EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page
|
|
|
- Alexia Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page. Submit answers to me using the blue Scantron sheet by Feb. 19, Once you have completed the exercise, transfer your answers to the blue Scantron sheet using a #2 pencil. Completely erase all mistakes and stray marks. LATE answer sheets will NOT be accepted. 1
2 6 Geographers Tools Maps and their Parts Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
3 MAP MAKING QUANDRY How do we transfer information from a large 3-D spheroid (Planet Earth) onto a smaller 2-D object (flat sheet) without distorting that information? With difficulty! The mapmaker must deal with 3 obstacles: 1. Conversion of a sphere (curved surface) to a plane (flat surface). 2. Shrinking of the earth s surface to fit the smaller flat object. 3. Portrayal of information to make it understandable to the viewer. 3
4 MAP MAKING The mapmaker confronts the problem by using: 1. PROJECTION to convert a sphere to a flat surface. 2. SCALE to shrink the earth s surface proportionally to fit the object. 3. SYMBOLIZATION to portray information and make it understandable. 4
5 MAP PROJECTIONS Only a globe can portray the earth s surface without distortion. Only a globe can show: true shape true relative area true distance true direction Any flat map will sacrifice 1 or 2 or 3 or all 4 advantages of a globe. A map cannot show more than three advantages at any one time! But which 3? 5
6 MAP PROJECTIONS A map projection is a representation of the 3-D earth s grid on a flat surface. Each of these projections has a combination of unique characteristics to show shape, relative area, distance and direction. Read the section on maps and map projections in any thematic atlas. 6
7 MAP PROJECTIONS The basic concept behind a map projection is having a light source within the globe and having that light source project the earth s grid on to a flat object. However, today most map projections are mathematically derived and cannot be projected. 1 min intro to map projections maps have inaccuracies. 6 min illustration why all world 7
8 MAP DISTORTION Based on the spacing of lines of latitude and longitude (as illustrated by heads ), the continents have different appearances. All maps distort shape in some way. NOTE: In these illustrations, the circles and shape-of-head diagrams are used to show distortion. Distortion occurs because of the way lines of latitude and longitude are spaced in the different projections. 8
9 Geometrical Map Projections Cylindrical Planar Conical If the globe is wrapped in a cylinder, a cylindrical projection is created. A cone creates a conical projection. A plane (flat sheet) creates a planar projecttion. 9
10 CYLINDRICAL PROJECTION In this projection the lines of longitude are parallel! Cannot show the polar regions. Star illustrates areas of distortion. Notice the unusual scale on the map. 10
11 CONICAL PROJECTION In this projection: Lines of longitude are too close nearing the poles. Lines of longitude are too far apart at the equator. Least distortion in the mid-latitudes 11
12 PLANAR PROJECTION In this projection, a plane (flat sheet) is placed tangent to the globe and the earth s grid is transferred to the plane. Least distortion in the center of the map but perimeter areas are stretched. Used mainly for polar areas. 12
13 Comparing Projections So depending on the map maker s choice of projection, the resulting flat map will have a unique appearance with a unique set of distortions. 3-D Earth 13
14 Comparing Projections So depending on the map maker s choice of projection, the resulting flat map will have a unique appearance with a unique set of distortions. And then there are the numerous interrupted projections and mathematically derived projections! 3-D Earth with grid 14
15 Goode s Homolosine Projection A mathematically derived projection providing the illusion of a peeled orange. Its classification is interrupted projection. 15
16 Other Interrupted Projections Peeled globe designs min video map projection (no sound) 16
17 AuthaGraph Projection Attempts to accurately show the size of land areas in relation to each other by using 96 triangles placed on the sides of a 3-D pyramid and then converting it into a 2-D rectangle. 17
18 R. Buckminster Fuller Map Projection This map illustrates the world island nature of the earth s landmasses without an unnatural interruption. It can be used to illustrate diffusion (spread), including the migration of early humans and the recent movements of plants and animals. There is only a maximum distortion of 2% at any one place, thereby maintaining relative (true) shape and size. However, true direction and distance are sacrificed. 18
19 SCALE Scale is a RATIO. It is the relationship between distance: the distance on the map to the equivalent distance on the earth s surface (map to earth). Scale is a means of measurement. Scale influences detail (symbolization). There are 3 ways to show scale. 19
20 Showing Scale a) VERBAL/Written: in words b) GRAPHIC/Bar: as a line or bar c) FRACTION/Ratio: as a mathematical equation 20
21 SCALE Small scale Large area, little detail Scale can be designated large or small. Large scale: Shows greater detail but less of an area. Small scale: Shows greater area but in less detail. (A globe is a very, very small scale map.) Large scale Small area, great detail 21
22 Effect of Scale on DETAIL Same size squares but each square shows different total surface area and different detail. Note that each shaded box (a, b, c, d) fits into the next one. A C B D Map A 22
23 SYMBOLIZATION Symbolization is the portrayal of information. Ideal maps should have the following seven elements: 1. Title 2. Date 3. Grid 4. Direction 5. Scale 6. Projection used 7. Legend or key 23
24 Maps and Symbolization 24
25 Map Symbols: with a legend or key The reader must know what the shapes, colors, patterns and sizes mean. (texture) (color) (shade) Therefore a LEGEND or KEY is needed. Without it, what is presented are just meaningless shapes and colors.
