Quiz # How did the genus Homo differ from the earlier hominins? How did it s skull differ? How did its limb bones differ?
|
|
|
- Theodora Wilkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physical Anthropology Dr. Leanna Wolfe Quiz #13 Chapter 9 The Rise of Modern Humans 1. How did the genus Homo differ from the earlier hominins? How did it s skull differ? How did its limb bones differ? 2. When was the middle Pleistocene? The late Pleistocene? 3. The Mauer mandible is associated with a. H. neandertalensis b. H. heidelbergensis c. H. erectus d. H. sapiens 4. What is the difference between Homo erectus and Homo ergaster? 5. Physically, how did H. ergaster differ from the earlier hominins? 6. T/F There were two distinct hominid species present in Asia in the latter part of the middle Pleistocene. 7. T/F H. ergaster could run for long distances. 8. What is the H. ergaster tool tradition called? a. Oldowan b. Mousterian c. Acheulean d. Neandertalean e. Chatelperronian 9. What might hand axes been used for? 10. What sorts of tools might archaic H. sapiens made from organic materials? 11. What happened to the world s climate during the middle Pleistocene?
2 2 12. T/F Homo ergaster was likely to have been the first hominid to use fire in a controlled manner. 13.What were the likely uses of fire? 14. T/F From the neck down Homo erectus was essentially like modern humans. 15. Where was H. heidelbergensis found? a. Heidelberg, Germany b. Germany and France c. all over Europe d. all over the Old World 16. Why did H. erectus (Asia) and H. ergaster (Africa) have different kinds of tools? 17. T/F H. heidelbergensis may have co-existed with H. erectus in Asia. 18. When and where was the first Neanderthal discovered? What was it considered to be? 19. Neanderthals have been considered (select those that apply) a.archaic sapiens b. a subspecies of H. erectus c. a dead-end branch of human evolution d. a form of modern H. sapiens 20. During what period of time did Neanderthals live? Where did Neanderthals live? 21. T/F Neanderthal brains were somewhat smaller than the brains of modern humans. 22. How did Neanderthal bodies compare to those of modern humans? 23. How did Neanderthals treat their elderly and their dead? 24. T/F Neandertals buried their dead with elaborate grave goods. 25. What is the Neandertal tool tradition called? a. Aurignacian b. Mousterian c. Acheulean d. Neandertalean e. Chatelperronian 26. T/F Neandertals were skilled hunters. 27. T/F Neandertals evolved into the modern Europeans of today. 28. T/F Neandertals interbred with other early modern humans.
3 3 29. T/F DNA evidence was used to establish that Neandertals were not our ancestors. 30. T/F Like living humans, there is relatively little diversity in their mitochondrial DNA. 31. What color skin and hair did Neandertals living in Sidron Spain have? 32. T/F Neandertal life expectancy was about 45 years. 33. T/F Neandertals were just as capable of producing symbolic cultures as other early modern humans. 34. What anatomical differences are there between Neandertals and modern day humans? 35. T/F Neandertal newborns were similar in brain size to modern humans but may have matured somewhat faster. 36. Many Neanderthals 80% suffered trauma during their lives. 37. What evidence is there that a Neandertal might have healed from a wound? 38. T/F Most of the injuries sustained by the Neandertals do not seem to reflect deliberate violence. 39. What evidence is there that Neandertals cared for one another? 40. T/F It is only in recent times that human groups have cared for injured and aging members. 41. T/F Most Neandertals used their front teeth as cutting tools. 42. T/F It s likely that Neandertals were cannibals. 43. The postcranial skeleton of the Neandertals was compared with that of modern humans. a. small b. the same size c. massive d. more gracile 44. Which of the following best describes the lumper s perspective? a. Neandertals represent one of many distinct Middle Paleolithic hominid species. b. Archaic H. sapiens are actually members of the species H. heidelbergensis. c. Neandertals and archaic H. sapiens were all part of one potentially interbreeding species. d. Neandertals and archaic H. sapiens could not and did not interbreed.
4 4 Rethinking Neandertals and Modern Humans 1. T/F The collision between H. sapiens and Neandertals happened many times. 2. T/F The Neandertals were neither stupid nor easily driven to extinction. 3. How long have there been modern humans? 4. How big were Neandertal living groups? 5. T/F More fossil Neandertals have been found than any other extinct human species. 6. Around 40,000 years ago innovations occurred in Neandertal tool making technology, what may have caused this? 7. T/F The cultural styles of H. Sapiens and Neandertals remained distinct after they encountered each other. 8. What evidence supports the notion that H. Sapiens and Neandertals successfully mated (produced fertile offspring)? 9. What evidence is there that Neandertals are not our direct ancestors? 10. Do you think it s possible that once diverse populations left Africa and settle into the Old World they continued to mate (and thus exchange genes) with each other? 11. T/F Both Neandertals and Cro-Magnons (H. Sapiens) buried their dead. Emergence of Modern Humans The First Homo sapiens 1. When and where did fully modern humans first appear? 2. The Klasies River Mouth site in South Africa is noted for all the following EXCEPT: a. human fossils of modern appearance b. bifacial blades made with the punch technique b. evidence of big game hunting d. the first evidence of art e. heavy reliance on beach combing for shell fish 3. Humans first entered the New World years ago a. 15,000-20,000 b. 30,000 c. 60,000 d. 100,000 e. 500, What are the possible ways humans first entered the New World?
5 5 5. How important was meat in the diet of ancestral humans? 6. How might ancestral women have participated in hunting 7. How often did ancestral men engage in big game (e.g. mammoth) hunting? 8. T/F Human survival had little to do with macho men hurling spears at big-game animals. Origins and Dispersal of Homo sapiens 1. Where were the first fossils of modern humans found in Europe? 2. Which of the following characteristics distinguishes our species from archaic H. sapiens? a. a more gracile skull b. thick teeth enamel c. a rounded cranium d. relatively small teeth and jaws e. bipedalism 3. When did modern humans first enter Australia? 4. What was the tool industry of the Upper Paleolithic? a. Aurignacian b. Mousterian c. Acheulean d. Neandertalean e. Chatelperronian 5. T/F The peoples of the Upper Paleolithic lived at higher population densities than the Neandertals. 6. What are the basic differences between the Replacement Model and the Multiregional Model regarding the evolution of Homo sapiens? 7. T/F Both the replacement and multiregional models of human origins agree that there was an initial dispersal of H. erectus from Africa into the rest of the Old World.
