OChem2 Course Pack. Practice Problems by Chapter. Practice Exams
|
|
|
- Jeffrey Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chem2 Course Pack Practice Problems by Chapter Practice Exams
2 Chemistry 3720 Problem Sets
3 Chemistry 3720 Ch Synthesis Problems These problems are typical of those that will be on the upcoming exams in From Chapters 13-19: Show retrosynthetic analyses for each of the following molecules that go back only to the starting materials given below. Then, using any chemistry seen in 3719 and 3720 so far, give an efficient synthesis of each molecule showing the products formed in each step. Assume that you have access to any of the usual reagents such as 2, AlCl 3, Fe,, N 3, 2 S 4, etc. a. b. c. d. e. 2 N starting materials C 3 Cl Cl 2. From 13 and 14: Give structures of the products from each step within the following roadmap and match the spectral data to the product. 2,heat Mg, ether Na 2Cr S 4 2 ( 13 C200ppm) (IR 3300 cm -1 )
4 3. From 13-19: Give structures of the products from each step in the following reaction sequences. a. 1. 2,heat 2. 2 Li, ether 3. C 3 C b. 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 2. LiAl 4,ether Na, ether 5. C 3 C 2 c. 1. NaB 4,C Li, ether 4. C 3 C 2 C d S 4, 2 2. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 3. Mg, ether Na, ether 6. C 3 C 2 C 2 e. 1. PDC, C 2 Cl 2 2. C 3 Li, ether Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 5. Mg, ether f. 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 2. N 3, 2 S 4 3. NaB 4,C 3 4. Na, ether 5. C 3 C 2 C 2
5 4. From 1-19: Design syntheses of the following molecules using any of the chemistry seen so far in 3719 and 3720 and using only the sources of carbon shown below. Again, assume that you have access to all of the common inorganic reagents ( 2, AlCl 3, Fe,, etc.). a. Cl N 2 b. c. C 3 C 3 d. e. C 3 C 2
6 Chemistry 3720 Chapter 16 - Spectroscopy Problems 1. (10 pts) An unknown organic compound has the molecular formula C 5 12, in the mass spectrum, M+ = Given the following 1 and 13 C data, give the structure of the unknown and assign all of the 1 and 13 C signals PPM NMR (ppm) 1.14 (t, 3, J = 7.2 z), 1.09 (d, 6, J = 7.0 z), 3.19 (septet, 1, J = 7.0 z), 3.50 (q, 2, J = 7.2 z) PPM C NMR (ppm) 15.5, 22.3 (double), 64.8,
7 2. (10 pts) Draw the approximate 13 C NMR spectrum of the following molecule. Include approximate chemical shifts and indicate which signal corresponds to which carbon(s) in the molecule. 3 C C 3 3. (10 pts) A chemist produces a new compound with the following spectral characteristics and considers the new material to be one of the possibilities shown below. Which structure is correct and why? Include a complete assignment of all of the spectral data in your answer. 1 NMR (ppm) 1.32 (t, 3, J = 7.0 z), 3.30 (s, 3,), 4.09 (q, 2, J = 7.0 z), 4.63 (s, 2), 7.10 (m, 2), 7.83 (m, 2) 13 C NMR (ppm) 14.8, 57.2, 64.6, 81.2, 126.1, (double), (double), 163.8, IR (cm -1 ) 1740, 810 C 3 C 3 C 3 2
8 4. (10 pts) Draw the expected 1 and 13 C NMR spectra of the following molecules. Include chemical shifts and line shapes (singlet, doublet, etc.) in the 1 spectra and intensities in the 13 C spectra. Also indicate which signal corresponds to which proton(s) and carbon(s). a. b. c. d. 5. (10 pts) An unknown organic compound has the molecular formula C Given the following spectral data, provide a structure for the unknown that agrees with the data, and then assign the data. 1 NMR (ppm) 2.50 (s, 3), 2.75 (t, 2, J = 7.2 z), 3.30 (s, 3), 2.52 (t, 2, J = 7.2 z), (m, 4) 13 C NMR (ppm) 26.6, 35.3, 59.3, 73.0, 126.0, 127.7, 128.5, 132.1, 1391, 139.2, Mass spectrum (m/z) (M+) Infra Red (cm -1 ) 1730, 760, (10 pts) An unknown organic compound has the molecular formula C and, in the mass spectrum, M+ = Given the following 1 and 13 C data, give the structure of the unknown and then assign all of the 1 signals. 1 NMR (ppm) 1.20 (d, 6, J = 7.0 z), 1.29 (t, 3, J = 7.1 z), 2.87 (septet, 1, J = 7.0 z), 4.30 (q, 2, J = 7.1 z), 7.41 (d, 2), 7.97 (d, 2) 13 C NMR (ppm) 14.1, 23.3 (double), 33.2, 60.9, (double), 127.3, (double), 155.7,
9 Chemistry 3720 Chapter 19 - Benzene Synthesis Problems Provide an efficient synthesis of each of the following substituted benzenes from benzene itself. Use any of the reagents seen in Chemistry 3719/3720 so far and pay careful attention to the order of steps. Assume that mixtures may be separated. C 3 C 2 N 2 S 3 C 2 C 3 S 3
10 Chemistry 3720 Chapters Synthesis Problems These problems are typical of those that will be on the next exams in You should be comfortable with each reaction in the forward direction, how to think about each reaction in a retrosynthetic manner, and then be able to complete multi-step syntheses. 1. Give the major organic product(s) from each of the following reaction sequences and then a detailed mechanism for each reaction. Be careful with any regiochemical issues. a. b. xs C 3 xs C 3 Cl cat. + cat. + c. C 2 C 2 d xs C 3 cat. + C 3 cat. + e. f. xs Et cat. + Me xs Me cat Give the major organic product(s) from each step of the following synthetic scheme. 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl ,Fe 3. C 2 C 2, cat. Ts 4. Mg, ether 5. 2 C=, ether 6. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 7. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 8. (C 3 ) 2 CLi, TF 9. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 10. PDC, C 2 Cl Mg, TF 12. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 13.Na,ether 14. C 2, ether 15. 5% Cl, 3 h, RT 16. NaB 4,C NaC 3,C m-cpba, C 2 Cl Mg, ether 21. aq. N 4 Cl (quench)
11 3. In the boxes provided, give the products from each step in the following road-map scheme. Me PCC C 2 Cl 2 xs. Me cat. + 2C 3 Li TF C 3 NaN 2 TF 3 + (quench) 5% Cl TF Mg TF 3 + (quench) m-cpba C 2 Cl 2 PCC C 2 Cl 2 13 C=175ppm 4. Give retrosynthetic analyses for the following molecules that go back to the given starting materials, and then provide the synthesis in the forward direction. Assume you have access to the usual other reagents (, N 3, NaB 4, etc.) in the lab. a. Cl N 2 b. N N 2 c.
