The seismic response to strong vertical velocity change
|
|
|
- Allyson Liliana Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P-073 The seismic response to strong vertical velocity change Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology Summary Conventional seismic data processing, whether it be pre-stack data conditioning or migration, is designed with the theory of P-wave reflected energy in-mind, for travel paths involving only a single reflection. Any energy propagating with other modes or travel paths will not be dealt with appropriately during conventional seismic data processing. It is primarily for this reason that we spend so much time pre-conditioning seismic data, so as to meet the assumptions of the subsequent migration. In this study, looking at shallow-water marine data from high velocity- contrast environments (such as found with basalt or carbonates), I assess the behaviour of some other classes seismic energy, when subjected to conventional processing, so as to better understand the anomalous events appearing in migrated CRP gathers and images, due to contamination of the data with remnant refraction and mode-converted energy. Keywords: P-wave processing, artifact, mode-conversion, refraction Introduction Due to the high velocity and density contrasts associated with basalt, chalk, or salt layers, and large vertical velocity gradients in the overlying sediments, we often record refraction and sometimes converted mode (PSSP, PSPP, PPSP) seismic arrivals. During conventional processing, these arrivals are dealt with as if it they were P energy, giving-rise to anomalous behaviour in the migrated data. Ideally, the data pre-conditioning steps (such as linear noise removal) should remove these events prior to velocity estimation and migration, but often spurious remnants of them remain. Here I present a modelling study to assess behaviour of chalk-related seismic reflection and refraction events on a shallow-water marine survey (Jones, 2013b). Diving rays and refractions resulting from large vertical compaction velocity gradients are also addressed, as remnant energy from these events impinges on the underlying chalk reflections. The study attempts to qualitatively highlight some of these effects, so as to give insight into the nature of the observed results on real data associated with unusual behaviour observed in gathers during velocity model building and images after migration. Modelling study The P-wave velocities were derived from the high resolution tomographic presdm model derived on a commercial presdm project over a region in the North Sea (using a tomographic inversion cell size of 50m * 50m * 50m in the chalk to resolve thin intra-chalk layering). This was verified and calibrated using available well sonic logs. Density was estimated using a modified Gardner relationship, calibrated to the available density logs, with reasonable values used in the shallow section (which was not logged). In addition, some literature was reviewed to determine a range of realistic shear-wave velocity and density values near the sea bed (e.g. Carbone et al., 1998; Muyzert 2006; Shillington et al., 2008). 2D modelling was performed using both finite difference (FD) and ray-trace techniques, both acoustically and elastically. All modelling was isotropic, and for investigation of post-critical phase change, attenuation was turned-off so as not to further change the wavelet s phase. The modelling was performed primarily using GXII, but also in ProMax. For the ray-trace part of the study, a layered model was constructed, and for the detailed analysis of elastic events, a locally flat model analog was made to remove any structural bias. ION GX Technology, Integra House, Vicarage Road, Egham, Surrey TW20 9JZ, UK. Ian.Jones@iongeo.com
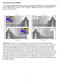
2 The study concentrated on a single representative inline, and four nearby wells. A depth migrated seismic section with superimposition of these wells shows that we have at least three high velocity bands within the chalk and a strong compaction gradient above it (Figure 1). Figure 3, real data from near the seismic presdm section shown in Figure 1. Many of the features seen in the modelled data (Figure 2) are also present here. Maximum offset 5.2km. Simplified modelling to help understand complex arrivals Figure 1: smoothed interval velocity logs superimposed on the presdm image, with tomographic velocity colour overlay. The wells are from nearby locations, so do not tie the line perfectly. The locations of the top and base chalk, and mid-tertiary reflector are also indicated. Figure 2 shows the elastically modeled FD synthetic data (created with the model shown in Figure 1) after presdm using the correct model (that used to create the synthetic data). Real 3D presdm data, from an intermediate stage in the production project (not final gathers) are shown in Figure 3: these gathers exhibit many of the features seen in the modelled data. Figure 2, presdm of the FD modelled gathers (using the correct velocity model), converted to time. The refracted energy looks anomalous, as migration is not designed to handle refracted events The moveout behaviour observed in the modelling performed using finite differencing with the complex velocity model does indeed produce results resembling the observed data. However, to better understand the nature of the observed events, I ll commence the analysis by first considering a grossly simplified set of models, and then move on to introducing converted modes in the modelling by using elastic rather than acoustic modelling. Before considering more complex multi-layered models lets first look at the behaviour of a half-space (that is, a model with two solid regions, with a reflecting boundary at some depth between them). Figure 4 shows FD acoustic modelling of a half-space with reflection and refraction events for a top chalk reflector model, with upper medium velocity = 2700m/s and lower region chalk velocity = 4800m/s. Visible are the direct wave arrival, the top chalk reflection, and commencing at the critical-angle offset, a refraction event can be seen slightly above the post critical reflection trajectory. Figure 5 shows a more complex model with several layers, and Figure 6 shows these data after application of NMO with the corresponding RMS velocity. The chalk event is flattened, the refracted head wave curls upwards (resembling anisotropic reflection behaviour), and elements of the chalk reflector are distorted into a linear downward trending event by the NMO process. 2
3 Converted mode arrivals For the synthetic modelling performed, converted modes are associated with the mid-tertiary and top chalk reflectors, but for the purposes of demonstration, I ll discus only those related to the top-chalk event, as this was present across the entire region. For the various converted modes seen, the conversion takes place at the sea bed for transmitted events and at the high velocity-contrast interfaces for reflected events. Figure 4: FD acoustic modelling. reflection and refraction events for a top chalk half-space reflector model In Figure 7 I show the elastic ray-trace modelled data for the 1D model, showing the input and NMO d CMP but just for the top-chalk reflection and associated modeconverted arrivals. Conversion is occurring at the sea bed for transmission and at the top chalk for reflection, so we are seeing PSPP, PSSP, and PPSP arrivals, as well as the usual PPPP arrival (the PSPP and PPSP events are coincident as their arrival times are the same for the 1D model). On the right is shown the full FD elastic modelled result for all events in the 1D model result for comparison. In the full FD modelling, we see modeconverted energy from both the tertiary and top chalk events. Amplitudes will differ between the ray-traced and FD modelled data, as ray tracing primarily delivers reasonable kinematics, whereas FD modelling should also produce reasonable dynamics. Figure 5: FD acoustic modelling of more complex 1D model. Figure 6: FD acoustic modelling. NMO of the data in Figure 5 produces various kinds of distortion: the downward trending NMO high-velocity contrast boundary artefact is visible, and other non-p reflection events are distorted by the NMO function. Figure 7: elastic ray-trace modelled data with 18Hz peak frequency for the chalk layer 1D model, showing the input, and NMO d CMP, for the top-chalk reflection and associated modeconverted arrivals.on the right is shown the FD elastic result for comparison. We see mode- converted energy from both the tertiary and top chalk events, as well as the strong travel time bifurcation related event. 3
4 Comparison with Real data. In Figure 8, I show the synthetic FD data where the moveout trajectories of the converted mode events have been picked on the migrated CRP gather (yellow dotted lines), and then also superimposed on the real data shown in Figure 9. The real data shown in the left panel of Figure 9 are those used as input to the migration (with various linear noise and some demultiple processing). Both after NMO (centre panel) and after presdm (right panel), the data still show some remnant noise associated with the converted mode energy. The downward (and upward) dipping linear noise from the chalk refractions can be partly removed using a Radon filter. These classes of remnant energy are still quite persistent even after significant pre-processing efforts. They could indeed be further attenuated, but this would most likely require more heavy-handed pre-processing that would probably also damage the underlying desired signal. Their presence after the pre-processing leads to misleading events in the CRP gathers, and can thereby especially hamper velocity model building, as the quasilinear trends and abrupt amplitude anomalies can degrade the performance of the various transforms used in velocity analysis (Jones, 2013a). They are less of a problem in the final image, as they tend to stack-out. Figure 9: real data at with pre-processing as input to final migration, showing input data, after NMO correction, after 3D presdm. The yellow trajectories on the presdm are the refractions and modelled converted modes from the tertiary and top-chalk as picked on the modelled data migrated gathers. It can be seen that remnant noise in the real data does appear to correspond with the modelled residual refraction and converted mode events. Conclusions Refraction and mode-converted energy is not correctly handled by conventional P-wave single reflection processing, and hence should ideally be removed prior to migration. However, remnant energy from such events invariably remains in the data after pre-processing, and contaminates the resultant CRP gathers and images. Here I have tried to demonstrate the nature and behaviour of this remnant energy, so as to give some insight into what detail we should be focusing on and what we should be ignoring in resultant gathers and images. Acknowledgements My thanks to Juergen Fruehn, Jacques Leveille, and John Brittan for detailed proof reading, and Rob Bloor for insightful discussions on Kirchhoff and NMO behaviour, and to ION-GX Technology for permission to present this work. Figure 8: FD elastically modelled data with all multiples, showing raw data, after NMO correction, after presdm. Superimposed on the migrated gather are show manual picks of the moveout trajectories of the converted and refracted events (yellow dotted lines) References Carbone, N.M, Deane, G.B., and Buckingham, M.J., 1998, Estimating the compressional and shear wave speeds of a shallow water seabed from the vertical coherence of ambient noise in the water column, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103 (2). pdfs/estimating_the.pdf 4
5 Jones, I.F., 2010, An introduction to velocity model building, EAGE, ISBN , 296 pages. Jones, I.F, 2013a, Tutorial: Transforms, orthogonality, eigenvectors, and eigenvalues. First Break, 31, no.1., Jones, I.F, 2013b, Tutorial: The seismic response to strong vertical velocity change. First Break, 31, no.6., Muyzert, E., 2006, Seabed Properties Derived from Ambient Noise, EAGE 68th Conference & Exhibition Pelissier, M.A., Hoeber, H., van de Coevering, N., Jones, I.F., 2007, Classics of Elastic Wave Theory, SEG Geophysics Reprints, 24, Series Editor: Daniel A. Ebrom, 534 pages. Shillington, D.P., Minshull, T.A., Peirce, C., O Sullivan, J.M., 2008, P and S wave velocities of consolidated sediments from a seafloor seismic survey in the North Celtic Sea Basin, offshore Ireland es_loaded.pdf Tatham, R.H., and McCormack M.D., 1991, Multicomponent Seismology in Petroleum Exploration, SEG, 256 pages. 5
Th N Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data
 Th N107 11 Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data A. Castiello* (ION GXT), Y. Ren (ION GXT), S. Greenwood (ION GXT), T. Martin (ION GXT),
Th N107 11 Seismic Imaging in Gas Obscured Areas - Q Anomaly Detection and Q Migration Applied to Broadband Data A. Castiello* (ION GXT), Y. Ren (ION GXT), S. Greenwood (ION GXT), T. Martin (ION GXT),
A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography
 A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography Ian Jones* GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom ijones@gxt.com Emma Evans and Darren Judd GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom and
A Southern North Sea Multi-Survey presdm using Hybrid Gridded Tomography Ian Jones* GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom ijones@gxt.com Emma Evans and Darren Judd GX Technology, Egham, United Kingdom and
Th P7 02 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling
 Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
H Seismic imaging in and around salt bodies: problems and pitfalls. Ian Jones 1, Ian Davison 2. Summary
 H1-2-3 Seismic imaging in and around salt bodies: problems and pitfalls Ian Jones 1, Ian Davison 2 1 ION, Chertsey, UK, 2 EarthMoves, Egham, UK Summary Salt movement often results in steeply-dipping complex
H1-2-3 Seismic imaging in and around salt bodies: problems and pitfalls Ian Jones 1, Ian Davison 2 1 ION, Chertsey, UK, 2 EarthMoves, Egham, UK Summary Salt movement often results in steeply-dipping complex
Absorption related velocity dispersion below a possible gas hydrate geobody. Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology, UK
 Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology, UK Abstract Velocity dispersion is not usually a problem in surface seismic data processing, as the seismic bandwidth is relatively narrow, and thus for most Q values,