26 TOP DIRECTION Every map needs to have an indication of major compass points: north, south, east and west. LEFT RIGHT This can be done with a compass arrow, marking of lines of latitude and longitude and/or indication of quadrant. BOTTOM Where is north on this map? 26
27 Southern Hemisphere Which way is north? N By following the meridians of longitude away from the South Pole, you will eventually end at the North Pole. N + South Pole N N 27
28 Which arrows point North? A B E F D C 28
29 This way is North!! West A B North Pole E East F C D Must always follow lines of latitude and longitude to ascertain direction. Arrows B, C and E point to the North Pole. 29
30 Representing the World What is wrong with this world map? Nothing. It s a Pacific Ocean-centered world map 30
31 World Map What is wrong with this map? It s a World Map Centered on Australia. 31
32 Presenting Mapped Information Mapped data can be presented in various formats. There are 5 general categories of maps. 1. Point 2. Flow line 3. Isoline 4. Choropleth 5. Cartogram See Fig in your textbook. The five can be sub-divided into seven groups which present mapped information differently. 32
33 Map Formats 1. Point Symbol: a. Dot - Uses dots to indicate values at a location; shows distribution and density. b. Graduated symbol - Uses proportionallysized circles or symbols to indicate quantities present. 2. Isoline: Uses lines to connect points of equal value. 3. Flow Line: Uses lines of varying widths with arrowheads to portray amount of movement. 4. Choropleth: Uses colors or shading to convey information a. Qualitative = characteristics b. Quantitative = amounts 5. Cartogram: Uses data other than land area to portray the size of a unit. 33
34 Types of Maps: Point Symbols Both maps portray the population distribution of California. 1. Dot: Uses dots to indicate point values at a location. Shows distribution and density well. 2. Graduated: Uses proportionally-sized circles or other symbols to indicate quantities present at a location. 1 2 Good for comparing areas although the map may become visually cluttered. 34
35 Graduated Circles Format 35
36 Types of Maps: Isoline Uses lines to connect points of equal value. 36
37 Types of Maps - Flow Line Uses lines of varying widths (representing amounts) with arrowheads (indicating direction) to portray linear movement. Flow of smuggled 37guns
38 Uses colors, shading and symbols to convey an area s characteristics (qualitative) without regard for man-made borders. Types of Maps: Choropleth (qualitative) 38
39 Types of Maps: Choropleth (quantitative) Uses colors and shading to convey amounts by unit area (quantitative). Better for general use. Problem here is that this method does not differentiate within an area. 39
40 Types of Maps: Cartogram Uses data other than land area to portray the size of an area. It is based on the unit value of the topic portrayed, not land area. States are sized by population 1 box = 100,000 people 40
41 Based on the patterns can you guess what data is being shown? A Portraying Data B Presentation of same data in 4 formats: A. Graduated. Circle map B. Dot map C. Choropleth map D. Isoline map C D Four ways to portray AIDS cases in Pennsylvania 41
42 Summary: TYPES of MAPS Point: dot distribution 2. Point: graduated symbol 3. Flow Line 4. Isoline 5. Choropleth: qualitative 6. Choropleth: quantitative 7. Cartogram This diagram is from your textbook (1.27). 42
43 43
44 FIRST EXAM Tuesday, February 26, Combination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation. Bring a #2 pencil with eraser. Based on class lectures supplementing Chapter 1. Review lectures 1-8 on home page. If you miss this exam, a written-response make up test consisting of definitions, concepts and explanations, plus the place name maps will be given. 44
EXTRA CREDIT. 6 Geographers Tools. Maps and their Parts MAP MAKING QUANDRY MAP MAKING
 EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page. Submit answers to me using the blue Scantron sheet by Feb. 19, 2019. Once you have completed the exercise, transfer
EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page. Submit answers to me using the blue Scantron sheet by Feb. 19, 2019. Once you have completed the exercise, transfer
EXTRA CREDIT. 6 Geographers Tools. Maps and their Parts MAP MAKING QUANDRY MAP MAKING 2/15/19 MAP PROJECTIONS MAP PROJECTIONS
 EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page. Submit answers to me using the blue Scantron sheet by Feb. 19, 2019. Once you have completed the exercise, transfer
EXTRA CREDIT Extra Credit Atlas Exercise for Exam I is available on the course home page. Submit answers to me using the blue Scantron sheet by Feb. 19, 2019. Once you have completed the exercise, transfer
First Exam: New Date. 6 Geographers Tools. Maps and their Parts 2/16/2018 MAP MAKING MAP PROJECTIONS MAP PROJECTIONS MAP MAKING QUANDRY
 First Exam: ew ate Friday, March 2, 2018. ombination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation. ring a #2 pencil with eraser. ased on class lectures supplementing chapter 1. Review lecture slides.