6 6 8. The Multiregional Model claims Homo sapiens first emerged years ago. a. 2 million b. 1 million c. 150, ,000 d. 500,000 e. 36, When does the Replacement Model claim Homo sapiens first emerged? 10. T/F The Replacement Model says that transitional forms between archaic and modern humans should be found throughout the Old World. 11. Why does the Replacement Model contend that modern humans should show little genetic diversity? 12. The Multiregional Model says that all proposed species of Homo after habilis should be lumped into which of the following: a. Homo erectus b. Homo heidelbergensis c. Homo neanderthalensis d. Homo sapiens 13. How would proponents of the Replacement Model explain the simultaneous existence of Homo sapiens and Homo neandertalensis in Europe? 14. Should large continuous brow ridges be considered an example of a not-yet-modern human? 15. According to the splitters how many pre-modern species of Homo are there? What are they? 16. T/F Mitochondria are the energy factories of cells. 15. Mitochondria are inherited from: a. one s father b. one s mother c. both parents d. cannot be predicted 16. T/F Mitochondrial Eve Hypothesis traces all of our mtdna to a 200,000 year old African woman. 17. T/FMitochondrial DNA mutates at about the same rate as nuclear DNA. 18. T/F mtdna that was extracted from a Neanderthal specimen established that it was outside the range of modern human variation. 19. Why, according to Christopher Stringer was gene flow (e.g. Multiregional Model) unlikely? (select those that apply)
7 7 a. hominid populations were very thinly spread b. there were many geographical barriers c. they weren t attracted to members of other Homo populations d. there is no precedence for a multi-regional theory in any animals species 20. The chromosome is the male equivalent of female mitochondrial DNA. a. X b. 23 rd c. 14 th d. Y 21. The most recent common ancestor (MRCA) measurements from both Y chromosome and mtdna show that a. humans evolved in Africa and then moved out less than 200,000 years ago b. humans evolved millions of years ago in contradiction to all of our archaeological data c. humans are all related through Neandertal d. clear distinctions exist between European, African, and Australian humans The Littlest Human 1. Where is the island of Flores? 2. How tall was H. floresiensis? 3. T/F H. floresiensis had a cranium similar in size to a small australopithecine. 4. How long ago did H. floresiensis live? 5. What animals lived along side H. floresiensis? 6. What happens to mammals isolated on small islands? (select all that apply) a. mammals larger than rabbits tend to shrink b. mammals smaller than rabbits tend to increase in size c. hominds tend to shrink d. hominids tend to grow e. large mammals die off 7. T/F H. floresiensis tools reveal a sophistication comparable to H. sapiens. 8. What activities might H. floresiensis have engaged in? (select those that apply) a. group hunting b. craft production c. controlled use of fire d. warfare e. horticulture
8 8 9. How might the Flores Island find best be classified? a. microcephalic H. sapiens b. dwarfed descendant of H. erectus b. an ancestor parallel to H. habilis d. a descendant of A. africanus e. a new species H. floresiensis 10. T/F There may not be a direct relationship between brain size and the ability to manufacture sophisticated tools. 11. How did H. floresiensis get so small? 12. T/F For 15,000 years H. floresiensis, H. erectus and H. sapiens lived contemporaneously in Indonesia. The Birth of Childhood 1. T/F Human children have been known to survive on their own after weaning. 2. T/F Humans take twice as long as chimpanzees to reach adulthood. 3. T/F Australopithecine children matured at the rates of apes as opposed to humans. 4. New dating techniques have revised the age of the Turkana boy from to. a. 8, 13 b. 15, 10 c. 12, 9 d. 13, 8 1. T/F Homo erectus families were similar to our own. 2. What techniques are used to measure the ages of fossil children? 3. T/F A long childhood is necessary for a larger brain to mature. 4. The human brain reaches 95% of its size by age a. 5 b. 11 c. 15 d. 18 e. 25 Neanderthals Overlapped with Modern Humans 1. T/F Neanderthals and Modern Humans lived contemporaneously in Europe for about 1,000 years. 2. T/F Neanderthals were rapidly replaced by modern humans. 3. T/F There was ample time for interaction and interbreeding between Neanderthals and Modern Humans
9 9 4. What percent of Neanderthal DNA occurs in modern non-african human populations? a. Less than one percent b. 2-3 percent c. 5 percent d. none 5. T/F Neanderthals may have survived in dwindling populations in pockets of Europe before they became extinct. 6. T/F Rather than modern humans impacting the cultural practices of Neanderthals, there may have been regional differences in tool making and design. Theory on Human Gestation Refuted 1. What does the obstetric dilemma refer to? 2. T/F Hips wide enough to deliver a more developed baby would be a detriment to walking. 3. T/F Human gestation is relatively long compared to other primates. 4. T/F The primary evolutionary constraint on fetal growth and gestation is the Mom s energy. 5. T/F It would have been physiologically impossible regardless of pelvic anatomy to birth a more developed baby.
Evolution Problem Drill 10: Human Evolution
 Evolution Problem Drill 10: Human Evolution Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the human phylogenetic relationship with the African great apes? Question
Evolution Problem Drill 10: Human Evolution Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements is true regarding the human phylogenetic relationship with the African great apes? Question
First human-like ancestor = 4Ma. Misconceptions:
 Misconceptions: A Recipe for Disaster: Rise of the Hominids 1) Our ancestors were apes Contrary to popular belief, evolutionists do not claim we evolved directly from apes. More likely, we evolved from
Misconceptions: A Recipe for Disaster: Rise of the Hominids 1) Our ancestors were apes Contrary to popular belief, evolutionists do not claim we evolved directly from apes. More likely, we evolved from
CHAPTER 10. Premodern Humans
 CHAPTER 10 Premodern Humans Chapter Outline * Premodern Humans of the Middle Pleistocene * Middle Pleistocene evolution and culture * Neandertals: Premodern Humans of the Late Pleistocene -Molecular Connections:
CHAPTER 10 Premodern Humans Chapter Outline * Premodern Humans of the Middle Pleistocene * Middle Pleistocene evolution and culture * Neandertals: Premodern Humans of the Late Pleistocene -Molecular Connections:
Casey Leonard. Multiregional model vs. Out of Africa theory SLCC
 Casey Leonard Multiregional model vs. Out of Africa theory SLCC 2 It is debated where humans came from and how they spread across the world. Since people don't all look the same, or are categorized into
Casey Leonard Multiregional model vs. Out of Africa theory SLCC 2 It is debated where humans came from and how they spread across the world. Since people don't all look the same, or are categorized into
YEAR 12 HUMAN BIOLOGY EVOLUTION / NATURAL SELECTION TEST TOTAL MARKS :
 YEAR 12 HUMAN BIOLOGY EVOLUTION / NATURAL SELECTION TEST TOTAL MARKS : 1.Natural selection is occurring in a population. Which of the following statements is CORRECT? The population must be completely
YEAR 12 HUMAN BIOLOGY EVOLUTION / NATURAL SELECTION TEST TOTAL MARKS : 1.Natural selection is occurring in a population. Which of the following statements is CORRECT? The population must be completely
Human Evolution
 http://www.pwasoh.com.co Human Evolution Cantius, ca 55 mya The continent-hopping habits of early primates have long puzzled scientists, and several scenarios have been proposed to explain how the first
http://www.pwasoh.com.co Human Evolution Cantius, ca 55 mya The continent-hopping habits of early primates have long puzzled scientists, and several scenarios have been proposed to explain how the first
Class updates. Ch 10 Middle Pleistocene hominins and Neandertal
 Class updates Ch 10 Middle Pleistocene hominins and Neandertal 1 Class updates Quiz 2 - Next Wednesday, May 16 Need: Scantron 882-E (big one) and note paper for short answer questions Topics: End of chapter
Class updates Ch 10 Middle Pleistocene hominins and Neandertal 1 Class updates Quiz 2 - Next Wednesday, May 16 Need: Scantron 882-E (big one) and note paper for short answer questions Topics: End of chapter
Human Evolution. Darwinius masillae. Ida Primate fossil from. in Germany Ca.47 M years old. Cantius, ca 55 mya
 http://www.pwasoh.com Human Evolution Cantius, ca 55 mya The continent-hopping habits of early primates have long puzzled scientists, and several scenarios have been proposed to explain how the first true
http://www.pwasoh.com Human Evolution Cantius, ca 55 mya The continent-hopping habits of early primates have long puzzled scientists, and several scenarios have been proposed to explain how the first true
Out of Africa: The origin of Homo Sapiens (Us!)
