Troubleshooting Liquid Chromatographic Separations: Avoiding Common Issues through Informed Method Development Practices
|
|
|
- Corey Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Troubleshooting Liquid Chromatographic Separations: Avoiding Common Issues through Informed Method Development Practices Dave S. Bell Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Bellefonte, PA USA T sigma-aldrich.com/analytical 2014 Sigma-Aldrich Co. All rights reserved.
2 bjective Most of the difficult problems encountered are a result of poor method development not column or instrument failure Lofty Goal: To provide HPLC troubleshooting tips by walking through the entire method development process Sample of questions addressed: Why do we choose certain columns? Why do we run at a certain wavelength? Use ESI vs. APCI? Why 10 mm phosphate buffer? Why acetonitrile? Why ph 3? Why certain flow rates and sample volumes? What does temperature have to do with it? What are the best tools for a given separation? What are the limits based on detection? Avoid living on the edge and KISS it! 2
3 utline Twelve most common problems encountered in HPLC Review common method development practices, potential pitfalls Discuss alternatives to Force-Fed C18 methods Embedded polar group phases Fluorinated aromatic phases Relate back to the 12 common problems (maybe) some further issues 3
4 Introduction: The 12 Problems Poor resolution Poor peak shape Lack of retention of polar compounds Time to develop a method Separation of critical pairs High throughput Wide range of sample polarities Ruggedness/robustness Column stability Mass spec compatibility Low detection limits Scale-up to prep Each problem can be circumvented by utilizing proper method development strategies and tools 4
5 Schematic of a Separation Chromatography is all about differential interactions of the analytes with the solvent and the stationary phase ur methods must be developed with an understanding of how these interactions work and how they are controlled Also about staying within the boundaries of physical parameters solubility chemical stability detection compatibility 5
6 Method Development Scenario General Steps: Understand the goals of the method: Fit for Purpose Assay need only retain and resolve a target analyte Purity need to retain and resolve all potential impurities Quantification from dirty matrix sample prep Understand analyte properties Ionization pk a, acidic, basic Solubility logp/logd, UV absorption/ms ionization detection The iterative process: Choose a column Choose a scouting mobile phase Test results Adapt conditions Test results.. 6
7 Choice of Column and the 12 Problems Resolution Retention, efficiency and selectivity Peak shape Silanol activity Retention of polar compounds Availability of polar and ionic interactions Time to develop a method The right tool speeds the job Separation of critical pairs Availability of needed interactions High throughput Smaller dimension = faster analysis Superior selectivity = faster analysis UPLC/SP particles = flatter van D Wide range of sample polarities Correct blend of interactions Ruggedness/robustness Column stability Mass spec compatibility Low column bleed Low detection limits Efficiency Scale-up to prep Availability of preparative dimensions and particle sizes 7
8 Resolution Efficiency N k R= N 4 Retention k k +1.. Selectivity -1 - Increase column length - Decrease particle size (N ~ 1/d p ) - Change stationary phase - Change mobile phase solvent - Change buffer ph - Increase (weaker solvent) - Decrease (stronger solvent) - Invoke different interactions Resolution (R) Zhao, J.H. and P.W. Carr. Analytical Chemistry, (14): p N k N k 8
9 Selectivity Interactions that contribute to retention and selectivity Stationary phase selectivity and method development practices What do we know about the different chemistries/how can we apply them intelligently to solve problems? Embedded polar group (EPG) stationary phases Aromatic Fluorinated Stationary Phases 9
10 Selectivity (contd.) Interactions that contribute to retention and selectivity Dispersive or hydrophobic interactions Polar interactions (hydrogen bonding and other dipole interactions) Ionic interactions Dispersive interactions are commonly considered most important in reversedphase chromatography Polar and ionic interactions, however, are often responsible for a significant amount of retention and selectivity 10
11 Stationary Phase Selectivity and Method Development Practices Common practice is to commence method development with a C18 ften a second C18 will be utilized if separation/retention not achieved Two alternatives; Force-feed the C18 (ion-pair, high ph, exotic mobile phases) Use alternative stationary phase chemistries Forced C18 methods generally suffer robustness, reproducibility problems very complicated, dynamic systems Alternative stationary phases are generally not well understood, resulting in method development difficulties 11
12 Caffeine and Green Tea Catechins H H Catechin H Epicatechin Gallate H N N Caffeine H N N Epigallocatechin H H H H Gallocatechin Gallate H H Catechin Gallate H H Epigallocatechin Gallate H Epicatechin H H Gallocatechin 12
13 Lack of Selectivity for Catechins using C18 - Resolution X X X X X X=co-elution Gradient 1 Gradient X X X X X Gradient 2 Gradient
14 Successful Separation of Catechins and Caffeine using a Polar Embedded Phase Peak ID and m/z ratio 1. Gallocatechin, m/z Caffeine, m/z Epigallocatechin, m/z Catechin, m/z Epicatechin, m/z Epigallocatechin gallate, m/z Gallocatechin gallate, m/z Epicatechin gallate, m/z Catechin gallate, m/z 441 column: Ascentis RP-Amide, 15 cm x 4.6 mm, 5 µm particles mobile phase: (A) 10 mm ammonium formate, ph 3.0 with concentrated formic acid (B) methanol flow rate: 1 ml/min., split to the mass spectrometer temp.: 35 C det.: MS, ESI (-) and (+) in selected ion recording (SIR) mode (combined) injection: 5 µl sample: 10 µg/ml each in 80:20, 10 mm ammonium formate, ph 3.0 with concentrated formic acid:methanol gradient: Min %A %B
15 DN and Related Compounds H 3 C H H H 3 C H H CH 3 Deoxynivalenol CH 3 Nivalenol H 3 C H H H 3 C H H H 3 C CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 3-Acetyldeoxynivalenol 15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol 15
16 Resolution Comparison between C18 and Aromatic Stationary Phases C18 resolution peaks 3 & 4 = Time (min) F5 resolution peaks 3 & 4 = Time (min) Phenyl-Hexyl resolution peaks 3 & 4 = Time (min) 16
17 Hydrophobic Selectivity M.R. Euerby, P. Petersson, J. Chromatogr. A 994 (2003) 13. Column k PB a CH2 a T/ a C/P a B/P_7.6 a B/P_2.7 Large difference in hydrophobicity Ascentis C Discovery C Little difference in selectivity Discovery HS C ACE Luna (2) Symmetry Inertsil (3)
18 Selectivity Comparison Between Alkyl Stationary Phases log k' C log k' C18 18
19 Selectivity Comparison Between EPG and C18 Stationary Phases y = x R 2 = log k' Ascentis RP-Amide log k' Ascentis C18 19
20 EPG Phases R 1 Si R 1 P R 2 Nitrogen-containing EPG phases Also ether type phases Where P can be: NH R R HN NH NH R R R R Amide Urea Carbamate 20
21 Linear Solvation Energy Relationships (LSER) The LSER model relates fundamental molecular solute descriptors to the free energy related to a phase transfer process. Properties include dispersion and molecular volume (V), polarizability (S), electron lone pair interactions (E) and hydrogen bonding contributions to free energy (A and B). log k = c + ee + ss + aa + bb + vv 21
22 Multiple Linear Regression Analysis Stationary Phase Constant (c) v e s a b Ascentis RP- Amide ± ± ± ± ± ±0.13 Ascentis C ± ± ± ± ± ±0.18 The molar volume (v) and electron lone pair (e) descriptors are shown to be statistically the same The polarization (s), hydrogen bonding acceptor (a) and hydrogen bond donator (b) terms are statistically different 22
23 4-nitroaniline 2-nitroaniline hexanophenone Acetanilide anisole benzamide benzylbenzoate valerophenone Difference in Retention [log k (RP-Amide) log k (C18)] Phenolics R toluene 4-nitrotoluene benzene nitrobenzene ethylbenzene naphthalene biphenyl Phenol 2-nitrophenol 4-MePhenol 4-phenylPhenol 2,6-DiMePhenol 3-bromophenol 4-chlorophenol acetophenone butyrophenone benzophenone polarizables 2014 Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC. All rights reserved Sigma-Aldrich Co. All rights reserved. Anilines NH 2 R 23
24 Example Application: Separation of Catechols and Resorcinols Based on the LSER and classification studies, analytes that can donate toward hydrogen bonding should provide differential retention on EPG phases compared to C18 phases. Catechol Resorcinol 24
25 Example Application: Separation of Catechols and Resorcinols column: Ascentis RP-Amide or C18, 15 cm x 4.6 mm, 5 µm particles mobile phase: 75:25, 20 mm phosphoric acid (ph 2.0 unadjusted):ch 3 CN temp: 30 C flow rate: 1.5 ml/min det: UV, 270 nm 2 injection: 25 µl sample: as indicated (in 20 mm H 3 P 4 ph 2.0) 1 1. Resorcinol (50 g/ml) 2. Catechol (50 g/ml) 3. 2-methyl resorcinol (50 g/ml) 4. 4-methyl catechol (50 g/ml) 5. 2,5-dimethyl resorcinol (50 g/ml) 6. 3-methyl catechol (50 g/ml) 7. 4-nitro catechol (50 g/ml) RP-Amide C Time (min) Time (min) 25
26 Vitexin and Related Compounds column: Ascentis RP-Amide or C18, 10 cm x 3 mm, 2.7 µm particles mobile phase: water/acetonitrile (85:15 v/v); 10 mm citric acid temp: 55 C flow rate: 1.5 ml/min injection: 2 µl vitexin and related.esp Vitexin 2. Isovitexin 3. Vitexin glucoside 4. Vitexin Rhamnoside H H Retention Time (min)
27 Euerby Column Classification Results Column k PB CH2 T/ C/P B/P 2.7 B/P 7.6 Discovery C18 (Control) Ascentis RP- Amide Ascentis C Ion-exchange capacity 27
28 Tamoxifen and Metabolites 0.1 % formic acid in water Peak IDs 1. 4-hydroxytamoxifen (E and Z) isomers (50 g/ml) 2. Tamoxifen (50 g/ml) EPG (Amide) C18 1EZ 1EZ 2 USP tail Area Height EZ 2 USP tail Area Height Time (min) Time (min) Peak heights is > 2.5 greater; lower LDs expected with EPG, the end of the peak becomes difficult to determine with C18. As a result, the baseline is therefore drawn in different places for multiple injections; resulting in error in measurement accuracy and precision are lost due to tailing peaks. 28
29 EPG Phases Two key observations: Provides different selectivity as a result of hydrogen bond accepting ability Provides shielding of surface silanol interactions with basic analytes Where to use them? First line for hydrophobic bases! Good alternative for moderately polar compounds as well as those that can donate toward a hydrogen bond ften find improved selectivity for positional isomers as compared to C18 29
30 Fluorinated Stationary Phases: Introduction Fluorinated phases have also become a popular alternative to alkyl phases in recent years Fluorinated phases such as pentafluorophenylpropyl-modified silica (PFPP/PFP or F5) offer the potential for: Dipole-dipole interactions F - interactions Charge-transfer interactions F F Ionic interactions Si Si Rigidity imparts some steric selectivity F F 30
31 Shape Selectivity and IEX Differences HPLC Column Selector Build version: 08 February 2010 The Column Selector is based on an article by M.R. Euerby and P. Petersson published in J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 994, Single pair column comparison CDF = Parameters Weightings kpb (1.00) ach2 (1.00) at (1.00) acp (1.00) abp76 (1.00) abp27 (1.00) Column 1: Discovery C18 HS Column 2: Discovery F5 HS
32 Selegiline and Amphetamines Retained and Separated using PFP CH 3 N H 3 C Selegiline NH CH 3 CH column: Ascentis Express F5, 10 cm x 4.6 mm, 2.7 µm particles, mobile phase: (A) 10 mm ammonium acetate, ph 4.0 with acetic acid (B) acetonitrile; A:B = 20:80 flow rate: 1.0 ml/min. pressure: 160 bar (2300 psi) temp.: 35 C det.: MS ESI (+), SIR m/z 136, 150, 188 injection: 2 µl sample: 10 µg/ml in methanol CH 3 selegiline_amphets_20_80.esp 3 Methamphetamine CH 3 No. Name tr 1 selegiline amphetamine methamphetamine NH 2 1 Amphetamine Retention Time (min)
33 Altering Retention and Selectivity through Manipulation of Ion-Exchange and Percent rganic Components HS F5 25_ _hilic_009 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 90 75% Acetonitrile 5.97; : SIR of 6 Channels ES+ 188 (selegiline) 3.20e5 Area _hilic_009 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 1: SIR of 6 Channels ES+ 7.28; (methamphetamine) 2.40e6 90 Area _hilic_009 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 1: SIR of 6 Channels ES+ 5.72; (amphetamine) 1.58e6 90 Area Time HS F5 40_ _hilic_003 Sm (Mn, 2x3) ; : SIR of 6 Channels ES+ 188 (selegiline) 1.25e5 Area _hilic_003 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 1: SIR of 6 Channels ES+ 6.98; (methamphetamine) 1.86e6 90 Area _hilic_003 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 1: SIR of 6 Channels ES+ 5.19; (amphetamine) 9.85e5 90 Area % % % % % % % Acetonitrile HS F5 20_ _hilic_015 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 90 80% Acetonitrile 8.39; : SIR of 6 Channels ES+ 188 (selegiline) 7.33e5 Area _hilic_015 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 1: SIR of 6 Channels ES ; (methamphetamine) 4.18e6 90 Area _hilic_015 Sm (Mn, 2x3) 1: SIR of 6 Channels ES ; (amphetamine) 2.67e6 90 Area % % % Time Time
34 Solving Real Issues with Alternative Selectivity Conditions: column: Discovery C18, 15 cm x 4.6 mm, 5 µm mobile phase: 10 mm KH 2 P 4, ph 2.5, acetonitrile (55:45, v/v) det.: nm N mau 250 VWD1 A, Wavelength=220 nm (DSB\ D) piroxicam NH S N CH 3 2AMP, t 0 N min H 2 N 34
35 Solving Real Issues with Alternative Selectivity (contd.) Conditions: column: Discovery HS F5, 15 cm x 4.6 mm, 5 µm mobile phase: 10 mm KH 2 P 4, ph 2.5, acetonitrile (55:45, v/v) det.: nm mau VWD1 A, Wavelength=220 nm (DSB\ D) AMP piroxicam min 35
36 Apparent Shape Selectivity using PFP mobile phase: water:methanol (50:50, v/v) H CH 3 H CH 3 CH 3 H CH 3 Peak ID 1. Hydrocortisone 2. Prednisolone 3. Prednisone 3 1,2 H H Hydrocortisone [*{BAN}; *{INN}; *{JAN}] Monoisotopic Mass = Da H H Prednisone [*{BAN}; *{INN}] Monoisotopic Mass = Da C18 H CH 3 H CH Time (min) H H Prednisolone [*{BAN}; *{INN}; *{JAN}] Monoisotopic Mass = Da PFP Time (min) 36
37 Structures H 3 C CH 3 H H 3 C CH 3 H 3 C CH 3 H H CH 3 CH 3 H H H CH 2 H H H CH 2 H 25-Hydroxyvitamin D H 3-epi-25-Hydroxyvitamin D H 3 C CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 C H 3 H CH 2 H 25-Hydroxyvitamin D2 37
38 Vitamin D Metabolites on C18 column: Ascentis Express C18, 5 cm x 2.1 mm, 2.7 µm (53822-U) mobile phase: (A) 15%, 5 mm ammonium formate water (B) 85%, 5 mm ammonium formate (95:5 acetonitrile:water) flow rate: 0.4 ml/min temp.: 35 C det.: UV 265 nm, MS ESI m/z injection: 1 µl Retention Time: 25 hydroxyvitamin D min 3-epi-25 hydroxyvitamin D min 25 hydroxyvitamin D min AU 25 hydroxyvitamin D
39 Vitamin D Metabolites on PFP column: Ascentis Express F5, 10 cm x 2.1 mm, 2.7 µm (53569-U) mobile phase: (A) 25%, 5 mm ammonium formate water (B) 75%, 5 mm ammonium formate methanol flow rate: 0.4 ml/min temp.: 40 C det.: UV 265 nm, MS ESI m/z injection: 1 µl Retention Time: 25 hydroxyvitamin D min epi-25 hydroxyvitamin D min 25 hydroxyvitamin D min 25 hydroxyvitamin D 3 epi-25 hydroxyvitamin D 3 Isobaric pair Aurand, C. R., Bell, D. S, Wright, M., (2012). Bioanalysis 4(22): Time (min) 39
40 Fluorophenyl Phases Increased IEX behavior over alkyl and phenyl phases (let it happen) Increased shape selectivity. Notable for separation improvements for basic (polar and nonpolar) as well as rigid structures. 40
41 Classification by Chemical Interaction Type a Bonded Phase Hydrophobic H-Bonding Dipolar π-π Steric Ion- Exchange b C18 V. Strong Weak No No No Moderate C8 Strong Weak No No No Moderate Amide Strong Strong Acceptor Moderate No Weak Very weak Phenyl Moderate Weak Acceptor Weak Strong Donor Strong (Rigid) Moderate Cyano Weak Moderate Strong Weak No Strong PFP Moderate Moderate Acceptor Strong Strong Acceptor Strong (Rigid) Strong a. Using Euerby adaptation of Snyder-Dolan-Carr Hydrophobic Subtraction Model. b. May include interactions with acidic silica substrate 41
42 I. Choice of Column and the 12 Problems Resolution Retention, efficiency and selectivity Peak shape Silanol activity Retention of polar compounds Availability of polar and ionic interactions Time to develop a method The right tool speeds the job Separation of critical pairs Availability of needed interactions High throughput Smaller dimension = faster analysis Superior selectivity = faster analysis UPLC/SP particles = flatter van D Wide range of sample polarities Correct blend of interactions Ruggedness/robustness Column stability Mass spec compatibility Low column bleed Low detection limits Efficiency Scale-up to prep Availability of preparative dimensions and particle sizes 42
43 Dealing with some of the other problems Retention of polar compounds: HILIC Same reasoning in terms of stationary phases Must keep mechanisms in mind Retention Mechanisms in HILIC Chromatography - High throughput, Low detection limits: Sub 2 µm, Superficially Porous Both approaches provide increased efficiency Both approaches provide flatter van Deemter profiles Ruggedness/robustness Most modern phases provide intrinsic robustness As long as methods are developed with appropriate controls and away from edges.. Mass spec compatibility use modern phases Scale-up to prep 43
44 Speeding Up the Method Development Process Receives request, available information and samples Determines most appropriate starting point (usually C18) Modifies conditions (%organic, organic component, ph) Acceptable Not acceptable Done Add ion-pair, ion suppression reagents, etc. (force-feed) Change Stationary Phase Modify as new data and/or formulations develop ften a poor choice 44
45 Mobile Phase Modifiers: Buffers and the 12 Problems Resolution Retention, efficiency and selectivity Peak shape Silanol activity Retention of polar compounds Availability of polar interactions Time to develop a method The right tool speeds the job Separation of critical pairs Availability of needed interactions High throughput Wide range of sample polarities Correct blend of interactions Ruggedness/robustness Column stability Mass spec compatibility Mobile phase considerations Low detection limits Mobile phase considerations Efficiency Scale-up to prep 45
46 Mobile Phase: Buffer Buffers Ionizable analytes make ph control a must Buffers, by definition, help to control ph but only near their pk a A common problem is that developers use the wrong buffer for a given ph Rule: adjust ph +/- 1 ph unit about a buffer pk a Note that some situations require the use of a given buffer outside this range 46
47 Controlling Retention in RP-HPLC: ph Acids are more non-polar at low ph where they are protonated, and bases are more non-polar at high ph were they are not protonated. Effect of ph on Hydrophobicity of Acid (A) and Base (B) reversed phase retention (hydrophobicity) AH BH + BH <--> B + H 2 acidic mobile phases B Consider the analyte and the mobile buffer pka! A- A - + H 3 + <--> AH + H 2 basic mobile phases ph 47
48 Buffers and Salts for HPLC Buffers pk a Acetate 4.75 Ammonium 9.24 Borate Borate Borate Citrate Citrate Citrate Formate 3.75 xalate xalate Phosphate Phosphate Phosphate Triethylamine Trifluoroacetic acid 0.5 Tris* 8.08 *Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane Salts NaCl KCl NH 4 Ac Acids H 3 P 4 HCl TFA Acetic Formic Carbonic Bases TEA K Na Qualities UV-transparent Clean Particle-free Non-reactive Miscible with other solvents and samples LC/MS-compatible (volatile) 48
49 Mobile Phase (contd.) Buffers Control the ionization state of the analyte AND the surface silanols Consider both Generally, 10 mm is enough if greater shows better peak shape likely dealing with secondary interactions Watch high organic percentage and buffer solubility Use volatile organic buffers for MS (ammonium acetate, ammonium formate) Counterion often very important mediates ion-exchange interactions Consider ph AFTER mixing with organic 49
50 Mobile Phase: rganic Modifier and the 12 Problems Resolution Retention, efficiency and selectivity Peak shape Silanol activity Retention of polar compounds Availability of polar interactions Time to develop a method The right tool speeds the job Separation of critical pairs Availability of needed interactions High throughput Wide range of sample polarities Correct blend of interactions Ruggedness/robustness Column stability Mass spec compatibility Mobile phase considerations Low detection limits Mobile phase considerations Efficiency Scale-up to prep 50
51 Mobile Phase: rganic Modifier rganic modifier: Why acetonitrile, for example? Used to control the retention based on dispersive interactions Can effect polar interactions as well Choices: Acetonitrile, Methanol, THF Why these? Low viscosity backpressure issues Low UV absorbance detection issues Water miscibility Can other be used? Sure, but often with penalties 51
52 Mobile Phase: rganic Modifier Avoid very low organic on standard C18 phases (so-called phase collapse) If very low organic is required use a stationary phase that is 100% aqueous compatable Avoid very high organic when using inorganic buffers (solubility) Avoid >20% THF with PEEK 52
53 100% Aqueous Stability column: Ascentis RP-Amide, 15 cm x 4.6 mm, 5 µm (53569-U) mobile phase: 25mM monobasic potassium phosphate (ph 3.0 with H 3 P 4 ) flow rate: 1 ml/min temp.: 35 C det.: UV 230 injection: 10 µl H H dehydroascorbic acid 2 Peak identification: 1. Dehydroascorbic acid 2. Ascorbic acid H H ascorbic acid 1 H Time (min) 53
54 Peak Tailing Peak tailing due to secondary interactions with the silanol surface of C18 columns. C18 phases are not designed to take advantage of these interactions, therefore we do not have control. nly part of the analyte population sees this interaction, thus tailing occurs. A more base-deactivated C18 means that there are less available ionized silanols for bases to interact with. Polar phases take more advantage of silanol interactions. 54
55 rigins of Peak Tailing nly some of the analyte population has access to surface ionized silanols
56 rigins of Peak Tailing (contd.) All analyte molecules have equal access to ionized surface silanols. F F F + + F F + F F F + F F FF F F F FF F + F F 56
57 Ephedra Alkaloids H 3 C H 3 C NH H 3 C H 3 C N CH 3 NH 2 H 3 C ephedrine methylephedrine norephedrine H 3 C NH CH 3 C H 3 NH 2 HN H CH 3 pseudoephedrine norpseudoephedrine synephrine D.S. Bell and A. D. Jones, J. Chromatogr. A.,
58 Ephedrine Alkaloids column: Discovery HS F5, 15 cm x 24.6 mm, 5 µm particles ( U) mobile phase: 4 mm ammonium acetate in 90:10, CH 3 CN:water flow rate: 1 ml/min temp.: 45 C det.: UV at 215 nm injection: 10 µl sample: 10 µg/ml in 40:60, mobile phase:ch Peak identification: 1. Norephedrine 2. Synephrine 3. Methylephedrine 4. Ephedrine 5. Pseudoephedrine Time (min) 58
59 Peak Tailing Remedies for peak tailing issues Lower ph minimizes population of ionized silanols (pk a 4-6) There are always some ionized silanols Reported pk a values are averages Solvent system has impact on silanol pk a Greater organic proportions = higher silanol pk a values Stationary phase chemistry also has an effect on silanol pk a values Solvation at surface is altered Sometimes better to allow ion-exchange interactions rather than try to hide them. Some stationary phases, such as polar embedded phases, show improved peak shape for basic analytes due to masking of surface silanols. 59
60 V. Injection Volume and Sample Composition Generally effect peak shape/ruggedness of method Separation is based on setting up an equilibrium When samples are injected equilibrium is disrupted Need to balance injection volume with required detection limits Typically greater concentration (if possible) and lower volume is better than the opposite Most injectors are capable of L Stay away from the edges Stay within calibrated (qualified) volumes 60
61 V. Injection Volume and Sample Composition (contd.) Best to keep sample solvent as close to mobile phase as possible Very common problem Sample solvent should be weaker elution solvent than MP Strong solvent results in fronting peaks Can limit the effect by using small volumes Dirty samples! Use guard columns and filters Know when to change them 61
62 Summary Although many HPLC issues are instrument related (leaks, faulty detectors, extra column volume ) a large percentage are related to poor method development. Understanding why certain components are in there and some knowledge of usable ranges is critical for avoiding issues. Trouble is usually avoidable through the development of sound methods. Proper column, mobile phase and external parameters (ie temperature) are essential. Column screening early in MD is highly recommended. Use simplest system - KISS Stay away from the edges 62
63 Acknowledgements Hillel Brandes Carmen Santasania Xiaoning Lu Gaurang Parmar Hugh Cramer Craig Aurand Wayne Way 63
Novel LC/MS-Compatible Stationary Phase with Polar Selectivity
 Novel LC/MS-Compatible Stationary Phase with Polar Selectivity Carmen T. Santasania and David S. Bell Supelco 595 N. Harrison Rd., Bellefonte, PA 16823 T403168 GJU Introduction Stationary phases based
Novel LC/MS-Compatible Stationary Phase with Polar Selectivity Carmen T. Santasania and David S. Bell Supelco 595 N. Harrison Rd., Bellefonte, PA 16823 T403168 GJU Introduction Stationary phases based
Trends in Method Development for HPLC and UHPLC... the movement toward using solid-core particles
 Trends in Method Development for HPLC and UHPLC... the movement toward using solid-core particles Richard A. Henry, Separation Technology Consultant On behalf of: Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, Bellefonte, USA
Trends in Method Development for HPLC and UHPLC... the movement toward using solid-core particles Richard A. Henry, Separation Technology Consultant On behalf of: Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, Bellefonte, USA
Reversed Phase Solvents
 Part 1. General Chromatographic Theory Part 2. verview of HPLC Media Part 3. The Role of the Mobile Phase in Selectivity Part 4. Column Care and Use Reversed Phase Solvents 2 Solvents for RP Chromatography
Part 1. General Chromatographic Theory Part 2. verview of HPLC Media Part 3. The Role of the Mobile Phase in Selectivity Part 4. Column Care and Use Reversed Phase Solvents 2 Solvents for RP Chromatography
Investigation of retention mechanisms in HILIC chromatography: Important considerations for robust method development
 Investigation of retention mechanisms in HILIC chromatography: Important considerations for robust method development Anders Fridström Sigma- Aldrich GMBH Abstract Investigation of Retention Mechanisms
Investigation of retention mechanisms in HILIC chromatography: Important considerations for robust method development Anders Fridström Sigma- Aldrich GMBH Abstract Investigation of Retention Mechanisms
Zirconia-Based Phases as a Powerful Complement to Silica-Based Phases for LC and LC-MS under Non-extreme Mobile Phase Conditions
 Zirconia-Based Phases as a Powerful Complement to Silica-Based Phases for LC and LC-MS under on-extreme Mobile Phase Conditions Richard A. Henry, Shawn R. Wyatt, Carmen T. Santasania and David S. Bell
Zirconia-Based Phases as a Powerful Complement to Silica-Based Phases for LC and LC-MS under on-extreme Mobile Phase Conditions Richard A. Henry, Shawn R. Wyatt, Carmen T. Santasania and David S. Bell
HPLC method development using alternative selectivities
 HPLC method development using alternative selectivities Frank Michel, Sigma-Aldrich Germany R. A. Henry, W. K. Way, C. T. Santasania, D. S. Bell Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, USA Three Factors Control HPLC and
HPLC method development using alternative selectivities Frank Michel, Sigma-Aldrich Germany R. A. Henry, W. K. Way, C. T. Santasania, D. S. Bell Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, USA Three Factors Control HPLC and
Method Development with Modern HPLC Phases
 Method Development with Modern HPLC Phases Frank Michel, Sigma-Aldrich Germany R. A. Henry, W. K. Way, C. T. Santasania, D. S. Bell Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, USA Three Factors Control HPLC and UHPLC Resolution
Method Development with Modern HPLC Phases Frank Michel, Sigma-Aldrich Germany R. A. Henry, W. K. Way, C. T. Santasania, D. S. Bell Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich, USA Three Factors Control HPLC and UHPLC Resolution
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS
 penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS penta-hilic Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS penta-hilic Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
Thermo Scientific Accucore XL HPLC Columns. Technical Manual
 Thermo Scientific Accucore XL HPLC Columns Technical Manual Thermo Scientific Accucore XL HPLC Columns Based on Core Enhanced Technology using µm solid core particles, Accucore XL HPLC columns allow users
Thermo Scientific Accucore XL HPLC Columns Technical Manual Thermo Scientific Accucore XL HPLC Columns Based on Core Enhanced Technology using µm solid core particles, Accucore XL HPLC columns allow users
Choosing Columns and Conditions for the Best Peak Shape
 Choosing Columns and Conditions for the Best Peak Shape What is Good Peak Shape and Why is it Important? Good peak shape can be defined as a symmetrical or gaussian peak and poor peak shape can include
Choosing Columns and Conditions for the Best Peak Shape What is Good Peak Shape and Why is it Important? Good peak shape can be defined as a symmetrical or gaussian peak and poor peak shape can include
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS
 penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand penta-hilic Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand penta-hilic Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
Product Bulletin. ACE LC/MS and Rapid Analysis HPLC Columns. HPLC Columns
 Product Bulletin HPLC Columns ACE LC/MS and Rapid Analysis HPLC Columns 0 mm, 30 mm, 35 mm and 50 mm column lengths.0,., 3.0, 4.0 and 4.6 mm column diameters Configured for High Sample Throughput Specially
Product Bulletin HPLC Columns ACE LC/MS and Rapid Analysis HPLC Columns 0 mm, 30 mm, 35 mm and 50 mm column lengths.0,., 3.0, 4.0 and 4.6 mm column diameters Configured for High Sample Throughput Specially
Packings for HPLC. Packings for HPLC
 Summary of packings for HPLC In analytical HPLC, packings with particle sizes of 3 to 10 µm are preferred. For preparative separation tasks, also particles with diameters larger than 10 µm are applied.
Summary of packings for HPLC In analytical HPLC, packings with particle sizes of 3 to 10 µm are preferred. For preparative separation tasks, also particles with diameters larger than 10 µm are applied.
Comparison of different aqueous mobile phase HPLC techniques
 June 009 ewsletter Pharmaceutical Analysis: What is Your Problem? SIELC Technologies, Inc., Prospect Heights, IL 0070 Pharmaceutical analysis involves liquid chromatography of various compounds, from active
June 009 ewsletter Pharmaceutical Analysis: What is Your Problem? SIELC Technologies, Inc., Prospect Heights, IL 0070 Pharmaceutical analysis involves liquid chromatography of various compounds, from active
Inertsil ODS-EP Technical Information
 Technical Information Advantages of The selectivity is completely different from those of conventional columns such as ODS column due to its specific polar group in the stationary phase. Durability can
Technical Information Advantages of The selectivity is completely different from those of conventional columns such as ODS column due to its specific polar group in the stationary phase. Durability can
William E. Barber, Ph.D. Applications Chemist October
 William E. Barber, Ph.D. Applications Chemist ctober 0 00 Secrets of Good Peak Shape in HPLC Time: :00 p.m. CET Telephone Number: + 44 0 76 088 Chairperson: John Vis The Secrets of Good Peak Shape in HPLC
William E. Barber, Ph.D. Applications Chemist ctober 0 00 Secrets of Good Peak Shape in HPLC Time: :00 p.m. CET Telephone Number: + 44 0 76 088 Chairperson: John Vis The Secrets of Good Peak Shape in HPLC
Application of Bio-SPME for the Enrichment of Illicit Phenethylamine and Cathinone Compounds from Biological Samples
 Application of Bio-SPME for the Enrichment of Illicit Phenethylamine and Cathinone Compounds from Biological Samples Craig R. Aurand 1, Robert Shirey 1, Leonard Sidisky 1 Janusz Pawliszyn 2, and Yong Chen
Application of Bio-SPME for the Enrichment of Illicit Phenethylamine and Cathinone Compounds from Biological Samples Craig R. Aurand 1, Robert Shirey 1, Leonard Sidisky 1 Janusz Pawliszyn 2, and Yong Chen
Method Development Kits
 Method Development Kits sales representative for ordering information or contact...77 Method Development Kits First column choice for Pharma Development USP L C Method Development Kits Maximize retention
Method Development Kits sales representative for ordering information or contact...77 Method Development Kits First column choice for Pharma Development USP L C Method Development Kits Maximize retention
for Acclaim Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column
 for Acclaim Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Page 1 of 17 Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column 5µm, 4.6 x 250mm, P/N 066844 5µm, 4.6 x 150mm, P/N
for Acclaim Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Page 1 of 17 Product Manual for ACCLAIM Mixed-Mode HILIC-1 Column 5µm, 4.6 x 250mm, P/N 066844 5µm, 4.6 x 150mm, P/N
P R O D U C T B U L L E T I N. Fused-Core particle technology for hyper-fast and super-rugged HPLC columns
 P R O D U C T B U L L E T I N Fused-Core particle technology for hyper-fast and super-rugged HPLC columns HALO column packings are not made the typical way. Instead, the particles packed into HALO columns
P R O D U C T B U L L E T I N Fused-Core particle technology for hyper-fast and super-rugged HPLC columns HALO column packings are not made the typical way. Instead, the particles packed into HALO columns
Shodex TM ODP2 HP series columns
 HPLC Columns Shodex TM ODP2 HP series columns Better retention of highly polar substances Technical notebook No. 6 Contents 1. Introduction 1-1. Specifications 1-2. Eluent Compatibility of ODP2 HP Series
HPLC Columns Shodex TM ODP2 HP series columns Better retention of highly polar substances Technical notebook No. 6 Contents 1. Introduction 1-1. Specifications 1-2. Eluent Compatibility of ODP2 HP Series
Small Molecule Selectivity Sampler
 Small Molecule Selectivity Sampler HALO 90 Å C18, AQ-C18, BIPHENYL Fused-Core Particle Technology Why Choose Fused-Core Particle Technology? Fused-Core Out-Performs Totally Porous Particles. HALO particles
Small Molecule Selectivity Sampler HALO 90 Å C18, AQ-C18, BIPHENYL Fused-Core Particle Technology Why Choose Fused-Core Particle Technology? Fused-Core Out-Performs Totally Porous Particles. HALO particles
LC and LC/MS Column Selection Flow Chart
 LC and LC/MS Column Selection Flow Chart To use the column selection diagram below, simply follow the path for your analyte and mobile phase. At the far right, follow your final column selection to the
LC and LC/MS Column Selection Flow Chart To use the column selection diagram below, simply follow the path for your analyte and mobile phase. At the far right, follow your final column selection to the
Uptisphere CS Evolution Core Shell columns for fast & highly efficient identification & quantification of small molecules
 Uptisphere CS Evolution Core Shell columns for fast & highly efficient identification & quantification of small molecules www.interchim.com www.blog.interchim.com www.forum.interchim.com www.facebook.com/interchim
Uptisphere CS Evolution Core Shell columns for fast & highly efficient identification & quantification of small molecules www.interchim.com www.blog.interchim.com www.forum.interchim.com www.facebook.com/interchim
Sunniest C18 Sunniest RP-AQUA Sunniest C8 Patent pending
 Patent pending Website : www.chromtech.net.au E-mail : info@chromtech.net.au telno : 0 97 0... in AUSTRALIA A Novel Bonding Technique (patent pending) An unique trifunctional silyl-reagent was developed
Patent pending Website : www.chromtech.net.au E-mail : info@chromtech.net.au telno : 0 97 0... in AUSTRALIA A Novel Bonding Technique (patent pending) An unique trifunctional silyl-reagent was developed
Alltech Alltima HP Introduction
 Alltech Introduction High-Stability, High-Purity, High-Performance, Low-Bleed Columns for Demanding Applications Better Peak Symmetry high-purity silica eliminates peak tailing problems Long Column Life
Alltech Introduction High-Stability, High-Purity, High-Performance, Low-Bleed Columns for Demanding Applications Better Peak Symmetry high-purity silica eliminates peak tailing problems Long Column Life
An HPLC column offering moderate retentivity with superb peak shape Inertsil ODS Sprint
 An HPLC column offering moderate retentivity with superb peak shape Inertsil ODS Sprint An important new column in the Inertsil series Bonded-Phase Structure Perfect balance of retention for both polar
An HPLC column offering moderate retentivity with superb peak shape Inertsil ODS Sprint An important new column in the Inertsil series Bonded-Phase Structure Perfect balance of retention for both polar
Mechanisms of retention in HPLC
 Mechanisms of retention in HPLC María Celia García-Álvarez-Coque Department of Analytical Chemistry University of Valencia Valencia, Spain https://sites.google.com/site/fuschrom/ 1 Part 3 Mechanisms of
Mechanisms of retention in HPLC María Celia García-Álvarez-Coque Department of Analytical Chemistry University of Valencia Valencia, Spain https://sites.google.com/site/fuschrom/ 1 Part 3 Mechanisms of
C18 Column. Care & Use Sheet
 C18 Column Care & Use Sheet HALO Description HALO C18 is a high-speed, high-performance liquid chromatography column based on a new Fused-CoreTM particle design. The Fused-Core particle provides a thin
C18 Column Care & Use Sheet HALO Description HALO C18 is a high-speed, high-performance liquid chromatography column based on a new Fused-CoreTM particle design. The Fused-Core particle provides a thin
Overview Applications of NUCLEODUR HPLC Phases
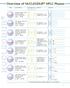 verview Applications of HPLC Phases Phase Specification Characteristics* Stability Structure A B C octadecyl phase, high density coating multi-endcapping 8% C USP L ph stability -, suitable for LC/MS (Si-
verview Applications of HPLC Phases Phase Specification Characteristics* Stability Structure A B C octadecyl phase, high density coating multi-endcapping 8% C USP L ph stability -, suitable for LC/MS (Si-
Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1
 Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1 Product Manual for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1 Column Page 1 of 28 PRODUCT MANUAL for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1 Columns 4.6 x 150 mm, P/N (068353) 4.6 x 250 mm, P/N (068352)
Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1 Product Manual for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1 Column Page 1 of 28 PRODUCT MANUAL for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1 Columns 4.6 x 150 mm, P/N (068353) 4.6 x 250 mm, P/N (068352)
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
ProntoSIL C18-EPS Reversed-Phase HPLC Columns
 ProntoSIL C8-EPS Reversed-Phase HPLC Columns Provides excellent separation of polar compounds Better peak shape for acids and bases Stabilized bonded phase for rugged, robust HPLC methods More retentive
ProntoSIL C8-EPS Reversed-Phase HPLC Columns Provides excellent separation of polar compounds Better peak shape for acids and bases Stabilized bonded phase for rugged, robust HPLC methods More retentive
New 5-micron HALO-5 columns based on Fused- Core particle technology boost the performance of HPLC. Compared to other HPLC columns, HALO-5 columns
 New 5-micron HALO-5 columns based on Fused- Core particle technology boost the performance of HPLC. Compared to other HPLC columns, HALO-5 columns have: the highest plate number versus any other 5-micron
New 5-micron HALO-5 columns based on Fused- Core particle technology boost the performance of HPLC. Compared to other HPLC columns, HALO-5 columns have: the highest plate number versus any other 5-micron
Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography: Some Aspects of Solvent and Column Selectivity
 Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography: Some Aspects of Solvent and Column Selectivity Monica Dolci, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Technical Note 20544 Key Words Hydrophilic, HILIC,
Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography: Some Aspects of Solvent and Column Selectivity Monica Dolci, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Technical Note 20544 Key Words Hydrophilic, HILIC,
Fast Separation of Vastly Different Compounds by Isocratic HPLC
 Fast Separation of Vastly Different Compounds by Isocratic HPLC Aimee N. Heyrman and Yury Zelechonok Resolution Systems, Inc. 590 E. 32nd St. Holland. MI, 49423 SIELC Technologies, 15 E. Palatine Rd, Suite
Fast Separation of Vastly Different Compounds by Isocratic HPLC Aimee N. Heyrman and Yury Zelechonok Resolution Systems, Inc. 590 E. 32nd St. Holland. MI, 49423 SIELC Technologies, 15 E. Palatine Rd, Suite
Barry E. Boyes, Ph.D. Consumables and Accessories Business Unit May 10, 2000
 Barry E. Boyes, Ph.D. Consumables and Accessories Business Unit May 0, 000 HPLC Column Troubleshooting What Every HPLC User Should Know :00 a.m. EST Telephone Number: 86-650-06 Chair Person: Tim Spaeder
Barry E. Boyes, Ph.D. Consumables and Accessories Business Unit May 0, 000 HPLC Column Troubleshooting What Every HPLC User Should Know :00 a.m. EST Telephone Number: 86-650-06 Chair Person: Tim Spaeder
The Theory of HPLC. Ion Pair Chromatography
 The Theory of HPLC Ion Pair Chromatography i Wherever you see this symbol, it is important to access the on-line course as there is interactive material that cannot be fully shown in this reference manual.
The Theory of HPLC Ion Pair Chromatography i Wherever you see this symbol, it is important to access the on-line course as there is interactive material that cannot be fully shown in this reference manual.
UPLC Method Development and Validation
 UPLC Method Development and Validation Rev. 2 2008 Waters Corporation Challenges of Method Development Methods are developed throughout the drug development process Samples vary in complexity Redundancy
UPLC Method Development and Validation Rev. 2 2008 Waters Corporation Challenges of Method Development Methods are developed throughout the drug development process Samples vary in complexity Redundancy
Next Generation of Phenyl Columns. Chromatography Products.
 Next Generation of Phenyl Columns Chromatography Products RESOLUTION EVOLUTION The Next Generation of Phenyl Column Chemistry The phase is the next generation of phenyl column chemistries, providing both
Next Generation of Phenyl Columns Chromatography Products RESOLUTION EVOLUTION The Next Generation of Phenyl Column Chemistry The phase is the next generation of phenyl column chemistries, providing both
LC Technical Information
 LC Technical Information Method Transfer to Accucore.6 μm Columns Containing solid core particles, which are engineered to a diameter of.6μm and a very narrow particle size distribution; Accucore HPLC
LC Technical Information Method Transfer to Accucore.6 μm Columns Containing solid core particles, which are engineered to a diameter of.6μm and a very narrow particle size distribution; Accucore HPLC
Zirconia: the Ideal Substrate for Ion-Exchange LC and LC-MS
 Zirconia: the Ideal Substrate for Ion-Exchange LC and LC-MS EAS 2005 Bingwen Yan 1, Clayton V. McNeff 1, Richard A. Henry 2, and David S. Bell 2 1 ZirChrom Separations, Inc., 617 Pierce Street, Anoka,
Zirconia: the Ideal Substrate for Ion-Exchange LC and LC-MS EAS 2005 Bingwen Yan 1, Clayton V. McNeff 1, Richard A. Henry 2, and David S. Bell 2 1 ZirChrom Separations, Inc., 617 Pierce Street, Anoka,
8. Methods in Developing Mobile Phase Condition for C18 Column
 I. HPLC Columns Technical Information 8. Methods in Developing Mobile Phase Condition for C18 Column Introduction In reversed phase HPLC, octadecyl group bonded silica columns (C18, ODS) are the most widely
I. HPLC Columns Technical Information 8. Methods in Developing Mobile Phase Condition for C18 Column Introduction In reversed phase HPLC, octadecyl group bonded silica columns (C18, ODS) are the most widely
Hillel K. Brandes and David S. Bell Supelco, Liquid Separations, Bellefonte PA T GIH
 Hillel K. Brandes and David S. Bell Supelco, Liquid Separations, Bellefonte PA 16823 T403163 GIH Abstract 2 ucleotides are ubiquitous in cells, with major functions including the control of cellular energetics,
Hillel K. Brandes and David S. Bell Supelco, Liquid Separations, Bellefonte PA 16823 T403163 GIH Abstract 2 ucleotides are ubiquitous in cells, with major functions including the control of cellular energetics,
ACE. For increased polar retention and alternative selectivity. Alternative selectivity for method development
 ACE C8-Amide For increased polar retention and alternative selectivity Alternative selectivity for method development Improved separations with polar, acidic, basic and phenolic compounds High efficiency
ACE C8-Amide For increased polar retention and alternative selectivity Alternative selectivity for method development Improved separations with polar, acidic, basic and phenolic compounds High efficiency
Epic Aromatic Selectivity
 Epic Aromatic Selectivity HPLC Columns p h a r m a c e u t i c a l e n v i r o n m e n t a l c h e m i c a l b i o c h e m i c a l s e p a r a t i o n & p u r i f i c a t i o n ES Industries 701 S. Route
Epic Aromatic Selectivity HPLC Columns p h a r m a c e u t i c a l e n v i r o n m e n t a l c h e m i c a l b i o c h e m i c a l s e p a r a t i o n & p u r i f i c a t i o n ES Industries 701 S. Route
for Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1
 for Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- Product Manual for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- Column Page of 8 Product Manual for Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- Columns Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-, 3µm, Analytical column, 3.0 x 50mm
for Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- Product Manual for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- Column Page of 8 Product Manual for Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- Columns Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-, 3µm, Analytical column, 3.0 x 50mm
Part 2. Overview of HPLC Media
 Part 1. General Chromatographic Theory Part 2. Overview of HPLC Media Part 3. The Role of the Mobile Phase in Selectivity Part 4. Column Care and Use 1 HPLC Particle Technology Core-Shell Particle Fully
Part 1. General Chromatographic Theory Part 2. Overview of HPLC Media Part 3. The Role of the Mobile Phase in Selectivity Part 4. Column Care and Use 1 HPLC Particle Technology Core-Shell Particle Fully
Impact of Instrument Dispersion on Performance of HPLC Capillary Columns
 Impact of Instrument Dispersion on Performance of HPLC Capillary Columns Wendy Roe, Richard A. Henry, and Hillel Brandes Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Bellefonte, PA 16823 USA T413131 sigma-aldrich.com/analytical
Impact of Instrument Dispersion on Performance of HPLC Capillary Columns Wendy Roe, Richard A. Henry, and Hillel Brandes Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Bellefonte, PA 16823 USA T413131 sigma-aldrich.com/analytical
Important Guidelines for Optimizing Speed and Sensitivity in Small-Molecule LC UV and LC MS
 Página 1 de 6 Important Guidelines for Optimizing Speed and Sensitivity in Small-Molecule LC UV and LC MS May 1, 2005 By: Richard A. Henry, David S. Bell LCGC North America The task of developing a new
Página 1 de 6 Important Guidelines for Optimizing Speed and Sensitivity in Small-Molecule LC UV and LC MS May 1, 2005 By: Richard A. Henry, David S. Bell LCGC North America The task of developing a new
( )( ) Selectivity Choices in Reversed-Phase Fast LC. Introduction. R s = 1 a 1 k 4 a 1 + k
 Selectivity Choices in Reversed-Phase Fast LC Luisa Pereira, Monica Dolci, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Technical Note 20543 Key Words Accucore, Hypersil GOLD, Syncronis, Column Chemistry,
Selectivity Choices in Reversed-Phase Fast LC Luisa Pereira, Monica Dolci, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Technical Note 20543 Key Words Accucore, Hypersil GOLD, Syncronis, Column Chemistry,
Fast Screening Methods for Steroids by HPLC with Agilent Poroshell 120 Columns
 Fast Screening Methods for Steroids by HPLC with Agilent Poroshell 2 Columns Application Note Pharma, BioPharma, and Clinical Research Author William Long Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction Steroids
Fast Screening Methods for Steroids by HPLC with Agilent Poroshell 2 Columns Application Note Pharma, BioPharma, and Clinical Research Author William Long Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction Steroids
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 High Performance Liquid Chromatography () Instrumentation Normal Phase Chromatography Normal Phase - a polar stationary phase with a less polar mobile phase.
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 28 High Performance Liquid Chromatography () Instrumentation Normal Phase Chromatography Normal Phase - a polar stationary phase with a less polar mobile phase.
Analysis - HPLC A.136. Primesep 5 µm columns B.136
 Primesep 5 µm columns Primesep columns feature double functionality of the bonding i.e : alkyl chain with anionic or cationic group, chelating group. This feature creates unique selectivities when using
Primesep 5 µm columns Primesep columns feature double functionality of the bonding i.e : alkyl chain with anionic or cationic group, chelating group. This feature creates unique selectivities when using
columns Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX-1 for Separating Basic Molecules
 columns Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- for Separating Basic Molecules The Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- is a novel, high-efficiency, silica-based column specially designed for separating various basic analytes. This
columns Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- for Separating Basic Molecules The Acclaim Mixed-Mode WCX- is a novel, high-efficiency, silica-based column specially designed for separating various basic analytes. This
Colin F. Poole Department of Chemistry Wayne State University USA
 Colin F. Poole Department of Chemistry Wayne State University USA Method Development Process Method Development Process Need to know what to do Before beginning experiments need to decide how to do it
Colin F. Poole Department of Chemistry Wayne State University USA Method Development Process Method Development Process Need to know what to do Before beginning experiments need to decide how to do it
The Secrets of Rapid HPLC Method Development. Choosing Columns for Rapid Method Development and Short Analysis Times
 The Secrets of Rapid HPLC Method Development Choosing Columns for Rapid Method Development and Short Analysis Times Rapid Analysis Is More Than Run Time It is developing a method to meet a goal and developing
The Secrets of Rapid HPLC Method Development Choosing Columns for Rapid Method Development and Short Analysis Times Rapid Analysis Is More Than Run Time It is developing a method to meet a goal and developing
Too Polar for Reversed Phase What Do You Do?
 Too Polar for Reversed Phase What Do You Do? June 20, 2013 Mark Powell Columns and Consumables Technical Support Page 1 C8 or C18 Doesn t Always Do the Job Typical reversed phase conditions involve water/buffer
Too Polar for Reversed Phase What Do You Do? June 20, 2013 Mark Powell Columns and Consumables Technical Support Page 1 C8 or C18 Doesn t Always Do the Job Typical reversed phase conditions involve water/buffer
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Chemistry SOLUTE ATTRIBUTES AND MOLECULAR INTERACTIONS CONTRIBUTING TO
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Chemistry SLUTE ATTRIBUTES AND MLECULAR INTERACTINS CNTRIBUTING T RETENTIN N A FLURINATED HIGH-PERFRMANCE LIQUID CHRMATGRAPHY STATINARY
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Chemistry SLUTE ATTRIBUTES AND MLECULAR INTERACTINS CNTRIBUTING T RETENTIN N A FLURINATED HIGH-PERFRMANCE LIQUID CHRMATGRAPHY STATINARY
How proteins separate on reverse-phase HPLC
 1 Reverse Phase How proteins separate on reverse-phase HPLC RP chromatography separates proteins through the interaction of the hydrophobic foot of the protein with a nonpolar surface of the particle RP
1 Reverse Phase How proteins separate on reverse-phase HPLC RP chromatography separates proteins through the interaction of the hydrophobic foot of the protein with a nonpolar surface of the particle RP
FluoroPhenyl. Stationary Phase: Get the Power of HILIC and RP Modes in One LC Column. Pure Chromatography. Selectivity Accelerated
 Get the Power of HILIC and RP Modes in One LC Column Selectivity Accelerated Stationary Phase: luorophenyl CH 3 Si CH 3 O Pure Chromatography www.restek.com/raptor The Raptor luorophenyl Column With Raptor
Get the Power of HILIC and RP Modes in One LC Column Selectivity Accelerated Stationary Phase: luorophenyl CH 3 Si CH 3 O Pure Chromatography www.restek.com/raptor The Raptor luorophenyl Column With Raptor
Yuhui Yang, An Trinh, Michael Ye, and Tom Henderson 595 North Harrison Road, Bellefonte, PA T HKB
 Use of An Improved Version of C8+SCX Mixed-Mode Solid Phase Extraction Material for Clean Extraction and Recovery of Basic, Zwitterionic, Neutral and Acidic Compounds from Biological Fluids Yuhui Yang,
Use of An Improved Version of C8+SCX Mixed-Mode Solid Phase Extraction Material for Clean Extraction and Recovery of Basic, Zwitterionic, Neutral and Acidic Compounds from Biological Fluids Yuhui Yang,
STUDY OF LOADABILITY AND SELECTIVITY OF PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOUNDS ON RPLC COLUMNS
 STUDY OF LOADABILITY AND SELECTIVITY OF PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOUNDS ON RPLC COLUMNS Fang Xia, Jie Y. Cavanaugh, Uwe Neue, Jeffrey R. Mazzeo, Diane M. Diehl Waters Corporation, Milford, MA USA OVERVIEW- INTRODUCTION-
STUDY OF LOADABILITY AND SELECTIVITY OF PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOUNDS ON RPLC COLUMNS Fang Xia, Jie Y. Cavanaugh, Uwe Neue, Jeffrey R. Mazzeo, Diane M. Diehl Waters Corporation, Milford, MA USA OVERVIEW- INTRODUCTION-
High Resolution Fast LC
 High Resolution Fast LC Easier Than You Think Rita Steed LC Columns Application Engineer May 9, 2013 What is High Resolution Fast LC? Maintain Resolution with Faster Run Time Increased Resolution with
High Resolution Fast LC Easier Than You Think Rita Steed LC Columns Application Engineer May 9, 2013 What is High Resolution Fast LC? Maintain Resolution with Faster Run Time Increased Resolution with
for Acclaim Trinity TM P1
 for Acclaim Trinity TM P Product Manual for Acclaim TRINITY P Columns Page of 4 Product Manual for Acclaim Trinity TM P Columns 07556 Acclaim Trinity P, 3µm, 4.6 x 00mm 07556 Acclaim Trinity P, 3µm, 4.6
for Acclaim Trinity TM P Product Manual for Acclaim TRINITY P Columns Page of 4 Product Manual for Acclaim Trinity TM P Columns 07556 Acclaim Trinity P, 3µm, 4.6 x 00mm 07556 Acclaim Trinity P, 3µm, 4.6
Fluophase and Fluofix Columns
 TG 0-0 Fluophase and Columns Introduction Fluorinated packings exhibit extra retention and selectivity for compounds that have fluorine and chlorine substituents. They also exhibit shape selectivity for
TG 0-0 Fluophase and Columns Introduction Fluorinated packings exhibit extra retention and selectivity for compounds that have fluorine and chlorine substituents. They also exhibit shape selectivity for
A Look at Agilent HPLC Columns Choices
 A Look at Agilent HPLC Columns Choices Brno & Prague, May 29-30 2018 Giorgio Ferlat IDO Product Specialist Chemistries and Consumable 1 Considerating Column Properties for Column Selection Silica Particle
A Look at Agilent HPLC Columns Choices Brno & Prague, May 29-30 2018 Giorgio Ferlat IDO Product Specialist Chemistries and Consumable 1 Considerating Column Properties for Column Selection Silica Particle
HPLC & LC-MS. Techniques to Improve Speed, Resolution and Sensitivity without Investing in Capital Equipment
 HPLC & LC-MS Techniques to Improve Speed, Resolution and Sensitivity without Investing in Capital Equipment 2010 Innovation Seminar Series Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Overview of Presentation Chromatographer
HPLC & LC-MS Techniques to Improve Speed, Resolution and Sensitivity without Investing in Capital Equipment 2010 Innovation Seminar Series Supelco, Div. of Sigma-Aldrich Overview of Presentation Chromatographer
Successfully Scaling and Transferring HPLC and UPLC Methods
 Successfully Scaling and Transferring HPLC and UPLC Methods Esa Lehtorinne Esa_Lehtorinne@waters.com Tel: +358-9-5659 6288 Fax: +358-9-5659 6282 Waters Finland Kutomotie 16 00380 Helsinki 2013 Waters Corporation
Successfully Scaling and Transferring HPLC and UPLC Methods Esa Lehtorinne Esa_Lehtorinne@waters.com Tel: +358-9-5659 6288 Fax: +358-9-5659 6282 Waters Finland Kutomotie 16 00380 Helsinki 2013 Waters Corporation
(HILIC) Bill Champion Agilent Technologies, Inc opt 3/opt3/opt 2 HILIC - Agilent Restricted
 Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) Bill Champion Agilent Technologies, Inc. 800-227-9770 opt 3/opt3/opt 2 william_champion@agilent.com Page 1 HILIC A method of recent attention Bill Champion
Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) Bill Champion Agilent Technologies, Inc. 800-227-9770 opt 3/opt3/opt 2 william_champion@agilent.com Page 1 HILIC A method of recent attention Bill Champion
FluoroPhenyl. Stationary Phase: Get the Power of HILIC and RP Modes in One LC Column. Pure Chromatography. Selectivity Accelerated
 Get the Power of HILIC and RP Modes in One LC Column Selectivity Accelerated Stationary Phase: luorophenyl CH 3 Si CH 3 O Pure Chromatography www.bgb-shop.com/raptor The Raptor luorophenyl Column With
Get the Power of HILIC and RP Modes in One LC Column Selectivity Accelerated Stationary Phase: luorophenyl CH 3 Si CH 3 O Pure Chromatography www.bgb-shop.com/raptor The Raptor luorophenyl Column With
It s hot! ZIC -chilic
 It s hot! ZIC -chilic Complementary selectivity for HPLC and LC-MS separation of polar hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany ZIC -chilic Your benefits
It s hot! ZIC -chilic Complementary selectivity for HPLC and LC-MS separation of polar hydrophilic compounds EMD Millipore Corp. is a subsidiary of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany ZIC -chilic Your benefits
Analysis of Tobacco Alkaloids
 Analysis of Tobacco Alkaloids UCT Part Number: EUBCX1HL2Z (200 mg benzenesulfonic acid high load, 10 ml) October 2012 Tobacco alkaloids are extracted with a strong cation exchange sorbent using an acidic
Analysis of Tobacco Alkaloids UCT Part Number: EUBCX1HL2Z (200 mg benzenesulfonic acid high load, 10 ml) October 2012 Tobacco alkaloids are extracted with a strong cation exchange sorbent using an acidic
HPLC column C18 C8 PFP. SunShell. Core Shell Particle
 HPLC column C8 C8 PFP SunShell Core Shell Particle ChromaNik Technologies Inc. SunShell is a core shell silica column made by ChromaNIk Technologies. The next generation to Core Shell particle Features
HPLC column C8 C8 PFP SunShell Core Shell Particle ChromaNik Technologies Inc. SunShell is a core shell silica column made by ChromaNIk Technologies. The next generation to Core Shell particle Features
HPLC Column Selection: Solve the Separation Mystery. The world leader in serving science
 HPLC Column Selection: Solve the Separation Mystery The world leader in serving science verview Introduction Historical verview in Stationary Phases Basics in Column Selection Resolution, Efficiency and
HPLC Column Selection: Solve the Separation Mystery The world leader in serving science verview Introduction Historical verview in Stationary Phases Basics in Column Selection Resolution, Efficiency and
Technical Guide Thermo Scientific Syncronis HPLC Columns
 Technical Guide Thermo Scientific Syncronis HPLC Columns Consistent, predictable separations, Column after column, time after time Thermo Scientific Syncronis Columns When developing a new method, one
Technical Guide Thermo Scientific Syncronis HPLC Columns Consistent, predictable separations, Column after column, time after time Thermo Scientific Syncronis Columns When developing a new method, one
Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX-1 Columns
 User Manual Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX- Columns 06565 Revision 03 October 05 Product Manual for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX- Column Page of 3 Product Manual for Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX- Columns 5µm, 0 x 50 mm,
User Manual Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX- Columns 06565 Revision 03 October 05 Product Manual for the Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX- Column Page of 3 Product Manual for Acclaim Mixed-Mode WAX- Columns 5µm, 0 x 50 mm,
HICHROM. Chromatography Columns and Supplies. LC COLUMNS SIELC Primesep. Catalogue 9. Hichrom Limited
 HICHROM Chromatography Columns and Supplies LC COLUMNS SIELC Primesep Catalogue 9 The Markham Centre, Station Road Theale, Reading, Berks, RG7 4PE, UK Tel: +44 (0)8 90 660 Fax: +44 (0)8 9 484 Email: sales@hichrom.co.uk
HICHROM Chromatography Columns and Supplies LC COLUMNS SIELC Primesep Catalogue 9 The Markham Centre, Station Road Theale, Reading, Berks, RG7 4PE, UK Tel: +44 (0)8 90 660 Fax: +44 (0)8 9 484 Email: sales@hichrom.co.uk
Chromatography. Gas Chromatography
 Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Tips and tricks to increase HPLC column lifetime. Dr. Frank Michel
 Tips and tricks to increase HPLC column lifetime Dr. Frank Michel Overview How to influence HPLC column life time? HPLC method Helpful accessories Best practice 2 HPLC Method Mobile Phase Mobile phase
Tips and tricks to increase HPLC column lifetime Dr. Frank Michel Overview How to influence HPLC column life time? HPLC method Helpful accessories Best practice 2 HPLC Method Mobile Phase Mobile phase
Hypersil BDS Columns TG 01-05
 TG 0-0 Hypersil BDS Columns Introduction Hypersil BDS columns have gained a reputation over the years as one of the most robust, reproducible and reliable HPLC column brands available. This Technical Guide
TG 0-0 Hypersil BDS Columns Introduction Hypersil BDS columns have gained a reputation over the years as one of the most robust, reproducible and reliable HPLC column brands available. This Technical Guide
Method Development in Solid Phase Extraction using Non-Polar ISOLUTE SPE Columns for the Extraction of Aqueous Samples
 Technical Note 101 Method Development in Solid Phase Extraction using Non-Polar ISOLUTE SPE Columns for the Extraction of Aqueous Samples This technical note includes by specific information on the extraction
Technical Note 101 Method Development in Solid Phase Extraction using Non-Polar ISOLUTE SPE Columns for the Extraction of Aqueous Samples This technical note includes by specific information on the extraction
Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography
 Application Note Inorganic Ions, Water Testing, Minerals, Metals, Basic Chemicals Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Authors Anne Mack, Adam Bivens
Application Note Inorganic Ions, Water Testing, Minerals, Metals, Basic Chemicals Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Authors Anne Mack, Adam Bivens
Reversed Phase Chromatography: Mobile phase Considerations
 Reversed Phase: Mobile Phase Considerations Dr. www.forumsci.co.il/hplc Example of a Reversed Phase Method with UV Detection 1 Chromatographic Process B+A Mobile phase Elution through the Column-movie
Reversed Phase: Mobile Phase Considerations Dr. www.forumsci.co.il/hplc Example of a Reversed Phase Method with UV Detection 1 Chromatographic Process B+A Mobile phase Elution through the Column-movie
Optimisil HPLC & UPLC Column catalogue
 Optimisil HPLC & UPLC Column catalogue Analytical Hub Plot No: 37, P & T Colony, Vikrampuri, Secunderabad 500009 Tel: 040-64621313, Mobile: +91 7799931313 Website: www.analyticalhub.com email: contact@analyticalhub.com
Optimisil HPLC & UPLC Column catalogue Analytical Hub Plot No: 37, P & T Colony, Vikrampuri, Secunderabad 500009 Tel: 040-64621313, Mobile: +91 7799931313 Website: www.analyticalhub.com email: contact@analyticalhub.com
QUALITY HPLC COLUMNS PARTICLE PORE PAGE SIZE SIZE. C18 Bidentate C18 Extremely long column life and rugged 4um 100Å 3
 Cogent HPLC Columns Manufactured by Table of Contents QUALITY HPLC COLUMNS PARTICLE PORE PAGE SIZE SIZE C18 Bidentate C18 Extremely long column life and rugged 4um 100Å 3 C8 Bidentate C8 Extremely long
Cogent HPLC Columns Manufactured by Table of Contents QUALITY HPLC COLUMNS PARTICLE PORE PAGE SIZE SIZE C18 Bidentate C18 Extremely long column life and rugged 4um 100Å 3 C8 Bidentate C8 Extremely long
Chromatographic Analysis
 Chromatographic Analysis Distribution of Analytes between Phases An analyte is in equilibrium between the two phases [S 1 ] [S 2 ] (in phase 1) (in phase 2) AS [S2 ] K 2 A S [S1 ] 1 AS, A 1 S Activity
Chromatographic Analysis Distribution of Analytes between Phases An analyte is in equilibrium between the two phases [S 1 ] [S 2 ] (in phase 1) (in phase 2) AS [S2 ] K 2 A S [S1 ] 1 AS, A 1 S Activity
An Introduction to Liquid Chromatography
 An Introduction to Liquid Chromatography Brian A. Rappold Scientific Director Essential Testing (Collinsville, IL) Financial Disclosures: Grant/Research Support: None Salary/Consultant Fees: Essential
An Introduction to Liquid Chromatography Brian A. Rappold Scientific Director Essential Testing (Collinsville, IL) Financial Disclosures: Grant/Research Support: None Salary/Consultant Fees: Essential
Our Expanding Understanding and Use of Reversed-Phase Column Selectivity
 L-1904 ur Expanding Understanding and Use of Reversed-Phase Column Selectivity John W. Dolan Lloyd R. Snyder LC Resources, Inc. 1 for additional information, contact John Dolan: John.Dolan @LCResources.com
L-1904 ur Expanding Understanding and Use of Reversed-Phase Column Selectivity John W. Dolan Lloyd R. Snyder LC Resources, Inc. 1 for additional information, contact John Dolan: John.Dolan @LCResources.com
Thermo Scientific Syncronis HPLC Columns. Remarkable separations guaranteed time after time
 Thermo Scientific Syncronis HPLC Columns Remarkable separations guaranteed time after time Syncronis HPLC and UHPLC Columns Remarkable separations guaranteed time after time When developing a new method,
Thermo Scientific Syncronis HPLC Columns Remarkable separations guaranteed time after time Syncronis HPLC and UHPLC Columns Remarkable separations guaranteed time after time When developing a new method,
Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS
 Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS 1. List two advantages of temperature programming in GC. a) Allows separation of solutes with widely varying retention factors in a reasonable
Chem 230, Fall, 2014 Homework Set # 3 Short Answer SOLUTIONS 1. List two advantages of temperature programming in GC. a) Allows separation of solutes with widely varying retention factors in a reasonable
Improve Peak Shape and Productivity in HPLC Analysis of Pharmaceutical Compounds with Eclipse Plus C8 Columns Application
 Improve Peak Shape and Productivity in HPLC Analysis of Pharmaceutical Compounds with Eclipse Plus C8 Columns Application Pharmaceuticals Authors John W. Henderson Jr., Nona Martone, and Cliff Woodward
Improve Peak Shape and Productivity in HPLC Analysis of Pharmaceutical Compounds with Eclipse Plus C8 Columns Application Pharmaceuticals Authors John W. Henderson Jr., Nona Martone, and Cliff Woodward
Silanol. Groups Liquid Chromatography
 Abstract umber: 0-8P Study of Secondary Interaction Based on Residual lanol Groups for Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography II orikazu agae Ph.D, Kouji Yamamoto, Chiaki Kadota Chromaik Technologies Inc.
Abstract umber: 0-8P Study of Secondary Interaction Based on Residual lanol Groups for Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography II orikazu agae Ph.D, Kouji Yamamoto, Chiaki Kadota Chromaik Technologies Inc.
Hints for Strong Ion Exchange Resins
 Hints for Strong Ion Exchange Resins Chromatography Application Note AN98 Abstract Ion exchange columns are a powerful means of isolating and purifying compounds, but their use is limited due to lack of
Hints for Strong Ion Exchange Resins Chromatography Application Note AN98 Abstract Ion exchange columns are a powerful means of isolating and purifying compounds, but their use is limited due to lack of
Multi-mode Separations Using Zirconiabased Stationary Phases
 Multi-mode Separations Using Zirconiabased Stationary Phases PITTC 2010 Dan owlan 1, Bingwen Yan 1, Clayton V. Mceff 1, R.A. Henry 2 1 ZirChrom Separations, Inc. 617 Pierce St., Anoka, M 55303 2 Independent
Multi-mode Separations Using Zirconiabased Stationary Phases PITTC 2010 Dan owlan 1, Bingwen Yan 1, Clayton V. Mceff 1, R.A. Henry 2 1 ZirChrom Separations, Inc. 617 Pierce St., Anoka, M 55303 2 Independent
Leveraging Bonded Phase Selectivity. to Achieve Better Reversed Phase HPLC Separations
 Leveraging Bonded Phase Selectivity to Achieve Better Reversed Phase HPLC Separations Introduction There has been a great deal of emphasis in the past several years on column efficiency (theoretical plates,
Leveraging Bonded Phase Selectivity to Achieve Better Reversed Phase HPLC Separations Introduction There has been a great deal of emphasis in the past several years on column efficiency (theoretical plates,
HICHROM. Chromatography Columns and Supplies. LC COLUMNS HALO and HALO-5. Catalogue 9. Hichrom Limited
 HICHROM Chromatography Columns and Supplies LC COLUMNS HALO and HALO- Catalogue 9 The Markham Centre, Station Road Theale, Reading, Berks, RG PE, UK Tel: + (0)8 90 0 Fax: + (0)8 9 8 Email: sales@hichrom.co.uk
HICHROM Chromatography Columns and Supplies LC COLUMNS HALO and HALO- Catalogue 9 The Markham Centre, Station Road Theale, Reading, Berks, RG PE, UK Tel: + (0)8 90 0 Fax: + (0)8 9 8 Email: sales@hichrom.co.uk
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
Put the. C18 aside. and take a look... Reasons. to try the. NEW Gemini C6-Phenyl
 Put the C18 aside and take a look... 6 Reasons to try the EW Gemini Reason #6 ALTERATE SELECTIVITY to your C18 Column Adding to your method development options, Gemini offers additional polar and aromatic
Put the C18 aside and take a look... 6 Reasons to try the EW Gemini Reason #6 ALTERATE SELECTIVITY to your C18 Column Adding to your method development options, Gemini offers additional polar and aromatic
