YILGARN REGOLITH AND LANDSCAPE
|
|
|
- Hugh Dickerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short Course for Northern Star Resources YILGARN REGOLITH AND LANDSCAPE Mehrooz F Aspandiar Department of Applied Geology Western Australian School of Mines
2 The Yilgarn Craton surface regolith Image: Churhward & Anand, 2000
3 Regolith-landforms: Variable Regolith Fe saprolite Lateritic residuum Mottled saprolite saprolite Cenozoic sediments Mottled saprolite Photograph & Concept C. Butt
4 Relict Erosional Depositional Scheme R lateritic gravel and duricrust dominated terrane E Saprolite, shallow soil and bedrock dominated terrane D Sediment dominated terrane
5 Remote Sensing & Regolith-landforms 20 km Tertiary sediments Interface saprolite saprolite
6 Regolith-landforms of Northern Yilgarn From Anand & Butt (2010)
7 Main Phanerozoic Sediment relationships Transported regolith 4. Miocene gravelly sand 5. Miocene to Pliocene gravelly to sand variable sediments 6. Quaternary sand dunes Saprolite Bedrock 1. Permian boulder clays, grits, sandstone 2. Paleocene Wollabur gravel & sandstone 3. Miocene Perkolli shale (clays & lenses of gravel) From Anand & Butt (2010)
8 Stratigraphy of transported regolith in the Yilgarn Lithology Age Pleistocene Regolith Unit Hardpan Description Sandy clay to clay sand with Fe gravel Interpreted depositional environment Aeolian, fluvial, colluvial Pliocene Nodular ferricrete Fe gravel + clay Sandy clay with clay spherites Granule to pebble, hematite + maghemite Overbank deposits Fluvial, colluvial Early Eocene to Mid Miocene Permian Archean Megamottled clay Fe pisolitic clay Gravel + sand Mottled mudstone Sandstone Saprolite White to cream clay with quartz, kaolinite, lignite Grey clay with kaolinite, smectite Fe gravel & sand, vein quartz Mudstone to sandstone with conglomerate base Compiled from Dusci (1994), debrokert (2002), Anand et al. (2013) Overbank shallow wetland Fluvial channel Glacial outflow
9 Weathering history and landscape evolution - 1 Late Permian to Cretaceous extension weathering with stable landsurface conditions Late Cretaceous to Eocene drop in sea-levels (base level change) caused inset valleys to develop in the landscape with erosion After Anand & Butt (2010)
10 Weathering history and landscape evolution - 2 Mid Eocene - Miocene filling of inset valleys due higher sea-levels Saprolite Bedrock Mid-Miocene stable conditions favouring weathering Late Miocene to current local erosion and sedimentation and onset of aridity drop in water tables
11 Yilgarn Inset valley paleochannel fills Salt lakes Paleodrainage Trunk inset valley fill Trunk inset valley fill (inferred) After de Brokert (2002), compiled from Kern & Commander (1993)
12 Yilgarn Inset Valley Paleochannels - Magnetics RTP southeast of Laverton 1VD 30 km southeast of Laverton 6 km 6 km Paleochannel sediments that have maghemite bearing pisolites show up on magnetic survey images distributary channel form
13 Paleochannels (Inset-valley fills) Images: Ravi Anand
14 From Dusci (1994) Inset valley paleochannel fill stratigraphy Pliocene Mixed facies polymictic Fe gravel Mixed facies polymictic Fe gravel Oligo- Miocene Sandy-clay facies with Fe gravels Sandy-clay facies with Fe gravels Late Eocene Mega mottled clay facies White clay Grey to mega mottled clay facies Perkolilli shale Mega mottled clay Grey clay Middle Eocene Sand facies Sand facies Wollabur sandstone Quartz pebble Quartz pebble White clay Paleocene Hiatus Sand facies Precambrian
15 Late Cenozoic sediments & regolith Calcrete Late Cenzoic sediments Mottled ultramafic saprolite Slabby ferricrete Mottled sandy clay Stratigraphic column from Anand & Butt (2010)
16 Late Cenozoic sediments & regolith Vermiform ferricrete formd within pebbly clay sand sediments- unconformable over saprolite Slabby to nodular ferricrete in clay sediments
17 Pleistocene sediments - hardpan
18 Regolith-Landform relationships Erosional rises/low hills
19 Regolith-Landform relationships Erosional - Breakaways
20 Regolith-landform relationships Relief Inversion in landscapes
21 Profile modifications across the Yilgarn- Onset of aridity Profiles have mineralogical & geochemical characteristics of present climate superimposed on those from previous one Humid Iron oxides Acid Ferruginous duricrust, ferricrete Silica Acid Pedogenic silcrete Aluminosilicates Acid-nuetral Hardpan Silica Acid-neutral Hardpan, groundwater silcrete Carbonates, Alkaline Calcrete, gypcrete Arid Halides, sulfates Alkaline Evaporites in playas, soils Lowering of water-table Leaching of vadose zone under oxidizing & possibly saline conditions Dehydration of hardening of phases
22 Regolith Minerals Types, Nature & Significance
23 Types of regolith minerals Phyllosilicates or Clay Minerals (layer silicates) Smectites, kaolinite, illite, vermiculite & interstratified varieties of these Framework Silicates opal A & opal-ct, quartz Oxides & hydroxides of Fe, Mn, Al & Ti Geothite, hematite, maghemite (all Fe), gibbsite (Al), lithophorite (Mn) Sulfates - gypsum, jarosite, alunite Carbonates calcite, dolomite, magnesite Chlorides - halite Phosphates crandalite, florencite, plumbogummite
24 Regolith Minerals Fine Grained Mixtures 2 mic Most are very fine-grained (high surface areas) The fine size and crystal-chemical properties impart a dynamic nature to them hydrolyzable surfaces or functional groups = excellent adsorbers of elements flexibility in exchanging metals (cation exchange) Illite Hem 5nm
25 Why identify, quantify and understand regolith minerals? They provide clues to the physiochemical conditions of the regolith such as ph, Eh, temperature, drainage, presence of anions Present & past environments and processes They regulate trace and major element mobility in the regolith and therefore impact on geochemistry of regolith, groundwaters and surface waters Mineral Hosts According to a geochemist, to interpret most forms of geochemical data- three rules apply: mineralogy, mineralogy and mineralogy!
26 Iron oxide types and their formation conditions Hematite Fe 2 O 3 Red to reddish brown. Favoured under low water activity, low Al activity, high organic matter and high temperature. Forms due to transformation of ferrihydrite (rapid oxidation of Fe 2+ ) Goethite FeOOH Brownish-yellow. High water activity, high organic matter, high Al activity and low temperatures. Forms from oxidation of Fe 2+
27 Iron oxide types and their formation conditions Maghemite γ-fe 3 O 4 Dark brown to black. Magnetic. Forms by the oxidation of magnetite, or dehydration of lepidocrocite or heating of Fe hydroxides with organic matter. Highly weathered regolith & forest fires Lepidocrocite γ-feooh Orange-brown. Polymorph of goethite (different structure same composition). Forms by slow oxidation of Fe 2+. Found in seasonally anaerobic but non-calcerous soils by slow oxidation Magnetite Fe 3 O 4 Black. Magnetic. Inherited from parent rock or forms in reducing conditions or via magnetotactic bacteria. Submerged soils
28 Iron oxide formation, dissolution and transformations Once formed, iron oxides transform via two processes Via dissolution and reprecipitation as another oxide Via structural rearrangement of another oxide where the structure reorganizes to a new one Modified after Bigham et al (2001)
29 Minerals & regolith environments ph vs Anions The presence of specific minerals provides information on ph and type of dominant anion present in the system Modified Taylor & Eggleton
30 Minerals & regolith environments ph vs Eh (redox condition) Iron oxides, iron-sulfates, iron sulfides and carbonate minerals are indicators of ph and redox (oxidizing or reducing) conditions Sulfide weathering Acid sulfate soils Acid Mine Drainage Salt Lakes Wetlands Constructed drains Modified after Taylor & Eggleton (2001)
31 Minerals & regolith environments Profile Drainage (& Climate) Impeded or slow groundwater flow results in smectite-carbonategoethite association Free flow (well-drained) results in most stable assemblage -kaolinitehematite Need to consider climate and drainage together Well drained, dry Hematite + kaolinite + quartz e.g. smectites may indicate aridity and/or impeded drainage Magnesite Smectite + smectite Goethite
32 Regolith Environments Wet vs Dry Use iron oxides as indicators Goethite (yellow-brown) high water activity Hematite (red to dark red) low water activity This association provides wet vs dry environmental information on Micro fine mottles Profile brown mottles below red soil Landscape red crests versus yellow valleys Regional scale - red areas versus yellow 1m Hematite dominant Goethite dominant
33 Minerals & regolith environments Drainage & Landsacpe Local regolith environment is dictated by landscape position because landscape position controls drainage Generally, hill crests are drier because they are well drained Valleys are wetter because poorly drained
34 In Situ vs Transported Kaolinite Crystallinity Kaolinite crystallinity or disorder Kaolinite Crystallinity Index (KCI) determined via reflectance spectra (ASD or HyLogger) using kaolinite doublet In situ = well crystalline (ordered) Transported = poorly crystalline Saprolite Hardpan - colluvium However, not always true Saprock After Phang (2000)
INTRODUCTION TO REGOLITH GEOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO REGOLITH GEOLOGY Mehrooz F Aspandiar Department of Applied Geology Western Australian School of Mines What is Regolith? Regos cover Lithos - rock Crap on the surface! Chocolate icing on
INTRODUCTION TO REGOLITH GEOLOGY Mehrooz F Aspandiar Department of Applied Geology Western Australian School of Mines What is Regolith? Regos cover Lithos - rock Crap on the surface! Chocolate icing on
Beneath the sand of the Tanami Desert
 Beneath the sand of the Tanami Desert ARGA 2018, Wallaroo, SA Nadir de Souza Kovacs Ngururrpa program The program area covers the traditional land of the Parna Ngururrpa People in a remote part of the
Beneath the sand of the Tanami Desert ARGA 2018, Wallaroo, SA Nadir de Souza Kovacs Ngururrpa program The program area covers the traditional land of the Parna Ngururrpa People in a remote part of the
Cretes and Chemical Landscapes, South Australia
 5 th ARGA Conference Wallaroo, S.A. 8-12 April, 2018 Cretes and Chemical Landscapes, South Australia K.G. McQueen IAE, University of Canberra Physical and Chemical Landscapes Processes Landscapes erosion
5 th ARGA Conference Wallaroo, S.A. 8-12 April, 2018 Cretes and Chemical Landscapes, South Australia K.G. McQueen IAE, University of Canberra Physical and Chemical Landscapes Processes Landscapes erosion
GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA
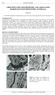 254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
254 GROUNDWATER GEOCHEMISTRY AND ASSOCIATED HARDPANS IN SOUTHWESTERN AUSTRALIA Sam Lee CRC LEME, Department of Applied Geology, Curtin University of Technology, Bentley, Western Australia, 6485 INTRODUCTION
MT. PERCY GOLD DEPOSIT AREA, WESTERN AUSTRALIA C.R.M. Butt CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102
 MT. PERCY GOLD DEPOSIT AREA, WESTERN AUSTRALIA C.R.M. Butt CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 Charles.Butt@csiro.au LOCATION The Mt Percy Gold Deposit is located two
MT. PERCY GOLD DEPOSIT AREA, WESTERN AUSTRALIA C.R.M. Butt CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 Charles.Butt@csiro.au LOCATION The Mt Percy Gold Deposit is located two
Sedimentary Geology. Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1
 Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Sedimentary Geology Strat and Sed, Ch. 1 1 Sedimentology vs. Stratigraphy Sedimentology is the study of the origin and classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks Mostly the physical and chemical
Geochemical exploration in regolithdominated terrains global perspective. Ravi Anand May 2014
 Geochemical exploration in regolithdominated terrains global perspective Ravi Anand May 2014 Acknowledgements Numerous mining companies CSIRO/CRC LEME/MDU AMIRA Why regolith research for mineral exploration
Geochemical exploration in regolithdominated terrains global perspective Ravi Anand May 2014 Acknowledgements Numerous mining companies CSIRO/CRC LEME/MDU AMIRA Why regolith research for mineral exploration
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes
 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Weathering Sedimentary Processes Breakdown of pre-existing rock by physical and chemical processes Transport Movement of sediments from environments of relatively high potential
Figure 1. Geological map of the Mt Magnet area (after Thompson et al., 1990). Figure 2. Simplified regolith landform map of the Mt Magnet
 Mt MAGNET DISTRICT, WESTERN AUSTRALIA R.R. Anand 1, J.D. King 2 and I.D.M. Robertson 1 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. Weston Consultancy Group, PO Box 64, Maylands,
Mt MAGNET DISTRICT, WESTERN AUSTRALIA R.R. Anand 1, J.D. King 2 and I.D.M. Robertson 1 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. Weston Consultancy Group, PO Box 64, Maylands,
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Nanoparticles in Soils
 Diversity of Natural Nanoparticles in Soils Joe B. Dixon Emeritus Professor of Soil Clay Mineralogy Soil and Crop Sciences Dept. Texas A&M University Ferrihydrite Structure update: Michel, et al., Science
Diversity of Natural Nanoparticles in Soils Joe B. Dixon Emeritus Professor of Soil Clay Mineralogy Soil and Crop Sciences Dept. Texas A&M University Ferrihydrite Structure update: Michel, et al., Science
LOCATION. Figure 1. Location of the Buckley River Lady Loretta study area; generalised geomorphic provinces of the Mt Isa region are included.
 LOCATION BUCKLEY RIVER LADY LORETTA DISTRICT, QUEENSLAND R.R. Anand 1, J. Wilford 2, C. Phang 1 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. CRC LEME, Geoscience Australia,
LOCATION BUCKLEY RIVER LADY LORETTA DISTRICT, QUEENSLAND R.R. Anand 1, J. Wilford 2, C. Phang 1 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. CRC LEME, Geoscience Australia,
REGOLITH GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE NORTH KIMBERLEY, WESTERN AUSTRALIA: A STRONG PROXY FOR BEDROCK
 REGOLITH GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE NORTH KIMBERLEY, WESTERN AUSTRALIA: A STRONG PROXY FOR BEDROCK Paul A. Morris 1 1 Geological Survey of Western Australia, 100 Plain Street, East Perth 6004, Western Australia;
REGOLITH GEOCHEMISTRY OF THE NORTH KIMBERLEY, WESTERN AUSTRALIA: A STRONG PROXY FOR BEDROCK Paul A. Morris 1 1 Geological Survey of Western Australia, 100 Plain Street, East Perth 6004, Western Australia;
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Lecture 6. Physical Properties. Solid Phase. Particle Composition
 Lecture 6 Physical Properties Solid Phase Particle Composition 1 Questions What are tetrahedrons and octahedrons? How do silica tetrahedra bonds affect mineral weathering? Difference between primary and
Lecture 6 Physical Properties Solid Phase Particle Composition 1 Questions What are tetrahedrons and octahedrons? How do silica tetrahedra bonds affect mineral weathering? Difference between primary and
residuum resulting from weathering over an extended period of time has vertical layers called soil profile from surface down to fresh parent material
 Soil residuum resulting from weathering over an extended period of time has vertical layers called soil profile from surface down to fresh parent material time to develop soil profile varies with intensity
Soil residuum resulting from weathering over an extended period of time has vertical layers called soil profile from surface down to fresh parent material time to develop soil profile varies with intensity
Sediment. Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface
 Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Chapter 6 9/25/2012. Weathering, Erosion and Soils. Introduction. How Are Earth Materials Altered? Introduction. How Are Earth Materials Altered?
 Chapter 6 Introduction Rocks and minerals are disintegrated and decomposed by the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering. Weathering, Erosion and Soils This breakdown occurs because the parent
Chapter 6 Introduction Rocks and minerals are disintegrated and decomposed by the processes of mechanical and chemical weathering. Weathering, Erosion and Soils This breakdown occurs because the parent
Chapter 3 Sedimentation of clay minerals
 Chapter 3 Sedimentation of clay minerals 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land 3.2 From land to sea 3.3 Clay sedimentation in the sea 1 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land Deserts Glaciers Rivers Lacustrine 2 University
Chapter 3 Sedimentation of clay minerals 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land 3.2 From land to sea 3.3 Clay sedimentation in the sea 1 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land Deserts Glaciers Rivers Lacustrine 2 University
Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces. & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry
 Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry 3. charge transfer (e.g., ligand/donor sorption): Sorption involves a number of related processes that all
Lecture 13 More Surface Reactions on Mineral Surfaces & Intro to Soil Formation and Chemistry 3. charge transfer (e.g., ligand/donor sorption): Sorption involves a number of related processes that all
Rocks Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3
 Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification VI. Additional sub-classes
Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification VI. Additional sub-classes
Rocks Environmental Significance. Rocks Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3. Rocks Definition of a rock
 Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 Environmental Significance I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification
Reading this week: Ch. 2 and App. C Reading for next week: Ch. 3 Environmental Significance I. Environmental significance II. Definition III. 3 major classes IV. The Rock Cycle V. Secondary classification
Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record. John Grotzinger
 Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record John Grotzinger Modern Mars: Recurring Slope Lineae McEwan et al., 2014 Mars Timeline: Water-related environments Ehlmann et al., 2011,
Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record John Grotzinger Modern Mars: Recurring Slope Lineae McEwan et al., 2014 Mars Timeline: Water-related environments Ehlmann et al., 2011,
Lecture 29: Soil Formation
 Lecture 29: Soil Formation Factors Controlling Soil Formation 1. Parent material: Soil precursor 2. Climate: Temperature and precipitation 3. Biota: Native vegetation, microbes, soil animals, humans 4.
Lecture 29: Soil Formation Factors Controlling Soil Formation 1. Parent material: Soil precursor 2. Climate: Temperature and precipitation 3. Biota: Native vegetation, microbes, soil animals, humans 4.
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Figure 2. Location map of Harmony in the Peak Hill Mining District, showing the surrounding ranges and main roads.
 HARMONY-PEAK HILL GOLD DEPOSIT, WESTERN AUSTRALIA I.D.M. Robertson, C. Phang and T.J. Munday CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 Ian.Robertson@csiro.au INTRODUCTION The
HARMONY-PEAK HILL GOLD DEPOSIT, WESTERN AUSTRALIA I.D.M. Robertson, C. Phang and T.J. Munday CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 Ian.Robertson@csiro.au INTRODUCTION The
Geology 252, Historical Geology, California State University, Los Angeles - professor: Dr. Alessandro Grippo
 LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
LAB # 1 - CLASTIC ROCKS Background: - Mechanical and Chemical Weathering - Production of Clastic Sediment - Classification of Sediment according to size: Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay - Erosion, Transportation
14. Weathering and Regolith
 The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Weathering and Regolith 123 14. Weathering and Regolith The regolith consists of the zone at the Earth's surface between fresh rock and the interface with
The Australian Continent: A Geophysical Synthesis Weathering and Regolith 123 14. Weathering and Regolith The regolith consists of the zone at the Earth's surface between fresh rock and the interface with
GRAVITY. Raymond M. Tracey and Nicholas G. Direen
 GRAVITY Raymond M. Tracey and Nicholas G. Direen Geoscience Australia. PO Box 378, Canberra, ACT 2601. E-mail: ray.tracey@ga.gov.au, nick.direen@ga.gov.au 1. DESCRIPTION Gravity surveys measure variations
GRAVITY Raymond M. Tracey and Nicholas G. Direen Geoscience Australia. PO Box 378, Canberra, ACT 2601. E-mail: ray.tracey@ga.gov.au, nick.direen@ga.gov.au 1. DESCRIPTION Gravity surveys measure variations
Soil Colloidal Chemistry. Compiled and Edited by Dr. Syed Ismail, Marthwada Agril. University Parbhani,MS, India
 Soil Colloidal Chemistry Compiled and Edited by Dr. Syed Ismail, Marthwada Agril. University Parbhani,MS, India 1 The Colloidal Fraction Introduction What is a colloid? Why this is important in understanding
Soil Colloidal Chemistry Compiled and Edited by Dr. Syed Ismail, Marthwada Agril. University Parbhani,MS, India 1 The Colloidal Fraction Introduction What is a colloid? Why this is important in understanding
STUDY OF LATERITES AROUND TALMOD, MAHARASHTRA STATE, INDIA
 STUDY OF LATERITES AROUND TALMOD, MAHARASHTRA STATE, INDIA Vadagbalkar Shrinivas Krishnaji Department of Geology, D.B.F. Dayanand College of Arts and Science, Solapur-413002, Maharashtra State, INDIA (Email:
STUDY OF LATERITES AROUND TALMOD, MAHARASHTRA STATE, INDIA Vadagbalkar Shrinivas Krishnaji Department of Geology, D.B.F. Dayanand College of Arts and Science, Solapur-413002, Maharashtra State, INDIA (Email:
Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream as it enters a lake. At which points along the stream are erosion and deposition dominant?
 1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
A few more details on clays, Soil Colloids and their properties. What expandable clays do to surface area. Smectite. Kaolinite.
 A few more details on clays, Soil Colloids and their properties What expandable clays do to surface area Kaolinite Smectite Size 0.5-5 µm External surface 10-30 m 2 /g Internal surface - Size 0.1-1 µm
A few more details on clays, Soil Colloids and their properties What expandable clays do to surface area Kaolinite Smectite Size 0.5-5 µm External surface 10-30 m 2 /g Internal surface - Size 0.1-1 µm
Landscapes & Hydric Soils Bruce Vasilas University of Delaware
 Landscapes & Hydric Soils Bruce Vasilas University of Delaware Hydric soils are defined as soils that formed under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding long enough during the growing season to
Landscapes & Hydric Soils Bruce Vasilas University of Delaware Hydric soils are defined as soils that formed under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding long enough during the growing season to
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Mechanical & Chemical Weathering. Sediments. Lithification. Deposition. Transport. Erosion.
 Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
UNRAVELLING THE REGOLITH WITH GEOCHEMISTRY
 UNRAVELLING THE REGOLITH WITH GEOCHEMISTRY Kenneth G. McQueen CRC LEME, Department of Earth and Marine Sciences, Australian National University, ACT, 0200 INTRODUCTION Geochemical data from the regolith
UNRAVELLING THE REGOLITH WITH GEOCHEMISTRY Kenneth G. McQueen CRC LEME, Department of Earth and Marine Sciences, Australian National University, ACT, 0200 INTRODUCTION Geochemical data from the regolith
WEATHERING-CONTROLLED FRACTIONATION OF ORE AND PATHFINDER ELEMENTS AT COBAR, NSW
 296 WEATHERING-CONTROLLED FRACTIONATION OF ORE AND PATHFINDER ELEMENTS AT COBAR, NSW Kenneth G. McQueen 1,2 & Dougal C. Munro 1 1 CRC LEME, Department of Geology, Australian National University, ACT, 0200
296 WEATHERING-CONTROLLED FRACTIONATION OF ORE AND PATHFINDER ELEMENTS AT COBAR, NSW Kenneth G. McQueen 1,2 & Dougal C. Munro 1 1 CRC LEME, Department of Geology, Australian National University, ACT, 0200
Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time
 Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time A rock is any naturally formed, nonliving, coherent aggregate mass of solid matter that constitutes part of a planet, asteroid, moon, or other planetary
Sedimentary Rocks, Stratigraphy, and Geologic Time A rock is any naturally formed, nonliving, coherent aggregate mass of solid matter that constitutes part of a planet, asteroid, moon, or other planetary
Sediments and. Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks Bottom Line Sedimentary rocks form from particles accumulated in sedimentary layers Sedimentary layers can be formed by clastic or detrital particles (e.g., sand grains,
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks Bottom Line Sedimentary rocks form from particles accumulated in sedimentary layers Sedimentary layers can be formed by clastic or detrital particles (e.g., sand grains,
Uranium in the Frome Embayment: Recent results from Geoscience Australia s Onshore Energy Security Program
 Uranium in the Frome Embayment: Recent results from Geoscience Australia s Onshore Energy Security Program Simon van der Wielen A. Britt, E. Bastrakov, A. Cross, S. Jaireth, M. Le Gleuher, A. Schofield,
Uranium in the Frome Embayment: Recent results from Geoscience Australia s Onshore Energy Security Program Simon van der Wielen A. Britt, E. Bastrakov, A. Cross, S. Jaireth, M. Le Gleuher, A. Schofield,
Alicja M Lacinska, Michael T Styles. British Geological Survey. NERC All rights reserved
 Silicified serpentinite and the Barzaman Formation in the United Arab Emirates: a natural analogue for CO 2 sequestration through mineral carbonation of ultramafic rocks. Alicja M Lacinska, Michael T Styles
Silicified serpentinite and the Barzaman Formation in the United Arab Emirates: a natural analogue for CO 2 sequestration through mineral carbonation of ultramafic rocks. Alicja M Lacinska, Michael T Styles
WEATHERING OF SULFIDE MINE TAILING IMPOUNDMENT O. LINTNEROVÁ
 WEATHERING OF SULFIDE MINE TAILING IMPOUNDMENT O. LINTNEROVÁ Comenius University Faculty of Science, Department of Mineral Deposits Geology, Mlynská dolina G, 842 15 Bratislava, Slovakia; lintnerova@fns.uniba.sk
WEATHERING OF SULFIDE MINE TAILING IMPOUNDMENT O. LINTNEROVÁ Comenius University Faculty of Science, Department of Mineral Deposits Geology, Mlynská dolina G, 842 15 Bratislava, Slovakia; lintnerova@fns.uniba.sk
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks
 GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
Understanding Mineralogical Composition, Weathering, and Alteration, to Manage ML/ARD in a Base-Metal Tailings Storage Facility
 Understanding Mineralogical Composition, Weathering, and Alteration, to Manage ML/ARD in a Base-Metal Tailings Storage Facility Jennifer L. Durocher Lindsay A. Robertson Outline: Background Project Objectives
Understanding Mineralogical Composition, Weathering, and Alteration, to Manage ML/ARD in a Base-Metal Tailings Storage Facility Jennifer L. Durocher Lindsay A. Robertson Outline: Background Project Objectives
GOURDIS AND EMPIRE LATERITIC GOLD DEPOSITS, WESTERN AUSTRALIA
 GOURDIS AND EMPIRE LATERITIC GOLD DEPOSITS, WESTERN AUSTRALIA INTRODUCTION M.D. Paine1 and M.F.P. Foo2 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. 20 Hibbertia Court, Forrest
GOURDIS AND EMPIRE LATERITIC GOLD DEPOSITS, WESTERN AUSTRALIA INTRODUCTION M.D. Paine1 and M.F.P. Foo2 1. CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, PO Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 2. 20 Hibbertia Court, Forrest
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Mechanisms
 Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
Monument Valley, Utah. What weathering processes contributed to the development of these remarkable rock formations? Weathering Includes Physical, Chemical, Biological processes WEATHERING CHAPTER 7 Weathering
FROM LITTLE THINGS BIG THINGS GROW: RECONSTRUCTING PAST ENVIRONMENTS FROM QUATERNARY DESERT DUNE SEDIMENTS AND STRATIGRAPHY
 102 FROM LITTLE THINGS BIG THINGS GROW: RECONSTRUCTING PAST ENVIRONMENTS FROM QUATERNARY DESERT DUNE SEDIMENTS AND STRATIGRAPHY Kathryn E. Fitzsimmons CRC LEME, Department of Earth and Marine Sciences,
102 FROM LITTLE THINGS BIG THINGS GROW: RECONSTRUCTING PAST ENVIRONMENTS FROM QUATERNARY DESERT DUNE SEDIMENTS AND STRATIGRAPHY Kathryn E. Fitzsimmons CRC LEME, Department of Earth and Marine Sciences,
ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION
 Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
Name: Miramar College Grade: GEOL 101 - Physical Geology Laboratory SEDIMENTARY ROCK CLASSIFICATION AND IDENTIFICATION PRELAB SECTION To be completed before labs starts: I. Introduction & Purpose: The
Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
 Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20
 Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Minerals and Rocks Chapter 20 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
CLASS EXERCISE 5.1 List processes occurring in soils that cause changes in the levels of ions.
