mankind is the primary cause
 The light at the end of the tunnel is the oncoming 6 th Mass Extinction YOURS! And mankind is the primary cause Preparing to live with climate change We all know what happened to the Dinosaurs 65 million
The light at the end of the tunnel is the oncoming 6 th Mass Extinction YOURS! And mankind is the primary cause Preparing to live with climate change We all know what happened to the Dinosaurs 65 million
LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts...
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts... Date: 19 April 2018 I. Time & Life on Earth geologic time scale o divided into named
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #25: Mega Disasters - Mass Extinctions, Meteorite Impacts... Date: 19 April 2018 I. Time & Life on Earth geologic time scale o divided into named
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
Earth & Earthlike Planets. David Spergel
 Earth & Earthlike Planets David Spergel Course Logistics Life Everywhere and Rare Earths are now in the U-Store Each precept will be divided into two teams (at this week s s precept). Debate topic: Are
Earth & Earthlike Planets David Spergel Course Logistics Life Everywhere and Rare Earths are now in the U-Store Each precept will be divided into two teams (at this week s s precept). Debate topic: Are
3. The diagram below shows how scientists think some of Earth's continents were joined together in the geologic past.
 1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
1. The map below shows the present-day locations of South America and Africa. Remains of Mesosaurus, an extinct freshwater reptile, have been found in similarly aged bedrock formed from lake sediments
Outline. Origin and History of Life
 Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Use Target Reading Skills
 The Geologic Time Scale (pp. 286 297) This section tells why the geologic time scale is used to show Earth s history, and what the organisms were like and the major events that happened in the different
The Geologic Time Scale (pp. 286 297) This section tells why the geologic time scale is used to show Earth s history, and what the organisms were like and the major events that happened in the different
Geologic Time. What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils?
 Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
Chapter 14 The History of Life
 Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change Section 2: The Origin of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 14.1 Fossil Evidence of Change Land Environments Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Gravity pulled
Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change Section 2: The Origin of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 14.1 Fossil Evidence of Change Land Environments Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Gravity pulled
5 HOW DO EARTH & LIFE INTERACT?
 5 HOW DO EARTH & LIFE INTERACT? In this four-part lecture, David Christian will explain what the biosphere is and discuss the interplay between life and the Earth. David will explain how astronomy, geology,
5 HOW DO EARTH & LIFE INTERACT? In this four-part lecture, David Christian will explain what the biosphere is and discuss the interplay between life and the Earth. David will explain how astronomy, geology,
MOR TIME TEACHERS. ONCE UPON A TIME Activity Overview BIG IDEA
 MOR TIME 04 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND The geologic time scale can be challenging for students to understand. This activity explores how scientists divide the Earth s long history
MOR TIME 04 Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND The geologic time scale can be challenging for students to understand. This activity explores how scientists divide the Earth s long history
5 EXTINCTION LEVEL EVENTS 1040L
 5 EXTINCTION LEVEL EVENTS 1040L EXTINCTION LEVEL EVENTS By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Life on Earth has seen several periods when a large portion of its species died off. Yet, they ve always
5 EXTINCTION LEVEL EVENTS 1040L EXTINCTION LEVEL EVENTS By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Life on Earth has seen several periods when a large portion of its species died off. Yet, they ve always
Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions
 Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions Measuring Diversity John Phillips produced the first estimates of Phanerozoic diversity in 1860, based on the British fossil record Intuitively it seems simple
Phanerozoic Diversity and Mass Extinctions Measuring Diversity John Phillips produced the first estimates of Phanerozoic diversity in 1860, based on the British fossil record Intuitively it seems simple
The History of Life. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries
 ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries Introduction to Natural Hazards Natural Hazards: Geological and climatic events that pose a threat to human populations, property and activities. Typically uncontrollable
ERTH20001 Dangerous Earth Lecture Summaries Introduction to Natural Hazards Natural Hazards: Geological and climatic events that pose a threat to human populations, property and activities. Typically uncontrollable
Historical Geology GEL 102 Syllabus Spring, 2015
 Historical Geology GEL 102 Syllabus Spring, 2015 Dr. Jacob Sewall sewall@kutztown.edu 484-646-5864 http://faculty.kutztown.edu/sewall Boehm Bldg. 422 Office hours: M: 10 12, T: 9:30 10 W: 10 12, TH: 9:30
Historical Geology GEL 102 Syllabus Spring, 2015 Dr. Jacob Sewall sewall@kutztown.edu 484-646-5864 http://faculty.kutztown.edu/sewall Boehm Bldg. 422 Office hours: M: 10 12, T: 9:30 10 W: 10 12, TH: 9:30
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 27 Dec
 Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Mesozoic Era 251 m.y.a 65.5 m.y.a
 Mesozoic Cenozoic notes.notebook Mesozoic & Cenozoic 251 m.y.a Present at the end of the Permian, 90% of marine organisms and more than 70% of land organisms died. because resources and space were readily
Mesozoic Cenozoic notes.notebook Mesozoic & Cenozoic 251 m.y.a Present at the end of the Permian, 90% of marine organisms and more than 70% of land organisms died. because resources and space were readily
 The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
Diversity, Change and Continuity. History of Life
 Diversity, Change and Continuity History of Life Change throughout the history of Life. A summary of content covered 1 2 3 4 Changes in the atmosphere Changes in climate Geological events Biogeography
Diversity, Change and Continuity History of Life Change throughout the history of Life. A summary of content covered 1 2 3 4 Changes in the atmosphere Changes in climate Geological events Biogeography
Fossils. Name Date Class. A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary
 Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Geological Timeline. Important EvEnts In the Earth s history
 Geological Timeline In this pack you will find information and activities to help your class grasp the concept of geological time, just how old our planet is, and just how young we, as a species, are.
