Hypsometric analysis of the Tuirini drainage basin: A Geographic Information System approach
|
|
|
- Jayson Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 6, No 3, 26 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3. Research article ISSN Hypsometric analysis of the Tuirini drainage basin: A Geographic Information System approach Fuzal Ahmed and Srinivasa Rao K. Department of Geology, Mizoram University (Central), Post box: 9, Aizawl- 7964, India fuzalahmed@gmail.com ABSTRACT Hypsometric analysis deals with measurement of the interrelationships between basin area and altitude of basin which has been used to understand the influence of climatic, geologic and tectonic factors on topographic changes. GIS provides advanced tools to obtain hypsometric information and also helps to estimate the associated parameters of landforms. The study of hypsometry has been performed to differentiate between erosional landforms at different stages during their evolution. The Tuirini basin is characterized by steep to very steep slopes whereas the altitude varies from 95 m to 78 m above msl. The present study was carried out using ArcGIS -.2 tools. The entire study area was sub-divided into 22 subbasins for hypsometric analysis and there area ranges from 4.75 to sq.km. The hypsometric curve of the whole Tuirini basin reflects the mature geomorphic terrain whereas hypsometric integral indicates that the drainage basin has already eroded 58 per cent of land masses. The overall hypsometric results suggest that the sub-basins are in the mature stages of geologic development with moderately eroded landscapes and the entire basin is progressively approaching towards the monadnock phase of erosion. Keywords: Hypsometry, Geologic stage, Drainage basin, GIS, Mizoram. Introduction The landforms of Mizoram state is characterized by a large number of river networks passing through the hills and valleys where monsoon rainfall is high from June to September. The steep slopes of the mountains are composed of lose sedimentary rocks and are more prone to soil erosion in rainy season. Although the region is abundant in various natural resources, most parts of the areas remain inaccessible due to the mountainous nature of the terrain. Conservation of land and water resources are an important aspect of basin management. A drainage basin is the land surfaces from which all precipitation flows to a particular water body, such as tributary stream, river or sea and is considered as a fundamental geomorphic unit. The evolution of a landscape is the results of weathering processes, depositional processes, stream erosion patterns and tectonic processes that are acting upon it. Therefore, analysis of the drainage basin helps to understand the landform evolution through successive stages of geological time, fluvial process, lithologic character and hydrological behaviour of a basin as well as tectonic activity of a region. The idea of hypsometry was first introduced by Langbein and Basil in 947 to express the overall slope and the forms of drainage basin, and was later extended by Strahler (952) to include the percentage hypsometric curve and the hypsometric integral. Hypsometry describes the measurement and analysis of relationships between the distribution of elevations across an area of land surface and basin area. Weissel et al. (994) suggested that hypsometry may reflects the interaction between tectonic and degree of disequilibria in Submitted on November 25 published on February
2 23 33'N 23 42'N 23 5'N Hypsometric analysis of the Tuirini drainage basin: A Geographic Information System approach the balance of erosive, and could provide a valuable geomorphic index that constrains the relative importance of these processes. Hypsometric analysis is a useful method to identify the stage reached by a drainage basin in the present cycle of erosion and evaluate the erosional status of a basin, and also expresses the denudational processes over a region. Besides erosional stage of landform evolution, the influence of tectonic activity, climate change and lithological factors controlling on landform evolution can be analysed from hypsometric analysis (Lifton and Chase, 992; Moglen and Bras, 995; Willgoose and Hancock, 998; Hurtrez and Lucazeau, 999; Chen et al., 23; Huang and Niemann, 26). Thus, hypsometric analysis can be used as an estimator of erosional status of a drainage basin and prioritize them for taking up soil and water conservation measures, which is the prerequisite for planning and management of the basin. Geographic information system (GIS) and digital elevation model (DEM) have played an important role in in drainage basin analysis. Hence, GIS technique is used as a convenient tool for hypsometric analysis. The objective of the present study is to find out the geological stages of development and erosional status of the Tuirini basin and its sub-basins. INDIA Aizawl Serchhip km N± Figure : Location map of the study area Sub-basins name - Maudarh 2 - Khuai 3 - Tuizal 4 - Lungding 5 - Chal 6 - Saibual 7 - Maltliak 8 - Ramri 9 - Kaihzawl - Sathang - Thangzai 2 - Kang 3 - Tuikhan 4 - Sakei 5 - Maumit 6 - Dam 7 - Inran 8 - Inrum 9 - Minpui 2 - Damdiai 2 - Chhimluang 22 - Phekphe Sub-basinsboundary 2. Characteristics of the study area The study area extends between longitudes 92 o o E and latitudes 23 o o 53 2 N, which covers an area of about 42.7 sq.km with basin perimeter of.7 km. The Tuirini drainage basin forms parts of two districts viz. Aizawl district and a small part of Serchhip district of Mizoram in India (Fig. ). The basin is extremely rugged terrain cut by deep valleys and crossed by hill ranges along with the average elevation of 83 m above mean sea level (msl). The entire study area is covered by thick sedimentary rocks constituting the Surma Group. Soils are mostly of red and yellow loamy with acidic in nature. The study area has been sub-divided into twenty two sub-basins based on the basin areas of Tuirini river and its major tributaries (Fig. ). The climate of the basin area is influenced by the southwest monsoon system that brings heavy precipitation, more than 8 per cent of rainfall occurs International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 686 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
3 23 33'N 23 33'N 23 42'N 23 42'N 23 5'N 23 5'N Hypsometric analysis of the Tuirini drainage basin: A Geographic Information System approach during June to September. The temperature of the study area varies from a minimum of C ~ to a maximum of 3 C ~ with average annual relative humidity is about 7 %. N ± 92 44'E W N S E Aspect orientation Flat (-) North (-22.5) Northeast ( ) East ( ) Southeast ( ) Relief (m) < > km Figure 2: Relief map of the study area 92 44'E South ( ) Southwest ( ) West ( ) Northwest ( ) North ( ) km Figure 3: Aspect map of the study area 2. Relief The term relief is used to describe the vertical dimension or amplitude of topography, which is mainly governed by erosional and tectonic processes of an area. In the present study, relief values have been grouped into three categories viz. high, moderate and low. The relief value < 5 m has been categorized as altitude of low relief zone occupy about 9.56 sq.km of the basin area, moderate relief region ranges from altitudes of 5 to m covers maximum area of about sq.km and above m as high relief zone occupies about sq.km of the total basin area. The relief map of the basin (Fig. 2) shows that major portion of the basin area falls under moderate relief (57.89 %) followed by low relief (26.8 %) and only 6.3 % of the total area characterize as high relief zone. The northeastern and southeastern parts of the basin are characterized by a higher altitude than the other parts. 