First Exam: ew ate Friday, March 2, 2018. ombination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation. ring a #2 pencil with eraser. ased on class lectures supplementing chapter 1. Review lecture slides.
First Exam: New Date. 6 Geographers Tools Maps and their Parts 9/14/2017 MAP MAKING MAP MAKING MAP PROJECTIONS MAP PROJECTIONS
 6 Geographers Tools Maps and their Parts Prof. nthony Grande Hunter ollege Geography Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0917. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
6 Geographers Tools Maps and their Parts Prof. nthony Grande Hunter ollege Geography Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0917. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
Geographers Tools: Maps and their Parts
 MP MKIG Geographers Tools: Maps and their Parts Prof. nthony Grande Hunter ollege Geography Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0616. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior
MP MKIG Geographers Tools: Maps and their Parts Prof. nthony Grande Hunter ollege Geography Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0616. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior
Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography
 5 Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
5 Geographers Tools: Location Systems Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY
 MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
MR. GOFF S WORLD HISTORY UNIT ONE: GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY BYOD BRING YOUR OWN DEVICE IN SMALL GROUPS (3-4), USE YOUR ELECTRONIC DEVICE(S) AND DEFINE THE FOLLOWING VOCAB. WORDS 1. GEOGRAPHY 2.
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Studying Geography: Tools of the Trade
 GEOG 101 TUTORING AVAILABLE Free tutoring is available to all GEOG 101 students by experienced teachers. No appointment is necessary. Walk in/walk out sessions. Bring your notes, textbook, handouts, and
GEOG 101 TUTORING AVAILABLE Free tutoring is available to all GEOG 101 students by experienced teachers. No appointment is necessary. Walk in/walk out sessions. Bring your notes, textbook, handouts, and
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools
 Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Maps: Geography s Basic Tools What is a map? - A map is a representation of the earth s features drawn on a flat surface. - Maps use points, lines, colours, and symbols to represent the features of an
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
Introduction to Geography What is geography? Geography comes from the Greek word Geographia. Geo means earth and graphia means to describe or chart. Geographers study the earth in relation to space and
9/7/ Studying Geography: Introduction to Mapping. Cartographic Terms. Cartographic Terms. Geographers Tools. Geographers Needs.
 Geographers Tools Studying Geography: Introduction to Mapping Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG0918. Individual images and illustrations may be
Geographers Tools Studying Geography: Introduction to Mapping Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG0918. Individual images and illustrations may be
4 Studying Geography:
 4 Studying Geography: Introduction to Mapping Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior
4 Studying Geography: Introduction to Mapping Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG0119 Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are?
 AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
What is Geography? *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study.
 World Geography What is Geography? *It is the study of the earth *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study. *Shows the relationship between people and the environment.
World Geography What is Geography? *It is the study of the earth *Mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world into one field of study. *Shows the relationship between people and the environment.
2. What does the map scale tell the map reader? a ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the length given to that distance on a map
 AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
AP Human Geography - Damon Name Unit 1 - Intro to Human Geography Hour Map and Globe Skills Review Note: All links in this packet are found on our Wikispace under Map and Globe Skills Review First, read
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Pool Canvas. Add. Creation Settings. Chapter 1--Objectives and Tools of World Regional Geography. Description Instructions.
 1 of 6 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
1 of 6 TEST BANK > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Pool Canvas Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add Question drop-down list and click Go to add questions. Use
The World of Geography Pre-Test/Study Guide Chapter 1 Test
 Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
Read each statement or question. On the lines below write the letter of the best answer. 1. Geographers look at the Earth 5. What are the two specific A. by studying cities first. measurements of Earth
2 Mapping Earth Reading Essentials. 2. Contrast What is the difference between a map view and a profile view?
 Mapping Earth Maps What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree.