 5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas
 Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas Written By: Steven D.J. Baumann G-102010-1A Outcrop looking southeast Photo taken by: Steven Baumann on 10-20-2010
Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas Written By: Steven D.J. Baumann G-102010-1A Outcrop looking southeast Photo taken by: Steven Baumann on 10-20-2010
Weathering Cycle Teacher Notes
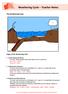 The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
The Weathering Cycle Stages of the Weathering Cycle: 1. Carbon Dioxide and Water In clouds, carbon dioxide reacts with water to form a weak acid. H 2 O + CO 2 --> H 2 CO 3 H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3-2. Acid
3D model of a Supergene Gold Deposit derived from Spectral Mapping
 3D model of a Supergene Gold Deposit derived from Spectral Mapping Exploration Technologies 2011 Scott Halley ABSTRACT: A 3D MODEL OF A SUPERGENE GOLD DEPOSIT CREATED FROM SPECTRALLY DERIVED MINERALOGY
3D model of a Supergene Gold Deposit derived from Spectral Mapping Exploration Technologies 2011 Scott Halley ABSTRACT: A 3D MODEL OF A SUPERGENE GOLD DEPOSIT CREATED FROM SPECTRALLY DERIVED MINERALOGY
Pre-Lab Reading Questions ES202
 ES202 The are designed to encourage students to read lab material prior to attending class during any given week. Reading the weekly lab prior to attending class will result in better grade performance
ES202 The are designed to encourage students to read lab material prior to attending class during any given week. Reading the weekly lab prior to attending class will result in better grade performance
Epstein, S. and Yapp, C.J. (1977) Isotope tree thermometers, Nature 266, 477.
 1 Crayton J. Yapp PUBLICATIONS in refereed journals: Epstein, S., Yapp, C.J. and Hall, J.H. (1976) The determination of the D/H ratio of nonexchangeable hydrogen in cellulose extracted from aquatic and
1 Crayton J. Yapp PUBLICATIONS in refereed journals: Epstein, S., Yapp, C.J. and Hall, J.H. (1976) The determination of the D/H ratio of nonexchangeable hydrogen in cellulose extracted from aquatic and
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
Minerals and Rocks. Environmental Learning Community CORC 1332 Sept 21, 2010
 Minerals and Rocks Environmental Learning Community CORC 1332 Sept 21, 2010 Outline Quiz More on minerals Twinkies Rocks How can you identify one mineral from another? Distinguishing One Mineral from Another
Minerals and Rocks Environmental Learning Community CORC 1332 Sept 21, 2010 Outline Quiz More on minerals Twinkies Rocks How can you identify one mineral from another? Distinguishing One Mineral from Another
G470/570 Regional Landscapes of Oregon Basics of Soils and Rock Weathering
 G470/570 Regional Landscapes of Oregon Basics of Soils and Rock Weathering I. SOIL BASICS A. Soils Defined 1. Soils represent the weathered mantle of unconsolidated surficial material that covers land
G470/570 Regional Landscapes of Oregon Basics of Soils and Rock Weathering I. SOIL BASICS A. Soils Defined 1. Soils represent the weathered mantle of unconsolidated surficial material that covers land
MEMO. TO: Dennis Lapoint CC: FROM: Eriaan Wirosono DATE: April, 20 th 2014 SUBJECT: Exploration activity report March-April 2014_EW
 TO: Dennis Lapoint CC: FROM: Eriaan Wirosono DATE: April, 20 th 2014 SUBJECT: Exploration activity report March-April 2014_EW MEMO 1. Highlights and Productivity Overview pan sampling on target Areas 1
TO: Dennis Lapoint CC: FROM: Eriaan Wirosono DATE: April, 20 th 2014 SUBJECT: Exploration activity report March-April 2014_EW MEMO 1. Highlights and Productivity Overview pan sampling on target Areas 1
Michigan s Geology and Groundwater
 Michigan s Geology and Groundwater Ralph J. Haefner Deputy Director U.S. Geological Survey Michigan-Ohio Water Science Center Lansing, Michigan Outline About the USGS Geology 101 Michigan s geology Bedrock
Michigan s Geology and Groundwater Ralph J. Haefner Deputy Director U.S. Geological Survey Michigan-Ohio Water Science Center Lansing, Michigan Outline About the USGS Geology 101 Michigan s geology Bedrock
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
About Earth Materials
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 3: EARTH MATERIALS Minerals and Rocks 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company About Earth Materials All Earth materials are composed of atoms bound
A study of the variation in the Rooikoppie gravels in the Lower Vaal area
 A study of the variation in the Rooikoppie gravels in the Lower Vaal area A study of the variation in the Rooikoppie gravels in the Lower Vaal area M. Ndwammbi Rockwell Diamonds Inc The Rooikoppie gravel
A study of the variation in the Rooikoppie gravels in the Lower Vaal area A study of the variation in the Rooikoppie gravels in the Lower Vaal area M. Ndwammbi Rockwell Diamonds Inc The Rooikoppie gravel
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite. An arrangement of atoms such as the one shown in the diagram determines
1. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents a part of the crystal structure of the mineral kaolinite. An arrangement of atoms such as the one shown in the diagram determines
Emily and Megan. Earth System Science. Elements of Earth by weight. Crust Elements, by weight. Minerals. Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight
 Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Emily and Megan Chapter 20 MINERALS AND ROCKS Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Elements of Earth by weight Made of atoms Earth
Mechanical Weathering
 Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface. Erosion is the incorporation and transportation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice. Geologists
CET Discovery Day. Mulga Rock Project The Ambassador, Emperor and Shogun discoveries. 24 February Xavier Moreau GM Geology & Exploration
 CET Discovery Day Mulga Rock Project The Ambassador, Emperor and Shogun discoveries 24 February 2015 Xavier Moreau GM Geology & Exploration Mulga Rock Uranium Project Presentation Outline: 1. Context behind
CET Discovery Day Mulga Rock Project The Ambassador, Emperor and Shogun discoveries 24 February 2015 Xavier Moreau GM Geology & Exploration Mulga Rock Uranium Project Presentation Outline: 1. Context behind
WEATHERING. Weathering breakdown of rock materials Erosion transport of broken-down materials
 WEATHERING the interacting physical, chemical & biological processes that progressively alter the original lithologic character of rocks to produce secondary minerals (e.g. clays) & unconsolidated regolith
WEATHERING the interacting physical, chemical & biological processes that progressively alter the original lithologic character of rocks to produce secondary minerals (e.g. clays) & unconsolidated regolith
A synopsis of the channel iron deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia
 A synopsis of the channel iron deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia E. R. Ramanaidou and R. C. Morris Erick Raymond Ramanaidou Minerals Down Under Flagship CSIRO ARRC PO Box 1130 Bentley
A synopsis of the channel iron deposits of the Hamersley Province, Western Australia E. R. Ramanaidou and R. C. Morris Erick Raymond Ramanaidou Minerals Down Under Flagship CSIRO ARRC PO Box 1130 Bentley
UNDERSTANDING THE REGOLITH IN TROPICAL AND SUB-TROPICAL TERRAINS: THE KEY TO EXPLORATION UNDER COVER.
 UNDERSTANDING THE REGOLITH IN TROPICAL AND SUB-TROPICAL TERRAINS: THE KEY TO EXPLORATION UNDER COVER. C.R.M. Butt Cooperative Research Centre for Landscape Environments and Mineral Exploration CSIRO Exploration
UNDERSTANDING THE REGOLITH IN TROPICAL AND SUB-TROPICAL TERRAINS: THE KEY TO EXPLORATION UNDER COVER. C.R.M. Butt Cooperative Research Centre for Landscape Environments and Mineral Exploration CSIRO Exploration
Chapter 6. Weathering, Erosion, and Soil
 Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
Chapter 6 Weathering, Erosion, and Soil Introduction Rocks and minerals disintegrate and decompose by the processes of physical and chemical weathering. This breakdown occurs because the parent material
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
PREDICTION OF ACID MINE DRAINAGE POTENTIAL FROM COAL MINES
 PREDICTION OF ACID MINE DRAINAGE POTENTIAL FROM COAL MINES Arthur W. Rose, Professor of Geochemistry Eugene G. Williams, Professor of Geology Richard R. Parizek, Professor of Hydrogeology Acid mine drainage
PREDICTION OF ACID MINE DRAINAGE POTENTIAL FROM COAL MINES Arthur W. Rose, Professor of Geochemistry Eugene G. Williams, Professor of Geology Richard R. Parizek, Professor of Hydrogeology Acid mine drainage
The Geochemistry of Natural Waters
 The Geochemistry of Natural Waters Surface and Groundwater Environments Third Edition James I. Drever University of Wyoming Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River. NJ 07458 Contents 3 Preface xi 1 The Hydrologie
The Geochemistry of Natural Waters Surface and Groundwater Environments Third Edition James I. Drever University of Wyoming Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River. NJ 07458 Contents 3 Preface xi 1 The Hydrologie
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs. LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes Last week we covered the basic types of rocks and the rock cycle. This lab concentrates on sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks have special
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 2: Sedimentary rocks and processes Last week we covered the basic types of rocks and the rock cycle. This lab concentrates on sedimentary rocks. Sedimentary rocks have special
APPENDIX G GLOSSARY. Mn/DOT/WR-0200
 APPENDIX G GLOSSARY Mn/DOT/WR-0200 Alluvial - comprised of clay, silt, sand, gravel, and/or other detritus deposited by water. Usually refers to accretionary overbank, floodplain or levee deposits. Biomantling
APPENDIX G GLOSSARY Mn/DOT/WR-0200 Alluvial - comprised of clay, silt, sand, gravel, and/or other detritus deposited by water. Usually refers to accretionary overbank, floodplain or levee deposits. Biomantling
GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY AND EXPLORATION OF MINERAL DEPOSITS IN DEEPLY WEATHERED TERRAINS. Estela Nascimento & John Barr
 GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY AND EXPLORATION OF MINERAL DEPOSITS IN DEEPLY WEATHERED TERRAINS Estela Nascimento & John Barr SIMEXMIN BRAZIL, MAY 2014 OVERVIEW Geology & Geochemistry of Mineralization in Areas
GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY AND EXPLORATION OF MINERAL DEPOSITS IN DEEPLY WEATHERED TERRAINS Estela Nascimento & John Barr SIMEXMIN BRAZIL, MAY 2014 OVERVIEW Geology & Geochemistry of Mineralization in Areas
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Chapter 4 Implications of paleoceanography and paleoclimate
 Age ka / Chapter 4 Implications of paleoceanography and paleoclimate 4.1 Paleoclimate expression 4.2 Implications of paleocirculation and tectonics 4.3 Paleoenvironmental reconstruction MD05-2901 (Liu
Age ka / Chapter 4 Implications of paleoceanography and paleoclimate 4.1 Paleoclimate expression 4.2 Implications of paleocirculation and tectonics 4.3 Paleoenvironmental reconstruction MD05-2901 (Liu
Maggie Payne Jim Turenne
 Maggie Payne Jim Turenne USDA-NRCS 60 Quaker Lane, Suite 46 Warwick, RI. 02886 401-822-8832 maggie.payne@ri.usda.gov U.S. Department of Agriculture 1935: Soil Conservation Service (SCS) Natural Resources
Maggie Payne Jim Turenne USDA-NRCS 60 Quaker Lane, Suite 46 Warwick, RI. 02886 401-822-8832 maggie.payne@ri.usda.gov U.S. Department of Agriculture 1935: Soil Conservation Service (SCS) Natural Resources
WEATHERING. Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions 10/22/2012
 WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
WEATHERING Turning Rock to Sediment and Solutions Igneous rocks form at high temperatures; at the Earth s surface they are chemically unstable and will begin to disintegrate and decompose in a process
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69
 EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Facies Cryptic description Depositional processes Depositional environments Very well sorted. Desert dunes. Migration of straight crested mega ripples
 Very well sorted Travelled grate distance, effective sorting 5 medium-grained sandstone with well rounded grains; large scale high angle planar cross-beds. Migration of straight crested mega ripples Desert
Very well sorted Travelled grate distance, effective sorting 5 medium-grained sandstone with well rounded grains; large scale high angle planar cross-beds. Migration of straight crested mega ripples Desert
A. IGNEOUS Rocks formed by cooling and hardening of hot molten rock called magma (within crust or at its surface).
 EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks
 Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks. Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring.
 Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring. Sedimentary rocks give us evidence to earth s earlier history. We look at processes happening
Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring. Sedimentary rocks give us evidence to earth s earlier history. We look at processes happening
Jim Turenne. Soils on Social Media
 Jim Turenne USDA-NRCS 60 Quaker Lane, Suite 46 Warwick, RI. 02886 401-822-8832 Jim.turenne@ri.usda.gov Soils on Social Media www.twitter.com/soilsne www.fb.com/soilsne www.nesoil.com U.S. Department of
Jim Turenne USDA-NRCS 60 Quaker Lane, Suite 46 Warwick, RI. 02886 401-822-8832 Jim.turenne@ri.usda.gov Soils on Social Media www.twitter.com/soilsne www.fb.com/soilsne www.nesoil.com U.S. Department of
Crust Elements. Elements of Earth. Minerals. Crystals. Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air
 Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Emily and Megan Earth System Science Interconnected Rocks and minerals Interior processes Erosion and deposition Water and air Made of atoms Earth is mostly iron, by weight Elements of Earth Made of atoms
Geology 229 Engineering Geology. Lecture 6. Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Variations in the Rus Formation
 Variations in the Rus Formation The Need for Consistent Core Logging Sallie Vest Halcrow / CH2M Hill 7 Nov 2012- TIME Not exposed at ground surface Umm Er- Raduh ma Paleogen e Eocene Damma m Cenozoic Oligoce
Variations in the Rus Formation The Need for Consistent Core Logging Sallie Vest Halcrow / CH2M Hill 7 Nov 2012- TIME Not exposed at ground surface Umm Er- Raduh ma Paleogen e Eocene Damma m Cenozoic Oligoce
GEOCHEMICAL DISPERSION, PROCESS AND EXPLORATION MODELS
 GEOCHEMICAL DISPERSION, PROCESS AND EXPLORATION MODELS C.R.M. Butt CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, P.O. Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 INTRODUCTION The surface geochemical signature of each mineral
GEOCHEMICAL DISPERSION, PROCESS AND EXPLORATION MODELS C.R.M. Butt CRC LEME, CSIRO Exploration and Mining, P.O. Box 1130, Bentley, WA 6102 INTRODUCTION The surface geochemical signature of each mineral
Weathering & Soil. Chpt 6
 Weathering & Soil Chpt 6 Some important processes that break-down and transport solid material at the Earth s surface Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the
Weathering & Soil Chpt 6 Some important processes that break-down and transport solid material at the Earth s surface Weathering the physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock Mass wasting the
Lecture 11: Non-Carbonate Biogenic and Chemical Sedimentary Rocks
 Lecture 11: Non-Carbonate Biogenic and Chemical Sedimentary Rocks Siliceous Sediments & Chert Phosphorites Evaporites Banded Iron Siliceous Sedimentary Rocks Fine-grained, dense, hard rocks composed predominantly
Lecture 11: Non-Carbonate Biogenic and Chemical Sedimentary Rocks Siliceous Sediments & Chert Phosphorites Evaporites Banded Iron Siliceous Sedimentary Rocks Fine-grained, dense, hard rocks composed predominantly
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p )
 13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
GLS100-01 Quiz#7 chapters 5 and 6 Fall 2009 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Clay minerals formed from gabbro or diorite bedrock