2.2 Aspect Aspect is azimuthal direction with reference to true north (zero degree) and indicates the maximum slope direction of a terrain to which it faces, and also provides clues about the direction of the water flow. It is influenced by vegetation, climate, precipitation patterns, agricultural productivity, snow melt and wind exposure. The aspect of a slope can create a very significant influence on its local climate because the sun s rays are in the west at the hottest time of day in the afternoon and so in most cases, a west-facing slope will be warmer than sheltered east-facing slope (Magesh et al., 2). Generally, aspect is used in hilly region, because shadow plays an important role for determining the soil moisture regime. The entire study area is hilly region and there is very less flat area. From the aspect map (Fig. 3), it can be seen that east facing slopes mainly occur in the western part of the basin, whereas International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 687 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
4 west facing slopes are seen in the eastern part of the basin. Therefore, east facing slopes have higher moisture content and lower evaporation rate then the west facing slopes. 3. Materials and methods The Tuirini basin and its sub-basins boundary were delineated from rectified, mosaiced Survey of India (SoI) topographic maps no. 84A/3, 84A/4 and 84A/5 on the scale : 5, assigning UTM, WGS 984, 46N zone projection system. Contour interval of 4 m was accurately digitized within GIS environment from the scanned SoI topographic maps and also spot heights were digitized. The digitized contours and spot heights were further processed in ArcGIS (Version.2) using the spatial analyst tools to generate the digital elevation model (DEM). From the DEM, relief and aspect maps have been prepared with the help of ArcGIS software. The hypsometric curves for the Tuirini basin and its sub-basins were prepared based on Strahler (952) method. Hypsometric integrals of all the sub-basins have been calculated using empirical formula proposed by Pike and Wilson (97). 4. Results and discussion Hypsometry can be evaluated through the hypsometric curve and hypsometric integral. The shapes of the hypsometric curve and the values of hypsometric integral are important elements in the landform analysis. These can be explained in terms of degree of landscape dissection and relative landform age. The hypsometric curves and hypsometric integral values of the Tuirini basin and its sub-basins are discussed below. 4. Hypsometric curve The hypsometric curve describes the distribution of elevations across an area of land, which has been used to evaluate the evolutionary status of landforms. It is related to the volume of the soil mass in the basin and the amount of erosion that had occurred in a basin against the remaining mass (Hurtrez et al., 999). Hypsometric curves are related to geomorphic and tectonic evolution of drainage basins in terms of their forms and processes (Schumm, 956; Strahler, 964; Leopold et al., 964; Hurtrez et al., 999). A useful attribute of the hypsometric curve is that drainage basins of different sizes can be compared with each other because area and elevation are plotted as functions of total area and total elevation. That is, the hypsometric curve is independent of differences in basin size and relief (Strahler, 952). A. N. Strahler (952) has classified three types of landforms on the basis of shapes of the hypsometric curve, each denoting the three typical stages of basin dissection, namely (i) young stage, (ii) mature stage and (iii) old stage. Convex shaped curves are associated with young stage of basin, which indicate that the region is slightly eroded and undisseceted, mature stage is correspond to S shaped curves being concave upwards at higher elevations and convex downwards at lower elevations characterized by moderately eroded regions and old stage of basin is related to concave shaped curves indicate highly eroded and deeply dissected landscapes. With the progress of erosion, the shape of hypsometric curve changes from convex-up to essentially straight to concave-up (Schumm, 956). 4.2 Plotting of hypsometric curves The percentage hypsometric method has been used for the present study. There are two ratios involved in this method and plotted against each other on a graph. The ordinate represents the ratio of relative elevation (h/h) and the abscissa represents the ratio of relative area (a/a). The relative elevation is computed as the ratio of the height of a given contour (h) from the International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 688 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
5 base plane to the maximum basin elevation (H). The relative area is obtained as a ratio of the area above a particular contour (a) to the total area of the basin above the outlet (A). The value of relative area (a/a) is in a range from one to zero. One at the lowest point in the drainage basin (h/h = ) and zero at the highest point in the basin (h/h = )..8 Tuirini basin.8 Maudarh sub-basin.8 Khuai sub-basin Tuizal sub-basin.8 Lungding sub-basin.8 Chal sub-basin Saibual sub-basin.8 Maltliak sub-basin.8 Ramri sub-basin Kaihzawl sub-basin.8 Sathang sub-basin.8 Thangzai sub-basin Figure 4a: Hypsometric curves of the Tuirini basin and its sub-basins International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 689 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
6 .8 Kang sub-basin.8 Tuikhan sub-basin.8 Sakei sub-basin Maumit sub-basin Dam sub-basin Inran sub-basin Inrum sub-basin Minpui sub-basin Damdiai sub-basin Chhimluang sub-basin Phekphe sub-basin Figure 4b: Hypsometric curves of sub-basins of the Tuirini basin In the present study, hypsometric curves have been prepared for the Tuirini basin and its 22 sub-basins as shown in figures 4a 4b. The hypsometric curve of the entire Tuirini basin represents S-shape curve indicating a mature stage of landscape development. It was also observed from the figures (4a 4b) that there was a combination of convex, concave and S-shape of curves, suggest that the sub-basins attain mature stage from the youth stage. The difference between the shapes of the hypsometric curve in the study area might be due to International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 69 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