Mapping Earth Maps What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree.
Number in your response section 1-5. Write the letter to the matching Theme of Geography. (Do not use your notes)
 Matching/Review Number in your response section 1-5. Write the letter to the matching Theme of Geography. (Do not use your notes) 1. Location a. The ability of people, goods, and ideas to spread from one
Matching/Review Number in your response section 1-5. Write the letter to the matching Theme of Geography. (Do not use your notes) 1. Location a. The ability of people, goods, and ideas to spread from one
Chapter 2 - Lessons 1 & 2 Studying Geography, Economics
 Chapter 2 - Lessons 1 & 2 Studying Geography, Economics How does geography influence the way people live? Why do people trade? Why do people form governments? Lesson 1 - How Does Geography Influence the
Chapter 2 - Lessons 1 & 2 Studying Geography, Economics How does geography influence the way people live? Why do people trade? Why do people form governments? Lesson 1 - How Does Geography Influence the
Understanding Projections
 GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections The earth is a sphere and is best shown as a globe. For books and posters, though, the earth has to be represented as a flat object. To do this, mapmakers create
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map
 What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
What is a map? A Map is a two or three-dimensional model or representation of the Earth s surface. 2-Dimensional map What is a Map Projection? Planar Projection Projection A Projection is a mathematical
Course Introduction II
 CULTURE GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Course Introduction II Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College-CUNY AFG 2015 Culture is the essence of human geography because it influences all aspects of life on earth.
CULTURE GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Course Introduction II Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College-CUNY AFG 2015 Culture is the essence of human geography because it influences all aspects of life on earth.
Map Skills Unit. Note taking unit
 Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
Map Skills Unit Note taking unit Introduction To learn about the Earth, we are going to learn about two geographic tools you can use.globes and maps. Globe A globe is a round model of the planet Earth
Using Maps. Using Maps. Using Maps. Using Maps
 A is a visual representation, or model, of part or all of the earth. lines are imaginary lines that run east to west around the globe; they are also known as parallels. They show distances in degrees north
A is a visual representation, or model, of part or all of the earth. lines are imaginary lines that run east to west around the globe; they are also known as parallels. They show distances in degrees north
GEOGRAPHY. Map Skills. Mrs. Pere ~ 2013
 GEOGRAPHY Map Skills Mrs. Pere ~ 2013 WHAT IS A GLOBE? A globe is a model of the Earth. North Pole Equator South Pole WHAT IS A MAP? A map is a flat drawing of a place. THE IMPORTANT PARTS OF A MAP 1.
GEOGRAPHY Map Skills Mrs. Pere ~ 2013 WHAT IS A GLOBE? A globe is a model of the Earth. North Pole Equator South Pole WHAT IS A MAP? A map is a flat drawing of a place. THE IMPORTANT PARTS OF A MAP 1.
Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006
 I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
Name Class Date. For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. 1. true north and magnetic north 2. latitude and longitude 3. equator and prime meridian
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS For each pair of terms, explain how the meanings of the terms differ. 1. true north and magnetic north 2. latitude and longitude 3. equator and prime meridian
Unit 1 All. Study online at quizlet.com/_3l51hr
 Unit 1 All Study online at quizlet.com/_3l51hr 1. geography: 4. 7 APHG Units+: The study of the distribution and interaction of physical and human features on the earth 2. physical geography: 1. Geography:
Unit 1 All Study online at quizlet.com/_3l51hr 1. geography: 4. 7 APHG Units+: The study of the distribution and interaction of physical and human features on the earth 2. physical geography: 1. Geography:
Map Projections. Chapter 4 MAP PROJECTION
 Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Mapping Earth. How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled?
 Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Chapter 2: Studying Geography, Economics, and Citizenship
 Chapter 2: Studying Geography, Economics, and Citizenship Lesson 2.1 Studying Geography I. Displaying the Earth s Surface A. A globe of the Earth best shows the sizes of continents and the shapes of landmasses
Chapter 2: Studying Geography, Economics, and Citizenship Lesson 2.1 Studying Geography I. Displaying the Earth s Surface A. A globe of the Earth best shows the sizes of continents and the shapes of landmasses
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
Planet Classification Schemes Temperature Rings Presence of life Size Composition Moons Distance from Sun Length of day
 Solar noon on Winter Solstice in Fairbanks, Alaska (64º 50 N). Solar angle is 2 ; day length, 3.7 hours (sunrise 11:00, set 2:42). Planet Classification Schemes Temperature Rings Presence of life Size
Solar noon on Winter Solstice in Fairbanks, Alaska (64º 50 N). Solar angle is 2 ; day length, 3.7 hours (sunrise 11:00, set 2:42). Planet Classification Schemes Temperature Rings Presence of life Size
Warmup. geography compass rose culture longitude
 Warmup geography compass rose culture longitude ecosystem latitude 1. study of the special physical and human characteristics of a place or region 2. learned system of shared beliefs, traits, and values
Warmup geography compass rose culture longitude ecosystem latitude 1. study of the special physical and human characteristics of a place or region 2. learned system of shared beliefs, traits, and values
Introduction to Cartography Part I
 Introduction to Cartography Part I Introduction to Cartography Maps vs. Globes General Types of Maps Standard Map Features Maps versus Globes Map: a representation of the world, or part of it, in two dimensions
Introduction to Cartography Part I Introduction to Cartography Maps vs. Globes General Types of Maps Standard Map Features Maps versus Globes Map: a representation of the world, or part of it, in two dimensions
Course Introduction II
 CULTURE GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Course Introduction II Prof. nthony Grande Hunter College-CUNY FG 2017 Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0817. Individual images and illustrations may be subject
CULTURE GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Course Introduction II Prof. nthony Grande Hunter College-CUNY FG 2017 Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0817. Individual images and illustrations may be subject
UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH
 UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH How many planets are there in our Solar System? What is the Equator? Why does life exist in our planet? Does The Earth move? What is a map? 1. Planet Earth TOPICS 2. Movements
UNIT 1: THE PLANET EARTH How many planets are there in our Solar System? What is the Equator? Why does life exist in our planet? Does The Earth move? What is a map? 1. Planet Earth TOPICS 2. Movements
Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude..
 Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude.. Stuart Green Teagasc Spatial Analysis Group Stuart.green@teagasc.ie Web for the Week: http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gps.htm http://www.cstars.ucdavis.edu/classes/ers186-w03/lecture17/lecture17.ppt
Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude.. Stuart Green Teagasc Spatial Analysis Group Stuart.green@teagasc.ie Web for the Week: http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gps.htm http://www.cstars.ucdavis.edu/classes/ers186-w03/lecture17/lecture17.ppt
Warm up: (8 min) Use the Map, On the Prom (Color) Paper (Blk/White) and answer the questions on your paper
 Warm up: (8 min) Use the Map, On the Prom (Color) Paper (Blk/White) and answer the questions on your paper TX History: Mapping and Geography of Texas: We will discuss some slides and write notes on others
Warm up: (8 min) Use the Map, On the Prom (Color) Paper (Blk/White) and answer the questions on your paper TX History: Mapping and Geography of Texas: We will discuss some slides and write notes on others
Map Projections. Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps
 Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
netw rks Guided Reading Activity Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? What Is Geography?
 Guided Reading Activity What Is Geography? Lesson 1 Thinking Like a Geographer Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Directions: Read the lesson and use your textbook to
Guided Reading Activity What Is Geography? Lesson 1 Thinking Like a Geographer Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? Directions: Read the lesson and use your textbook to
Some of these parallels are very important. In the Northern Hemisphere, there is the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle.
 PDF 2 Geographic coordinates 1 The geographic coordinates system is network of imaginary horizontal and vertical lines that are drawn on globes or maps. These lines are called parallels (lines of latitude)
PDF 2 Geographic coordinates 1 The geographic coordinates system is network of imaginary horizontal and vertical lines that are drawn on globes or maps. These lines are called parallels (lines of latitude)
Word Cards. 2 map. 1 geographic representation. a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth. a visual representation of an area
 Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
Name: Date: Hour: Word Cards 1 geographic representation a description or portrayal of the Earth or parts of the Earth Example: A map is a representation of an actual location or place. 2 map a visual
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
What Is a Globe? Hemispheres. Main Idea Globes and maps provide different ways of showing features of the earth. Terms to Know
 r Main Idea Globes and maps provide different ways of showing features of the earth. Terms to Know hemisphere latitude longitude scale bar scale relief elevation contour line What Is a Globe? A globe is
r Main Idea Globes and maps provide different ways of showing features of the earth. Terms to Know hemisphere latitude longitude scale bar scale relief elevation contour line What Is a Globe? A globe is
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Geography Can Be Cool. Seriously
 Geography Can Be Cool Seriously Why does geography matter? Geography: the study of looking at every aspect of the Earth s systems, such as human economies, societies, cultures, plants, animals, & climate.
Geography Can Be Cool Seriously Why does geography matter? Geography: the study of looking at every aspect of the Earth s systems, such as human economies, societies, cultures, plants, animals, & climate.