12 Chemistry 3720 Chapters Synthesis Problems These problems are from various parts of 3719 and 3720 and deal with the two main synthetic issues studied; C-C bond formation and manipulation of functional groups.. 1. Give the major organic product(s) from each of the following aldol reactions as well as a detailed mechanism for each case. Be careful with any regiochemical issues. a. b. Na C 3, K C 3, K c. d. Et, reflux Na C 3, e. f. K Na Et, reflux C 3, 2. Draw all of the possible aldol condensation products formed under the following conditions. + Na, 2 reflux 3. Provide the reagents required to make each of the following compounds via 1,4-addition chemistry. 4. In the following Robinson annulation, 3 aldol products are possible; draw them and then explain why only the one shown below is formed. Give a complete mechanism for the reaction including important resonance structures. Na, 2
13 5. Give the major products from each step of the following reaction sequences. a. b. 1. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 2. m-cpba, C 2 Cl 2 1. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 2 S 4 2. C 3, + c P=C 2 d. 2. 2,Pd 1. m-cpba, C 2 Cl 2 2. C 3, cat Provide complete mechanisms for the following conversions. Include all resonance structures for any intermediates that may be formed. Na C 3, + C 3 7. Give structures for each of the products in the following roadmap. PCC C 2 Cl 2 Na, Et reflux Et 2 CuLi TF Na 2 Cr S 4, 2 aq. N4 Cl (quench) xs C 3, + 2Li ether aq. N 4 Cl (quench)
14 8. The polyether compound chauncydermolide G (shown below) was recently isolated by Triplet armaceuticals Inc. and found to have promising antibiotic properties. In order to prove the structure unequivocally, a total synthesis beginning with the shown starting material was carried out. Give structures for each of the products in the synthetic sequence. 1. Na, TF 2. C 2 3. Li, TF 4. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 5. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 6. xs C 3,cat ,Pt 8. PDC, C 2 Cl 2 9. (C 3 ) 2 CC 2 Mg, ether 10. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 11.Na,TF 12. C 3 C 2 C % Cl, 3 h, RT 14. 2,Fe 15. (C 2 ) 2,cat Li, TF C= 18. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 19. PCC, C 2 Cl P=C 2,ether 21. m-cpba, C 2 Cl (C 3 ) 2 CMg, ether 23. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 24. PCC, C 2 Cl , 2, TF 26. NaC 3,C C 3 C 2 C 2 Mg, ether 28. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 29. Na, TF 30. C C 2 I 2,Zn,TF 32. 5% Cl, 3 h, RT 33. LDA, TF, -78 o C 34. C 3 C 2 35.,TF P 3 Me chauncy der molide G 36. dil. 2 S 4 37.
15 Chemistry 3720 Chapters Additional Synthesis Problems 1. Give retrosynthetic analyses for the following molecules that go back to the given starting materials, and then provide the synthesis in the forward direction. Assume you have access to the usual other reagents (, N 3, NaB 4, etc.) in the lab. a. C 2 b. c. d. C 3 C 3 e. N C 3 2. Give the major organic product(s) from each step of the following synthetic sequence. 1. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 2. xs C 3,cat. 2 S 4 3. NaC 3,C 3 4. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 5. NaC 3,TF 6. C 3 C 2 7. Na, aq. TF 8. dil. Cl (quench) o C (-C 2 ) 10.LDA,TF,-78 o C 11. C 2
16 3. In the boxes provided, give the products from each step in the following road-map scheme. Predict the 1 NMR spectra of each of the organic products from each step. 2 Fe Mg ether C 2 N 3 2 S 4 xs C 3 cat. 2 S 4 dil. Cl (quench) 2xC 3 Li TF aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Na TF Sn, Cl C 3 4. Give complete mechanisms, including any important resonance structures for intermediates where applicable, that explain the bond-making and bond-breaking events, in each step of the following conversions. a. 3 C C 3 1. NaC 3,C 3 2. dilute Cl (quench) 3. NaC 3,TF 4. C 2 5. Na, aq. TF 6. dilute Cl (quench) o C(-C 2 ) b. 1. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 2. xs C 3, cat. Cl 3. NaC 3,C 3 4. dilute Cl (quench) 5. Na, aq. TF 6. dilute Cl (quench)
17 Chemistry 3720 Further Synthesis Problems 1 1. Give retrosynthetic analyses for the following molecules that go back to the given starting materials, and then provide the synthesis in the forward direction. Assume you have access to the usual other reagents (, N 3, NaB 4, etc.) in the lab. a. P 3 b. c. Cl d. e. 2. Give the major organic product(s) from each step of the following synthetic scheme. 1. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 2. Na, Et, reflux 3. (C 3 ) 2 CuLi, ether 4. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 5. Mg, ether 6. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 7. NaN 2,TF 8. C 3
18 3. In the boxes provided, give the products from each step in the following road-map scheme. PCC Mg C 2 Cl 2 TF aq. N 4 Cl (quench) aq. N 4 Cl (quench) (C 3 ) 2 CuLi TF C 3 PCC C 2 Cl 2 2 CCl 3 NaC 3 C 3 (C 3 ) 2 CuLi TF NaB 4 C 3 aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 4. Give complete mechanisms, including any important resonance structures for intermediates where applicable, that explain the bond-making and bond-breaking events in the following conversions. a. 1. m-cpba, C 2 Cl Mg, TF 3. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) b. 1. N 3, 2 S 4 2. LDA, TF, -78 o C aq. N 4 Cl (quench) N 2
19 Chemistry 3720 Problem Set Keys
20 Chemistry 3720 Chapters 1-19 Synthesis Problems - Key These problems are typical of those that will be on the upcoming exams in From Chapters 1-19: Show retrosynthetic analyses for each of the following molecules that go back only to the starting materials given below. Then, using any chemistry seen in 3719 and 3720 so far, give an efficient synthesis of each molecule showing the products formed in each step. Assume that you have access to any of the usual reagents such as 2, AlCl 3, Fe,, N 3, 2 S 4, etc. a. Retrosynthesis Li Synthesis 2,heat 2 Li, ether Li 3 + Li b Retrosynthesis Li Synthesis 2,Fe 2 Li, ether Li 3 + Li
21 c. Retrosynthesis Li Synthesis 2,eat 2Li,ether Li 3 + Li d. Retrosynthesis Mg Synthesis Mg Cl C 3 CCl Mg AlCl 3 ether 3 + Mg ether Mg
22 e. Retrosynthesis 2 N 2 N 2 N Mg Synthesis Cl C 3 CCl N 3 2 N AlCl 3 2 S 4 C 3 Cl AlCl 3 C 3 2 heat Mg ether Mg ether 2 N N Mg 2. From 13 and 14: Give structures of the products from each step within the following roadmap and match the spectral data to the product. 2,heat Mg, ether Mg Na 2Cr Mg 2 S 4 2 ( 13 C200ppm) (IR 3300 cm -1 )
23 3. From 13-19: Give structures of the products from each step in the following reaction sequences. a. 1. 2,heat 2. 2 Li, ether 3. C 3 C 1. Li Li b. 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 2. LiAl 4,ether Al Li + 4. Na Na, ether 5. C 3 C 2 4 c. 1. NaB 4,C Li, ether Li Li C 3 C 2 C d S 4, 2 2. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 3. Mg, ether Mg Na, ether 6. C 3 C 2 C 2 5. Na 6. e. 1. PDC, C 2 Cl 2 2. C 3 Li, ether Li Mg Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 5. Mg, ether f. 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 2. N 3, 2 S 4 3. NaB 4,C Na Na, ether 5. C 3 C 2 C 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2
24 4. From 1-19: Design syntheses of the following molecules using any of the chemistry seen so far in 3719 and 3720 and using only the sources of carbon shown below. Again, assume that you have access to all of the common inorganic reagents ( 2, AlCl 3, Fe,, etc.). a. Design (Retrosynthesis) Cl N 2 + N 2 N 2 N 2 Li + N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 + Cl Construction (Synthesis) 2 Li ether Li Cl AlCl 3 N 3 2 S 4 N 2 ether Na Sn Cl Na ether N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2
25 b. Design (Retrosynthesis) Li Mg Construction (Synthesis) 2 heat Mg ether Mg PDC C 2 Cl 2 2Li ether Li ether ether PDC 3 + C 2 Cl 2 Li Mg 3 +
26 c. Design (Retrosynthesis) C 3 C 3 3 C + C 3 Mg C 3 3 o alcohol (2 equiv. subst.) Construction (Synthesis) Mg C 3 ether C 3 Mg 0.5 ether C 3 Mg 3 + Na Na ether d. Design (Retrosynthesis - several ways to do this one) Li
27 d. (cont d.) Li Li Construction (Synthesis) heat heat Fe 2Li ether 2Li ether 2Li ether Li Li Li Li ether Li ether PCC C 2 Cl Li 3 + PCC Li C 2 Cl 2 ether Li 3 +
28 e. Design (Retrosynthesis) C 3 C 2 Li Li Construction (Synthesis) Li 2Li ether Li 2 Fe 2Li ether PCC Li 3 + C 2 Cl 2 ether Li (quench) Li dil. 2 S 4 (E 1 ) Li m-cpba ether C 2 Cl (quench) "steric control" (E/Z) isomers dil. 2 S 4 (E 1 ) major product : tetrasubstituted (E) isomer, alkene conjugated with ring
29 Chemistry 3720 Spectroscopy Problems - Key 1. (10 pts) An unknown organic compound has the molecular formula C 5 12, in the mass spectrum, M+ = Given the following 1 and 13 C data, give the structure of the unknown and assign all of the 1 and 13 C signals PPM NMR (ppm) 1.14 (t, 3, J = 7.2 z), 1.09 (d, 6, J = 7.0 z), 3.19 (septet, 1, J = 7.0 z), 3.50 (q, 2, J = 7.2 z) PPM C NMR (ppm) 15.5, 22.3 (double), 64.8, (d) 3 C 3 C 3.19 (sept) 3.50 (q) C 3 C 3 C (t)
30 2. (10 pts) Draw the approximate 13 C NMR spectrum of the following molecule. Include approximate chemical shifts and indicate which signal corresponds to which carbon(s) in the molecule C C PPM 3. (10 pts) A chemist produces a new compound with the following spectral characteristics and considers the new material to be one of the possibilities shown below. Which structure is correct and why? Include a complete assignment of all of the spectral data in your answer NMR (ppm) 1.43 (t, 3, J = 7.0 z), 3.47 (s, 3,), 4.11 (q, 2, J = 7.0 z), 4.76 (s, 2), 7.17 (m, 2), 7.83 (m, 2) 13 C NMR (ppm) 14.8, 57.2, 64.6, 81.2, 126.1, (double), (double), 163.8, IR (cm -1 ) 1740, C 3 C 3 C IR: 1740 = C=, 810 = para disubstitution 2
31 4. (10 pts) Draw the expected 1 and 13 C NMR spectra of the following molecules. Include chemical shifts and line shapes (singlet, doublet, etc.) in the 1 spectra and intensities in the 13 C spectra. Also indicate which signal corresponds to which proton(s) and carbon(s). a PPM PPM
32 b PPM PPM
33 c PPM PPM
34 d PPM PPM
35 5. (10 pts) An unknown organic compound has the molecular formula C Given the following spectral data, provide a structure for the unknown that agrees with the data, and then assign the data. 1 NMR (ppm) 2.50 (s, 3), 2.75 (t, 2, J = 7.2 z), 3.30 (s, 3), 2.52 (t, 2, J = 7.2 z), (m, 4) 13 C NMR (ppm) 26.6, 35.3, 59.3, 73.0, 126.0, 127.7, 128.5, 132.1, 1391, 139.2, Mass spectrum (m/z) (M+) Infra Red (cm -1 ) 1730, 760, NMR data C PPM C NMR data C PPM (m/z) (M+): this means that C is the actual formula of the unknown Infra Red (cm -1 ): 1730 corresponds to C=; 760, 690 correspond to meta substitution 7
36 6. (10 pts) An unknown organic compound has the molecular formula C and, in the mass spectrum, M+ = Given the following 1 and 13 C data, give the structure of the unknown and then assign all of the 1 signals. 1 NMR (ppm) 1.20 (d, 6, J = 7.0 z), 1.29 (t, 3, J = 7.1 z), 2.87 (septet, 1, J = 7.0 z), 4.30 (q, 2, J = 7.1 z), 7.41 (d, 2), 7.97 (d, 2) 13 C NMR (ppm) 14.1, 23.3 (double), 33.2, 60.9, (double), 127.3, (double), 155.7, NMR data PPM C NMR data PPM M+ = means that C is the actual formula of the compound 8
37 Chemistry 3720 Chapter 19 - Benzene Synthesis Problems - Key Provide an efficient synthesis of each of the following substituted benzenes from benzene itself. Use any of the reagents seen in Chemistry 3719/3720 so far and pay careful attention to the order of steps. Assume that mixtures may be separated. C 3 1. C 3 Cl, AlCl 3 2. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 Put C 3 on first then send next gr oup o/p major and separate the isomers 1. 2,Fe 2. C 3 Cl, AlCl 3 (separate from o-isomer) 3. KMn 4 C 2 and C 3 both o/ p dir ectors but C 3 is activating - probably a cleaner reaction (fewer over-substituted products if goes on fir st - have to oxidize last as -C 2 is a meta director 1. C 3 C 2 CCl, AlCl 3 2. N 3, 2 S 4 3. Sn, Cl 4. Zn, Cl N 2 Putting N 2 or the acyl group on f i rst would send the next gr oup to themetaposition(either woulddo) and then reduction would give the desired product 1. C 3 Cl, AlCl 3 2. S 3, 2 S 4 (separate from o-isomer) 3. KMn 4 S 3 C 2 Put C 3 on first (o/p director) then bringins 3 group (m director) - oxidize C 3 to C 2 (mdirector) C 3 1. C 3 Cl, AlCl 3 S 3 Introduce C 3 first (o/p director), separate isomers, then bring in 2. S 3, 2 S 4 S 3 group (m director) 1. C 3 Cl, AlCl 3 2. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 (separate from o-director) 3. KMn 4 Put C 3 on first (o/p director) then bring in acyl gr oup (m director) - separate from o-isomer - then oxidise the C 3 group to C 2
38 Chemistry 3720 Ch 1-23 Synthesis Problems Key These problems are typical of those that will be on the next exams in You should be comfortable with each reaction in the forward direction, how to think about each reaction in a retrosynthetic manner, and then be able to complete multi-step syntheses. 1. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following sets of reaction conditions and then a detailed mechanism for each reaction. Be careful with any regiochemical issues. a. Cl xs C 3 cat. + Cl C 3 C Cl C 3 C 3 ketone gives acetal C 3 Cl is completely unreactive under these conditions C 3 Cl Cl C 3 C 3 C 3 + trans. C 3-2 C 3 Cl Cl Cl Cl b. C 3 xs C 3 cat. + C 3 carb. acid gives ester - + C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 + trans. C C 3
39 c. C 2 C 2 cat R aldehyde gives acetal The aldehyde is much more reactive than the alkene under these conditions so the alkene survives + trans. - 2 d. C 3 C 3 xs C 3 cat. + C 3 C 3 C 3 ketone gives acetal - + C 3 C 3 C 3 ester could also react but overall there would be no net change (C 3 swapped for C 3 ) C 3 C 3 C 3 + trans. - 2 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3
40 e. R xs Et Et Et - + Et Et cat. + ketone gives acetal the bromide is completely unreactive under these reaction conditions Et + trans. Et - 2 Et Et Et Et f. Me xs Me cat. + Me Me Me - + Me Me Me Me ketone gives acetal the ester would not change overall even if it did react under these conditions Me Me Me Me Me Me Me + trans. Me Me - 2 Me Me Me
41 2. Give the major organic product(s) from each step of the following synthetic scheme. 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl ,Fe 3. C 2 C 2, cat. Ts 4. Mg, ether C=, ether 6. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 7. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 8. (C 3 ) 2 CLi, TF 9. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 10. PDC, C 2 Cl Mg, TF 12. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 13.Na,ether 14. C 2, ether 15. 5% Cl, 3 h, RT 16. NaB 4,C NaC 3,C m-cpba, C 2 Cl Mg, ether 21. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Mg Li Li Mg Na C 2 C C 2 C 2 Mg C C 2 C 2 C 2
42 3. In the boxes provided, give the products from each step in the following road-map scheme. Me PCC C 2 Cl 2 Me xs. Me cat. + Me Me Me 2C 3 Li TF C 3 Na Me NaN 2 Me 3 + Li Me Me Me Me TF Me Me Me (quench) Me Me Me Me Me 5% Cl Me Mg Me Mg 3 + Me Me Me TF Me Me TF Me Me (quench) Me m-cpba Me PCC Me Me Me C 2 Cl 2 Me Me C 2 Cl 2 Me Me 13 C=175ppm 4. Give retrosynthetic analyses for the following molecules that go back to the given starting materials, and then provide the synthesis in the forward direction. Assume you have access to the usual other reagents (, N 3, NaB 4, etc.) in the lab. a. Cl N 2 Mg N 2 N 2 N 2
43 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 Cl Synthesis Mg ether Mg Cl N 3 NaB 4 AlCl 3 2 S 4 C 3 3 P 4 m-cpba N 2 Mg Mg N 2 aq. N 4 Cl heat N 2 C 2 Cl 2 N 2 ether N 2 (quench) Na Na Sn TF TF Cl N 2 N 2 N 2 N 2
44 b. N N 2 Mg N 2 Mg Synthesis Mg ether Mg 3 P 4 heat m-cpba C 2 Cl 2 ether PCC 3 + Mg C 2 Cl 2 (quench) cat. + N 2 N
45 c. Mg Synthesis 2 Mg Mg Mg Fe ether ether NaB 4 aq. N 4 Cl (quench) C 3 cat. + Na 2 Cr S 4
46 Chemistry 3720 Chapters Synthesis Problems Key These problems are from various parts of 3719 and 3720 and deal with the two main synthetic issues studied; C-C bond formation and manipulation of functional groups. 1. Give the major organic product(s) from each of the following aldol reactions as well as a detailed mechanism for each case. Be careful with any regiochemical issues. a. Na, C 3, C 3 Intramolecular aldol is much faster than the intermolecular reaction, therefore a cycle is formed. Refluxing the mixture promotes loss of 2 in the final step and formation of the α,β-unsaturated product. There are two types of α- but loss of the other type would lead to an unstable 3-membered ring. b. K, C 3, C 3 Intermolecular aldol reaction is the only possibility here since there isn t a second carbonyl in the substrate. The use of K as base ensures that both some enolate and some of the starting ketone are present. Running these reactions at higher temp usually results in loss of 2, especially when conjugation is possible. c. K, Et, reflux R Again, intermolecular aldol reaction is the only possibility here since there isn t a second carbonyl in the substrate. The use of K as base ensures that both some enolate and some of the starting aldehyde are present. Carrying out these reactions at higher temp usually results in elimination of 2 to form α,β-unsaturated product. Et
47 d. Na, C 3, The intramolecular aldol is much faster than intermolecular reaction, therefore a cycle is formed. There are two types of α- in the starting material, however only one cyclization leads to a stable ring. Refluxing (boiling) the mixture promotes loss of 2 in the final step. C 3 e. K, Et reflux -Et The intramolecular aldol much faster than the intermolecular reaction, therefore a cycle is formed. There are several types of α- in the starting material; so several cyclization paths may be possible. The reaction is reversible and will yield the most stable product, the one shown. Refluxing the mixture promotes loss of 2 in the final step. f. Na, C 3, C 3 The intramolecular aldol much faster than the intermolecular reaction, therefore a cycle is formed. Two types of α- but only one pathway leads to a stable product, in this case a five-membered ring. Refluxing the mixture promotes loss of 2 in the final step.
48 2. Draw all of the possible aldol condensation products possible in the following reaction. + Na, 2 reflux A B Na C-A C-B + D-A D-B C D followed by protonation and elimination E F E-A E-B F-A F-B 3. Provide the reagents required to make each of the following compounds via 1,4-addition chemistry. CuLi 2 CuLi 2 CuLi 2
49 4. In the following Robinson annulation, 3 aldol products are possible; explain why only one is formed. Na, Since there are 3 different types of α- there are 3 different enolates possible here. The outcome of the reaction is governed by thermodynamics (i.e. stability) since the steps are reversible, therefore the most stable product will result. The enolate formed by removal of 1 would generate a bicylic system (somewhat strained), the one formed by removal of 2 would only afford a 4-membered ring (quite strained), whereas the enolate generated by removal of 3 would give the favourable 6-membered ring shown above. 5. Give the major products from each step of the following reaction sequences. a. 1. PCC, C 2 Cl m-cpba, C 2 Cl 2 b. 1. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 2 S 4 2. C 3, C 3 c P=C 2 C C ,Pd d. 1. m-cpba, C 2 Cl C 3 2. C 3, cat. +
50 6. Provide complete mechanisms for the following conversions. Include all resonance structures for any intermediates that may be formed. Na enol form keto form - + C 3, + C C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C3
51 7. Give structures for each of the products in the following roadmap. PCC C 2 Cl 2 Na, Et reflux Et 2 CuLi TF Na 2 Cr S 4, 2 aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Li xs C 3, + C 3 2Li ether Li aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 8. The polyether compound chauncydermolide G (shown below) was recently isolated by Triplet armaceuticals Inc. and found to have promising antibiotic properties. In order to prove the structure unequivocally, a total synthesis beginning with the shown starting material was carried out. Give structures for each of the products in the synthetic sequence. Li Na C 2 C 2 C 2 C C C C C C C C C C C 3 C 2 Mg C C C C Na
52 Li 18. Li C Mg Mg Na Me Me Me 33. Li Me Me Me Me Me
53 Chemistry 3720 Chapters Additional Synthesis Problems Key 1. Give retrosynthetic analyses for the following molecules that go back to the given starting materials, and then provide the synthesis in the forward direction. Assume you have access to the usual other reagents (, N 3, NaB 4, etc.) in the lab. a. Retrosynthesis C 2 X X =, Cl, C Mg C 2 Synthesis 2 Mg Mg Fe ether C 2 NaB 4 C 3 Mg xs dil. Cl (quench) cat. 2 S 4 If the alcohol is inexpensive and readily available then the Fischer esterification works well, however if the alcohol is expensive, it is better to convert the carboxylic acid to the acid chloride (X = Cl) using SCl 2 /pyridine or the anhydride (X = C) by heating and removing 2. Both of these reactive carboxylic acid derivatives require 1 equivalent of alcohol to give the ester (with pyridine as a base).
54 b. Retrosynthesis Synthesis Na 2 Cr S 4 heat (- 2 ) The most straightforward way to make an anhydride from a volatile (i.e. easily distillable) carboxylic acid is to heat it up with a small amount of a mineral acid and remove the water that is formed. You could also form the acid chloride from a portion of the carboxylic acid (using SCl 2 /pyridine) and then react that with more of the remaining carboxylic acid. c. Retrosynthesis Synthesis dil. 2 S 4 Na 2 Cr 2 7 m-cpba 2 S 4 C 2 Cl 2 All of the required carbon atoms for the product are found in the given starting material, which needs to be manipulated to introduce oxygen. The system has to be oxidized to produce the lactone (cyclic ester) so the Baeyer-Villager oxidation is appropriate.
55 d. Retrosynthesis C 3 C 3 C 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 C 3 C 2 C 2 C 3 Synthesis Na 2 Cr S 4 C 2 C 2 xs C 3 cat. 2 S 4 C 2 C 3 C 2 C 3 NaC 3 C 3 dil Cl C 3 (quench) C 3 e. Retrosynthesis N C 3 N Cl N 2 C 3 2 C= Li N 2
56 Synthesis C 3 PCC C 2 Cl 2 2 C= Li 2Li TF Li aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Na 2 Cr S 4 N 3 N 2 Sn N 2 SCl 2 pyridine 2 S 4 Cl Cl pyridine N 2. Give the major organic product(s) from each step of the following synthetic sequence. 1. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 2. xs C 3,cat. 2 S 4 3. NaC 3,C 3 4. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) C 3 3. C 3 5. NaC 3,TF 6. C 3 C 2 7. Na, aq. TF 8. dil. Cl (quench) o C (-C 2 ) 10.LDA,TF,-78 o C 11. C C 3 C C 3 Na Li 11.