7 23 33'N 23 33'N 23 42'N 23 42'N 23 5'N 23 5'N Hypsometric analysis of the Tuirini drainage basin: A Geographic Information System approach the lithological variations, incision of bed rock, down slope movement of eroded materials and removal of the sediments from the basin. HI value km ± N Figure 5: Hypsometric integral map (Value in meters) 72 Spot_height height 86 Cotnour km 9 Figure 6: Contour map with spot heights N 4.3 Estimation of hypsometric integral Integration of the hypsometric curve gives the hypsometric integral (HI), which is equivalent to the elevation-relief ratio (E) as proposed by Pike and Wilson (97). Mathematically, it is defined as E HI = [Mean elevation (E mean ) Minimum elevation (E min )]/ [Maximum elevation (Emax) Minimum elevation (Emin)]. The hypsometric integral value is controlled by basin geometry, relief and area of drainage basin (Lifton and Chase, 992; Masek et al., 994; Hurtrez et al., 999; Chen et al., 23). It was also found by Strahler (952) that the hypsometric integral is inversely correlated with total relief, slope steepness, drainage density and channel gradients. The geologic stages of landforms development and erosional status of the basins are quantified by hypsometric integral. High value of hypsometric integral indicates the youthful stage of less eroded areas and it decreases as the landscape is denuded towards the maturity and old stages. The HI is expressed as a percentage and is an indicator of the remnant of the present volume as compared to the original volume of the basin (Ritter et al., 22). The hypsometric integral is also an indication of the cycle of erosion (Strahler, 952; Garg, 983). The cycle of erosion is defined as the total time required for reduction of a land topological unit to the base level i.e. the lowest level. This entire period or the cycle of erosion can be grouped into three categories, each representing the three distinctive stages of the geomorphic cycle, viz. (i) the monadnock or old stage if HI.35, in which the basin is fully stabilized; International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 69 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
8 (ii) the equilibrium or mature stage if.35 HI.6, in which the basin development has attained steady state condition and (iii) the inequilibrium or young stage if HI.6, where the basin is highly susceptible to erosion and is under development (Strahler, 952). Table : Estimated hypsometric integral values of Tuirini basin and its sub-basins Sub-basins name Area (km 2 ) Elevation (m) Maximum Minimum Mean Hypsometric integral (HI) Geological stage Maudarh Early maturity Khuai Middle maturity Tuizal Middle maturity Lungding Middle maturity Chal Late youthful Saibual Early youthful Maltliak Middle maturity Ramri Early youthful Kaihzawl Middle maturity Sathang Middle maturity Thangzai Middle maturity Kang Early maturity Tuikhan Late maturity Sakei Early maturity Maumit Early maturity Dam Early maturity Inran Middle maturity Inrum Late maturity Minpui Early maturity Damdiai Middle maturity Chhimluang Middle maturity Phekphe Late youthful Tuirini basin Middle maturity The hypsometric integral (HI) values obtained for the Tuirini basin along with their 22 sub-basins are shown in the fig. 5 and presented in Table -. The HI value of the Tuirini basin is computed to be.42, which reveals that only 42 per cent of the land masses remain in the basin to be eroded. The calculated HI values for all the sub-basins of Tuirini basin ranged from.37 to.89 (Table - ). Out of the 22 sub-basins, only 4 sub-basins fall under younger stage, 2 sub-basins namely Saibual and Ramri belong to early youthful stage and 2 sub-basins namely Chal and Phekphe come under late youthful state of its development. The remaining 8 sub-basins belong to mature stage of landscape evolution. The 6 sub-basins viz. Maudarh, Kang, Sakei, Maumit, Dam and Minpui have just entered into early mature stage of erosional development. There are sub-basins namely Khuai, Tuizal, Lungding, Maltliak, Kaihzawl, International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 692 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
9 Sathang, Thangzai, Inran, Damdiai and Chhimluang are at middle maturity stage. Only Tuikhan and Inrum sub-basins represent late mature stage of landforms and reaching towards monadnock stage. South DEM High: 95 m Low: 78 m Figure 7: Topographic DEM of the study area (a) (b) Tuirini River Figure 8: Field photograph showing (a) Vertical cliff faces of the hill and eroded sandstone beds along the Tuirini river (Red arrow indicates flow direction); (b) Deposition of unconsolidated gravels, pebbles and boulders in the left bank of the Tuirini river near its outlet. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 693 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
10 Figure 9: Field photographs showing structural and dissected hills (erosional landforms) in the study area. 5. Conclusion In order to understand the erosional stages and relative age of landforms, hypsometric analysis has been carried out for the Tuirini basin along with their twenty sub-basins. GIS is gaining importance as a powerful tool in the natural resources management and its conservative work. Thus, GIS technique has been used as a convenient tool for hypsometric analysis. The hypsometric curve and hypsometric integral value of the entire Tuirini basin reflects the mature stage of geomorphic cycle development. Among the twenty sub-basins, four sub-basins are found to be under younger geomorphic stages with high hypsometric integral values while the eighteen sub-basins are at mature state, which are moving towards stabilization, and also indicate the erosional process differs from one sub-basin to another. No sub-basin comes in the old state of dissection in the study area. This analysis will help to take appropriate measures to conserve soil and water resources for sustainable development of the basin area. Acknowledgements The authors are thankful to the Head, Department of Geology, Mizoram University, Aizawl for providing laboratory facilities to carry out this research work. The financial assistance received from the UGC Division, Government of India, is gratefully acknowledged by Fuzal Ahmed. Anonymous reviewers and editorial board members of IJGGS are thankfully acknowledged for their critical reviews. 6. References. Chen, Y.C., Sung, Q., and Cheng, K., (23), Along-strike variations of morphotectonics features in the western foothills of Taiwan: tectonic implications based on stream-gradient and hypsometric analysis. Geomorphology, 56 ( 2), pp Garg, S.K., (983), Geology- the science of the earth. Khanna Publishers, New Delhi. 3. Huang, X.J., and Niemann, J.D., (26), Modelling the potential impacts of groundwater hydrology on long-term drainage basin evolution. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 3, pp International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 694 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
11 4. Hurtrez, J.E., and Lucazeau, F., (999), Lithological control on relief and hypsometry in the Herault drainage basin (France), Comptes Rendues Acade mie des Sciences de la terre et des planets. Earth and Planetary Sciences, 328 (), pp Hurtrez, J.E., Sol, C., and Lucazeau, F., (999), Effect of drainage area on hypsometry from an analysis of small-scale drainage basins in the Siwalik hills (Central Nepal). Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 24, pp Langbein, W.B., and Basil, W., (947), Topographic characteristics of drainage basins. USGS Water-Supply Paper, 947-C. 7. Leopold, L.B., Wolman, M.G., and Miller, J.P., (964), Fluvial processes in geomorphology, Free-man, San Francisco. 8. Lifton, N.A., and Chase, C.G., (992), Tectonic, climatic, and lithologic influences on landscape fractal dimension and hypsometry: implications for landscape evolution in the San Gabriel Mountains, California. Geomorphology, 5 ( 2), pp Magesh, N.S., Chandrasekar, N., and Soundranayagam, J.P., (2), Morphometric evaluation of Papanasam and Manimuthar watersheds, parts of Western Ghats, Tirunelveli district, Tamil Nadu, India: a GIS approach. Environmental Earth Science, 64, pp Masek, J.G., Isacks, B.L., Gubbels, T.L., and Fielding, E.J., (994), Erosion and tectonics at the margins of continental plateaus. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99 (B7), pp 3,94 3,956.. Moglen, G.E., and Bras, R.L., (995), The effect of spatial heterogeneities on geomorphic expression in a model of basin evolution. Water Resources Research, 3, pp Pike, R.J., and Wilson, S.E., (97), Elevation- relief ratio hypsometric integral and geomorphic area-altitude analysis. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 82, pp Ritter, D.F., Kochel, R.C., and Miller, J.R., (22), Process geomorphology. McGraw Hill, Boston. 4. Schumm, S.A., (956), Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 67, pp Strahler, A.N., (952), Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 63, pp Strahler, A.N., (964), Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks. In: VT Chow (ed.), Handbook of applied hydrology. McGraw Hill, New York, pp Weissel, J.K., Pratson, L.F., and Malinverno, A., (994), The length scaling properties of topography. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99, pp Willgoose, G., and Hancock, G., (998), Revisiting the hypsometric curve as an indicator of form and process in transport-limited catchment. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 23, pp International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences 695 Volume 6 Issue 3, 26
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
Sub-watershed prioritization based on potential zones of Kuttiadi river basin, A Geo-Morphometric approach using GIS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
Hypsometric Analysis of the Morna River basin, Akola District, Maharashtra, India
 Hypsometric Analysis of the Morna River basin, Akola District, Maharashtra, India Khadri, S.F.R Department of Geology Sant Gadge Baba Amravati University, Amravati, India. e.mail:syedkhadri_62@yahoo.com
Hypsometric Analysis of the Morna River basin, Akola District, Maharashtra, India Khadri, S.F.R Department of Geology Sant Gadge Baba Amravati University, Amravati, India. e.mail:syedkhadri_62@yahoo.com
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin
 Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
MORPHOTECTONIC STUDIES OF THE TUIRINI DRAINAGE BASIN: A REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM PERSPECTIVE
 International Journal of Geology, Earth & Environmental Sciences ISS: 2277-2081 (Online) MORPHOTECTOIC STUDIES OF THE TUIRII DRAIAGE BASI: A REMOTE SESIG AD GEOGRAPHIC IFORMATIO SYSTEM PERSPECTIVE *Fuzal
International Journal of Geology, Earth & Environmental Sciences ISS: 2277-2081 (Online) MORPHOTECTOIC STUDIES OF THE TUIRII DRAIAGE BASI: A REMOTE SESIG AD GEOGRAPHIC IFORMATIO SYSTEM PERSPECTIVE *Fuzal
A Case Study: Morphometric Characteristics of Sub-Watershed (P- 17) in Paras Region, Akola District, Maharashtra, India using Remote Sensing & GIS
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Earth Science and Engineering 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 492 499 ISSN: 2320 3609, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijaese.236 Case Study Open Access A Case
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Earth Science and Engineering 2017, Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 492 499 ISSN: 2320 3609, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijaese.236 Case Study Open Access A Case
GIS based quantitative morphometric analysis and its consequences: a case study from Shanur River Basin, Maharashtra India
 Appl Water Sci (2017) 7:861 871 DOI 10.1007/s13201-015-0298-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE GIS based quantitative morphometric analysis and its consequences: a case study from Shanur River Basin, Maharashtra India
Appl Water Sci (2017) 7:861 871 DOI 10.1007/s13201-015-0298-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE GIS based quantitative morphometric analysis and its consequences: a case study from Shanur River Basin, Maharashtra India
About the Author: E mail ID: Contact: proceedings. Page 1 of 8
 Catchment Delineation and Morphometric Analysis Using Geographical Information System of Naina Gorma Basin of Rewa District, M.P., India Vimala Singh 1, L.K. Sinha 2 Research Associate 1, DTRL, DRDO Scientist
Catchment Delineation and Morphometric Analysis Using Geographical Information System of Naina Gorma Basin of Rewa District, M.P., India Vimala Singh 1, L.K. Sinha 2 Research Associate 1, DTRL, DRDO Scientist
Prioritization of sub-watersheds in semi arid region, Western Maharashtra, India using Geographical Information System
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-10, pp-128-135 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Prioritization of sub-watersheds in semi arid
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-10, pp-128-135 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Prioritization of sub-watersheds in semi arid
International Journal of Research (IJR) Vol-1, Issue-10 November 2014 ISSN
 Morphological Parameter Estimation Derived From ASTER-DEM Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques A Study on Hosakote Watershed of Dakshina Pinakini River Basin, Karnataka, India K. Satish 1* and H.C.
Morphological Parameter Estimation Derived From ASTER-DEM Using GIS and Remote Sensing Techniques A Study on Hosakote Watershed of Dakshina Pinakini River Basin, Karnataka, India K. Satish 1* and H.C.
OBJECTIVES. Fluvial Geomorphology? STREAM CLASSIFICATION & RIVER ASSESSMENT
 STREAM CLASSIFICATION & RIVER ASSESSMENT Greg Babbit Graduate Research Assistant Dept. Forestry, Wildlife & Fisheries Seneca Creek, Monongahela National Forest, West Virginia OBJECTIVES Introduce basic
STREAM CLASSIFICATION & RIVER ASSESSMENT Greg Babbit Graduate Research Assistant Dept. Forestry, Wildlife & Fisheries Seneca Creek, Monongahela National Forest, West Virginia OBJECTIVES Introduce basic
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 4, 2011
 Morphometric analysis of Nanjangud taluk, Mysore District, Karnataka, India, using GIS Techniques Mahadevaswamy.G 1, Nagaraju.D 1, Siddalingamurthy.S 1, Lakshmamma 1, Mohammad Subhan lone, Nagesh.P.C 2,
Morphometric analysis of Nanjangud taluk, Mysore District, Karnataka, India, using GIS Techniques Mahadevaswamy.G 1, Nagaraju.D 1, Siddalingamurthy.S 1, Lakshmamma 1, Mohammad Subhan lone, Nagesh.P.C 2,
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF ADYAR WATERSHED
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF ADYAR WATERSHED A.K.Bharadwaj 1,Pradeep.C 2,D.Thirumalaivasan 3,C.P.Shankar 4, N.Madhavan 5 1,2,3,4,5 Institute of Remote Sensing, Anna University, Guindy, Chennai, India- 600025.
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF ADYAR WATERSHED A.K.Bharadwaj 1,Pradeep.C 2,D.Thirumalaivasan 3,C.P.Shankar 4, N.Madhavan 5 1,2,3,4,5 Institute of Remote Sensing, Anna University, Guindy, Chennai, India- 600025.
Morphometric Analysis of Chamundi Hills, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
 Volume-7, Issue-1, January-February 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 279-283 Morphometric Analysis of s, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
Volume-7, Issue-1, January-February 2017 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 279-283 Morphometric Analysis of s, Mysuru, India Using Geographical Information System
Simplify Equation to Calculate Elongation River Basin Proposed by Schumm (1956)
 Simplify Equation to Calculate Elongation River Basin Proposed by Schumm (1956) Dr. Saad.A.Mubark.aldarraji.Assisent Professor. Department of Geography. Faculty of Education.Ibn Rushed. Baghdad University.
Simplify Equation to Calculate Elongation River Basin Proposed by Schumm (1956) Dr. Saad.A.Mubark.aldarraji.Assisent Professor. Department of Geography. Faculty of Education.Ibn Rushed. Baghdad University.
Hypsometric analysis of Kali River Basin, Karnataka, India, using geographic information system
 Geocarto International Vol. 26, No. 7, November 2011, 553 568 Hypsometric analysis of Kali River Basin, Karnataka, India, using geographic information system Vipin Joseph Markose and K.S. Jayappa* Department
Geocarto International Vol. 26, No. 7, November 2011, 553 568 Hypsometric analysis of Kali River Basin, Karnataka, India, using geographic information system Vipin Joseph Markose and K.S. Jayappa* Department
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Review article ISSN 0976 4402 Morphometric analysis and
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Review article ISSN 0976 4402 Morphometric analysis and
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH
 GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Morphometric Analysis of Shaliganga Sub Catchment, Kashmir Valley, India Using Geographical Information System
 Morphometric Analysis of Shaliganga Sub Catchment, Kashmir Valley, India Using Geographical Information System Mohd Iqbal 1, Haroon Sajjad 1, F.A. Bhat 2 1 Department of Geography, Faculty of Natural Sciences,
Morphometric Analysis of Shaliganga Sub Catchment, Kashmir Valley, India Using Geographical Information System Mohd Iqbal 1, Haroon Sajjad 1, F.A. Bhat 2 1 Department of Geography, Faculty of Natural Sciences,
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF LAKSHMANTIRTHA RIVER BASIN AROUND HUNSUR TALUK, MYSORE, KARNATAKA, (INDIA)
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF LAKSHMANTIRTHA RIVER BASIN AROUND HUNSUR TALUK, MYSORE, KARNATAKA, (INDIA) Nilufer Arshad* and G.S. Gopalakrishna DOS in Geology University of Mysore, Mysore, (INDIA) Received
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF LAKSHMANTIRTHA RIVER BASIN AROUND HUNSUR TALUK, MYSORE, KARNATAKA, (INDIA) Nilufer Arshad* and G.S. Gopalakrishna DOS in Geology University of Mysore, Mysore, (INDIA) Received
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
MORPHOMETRY OF BUGGAVANKA WATERSHED IN KADAPA, ANDHRA PRADESH, INDIA USING SPATIAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
 BEST: International Journal of Humanities, Arts, Medicine and Sciences (BEST: IJHAMS) ISSN 2348-0521 Vol. 3, Issue 2, Feb 2015, 1-8 BEST Journals MORPHOMETRY OF BUGGAVANKA WATERSHED IN KADAPA, ANDHRA PRADESH,
BEST: International Journal of Humanities, Arts, Medicine and Sciences (BEST: IJHAMS) ISSN 2348-0521 Vol. 3, Issue 2, Feb 2015, 1-8 BEST Journals MORPHOMETRY OF BUGGAVANKA WATERSHED IN KADAPA, ANDHRA PRADESH,
Implication of drainage basin parameters for the Bunbuni River Basin in Chotanagpur Plateau region, India
 IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 21, Issue12, Ver. 4 (December. 2016) PP 01-08 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. www.iosrjournals.org Implication of drainage basin parameters
IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS) Volume 21, Issue12, Ver. 4 (December. 2016) PP 01-08 e-issn: 2279-0837, p-issn: 2279-0845. www.iosrjournals.org Implication of drainage basin parameters
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF RAJGARDH WATERSHED OF MADHYA PRADESH
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 1319 1328 Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_149 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtypeijciet&vtype8&itype4
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 4, April 2017, pp. 1319 1328 Article ID: IJCIET_08_04_149 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtypeijciet&vtype8&itype4
HW #2 Landscape Travel from A to B 12,
 HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
Morphometric analysis of Kharlikani watershed in Odisha, India using spatial information technology Kishor Choudhari 1, Panigrahi B 2, Paul J.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 4, 2014 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Morphometric analysis of Kharlikani
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 4, 2014 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Morphometric analysis of Kharlikani
Gully erosion and associated risks in the Tutova basin Moldavian Plateau
 Landform Analysis, Vol. 17: 193 197 (2011) Gully erosion and associated risks in the Tutova basin Moldavian Plateau University Alexandru Ioan Cuza of Iasi, Department of Geography, Romania, e-mail: catiul@yahoo.com
Landform Analysis, Vol. 17: 193 197 (2011) Gully erosion and associated risks in the Tutova basin Moldavian Plateau University Alexandru Ioan Cuza of Iasi, Department of Geography, Romania, e-mail: catiul@yahoo.com
Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India.
 Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India. Mr.S.S.Chokakkar 1, Mr.G.N.ChavanPatil, Dr.D.N.Mudgal 3, Dr..Shreenivasa 4 1M.Sc., B.Ed, NET, PhD(Pur.)
Morphometric Estimation of Parameters of Uttar Mand River Basin, Satara District, Maharashtra, India. Mr.S.S.Chokakkar 1, Mr.G.N.ChavanPatil, Dr.D.N.Mudgal 3, Dr..Shreenivasa 4 1M.Sc., B.Ed, NET, PhD(Pur.)
Morphometric Analysis Of Bhogavati River Basin, Kolhapur District, Maharashtra, India.
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN: 2278-1684, PP: 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Morphometric Analysis Of Bhogavati River Basin, Kolhapur District, Maharashtra, India. P. A.
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN: 2278-1684, PP: 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Morphometric Analysis Of Bhogavati River Basin, Kolhapur District, Maharashtra, India. P. A.
Evaluation of Morphometric parameters of drainage networks derived from Topographic Map and Digital Elevation Model using Remote Sensing and GIS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 4, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Evaluation of Morphometric
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 4, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Evaluation of Morphometric
Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Yahya Farhan, Ali Anbar, Omar Enaba, Nisrin Al-Shaikh Geomorphometric analysis was carried
Chapter 1 Quantitative Analysis of Geomorphometric Parameters of Wadi Kerak, Jordan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Yahya Farhan, Ali Anbar, Omar Enaba, Nisrin Al-Shaikh Geomorphometric analysis was carried
BASIC DETAILS. Morphometric features for landslide zonation A case study for Ooty Mettupalayam highway
 BASIC DETAILS Paper reference number : MWF PN 121 Title of the paper Name of the Presenter Author affiliation Mailing address Email address : Extraction of Topographic and Morphometric features for landslide
BASIC DETAILS Paper reference number : MWF PN 121 Title of the paper Name of the Presenter Author affiliation Mailing address Email address : Extraction of Topographic and Morphometric features for landslide
Chapter 4 : Morphometric Analysis
 Chapter : Morphometric Analysis. Introduction Geology, geomorphology, structure and drainage patterns especially in hard rock terrains are the primary determinants of river ecosystem functioning at the
Chapter : Morphometric Analysis. Introduction Geology, geomorphology, structure and drainage patterns especially in hard rock terrains are the primary determinants of river ecosystem functioning at the
Using GIS Techniques and Quantitative Morphometric Analysis to Evaluate the Groundwater Resources in the Central Flinders Ranges, South Australia
 Using GIS Techniques and Quantitative Morphometric Analysis to Evaluate the Groundwater Resources in the Central Flinders Ranges, South Australia Alaa A. Ismail and Ian Clark Centre for Water Management
Using GIS Techniques and Quantitative Morphometric Analysis to Evaluate the Groundwater Resources in the Central Flinders Ranges, South Australia Alaa A. Ismail and Ian Clark Centre for Water Management
Water & Climate; Floods & Droughts (The yin & yang of water availablilty) Water & Climate; Floods & Droughts (The yin & yang of water availablilty)
 (Acknowledgment: This presentation was developed in collaboration with ESA, NEON and NCEAS, federal agencies and academic team members from minority serving institutions.) Water & Climate; Floods & Droughts
(Acknowledgment: This presentation was developed in collaboration with ESA, NEON and NCEAS, federal agencies and academic team members from minority serving institutions.) Water & Climate; Floods & Droughts
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
CHAPTER 9 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER 9 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The following are the important conclusions and salient features of the present study. 1. The evaluation of groundwater potential is a prerequisite for any kind of planning
CHAPTER 9 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The following are the important conclusions and salient features of the present study. 1. The evaluation of groundwater potential is a prerequisite for any kind of planning
Mountain Rivers. Gutta cavat lapidem. (Dripping water hollows out a stone) -Ovid, Epistulae Ex Ponto, Book 3, no. 10, 1. 5
 Mountain Rivers Gutta cavat lapidem (Dripping water hollows out a stone) -Ovid, Epistulae Ex Ponto, Book 3, no. 10, 1. 5 Mountain Rivers Fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) High transport
Mountain Rivers Gutta cavat lapidem (Dripping water hollows out a stone) -Ovid, Epistulae Ex Ponto, Book 3, no. 10, 1. 5 Mountain Rivers Fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) High transport
International Journal of Remote Sensing & Geoscience (IJRSG) ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR-
 ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR- PHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION USING GIS TECHNOLOGY IN KOLLI HILL, SOUTH INDIA Gurugnanam.B, Centre for Applied Geology, Gandhigram Rural Institute-Deemed University, Tamilnadu,
ASTER DEM BASED GEOLOGICAL AND GEOMOR- PHOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION USING GIS TECHNOLOGY IN KOLLI HILL, SOUTH INDIA Gurugnanam.B, Centre for Applied Geology, Gandhigram Rural Institute-Deemed University, Tamilnadu,
Chapter 5. Morphometric Control on Food
 Chapter 5 Morphometric Control on Food Key Words: Morphometry, Linear Morphometry, Areal Morphometry, Relief Morphometry, Morphometric Control and Flood 5.1 Morphometric Aspects Drainage basin or basins
Chapter 5 Morphometric Control on Food Key Words: Morphometry, Linear Morphometry, Areal Morphometry, Relief Morphometry, Morphometric Control and Flood 5.1 Morphometric Aspects Drainage basin or basins
CAUSES FOR CHANGE IN STREAM-CHANNEL MORPHOLOGY
 CAUSES FOR CHANGE IN STREAM-CHANNEL MORPHOLOGY Chad A. Whaley, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, MobileAL, 36688. E-MAIL: caw408@jaguar1.usouthal.edu The ultimate goal of this
CAUSES FOR CHANGE IN STREAM-CHANNEL MORPHOLOGY Chad A. Whaley, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, MobileAL, 36688. E-MAIL: caw408@jaguar1.usouthal.edu The ultimate goal of this
[Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor
![[Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor [Penumaka, 7(1): January-March 2017] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/95/124653515.jpg) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES &MANAGEMENT HYDROGEOMORPHOLOGY OF CHEVELLA BASIN, RANGA REDDY DISTRICT, TELANGANA STATE Penumaka Ramesh* 1 & Podila Sankara Pitchaiah 2 * 1&2 Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES &MANAGEMENT HYDROGEOMORPHOLOGY OF CHEVELLA BASIN, RANGA REDDY DISTRICT, TELANGANA STATE Penumaka Ramesh* 1 & Podila Sankara Pitchaiah 2 * 1&2 Department of
Chapter IV MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS AND STREAM NETWORK CHARACTERISTICS IN GADAG DISTRICT
 Chapter IV MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS AND STREAM NETWORK CHARACTERISTICS IN GADAG DISTRICT 4.1 INTRODUCTION: Streams and rivers are the most dynamic parts of the earth s physical environment. The behavior of
Chapter IV MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS AND STREAM NETWORK CHARACTERISTICS IN GADAG DISTRICT 4.1 INTRODUCTION: Streams and rivers are the most dynamic parts of the earth s physical environment. The behavior of
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Surface Water Movement
 Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Which map shows the stream drainage pattern that most likely formed on the surface of this volcano? A) B)
 1. When snow cover on the land melts, the water will most likely become surface runoff if the land surface is A) frozen B) porous C) grass covered D) unconsolidated gravel Base your answers to questions
1. When snow cover on the land melts, the water will most likely become surface runoff if the land surface is A) frozen B) porous C) grass covered D) unconsolidated gravel Base your answers to questions
DRAINAGE BASIN MORPHOLOGY. Morphometric analysis is defined as the numerical
 C H A P T E R 3 DRAINAGE BASIN MORPHOLOGY 3.1 Introduction Morphometric analysis is defined as the numerical systematization of landform elements measured from topographic maps and provides real basis
C H A P T E R 3 DRAINAGE BASIN MORPHOLOGY 3.1 Introduction Morphometric analysis is defined as the numerical systematization of landform elements measured from topographic maps and provides real basis
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Morphotectonic and Lineament analysis from Bhatia and Jaigarh Creek, Ratnagiri, MS, India: Neotectonic Implication
 International Research Journal of Earth Sciences ISSN 2321 2527 Int. Res.J. Earth Sci. Morphotectonic and Lineament analysis from Bhatia and Jaigarh Creek, Ratnagiri, MS, India: Neotectonic Implication
International Research Journal of Earth Sciences ISSN 2321 2527 Int. Res.J. Earth Sci. Morphotectonic and Lineament analysis from Bhatia and Jaigarh Creek, Ratnagiri, MS, India: Neotectonic Implication
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Freshwater. 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table.
 Name: ate: 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. 3. Which conditions produce the most surface water runoff? A. steep slope,
Name: ate: 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. 3. Which conditions produce the most surface water runoff? A. steep slope,
Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist Belt Area, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh
 Open Journal of Geology, 2012, 2, 294-300 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2012.24028 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg) Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist
Open Journal of Geology, 2012, 2, 294-300 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2012.24028 Published Online October 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg) Study of Hydrometeorology in a Hard Rock Terrain, Kadirischist
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes
 Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS
 LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: April, 2016
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test
 Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
PRIORITIZATION BASED ON MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF DUDHGANGA CATCHMENT,KASHMIR VALLEY, INDIA. USING REMOTE SENSING & GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM.