Recall: The scale transformation
 Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
PART II. Physical Landscape Chapters 2 5 CLIMATE CLIMATE STUDYING CLIMATE R E M I N D E R S. PART II: People and their Physical Environment 10/19/2017
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
Maps and Map Projections
 38 The Global Positioning System The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a modern technology for determining a location on Earth. This high-tech system was originally created for military applications but
38 The Global Positioning System The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a modern technology for determining a location on Earth. This high-tech system was originally created for military applications but
CLIMATE CLIMATE STUDYING CLIMATE. PART II: People and their 3/20/2018. GEOG 101 Part II People and their Physical Environment R E M I N D E R S
 Two required essays are due by March 27, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer, earth scientist
Two required essays are due by March 27, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer, earth scientist
About places and/or important events Landmarks Maps How the land is, hills or flat or mountain range Connected to maps World Different countries
 What do you think you know about geography? About places and/or important events Landmarks Maps How the land is, hills or flat or mountain range Connected to maps World Different countries What do you
What do you think you know about geography? About places and/or important events Landmarks Maps How the land is, hills or flat or mountain range Connected to maps World Different countries What do you
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
CLIMATE DEFINED CLIMATE INFLUENCES STUDYING CLIMATE R E M I N D E R S. PART II: People and their 10/19/2018
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Oct. 30, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Oct. 30, 2018. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
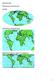 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Cartography = Science of Mapmaking
 Mapping Cartography = Cartography = Science of Mapmaking Eratosthenes (Era TOS the neez) Ancient Greek Librarian at Alexandria in Egypt (3rd c. BCE). First accurate measurement of circumference of the
Mapping Cartography = Cartography = Science of Mapmaking Eratosthenes (Era TOS the neez) Ancient Greek Librarian at Alexandria in Egypt (3rd c. BCE). First accurate measurement of circumference of the
Texas Geography. Understanding the physical and human characteristics of our state
 Texas Geography Understanding the physical and human characteristics of our state To understand Texas you must first learn about its Geography. Geography- The study of the world, its people, and the interaction
Texas Geography Understanding the physical and human characteristics of our state To understand Texas you must first learn about its Geography. Geography- The study of the world, its people, and the interaction
What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps
 Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles. Name
 GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
GEOL 309 Laboratory Activity: Euler Poles Name Instructions: Follow the directions given. Take a picture (with your phone) of your work showing final pole locations on the globe. Print pictures and turn
MR. JOHNSON S. Geography OHIO COUNTY MIDDLE SCHOOL
 MR. JOHNSON S Geography OHIO COUNTY MIDDLE SCHOOL CHAPTER 1 Geography The science of geography is likely the oldest of all sciences. Geography is the answer to the question that the earliest humans asked,
MR. JOHNSON S Geography OHIO COUNTY MIDDLE SCHOOL CHAPTER 1 Geography The science of geography is likely the oldest of all sciences. Geography is the answer to the question that the earliest humans asked,
PART II. Physical Landscape Chapters 2 5 CLIMATE CLIMATE STUDYING CLIMATE R E M I N D E R S. PART II: People and their Physical Environment 10/26/2017
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by Nov. 13, 2017. (A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay.) ESSAY TOPIS (choose any two): ontributions of a noted geographer,
Visit us at...
 Thanks for your purchase. We hope you are pleased. We think you might like the website that we are working on. You will find websites that go along with your unit and word wall cards. We hope you enjoy.
Thanks for your purchase. We hope you are pleased. We think you might like the website that we are working on. You will find websites that go along with your unit and word wall cards. We hope you enjoy.
