grams grams Crystalline matrix Breccia
|
|
|
- Gwendoline Hillary Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
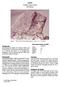
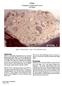
1 grams grams Crystalline matrix Breccia Figure 1: Photo of 14069,0. Scale in cm and mm. S Figure 2: Photo of Scale is in cm. S Introduction and are small breccia samples that were picked up by tongs from between the MET tracks in the boulder field on the rim of Cone Crater (Swann et al. 1971) (figure 3). They are similar, but have different exposure ages. Figure 3: Traverse map for Apollo 14 showing location of on rim of Cone Crater.
2 14070 Figure 4: Location of between tracks left by MET. S Petrography and are tan impact melt rocks with fine crystalline matrix (Carlson and Kramer 1987). They have vesicles, mare basalt clasts and other similarity with and are most likely pieces of the Fra Mauro Formation (Wilshire and Jackson 1972, Simonds et al. 1977). Chemistry The chemical composition of and have not been determined. Cosmogenic isotopes and exposure ages Stadermann et al. (1991) determined an exposure age of 95 m.y. for and 30 m.y. for by the 38 Ar method. Processing These samples were returned, under vacuum, in ALSRC There are three thin sections each for and Radiogenic age dating Stadermann et al. (1991) determined Ar/Ar plateau ages of 3.78 ± 0.02 b.y. for and 3.71 ± 0.02 b.y. for (figure ).
3 scale = 2.8 mm across Figure 5: 14069,5
4 scale = 2.8 mm acrosss igure 6: 4070,3
5 Figure7 : Ar plateau diagrams for and (Stadermann et al. 1991). Summary of Age Data for 14069, Ar/Ar ± 0.02 b.y ± 0.02 Stadermann et al Caution : Ar standard? C Meyer grams CMeyer grams, g,1,6,3 0.2 g, g,0 30 g,1,4,11,4,5,8,2,6,13
6 References for Carlson I.C. and Walton W.J.A. (1978) Apollo 14 Rock Samples. Curators Office. JSC Deutsch A. and Stoffler D. (1987) Rb-Sr analysis of Apollo 16 melt rocks and a new age estimate for the Imbrium basin: Lunar basin chronology and the early heavy bombardment of the moon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 51, LSPET (1971a) Preliminary examination of lunar samples from Apollo 14. Science 173, Warner J.L. and Duke M.B. (1971) Apollo 14 lunar sample information catalog. NASA TM X Williams R.J. (1972) The lithification of metamorphism of lunar breccias. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 16, Wilshire H.G. and Jackson E.D. (1972b) Petrology and stratigraphy of the Fra Mauro Formation at the Apollo 14 site. US Geol. Survey Prof. Paper 785 LSPET (1971b) Preliminary examination of lunar samples from Apollo 14. In Apollo 14 Preliminary Sci. Rpt. NASA SP-272 Mitchell J.K., Bromwell L.G., Carrier W.D., Costes N.C. and Scott R.F. (1971) Soil Mechanics Experiment. In Apollo 14: Preliminary Science Report NASA SP-272. Phinney W.C., McKay D.S., Simonds C.H. and Warner J.L. (1976a) Lithification of vitric- and elastic-matrix breccias: SEM photography. Proc. 7 th Lunar Sci. Conf Simonds C.H., Phinney W.C., Warner J.L., McGee P.E., Geeslin J., Brown R.W. and Rhodes J.M. (1977) Apollo 14 revisited, or breccias aren t so bad after all. Proc. 8 th Lunar Sci. Conf Stadermann F.J., Heusser E., Jessberger E.K., Lingner S. and Stoffler D. (1991) The case for a younger Imbrium basin: New 40Ar-39Ar ages of Apollo 14 rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 55, Sutton R.L., Hait M.H. and Swann G.A. (1972) Geology of the Apollo 14 landing site. Proc. 3 rd Lunar Sci. Conf Swann G.A., Trask N.J., Hait M.H. and Sutton R.L. (1971a) Geologic setting of the Apollo 14 samples. Science 173, Swann G.A., Bailey N.G., Batson R.M., Eggleton R.E., Hait M.H., Holt H.E., Larson K.B., Reed V.S., Schaber G.G., Sutton R.L., Trask N.J., Ulrich G.E. and Wilshire H.G. (1977) Geology of the Apollo 14 landing site in the Fra Mauro Highlands. U.S.G.S. Prof. Paper 880. Swann G.A., Bailey N.G., Batson R.M., Eggleton R.E., Hait M.H., Holt H.E., Larson K.B., McEwen M.C., Mitchell E.D., Schaber G.G., Schafer J.P., Shepard A.B., Sutton R.L., Trask N.J., Ulrich G.E., Wilshire H.G. and Wolfe E.W. (1972) 3. Preliminary Geologic Investigation of the Apollo 14 landing site. In Apollo 14 Preliminary Science Rpt. NASA SP-272. pages
14041, and Regolith Breccia 166.3, and 65.2 grams
 14041, and 14045 Regolith Breccia 166.3, 103.2 and 65.2 grams Figure 1a: Sample 14041-14045 on lunar surface. MET and LM in distance. AS14-68-9409. Introduction Samples 14041 14046 are fragments from a
14041, and 14045 Regolith Breccia 166.3, 103.2 and 65.2 grams Figure 1a: Sample 14041-14045 on lunar surface. MET and LM in distance. AS14-68-9409. Introduction Samples 14041 14046 are fragments from a
14315 Unusual Regolith Breccia 115 grams
 Unusual Regolith Breccia 115 grams Figure 1: Photo of,0 after chipping and dusting. Sample is 5 cm across. NASA S86-36340. Introduction was collected as a grab sample from the North Boulder Field (station
Unusual Regolith Breccia 115 grams Figure 1: Photo of,0 after chipping and dusting. Sample is 5 cm across. NASA S86-36340. Introduction was collected as a grab sample from the North Boulder Field (station
14049 Regolith Breccia grams
 Regolith Breccia 200.1 grams Figure 1: Photo of. Edge of cube is 1 inch. NASA S71-29143. Figure 2: Map of Apollo 14 showing traverse for EVA 2. Introduction The Apollo 14 regolith breccias (vitric matrix
Regolith Breccia 200.1 grams Figure 1: Photo of. Edge of cube is 1 inch. NASA S71-29143. Figure 2: Map of Apollo 14 showing traverse for EVA 2. Introduction The Apollo 14 regolith breccias (vitric matrix
15009 Single Drive Tube Station 6
 15009 Single Drive Tube Station 6 Figure 2: Location of soil samples, trench and drive tube at station 6, Apollo 15. Figure 1: Photo of drive tube 15009 driven in all the way. AS15-86-11565. Introduction
15009 Single Drive Tube Station 6 Figure 2: Location of soil samples, trench and drive tube at station 6, Apollo 15. Figure 1: Photo of drive tube 15009 driven in all the way. AS15-86-11565. Introduction
grams g g g g Regolith Breccia
 15306 134.2 grams 15315 35.6 g 15324 32.3 g 15325 57.8 g 15330 57.8 g Regolith Breccia Figure 1a,b: Photo of dust-covered 15306. Sample is 7 cm across. S71-43064 and 067. Introduction 15306 is a regolith
15306 134.2 grams 15315 35.6 g 15324 32.3 g 15325 57.8 g 15330 57.8 g Regolith Breccia Figure 1a,b: Photo of dust-covered 15306. Sample is 7 cm across. S71-43064 and 067. Introduction 15306 is a regolith
15595 and Vuggy Vitrophyric Pigeonite Basalt and grams
 and 15596 Vuggy Vitrophyric Pigeonite Basalt 237.6 and 224.8 grams Figure 1: Photo of. Sample is about 9 cm across. NASA S71-44491. Figure 2: Photo of 15596 showing surface that was exposed to micrometeorites.
and 15596 Vuggy Vitrophyric Pigeonite Basalt 237.6 and 224.8 grams Figure 1: Photo of. Sample is about 9 cm across. NASA S71-44491. Figure 2: Photo of 15596 showing surface that was exposed to micrometeorites.
,1,2,3,4,9, Impact Melt Breccia 65.4 grams
 63335 Impact Melt Breccia 65.4 grams,1,2,3,4,9,10,8 Figure 2: 63335,6. Cube is 1 cm. S75-33389.,7 Introduction 63335 is a sample chipped off of Shadow Rock (Ulrich 1973). It was collected as several fragments
63335 Impact Melt Breccia 65.4 grams,1,2,3,4,9,10,8 Figure 2: 63335,6. Cube is 1 cm. S75-33389.,7 Introduction 63335 is a sample chipped off of Shadow Rock (Ulrich 1973). It was collected as several fragments
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR GEOLOGICAL SURVEY
 UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR GEOLOGICAL SURVEY INTERAGENCY REPORT: 2 7 Documentation of the Apollo 14 samples by G. A. Swann, R. M. Batson, R. E. Eggleton, K. B. Larson, J.P. Schafer, and R.
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR GEOLOGICAL SURVEY INTERAGENCY REPORT: 2 7 Documentation of the Apollo 14 samples by G. A. Swann, R. M. Batson, R. E. Eggleton, K. B. Larson, J.P. Schafer, and R.
grams grams Poikilitic Impact Melt Breccia
 64567 13.8 grams 64569-14.3 grams Poikilitic Impact Melt Breccia Figure 1: Photo of 64567. Scale in mm. S72-55386 Mineralogical Mode by Simonds et al. (1973) 64567 64569 Plagioclase 69% 57 Pyroxene 10
64567 13.8 grams 64569-14.3 grams Poikilitic Impact Melt Breccia Figure 1: Photo of 64567. Scale in mm. S72-55386 Mineralogical Mode by Simonds et al. (1973) 64567 64569 Plagioclase 69% 57 Pyroxene 10
grams grams Double Drive tube 61 cm
 68002 583.5 grams 68001 840.7 grams Double Drive tube 61 cm Figure 1a: Surface photo for double drive tube 68001-2. AS16-108-17684. Introduction Station 8 was the closest to South Ray Crater so premission
68002 583.5 grams 68001 840.7 grams Double Drive tube 61 cm Figure 1a: Surface photo for double drive tube 68001-2. AS16-108-17684. Introduction Station 8 was the closest to South Ray Crater so premission
65055 Basaltic Impact Melt grams
 65055 Basaltic Impact Melt 500.8 grams Figure 1: Photo of 65055 showing large zap pit. Cube is 1 cm. S72-43869. Introduction According to the Apollo 16 Catalog by Ryder and Norman, 65055 is an aluminous,
65055 Basaltic Impact Melt 500.8 grams Figure 1: Photo of 65055 showing large zap pit. Cube is 1 cm. S72-43869. Introduction According to the Apollo 16 Catalog by Ryder and Norman, 65055 is an aluminous,
15556 Vesicular Olivine-normative Basalt grams
 15556 Vesicular Olivine-normative Basalt 1542.3 grams Figure 1: Photo of 15556,0. Largest vesicles are about 6 mm. NASA S87-48187. Introduction 15556 was collected about 60 meters from the edge of Hadley
15556 Vesicular Olivine-normative Basalt 1542.3 grams Figure 1: Photo of 15556,0. Largest vesicles are about 6 mm. NASA S87-48187. Introduction 15556 was collected about 60 meters from the edge of Hadley
grams grams Regolith Breccia
 10019 297 grams 10066 60 grams Regolith Breccia Figure 1: Photo of 10019,1. Cube is 1 inch and scale is in cm. NASA S76-23354. Introduction Kramer et al. (1077) reported that 10019 and 10066 appeared to
10019 297 grams 10066 60 grams Regolith Breccia Figure 1: Photo of 10019,1. Cube is 1 inch and scale is in cm. NASA S76-23354. Introduction Kramer et al. (1077) reported that 10019 and 10066 appeared to
DRAFT Regolith Breccia 155 grams
 12034 Regolith Breccia 155 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Lunar sample 12034 after first saw cut in 1970. NASA S75-34235. Cube is 1 cm. Introduction 12034 was collected from the bottom of the same trench as soil
12034 Regolith Breccia 155 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Lunar sample 12034 after first saw cut in 1970. NASA S75-34235. Cube is 1 cm. Introduction 12034 was collected from the bottom of the same trench as soil
74235 Vitrophric Basalt 59 grams
 74235 Vitrophric Basalt 59 grams Figure 1: Photo of 74235. Cube is 1 cm. S73-16017 Figure 2: Map of station 4, Apollo 17. Transcript (while the LMP was discussing the core with CC, the CDR made a discovery)
74235 Vitrophric Basalt 59 grams Figure 1: Photo of 74235. Cube is 1 cm. S73-16017 Figure 2: Map of station 4, Apollo 17. Transcript (while the LMP was discussing the core with CC, the CDR made a discovery)
72335 Impact melt Breccia grams
 Impact melt Breccia 108.9 grams Figure 1: Location of on boulder #2 on landslide off of South Massif. Boulder is ~ 2-3 meters high. AS17-137-20918. Transcript Hey, that s a different rock, Gene (station
Impact melt Breccia 108.9 grams Figure 1: Location of on boulder #2 on landslide off of South Massif. Boulder is ~ 2-3 meters high. AS17-137-20918. Transcript Hey, that s a different rock, Gene (station
76215 Vesicular Micropoikilitic Impact Melt Breccia 644 grams
 76215 Vesicular Micropoikilitic Impact Melt Breccia 644 grams 76215 76215 Figure 1: Photo of station 6 boulder with location of 76215 indicated. AS17-140-21421 Figure 2: Photo of 76215. Sample is about
76215 Vesicular Micropoikilitic Impact Melt Breccia 644 grams 76215 76215 Figure 1: Photo of station 6 boulder with location of 76215 indicated. AS17-140-21421 Figure 2: Photo of 76215. Sample is about
72320 Partially Shadowed Soil (portion frozen) grams. boulder # 2 station 2 South Massif
 Partially Shadowed Soil (portion ) 106.31 grams Nansen Crater boulder # 2 station 2 South Massif Figure 1: Location of soil sample in shadow of boulder 2, at station 2, Apollo 17. NASA photo #AS17-137-20925.
Partially Shadowed Soil (portion ) 106.31 grams Nansen Crater boulder # 2 station 2 South Massif Figure 1: Location of soil sample in shadow of boulder 2, at station 2, Apollo 17. NASA photo #AS17-137-20925.
62255 Anorthosite with melt 1239 grams
 62255 Anorthosite with melt 1239 grams Figure 1: Photo of 62255 showing glass splash on anorthosite. Cube is 1 cm. NASA S # S72-38309. Introduction Lunar sample 62255 is significant because it is largely
62255 Anorthosite with melt 1239 grams Figure 1: Photo of 62255 showing glass splash on anorthosite. Cube is 1 cm. NASA S # S72-38309. Introduction Lunar sample 62255 is significant because it is largely
61015 Dimict Breccia 1789 grams
 61015 Dimict Breccia 1789 grams Figure 1: Photo of 61015. NASA # S72-37758. Scale and cube in cm. Note the zap pits on the T1 surface and the residual black glass coating on the sides. Introduction Breccia
61015 Dimict Breccia 1789 grams Figure 1: Photo of 61015. NASA # S72-37758. Scale and cube in cm. Note the zap pits on the T1 surface and the residual black glass coating on the sides. Introduction Breccia
DRAFT Coarse-fines 569 grams
 10085 Coarse-fines 569 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Selected coarse fines from 10085. Scale is in mm. Photo from Wood et al. 1969. Introduction!0085 and 10084 were created during the Apollo 11 preliminary examination
10085 Coarse-fines 569 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Selected coarse fines from 10085. Scale is in mm. Photo from Wood et al. 1969. Introduction!0085 and 10084 were created during the Apollo 11 preliminary examination
70035 Ilmenite Basalt 5765 grams
 Ilmenite Basalt 5765 grams Figure 1: Photograph of top surface of illustrating vugs and vesicles. Note the smooth, rounded surface shaped by micrometeorite bombardment. Small cube is 1 cm. NASA photo #
Ilmenite Basalt 5765 grams Figure 1: Photograph of top surface of illustrating vugs and vesicles. Note the smooth, rounded surface shaped by micrometeorite bombardment. Small cube is 1 cm. NASA photo #
DRAFT Feldspathic Basalt? 3439 grams
 14310 Feldspathic Basalt? 3439 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Photograph of 14310 before cutting. Scale is 1 cm, cube is 1 inch. NASA photo # S71-30340. Introduction Sample 14310 was found as a separate sample
14310 Feldspathic Basalt? 3439 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Photograph of 14310 before cutting. Scale is 1 cm, cube is 1 inch. NASA photo # S71-30340. Introduction Sample 14310 was found as a separate sample
Ilmenite Basalt grams
 Ilmenite Basalt 737.6 grams Figure 1: Picute of 5 meter boulder on rim of Shorty Crater showing where was collected. Trench in forground is location of orange soil sample 74220. Photo number AS17-137-20990
Ilmenite Basalt 737.6 grams Figure 1: Picute of 5 meter boulder on rim of Shorty Crater showing where was collected. Trench in forground is location of orange soil sample 74220. Photo number AS17-137-20990
10020 Ilmenite Basalt (low K) 425 grams
 10020 Ilmenite Basalt (low K) 425 grams Figure 1: Photo of 10020 taken in the F-201 during initial processing. Sample is 6 cm across. NASA S-69-45261. Introduction 10020 is a low-k variety of fine-grained
10020 Ilmenite Basalt (low K) 425 grams Figure 1: Photo of 10020 taken in the F-201 during initial processing. Sample is 6 cm across. NASA S-69-45261. Introduction 10020 is a low-k variety of fine-grained
EXERCISE 2 (16 POINTS): LUNAR EVOLUTION & APOLLO EXPLORATION
 1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
Background Image: SPA Basin Interior; LRO WAC, NASA/GSFC/ASU
 B. L. Jolliff1, C. K. Shearer2, N. E. Petro3, D. A. Papanastassiou,4 Y. Liu,4 and L. Alkalai4 1Dept. of Earth & Planetary Sciences, Washington University, St. Louis, MO 2Institute of Meteoritics, University
B. L. Jolliff1, C. K. Shearer2, N. E. Petro3, D. A. Papanastassiou,4 Y. Liu,4 and L. Alkalai4 1Dept. of Earth & Planetary Sciences, Washington University, St. Louis, MO 2Institute of Meteoritics, University
LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY.
 LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY. Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 Editors: Z. KOPAL and A.G.W. CAMERON Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY
LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY. Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 Editors: Z. KOPAL and A.G.W. CAMERON Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY
Signature: GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050
 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
Signature: Name: Banner ID#:
 1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
1 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
15016 Vesicular Olivine-normative Basalt grams
 15016 Vesicular Olivine-normative Basalt 923.7 grams Figure 1: Photograph of vesicular basalt 15016. NASA# S71-46632. Cube is 1 inch. Introduction Lunar Sample 15016 is a highly-vesicular, olivinenormative,
15016 Vesicular Olivine-normative Basalt 923.7 grams Figure 1: Photograph of vesicular basalt 15016. NASA# S71-46632. Cube is 1 inch. Introduction Lunar Sample 15016 is a highly-vesicular, olivinenormative,
10003 Ilmenite Basalt (low K) 213 grams
 10003 Ilmenite Basalt (low K) 213 grams Figure 1: Photo of 10003,25. Sample is 5 cm across. NASA S76-25545. Introduction Lunar sample 10003 is a low-k, high-ti basalt (figure 1). It is about 3.9 b.y. old,
10003 Ilmenite Basalt (low K) 213 grams Figure 1: Photo of 10003,25. Sample is 5 cm across. NASA S76-25545. Introduction Lunar sample 10003 is a low-k, high-ti basalt (figure 1). It is about 3.9 b.y. old,
Moon 101. By: Seacrest School Moon Crew Blake Werab David Prue
 Moon 101 By: Seacrest School Moon Crew Blake Werab David Prue The 101 images The smooth Mare surfaces common on the nearside of the Moon Mare Surfaces from Late heavy Bombardment We find that the 3 images
Moon 101 By: Seacrest School Moon Crew Blake Werab David Prue The 101 images The smooth Mare surfaces common on the nearside of the Moon Mare Surfaces from Late heavy Bombardment We find that the 3 images
67016 Feldspathic Fragmental Breccia 4262 grams
 67016 Feldspathic Fragmental Breccia 4262 grams Figure 1: Photo of 67016,1. Cube is 1 inch. NASA # S81-26050. Introduction 67016 is a feldspathic fragmental breccia with both light and dark clasts (figures
67016 Feldspathic Fragmental Breccia 4262 grams Figure 1: Photo of 67016,1. Cube is 1 inch. NASA # S81-26050. Introduction 67016 is a feldspathic fragmental breccia with both light and dark clasts (figures
Lunar Field Exploration Science
 Lunar Field Exploration Science Harrison H. Schmitt (In Conjunction with FEAT) Workshop on Science Associated with the Lunar Exploration Architecture The Tempe Conference February 26-March 2 What Lunar
Lunar Field Exploration Science Harrison H. Schmitt (In Conjunction with FEAT) Workshop on Science Associated with the Lunar Exploration Architecture The Tempe Conference February 26-March 2 What Lunar
65015 Poikilitic Impact Melt Breccia 1802 grams
 65015 Poikilitic Impact Melt Breccia 1802 grams Figure 1: Photos of 65015 showing rounded exposed surface with numerous zap pits and angular portion without zap pits protected by burial in soil. NASA photos
65015 Poikilitic Impact Melt Breccia 1802 grams Figure 1: Photos of 65015 showing rounded exposed surface with numerous zap pits and angular portion without zap pits protected by burial in soil. NASA photos
12052 Pigeonite Basalt 1866 grams
 12052 Pigeonite Basalt 1866 grams Revised Figure 1: Photo of broken side of 12052 showing vugs. Sample is 6.5 cm high. NASA # S70-44633. Summary of Age Data for 12052 Ar/Ar Rb/Sr Nyquist 1977 (recalculated)
12052 Pigeonite Basalt 1866 grams Revised Figure 1: Photo of broken side of 12052 showing vugs. Sample is 6.5 cm high. NASA # S70-44633. Summary of Age Data for 12052 Ar/Ar Rb/Sr Nyquist 1977 (recalculated)
The most-cited publications (ISI Web of Knowledge)
 The most-cited publications (ISI Web of Knowledge) H-Index = 27 September 2008 Citations 1 129 Metzler K., Bischoff A. and Stöffler D.: Accretionary dust mantles in CMchondrites: Evidence for nebula processes.
The most-cited publications (ISI Web of Knowledge) H-Index = 27 September 2008 Citations 1 129 Metzler K., Bischoff A. and Stöffler D.: Accretionary dust mantles in CMchondrites: Evidence for nebula processes.
The density and porosity of lunar rocks
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051319, 2012 The density and porosity of lunar rocks Walter S. Kiefer, 1 Robert J. Macke, 2,3 Daniel T. Britt, 2 Anthony J. Irving, 4 and Guy J.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051319, 2012 The density and porosity of lunar rocks Walter S. Kiefer, 1 Robert J. Macke, 2,3 Daniel T. Britt, 2 Anthony J. Irving, 4 and Guy J.
The Moon. Part II: Solar System. The Moon. A. Orbital Motion. The Moon s Orbit. Earth-Moon is a Binary Planet
 Part II: Solar System The Moon Audio update: 2014Feb23 The Moon A. Orbital Stuff B. The Surface C. Composition and Interior D. Formation E. Notes 2 A. Orbital Motion 3 Earth-Moon is a Binary Planet 4 1.
Part II: Solar System The Moon Audio update: 2014Feb23 The Moon A. Orbital Stuff B. The Surface C. Composition and Interior D. Formation E. Notes 2 A. Orbital Motion 3 Earth-Moon is a Binary Planet 4 1.
79035 Soil breccia 2806 grams
 Soil breccia 2806 grams Figure 1: Photo of,1. Lines limit band of apparent coarse material. NASA S73-15730. Sample about 8 cm across. Figure 2: Photo of,2. NASA S73-15738. Cube is 1 cm. Figure 3: Photo
Soil breccia 2806 grams Figure 1: Photo of,1. Lines limit band of apparent coarse material. NASA S73-15730. Sample about 8 cm across. Figure 2: Photo of,2. NASA S73-15738. Cube is 1 cm. Figure 3: Photo
crater density: number of craters per unit area on a surface
 Reading for this week: Chap. 9, Sect. 9.4-9.5, Chap. 10, Sect. 10.1-10.5 Homework 6: due in recitation Friday/Monday (Oct. 13, 16) Midterm grade estimates posted on Blackboard this week Astro 120 Fall
Reading for this week: Chap. 9, Sect. 9.4-9.5, Chap. 10, Sect. 10.1-10.5 Homework 6: due in recitation Friday/Monday (Oct. 13, 16) Midterm grade estimates posted on Blackboard this week Astro 120 Fall
New Perspectives on the Lunar Cataclysm from Pre-4 Ga Impact Melt Breccia and Cratering Density Populations
 New Perspectives on the Lunar Cataclysm from Pre-4 Ga Impact Melt Breccia and Cratering Density Populations Marc Norman 1,2 and Charles H. Lineweaver 1 1 Planetary Science Institute of the Research School
New Perspectives on the Lunar Cataclysm from Pre-4 Ga Impact Melt Breccia and Cratering Density Populations Marc Norman 1,2 and Charles H. Lineweaver 1 1 Planetary Science Institute of the Research School
Dept., Univ. of ela as are, 'i?ewark, DE Approximately 130 low specific gravity ((2.601, high silica
 HIGH (760%) SiO LUNAR GLASS%. ir.f. Glass, Geoloey Dept., Univ. of ela as are, 'i?ewark, DE. 1971 1 Approximately 130 low specific gravity ((2.601, high silica p602) glass particles recovered from a 4.88
HIGH (760%) SiO LUNAR GLASS%. ir.f. Glass, Geoloey Dept., Univ. of ela as are, 'i?ewark, DE. 1971 1 Approximately 130 low specific gravity ((2.601, high silica p602) glass particles recovered from a 4.88
Lecture 11 Earth s Moon January 6d, 2014
 1 Lecture 11 Earth s Moon January 6d, 2014 2 Moon and Earth to Scale Distance: a = 385,000 km ~ 60R Eccentricity: e = 0.055 Galileo Spacecraft Dec. 1992 3 [Review question] Eclipses do not occur each month
1 Lecture 11 Earth s Moon January 6d, 2014 2 Moon and Earth to Scale Distance: a = 385,000 km ~ 60R Eccentricity: e = 0.055 Galileo Spacecraft Dec. 1992 3 [Review question] Eclipses do not occur each month
Student Guide to Moon 101
 Student Guide to Moon 101 LINKS TO WEBSITES AND DOCUMENTS NECESSARY TO COMPLETE MOON 101 CAN BE FOUND AT: 1) Read the following articles: PART 1 - FORMATION OF THE MOON a) The Scientific Legacy of Apollo,
Student Guide to Moon 101 LINKS TO WEBSITES AND DOCUMENTS NECESSARY TO COMPLETE MOON 101 CAN BE FOUND AT: 1) Read the following articles: PART 1 - FORMATION OF THE MOON a) The Scientific Legacy of Apollo,
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 9.1 Apollo 11 Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin on the Surface of the Moon. Because there is no atmosphere, ocean, or geological activity
ASTRONOMY Chapter 9 CRATERED WORLDS PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 9.1 Apollo 11 Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin on the Surface of the Moon. Because there is no atmosphere, ocean, or geological activity
Geological Setting of the Luna Glob Candidate Landing Site Region in the Northern High Latitudes: Characterization from LOLA and Related Data
 Geological Setting of the Luna Glob Candidate Landing Site Region in the Northern High Latitudes: Characterization from LOLA and Related Data A.M. Abdrakhimov, A.T. Basilevsky, M.A. Ivanov, Vernadsky Institute,
Geological Setting of the Luna Glob Candidate Landing Site Region in the Northern High Latitudes: Characterization from LOLA and Related Data A.M. Abdrakhimov, A.T. Basilevsky, M.A. Ivanov, Vernadsky Institute,
Lunar Exploration Initiative
 Briefing Topic: Expanding BPLF Activity to the West David A. Kring November 2008 Contents: Regional Geologic Context 2 Location of Desert RATS 2008-2009 Activities 10 Potential Expansion of Test Area to
Briefing Topic: Expanding BPLF Activity to the West David A. Kring November 2008 Contents: Regional Geologic Context 2 Location of Desert RATS 2008-2009 Activities 10 Potential Expansion of Test Area to
Vital Statistics. The Moon. The Tides The gravitational pull between the Earth, the Moon and the Sun causes three inter-related effects: Lunar Phases
 Vital Statistics Orbit & tides Apollo & beyond Surface Interior Origin The Moon Vital Statistics Mean distance from Earth 384400 km Orbital period (sidereal) Rotational period 27.322 days Eccentricity
Vital Statistics Orbit & tides Apollo & beyond Surface Interior Origin The Moon Vital Statistics Mean distance from Earth 384400 km Orbital period (sidereal) Rotational period 27.322 days Eccentricity
The Moon. Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon
 The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
DRAFT. fillet grams grams grams (frozen) grams Vesicular Ilmenite Basalt
 71055 669.6 grams 71035 141.8 grams 71036 118.4 grams (frozen) 71037 14.39 grams Vesicular Ilmenite Basalt DRAFT 71040 71060 71055 71035 71036 71037 fillet Figure 1: This boulder of vesicular basalt from
71055 669.6 grams 71035 141.8 grams 71036 118.4 grams (frozen) 71037 14.39 grams Vesicular Ilmenite Basalt DRAFT 71040 71060 71055 71035 71036 71037 fillet Figure 1: This boulder of vesicular basalt from
Lunar Glossary. Note to the User: Glossary
 Lunar Glossary Note to the User: A number of terms are unique to lunar science or are at least used in a specialized sense. The following brief glossary is an attempt to define these unique terms plus
Lunar Glossary Note to the User: A number of terms are unique to lunar science or are at least used in a specialized sense. The following brief glossary is an attempt to define these unique terms plus
Revised Impact Melt Rock with Shocked/Melted Anorthosite Cap 11,745 grams
 61016 Impact Melt Rock with Shocked/Melted Anorthosite Cap 11,745 grams Revised Figure 1: Close-up photo of a portion of the top surface of 61016,456 showing dimorphic nature of stone and numeraous zap
61016 Impact Melt Rock with Shocked/Melted Anorthosite Cap 11,745 grams Revised Figure 1: Close-up photo of a portion of the top surface of 61016,456 showing dimorphic nature of stone and numeraous zap
Name Date. Partners. Comparative Planetology by Mary Lou West after Paul Johnson and Ron Canterna
 Name Date Partners Comparative Planetology by Mary Lou West after Paul Johnson and Ron Canterna Purpose : to become familiar with the major features of the planets of the solar system, especially the Earth,
Name Date Partners Comparative Planetology by Mary Lou West after Paul Johnson and Ron Canterna Purpose : to become familiar with the major features of the planets of the solar system, especially the Earth,
In-situ geochronology General overview
 In-situ geochronology General overview Timothy D. Swindle, University of Arizona, Tucson AZ F. Scott Anderson, Southwest Research Institute, Boulder CO October 26, 2009 Decadal Survey Inner Planets Panel
In-situ geochronology General overview Timothy D. Swindle, University of Arizona, Tucson AZ F. Scott Anderson, Southwest Research Institute, Boulder CO October 26, 2009 Decadal Survey Inner Planets Panel
12042 Soil 255 grams
 Soil 255 grams Figure 1: Photo of location of (Halo Crater). AS12-48-7072 Introduction are fines collected in documented bag 12. They were from the outer flank of Surveyor Crater (figure 2). Figure 2:
Soil 255 grams Figure 1: Photo of location of (Halo Crater). AS12-48-7072 Introduction are fines collected in documented bag 12. They were from the outer flank of Surveyor Crater (figure 2). Figure 2:
60016 Ancient Regolith Breccia 4307 grams
 60016 Ancient Regolith Breccia 4307 grams Figure 1: Photo of 60016 showing large glass-lined micrometeorite crater with significant spall zone. Glass lining about 0.8 cm in size. Sample is about 15 cm
60016 Ancient Regolith Breccia 4307 grams Figure 1: Photo of 60016 showing large glass-lined micrometeorite crater with significant spall zone. Glass lining about 0.8 cm in size. Sample is about 15 cm
12013 Breccia with granite 82.3 grams
 12013 Breccia with granite 82.3 grams Figure 1: Close-up photo of 12013,11. Field of view is 4.5 cm. NASA# S70-43636 Introduction 12013 is a unique lunar sample, but it did not appear to be remarkable
12013 Breccia with granite 82.3 grams Figure 1: Close-up photo of 12013,11. Field of view is 4.5 cm. NASA# S70-43636 Introduction 12013 is a unique lunar sample, but it did not appear to be remarkable
of Copernicus and the source of nonmare materials
 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70 (2006) 6016 6031 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca 40 Ar/ 39 Ar dating of Apollo 12 regolith: Implications for the age of Copernicus and the source of nonmare materials Fernando
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70 (2006) 6016 6031 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca 40 Ar/ 39 Ar dating of Apollo 12 regolith: Implications for the age of Copernicus and the source of nonmare materials Fernando
Moon 101 Presentation. Mike Delmonaco Trevor Rosenlicht Nicole La Reddola
 Moon 101 Presentation Mike Delmonaco Trevor Rosenlicht Nicole La Reddola Feature 1: Dome Feature 2: Cone Feature 3: Main dome crater Image 1 Color key: Dome/Cone: Dome Crater Cone Dome Craters: Endogenic
Moon 101 Presentation Mike Delmonaco Trevor Rosenlicht Nicole La Reddola Feature 1: Dome Feature 2: Cone Feature 3: Main dome crater Image 1 Color key: Dome/Cone: Dome Crater Cone Dome Craters: Endogenic
Chapter 21. The Moon and Mercury: Comparing Airless Worlds
 Chapter 21 The Moon and Mercury: Comparing Airless Worlds Outline I. The Moon A. The View From Earth B. The Apollo Missions C. Moon Rocks D. The History of the Moon E. The Origin of Earth's Moon II. Mercury
Chapter 21 The Moon and Mercury: Comparing Airless Worlds Outline I. The Moon A. The View From Earth B. The Apollo Missions C. Moon Rocks D. The History of the Moon E. The Origin of Earth's Moon II. Mercury
Time to Solidify an Ocean of Magma
 1 of 6 March 25, 2009 Time to Solidify an Ocean of Magma --- A small mineral grain places limits on how long it took the lunar magma ocean to solidify. Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai i Institute of
1 of 6 March 25, 2009 Time to Solidify an Ocean of Magma --- A small mineral grain places limits on how long it took the lunar magma ocean to solidify. Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai i Institute of
Mercury = Hermes Mythology. Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff
 Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Classroom Space Regolith Formation Teacher s Guide
 Regolith Formation on the Earth and the Moon. Background The loose fragments of material on the Moon s surface are called regolith. This regolith, a product of bombardment by meteorites, is the debris
Regolith Formation on the Earth and the Moon. Background The loose fragments of material on the Moon s surface are called regolith. This regolith, a product of bombardment by meteorites, is the debris
9/15/16. Guiding Questions. Our Barren Moon. The Moon s Orbit
 Our Barren Moon Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior have a
Our Barren Moon Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior have a
DRAFT Cataclastic Dunite grams
 72415-72418 Cataclastic Dunite 58.74 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Boulder 3 at Station 2, with large dunite clast (72415-72418). The bright spot is the location of samples. A sample of the boulder matrix (72435)
72415-72418 Cataclastic Dunite 58.74 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Boulder 3 at Station 2, with large dunite clast (72415-72418). The bright spot is the location of samples. A sample of the boulder matrix (72435)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Sample Description Rock 14053 is one of the most well-studied high-al basalts in the Apollo collection 2,3. This sample (14053,241) was chipped from a large (approx. 0.5 m long) boulder at station C2,
Sample Description Rock 14053 is one of the most well-studied high-al basalts in the Apollo collection 2,3. This sample (14053,241) was chipped from a large (approx. 0.5 m long) boulder at station C2,
THE MOON: Geologic History and Future Exploration
 THE MOON: Geologic History and Future Exploration What did we know about the Moon before Apollo? Two types of Terrain Highlands Maria This picture of the moon was taken with a telescope at Lick Observatory,
THE MOON: Geologic History and Future Exploration What did we know about the Moon before Apollo? Two types of Terrain Highlands Maria This picture of the moon was taken with a telescope at Lick Observatory,
10. Our Barren Moon. Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers. Moon Data: Special Features 1. The Moon As Seen From Earth
 10. Our Barren Moon Lunar plains & craters Manned lunar exploration The lunar interior The Moon s geologic history The formation of the Moon Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers Diameter: 3,476.km
10. Our Barren Moon Lunar plains & craters Manned lunar exploration The lunar interior The Moon s geologic history The formation of the Moon Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers Diameter: 3,476.km
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10326 Supplementary Discussion All known modern terrestrial mantle reservoirs evolved from a primitive precursor with superchondritic 143 Nd/ 144 Nd. What is this reservoir? The terms
doi:10.1038/nature10326 Supplementary Discussion All known modern terrestrial mantle reservoirs evolved from a primitive precursor with superchondritic 143 Nd/ 144 Nd. What is this reservoir? The terms
15058 Pigeonite Basalt 2672 grams
 15058 Pigeonite Basalt 2672 grams Figure 1: Photo of mare basalt 15058 (before dusting). NASA S71-44205. Sample is shaped like a brick about 6 inches long and 3 inches high. Note: see also figures 17 and
15058 Pigeonite Basalt 2672 grams Figure 1: Photo of mare basalt 15058 (before dusting). NASA S71-44205. Sample is shaped like a brick about 6 inches long and 3 inches high. Note: see also figures 17 and
Complex magmatic and impact history prior to 4.1 Ga recorded in zircon from Apollo 17 South Massif aphanitic breccia 73235
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln NASA Publications National Aeronautics and Space Administration 2011 Complex magmatic and impact history prior to 4.1 Ga
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln NASA Publications National Aeronautics and Space Administration 2011 Complex magmatic and impact history prior to 4.1 Ga
Report to the Planetary Science Subcommittee September, 2016 Hap McSween, Chair
 Dedicated to maximizing planetary sample science while protecting the integrity of NASA-collected extraterrestrial materials Report to the Planetary Science Subcommittee September, 2016 Hap McSween, Chair
Dedicated to maximizing planetary sample science while protecting the integrity of NASA-collected extraterrestrial materials Report to the Planetary Science Subcommittee September, 2016 Hap McSween, Chair
The Moon. Impacts in the Earth-Moon System What, When and Why? N. E. B. Zellner Department of Physics. To the Moon! The Moon
 Impacts in the Earth-Moon System What, When and Why? The Moon N. E. B. Zellner Department of Physics Apollo 11 footprint in soft lunar regolith 1/4 the size of Earth 1/6 the gravity of Earth Covered in
Impacts in the Earth-Moon System What, When and Why? The Moon N. E. B. Zellner Department of Physics Apollo 11 footprint in soft lunar regolith 1/4 the size of Earth 1/6 the gravity of Earth Covered in
Refining lunar impact chronology through high spatial resolution 40 Ar/ 39 Ar dating of impact melts
 SPACE SCIENCES Refining lunar impact chronology through high spatial resolution 40 Ar/ 39 Ar dating of impact melts Cameron M. Mercer, 1 * Kelsey E. Young, 1 John R. Weirich, 1 Kip V. Hodges, 1 Bradley
SPACE SCIENCES Refining lunar impact chronology through high spatial resolution 40 Ar/ 39 Ar dating of impact melts Cameron M. Mercer, 1 * Kelsey E. Young, 1 John R. Weirich, 1 Kip V. Hodges, 1 Bradley
Our Barren Moon. Chapter Ten. Guiding Questions
 Our Barren Moon Chapter Ten Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior
Our Barren Moon Chapter Ten Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior
LUNAR OBSERVING. What will you learn in this lab?
 LUNAR OBSERVING What will you learn in this lab? The Moon is the second most noticeable object in the sky. This lab will first introduce you to observing the Moon with a telescope. You will be looking
LUNAR OBSERVING What will you learn in this lab? The Moon is the second most noticeable object in the sky. This lab will first introduce you to observing the Moon with a telescope. You will be looking
COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2012
 Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2012 Geologic mapping Goals: To recognize the similarities and differences in the processes affecting the outer planet satellites, and in the resulting landforms. To demonstrate
Name COSMORPHOLOGY - May 2012 Geologic mapping Goals: To recognize the similarities and differences in the processes affecting the outer planet satellites, and in the resulting landforms. To demonstrate
Two types of Terrain Highlands Maria This picture of the moon was taken with a telescope at Lick Observatory, CA
 Two types of Terrain Highlands Maria This picture of the moon was taken with a telescope at Lick Observatory, CA A view seen by Apollo 17 astronauts as they orbited the Moon The Maria are smoother, lower,
Two types of Terrain Highlands Maria This picture of the moon was taken with a telescope at Lick Observatory, CA A view seen by Apollo 17 astronauts as they orbited the Moon The Maria are smoother, lower,
Moon and Mercury 3/8/07
 The Reading Assignment Chapter 12 Announcements 4 th homework due March 20 (first class after spring break) Reminder about term paper due April 17. Next study-group session is Monday, March 19, from 10:30AM-12:00Noon
The Reading Assignment Chapter 12 Announcements 4 th homework due March 20 (first class after spring break) Reminder about term paper due April 17. Next study-group session is Monday, March 19, from 10:30AM-12:00Noon
Complete the crossword puzzle. The Moon. (Key # )
 Name Complete the crossword puzzle. The Moon Date (Key # 1-168014) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Across 1 : The moon appears bigger on the horizon than it does high in the sky, but in reality it is the same
Name Complete the crossword puzzle. The Moon Date (Key # 1-168014) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Across 1 : The moon appears bigger on the horizon than it does high in the sky, but in reality it is the same
Lunar meteorites: new insights into the geological history of the Moon
 Lunar meteorites: new insights into the geological history of the Moon Katherine H Joy and Tomoko Arai discuss the evidence from lunar meteorites about the shared history of Earth and the Moon. 1 The Moon
Lunar meteorites: new insights into the geological history of the Moon Katherine H Joy and Tomoko Arai discuss the evidence from lunar meteorites about the shared history of Earth and the Moon. 1 The Moon
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 10. Geology and life. Part 1 (Page 99-123)
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 10. Geology and life. Part 1 (Page 99-123)
Lecture 15 Crater counting on Mars (Matt Smith, ESS)
 Tuesday, 24 February Lecture 15 Crater counting on Mars (Matt Smith, ESS) Reading assignment: Ch. 8.1-8.5 Radar Basics (p.626 648) Ch 8.20 - Passive microwave (p. 709-714) Next lecture Forest remote sensing,
Tuesday, 24 February Lecture 15 Crater counting on Mars (Matt Smith, ESS) Reading assignment: Ch. 8.1-8.5 Radar Basics (p.626 648) Ch 8.20 - Passive microwave (p. 709-714) Next lecture Forest remote sensing,
GSA Data Repository Qiao et al., 2017, Ina pit crater on the Moon: Extrusion of waning-stage lava lake magmatic foam results in extremely
 1 GSA Data Repository 2017135 Qiao et al., 2017, Ina pit crater on the Moon: Extrusion of waning-stage lava lake magmatic foam results in extremely young crater retention ages: Geology, doi:10.1130/g38594.1
1 GSA Data Repository 2017135 Qiao et al., 2017, Ina pit crater on the Moon: Extrusion of waning-stage lava lake magmatic foam results in extremely young crater retention ages: Geology, doi:10.1130/g38594.1
The Earth's Moon. The Earth's Moon, in many ways, is prototypical of a substantial fraction of the objects in the Solar System.
 1 The Earth's Moon The Earth's Moon, in many ways, is prototypical of a substantial fraction of the objects in the Solar System. Like many other moons and planets it exhibits a heavily cratered surface
1 The Earth's Moon The Earth's Moon, in many ways, is prototypical of a substantial fraction of the objects in the Solar System. Like many other moons and planets it exhibits a heavily cratered surface
SIMS U Pb study of zircon from Apollo 14 and 17 breccias: Implications for the evolution of lunar KREEP
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 7 (8) 668 689 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca SIMS U Pb study of zircon from Apollo 1 and 17 breccias: Implications for the evolution
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 7 (8) 668 689 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca SIMS U Pb study of zircon from Apollo 1 and 17 breccias: Implications for the evolution
Moon 101. Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi
 Moon 101 Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi Part I Formation of the Moon Planetary Formation In the solar nebula, dust particles coalesced to form smaller planetesimals and
Moon 101 Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi Part I Formation of the Moon Planetary Formation In the solar nebula, dust particles coalesced to form smaller planetesimals and
New evidence for lunar basalt metasomatism by underlying regolith.
 1 2 3 4 5 New evidence for lunar basalt metasomatism by underlying regolith. John F. Pernet-Fisher* School of Earth, Atmospheric, and Environmental Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 2PL,
1 2 3 4 5 New evidence for lunar basalt metasomatism by underlying regolith. John F. Pernet-Fisher* School of Earth, Atmospheric, and Environmental Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 2PL,
Grading Summary: Questions 1: 22 points. Question 2: 12 points. Question 3: 12 points. Question 4: 18 points. Question 5: 36 points.
 HOMEWORK #3 Moon Concepts Due Friday, May 5 th IN CLASS Answers to the questions must be given in complete sentences (except where indicated), using correct grammar and spelling. Please be as brief and
HOMEWORK #3 Moon Concepts Due Friday, May 5 th IN CLASS Answers to the questions must be given in complete sentences (except where indicated), using correct grammar and spelling. Please be as brief and
12032 Soil 310 grams
 Soil 310 grams Figure 1: Location of at Bench Crater site. AS12-48-7063. 25 20 Apollo soils FeO 15 10 5 Figure 2: Location of on traverse map, Apollo 12. Introduction are the fines collected in documented
Soil 310 grams Figure 1: Location of at Bench Crater site. AS12-48-7063. 25 20 Apollo soils FeO 15 10 5 Figure 2: Location of on traverse map, Apollo 12. Introduction are the fines collected in documented
Lunar Geology of Apollo 11 Landing Site. Chenango Forks High School Sharon Hartzell Sarah Maximowicz Benjamin Daniels Sarah Andrus Jackson Haskell
 Lunar Geology of Apollo 11 Landing Site Chenango Forks High School Sharon Hartzell Sarah Maximowicz Benjamin Daniels Sarah Andrus Jackson Haskell Lunar Maria Lunar Maria Lunar Maria Low albedo Volcanic
Lunar Geology of Apollo 11 Landing Site Chenango Forks High School Sharon Hartzell Sarah Maximowicz Benjamin Daniels Sarah Andrus Jackson Haskell Lunar Maria Lunar Maria Lunar Maria Low albedo Volcanic
The Importance of Impact Melts
 The Importance of Impact Melts Constrain bombardment histories [Chapman et al. (2007)] Ar-Ar age dating [e.g. Norman et al. (2006)] Identify type of impactor Highly Siderophile Elements (HSE) [e.g. Puchtel
The Importance of Impact Melts Constrain bombardment histories [Chapman et al. (2007)] Ar-Ar age dating [e.g. Norman et al. (2006)] Identify type of impactor Highly Siderophile Elements (HSE) [e.g. Puchtel
Moon Formation. Capture Hypothesis Many Hypothesis Fission Hypothesis Double Impact Hypothesis Giant Impact Hypothesis
 Moon Formation Capture Hypothesis Many Hypothesis Fission Hypothesis Double Impact Hypothesis Giant Impact Hypothesis Capture Hypothesis Earth seized a pre-formed moon Disproved when lunar samples showed
Moon Formation Capture Hypothesis Many Hypothesis Fission Hypothesis Double Impact Hypothesis Giant Impact Hypothesis Capture Hypothesis Earth seized a pre-formed moon Disproved when lunar samples showed
Moonstruck: Illuminating Early Planetary History
 Moonstruck: Illuminating Early Planetary History G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai`i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology University of Hawai`i at Manoa Jeff Taylor Lunar Science 1 View of the Earth and Moon
Moonstruck: Illuminating Early Planetary History G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai`i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology University of Hawai`i at Manoa Jeff Taylor Lunar Science 1 View of the Earth and Moon
Mars Sample Return The Apollo Perspective
 Mars Sample Return The Apollo Perspective D. A. Papanastassiou Science Division, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Ground Truth from Mars, Albuquerque, NM, April 21-23, 2008 Purpose Share some of the excitement
Mars Sample Return The Apollo Perspective D. A. Papanastassiou Science Division, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Ground Truth from Mars, Albuquerque, NM, April 21-23, 2008 Purpose Share some of the excitement
American Association for the Advancement of Science is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Science.
 Geologic Exploration of Taurus-Littrow: Apollo 17 Landing Site Author(s): Apollo Field Geology Investigation Team Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 182, No. 4113 (Nov. 16, 1973), pp. 672-680 Published
Geologic Exploration of Taurus-Littrow: Apollo 17 Landing Site Author(s): Apollo Field Geology Investigation Team Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 182, No. 4113 (Nov. 16, 1973), pp. 672-680 Published
Terramechanics. Origin and nature of lunar soil Soil mechanics Wheel-soil interactions Tandem wheel calculations Grousers MARYLAND
 Terramechanics Origin and nature of lunar soil Soil mechanics Wheel-soil interactions Tandem wheel calculations Grousers 1 16 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu Lunar Regolith
Terramechanics Origin and nature of lunar soil Soil mechanics Wheel-soil interactions Tandem wheel calculations Grousers 1 16 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu Lunar Regolith
Assignment 2. Due March 4, 2019
 Assignment 2 Due March 4, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
Assignment 2 Due March 4, 2019 Show all work and turn in answers on separate pages, not on these pages. Circle your final answers for clarity. Be sure to show/explain all of your reasoning and that your