 ISSN: 2307-6992 Available Online: http://ajgr.rstpublishers.com/ PRIORITIZATION BASED ON MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF DUDHGANGA CATCHMENT,KASHMIR VALLEY, INDIA. USING REMOTE SENSING & GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION
ISSN: 2307-6992 Available Online: http://ajgr.rstpublishers.com/ PRIORITIZATION BASED ON MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF DUDHGANGA CATCHMENT,KASHMIR VALLEY, INDIA. USING REMOTE SENSING & GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION
GOVERNMENT OF NEPAL MINISTRY OF IRRIGATION GROUND WATER RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT BOARD BABARMAHAL, KATHMANDU, NEPAL
 GOVERNMENT OF NEPAL MINISTRY OF IRRIGATION GROUND WATER RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT BOARD BABARMAHAL, KATHMANDU, NEPAL GIS Based Updating of Groundwater Level Siraha District Final Report Submitted to Ground
GOVERNMENT OF NEPAL MINISTRY OF IRRIGATION GROUND WATER RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT BOARD BABARMAHAL, KATHMANDU, NEPAL GIS Based Updating of Groundwater Level Siraha District Final Report Submitted to Ground
ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh District, Jharkhand, India
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
Geographical Information System Based Morphometric Analysis of Halia Drainage Area, Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India
 Geographical Information System Based Morphometric Analysis of Halia Drainage Area, Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India Sarala.C Associate Professor, Centre for Water Resources, Institute of Science
Geographical Information System Based Morphometric Analysis of Halia Drainage Area, Nalgonda District, Andhra Pradesh, India Sarala.C Associate Professor, Centre for Water Resources, Institute of Science
RIVERS, GROUNDWATER, AND GLACIERS
 RIVERS, GROUNDWATER, AND GLACIERS Delta A fan-shaped deposit that forms when a river flows into a quiet or large body of water, such as a lake, an ocean, or an inland sea. Alluvial Fan A sloping triangle
RIVERS, GROUNDWATER, AND GLACIERS Delta A fan-shaped deposit that forms when a river flows into a quiet or large body of water, such as a lake, an ocean, or an inland sea. Alluvial Fan A sloping triangle
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
Landforms. Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks
 Landforms Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks Landforms Made by Running Water Stream erosion The evolution of a river system Entrenched meanders Fluvial
Landforms Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks Landforms Made by Running Water Stream erosion The evolution of a river system Entrenched meanders Fluvial
MOUNTAIN ORDERING: A METHOD FOR CLASSIFYING MOUNTAINS BASED ON THEIR MORPHOMETRY
 Earth Surface Processes and Landforms Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 24, 653±660 (1999) MOUNTAIN ORDERING: A METHOD FOR CLASSIFYING MOUNTAINS BASED ON THEIR MORPHOMETRY SHUJI YAMADA Department of Geography,
Earth Surface Processes and Landforms Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 24, 653±660 (1999) MOUNTAIN ORDERING: A METHOD FOR CLASSIFYING MOUNTAINS BASED ON THEIR MORPHOMETRY SHUJI YAMADA Department of Geography,
NATURAL RIVER. Karima Attia Nile Research Institute
 NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
Morphometric Analysis for Hard Rock Terrain of Upper Ponnaiyar Watershed, Tamilnadu A GIS Approach
 International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 9, December 2014, PP 205-209 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Morphometric Analysis for
International Journal of Research Studies in Science, Engineering and Technology Volume 1, Issue 9, December 2014, PP 205-209 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Morphometric Analysis for
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70. Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills
 Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Keywords: Morphometry, Upper river basin, Remote sensing GIS, spatial information technology
 A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES OF UPPER NIRA DRAINAGE BASIN, MAHARASHTRA Anuradha Ohal Dept. of Geography Tilak Maharashtra Vidyapeeth, Pune ABSTRACT Nira is tributary
A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS USING REMOTE SENSING TECHNIQUES OF UPPER NIRA DRAINAGE BASIN, MAHARASHTRA Anuradha Ohal Dept. of Geography Tilak Maharashtra Vidyapeeth, Pune ABSTRACT Nira is tributary
a) Piedmont: e) Monument: f) Plateau: g) Mesa: h) Butte: i) Playa: j) Perennial Stream:
 Name: Lab day: Tuesday Wednesday CEEES/SC 10110L-20110L Planet Earth Laboratory Laboratory #11: Arid Environments & Landforms Readings: See handout at http://www.nd.edu/~cneal/physicalgeo/lab-deserts/index.html.
Name: Lab day: Tuesday Wednesday CEEES/SC 10110L-20110L Planet Earth Laboratory Laboratory #11: Arid Environments & Landforms Readings: See handout at http://www.nd.edu/~cneal/physicalgeo/lab-deserts/index.html.
Morphometric Analysis for Evaluating Groundwater Potential Zones, In Kusangai Jor Watershed Area, Dist. Bolangir, Orissa.
 Morphometric Analysis for Evaluating Groundwater Potential Zones, In Kusangai Jor Watershed Area, Dist. Bolangir, Orissa. Alokesh Chatterjee 1, Asish Tantubay 1 1 Department of Geology, Presidency College,
Morphometric Analysis for Evaluating Groundwater Potential Zones, In Kusangai Jor Watershed Area, Dist. Bolangir, Orissa. Alokesh Chatterjee 1, Asish Tantubay 1 1 Department of Geology, Presidency College,
Gis Based On Morphometric Analysis of Part of Manair River Basin in Karimnagar District, Telangana State.
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 0990, p-issn: 098.Volume, Issue Ver. II (Sep. Oct. 07), PP 0-07 www.iosrjournals.org Gis Based On Morphometric Analysis of Part of Manair
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 0990, p-issn: 098.Volume, Issue Ver. II (Sep. Oct. 07), PP 0-07 www.iosrjournals.org Gis Based On Morphometric Analysis of Part of Manair
MODULE 7 LECTURE NOTES 5 DRAINAGE PATTERN AND CATCHMENT AREA DELINEATION
 MODULE 7 LECTURE NOTES 5 DRAINAGE PATTERN AND CATCHMENT AREA DELINEATION 1. Introduction Topography of the river basin plays an important role in hydrologic modelling, by providing information on different
MODULE 7 LECTURE NOTES 5 DRAINAGE PATTERN AND CATCHMENT AREA DELINEATION 1. Introduction Topography of the river basin plays an important role in hydrologic modelling, by providing information on different
CHAPTER V WATERSHED CHARACTERIZATION USING GIS
 61 CHAPTER V WATERSHED CHARACTERIZATION USING GIS 5.1 GENERAL: In this chapter, introduction to watershed characterization and analysis has been presented in the first part. Methodology to compute important
61 CHAPTER V WATERSHED CHARACTERIZATION USING GIS 5.1 GENERAL: In this chapter, introduction to watershed characterization and analysis has been presented in the first part. Methodology to compute important
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE.
 PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
PROANA A USEFUL SOFTWARE FOR TERRAIN ANALYSIS AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL APPLICATIONS STUDY CASE ON THE GEODYNAMIC EVOLUTION OF ARGOLIS PENINSULA, GREECE. Spyridoula Vassilopoulou * Institute of Cartography
3. The map below shows an eastern portion of North America. Points A and B represent locations on the eastern shoreline.
 1. Most tornadoes in the Northern Hemisphere are best described as violently rotating columns of air surrounded by A) clockwise surface winds moving toward the columns B) clockwise surface winds moving
1. Most tornadoes in the Northern Hemisphere are best described as violently rotating columns of air surrounded by A) clockwise surface winds moving toward the columns B) clockwise surface winds moving
Assessing Vulnerability to Soil Erosion of a Watershed of Tons River Basin in Madhya Pradesh using Remote Sensing and GIS
 International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
University Grants Commission, New Delhi Recognized Journal No ISSN: Print: ISSN: Online: X
 Morphometric Analysis of Lower Bhavani River Basin, Using Geographical Information System Ipsita Pradhan 1, Dr S.Vasudevan 2, R. Selvaganapathi 3, G. Sathiyamoorthy 4, Subhrajit Das 5 1,3,4,5 Ph.D. Research
Morphometric Analysis of Lower Bhavani River Basin, Using Geographical Information System Ipsita Pradhan 1, Dr S.Vasudevan 2, R. Selvaganapathi 3, G. Sathiyamoorthy 4, Subhrajit Das 5 1,3,4,5 Ph.D. Research
Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study
 Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
PHASE 1 STUDIES UPDATE EROSION WORKING GROUP
 PHASE 1 STUDIES UPDATE EROSION WORKING GROUP Presented By MICHAEL WOLFF, PG Erosion Study Area Manager West Valley Demonstration Project Quarterly Public Meeting February 24, 2016 OUTLINE Study 1 Terrain
PHASE 1 STUDIES UPDATE EROSION WORKING GROUP Presented By MICHAEL WOLFF, PG Erosion Study Area Manager West Valley Demonstration Project Quarterly Public Meeting February 24, 2016 OUTLINE Study 1 Terrain
Chapter- Three GEOMORPHOLOGY AND RAINFALL PATTERN
 Chapter- Three GEOMORPHOLOGY AND RAINFALL PATTERN 3.1 INTRODUCTION Geomorphology and its slope as a basic and applied science in general and as tool for searching groundwater resources in efficient geomorphological
Chapter- Three GEOMORPHOLOGY AND RAINFALL PATTERN 3.1 INTRODUCTION Geomorphology and its slope as a basic and applied science in general and as tool for searching groundwater resources in efficient geomorphological
Topographic metrics and bedrock channels Outline of this lecture
 Topographic metrics and bedrock channels Outline of this lecture Topographic metrics Fluvial scaling and slope-area relationships Channel steepness sensitivity to rock uplift Advancing understanding of
Topographic metrics and bedrock channels Outline of this lecture Topographic metrics Fluvial scaling and slope-area relationships Channel steepness sensitivity to rock uplift Advancing understanding of
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR
 Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Rivers. Regents Earth Science Weathering & Erosion
 Regents Earth Science Weathering & Erosion Name: Rivers Use your notes, the handout Weathering and Erosion and your review book to answer the following questions on Rivers. Be sure to read the information
Regents Earth Science Weathering & Erosion Name: Rivers Use your notes, the handout Weathering and Erosion and your review book to answer the following questions on Rivers. Be sure to read the information
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
The subject paper is being submitted for approval for publication in the annual volume entitled Geological Survey Research.
 Water Resources Division 345 Middlefield Road Menlo Park, California January 12, 1965 Memorandum To: Mr. Frank E. Clark, Chief, General Hydrology Branch Thru: Area Hydrologist PCA From: Valmore C. LaMarche
Water Resources Division 345 Middlefield Road Menlo Park, California January 12, 1965 Memorandum To: Mr. Frank E. Clark, Chief, General Hydrology Branch Thru: Area Hydrologist PCA From: Valmore C. LaMarche
Lab 4: Drainage Basin Morphometry
 Lab 4: Drainage Basin Morphometry Objectives: To better appreciate the usefulness of topographic maps as tools for investigating drainage basins and to master several morphometric variables used to characterize
Lab 4: Drainage Basin Morphometry Objectives: To better appreciate the usefulness of topographic maps as tools for investigating drainage basins and to master several morphometric variables used to characterize
Chapter 2. Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice. Physical Weathering
 Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
CHAPTER 4 THE INFLUENCE OF RIVER BASIN MORPHOLOGY ON RIVER GROUNDWATER INTERACTION
 CHAPTER 4 THE INFLUENCE OF RIVER BASIN MORPHOLOGY ON RIVER GROUNDWATER INTERACTION CHAPTER 4 THE INFLUENCE OF RIVER BASIN MORPHOLOGY ON RIVER-GROUNDWATER INTERACTION 4.0. INTRODUCTION The relationship
CHAPTER 4 THE INFLUENCE OF RIVER BASIN MORPHOLOGY ON RIVER GROUNDWATER INTERACTION CHAPTER 4 THE INFLUENCE OF RIVER BASIN MORPHOLOGY ON RIVER-GROUNDWATER INTERACTION 4.0. INTRODUCTION The relationship
The elevations on the interior plateau generally vary between 300 and 650 meters with
 11 2. HYDROLOGICAL SETTING 2.1 Physical Features and Relief Labrador is bounded in the east by the Labrador Sea (Atlantic Ocean), in the west by the watershed divide, and in the south, for the most part,
11 2. HYDROLOGICAL SETTING 2.1 Physical Features and Relief Labrador is bounded in the east by the Labrador Sea (Atlantic Ocean), in the west by the watershed divide, and in the south, for the most part,
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 5, May -2017 Watershed Delineation of Purna River using Geographical
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 5, May -2017 Watershed Delineation of Purna River using Geographical
International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced Engineering (IJIRAE) ISSN: Issue 09, Volume 3 (September 2016)
 Quantitative evaluation and analysis of morphometric parameters derived from ASTER DEM using ARC Hydro tool in a GIS Environment A study of Vaishali River Basin of Madhya Pradesh Monika Sharma S.N.Mohapatra
Quantitative evaluation and analysis of morphometric parameters derived from ASTER DEM using ARC Hydro tool in a GIS Environment A study of Vaishali River Basin of Madhya Pradesh Monika Sharma S.N.Mohapatra
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 5, No 1, Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 5, No 1, 2014 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4402 Manual and automated delineation
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES Volume 5, No 1, 2014 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4402 Manual and automated delineation
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
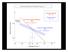 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Science EOG Review: Landforms
 Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Prashant P. Magar 1 and Nirupama P. Magar 2 1
 Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 4, 2016 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Application of Hack s Stream Gradient Index (SL Index) to Longitudinal Profiles of the Rivers Flowing
Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 4, 2016 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Application of Hack s Stream Gradient Index (SL Index) to Longitudinal Profiles of the Rivers Flowing