Ian F. Jones, ION GX Technology, UK Abstract Velocity dispersion is not usually a problem in surface seismic data processing, as the seismic bandwidth is relatively narrow, and thus for most Q values,
J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU)
 U008 Seismic Imaging Below "Dirty" Salt J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU) SUMMARY Base and sub salt seismic imaging is still an unresolved issue. To solve
U008 Seismic Imaging Below "Dirty" Salt J.A. Haugen* (StatoilHydro ASA), J. Mispel (StatoilHydro ASA) & B. Arntsen (NTNU) SUMMARY Base and sub salt seismic imaging is still an unresolved issue. To solve
Time vs depth in a North Sea case study of the ugly truth Abstract
 Time vs depth in a North Sea case study of the ugly truth Thomas Massip 1, Lauren Braidwood 1, Juergen Fruehn 1, Owen Isaac 1, Jonathan Denly 1, Robert Richardson 2, Phil Mollicone 3 1 ION Geophysical;
Time vs depth in a North Sea case study of the ugly truth Thomas Massip 1, Lauren Braidwood 1, Juergen Fruehn 1, Owen Isaac 1, Jonathan Denly 1, Robert Richardson 2, Phil Mollicone 3 1 ION Geophysical;
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection
 A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
P Edward Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian Davies 2, Henna Selby 2, Emma Evans 2, Mark Johnson 1. Abstract
 P1-3-10 De-risking Drill Decisions. A case study on the benefit of re-processing conventionally acquired seismic data with the latest broadband processing technology Edward Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian
P1-3-10 De-risking Drill Decisions. A case study on the benefit of re-processing conventionally acquired seismic data with the latest broadband processing technology Edward Knight 1, James Raffle 2, Sian
Model Building Complexity in the Presence of a Rugose Water Bottom Gippsland Basin Australia
 Model Building Complexity in the Presence of a Rugose Water Bottom Gippsland Basin Australia Paul Bouloudas, Apache Energy, Juergen Fruehn, ION GX Technology Introduction Situated offshore south-eastern
Model Building Complexity in the Presence of a Rugose Water Bottom Gippsland Basin Australia Paul Bouloudas, Apache Energy, Juergen Fruehn, ION GX Technology Introduction Situated offshore south-eastern
Synthetic seismic modelling and imaging of an impact structure
 Modelling and imaging of an impact structure Synthetic seismic modelling and imaging of an impact structure Matteo Niccoli ABSTRACT A geologic depth and velocity model of an impact crater was created and
Modelling and imaging of an impact structure Synthetic seismic modelling and imaging of an impact structure Matteo Niccoli ABSTRACT A geologic depth and velocity model of an impact crater was created and
Near surface velocity adjustments in presence of rugose water bottom A quantitative approach for Canyon Scaling
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 406 Near surface velocity adjustments in presence of rugose water bottom A quantitative approach for Canyon Scaling Himanshu Kumar*, Pramod Srivastava*,
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 406 Near surface velocity adjustments in presence of rugose water bottom A quantitative approach for Canyon Scaling Himanshu Kumar*, Pramod Srivastava*,
Anisotropic Depth Migration and High-Resolution Tomography in Gulf of Mexico: A Case History
 Anisotropic Depth Migration and High-Resolution Tomography in Gulf of Mexico: A Case History Gary Rodriguez, Sherry Yang, Diane Yang, Quincy Zhang, Steve Hightower, TGS Summary We present a case study
Anisotropic Depth Migration and High-Resolution Tomography in Gulf of Mexico: A Case History Gary Rodriguez, Sherry Yang, Diane Yang, Quincy Zhang, Steve Hightower, TGS Summary We present a case study
H005 Pre-salt Depth Imaging of the Deepwater Santos Basin, Brazil
 H005 Pre-salt Depth Imaging of the Deepwater Santos Basin, Brazil Y. Huang* (CGGVeritas), D. Lin (CGGVeritas), B. Bai (CGGVeritas), S. Roby (CGGVeritas) & C. Ricardez (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Several discoveries,
H005 Pre-salt Depth Imaging of the Deepwater Santos Basin, Brazil Y. Huang* (CGGVeritas), D. Lin (CGGVeritas), B. Bai (CGGVeritas), S. Roby (CGGVeritas) & C. Ricardez (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Several discoveries,
The Estimation of PS Wave Statics By Using SCDCC + Stack Power Method
 The Estimation of PS Wave Statics By Using SCDCC + Stack Power Method ABSTRACT Summary Aimin Xue * Petrol Sound Geoservices. 8, MacEwan Ridge Close, N.W., Calgary, Alberta T3K3A7, Canada. aiminx@telus.net
The Estimation of PS Wave Statics By Using SCDCC + Stack Power Method ABSTRACT Summary Aimin Xue * Petrol Sound Geoservices. 8, MacEwan Ridge Close, N.W., Calgary, Alberta T3K3A7, Canada. aiminx@telus.net
SUMMARY ANGLE DECOMPOSITION INTRODUCTION. A conventional cross-correlation imaging condition for wave-equation migration is (Claerbout, 1985)
 Comparison of angle decomposition methods for wave-equation migration Natalya Patrikeeva and Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Angle domain common image gathers offer
Comparison of angle decomposition methods for wave-equation migration Natalya Patrikeeva and Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY Angle domain common image gathers offer
Statics preserving projection filtering Yann Traonmilin*and Necati Gulunay, CGGVeritas
 Yann Traonmilin*and Necati Gulunay, CGGVeritas Summary Projection filtering has been used for many years in seismic processing as a tool to extract a meaningful signal out of noisy data. We show that its
Yann Traonmilin*and Necati Gulunay, CGGVeritas Summary Projection filtering has been used for many years in seismic processing as a tool to extract a meaningful signal out of noisy data. We show that its
P S-wave polarity reversal in angle domain common-image gathers
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? P S-wave polarity reversal in angle domain common-image gathers Daniel Rosales and James Rickett 1 ABSTRACT The change in the reflection
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? P S-wave polarity reversal in angle domain common-image gathers Daniel Rosales and James Rickett 1 ABSTRACT The change in the reflection
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation. for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea. R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.
 Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
Rock Physics and Quantitative Wavelet Estimation for Seismic Interpretation: Tertiary North Sea R.W.Simm 1, S.Xu 2 and R.E.White 2 1. Enterprise Oil plc, Grand Buildings, Trafalgar Square, London WC2N
PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%)
 PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%) Your answers should be brief (just a few words) and may be written on these pages if you wish. Remember to hand these pages in with your other exam pages!
PART A: Short-answer questions (50%; each worth 2%) Your answers should be brief (just a few words) and may be written on these pages if you wish. Remember to hand these pages in with your other exam pages!
Sea-bottom shear-wave velocities and mode conversions
 Sea-bottom mode conversions Sea-bottom shear-wave velocities and mode conversions Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Elastic parameters for shallow marine sediments are compiled using
Sea-bottom mode conversions Sea-bottom shear-wave velocities and mode conversions Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Elastic parameters for shallow marine sediments are compiled using
Chapter 7: Reflection Seismology Homework Solutions (Jan. 2010)
 Chapter 7: eflection Seismology Homework Solutions (Jan. 200). Why do marine seismic reflection surveys not record (a) S waves? (b) refracted rays? 2 μ a) For ideal fluid, μ=0, thus, v s = = 0 ρ b) eflection
Chapter 7: eflection Seismology Homework Solutions (Jan. 200). Why do marine seismic reflection surveys not record (a) S waves? (b) refracted rays? 2 μ a) For ideal fluid, μ=0, thus, v s = = 0 ρ b) eflection
Enhancing Sub Basalt Imaging Using Depth Domain Processing
 Enhancing Sub Basalt Imaging Using Depth Domain Processing A.K.Sarkar*, P.V.Rao, S.Panigrahi and S.R.M.Karnawat Regional Computer Centre, ONGC, Vadodara, India E-mail:sarkararun@hotmail.com Summary Processing
Enhancing Sub Basalt Imaging Using Depth Domain Processing A.K.Sarkar*, P.V.Rao, S.Panigrahi and S.R.M.Karnawat Regional Computer Centre, ONGC, Vadodara, India E-mail:sarkararun@hotmail.com Summary Processing
Tomography for Static Corrections and Prestack Depth Imaging
 Tomography for Static Corrections and Prestack Depth Imaging Xianhuai Zhu, Ph.D. Fusion Petroleum Technologies Inc. 25231 Grogan's Mill Road, Suite 175 The Woodlands, TX 77380, USA Summary Turning-ray
Tomography for Static Corrections and Prestack Depth Imaging Xianhuai Zhu, Ph.D. Fusion Petroleum Technologies Inc. 25231 Grogan's Mill Road, Suite 175 The Woodlands, TX 77380, USA Summary Turning-ray
Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Case histories from West Africa
 P-263 Summary Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Patrizia Cibin*, Maurizio Ferla Eni E&P Division (Milano, Italy), Emmanuel Spadavecchia - Politecnico di Milano (Milano,
P-263 Summary Interval anisotropic parameters estimation in a least squares sense Patrizia Cibin*, Maurizio Ferla Eni E&P Division (Milano, Italy), Emmanuel Spadavecchia - Politecnico di Milano (Milano,
Summary. Introduction
 Multi-layer tomography and its application for improved depth imaging Patrice Guillaume, Steve Hollingworth*, Xiaoming Zhang, Anthony Prescott, Richard Jupp, Gilles Lambaré, Owen Pape, CGGVeritas Summary
Multi-layer tomography and its application for improved depth imaging Patrice Guillaume, Steve Hollingworth*, Xiaoming Zhang, Anthony Prescott, Richard Jupp, Gilles Lambaré, Owen Pape, CGGVeritas Summary
Hybrid Gridded Tomography. Ian F. Jones Mick Sugrue Pierre Hardy. GX Technology, 180 High Street, Egham, Surrey TW20 9DN, UK
 Hybrid Gridded Tomography By Ian F. Jones Mick Sugrue Pierre Hardy GX Technology, 8 High Street, Egham, Surrey TW 9DN, UK First Break V 5 April 7 P5- Corresponding Author Ian F. Jones ijones@gxt.com Hybrid
Hybrid Gridded Tomography By Ian F. Jones Mick Sugrue Pierre Hardy GX Technology, 8 High Street, Egham, Surrey TW 9DN, UK First Break V 5 April 7 P5- Corresponding Author Ian F. Jones ijones@gxt.com Hybrid
ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS. Abstract
 ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS Lindsay M. Mayer, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Julian Ivanov,
ANGLE-DEPENDENT TOMOSTATICS Lindsay M. Mayer, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS Julian Ivanov,
Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data
 Inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Patricia E. Gavotti, Don C. Lawton, Gary F. Margrave and J. Helen Isaac ABSTRACT The Hussar
Inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data Patricia E. Gavotti, Don C. Lawton, Gary F. Margrave and J. Helen Isaac ABSTRACT The Hussar
Reflection Seismic Method
 Reflection Seismic Method Data and Image sort orders; Seismic Impedance; -D field acquisition geometries; CMP binning and fold; Resolution, Stacking charts; Normal Moveout and correction for it; Stacking;
Reflection Seismic Method Data and Image sort orders; Seismic Impedance; -D field acquisition geometries; CMP binning and fold; Resolution, Stacking charts; Normal Moveout and correction for it; Stacking;
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing
 From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
From PZ summation to wavefield separation, mirror imaging and up-down deconvolution: the evolution of ocean-bottom seismic data processing Sergio Grion, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present
The i-stats: An Image-Based Effective-Medium Modeling of Near-Surface Anomalies Oz Yilmaz*, GeoTomo LLC, Houston, TX
 The i-stats: An Image-Based Effective-Medium Modeling of Near-Surface Anomalies Oz Yilmaz*, GeoTomo LLC, Houston, TX Summary Near-surface modeling for statics corrections is an integral part of a land
The i-stats: An Image-Based Effective-Medium Modeling of Near-Surface Anomalies Oz Yilmaz*, GeoTomo LLC, Houston, TX Summary Near-surface modeling for statics corrections is an integral part of a land
3D beam prestack depth migration with examples from around the world
 A Publication of Petroleum Geo-Services Vol. 8 No. 8 August 2008 3D beam prestack depth migration with examples from around the world Introduction In 1999 AGS specialized in 2D seismic depth processing.
A Publication of Petroleum Geo-Services Vol. 8 No. 8 August 2008 3D beam prestack depth migration with examples from around the world Introduction In 1999 AGS specialized in 2D seismic depth processing.
Comparison of two physical modeling studies of 3D P-wave fracture detection
 Comparison of two physical modeling studies of 3D P-wave fracture detection ZHONGPING QIAN 1,2, XIANG-YANG LI 1 AND SHANGXU WANG 3 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Comparison of two physical modeling studies of 3D P-wave fracture detection ZHONGPING QIAN 1,2, XIANG-YANG LI 1 AND SHANGXU WANG 3 1 British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
11th Biennial International Conference & Exposition. Keywords Sub-basalt imaging, Staggered grid; Elastic finite-difference, Full-waveform modeling.
 Sub-basalt imaging using full-wave elastic finite-difference modeling: A synthetic study in the Deccan basalt covered region of India. Karabi Talukdar* and Laxmidhar Behera, CSIR-National Geophysical Research
Sub-basalt imaging using full-wave elastic finite-difference modeling: A synthetic study in the Deccan basalt covered region of India. Karabi Talukdar* and Laxmidhar Behera, CSIR-National Geophysical Research
Investigating fault shadows in a normally faulted geology
 Investigating fault shadows in a normally faulted geology Sitamai Ajiduah* and Gary Margrave CREWES, University of Calgary, sajiduah@ucalgary.ca Summary Fault shadow poses a potential development risk
Investigating fault shadows in a normally faulted geology Sitamai Ajiduah* and Gary Margrave CREWES, University of Calgary, sajiduah@ucalgary.ca Summary Fault shadow poses a potential development risk
SeisLink Velocity. Key Technologies. Time-to-Depth Conversion
 Velocity Calibrated Seismic Imaging and Interpretation Accurate Solution for Prospect Depth, Size & Geometry Accurate Time-to-Depth Conversion was founded to provide geologically feasible solutions for
Velocity Calibrated Seismic Imaging and Interpretation Accurate Solution for Prospect Depth, Size & Geometry Accurate Time-to-Depth Conversion was founded to provide geologically feasible solutions for
Static Corrections for Seismic Reflection Surveys
 Static Corrections for Seismic Reflection Surveys MIKE COX Volume Editors: Series Editor: Eugene F. Scherrer Roland Chen Eugene F. Scherrer Society of Exploration Geophysicists Tulsa, Oklahoma Contents
Static Corrections for Seismic Reflection Surveys MIKE COX Volume Editors: Series Editor: Eugene F. Scherrer Roland Chen Eugene F. Scherrer Society of Exploration Geophysicists Tulsa, Oklahoma Contents
P137 Our Experiences of 3D Synthetic Seismic Modeling with Tip-wave Superposition Method and Effective Coefficients
 P137 Our Experiences of 3D Synthetic Seismic Modeling with Tip-wave Superposition Method and Effective Coefficients M. Ayzenberg (StatoilHydro), A. Aizenberg (Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics),
P137 Our Experiences of 3D Synthetic Seismic Modeling with Tip-wave Superposition Method and Effective Coefficients M. Ayzenberg (StatoilHydro), A. Aizenberg (Institute of Petroleum Geology and Geophysics),
Sub Basalt Imaging Using Low Frequency Processing and Angle stack In Saurashtra Region, Western India
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 90-94 Sub Basalt Imaging Using Low Frequency Processing and Angle stack In Saurashtra Region, Western India A.K.Sarkar & R.Mohan
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 90-94 Sub Basalt Imaging Using Low Frequency Processing and Angle stack In Saurashtra Region, Western India A.K.Sarkar & R.Mohan
Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Seismic Inversion Techniques
 P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
P-205 Reservoir Characterization using AVO and Summary *Abhinav Kumar Dubey, IIT Kharagpur Reservoir characterization is one of the most important components of seismic data interpretation. Conventional
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story
 Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Observation of shear-wave splitting from microseismicity induced by hydraulic fracturing: A non-vti story Petr Kolinsky 1, Leo Eisner 1, Vladimir Grechka 2, Dana Jurick 3, Peter Duncan 1 Summary Shear
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 248 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 First-order lateral interval velocity estimates without picking
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 248 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 249 264 First-order lateral interval velocity estimates without picking
An Alternative Approach to Process the Wide-Angle Reflection Data By Pre-stack Compositing of Gathers for Sub-basalt Imaging
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 288-293 An Alternative Approach to Process the Wide-Angle Reflection Data By Pre-stack Compositing of Gathers for Sub-basalt
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 288-293 An Alternative Approach to Process the Wide-Angle Reflection Data By Pre-stack Compositing of Gathers for Sub-basalt
Residual Statics using CSP gathers
 Residual Statics using CSP gathers Xinxiang Li and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT All the conventional methods for residual statics analysis require normal moveout (NMO) correction applied on the seismic data.
Residual Statics using CSP gathers Xinxiang Li and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT All the conventional methods for residual statics analysis require normal moveout (NMO) correction applied on the seismic data.
OBS wavefield separation and its applications
 P-088 OBS wavefield separation and its applications Sergio Grion*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present trends in ocean-bottom seismic (OBS) data processing. Current industrial practices for
P-088 OBS wavefield separation and its applications Sergio Grion*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper discusses present trends in ocean-bottom seismic (OBS) data processing. Current industrial practices for
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310
 Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
A Case Study on Simulation of Seismic Reflections for 4C Ocean Bottom Seismometer Data in Anisotropic Media Using Gas Hydrate Model
 A Case Study on Simulation of Seismic Reflections for 4C Ocean Bottom Seismometer Data in Anisotropic Media Using Gas Hydrate Model Summary P. Prasada Rao*, N. K. Thakur 1, Sanjeev Rajput 2 National Geophysical
A Case Study on Simulation of Seismic Reflections for 4C Ocean Bottom Seismometer Data in Anisotropic Media Using Gas Hydrate Model Summary P. Prasada Rao*, N. K. Thakur 1, Sanjeev Rajput 2 National Geophysical
Baseline VSP processing for the Violet Grove CO 2 Injection Site
 Baseline VSP processing for Violet Grove Baseline VSP processing for the Violet Grove CO 2 Injection Site Marcia L. Couëslan, Don C. Lawton, and Michael Jones * ABSTRACT Injection of CO 2 for enhanced
Baseline VSP processing for Violet Grove Baseline VSP processing for the Violet Grove CO 2 Injection Site Marcia L. Couëslan, Don C. Lawton, and Michael Jones * ABSTRACT Injection of CO 2 for enhanced
Velocity model building in complex media by multi-layer non-linear slope tomography. Summary Introduction Non-linear slope tomography
 Velocity model building in complex media by multi-layer non-linear slope tomography. Patrice Guillaume, Jean-Philippe Montel*, Xiaoming Zhang, Gilles Lambaré, Anthony Prescott, Matthieu Reinier, Richard
Velocity model building in complex media by multi-layer non-linear slope tomography. Patrice Guillaume, Jean-Philippe Montel*, Xiaoming Zhang, Gilles Lambaré, Anthony Prescott, Matthieu Reinier, Richard
Tu N Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography
 Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
Tu N118 05 Fault Shadow Removal over Timor Trough Using Broadband Seismic, FWI and Fault Constrained Tomography Y. Guo* (CGG), M. Fujimoto (INPEX), S. Wu (CGG) & Y. Sasaki (INPEX) SUMMARY Thrust-complex
A018 Combining Bandwidth Extension Techniques and Pre-stack Q Inversion for Enhanced Imaging of Intra-basalt Plays
 A018 Combining Bandwidth Extension Techniques and Pre-stack Q Inversion for Enhanced Imaging of Intra-basalt Plays A.J. Hardwick* (TGS), J. Whittaker (University of Leeds) & N. Woodburn (TGS) SUMMARY Extensive
A018 Combining Bandwidth Extension Techniques and Pre-stack Q Inversion for Enhanced Imaging of Intra-basalt Plays A.J. Hardwick* (TGS), J. Whittaker (University of Leeds) & N. Woodburn (TGS) SUMMARY Extensive
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 3D full-waveform inversion at Mariner a shallow North Sea reservoir Marianne Houbiers 1 *, Edward Wiarda 2, Joachim Mispel 1, Dmitry Nikolenko 2, Denes Vigh 2, Bjørn-Egil Knudsen 1, Mark Thompson 1, and
3D full-waveform inversion at Mariner a shallow North Sea reservoir Marianne Houbiers 1 *, Edward Wiarda 2, Joachim Mispel 1, Dmitry Nikolenko 2, Denes Vigh 2, Bjørn-Egil Knudsen 1, Mark Thompson 1, and
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study
 AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian*, Gary F. Margrave, and Joe Wong, University of Calgary. CREWES fmahmoud@ucalgary.ca Summary We present
AVAZ inversion for fracture orientation and intensity: a physical modeling study Faranak Mahmoudian*, Gary F. Margrave, and Joe Wong, University of Calgary. CREWES fmahmoud@ucalgary.ca Summary We present
Dip-constrained tomography with weighting flow for paleo-canyons: a case study in Para- Maranhao Basin, Brazil Guang Chen and Lingli Hu, CGG
 Dip-constrained tomography with weighting flow for paleo-canyons: a case study in Para- Maranhao Basin, Brazil Guang Chen and Lingli Hu, CGG Summary Para-Maranhao Basin offshore Brazil is well-known for
Dip-constrained tomography with weighting flow for paleo-canyons: a case study in Para- Maranhao Basin, Brazil Guang Chen and Lingli Hu, CGG Summary Para-Maranhao Basin offshore Brazil is well-known for
An Improved Dual Sensor Summation Method with Application to Four-Component (4-C) Seafloor Seismic Data from the Niger Delta
 Earth Science Research; Vol. 4, No. 2; 2015 ISSN 1927-0542 E-ISSN 1927-0550 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education An Improved Dual Sensor Summation Method with Application to Four-Component
Earth Science Research; Vol. 4, No. 2; 2015 ISSN 1927-0542 E-ISSN 1927-0550 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education An Improved Dual Sensor Summation Method with Application to Four-Component
Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains
 Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Frequency-dependent AVO attribute: theory and example Xiaoyang Wu, 1* Mark Chapman 1,2 and Xiang-Yang Li 1 1 Edinburgh Anisotropy Project, British Geological Survey, Murchison House, West Mains Road, Edinburgh
Summary. Introduction
 Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Detailed velocity model building in a carbonate karst zone and improving sub-karst images in the Gulf of Mexico Jun Cai*, Hao Xun, Li Li, Yang He, Zhiming Li, Shuqian Dong, Manhong Guo and Bin Wang, TGS
Tutorial: time conversion of depth migrated data: part II, TTI presdm. Ian F. Jones,
 Tutorial: time conversion of depth migrated data: part II, TTI presdm Ian F. Jones, Ian.jones@iongeo.com ION 31 Windsor Street Chertsey, Surrey KT16 8AT, UK Office: +44 (0)1932 792200 1 Abstract Contemporary
Tutorial: time conversion of depth migrated data: part II, TTI presdm Ian F. Jones, Ian.jones@iongeo.com ION 31 Windsor Street Chertsey, Surrey KT16 8AT, UK Office: +44 (0)1932 792200 1 Abstract Contemporary
ANISOTROPIC PRESTACK DEPTH MIGRATION: AN OFFSHORE AFRICA CASE STUDY
 Copyright 000 by the Society of Exploration Geophysicists ANISOTROPIC PRESTACK DEPTH MIGRATION: AN OFFSHORE AFRICA CASE STUDY Philippe Berthet *, Paul Williamson *, Paul Sexton, Joachim Mispel * * Elf
Copyright 000 by the Society of Exploration Geophysicists ANISOTROPIC PRESTACK DEPTH MIGRATION: AN OFFSHORE AFRICA CASE STUDY Philippe Berthet *, Paul Williamson *, Paul Sexton, Joachim Mispel * * Elf
Seismic reflection notes
 1 of 13 20/02/2006 3:29 PM Seismic reflection notes Introduction This figure was modified from one on the Lithoprobe slide set. LITHOPROBE is "probing" the "litho" sphere of our continent, the ground we
1 of 13 20/02/2006 3:29 PM Seismic reflection notes Introduction This figure was modified from one on the Lithoprobe slide set. LITHOPROBE is "probing" the "litho" sphere of our continent, the ground we
Th Guided Waves - Inversion and Attenuation
 Th-01-08 Guided Waves - Inversion and Attenuation D. Boiero* (WesternGeco), C. Strobbia (WesternGeco), L. Velasco (WesternGeco) & P. Vermeer (WesternGeco) SUMMARY Guided waves contain significant information
Th-01-08 Guided Waves - Inversion and Attenuation D. Boiero* (WesternGeco), C. Strobbia (WesternGeco), L. Velasco (WesternGeco) & P. Vermeer (WesternGeco) SUMMARY Guided waves contain significant information
Depth Imaging for Unconventional Reservoir Characterization: Canadian Plains Case Study
 Depth Imaging for Unconventional Reservoir Characterization: Canadian Plains Case Study Bill Goodway 1, Greg Purdue 1, Shiang Yong Looi 2, Lijuan (Kathy) Du 2, Mark Rowland 2 1 Apache Canada, 2 Schlumberger
Depth Imaging for Unconventional Reservoir Characterization: Canadian Plains Case Study Bill Goodway 1, Greg Purdue 1, Shiang Yong Looi 2, Lijuan (Kathy) Du 2, Mark Rowland 2 1 Apache Canada, 2 Schlumberger
Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Imaging complex structure with crosswell seismic in Jianghan oil field QICHENG DONG and BRUCE MARION, Z-Seis, Houston, Texas, U.S. JEFF MEYER, Fusion
Velocity Update Using High Resolution Tomography in Santos Basin, Brazil Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas
 Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas Summary The exploration interest in the Santos Basin offshore Brazil has increased with the large deep water pre-salt discoveries, such as Tupi and Jupiter. As the
Lingli Hu and Jianhang Zhou, CGGVeritas Summary The exploration interest in the Santos Basin offshore Brazil has increased with the large deep water pre-salt discoveries, such as Tupi and Jupiter. As the
Observations of Azimuthal Anisotropy in Prestack Seismic Data
 Observations of Azimuthal Anisotropy in Prestack Seismic Data David Gray* CGGVeritas, Calgary, AB, Canada dave.gray@cggveritas.com Summary A method for displaying prestack seismic data that highlights
Observations of Azimuthal Anisotropy in Prestack Seismic Data David Gray* CGGVeritas, Calgary, AB, Canada dave.gray@cggveritas.com Summary A method for displaying prestack seismic data that highlights
Data Repository Item
 Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
Data Repository Item 2009003 An abrupt transition from magma-starved to magma-rich rifting in the eastern Black Sea Donna J. Shillington, Caroline L. Scott, Timothy A. Minshull, Rosemary A. Edwards, Peter
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site
 Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
Seismic tests at Southern Ute Nation coal fire site Sjoerd de Ridder and Seth S. Haines ABSTRACT We conducted a near surface seismic test at the Southern Ute Nation coal fire site near Durango, CO. The
FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys
 FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys 25 th January, 2018 Aleksandr Nikitin a.nikitin@gwl-geo.com Geology Without Limits Overview 2011-2016 GWL Acquired over 43000 km 2D seismic
FloatSeis Technologies for Ultra-Deep Imaging Seismic Surveys 25 th January, 2018 Aleksandr Nikitin a.nikitin@gwl-geo.com Geology Without Limits Overview 2011-2016 GWL Acquired over 43000 km 2D seismic
Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical
 Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical Summary This paper discusses rough-sea de-ghosting for variabledepth streamer data. The
Rough sea estimation for phase-shift de-ghosting Sergio Grion*, Rob Telling and Seb Holland, Dolphin Geophysical Summary This paper discusses rough-sea de-ghosting for variabledepth streamer data. The
Research Project Report
 Research Project Report Title: Prediction of pre-critical seismograms from post-critical traces Principal Investigator: Co-principal Investigators: Mrinal Sen Arthur Weglein and Paul Stoffa Final report
Research Project Report Title: Prediction of pre-critical seismograms from post-critical traces Principal Investigator: Co-principal Investigators: Mrinal Sen Arthur Weglein and Paul Stoffa Final report
Anisotropic inversion and imaging of PP and PS reflection data in the North Sea
 Anisotropic inversion and imaging of PP and PS reflection data in the North Sea VLADIMIR GRECHKA, Shell International Exploration and Production, Houston, Texas, U.S. ILYA TSVANKIN, Colorado School of
Anisotropic inversion and imaging of PP and PS reflection data in the North Sea VLADIMIR GRECHKA, Shell International Exploration and Production, Houston, Texas, U.S. ILYA TSVANKIN, Colorado School of
Subsalt imaging by common-azimuth migration
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 100, April 20, 1999, pages 113 125 Subsalt imaging by common-azimuth migration Biondo Biondi 1 keywords: migration, common-azimuth, wave-equation ABSTRACT The comparison
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 100, April 20, 1999, pages 113 125 Subsalt imaging by common-azimuth migration Biondo Biondi 1 keywords: migration, common-azimuth, wave-equation ABSTRACT The comparison
Imaging sub-basalt structures using locally converted waves
 10112 First Break June basis v4 07-05-2003 16:43 Pagina 29 Imaging sub-basalt structures using locally converted waves Mirko van der Baan 1, Tom Kerrane 2, J-Michael Kendall 3, Neil Taylor 4 Introduction
10112 First Break June basis v4 07-05-2003 16:43 Pagina 29 Imaging sub-basalt structures using locally converted waves Mirko van der Baan 1, Tom Kerrane 2, J-Michael Kendall 3, Neil Taylor 4 Introduction
Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO*
 Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO* *This paper has been submitted to the EAGE for presentation at the June 2001 EAGE meeting. SUMMARY
Pluto 1.5 2D ELASTIC MODEL FOR WAVEFIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF SUBSALT OBJECTIVES, DEEP WATER GULF OF MEXICO* *This paper has been submitted to the EAGE for presentation at the June 2001 EAGE meeting. SUMMARY
NMO residual reduction on medium anisotropy in field X using Fomel and Stovas method
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS NMO residual reduction on medium anisotropy in field X using Fomel and Stovas method To cite this article: M S Rosid et al 018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS NMO residual reduction on medium anisotropy in field X using Fomel and Stovas method To cite this article: M S Rosid et al 018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
AVO inversion in V (x, z) media
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 998, pages 75 94 AVO inversion in V (x, z) media Yalei Sun and Wenjie Dong keywords:.5-d Kirchhoff integral, AVO inversion, fluid-line section ABSTRACT
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 998, pages 75 94 AVO inversion in V (x, z) media Yalei Sun and Wenjie Dong keywords:.5-d Kirchhoff integral, AVO inversion, fluid-line section ABSTRACT
Towards Modelling Elastic and Viscoelastic Seismic Wave Propagation in Boreholes
 Towards Modelling Elastic and Viscoelastic Seismic Wave Propagation in Boreholes NA WANG, DONG SHI, BERND MILKEREIT Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada M5S 1A7 Summary We are
Towards Modelling Elastic and Viscoelastic Seismic Wave Propagation in Boreholes NA WANG, DONG SHI, BERND MILKEREIT Department of Physics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada M5S 1A7 Summary We are
Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer
 Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer Saul E. Guevara and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite difference 2D elastic modeling is used to study characteristics of the
Finite difference elastic modeling of the topography and the weathering layer Saul E. Guevara and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite difference 2D elastic modeling is used to study characteristics of the
Application of Seismic Reflection Surveys to Detect Massive Sulphide Deposits in Sediments-Hosted Environment
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 4 Ver. I (Jul - Aug. 2015), PP 46-51 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Seismic Reflection
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 4 Ver. I (Jul - Aug. 2015), PP 46-51 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Seismic Reflection
Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
Chapter 1. Introduction EARTH MODEL BUILDING
 Chapter 1 Introduction Seismic anisotropy in complex earth subsurface has become increasingly important in seismic imaging due to the increasing offset and azimuth in modern seismic data. To account for
Chapter 1 Introduction Seismic anisotropy in complex earth subsurface has become increasingly important in seismic imaging due to the increasing offset and azimuth in modern seismic data. To account for
The 2D/3D i-stats Workflow for Image-Based Near-Surface Modeling for Statics Corrections
 The 2D/3D i-stats Workflow for Image-Based Near-Surface Modeling for Statics Corrections Öz Yilmaz CTO, GeoTomo LLC With the i-stats workflow, you no longer need first-break picking as for traveltime tomography,
The 2D/3D i-stats Workflow for Image-Based Near-Surface Modeling for Statics Corrections Öz Yilmaz CTO, GeoTomo LLC With the i-stats workflow, you no longer need first-break picking as for traveltime tomography,
Improvement of stacking image by anisotropic velocity analysis using P-wave seismic data
 P-46 Improvement of stacking image by anisotropic velocity analysis using P-wave seismic data Laxmidhar Behera*, and Prakash Khare, National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI), Hyderabad Summary Anisotropy
P-46 Improvement of stacking image by anisotropic velocity analysis using P-wave seismic data Laxmidhar Behera*, and Prakash Khare, National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI), Hyderabad Summary Anisotropy
ACARP PROJECT C13029 INTEGRATED P-WAVE/PS-WAVE SEISMIC IMAGING FOR IMPROVED GEOLOGICAL CHARACTERISATION OF COAL ENVIRONMENTS
 ACARP PROJECT C1329 INTEGRATED P-WAVE/PS-WAVE SEISMIC IMAGING FOR IMPROVED GEOLOGICAL CHARACTERISATION OF COAL ENVIRONMENTS FINAL REPORT February 27 Natasha Hendrick Velseis Pty Ltd Velseis Pty Ltd ABN
ACARP PROJECT C1329 INTEGRATED P-WAVE/PS-WAVE SEISMIC IMAGING FOR IMPROVED GEOLOGICAL CHARACTERISATION OF COAL ENVIRONMENTS FINAL REPORT February 27 Natasha Hendrick Velseis Pty Ltd Velseis Pty Ltd ABN
The Deconvolution of Multicomponent Trace Vectors
 The Deconvolution of Multicomponent Trace Vectors Xinxiang Li, Peter Cary and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd., Calgary, Canada xinxiang_li@sensorgeo.com Summary Deconvolution of the horizontal components
The Deconvolution of Multicomponent Trace Vectors Xinxiang Li, Peter Cary and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd., Calgary, Canada xinxiang_li@sensorgeo.com Summary Deconvolution of the horizontal components
Downloaded 05/01/17 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Mapping Imbricate Structures in the Thrust Belt of Southeast Turkey by Large-Offset Seismic Survey Oz Yilmaz*, Anatolian Geophysical, Istanbul, Turkey; and Serdar Uygun, Ali Ölmez, and Emel Çalı, Turkish
Mapping Imbricate Structures in the Thrust Belt of Southeast Turkey by Large-Offset Seismic Survey Oz Yilmaz*, Anatolian Geophysical, Istanbul, Turkey; and Serdar Uygun, Ali Ölmez, and Emel Çalı, Turkish
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study
 The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
The effect of anticlines on seismic fracture characterization and inversion based on a 3D numerical study Yungui Xu 1,2, Gabril Chao 3 Xiang-Yang Li 24 1 Geoscience School, University of Edinburgh, UK
Tu N Estimation of Uncertainties in Fault Lateral Positioning on 3D PSDM Seismic Image - Example from the NW Australian Shelf
 Tu N118 06 Estimation of Uncertainties in Fault Lateral Positioning on 3D PSDM Seismic Image - Example from the NW Australian Shelf S. Birdus* (CGG), V. Ganivet (CGG), A. Artemov (CGG), R. Teakle (Chevron)
Tu N118 06 Estimation of Uncertainties in Fault Lateral Positioning on 3D PSDM Seismic Image - Example from the NW Australian Shelf S. Birdus* (CGG), V. Ganivet (CGG), A. Artemov (CGG), R. Teakle (Chevron)
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics
 Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Noise suppression and multiple attenuation using full-azimuth angle domain imaging: case studies
 first break volume 33, June 2015 special topic Noise suppression and multiple attenuation using full-azimuth angle domain imaging: case studies Aleksander Inozemtsev 1*, Zvi Koren 1 and Alexander Galkin
first break volume 33, June 2015 special topic Noise suppression and multiple attenuation using full-azimuth angle domain imaging: case studies Aleksander Inozemtsev 1*, Zvi Koren 1 and Alexander Galkin
Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin
 P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
P-276 Summary Feasibility and design study of a multicomponent seismic survey: Upper Assam Basin K.L.Mandal*, R.K.Srivastava, S.Saha, Oil India Limited M.K.Sukla, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough
 We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough K. Shiraishi* (JAMSTEC), M. Robb (Emerson Paradigm), K. Hosgood (Emerson
We A10 12 Common Reflection Angle Migration Revealing the Complex Deformation Structure beneath Forearc Basin in the Nankai Trough K. Shiraishi* (JAMSTEC), M. Robb (Emerson Paradigm), K. Hosgood (Emerson
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks
 An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
An empirical method for estimation of anisotropic parameters in clastic rocks YONGYI LI, Paradigm Geophysical, Calgary, Alberta, Canada Clastic sediments, particularly shale, exhibit transverse isotropic
Velocity structure of the methane hydrate formation at the Blake Outer Ridge
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 84, May 9, 2001, pages 1 123 Velocity structure of the methane hydrate formation at the Blake Outer Ridge Christine Ecker 1 ABSTRACT Seismic analysis of data from the
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 84, May 9, 2001, pages 1 123 Velocity structure of the methane hydrate formation at the Blake Outer Ridge Christine Ecker 1 ABSTRACT Seismic analysis of data from the
Cross-well seismic modelling for coal seam delineation
 P-134 Sanjeev Rajput, CSIRO, P. Prasada Rao*, N. K. Thakur, NGRI Summary Finite-difference analyses is attempted to simulate a multi layered complex coal seam model in order to differentiate top and bottom
P-134 Sanjeev Rajput, CSIRO, P. Prasada Rao*, N. K. Thakur, NGRI Summary Finite-difference analyses is attempted to simulate a multi layered complex coal seam model in order to differentiate top and bottom
Velocity model building challenges and solutions for seabed- and paleo-canyons: a case study in Campos Basin, Brazil
 Velocity model building challenges and solutions for seabed- and paleo-canyons: a case study in Campos Basin, Brazil Kai Zhang, Javier Subia, Chevron; Chanjuan Sun, Hao Shen, Nuree Han, CGG Summary The
Velocity model building challenges and solutions for seabed- and paleo-canyons: a case study in Campos Basin, Brazil Kai Zhang, Javier Subia, Chevron; Chanjuan Sun, Hao Shen, Nuree Han, CGG Summary The
Geophysical Applications Seismic Reflection Processing
 Seismic reflection data are routinely acquired for multiple purposes such as exploration, mining, or engineering problems. The seismic data are generally acquired in shot-gathers, i.e. the data is sorted
Seismic reflection data are routinely acquired for multiple purposes such as exploration, mining, or engineering problems. The seismic data are generally acquired in shot-gathers, i.e. the data is sorted
Applications of finite-difference modelling to coalscale seismic exploration
 Applications of finite-difference modelling to coalscale seismic exploration Shaun Strong 1,2, Troy Peters 1 1. Velseis Pty Ltd 2 University of Queensland Introduction Geological environments with significant
Applications of finite-difference modelling to coalscale seismic exploration Shaun Strong 1,2, Troy Peters 1 1. Velseis Pty Ltd 2 University of Queensland Introduction Geological environments with significant
F-K Characteristics of the Seismic Response to a Set of Parallel Discrete Fractures
 F-K Characteristics of the Seismic Response to a Set of Parallel Discrete Fractures Yang Zhang 1, Xander Campman 1, Samantha Grandi 1, Shihong Chi 1, M. Nafi Toksöz 1, Mark E. Willis 1, Daniel R. Burns
F-K Characteristics of the Seismic Response to a Set of Parallel Discrete Fractures Yang Zhang 1, Xander Campman 1, Samantha Grandi 1, Shihong Chi 1, M. Nafi Toksöz 1, Mark E. Willis 1, Daniel R. Burns