 Out of Africa: The origin of Homo Sapiens (Us!) Our History from the DNA Record and other methods Robin Clegg Genetics, DNA A Detective Story Involving. Fossils, skulls and skeletons - new extraction of
Out of Africa: The origin of Homo Sapiens (Us!) Our History from the DNA Record and other methods Robin Clegg Genetics, DNA A Detective Story Involving. Fossils, skulls and skeletons - new extraction of
Primate Diversity & Human Evolution (Outline)
 Primate Diversity & Human Evolution (Outline) 1. Source of evidence for evolutionary relatedness of organisms 2. Primates features and function 3. Classification of primates and representative species
Primate Diversity & Human Evolution (Outline) 1. Source of evidence for evolutionary relatedness of organisms 2. Primates features and function 3. Classification of primates and representative species
Homework. Guided Reading Recent Hominids (#22-31) Need ear buds/headphones for Monday!!
 Homework Guided Reading Recent Hominids (#22-31) Need ear buds/headphones for Monday!! Learning Target I can explore various hominids from the skull lab and describe the evolution of hominids. What are
Homework Guided Reading Recent Hominids (#22-31) Need ear buds/headphones for Monday!! Learning Target I can explore various hominids from the skull lab and describe the evolution of hominids. What are
ANTHROPOLOGY 202 October 6, 2014 An Introduction to World Prehistory. VI. Out of Africa: Middle Homo
 ANTHROPOLOGY 202 October 6, 2014 An Introduction to World Prehistory VI. Out of Africa: Middle Homo ANT 202 Wednesday October 6, 2014 STUDENTS WITH LAST NAMES S-Z PLEASE STAY FOR A DEMONSTRATION AT THE
ANTHROPOLOGY 202 October 6, 2014 An Introduction to World Prehistory VI. Out of Africa: Middle Homo ANT 202 Wednesday October 6, 2014 STUDENTS WITH LAST NAMES S-Z PLEASE STAY FOR A DEMONSTRATION AT THE
Name Class Date. 1. What group of mammals do apes, monkeys, lemurs, and humans belong to? a. primates b. cold-blooded c. hominid d.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Humans and Other Primates PRIMATES 1. What group of mammals do apes, monkeys, lemurs, and humans belong to? a. primates b. cold-blooded c. hominid d. primitive
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Humans and Other Primates PRIMATES 1. What group of mammals do apes, monkeys, lemurs, and humans belong to? a. primates b. cold-blooded c. hominid d. primitive
31/10/2012. Human Evolution. Cytochrome c DNA tree
 Human Evolution Cytochrome c DNA tree 1 Human Evolution! Primate phylogeny! Primates branched off other mammalian lineages ~65 mya (mya = million years ago) Two types of monkeys within lineage 1. New World
Human Evolution Cytochrome c DNA tree 1 Human Evolution! Primate phylogeny! Primates branched off other mammalian lineages ~65 mya (mya = million years ago) Two types of monkeys within lineage 1. New World
Unit 4 Evolution (Ch. 14, 15, 16)
 Ch. 16 - Evolution Unit 4 Evolution (Ch. 14, 15, 16) 1. Define Evolution 2. List the major events that led to Charles Darwin s development of his theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection 3. Summarize
Ch. 16 - Evolution Unit 4 Evolution (Ch. 14, 15, 16) 1. Define Evolution 2. List the major events that led to Charles Darwin s development of his theory of Evolution by means of Natural Selection 3. Summarize
Who Were Neanderthals and Did They Interbreed with Modern Humans?
 Anthropology 1020 Sharon Vidriales-Estrada Who Were Neanderthals and Did They Interbreed with Modern Humans? References 1. Wikipedia (Internet) www.wikipedia.org Neanderthals search 2. Scientific American
Anthropology 1020 Sharon Vidriales-Estrada Who Were Neanderthals and Did They Interbreed with Modern Humans? References 1. Wikipedia (Internet) www.wikipedia.org Neanderthals search 2. Scientific American
ANTHROPOLOGY 202 Wednesday October 8, 2014 An Introduction to World Prehistory. VII The Emergence of modern humans: Late Homo or Homo sapiens
 ANTHROPOLOGY 202 Wednesday October 8, 2014 An Introduction to World Prehistory VII The Emergence of modern humans: Late Homo or Homo sapiens ANT 202 Wednesday October 8, 2014 STUDENTS WITH LAST NAMES S-Z
ANTHROPOLOGY 202 Wednesday October 8, 2014 An Introduction to World Prehistory VII The Emergence of modern humans: Late Homo or Homo sapiens ANT 202 Wednesday October 8, 2014 STUDENTS WITH LAST NAMES S-Z
Four kinds of hominins lived about 1.8 mya near Lake Turkana N. Kenya: Australopithecus boisei, H. rudolfensis, H. habilis and H. erectus foraged in
 Four kinds of hominins lived about 1.8 mya near Lake Turkana N. Kenya: Australopithecus boisei, H. rudolfensis, H. habilis and H. erectus foraged in the same area. We don t know if they interacted. H.
Four kinds of hominins lived about 1.8 mya near Lake Turkana N. Kenya: Australopithecus boisei, H. rudolfensis, H. habilis and H. erectus foraged in the same area. We don t know if they interacted. H.
Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of trends in human evolution (91606)
 NCEA Level 3 Biology (91606) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of trends in human evolution (91606) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence
NCEA Level 3 Biology (91606) 2016 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2016 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of trends in human evolution (91606) Evidence Statement Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence
Our Origins Discovering Physical Anthropology
 W. W. Norton & Company Our Origins Discovering Physical Anthropology Second Edition by Clark Spencer Larsen Chapter 12 Clark Spencer Larsen Our Origins DISCOVERING PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY C. Milner-Rose
W. W. Norton & Company Our Origins Discovering Physical Anthropology Second Edition by Clark Spencer Larsen Chapter 12 Clark Spencer Larsen Our Origins DISCOVERING PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY C. Milner-Rose
H. habilis H. rudolfensis H. erectus. H. ergaster H. antecessor. H. heidelbergensis H. sapiens neanderthalensis H. floresiensis H.