57 3. In the boxes provided, give the products from each step in the following road-map scheme. Predict the 1 NMR spectra of each of the organic products from each step. 2 Mg Mg Fe ether C 2 C 2 C 3 xs C 3 C 2 dil. Cl C 2 Mg N 3 2 S 4 cat. 2 S 4 (quench) C 2 C 3 2xC 3 Li Li aq. N 4 Cl TF N 2 N 2 (quench) N 2 Na TF C 3 Sn, Cl C 3 C 3 Na N 2 N 2 N Mg PPM PPM Mg PPM PPM 4 2 0
58 N PPM PPM 2 0 Li N N PPM PPM 2 0 Na N N PPM PPM N PPM Give complete mechanisms, including any important resonance structures for intermediates where applicable, that explain the bond-making and bond-breaking events in the following conversions. a. 3 C 3 C C 3 C 3 C 3 1. NaC 3,C 3 2. dilute Cl (quench) 3. NaC 3,TF 4. C 2 5. Na, aq. TF 6. dilute Cl (quench) o C(-C 2 ) 3 C C 3 C 3 C 3 3 C 3 C contd...
59 2 3 C 3 C 3 C C 3 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 2 tautomerism
60 b. 1. Na 2 Cr 2 7, 2 S 4 2. xs C 3, cat. Cl 3. NaC 3,C 3 4. dilute Cl (quench) 5. Na, aq. TF 6. dilute Cl (quench) Na 2 Cr S 4 2 Cr Cr Cr Cr chromic acid C 2 R C 2 R Cr Cr R 2 2 Cr C 2 R Cr C 2 R C 2 R Cr 2 2 R 2 R 2 R CR Cr 2 CR Cr Cr R 2 Cr CR Cr CR Cr R 3 C R C 3 R R 2 C 3 C 3 3 C R 2 R C 3 R C 3 C 3 contd...
61 C 3 C 3 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 C 3 C 3 2 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 C 3 2 C 3
62 Chemistry 3720 Further Synthesis Problems 1 - Key 1. Give retrosynthetic analyses for the following molecules that go back to the given starting materials, and then provide the synthesis in the forward direction. Assume you have access to the usual other reagents (, N 3, NaB 4, etc.) in the lab. a. Retrosynthesis P 3 3 P 3 P P 3 Synthesis P 3 ether 3 P PCC n-buli TF C 2 Cl 2 3 P It would also be possible to use organometallic chemistry in this synthesis (e.g. turn one piece into a Grignard reagent and then add to a ketone, followed by acid-catalyzed elimination), however that might not give you this alkene as the major isomer in the elimination step. The Wittig route puts the double bond in the right place without any complications. 1
63 b. Retrosynthesis Mg Synthesis Mg Mg Mg ether PCC aq. N 4 Cl (quench) C 2 Cl 2 3 P 4 80 o C ne could also make the Grignard reagent from the cyclopentanol and the ketone from the isopropanol or even use Wittig chemistry here. Since the product is the most highly substituted alkene anyway, both methods work. c. Retrosynthesis Cl Cl 2
64 Synthesis Cl LDA Li AlCl 3 TF, -78 o C NaB 4 C 3 The limitation here is the starting materials that are given; the 2-carbon alcohol limits what type of chemistry can be applied and the only logical way really is to recognize that the alpha-carbon of the ketone may be deprotonated to form the nucleophilic enolate. d. Retrosynthesis Synthesis PCC C 2 Cl 2 PCC C 2 Cl 2 Na, Et reflux Logical to use crossed-aldol here since the alkene is alpha to the ketone carbonyl. eating ensures elimination. 3
65 e. Retrosynthesis Li Synthesis PCC Na C 2 Cl 2 Et, 2Li ether Li aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Li Given the two alcohols here the logical first disconnection is the ethyl group, which reveals a 6-carbon fragment that is then accessible by a simple intermolecular aldol reaction. eating the aldol step ensures that elimination occurs to give the required α,β-unsaturated product. 2. Give the major organic product(s) from each step of the following synthetic scheme. 1. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 2. Na, Et, reflux 3. (C 3 ) 2 CuLi, ether 4. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Li 5. Mg, ether 6. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) 7. NaN 2,TF 8. C 3 4. Mg Na C
66 3. In the boxes provided, give the products from each step in the following road-map scheme. PCC C 2 Cl 2 Mg TF Mg aq. N 4 Cl (quench) aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Li (C 3 ) 2 CuLi TF PCC C 2 Cl 2 2 CCl 3 NaC 3 C 3 (C 3 ) 2 CuLi TF NaB 4 C 3 aq. N 4 Cl (quench) Li 4. Give complete mechanisms, including any important resonance structures for intermediates where applicable, that explain the bond-making and bond-breaking events in the following conversions. a. R 1. m-cpba, C 2 Cl Mg, TF 3. aq. N 4 Cl (quench) CAr Ar Ar δ- δ+ Mg Mg Mg Mg δ- δ+ Mg Mg 5
67 b. 1. N 3, 2 S 4 2. LDA, TF, -78 o C aq. N 4 Cl (quench) N 2 3 S N 2 N - 2 N N 2 2 N 2 N 2 N 2 N(i-Pr) 2 N 2 Li N 3 N 2 N 2 N 2 6
68 Chemistry 3720 Practice Exams and Answer Keys
69 Chemistry 3720 Practice Exam 1 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use the attached spectroscopy sheet as needed. Good Luck. 1. (8 pts) Give the major final products from the following and explain the different regiochemical outcomes in terms of the mechanism(s) operating. (Klein Chapter 14) a. 1. Mg, ether (quench) b. C 3 catalytic + 1