A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools)
 A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools) Measuring Distance Using Map Scale All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale
A. Spatial Sense (Working with Maps, Globes, and Other Geographic Tools) Measuring Distance Using Map Scale All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
... Asia. Based on Bloom s Taxonomy. Human & Movement. Location Place. Regions. Environment. Interactions
 ... Asia Location Place Human & Environment Interactions Movement Regions LEVEL 1 Knowledge Match Show or Label List Information Recall Details (5Ws + H) Find Information LEVEL 2 Comprehension LEVEL 3
... Asia Location Place Human & Environment Interactions Movement Regions LEVEL 1 Knowledge Match Show or Label List Information Recall Details (5Ws + H) Find Information LEVEL 2 Comprehension LEVEL 3
FIND PLACES ON GLOBES USING LATITUDE
 GLOBES, MAPS & GRAPHS FIND PLACES ON GLOBES USING LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE LINES FIND PLACES ON MAPS USING A GRID SYSTEM NAME SEVERAL TYPES OF MAP PROJECTIONS AND EXPLAIN THEIR BENEFITS AND SHORTCOMINGS
GLOBES, MAPS & GRAPHS FIND PLACES ON GLOBES USING LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE LINES FIND PLACES ON MAPS USING A GRID SYSTEM NAME SEVERAL TYPES OF MAP PROJECTIONS AND EXPLAIN THEIR BENEFITS AND SHORTCOMINGS
Keith C. Clarke Department of Geologyand Geography Hunter College-CUNY 695 Park Avenue New York, NY 10021,USA
 DISTORTION ON THE INTERRUPTED MODIFIED COLLIGNON PROJECTION Keith C. Clarke Department of Geologyand Geography Hunter College-CUNY 695 Park Avenue New York, NY 10021,USA and Karen A. Mulcahy Earth and
DISTORTION ON THE INTERRUPTED MODIFIED COLLIGNON PROJECTION Keith C. Clarke Department of Geologyand Geography Hunter College-CUNY 695 Park Avenue New York, NY 10021,USA and Karen A. Mulcahy Earth and
GIST 3300 / Geographic Information Systems. Last Time. Today
 GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
2. Environmental issues in the relationship of humankind to the environment
 Course Goals to Understand 1. Processes operating on the earth s surface Atmosphere Lithosphere Hydrosphere Biosphere 2. Environmental issues in the relationship of humankind to the environment 3. Science
Course Goals to Understand 1. Processes operating on the earth s surface Atmosphere Lithosphere Hydrosphere Biosphere 2. Environmental issues in the relationship of humankind to the environment 3. Science
Chapter 1 Test on Geography Skills
 Name Score Chapter 1 Test on Geography Skills Part 1 Matching (14 pts.) Match each term in Column B with its correct definition in Column A by clearly writing the number in the blank space provided. Two
Name Score Chapter 1 Test on Geography Skills Part 1 Matching (14 pts.) Match each term in Column B with its correct definition in Column A by clearly writing the number in the blank space provided. Two
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS. Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output
 ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output Overview GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements GIS Output Formats Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output Overview GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements GIS Output Formats Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
Overview. GIS Data Output Methods
 Overview GIS Output Formats ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
Overview GIS Output Formats ENV208/ENV508 Applied GIS Week 2: Making maps, data visualisation, and GIS output GIS Output Map Making Types of Maps Key Elements Table Graph Statistics Maps Map Making Maps
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Geographic coordinate systems
 1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
Map Skills Lesson 1. Materials: maps, pencils, Lesson 1 Worksheet, strips of paper, grid paper
 Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
Map Skills Lesson 1 Use cardinal directions, map grids, scales, and titles to locate places on a map. Interpret a map using information from its title, compass rose, scale, and legend. Vocabulary: map,
DRAWING YOUR CONTINENT
 CONTINENT PROJECT PART I On the attached sheet, you will draw your own continent. Use your creativity to create a continent that is uniquely your own. Give the continent a name. When you are finished with
CONTINENT PROJECT PART I On the attached sheet, you will draw your own continent. Use your creativity to create a continent that is uniquely your own. Give the continent a name. When you are finished with
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
History of Cartography,
 Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
Maps History of Cartography, the art and science of making maps ~2300 BC ~600 BC Early oldest known maps: Babylonian clay tablets. Greek and Roman Ptolemy s (about AD 85-165) "world map" depicted the Old
page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #1 - Introduction to Latitude and Longitude Northern Hemisphere Southern Hemisphere
 page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #1 - Introduction to Latitude and Longitude A. Introduction There are many methods that can be used to locate ones position on the surface of the earth. A common method for
page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #1 - Introduction to Latitude and Longitude A. Introduction There are many methods that can be used to locate ones position on the surface of the earth. A common method for
Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do?
 Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do? Lesson 1.1 What is History? I. Why Study History? A. History is the study of the of the past. History considers both the way things
Name: Date: Period: #: Chapter 1: Outline Notes What Does a Historian Do? Lesson 1.1 What is History? I. Why Study History? A. History is the study of the of the past. History considers both the way things
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
 Name Period Parent Signature Geography/Map Skills Study Guide *For extra practice with these skills, check out Mr. Kath s website: http://rkath.weebly.com/activities--links.html Continents and Oceans of
Name Period Parent Signature Geography/Map Skills Study Guide *For extra practice with these skills, check out Mr. Kath s website: http://rkath.weebly.com/activities--links.html Continents and Oceans of
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems.
 Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Map Master Skills Handbook
 1 Map Master Skills Handbook Five Themes of Geography Understanding Globes How To Use A Map Human Migration Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 In this chapter, you ll be introduced
1 Map Master Skills Handbook Five Themes of Geography Understanding Globes How To Use A Map Human Migration Notebook Number Mr. Graver Old World Cultures Name Period 2 In this chapter, you ll be introduced
LANDSCAPES LANDSCAPES HUMAN IMPACT. PART II: People and their 4/10/2018. GEOG 101 Part II People and their Physical Environment R E M I N D E R S
 R E M I N D E R S Get study guide from course home page. TEXTBOOK READING FOR EXAM II WEATHER and CLIMATE: Ch. 2 LITHOSPHERE: chapter 3 BIOSPHERE: chapter 4 EARTH RESOURCES: chapter 5 Two required essays
R E M I N D E R S Get study guide from course home page. TEXTBOOK READING FOR EXAM II WEATHER and CLIMATE: Ch. 2 LITHOSPHERE: chapter 3 BIOSPHERE: chapter 4 EARTH RESOURCES: chapter 5 Two required essays
Sample file. Teacher Guide ... Before You Teach. Our resource has been created for ease of use by both TEACHERS and STUDENTS alike.
 8 7 9 10 12 13 14 11 Introduction T his resource provides ready-to-use information and activities for remedial students in grades five to eight. Written to grade and using simplified language and vocabulary,
8 7 9 10 12 13 14 11 Introduction T his resource provides ready-to-use information and activities for remedial students in grades five to eight. Written to grade and using simplified language and vocabulary,
Latitude and Longitude Pre Test
 Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Name Date Latitude and Longitude Pre Test Multiple Choice Directions: For questions, 1 10 circle the answer that letter that best answers the question. Each question is worth 1 point each. 1. To locate
Unit 1: Geography. For additional information, refer to this website: 1 G e o g r a p h y
 Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Unit 1: Geography For additional information, refer to this website: http://mryoungtms.weebly.com/ 1 G e o g r a p h y Continents and Oceans SOL USI. 2a Essential Understanding: Continents are large land
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3
 Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
Mapping Earth s Surface Chapter 2 Section 3 Day 1 Objective I will understand maps can be used to find locations on Earth and to represent information about features on Earth s Surface I will understand
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts.
 MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
1. Write down the term 2. Write down the book definition 3. Put the definition in your own words 4. Draw an image and/or put a Real Life Example
 Unit 1 Vocabulary 1. Write down the term 2. Write down the book definition 3. Put the definition in your own words 4. Draw an image and/or put a Real Life Example Absolute Location Where Is It EXACTLY?
Unit 1 Vocabulary 1. Write down the term 2. Write down the book definition 3. Put the definition in your own words 4. Draw an image and/or put a Real Life Example Absolute Location Where Is It EXACTLY?
First Exam. Geographers Tools: Automated Map Making. Digitizing a Map. Digitized Map. Revising a Digitized Map 9/22/2016.
 First Exam Monday, September 26, 206. Combination of multiple choice questions. Bring a #2 pencil with eraser. Based on class lectures and chapter. If you miss the exam, an essay style make up exam will
First Exam Monday, September 26, 206. Combination of multiple choice questions. Bring a #2 pencil with eraser. Based on class lectures and chapter. If you miss the exam, an essay style make up exam will
Globes, Maps, and Atlases. Plus, A Whole Bunch of Other Way Cool Geographic Information!!!
 Globes, Maps, and Atlases Plus, A Whole Bunch of Other Way Cool Geographic Information!!! Globes Are the Most Accurate Portrayal of the Earth The earth is about 24,900 miles in circumference, and about
Globes, Maps, and Atlases Plus, A Whole Bunch of Other Way Cool Geographic Information!!! Globes Are the Most Accurate Portrayal of the Earth The earth is about 24,900 miles in circumference, and about
Chapter 02 Maps. Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 02 Maps Multiple Choice Questions 1. Every projection has some degree of distortion because A. a curved surface cannot be represented on a flat surface without distortion. B. parallels and meridians
Chapter 02 Maps Multiple Choice Questions 1. Every projection has some degree of distortion because A. a curved surface cannot be represented on a flat surface without distortion. B. parallels and meridians
How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity
 Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Parts of a Map. Map Skills. The Title. There are 4 main parts of a map: The Title The Compass Rose The Map Key The Scale
 Map Skills Parts of a Map There are 4 main parts of a map: The Title The Compass Rose The Map Key The Scale The Title The title of the map is usually at the top and describes the topic of the map Example:
Map Skills Parts of a Map There are 4 main parts of a map: The Title The Compass Rose The Map Key The Scale The Title The title of the map is usually at the top and describes the topic of the map Example:
