Rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether over Al-MCM-41
|
|
|
- Augustus Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) Rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether over Al-MCM-41 Nevin T. Mathew, S. Khaire, S. Mayadevi, R. Jha, S. Sivasanker National Chemical Laboratory, Pune , India Received 13 July 2004; revised 29 September 2004; accepted 30 September 2004 Available online 24 November 2004 Abstract Claisen rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether to o-allylphenol and a dihydrobenzofuran derivative was investigated over MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios. Higher aluminum content, higher reaction temperatures, and longer run duration favor the formation of the ring compound 2,3-dihydro-2-methyl benzofuran. There is a close relationship between acidity and conversion, which suggests that the reaction occurs inside the large pores of MCM-41. The influence of temperature and catalyst Si/Al ratio on the reaction are examined by kinetic analysis, under the assumption of a first-order consecutive reaction Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Keywords: Claisen rearrangement; Allyl phenyl ether; Al-MCM-41; Molecular rearrangement; Solid acids; Mesoporous material 1. Introduction Claisen rearrangement involves the conversion of allyl phenyl ethers (APEs) to the corresponding o-allylphenols and is generally performed by heating the ethers at an elevated temperature (> 473 K), but has been reported to be susceptible to catalysis by Lewis and Brønsted acids [1,2]. Reports of the use of solid acids in the above rearrangement are rather scarce. Pitchumani et al. have observed shape selectivity in ZSM-5 and ZSM-11 during their study of photo-assisted Claisen rearrangement [3]. Sheldon et al. have investigated the use of H-FAU and H-MOR in the rearrangement of APE in benzene medium [4,5]. Other solid catalysts that have been investigated are mesoporous silica [6] and bentonite [7]. We have already reported our studies on the use of large-pore zeolites, especially beta, as catalysts for the rearrangement [8]. As we did not find any meaningful relationship between acidity and catalytic activity in these zeolites, we suggested that even over large-pore zeolites, the rearrangement occurs primarily at the external surface or at the pore mouth [8]. * Corresponding author. Fax: address: siva@cata.ncl.res.in (S. Sivasanker). Mesoporous molecular sieves of the MCM-41 type have received much attention because of their large surface area and the uniform size and shape of the pores over micrometerlength scales [9,10]. High thermal stability and the advantage of tuning the pore size make these materials interesting for use as supports and catalysts for various heterogeneously catalyzed reactions. In the present study, we have explored the use of Al-MCM-41 with large pores ( 30-Å diameter) as a catalyst in the Claisen rearrangement of APE. The effect of reaction parameters and catalyst Al content on conversion and product selectivity has been studied. A kinetic analysis of the formation of the different products under various reaction conditions is also presented. 2. Experimental Tetraethyl orthosilicate (Aldrich), aluminum sulfate (s.d. fine chemicals Ltd.), cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTMABr) (Loba Chemie), and tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAOH) (Aldrich) were used in the synthesis of the samples. Si-MCM-41 was prepared hydrothermally in alkaline medium with the use of a gel with the molar composition 1 SiO 2 :0.33 TMAOH:0.55 CTMABr:60 H 2 O /$ see front matter 2004 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. doi: /j.jcat
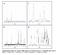
2 106 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) Al-MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios was prepared by the addition of aluminum sulfate to the Si-MCM-41 gel to get the molar composition 1 SiO 2 :0.33 TMAOH:0.55 CTMABr:60 H 2 O:x Al 2 O 3. Al-MCM-41 with Si/Al ratios of 20, 30, 50, and 100 was prepared by the variation of x in the gel composition from to moles. In all cases, the gel was aged at room temperature for 5 h with stirring and heated in an autoclave at 383 K for 5 days under autogenous pressure. The solid product was filtered, washed, dried, and calcined at 823 K for 8 h to get the final product. The product was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Rigaku D/MINI-Flex X-ray diffractometer, 40 kv, 20 ma, Ni filtered Cu-K α ), scanning electron microscopy (JEOL JSM 5200), nuclear magnetic resonance (Brucker MSL-300), and N 2 adsorption. The samples were characterized for their acidity by the temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) of NH 3 (Micromeritics, Autochem Z910). The standard procedure for TPD measurements involved the activation of the sample in flowing He at 873 K (3 h), cooling to 298 K, and adsorbing NH 3 from a stream of He NH 3 (10%), removing the physically adsorbed NH 3 by desorbing in He at 373 K for 1 h, and finally carrying out the TPD experiment by raising the temperature of the catalyst in a programmed manner (10 K min 1 ). The TPD curves were deconvoluted into two peaks, and the areas under the peaks were converted into meq NH 3 per gram of catalyst based on injection of known volumes of the He NH 3 mixture under similar conditions. All of the samples were calcined at 823 K for 8 h prior to use in catalytic experiments. APE (purity 99%) required for the reaction was synthesized by the reaction of allyl bromide and phenol in ethanol and purified by standard methods. The reactions were carried out in batch mode in a two-necked round-bottomed flask (capacity 25 ml) in a nitrogen atmosphere, with the use of 0.67 g of APE in 10 g of solvent (tetrachloroethylene, Loba Chemie) with g of freshly calcined catalyst. Aliquots of the reaction mixture were collected at different time intervals and analyzed by gas chromatography (Varian gas chromatograph; column: CP Sil 5CB, 30 m; i.d mm; FID detector). The products were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) and gas chromatography-infrared spectroscopy (GC-IR). 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Physicochemical characterization X-ray diffraction The XRD patterns of calcined Si- and Al-MCM-41 are shown in Fig. 1. The physicochemical properties of MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios are presented in Table 1. The XRD patterns are similar to those reported for MCM-41 materials [9] and show low angle (110) and (200) peaks for all of the samples, which is characteristic of longrange order of crystallinity of the materials. Kresge et al. [9] indexed these peaks for a hexagonal unit cell, the parameter for which was calculated with the equation a 0 = 2d 100 / 3(Table 1). The table shows that the d 100 reflection of Al-MCM-41 is shifted to higher values compared with its siliceous analogue. This is probably due to the framework substitution of Al in the MCM-41 structure [11]. The change in the T O T bond angle with Al substitution probably causes long-range disorder in the system and explains the slightly broader XRD peaks in Al-containing samples (Fig. 1) Nuclear magnetic resonance The 27 Al magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS NMR) spectrum of calcined Al-MCM-41 with Fig. 1. XRD patterns of calcined Si-MCM-41 and Al-MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios. Table 1 Physicochemical properties of Al-MCM-41 samples Sample Si/Al ratio (XRF) d 100 spacing a (Å) Unit cell a 0 parameter a (Å) Surface area b (m 2 /g) Pore diameter b (Å) Si-MCM Al-MCM-41 (100) Al-MCM-41 (50) Al-MCM-41 (30) Al-MCM-41 (20) a As-synthesized sample. b Calcined sample.