 H. habilis H. rudolfensis H. erectus H. ergaster H. antecessor H. heidelbergensis H. sapiens neanderthalensis H. floresiensis H. sapiens Homo floresiensis A recent discovery on Flores Island, Indonesia,
H. habilis H. rudolfensis H. erectus H. ergaster H. antecessor H. heidelbergensis H. sapiens neanderthalensis H. floresiensis H. sapiens Homo floresiensis A recent discovery on Flores Island, Indonesia,
(2) The drawings show stages in the evolution of the human skeleton.
 GENETICS AND EVOLUTION. Thornton College NAME.. Q. Charles Darwin proposed the theory of natural selection. (a) What is meant by natural selection? (b) The drawings show stages in the evolution of the
GENETICS AND EVOLUTION. Thornton College NAME.. Q. Charles Darwin proposed the theory of natural selection. (a) What is meant by natural selection? (b) The drawings show stages in the evolution of the
6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE?
 6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE? David Christian introduces the science of taxonomy and explains some of the important methods used to identify and classify different species and several key human ancestors.
6 HOW DID OUR ANCESTORS EVOLVE? David Christian introduces the science of taxonomy and explains some of the important methods used to identify and classify different species and several key human ancestors.
Level 3 Biology, 2014
 91606 916060 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Biology, 2014 91606 Demonstrate understanding of trends in human evolution 9.30 am Thursday 13 November 2014 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement
91606 916060 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Biology, 2014 91606 Demonstrate understanding of trends in human evolution 9.30 am Thursday 13 November 2014 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement
HUMAN EVOLUTION 17 APRIL 2013
 HUMAN EVOLUTION 17 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Consider the following aspects of Human Evolution: - Interpretation of a phylogenetic tree to show the place of the family Hominidae
HUMAN EVOLUTION 17 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Consider the following aspects of Human Evolution: - Interpretation of a phylogenetic tree to show the place of the family Hominidae
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011
 Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Evolution and Our Heritage
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 22 Evolution and Our Heritage Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 22 Evolution and Our Heritage Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
1/24/2008. The Creation of Two Worlds. The Creation of Two Worlds. The Creation of Two Worlds. Topics of Discussion. I. The Earth Calendar
 Topics of Discussion I. The Earth Calendar II. 225-200 MYA: Pangaea III. Centralization of Evolution IV. 200-180 MYA: Break-up of Pangaea V. Decentralization of Evolution VI. Hominids and Humans VII. Culture
Topics of Discussion I. The Earth Calendar II. 225-200 MYA: Pangaea III. Centralization of Evolution IV. 200-180 MYA: Break-up of Pangaea V. Decentralization of Evolution VI. Hominids and Humans VII. Culture
Biological Anthropology
 Biological Anthropology Sample Exam 3 Fall 2017 This sample exam, which contains questions from exams given sometime in the past, will provide you with an idea of the types of questions you will face on
Biological Anthropology Sample Exam 3 Fall 2017 This sample exam, which contains questions from exams given sometime in the past, will provide you with an idea of the types of questions you will face on
Essentials of Physical Anthropology
 Lecture Slides Essentials of Physical Anthropology THIRD EDITION Clark Spencer Larsen The Origins, Evolution, and Dispersal of Modern People 12 Larsen. Essentials of Physical Anthropology The Origins,
Lecture Slides Essentials of Physical Anthropology THIRD EDITION Clark Spencer Larsen The Origins, Evolution, and Dispersal of Modern People 12 Larsen. Essentials of Physical Anthropology The Origins,
The Human Animal. Molecular Evidence. H. Habilis Tools. Early Homo Evolution. Relationship with Large Cats. Homo ergaster and Homo erectus
 The Human Animal Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos Human
The Human Animal Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos Human
Ch. 19 The Neogene World
 Ch. 19 The Neogene World Neogene Period includes Miocene, Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs Beginning of Holocene was approx. 12,000 years ago 12,000 years Cenozoic 1.8 5.3 Neogene 24 Paleogene 65 Holocene
Ch. 19 The Neogene World Neogene Period includes Miocene, Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs Beginning of Holocene was approx. 12,000 years ago 12,000 years Cenozoic 1.8 5.3 Neogene 24 Paleogene 65 Holocene
Several species of early hominids may be living at the same time. A parental species may continue to exist after a daughter species emerges.
 Primates: Human Ancestors? Fossil Evidence Binocular eyesight: depth perception Hands that can grasp (nails not claws) Monkeys: (tails) Apes: no tails Hominids (bipedalism, slower, but able to use hands
Primates: Human Ancestors? Fossil Evidence Binocular eyesight: depth perception Hands that can grasp (nails not claws) Monkeys: (tails) Apes: no tails Hominids (bipedalism, slower, but able to use hands
The Human Animal. BIO 1300: The Human Animal
 The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
The Human Animal. Molecular Evidence. Early Homo Evolution
 The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
The Human Animal 1 Molecular Evidence Humans and Chimps/ Bonobos share 95% of our DNA in common The 5% is responsible for the important difference in body, brains and behaviours Gorilla Chimp. Bonobos
The Creation of Two Worlds
 Topics of Discussion I. The Earth Calendar II. 225-200 MYA: Pangaea III. Centralization of Evolution IV. 200-180 MYA: Break-up of Pangaea V. Decentralization of Evolution VI. Hominids and Humans VII. Culture
Topics of Discussion I. The Earth Calendar II. 225-200 MYA: Pangaea III. Centralization of Evolution IV. 200-180 MYA: Break-up of Pangaea V. Decentralization of Evolution VI. Hominids and Humans VII. Culture
Diversity and Human Evolution. Homo neanderthalensis. Homo neanderthalensis. Homo neanderthalensis. Homo neanderthalensis. Part II
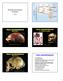 Diversity and Human Evolution Part II Neanderthal 1 La Chapelle-aux-Saints Photograph byrheinisches LandesmuseumBonn Photographs by John Reader Mount Circeo Photograph by Ministry of Culture, Italy An
Diversity and Human Evolution Part II Neanderthal 1 La Chapelle-aux-Saints Photograph byrheinisches LandesmuseumBonn Photographs by John Reader Mount Circeo Photograph by Ministry of Culture, Italy An
The History of Life on Earth
 CHAPTER 9 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET The History of Life on Earth By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary
CHAPTER 9 VOCABULARY & NOTES WORKSHEET The History of Life on Earth By studying the Vocabulary and Notes listed for each section below, you can gain a better understanding of this chapter. SECTION 1 Vocabulary
Date Hominin Significance
 Date Hominin Significance 7.0 mya Sahelanthropus tchadensis Oldest possible hominin ancestor - foramen magnum suggests bipedalism 6.0 mya Orrorin tugenensis Earliest known hominin, CT scans of the proximal
Date Hominin Significance 7.0 mya Sahelanthropus tchadensis Oldest possible hominin ancestor - foramen magnum suggests bipedalism 6.0 mya Orrorin tugenensis Earliest known hominin, CT scans of the proximal
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Fossil record
 Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Fossil record Fossil record - significance & interpretation Extinction - Background extinction rates and the big 5 mass extinction The K/T boundary - asteroid hypothesis;
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Fossil record Fossil record - significance & interpretation Extinction - Background extinction rates and the big 5 mass extinction The K/T boundary - asteroid hypothesis;
Last day we ended with the division of prosimians into two main groups:
 Last day we ended with the division of prosimians into two main groups: A Recipe for Disaster: Rise of the Hominids (plus condensed version of remaining course material) Reminder: Earth Sciences 083F Final
Last day we ended with the division of prosimians into two main groups: A Recipe for Disaster: Rise of the Hominids (plus condensed version of remaining course material) Reminder: Earth Sciences 083F Final
1 low Humans Evolved
 1 low Humans Evolved Robert Howl IOIIIB Silk UNIVERS1. i 1 \..UK I..1 I \ Nv I Technische Unive-^itdt Darmstadt FACHDCRLICH 10 BIOLOGIE B i!. I i o t h p k -_ ScLninspilinstiafiG 10 D-6 4287 Darmstadt
1 low Humans Evolved Robert Howl IOIIIB Silk UNIVERS1. i 1 \..UK I..1 I \ Nv I Technische Unive-^itdt Darmstadt FACHDCRLICH 10 BIOLOGIE B i!. I i o t h p k -_ ScLninspilinstiafiG 10 D-6 4287 Darmstadt
Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution. Lecture 15 & 16: Homo erectus to Homo neanderthalensis. Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier
 Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution Lecture 15 & 16: Homo erectus to Homo neanderthalensis Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier Reminder s Last Quiz.Thursday (5/14) Zoo extra credit due 5/21 Next week The Genus
Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution Lecture 15 & 16: Homo erectus to Homo neanderthalensis Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier Reminder s Last Quiz.Thursday (5/14) Zoo extra credit due 5/21 Next week The Genus
Examples of Phylogenetic Reconstruction
 Examples of Phylogenetic Reconstruction 1. HIV transmission Recently, an HIV-positive Florida dentist was suspected of having transmitted the HIV virus to his dental patients. Although a number of his
Examples of Phylogenetic Reconstruction 1. HIV transmission Recently, an HIV-positive Florida dentist was suspected of having transmitted the HIV virus to his dental patients. Although a number of his
HBio Evolution 2 Practice test
 HBio Evolution 2 Practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The genes carried by all members of a particular population make up the
HBio Evolution 2 Practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The genes carried by all members of a particular population make up the
ORIGIN OF MODERN HUMANS
 ORIGIN OF MODERN HUMANS Cut marks in bone 3.4 mya Stone tools 3.3 mya Harmand et al. Nature 521, 310-315 (2015) Oldowan tools 2.6-1.5 mya Figs. 17.13 & 17.14 Z&E 1 APPEARANCE OF THE GENUS HOMO Increasingly
ORIGIN OF MODERN HUMANS Cut marks in bone 3.4 mya Stone tools 3.3 mya Harmand et al. Nature 521, 310-315 (2015) Oldowan tools 2.6-1.5 mya Figs. 17.13 & 17.14 Z&E 1 APPEARANCE OF THE GENUS HOMO Increasingly
Evolution of human diversity. The history of Homo sapiens
 Evolution of human diversity The history of Homo sapiens!1 The primates Gibbon Orangutan Gorilla Bonobo Chimpanzee Human Human Chimpanzee Gorilla Orangutan Gibbon Macaque Millions years ago!2 Macaque Orangutan
Evolution of human diversity The history of Homo sapiens!1 The primates Gibbon Orangutan Gorilla Bonobo Chimpanzee Human Human Chimpanzee Gorilla Orangutan Gibbon Macaque Millions years ago!2 Macaque Orangutan
Homo habilis males feeding in East Africa. Two robust australopithecines are approaching. ( Myr ago) The Homo radiation
 The Homo radiation Homo habilis males feeding in East Africa. Two robust australopithecines are approaching. (1.5-2.0 Myr ago) Average 640cm 3 brain compared to 500cm 3 in the Australopithecines 1965-Louis
The Homo radiation Homo habilis males feeding in East Africa. Two robust australopithecines are approaching. (1.5-2.0 Myr ago) Average 640cm 3 brain compared to 500cm 3 in the Australopithecines 1965-Louis
Grade 12 Term Use the following diagram and list the characteristics we share with other African apes. 12 and 13 (13)
 Grade 1 Term 3 Total: 100 Time: hours Assignment: Hominid evolution Objectives To list the characteristics that humans and African apes share To compare the skulls of human ancestors, cousins and other
Grade 1 Term 3 Total: 100 Time: hours Assignment: Hominid evolution Objectives To list the characteristics that humans and African apes share To compare the skulls of human ancestors, cousins and other
Homo habilis. Classification as Homo
 Homo habilis Homo habilis is a species of the tribe Hominini, during the Gelasian and early Calabrian stages of the Pleistocene period, between roughly 2.8 and 1.5 million years ago. In its appearance
Homo habilis Homo habilis is a species of the tribe Hominini, during the Gelasian and early Calabrian stages of the Pleistocene period, between roughly 2.8 and 1.5 million years ago. In its appearance
The Evolution of Life
 APPENDIX 3 The Evolution of Life Life on Earth Air-breathing life cannot exist without oxygen, which was not part of earth s original atmosphere. However, life in the form of primeval bacteria and algae
APPENDIX 3 The Evolution of Life Life on Earth Air-breathing life cannot exist without oxygen, which was not part of earth s original atmosphere. However, life in the form of primeval bacteria and algae
Neanderthal vs Cro-Magnon 1of10 found at
 We will watch the excellent documentary Clash of the Cavemen to learn about Neanderthals and the early humans who lived in Europe. Do a search of Clash of the Cavemen at www.youtube.com. (In 2012, when
We will watch the excellent documentary Clash of the Cavemen to learn about Neanderthals and the early humans who lived in Europe. Do a search of Clash of the Cavemen at www.youtube.com. (In 2012, when
H. erectus. Middle Pleistocene Archaic H. sapiens kya. H. sapiens, present
 H. erectus Middle Pleistocene Archaic H. sapiens 780-125 kya H. sapiens, present 1 1 2 3 3 2 4 4 Atapuerca 5 Archaic H. sapiens 5 5 Modern Homo sapiens Middle Pleistocene and living humans compared Archaic
H. erectus Middle Pleistocene Archaic H. sapiens 780-125 kya H. sapiens, present 1 1 2 3 3 2 4 4 Atapuerca 5 Archaic H. sapiens 5 5 Modern Homo sapiens Middle Pleistocene and living humans compared Archaic
Last class. What are all the species in the Australopithecines?
 Last class What are all the species in the Australopithecines? Which are robust? Which are gracile? What are the differences between robust and gracile? When do they occur in time? Space? How did they
Last class What are all the species in the Australopithecines? Which are robust? Which are gracile? What are the differences between robust and gracile? When do they occur in time? Space? How did they
The Evolution of Primates
 The Evolution of Primates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Order Primates of class Mammalia includes lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys, apes, and humans. Non-human primates live primarily in the tropical or subtropical regions
The Evolution of Primates Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Order Primates of class Mammalia includes lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys, apes, and humans. Non-human primates live primarily in the tropical or subtropical regions
Four kinds of hominins lived about 1.8 mya near Lake Turkana N. Kenya: Australopithecus boisei, H. rudolfensis, H. habilis and H. erectus foraged in
 Four kinds of hominins lived about 1.8 mya near Lake Turkana N. Kenya: Australopithecus boisei, H. rudolfensis, H. habilis and H. erectus foraged in the same area. We don t know if they interacted. H.
Four kinds of hominins lived about 1.8 mya near Lake Turkana N. Kenya: Australopithecus boisei, H. rudolfensis, H. habilis and H. erectus foraged in the same area. We don t know if they interacted. H.
Excavating the Piltdown gravels in 1911, with Dawson (right) and Smith Woodward
 G02: Set in Stone The long way round WC 2030 Just over half a century ago, on 21 November 1953, and 40 years after his discovery in a Sussex gravel pit, so-called Piltdown Man was officially exposed as
G02: Set in Stone The long way round WC 2030 Just over half a century ago, on 21 November 1953, and 40 years after his discovery in a Sussex gravel pit, so-called Piltdown Man was officially exposed as
Bio1B Evolution 13 Last lecture:
 Bio1B Evolution 13 Last lecture: Macro-evolution (cont.) Mass extinctions Species selection Transitional forms - tetrapods, birds: exaptation Today Human evolution Evolutionary origins of Homo sapiens:
Bio1B Evolution 13 Last lecture: Macro-evolution (cont.) Mass extinctions Species selection Transitional forms - tetrapods, birds: exaptation Today Human evolution Evolutionary origins of Homo sapiens:
Evolution & Natural Selection
 Evolution & Natural Selection Human Origins & Adaptations Charles Darwin Darwin did not discover evolution Darwin explain how natural selection decided which genes would be selected and passed on to the
Evolution & Natural Selection Human Origins & Adaptations Charles Darwin Darwin did not discover evolution Darwin explain how natural selection decided which genes would be selected and passed on to the
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18)
 Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
The big 5 mass extinctions. The asteroid impact hypothesis - Luiz & Walter Alvarez, UC Berkeley (see Science, 5th March, p1214)
 Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
Bio1B Evolution 12 Last lecture: Speciation: outcomes of secondary contact Fossil record - significance & interpretation (Ch 18) Today Extinction - Background extinction rates vs big 5 mass extinctions
Text 3: Discoveries in Africa and Beyond. Topic 1: The Origins of Civilization (Prehistory B.C.E) Lesson 1: Learning About Our Past
 Text 3: Discoveries in Africa and Beyond Topic 1: The Origins of Civilization (Prehistory - 300 B.C.E) Lesson 1: Learning About Our Past Discoveries in Africa and Beyond Since the 1870s, scholars have
Text 3: Discoveries in Africa and Beyond Topic 1: The Origins of Civilization (Prehistory - 300 B.C.E) Lesson 1: Learning About Our Past Discoveries in Africa and Beyond Since the 1870s, scholars have
Session 17: Episode 5(2) Genomics, our African genesis and family tree
 Session 17: Episode 5(2) Genomics, our African genesis and family tree William P. Hall President Kororoit Institute Proponents and Supporters Assoc., Inc. - http://kororoit.org william-hall@bigpond.com
Session 17: Episode 5(2) Genomics, our African genesis and family tree William P. Hall President Kororoit Institute Proponents and Supporters Assoc., Inc. - http://kororoit.org william-hall@bigpond.com
ANTHROPOLOGY 150: EVOLUTION AND HUMAN EMERGENCE NM HED Area III: Laboratory Science Competencies UNM Core Area 3: Physical and Natural Sciences
 ANTHROPOLOGY 150: EVOLUTION AND HUMAN EMERGENCE NM HED Area III: Laboratory Science Competencies UNM Core Area 3: Physical and Natural Sciences Student Learning Objectives: At the end of the course, the
ANTHROPOLOGY 150: EVOLUTION AND HUMAN EMERGENCE NM HED Area III: Laboratory Science Competencies UNM Core Area 3: Physical and Natural Sciences Student Learning Objectives: At the end of the course, the
Biology Chapter 15 Evolution Notes
 Biology Chapter 15 Evolution Notes Section 1: Darwin's Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Charles Darwin- English naturalist that studied animals over a number of years before developing the theory
Biology Chapter 15 Evolution Notes Section 1: Darwin's Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Charles Darwin- English naturalist that studied animals over a number of years before developing the theory
Hominin Evolution Overview
 Genotype and Phenotype: - Each individual has a genotype (which genes they have) and a phenotype (the way in which those genes are expressed) - Some phenotypic traits will be beneficial for survival, some
Genotype and Phenotype: - Each individual has a genotype (which genes they have) and a phenotype (the way in which those genes are expressed) - Some phenotypic traits will be beneficial for survival, some
The Evolution of Speech
 The Evolution of Speech Q: How did speech arise in humans? A: We don t know. 1 How did speech arise in humans? scholars: interminable, acrimonious debates limited scientific data 1860: Paris Linguistic
The Evolution of Speech Q: How did speech arise in humans? A: We don t know. 1 How did speech arise in humans? scholars: interminable, acrimonious debates limited scientific data 1860: Paris Linguistic
How related are organisms?
 The Evolution and Classification of Species Darwin argued for adaptive radiation in which demes spread out in a given environment and evolved How related are organisms? Taonomy the science of classifying
The Evolution and Classification of Species Darwin argued for adaptive radiation in which demes spread out in a given environment and evolved How related are organisms? Taonomy the science of classifying
Understanding Natural Selection
 Understanding Natural Selection Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 What did Darwin s Travels reveal The diversity of living species was far greater than anyone had previously
Understanding Natural Selection Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 What did Darwin s Travels reveal The diversity of living species was far greater than anyone had previously
Paleoanthropology. The dawn of Homo floresiensis
 Paleoanthropology The dawn of Homo floresiensis New fossil findings from the Mata Menge site demonstrate that Homo floresiensis lived on the Indonesian island of Flores at least 700,000 years ago, and
Paleoanthropology The dawn of Homo floresiensis New fossil findings from the Mata Menge site demonstrate that Homo floresiensis lived on the Indonesian island of Flores at least 700,000 years ago, and
NJBibleScience.org. Early Man. Gerald Lenner, Ph.D. November 17, 2010
 Early Man Gerald Lenner, Ph.D. November 17, 2010 Talk Outline Review The Short Story - A Tale of Two Buckets False Ancestors of Man Candidate Ancestors - Neanderthals - Australopithecines - Homo erectus
Early Man Gerald Lenner, Ph.D. November 17, 2010 Talk Outline Review The Short Story - A Tale of Two Buckets False Ancestors of Man Candidate Ancestors - Neanderthals - Australopithecines - Homo erectus
4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]
![4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1] 4. Identify one bird that would most likely compete for food with the large tree finch. Support your answer. [1]](/thumbs/84/91138454.jpg) Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
Name: Topic 5B 1. A hawk has a genetic trait that gives it much better eyesight than other hawks of the same species in the same area. Explain how this could lead to evolutionary change within this species
12.1 The Fossil Record. KEY CONCEPT Specific environmental conditions are necessary in order for fossils to form.
 KEY CONCEPT Specific environmental conditions are necessary in order for fossils to form. Fossils can form in several ways. Premineralization occurs when minerals carried by water are deposited around
KEY CONCEPT Specific environmental conditions are necessary in order for fossils to form. Fossils can form in several ways. Premineralization occurs when minerals carried by water are deposited around
Lesson Topic Learning Goals
 Unit 2: Evolution Part B Lesson Topic Learning Goals 1 Lab Mechanisms of Evolution Cumulative Selection - Be able to describe evolutionary mechanisms such as genetic variations and key factors that lead
Unit 2: Evolution Part B Lesson Topic Learning Goals 1 Lab Mechanisms of Evolution Cumulative Selection - Be able to describe evolutionary mechanisms such as genetic variations and key factors that lead
Evolution Unit: What is Evolution?
 Evolution Unit: What is Evolution? What is The Theory of Evolution? Evolution is, a change (in the genetic composition) of a population over time. on a larger scale, the entire biological history, from
Evolution Unit: What is Evolution? What is The Theory of Evolution? Evolution is, a change (in the genetic composition) of a population over time. on a larger scale, the entire biological history, from
Clicker Questions, Test 4. April 8, 2015, Outline 19
 Clicker Questions, Test 4 April 8, 2015, Outline 19 1. What is the name of the orogeny that formed the Rocky Mountains, including the Teton Mountains of Wyoming? A. Laramide B. Alpine C. Caledonian D.
Clicker Questions, Test 4 April 8, 2015, Outline 19 1. What is the name of the orogeny that formed the Rocky Mountains, including the Teton Mountains of Wyoming? A. Laramide B. Alpine C. Caledonian D.
An Analysis of the Identity and Relationship Among Skeletal Remains of the Upper Paleolithic Era
 ESSAI Volume 3 Article 17 Spring 2005 An Analysis of the Identity and Relationship Among Skeletal Remains of the Upper Paleolithic Era Brian Kinsman College of DuPage Follow this and additional works at:
ESSAI Volume 3 Article 17 Spring 2005 An Analysis of the Identity and Relationship Among Skeletal Remains of the Upper Paleolithic Era Brian Kinsman College of DuPage Follow this and additional works at:
Biosc 41 Announcements 12/1
 Biosc 41 Announcements 12/1 Review: evolution (chapters 22, 23) Today s lecture: speciation and human evolution Today s lab: work on group presentations for Wed Wed s lecture: conservation biology Wed
Biosc 41 Announcements 12/1 Review: evolution (chapters 22, 23) Today s lecture: speciation and human evolution Today s lab: work on group presentations for Wed Wed s lecture: conservation biology Wed
15.3 Darwin Presents his Case. Biology Mr. Hines
 15.3 Darwin Presents his Case Biology Mr. Hines Darwin returned to England with a wealth of new data. He brought many specimens from the Galapagos to further his studies and to present his data to others.
15.3 Darwin Presents his Case Biology Mr. Hines Darwin returned to England with a wealth of new data. He brought many specimens from the Galapagos to further his studies and to present his data to others.
Human Evolution. Chapter Learning objectives Laboratory exercises Primates. Sebastián Vélez and Eli Minkoff
 Chapter 12 Human Evolution Sebastián Vélez and Eli Minkoff 12.1 Learning objectives 1. Understand the evolutionary relationships among primates. 2. Describe the evolutionary relationships between chimps,
Chapter 12 Human Evolution Sebastián Vélez and Eli Minkoff 12.1 Learning objectives 1. Understand the evolutionary relationships among primates. 2. Describe the evolutionary relationships between chimps,
Charles Darwin ( ) Sailed around the world
 Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 2. What did Darwin s Travels reveal The diversity of living species was far greater than anyone had previously known!! These observations led
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 2. What did Darwin s Travels reveal The diversity of living species was far greater than anyone had previously known!! These observations led
ABOUT THE LESEDI CHAMBER
 Homo naledi FACT SHEET EMBARGOED UNTIL TUESDAY 9 May 2017 10 am South African Time / 4 am EDT / 9 am London / 6 pm Sydney, Australia QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT THE LESEDI CHAMBER 1) What does the name
Homo naledi FACT SHEET EMBARGOED UNTIL TUESDAY 9 May 2017 10 am South African Time / 4 am EDT / 9 am London / 6 pm Sydney, Australia QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT THE LESEDI CHAMBER 1) What does the name
Bones of Contention (Lubenow) PPT
 From the SelectedWorks of Jordan P Ballard 2013 Bones of Contention (Lubenow) PPT Jordan P Ballard Available at: https://works.bepress.com/jordan_ballard/8/ A Creationist Assessment of Human Fossils Marvin
From the SelectedWorks of Jordan P Ballard 2013 Bones of Contention (Lubenow) PPT Jordan P Ballard Available at: https://works.bepress.com/jordan_ballard/8/ A Creationist Assessment of Human Fossils Marvin
Announcements. Today. Chapter 8 primate and hominin origins. Keep in mind. Quiz 2: Wednesday/Thursday May 15/16 (week 14)
 Announcements Today Chapter 8 primate and hominin origins Keep in mind Quiz 2: Wednesday/Thursday May 15/16 (week 14) Essay 2: Questions are up on course website 1 Recap the main points of ch 6 and 7 Evolutionary
Announcements Today Chapter 8 primate and hominin origins Keep in mind Quiz 2: Wednesday/Thursday May 15/16 (week 14) Essay 2: Questions are up on course website 1 Recap the main points of ch 6 and 7 Evolutionary
2. Overproduction: More species are produced than can possibly survive
 Name: Date: What to study? Class notes Graphic organizers with group notes Review sheets What to expect on the TEST? Multiple choice Short answers Graph Reading comprehension STRATEGIES Circle key words
Name: Date: What to study? Class notes Graphic organizers with group notes Review sheets What to expect on the TEST? Multiple choice Short answers Graph Reading comprehension STRATEGIES Circle key words
Early primates and hominins
 Early primates and hominins 1 Wild Card slide part deux 2 Hominins ~7-6 mya split from chimpanzees and bonobos -emerged and stayed in Africa until later Homo Mosaic evolution - these characteristics evolved
Early primates and hominins 1 Wild Card slide part deux 2 Hominins ~7-6 mya split from chimpanzees and bonobos -emerged and stayed in Africa until later Homo Mosaic evolution - these characteristics evolved
Evolution. Year Scientist Theory/Experiment Conclusion
 Evolution Origin of Life Year Scientist Theory/Experiment Conclusion 1927 Lemaitre Big Bang theory The universe expanded from explosion of a primordial, hot substance. 1924 Oparin and Chemical evolution
Evolution Origin of Life Year Scientist Theory/Experiment Conclusion 1927 Lemaitre Big Bang theory The universe expanded from explosion of a primordial, hot substance. 1924 Oparin and Chemical evolution
Homo heidelbergensis Homo heidelbergensis es una especie extinta del género Homo, que surgió hace más de años y perduró al menos hasta hace
 Homo heidelbergensis Homo heidelbergensis es una especie extinta del género Homo, que surgió hace más de 600 000 años y perduró al menos hasta hace 250 000 años. Clasificación superior: Homo Categoría:
Homo heidelbergensis Homo heidelbergensis es una especie extinta del género Homo, que surgió hace más de 600 000 años y perduró al menos hasta hace 250 000 años. Clasificación superior: Homo Categoría:
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 7 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 7 FLASHCARDS What did Darwin NOT understand about the process of evolution? A. the slowness of the process B. the role of genetics C. the importance of separation D. the importance
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 7 FLASHCARDS What did Darwin NOT understand about the process of evolution? A. the slowness of the process B. the role of genetics C. the importance of separation D. the importance
Evolution. Darwin s Voyage
 Evolution Darwin s Voyage Charles Darwin Explorer on an observation trip to the Galapagos Islands. He set sail on the HMS Beagle in 1858 from England on a 5 year trip. He was a naturalist (a person who
Evolution Darwin s Voyage Charles Darwin Explorer on an observation trip to the Galapagos Islands. He set sail on the HMS Beagle in 1858 from England on a 5 year trip. He was a naturalist (a person who
HOMINID SERIES. Lesson Plan. Skullduggery, Inc. 624 South B Street Tustin, CA (800) FAX (714)
 HOMINID SERIES Lesson Plan Skullduggery, Inc. 624 South B Street Tustin, CA 92680 (800) 336-7745 FAX (714) 832-1215 HOMINIDS OBJECTIVE The hominid set provides an opportunity for an up close, hands on
HOMINID SERIES Lesson Plan Skullduggery, Inc. 624 South B Street Tustin, CA 92680 (800) 336-7745 FAX (714) 832-1215 HOMINIDS OBJECTIVE The hominid set provides an opportunity for an up close, hands on
Introduction to Human Evolution Anthropology 102 KY150
 Introduction to Human Evolution Anthropology 102 KY150 Professor: Kate Pechenkina, Ph. D. Office: Powdermaker Hall 312A Telephone: (718) 997-5529 Fax: (718) 997-2885 E-mail: ekaterina.pechenkina@qc.cuny.edu
Introduction to Human Evolution Anthropology 102 KY150 Professor: Kate Pechenkina, Ph. D. Office: Powdermaker Hall 312A Telephone: (718) 997-5529 Fax: (718) 997-2885 E-mail: ekaterina.pechenkina@qc.cuny.edu
Humanity on the Record
 Humanity on the Record Humanity on the Record In the summer of 2012, paleontologists working on a fossil excavation in Kenya announced that the human race, as we know it, was never alone. Scientists unveiled
Humanity on the Record Humanity on the Record In the summer of 2012, paleontologists working on a fossil excavation in Kenya announced that the human race, as we know it, was never alone. Scientists unveiled
Evaluating the Finds of a Recent Discovery of Humanoid Bones Suggesting the Coexistence of and Mating Between Homo sapiens and Homo neanderthalensis
 ESSAI Volume 3 Article 15 Spring 2005 Evaluating the Finds of a Recent Discovery of Humanoid Bones Suggesting the Coexistence of and Mating Between Homo sapiens and Homo neanderthalensis Sara Heppner College
ESSAI Volume 3 Article 15 Spring 2005 Evaluating the Finds of a Recent Discovery of Humanoid Bones Suggesting the Coexistence of and Mating Between Homo sapiens and Homo neanderthalensis Sara Heppner College
Population Genetics of Modern Human Evolution
 Population Genetics of Modern Human Evolution John H Relethford, State University of New York College at Oneonta, Oneonta, New York, USA Rosalind M Harding, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK The aim of
Population Genetics of Modern Human Evolution John H Relethford, State University of New York College at Oneonta, Oneonta, New York, USA Rosalind M Harding, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK The aim of
Heredity and Evolution
 CHAPTER 9 Heredity and Evolution Multiple Choice Questions 1. Exchange of genetic material takes place in (a) vegetative reproduction (b) asexual reproduction (c) sexual reproduction (d) budding 2. Two
CHAPTER 9 Heredity and Evolution Multiple Choice Questions 1. Exchange of genetic material takes place in (a) vegetative reproduction (b) asexual reproduction (c) sexual reproduction (d) budding 2. Two
Human Evolution Chris Stringer The Natural History Museum London. Are we nearly there yet?
 Human Evolution Chris Stringer The Natural History Museum London Are we nearly there yet? Phases of human evolution Human phase 2 0 Ma: >>Global spread Human anatomy >>Encephalised >>Dietary range >>Behavioural
Human Evolution Chris Stringer The Natural History Museum London Are we nearly there yet? Phases of human evolution Human phase 2 0 Ma: >>Global spread Human anatomy >>Encephalised >>Dietary range >>Behavioural
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 10 1 Change Over Time SECTION The Evolution of Living Things 7.3.c, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 10 1 Change Over Time SECTION The Evolution of Living Things 7.3.c, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
of EVOLUTION???????????? states that existing forms of life on earth have arisen from earlier forms over long periods of time.
 Evolution The WHAT theory IS of EVOLUTION???????????? states that existing forms of life on earth have arisen from earlier forms over long periods of time. Some of the strongest evidence to support evolution
Evolution The WHAT theory IS of EVOLUTION???????????? states that existing forms of life on earth have arisen from earlier forms over long periods of time. Some of the strongest evidence to support evolution
Evolutionary Evidence of Evolution
 Evolutionary Evidence of Evolution Evolution - the process in which relative changes in the genetic makeup (characteristics) of a species occurs over time Sometimes changes in populations are environmental
Evolutionary Evidence of Evolution Evolution - the process in which relative changes in the genetic makeup (characteristics) of a species occurs over time Sometimes changes in populations are environmental