Geological Timeline In this pack you will find information and activities to help your class grasp the concept of geological time, just how old our planet is, and just how young we, as a species, are.
Biodiversity Through Earth History
 Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Geologic Time. Early Earth History
 chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
chapter 10 3 Geologic Time section 2 Early Earth History Before You Read Think of a picture of a volcano you have seen. Describe what Earth would be like if the land were almost completely covered with
Page 143: Geologic Time
 Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
Geologic time. 8 th Grade
 + Geologic time 8 th Grade + Trilobites n Trilobites are small, hard-shelled animals that lived in ancient seas. Trilobites are considered to be index fossils. n Index fossils lived over vast regions of
+ Geologic time 8 th Grade + Trilobites n Trilobites are small, hard-shelled animals that lived in ancient seas. Trilobites are considered to be index fossils. n Index fossils lived over vast regions of
Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time. What is geologic time?
 Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time What is geologic time? The division of Earth s history into time units back to 4.6 b.y.a. Usually based on the life-forms that lived during certain periods May be based
Earth Science Ch. 14 Geologic Time What is geologic time? The division of Earth s history into time units back to 4.6 b.y.a. Usually based on the life-forms that lived during certain periods May be based
Cycles in the Phanerozoic
 Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Cycles in the Phanerozoic Evolutionary trends: extinctions, adaptive radiations, diversity over time Glaciations Sea level change Ocean chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 biosphere Mass extinctions in the..you
Natural Climate Variability: Longer Term
 Natural Climate Variability: Longer Term Natural Climate Change Today: Natural Climate Change-2: Ice Ages, and Deep Time Geologic Time Scale background: Need a system for talking about unimaginable lengths
Natural Climate Variability: Longer Term Natural Climate Change Today: Natural Climate Change-2: Ice Ages, and Deep Time Geologic Time Scale background: Need a system for talking about unimaginable lengths
Biodiversity Through Earth History. What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events?
 Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
Chapter Introduction. Chapter Wrap-Up. Explosion
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Chapter Wrap-Up Geologic Time Ancient Earth The Cambrian Explosion How have natural events changed Earth over time? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Chapter Wrap-Up Geologic Time Ancient Earth The Cambrian Explosion How have natural events changed Earth over time? What do you think? Before you begin,
GO ON. Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1.
 d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
d i a g n o s t i c t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e question 1. 1. What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth s layers? A crust, outer core, inner core, mantle B mantle,
HOW OLD IS THE EARTH ANYWAYS?
 HOW OLD IS THE EARTH ANYWAYS? EXAMINING THE CONCEPT OF GEOLOGIC TIME Did you ever wonder about all of the things that have ever happened on Earth and how old it really is? As it turns out, Mother Earth
HOW OLD IS THE EARTH ANYWAYS? EXAMINING THE CONCEPT OF GEOLOGIC TIME Did you ever wonder about all of the things that have ever happened on Earth and how old it really is? As it turns out, Mother Earth
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life
 Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils
 Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
Warm Up Name the 5 different types of fossils Timeline that organizes the events in Earths history. Earth is about 4.7 billion years old. More complex organism such as land plants and fish evolved only
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Chapter 19. History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5
 College Guild PO Box 6448, Brunswick ME 04011 SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5 1 Over the past three units we have learned about the birth of the universe, the laws of nature, and the structure
College Guild PO Box 6448, Brunswick ME 04011 SCIENCE SAMPLER ~ Geology ~ Unit 4 of 5 1 Over the past three units we have learned about the birth of the universe, the laws of nature, and the structure
Patterns of Evolution: A. Mass Extinctions. B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution. E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium
 : A. Mass Extinctions B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium 1 A. Mass Extinctions: Over the past 540 million years, life on Earth has passed
: A. Mass Extinctions B. Adaptive Radiation C. Convergent Evolution D. Coevolution E. Gradualism F. Punctuated Equilibrium 1 A. Mass Extinctions: Over the past 540 million years, life on Earth has passed
Earth s s Geologic History
 The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom
 The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Many questions regarding the origins and evolutionary history of the animal kingdom continue to be researched and debated, as new fossil
The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Many questions regarding the origins and evolutionary history of the animal kingdom continue to be researched and debated, as new fossil
1 The origin of life (pp )
 ST chapter only Checkup Chapter 10 1 The origin of life (pp. 300 305) 1. Earth took millions of years to form. a) Where did the matter that formed our planet come from? From a cloud of gas and dust that
ST chapter only Checkup Chapter 10 1 The origin of life (pp. 300 305) 1. Earth took millions of years to form. a) Where did the matter that formed our planet come from? From a cloud of gas and dust that
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Earth and Space Science Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Earth and Space Science for Achievement Standard 91188 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Earth and Space Science Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Earth and Space Science for Achievement Standard 91188 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Earth and Space Science Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment
4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth.
 Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
2/16/2015. After this lecture, you will be able to: Evolution, Biodiversity and Population Ecology. Natural selection
 Evolution, Biodiversity and Population Ecology After this lecture, you will be able to: Chapter 3 Explain the process of natural selection and cite evidence for this process Describe the ways in which
Evolution, Biodiversity and Population Ecology After this lecture, you will be able to: Chapter 3 Explain the process of natural selection and cite evidence for this process Describe the ways in which
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History
 Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
GEOL 02: Historical Geology Lab 12: The Mesozoic Dies
 Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