3 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) asi/al ratio of 20 is presented in Fig. 2. It reveals two peaks. The major peak, with a chemical shift of ppm, is assigned to tetrahedrally coordinated Al presumably present in the Al-MCM-41 framework. The small peak at 0 ppm is due to octahedrally coordinated (nonframework) Al present in the material [12]. The spectrum shows that most of the Al in Al-MCM-41 is tetrahedrally coordinated, even at a high Al content (Si/Al = 20), and only a small amount of nonframework Al is present in the material Transmission electron microscopy TEM images of calcined Al-MCM-41 (Si/Al = 50) and Si-MCM-41 revealed characteristic regular hexagonal arrays of uniform channels for both Al-MCM-41 (Si/Al = 50) and Si-MCM-41. The periodicity of the structure was also confirmed by the electron diffraction pattern. Fig Al MAS-NMR spectrum of calcined Al-MCM-41 (Si/Al = 20) Nitrogen sorption The N 2 adsorption desorption isotherms of MCM-41 and Al-MCM-41 were typical for type IV, with a hysteresis loop characteristic of mesoporous materials (Fig. 3). The isotherms exhibit three stages. The first stage is due to monolayer adsorption of nitrogen to the walls of the meso- Fig. 3. Nitrogen adsorption isotherms and corresponding pore size distribution of calcined Al-MCM-41 with Si/Al ratios at 20 and 100.
4 108 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) pores at a low relative pressure (p/p 0 < 0.2). The second stage is characterized by a steep increase in adsorption (p/p 0 > 0.2). As the relative pressure increases, the isotherm exhibits a sharp inflection characteristic of capillary condensation within the uniform mesopores. The p/p 0 at the inflection is related to the diameter of the mesopore [13], and the steepness of this step indicates the uniformity of pore size distribution. The third stage in the adsorption isotherm is the gradual increase in volume with p/p 0 due to multilayer adsorption on the outer surface of the particles. The surface area and average pore diameters of MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios are given in Table 1. The table shows that the pore diameter increases with increasing Al content. The surface area decreases in general with increasing Al content in MCM-41, except in the case of the sample with Si/Al = 100, which shows a higher S BET value. The reason for the anomalous behavior of the sample could be the poor crystallinity of the sample (XRD; Fig. 1). The pore size distribution of calcined MCM-41 with Si/Al = 20 and 100 is also presented in Fig. 3. Thefigure shows that the materials possess pores of nearly uniform size with a narrow distribution. However, the distribution becomes broader as the Al content increases, because of the greater disorder caused by Al incorporation Temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia The TPD profiles of Al-MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios are presented in Fig. 4. The number and density of acid sites are expected to increase with the Al content [14]. Fig. 4 shows that the total acidity of MCM-41 increases with the Al content. The amounts of strong and weak acid sites in Al-MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios, estimated from the deconvoluted TPD profiles, are given in Table 2.Thetable shows that the total number of acid sites (the strong and the weak acid sites) increases with Al content. The ratio of strong acid sites to weak acid sites also increases with Al content. Strong acid sites (Brønsted) are generated by tetrahedrally coordinated Al atoms forming Al O(H) Si bridges. The increase in the ratio of strong to weak acid sites with Al content implies that most of the added Al is tetrahedrally coordinated in the framework. Assuming that the strong acid sites are directly related to the Al ions in the samples, the ratio NH 3 /Al (mole NH 3 desorbed per mole Al) was calculated (Table 2). The results indicate an increase in the ratio with decreasing Al content, suggesting an increasing dispersion of Al at higher Si/Al ratios Reaction studies Claisen rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether The catalytic activity of the calcined MCM-41 samples with different Si/Al ratios was compared for the Claisen rearrangement of APE. The reaction scheme is shown in Fig. 5. The ether first undergoes rearrangement to produce Fig. 4. (a) Temperature programmed desorption of ammonia from Al-MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios. (b) Typical deconvoluted plot for sample with Si/Al= 20. Table 2 Acidity of Al-MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios by TPDA Sample Weak acidity (mmol/g) Strong acidity (mmol/g) Total acidity (mmol/g) Al-MCM-41 (20) NH 3 /Al a (mmol/g) Al-MCM-41 (30) Al-MCM-41 (50) Al-MCM-41 (100) a Moles of NH 3 desorbed/mol of Al in the sample; based on NH 3 from strong acid sites. o-allylphenol (o-ap), which cyclizes to give 2,3-dihydro-2- methyl benzofuran (benzofuran) Influence of duration of run The effect of run duration (up to 12 h) on conversion and on o-ap and benzofuran selectivities over the catalysts (with different Si/Al
5 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) Fig. 5. Reaction scheme of Claisen rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether: I, allyl phenyl ether; II o-allylphenol; and III, 2,3-dihydro-2-methylbenzofuran Influence of temperature The influence of temperature on APE conversion and the o-ap and benzofuran selectivities for the samples with different Si/Al ratios are presented in Fig. 7. Conversion and ring formation increase with temperature for all Si/Al ratios, though the effect is less noticed for the most siliceous sample (Si/Al 100). o-ap selectivity increases with increasing Si/Al ratio and decreasing temperature; the influence of temperature is less at higher Si/Al ratios. Fig. 6. Influence of Si/Al ratio and duration of run on the conversion and selectivity (reaction temperature, 393 K; F, Si/Al 20; 1, Si/Al 30; Q, Si/Al 50; P,Si/Al 100). ratios) at 393 K are shown in Fig. 6. In general, the conversion and benzofuran formation increase with duration of run, whereas o-ap decreases. The activity increases with increasing Al content; the sample with the largest Si/Al ratio ( 100) is the least active Influence of Si/Al ratio Both conversion and selectivity in the Claisen rearrangement are found to be dependent on the Si/Al ratio of MCM-41. Purely siliceous (Al-free) MCM-41 exhibited negligible conversion. Fig. 8 shows the influence of the Si/Al ratio on the reaction at different temperatures. The APE conversion decreases with decreasing aluminum content (increase in the Si/Al ratio) of the catalyst. The figure shows that a maximum conversion of up to 86.7% can be obtained with Al-MCM-41 with asi/al ratio of 20 at 393 K at the end of a 12-h reaction. The selectivity for o-ap increases and that for benzofuran decreases with an increasing Si/Al ratio in Al-MCM-41. As the reaction is catalyzed by the acid sites of Al-MCM-41, the observed behavior must be due to the decrease in the acidity of Al-MCM-41 with increasing Si/Al ratio (Table 2). A plot of APE conversion and acidity (strong and weak) versus Al content is shown in Fig. 9a. It is found that both acidity and conversion increase with Al content. The close relationship between acidity and conversion suggests that the reaction occurs inside the pores of MCM-41. In the case of zeolites, however, the reaction was assumed to occur mainly on the external surface or at the pore mouth, as no relation between acidity (or Al content) and conversion was noticed [8]. The turnover frequency (TOF, mole of APE converted or product formed per hour per mole of Al present in the sample) is found to decrease with increasing Al content (for the samples with Si/Al 20, 30, and 50) (Fig. 9b). The data for the sample with Si/Al 100 do not fall in the above trend because of an unexpectedly small TOF, suggesting the nonaccessibility of the acid sites to the reactant molecules at low Al contents. On the other hand, a small increase in the TOF is noticed with increasing Al content for benzofuran formation. When the TOF (conversion of APE or formation of o-ap) is calculated based on the total number of acid sites (moles of NH 3 desorbed) in the three samples (Si/Al 20, 30, and 50), a nearly constant value (TOF = 8 ± 1mol/(mol NH3 h)) is obtained, revealing a direct relationship between acidity and activity in these samples.
6 110 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) Fig. 7. Influence of temperature on conversion and selectivity over Al-MCM-41 with different Si/Al ratios. Fig. 8. Influence of Si/Al ratio on conversion and selectivity at different temperatures (reaction time, 12 h; F, 373 K; 1, 383 K; Q, 393 K).
7 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) (a) (b) Fig. 9. Influence of Al-content on (a) APE conversion and catalyst acidity and (b) on TOF (reaction temperature, 393 K; time, 12 h) Mechanism of the reactions A plausible mechanism for production by the Claisen rearrangement of the allyl phenol and its subsequent conversion to the ring compound is presented in Figs. 10a and b. The steps are catalyzed by acid centers. First the acid site protonates the oxygen of the ether. This is followed by intramolecular rearrangement of the protonated (adsorbed) species into the o-allylphenol as shown in Fig. 10a. The allyl phenol is next protonated at the allylic double bond to produce the secondary carbenium ion that reacts again intramolecularly with the phenolic oxygen to produce the benzofuran (Fig. 10b) Kinetic analysis The scheme presented in Fig. 5 shows that the reaction involves two consecutive steps for the formation of benzofuran. Hence this was treated as a first-order series reaction with o-ap as the intermediate product, and the standard equations for a first-order series reaction were used for the determination of rate constants. These are C A /C A0 = e k 1t and C R /C A0 = k 1 (e k 1t e k 2t )/(k 2 k 1 ). (1) (2) Fig. 10. Plausible mechanism of Claisen rearrangement of APE over solid acids (Al-MCM-41), for the formation: (a) of o-ap and (b) of ring product. In the above equations, C A0 and C A are the concentrations of APE at initial time and at time t, respectively; C R is the concentration of the intermediate product o-ap at time t; and k 1 and k 2 are the rate constants for the first and second steps, respectively. The concentration profiles of APE, o-ap, and benzofuran for two temperatures (383 and 393 K) and Si/Al ratios (Si/Al = 20 and 30) in the Claisen rearrangement of APE are presented in Fig. 11. The lines represent the theoretical profiles. The profiles are those expected for typical first-order consecutive reactions. The nature of the profile, especially that for o-ap, depends on the relative values of k 1 and k 2. The rate equations and the time t max,atwhich the intermediate o-ap concentration is maximum, are presented in Table 3. It can be seen from the table that t max
8 112 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) Fig. 11. Parity plots for the Claisen rearrangement of allyl phenyl ether at two different Si/Al ratios and temperatures. Experimental values are presented by symbols; bold lines represent profiles based on generated equations. varies with both the reaction temperature and the Si/Al ratio of MCM-41. For a given catalyst, t max decreases with increasing temperature and Al content. The influence of temperature and Si/Al ratio (20 and 30) on the reaction rate constants, k 1 and k 2,ispresentedin Fig. 12. The figure shows that both k 1 and k 2 increase with increasing temperature. It is found that k 2 is not much affected by variation in the Si/Al ratio, whereas k 1 is sensitive. The reasons for this are not clear. The activation energy for the two steps was calculated with the Arrhenius expression. The activation energy for the reaction of APE on Al-MCM-41 with a Si/Al ratio of 20 is estimated to be 8.9 kcal/mol. The activation energy for the formation of benzofuran from o-ap is estimated to be 10.3 kcal/mol. The activation energy of the reactions was not found to be significantly affected by a change in the Si/Al ratio. Fig. 12. Influence of temperature and Si/Al ratio on the reaction rate constants. 4. Conclusions The Claisen rearrangement of APE over Al-MCM-41 proceeds with ease in tetrachloroethane. o-allyl phenol is produced initially, which then undergoes cyclization to form 2,3-dihydro-2-methylbenzofuran. The reaction takes place on the acid sites of the catalyst. Both the catalyst acidity and substrate conversion increase with the Al content in MCM- 41. There is a close relationship between acidity and conversion, which suggests that the reaction occurs inside the pores of MCM-41. The conversion and benzofuran formation increase with run duration, whereas the o-ap decreases, as expected for a consecutive reaction. The temperature effects on conversion and selectivity are more pronounced at low Si/Al ratios than at high Si/Al ratios. o-ap selectivity increases with increasing Si/Al ratio and decreasingtemperature. The reaction kinetics was analyzed under the assumption that it is Table 3 Results of kinetic analysis for Al-MCM-41 catalysts with Si/Al = 20 and 30 Si/Al T a Rate constants Rate expressions t max c (K) k 1 (1/h) k 2 (1/h) Eq. (1) b Eq. (2) b (h) C A /C A0 = e 0.13t C R /C A0 = 0.13(e 0.13t e 0.14t )/ C A /C A0 = e 0.16t C R /C A0 = 0.16(e 0.16t e 0.18t )/ C A /C A0 = e 0.07t C R /C A0 = 0.07(e 0.07t e 0.14t )/ C A /C A0 = e 0.10t C R /C A0 = 0.10(e 0.10t e 0.21t )/ a Reaction temperature. b See text, kinetic analysis. c The time at which the concentration of o-ap reaches a maximum value.
9 N.T. Mathew et al. / Journal of Catalysis 229 (2005) a first-order consecutive reaction. On Al-MCM-41, both k 1 and k 2 increase with increasing temperature. k 2 is not much affected by variation in the Si/Al ratio, whereas k 1 is sensitive. The time at which the intermediate o-ap concentration is maximum, t max, varies with both the reaction temperature and the Si/Al ratio of MCM-41. For a given catalyst, t max decreases with increasing temperature and Al content. References [1] J. March, Advanced Organic Chemistry, fourth ed., Wiley, New York, [2] R.P. Lutz, Chem. Rev. 84 (1984) 205. [3] K. Pitchumani, M. Warrier, V. Ramamurthy, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (1996) [4] J.A. Elings, R.S. Downing, R.A. Sheldon, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 94 (1995) 487. [5] R.A. Sheldon, J.A. Elings, S.K. Lee, H.E.B. Lempers, R.S. Downing, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 134 (1998) 129. [6] I. Sucholeiki, M.R. Pavia, C.T. Kresge, S.B. Mc Cullen, A. Malek, S. Schram, Mol. Divers. 3 (1998) 151, CA: 129: (1999). [7] R. Cruz-Almanza, F. Perez-Flores, L. Brena, E. Tapia, R. Ojeda, A.J. Fuentes, Heterocycl. Chem. 32 (1995) 219. [8] S.G. Wagholikar, S. Mayadevi, S.P. Mirajkar, S. Sivasanker, in: E. van Steen, L. Callanan, M. Claeys, C.T. O Connor (Eds.), Proceedings of 14th International Zeolite Conference, Cape Town, 2004, p [9] C.T. Kresge, M.E. Leonowicz, W.J. Roth, J.C. Vartuli, J.S. Beck, Nature 359 (1992) 710. [10] J.S. Beck, J.C. Vartuli, W.J. Roth, M.E. Leonowicz, C.T. Kresge, K.D. Schmitt, C.T.W. Chu, D.H. Olson, E.W. Scheppard, S.B. MacCullen, H.B. Higgins, J.L. Schlenker, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114 (1994) [11] R.B. Borade, A. Clearfield, Catal. Lett. 31 (1995) 267. [12] X. Chen, L. Huang, G. Ding, Q. Li, Catal. Lett. 44 (1997) 123. [13] S.J. Gregg, K.S.W. Suig, Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity, Academic Press, London, 1982, Ch. 4. [14] H. Kosslick, G. Lischke, B. Parlitz, W. Storek, R. Fricke, Appl. Catal. A. Gen. 184 (1999) 49.
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR
 University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
University Technology Malaysia From the SelectedWorks of Hadi Nur May, 2004 Quantitative measurement of a mixture of mesophases cubic MCM-48 and hexagonal MCM-41 by 13C CP/MAS NMR Hadi Nur, University
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 2006, 6, 318-323 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2006 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors Gas Sensing Properties of Ordered Mesoporous SnO 2 Thorsten Wagner 1,2,*, Claus-Dieter Kohl 1, Michael Fröba 2 and
Sensors 2006, 6, 318-323 sensors ISSN 1424-8220 2006 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors Gas Sensing Properties of Ordered Mesoporous SnO 2 Thorsten Wagner 1,2,*, Claus-Dieter Kohl 1, Michael Fröba 2 and
PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 11, No. 1, January - March 2016, p. 271-276 PREPARATION OF MCM-48 MESOPOROUS MOLECULAR SIEVE INFLUENCE OF PREPARATION CONDITIONS ON THE STRUCTURAL
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2007 69451 Weinheim, Germany Efficient Bifunctional Nanocatalysts by Simple Postgrafting of Spatially-Isolated Catalytic Groups on Mesoporous Materials By Krishna K. Sharma
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Catalytic activity of the beta zeolite with enhanced textural properties in the Friedel-Crafts acylation of aromatic compounds
 Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with HCl and H 2 O 2 to Produce. Dichloropropanols Catalyzed by Hollow TS-1 Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 216 Chlorohydrination of Allyl Chloride with and 2 O 2 to Produce Dichloropropanols Catalyzed
Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysts
 Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Homogeneous Liquid phase Low temperature High selectivity High diffusivity Easy heat transfer Difficult catalyst separation Expensive recycling Well-defined active
Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Homogeneous Liquid phase Low temperature High selectivity High diffusivity Easy heat transfer Difficult catalyst separation Expensive recycling Well-defined active
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information 2-Methylimidazole-Assisted Synthesis of Two-Dimensional MOF-5 Catalyst
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information 2-Methylimidazole-Assisted Synthesis of Two-Dimensional MOF-5 Catalyst
CHAPTER 6. SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST
 135 CHAPTER 6 SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST 6.1 INTRODUCTION -Pinene is a terpenoid family of organic compound which is inexpensive, readily available and renewable
135 CHAPTER 6 SOLVENT-FREE SELECTIVE OXIDATION OF -PINENE OVER Co-SBA-15 CATALYST 6.1 INTRODUCTION -Pinene is a terpenoid family of organic compound which is inexpensive, readily available and renewable
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Supplementary Information. Synthesis and Characterization of Fibrous Silica ZSM-5 for Cumene Hydrocracking
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 1 Supplementary Information Synthesis and Characterization of Fibrous Silica
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 1 Supplementary Information Synthesis and Characterization of Fibrous Silica
Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper Nanostructures for Hydrogen Generation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary data Methanolysis of Ammonia Borane by Shape-Controlled Mesoporous Copper
MCM-41 Ordered Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Synthesis and Characterization
 Materials Research, Vol. 2, No. 3, 173-179, 1999. 1999 MCM-41 Ordered Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Synthesis and Characterization Rogério A.A. Melo a, Marcus V. Giotto a, João Rocha b, Ernesto A. Urquieta-González
Materials Research, Vol. 2, No. 3, 173-179, 1999. 1999 MCM-41 Ordered Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Synthesis and Characterization Rogério A.A. Melo a, Marcus V. Giotto a, João Rocha b, Ernesto A. Urquieta-González
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Temperature Effect on Pore Structure of Nanostructured Zeolite Particles Synthesized by Aerosol Spray Method
 Temperature Effect on Pore Structure of Nanostructured Zeolite Particles Synthesized by Aerosol Spray Method Yu-Chih Lin 1 and Hsunling Bai 2 1. Department of Environmental Engineering and Health, Yuanpei
Temperature Effect on Pore Structure of Nanostructured Zeolite Particles Synthesized by Aerosol Spray Method Yu-Chih Lin 1 and Hsunling Bai 2 1. Department of Environmental Engineering and Health, Yuanpei
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Isomorphous Substitution of Zn 2+ in aluminosilicate framework creates two types of mesopores without templates
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.11 No.02, pp 365-369, 2018 Isomorphous Substitution of Zn 2+ in aluminosilicate framework creates
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.11 No.02, pp 365-369, 2018 Isomorphous Substitution of Zn 2+ in aluminosilicate framework creates
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS
 EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41
 ESO 25(6) #7759 Energy Sources, 25:591 596, 2003 Copyright 2003 Taylor & Francis 0090-8312/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/00908310390195651 Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41 S.-H.
ESO 25(6) #7759 Energy Sources, 25:591 596, 2003 Copyright 2003 Taylor & Francis 0090-8312/03 $12.00 +.00 DOI: 10.1080/00908310390195651 Photodecomposition of Water Catalyzed by Zr- and Ti-MCM-41 S.-H.
Characterization of Highly Ordered MCM-41 Silicas Using X-ray Diffraction and Nitrogen Adsorption
 Langmuir 1999, 15, 5279-5284 5279 Characterization of Highly Ordered MCM-41 Silicas Using X-ray Diffraction and Nitrogen Adsorption Michal Kruk and Mietek Jaroniec* Department of Chemistry, Kent State
Langmuir 1999, 15, 5279-5284 5279 Characterization of Highly Ordered MCM-41 Silicas Using X-ray Diffraction and Nitrogen Adsorption Michal Kruk and Mietek Jaroniec* Department of Chemistry, Kent State
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supporting Information. Size-tunable Ni nanoparticles supported on surface-modified, cage-type mesoporous
 Supporting Information Size-tunable Ni nanoparticles supported on surface-modified, cage-type mesoporous silica as highly active catalysts for CO 2 hydrogenation Ching-Shiun Chen, a,b* Canggih Setya Budi,
Supporting Information Size-tunable Ni nanoparticles supported on surface-modified, cage-type mesoporous silica as highly active catalysts for CO 2 hydrogenation Ching-Shiun Chen, a,b* Canggih Setya Budi,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Zn-MCM-48 Supporting Hydrated Dibromodioxomolybdenum(Ⅵ) for Facile Conversion of Methane to Methyl Oxygenated Products Fengbo Li, Guoqing Yuan*
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Zn-MCM-48 Supporting Hydrated Dibromodioxomolybdenum(Ⅵ) for Facile Conversion of Methane to Methyl Oxygenated Products Fengbo Li, Guoqing Yuan*
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material
 Electronic Supplementary Material Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous Si MCM-41 materials and their application as solid acid catalysts in some esterification reactions by Tarun F Parangi (pp
Electronic Supplementary Material Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous Si MCM-41 materials and their application as solid acid catalysts in some esterification reactions by Tarun F Parangi (pp
Synthesis of mesoporous aluminosilicates with low Si/Al ratios using a single-source molecular precursor under acidic conditions
 J Porous Mater (2006) 13: 187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10934-006-8003-8 Synthesis of mesoporous aluminosilicates with low Si/Al ratios using a single-source molecular precursor under acidic conditions Ying Li
J Porous Mater (2006) 13: 187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10934-006-8003-8 Synthesis of mesoporous aluminosilicates with low Si/Al ratios using a single-source molecular precursor under acidic conditions Ying Li
Supporting Information. Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-101(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid
 Supporting Information Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-11(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid Kunyue Leng a, Yinyong Sun a *, Xiaolin Li a, Shun Sun a, Wei Xu b a
Supporting Information Rapid synthesis of metal-organic frameworks MIL-11(Cr) without the addition of solvent and hydrofluoric acid Kunyue Leng a, Yinyong Sun a *, Xiaolin Li a, Shun Sun a, Wei Xu b a
photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation
 Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
One-Pot Reaction Cascades Catalyzed by Base and Acid Confined Inside Pores of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres
 One-Pot Reaction Cascades Catalyzed by Base and Acid Confined Inside Pores of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Yulin Huang, Brian Trewyn, Hung-ting Chen, Shu Xu, Victor S.-Y. Lin* Department of Chemistry
One-Pot Reaction Cascades Catalyzed by Base and Acid Confined Inside Pores of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres Yulin Huang, Brian Trewyn, Hung-ting Chen, Shu Xu, Victor S.-Y. Lin* Department of Chemistry
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-, and MTMS-Modified Particles
 Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
enzymatic cascade system
 Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department. Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials
 Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Bromination of phenol with NBSac over synthesized zeolite as a heterogeneous recyclable catalyst
 Bromination of phenol with NBSac over synthesized zeolite as a heterogeneous recyclable catalyst Maryam Abrishamkar, a,b Seyed Naser Azizi a* and Hossein Kazemian c a Analytical Division, Faculty of Chemistry,
Bromination of phenol with NBSac over synthesized zeolite as a heterogeneous recyclable catalyst Maryam Abrishamkar, a,b Seyed Naser Azizi a* and Hossein Kazemian c a Analytical Division, Faculty of Chemistry,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Utilization of Diatomite as Silica Source for the Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Materials
 Utilization of Diatomite as Silica Source for the Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Materials Jirapa Kraisit, Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Chutimon Satirapipathkul, Chulalongkorn University,
Utilization of Diatomite as Silica Source for the Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Silica Materials Jirapa Kraisit, Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Chutimon Satirapipathkul, Chulalongkorn University,
Supporting information
 Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Supporting information Hierarchical Macro-meso-microporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Hollow Fibers With Highly Efficient Catalytic Cracking Capability Jia Liu, a Guiyuan Jiang,* a Ying Liu, a Jiancheng Di, b Yajun
Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification
 Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Electronic Supporting Informations (ESI): Dry-gel conversion synthesis of Cr-MIL-101 aided by grinding: High surface area high yield synthesis with minimum purification Jun Kim, Yu-Ri Lee and Wha-Seung
Supporting Information
 upporting Information ynthesis of Thiol-functionalized Mesoporpous ilica Material (M) To synthesize the thiol-functionalized mesoporous silica (M), we modified the welldeveloped cetyltrimethylammonium
upporting Information ynthesis of Thiol-functionalized Mesoporpous ilica Material (M) To synthesize the thiol-functionalized mesoporous silica (M), we modified the welldeveloped cetyltrimethylammonium
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals
 A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
Xiufang Chen, Jinshui Zhang, Xianzhi Fu, Markus Antonietti, and Xinchen Wang*
 -Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol Using Hydrogen Peroxide and Visible Light Xiufang Chen, Jinshui Zhang, Xianzhi Fu, Markus Antonietti, and Xinchen Wang* Supporting Information: Synthesis of :
-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol Using Hydrogen Peroxide and Visible Light Xiufang Chen, Jinshui Zhang, Xianzhi Fu, Markus Antonietti, and Xinchen Wang* Supporting Information: Synthesis of :
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Microporous Organic Network Hollow Spheres: Useful Templates for Nanoparticulate Co 3 O 4 Hollow Oxidation Catalysts Narae Kang, Ji Hoon Park, Mingshi Jin, Nojin Park, Sang Moon
Supporting Information for Microporous Organic Network Hollow Spheres: Useful Templates for Nanoparticulate Co 3 O 4 Hollow Oxidation Catalysts Narae Kang, Ji Hoon Park, Mingshi Jin, Nojin Park, Sang Moon
Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins
 Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
NANOSILICEOUS MATRIX FOR DRUG INCAPSULATION
 NANOSILICEOUS MATRIX FOR DRUG INCAPSULATION L. G. HANU 1, A. M. HANU 1, E. POPOVICI 1, G. BURTICĂ 2, D. TIMPU 3 1 Faculty of Chemistry, Univ. Al. I. Cuza, Iaºi 2 University Politehnica, Timiºoara 3 P.
NANOSILICEOUS MATRIX FOR DRUG INCAPSULATION L. G. HANU 1, A. M. HANU 1, E. POPOVICI 1, G. BURTICĂ 2, D. TIMPU 3 1 Faculty of Chemistry, Univ. Al. I. Cuza, Iaºi 2 University Politehnica, Timiºoara 3 P.
PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF MCM-41/RHODAMINE B. Yue-Xiang Liu and Qing-Zhou Zhai *
 , 145-150. ISSN 1011-3924 Printed in Ethiopia 2009 Chemical Society of Ethiopia SHORT COMMUNICATION PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF MCM-41/RHODAMINE B Yue-Xiang Liu and Qing-Zhou
, 145-150. ISSN 1011-3924 Printed in Ethiopia 2009 Chemical Society of Ethiopia SHORT COMMUNICATION PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF MCM-41/RHODAMINE B Yue-Xiang Liu and Qing-Zhou
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Supplementary Information. Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses
 Supplementary Information Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses of Extra-Large Pore Germanosilicate Zeolites Risheng Bai, Qiming Sun, Ning Wang, Yongcun Zou, Guanqi Guo, Sara Iborra, Avelino
Supplementary Information Simple Quaternary Ammonium Cations-Templated Syntheses of Extra-Large Pore Germanosilicate Zeolites Risheng Bai, Qiming Sun, Ning Wang, Yongcun Zou, Guanqi Guo, Sara Iborra, Avelino
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation
 S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
S1 Supporting Information One-Pot Conversion of Methane to Light Olefins or Higher Hydrocarbons through H-SAPO-34 Catalyzed in-situ Halogenation Patrice T. D. Batamack, Thomas Mathew, G. K. Surya Prakash*
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials
 Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Solvent-free Synthesis of Zeolites from Solid Raw Materials Limin Ren, Qinming Wu, Chengguang Yang, Longfeng Zhu, Caijin Li, Pengling Zhang, Haiyan Zhang, Xiangju Meng,*, Feng-Shou Xiao*, Department of
Hydrothermal stability of MCM-48 improved by postsynthesis restructuring in salt solution
 Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 41 (2000) 119±127 www.elsevier.nl/locate/micromeso Hydrothermal stability of MCM-48 improved by postsynthesis restructuring in salt solution Shinae Jun a, Ji Man Kim
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 41 (2000) 119±127 www.elsevier.nl/locate/micromeso Hydrothermal stability of MCM-48 improved by postsynthesis restructuring in salt solution Shinae Jun a, Ji Man Kim
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Information for Exceptional Ammonia Uptake by a Covalent Organic Framework Christian J. Doonan, David J. Tranchemontagne,T. Grant Glover, Joseph R. Hunt, Omar M.
Supplementary information Supplementary Information for Exceptional Ammonia Uptake by a Covalent Organic Framework Christian J. Doonan, David J. Tranchemontagne,T. Grant Glover, Joseph R. Hunt, Omar M.
Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)231 237 Synthesis and Characterization of Magnesium Substituted Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves with AEL Structure Benjing Xu, Ling Qian, Xinmei Liu, Chunmin
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Catalytic oxidation of toluene with molecular oxygen over Cr-substituted mesoporous materials
 Applied Catalysis A: General 241 (2003) 205 215 Catalytic oxidation of toluene with molecular oxygen over Cr-substituted mesoporous materials Ch. Subrahmanyam a, B. Louis b, F. Rainone b, B. Viswanathan
Applied Catalysis A: General 241 (2003) 205 215 Catalytic oxidation of toluene with molecular oxygen over Cr-substituted mesoporous materials Ch. Subrahmanyam a, B. Louis b, F. Rainone b, B. Viswanathan
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core
 A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
A soft-templated method to synthesize sintering-resistant Au/mesoporous-silica core-shell nanocatalysts with sub-5 nm single-core Chunzheng Wu, ab Zi-Yian Lim, a Chen Zhou, a Wei Guo Wang, a Shenghu Zhou,
Supporting Information. for. Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under. Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via
 Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Supporting Information for Delamination of Layered Zeolite Precursors under Mild Conditions: Synthesis of UCB-1 via Fluoride/Chloride Anion-Promoted Exfoliation Isao Ogino, Michael M. Nigra, Son-Jong Hwang,
Application of Mesoporous MCM-48 and SBA-15 Materials for the Separation of Biochemicals Dissolved in Aqueous Solution
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 21(1), 246-251 (2004) Application of Mesoporous MCM-48 and SBA-15 Materials for the Separation of Biochemicals Dissolved in Aqueous Solution Jae Wook Lee, Dae Lim Cho*, Wang Geun
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 21(1), 246-251 (2004) Application of Mesoporous MCM-48 and SBA-15 Materials for the Separation of Biochemicals Dissolved in Aqueous Solution Jae Wook Lee, Dae Lim Cho*, Wang Geun
Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light
 Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Sintering-resistant Ni-based Reforming Catalysts via. the Nanoconfinement Effect
 Supporting Information Sintering-resistant Ni-based Reforming Catalysts via the Nanoconfinement Effect Chengxi Zhang a,b, Wancheng Zhu c, Shuirong Li a,b, Gaowei Wu a,b, Xinbin Ma a,b, Xun Wang c, and
Supporting Information Sintering-resistant Ni-based Reforming Catalysts via the Nanoconfinement Effect Chengxi Zhang a,b, Wancheng Zhu c, Shuirong Li a,b, Gaowei Wu a,b, Xinbin Ma a,b, Xun Wang c, and
Isomorphous Substitution of Trivalent Iron in Mesoporous MCM-48 Silicate Molecular Sieves: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Properties
 Isomorphous Substitution of Trivalent Iron in Mesoporous MCM-48 Silicate Molecular Sieves: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Properties S.E. Dapurkar, S.K. Badamali, A. Sakthivel and P. Selvam
Isomorphous Substitution of Trivalent Iron in Mesoporous MCM-48 Silicate Molecular Sieves: Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Properties S.E. Dapurkar, S.K. Badamali, A. Sakthivel and P. Selvam
Synthesis of uniform hollow silica spheres with ordered mesoporous shells in a CO 2 induced nanoemulsion. Supporting Information
 Synthesis of uniform hollow silica spheres with ordered mesoporous shells in a CO 2 induced nanoemulsion Yueju Zhao, Jianling Zhang, Wei Li, Chaoxing Zhang, Buxing Han* Beijing National Laboratory for
Synthesis of uniform hollow silica spheres with ordered mesoporous shells in a CO 2 induced nanoemulsion Yueju Zhao, Jianling Zhang, Wei Li, Chaoxing Zhang, Buxing Han* Beijing National Laboratory for
Supplementary Information. ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni(0) Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane
 Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Indium oxide nanocluster doped TiO 2 catalyst for activation of molecular
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Indium oxide nanocluster doped TiO 2 catalyst for activation of molecular
Kleitz et al. ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Insights into Pore Surface Modification of Mesoporous Polymer-Silica
 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Insights into Pore Surface Modification of Mesoporous Polymer-Silica Composites: Introduction of Reactive Amines Rémy Guillet-Nicolas, Louis Marcoux and Freddy Kleitz*
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Insights into Pore Surface Modification of Mesoporous Polymer-Silica Composites: Introduction of Reactive Amines Rémy Guillet-Nicolas, Louis Marcoux and Freddy Kleitz*
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid
 Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
Supplementary Information for Efficient catalytic conversion of fructose into hydroxymethylfurfural by a novel carbon based solid acid Jianjian Wang, Wenjie Xu, Jiawen Ren*, Xiaohui Liu, Guanzhong Lu,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Framework and Extraframework Tin Sites in Zeolite Beta React Glucose Differently
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Framework and Extraframework Tin Sites in Zeolite Beta React Glucose Differently Ricardo Bermejo-Deval, Rajamani Gounder and Mark E. Davis* Chemical Engineering, California Institute
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Framework and Extraframework Tin Sites in Zeolite Beta React Glucose Differently Ricardo Bermejo-Deval, Rajamani Gounder and Mark E. Davis* Chemical Engineering, California Institute
Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Temperature CO 2 Sorption on Hydrotalcite Having a High Mg/Al Molar Ratio Suji Kim, Sang Goo Jeon, and Ki Bong Lee*, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Korea
Synthesis and Alkylation of Phenol over Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas Functionalized with Sulfonic Acid Group
 Zeolitic Materials, Vol. 3, No. 1, December 2002, 20-28 Synthesis and Alkylation of Phenol over Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas Functionalized with Sulfonic Acid Group Xingdong Yuan, Hyung Ik Lee, Jin
Zeolitic Materials, Vol. 3, No. 1, December 2002, 20-28 Synthesis and Alkylation of Phenol over Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas Functionalized with Sulfonic Acid Group Xingdong Yuan, Hyung Ik Lee, Jin
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Min Bum Park, Sang Hyun Ahn, Nak Ho Ahn and Suk Bong Hong*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Total: 10 pages, 4 figures and 4 tables.
 Supporting Information Catalysis in flow: Nickel-catalyzed synthesis of primary amines from alcohols and NH 3 Andrew Yuk Keung Leung, Klaus Hellgardt and Mimi (King Kuok) Hii Total: 10 pages, 4 figures
Supporting Information Catalysis in flow: Nickel-catalyzed synthesis of primary amines from alcohols and NH 3 Andrew Yuk Keung Leung, Klaus Hellgardt and Mimi (King Kuok) Hii Total: 10 pages, 4 figures
Methane production from CO2 over Ni-Hydrotalcite derived catalysts
 Methane production from CO2 over Ni-Hydrotalcite derived catalysts Keerthivarman Veerappanchatram Kaliappan vkkeerthivarman@gmail.com Instituto Superior Tecnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal. October
Methane production from CO2 over Ni-Hydrotalcite derived catalysts Keerthivarman Veerappanchatram Kaliappan vkkeerthivarman@gmail.com Instituto Superior Tecnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal. October
Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
 (Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
(Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Supplementary Information for Chemical Communications This journal is of The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004
 Fine-tuning the Degree of Organic Functionalization of Mesoporous ilica Nanosphere Materials via an Interfacially Designed Co-condensation Method Daniela R. Radu, Cheng-Yu Lai, Jianguo Huang, Xu hu, Victor.-Y.
Fine-tuning the Degree of Organic Functionalization of Mesoporous ilica Nanosphere Materials via an Interfacially Designed Co-condensation Method Daniela R. Radu, Cheng-Yu Lai, Jianguo Huang, Xu hu, Victor.-Y.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Photocatalytic Suzuki Coupling Reaction using Conjugated Microporous Polymer with Immobilized Palladium Nanoparticles under Visible Light Zi Jun Wang, Saman Ghasimi, Katharina Landfester
Supporting Information Photocatalytic Suzuki Coupling Reaction using Conjugated Microporous Polymer with Immobilized Palladium Nanoparticles under Visible Light Zi Jun Wang, Saman Ghasimi, Katharina Landfester
A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO 2 adsorption
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Metal-Organic Framework-Templated Synthesis of γ-fe 2 O 3
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Metal-Organic Framework-Templated Synthesis of γ-fe 2 O 3
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Figure S1 XRD patterns of (a) Ti-MSE-A, (b) Ti-MSE-A-cal, (c) TS-1, (d) Ti-MWW, and (e) Ti-BEA.
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Ti-MCM-68 for Effective Oxidation Reactions Yoshihiro Kubota,* Yoshihito Koyama, Taku Yamada, Satoshi Inagaki, and Takashi
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Conversion and Kinetics Study of Fructose-to-5- Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) Using Sulfonic and Ionic Liquid Groups Bi-functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Recyclable
Supporting Information Conversion and Kinetics Study of Fructose-to-5- Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) Using Sulfonic and Ionic Liquid Groups Bi-functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Recyclable
Synthesis and characterisation of ZSM-5/SBA-15 composite material. Le Thi Hoai Nam*, Tran Quang Vinh* and Nguyen Duc Hoa
 466 Int. J. Nanotechnol., Vol. 12, Nos. 5/6/7, 2015 Synthesis and characterisation of ZSM-5/SBA-15 composite material Le Thi Hoai Nam*, Tran Quang Vinh* and Nguyen Duc Hoa Department of Green Chemistry,
466 Int. J. Nanotechnol., Vol. 12, Nos. 5/6/7, 2015 Synthesis and characterisation of ZSM-5/SBA-15 composite material Le Thi Hoai Nam*, Tran Quang Vinh* and Nguyen Duc Hoa Department of Green Chemistry,
Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