70 2. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s), including any stereochemical issues, expected from each step in the following reactions. You do not have to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapters 13 and 14) a. 1. C 3 Mg, ether 2. + quench 3. 2,Pd b P 4, heat 2. m-cpba, C 2 Cl 2 3. Na, 2 c. 1. N+ [( 3 Cr) 2 ] LiAlD 4, ether 3. aq. N 4 Cl d. 1. NaB 4,C 3 2. NaN 2,TF 3. C 3 C 2 C 2 S e. 1. NaC 3,TF (C 3 ) 2 C 3. xs 2 2, aq. TF 2
71 3. (16 pts) Give the expected major product from each step of the following reaction sequence. No need to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapter 13) 4. (9 pts) Give the expected final product(s) formed in each of the following cases. (Klein Chapter 14) a. excess b. excess c. excess I 3
72 5. (7 pts) Give the expected major product formed under the following reaction conditions, and then a detailed mechanism for the conversion. ow would you tell the product is an alcohol by IR spectroscopy? (Klein Chapters 13-15) 6. (8 pts) A recently isolated microbial metabolite is found to have the empirical formula C 4 7 and its mass spectrum shows M + = 142. Significant signals are seen in the IR spectrum at 1740 and 1650 cm -1. The 1 NMR spectrum, collected in CDCl 3, is given below. Provide a structure for the organic compound that matches the data, and then match the protons in the molecule to the 1 NMR signals. (Klein Chapter 15) Unsaturation number = [#C atoms ½# atoms ½#alogen atoms + ½#N atoms] NMR (ppm): 1.06 (d, 6, J = 7.1 z), 1.36 (t, 3, J = 7.0 z), 2.52 (octet, 1, J = 7.1 z), 4.20 (q, 2, J = 7.0 z), 5.83 (d, 1, J = 16.0 z), 6.88 (dd, 1, J = 7.1, 16.0 z) 4
73 7. (12 pts) Provide a retrosynthetic plan for the molecule below that uses only the given starting materials as sources of carbon. Then give a detailed synthesis of the compound that shows each product formed along the way. You have access to all of the usual reagents in the lab (, N 3, NaB 4, Zn, Mg, etc.), as well as techniques for separating isomers and byproducts (i.e. distillation, chromatography, etc.) as needed. (Klein Chapters 13-14) from and 5
74 8. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s) expected from each step in the following reactions. You do not have to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapters 13 and 14) a. 1. NaB 4,C 3 2. P 3 3. NaN 3,DMS b. Cl 1. Mg, ether 2. C 3 C 3. dil. aq. N 4 Cl c S 4, 2. s 4, 2 2,Na 3. I 4 d. 1. 2, 2 2. NaN 2,TF 3. NaSC 3,DMF e. 1. LiAl 4, ether 2. dil. aq. N 4 Cl 3. C 3 CCl, pyridine 6
75 Chemistry 3720 Practice Exam 1 - Key Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use the attached spectroscopy sheet as needed. Good Luck. 1. (8 pts) Give the major final products from the following and explain the different regiochemical outcomes in terms of the mechanism(s) operating. (Klein Chapter 14) 1
76 2. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s), including any stereochemical issues, expected from each step in the following reactions. You do not have to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapters 13 and 14) a. 1. C 3 Mg, ether 1. 3 C Mg 3 C C 2. + quench 3. 2,Pd racemic b P 4, heat m-cpba, C 2 Cl 2 3. Na, 2 meso racemic c. 1. N+ [( 3 Cr) 2 ] - 2 D AlR D 2. LiAlD 4, ether 3. aq. N 4 Cl racemic racemic d. 1. NaB 4,C 3 2. NaN 2,TF 3. C 3 C 2 C 2 Na e. S 1. NaC 3,TF 1. SNa 2. SC(C 3 ) 2 3. S 2 C(C 3 ) 2 2. (C 3 ) 2 C 3. xs 2 2, aq. TF 2
77 3. (16 pts) Give the expected major product from each step of the following reaction sequence. No need to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapter 13) 4. (9 pts) Give the expected final product(s) formed in each of the following cases. (Klein Chapter 14) a. excess + b. excess c. excess I I I + 3
78 5. (7 pts) Give the expected major product formed under the following reaction conditions, and then a detailed mechanism for the conversion. ow would you tell the product is an alcohol by IR spectroscopy? (Klein Chapters 13-15) The product would have a broad absorption at ~3600 cm 1 in the IR spectrum 6. (8 pts) A recently isolated microbial metabolite is found to have the empirical formula C 4 7 and its mass spectrum shows M + = 142. Significant signals are seen in the IR spectrum at 1740 and 1650 cm -1. The 1 NMR spectrum, collected in CDCl 3, is given below. Provide a structure for the organic compound that matches the data, and then match the protons in the molecule to the 1 NMR signals. (Klein Chapter 15) Unsaturation number = [#C atoms ½# atoms ½#alogen atoms + ½#N atoms] Unsat = = PPM 1 NMR (ppm): 1.06 (d, 6, J = 7.1 z), 1.36 (t, 3, J = 7.0 z), 2.52 (octet, 1, J = 7.1 z), 4.20 (q, 2, J = 7.0 z), 5.83 (d, 1, J = 16.0 z), 6.88 (dd, 1, J = 7.1, 16.0 z) 0 4
79 7. (12 pts) Provide a retrosynthetic plan for the molecule below that uses only the given starting materials as sources of carbon. Then give a detailed synthesis of the compound that shows each product formed along the way. You have access to all of the usual reagents in the lab (, N 3, NaB 4, Zn, Mg, etc.), as well as techniques for separating isomers and byproducts (i.e. distillation, chromatography, etc.) as needed. (Klein Chapters 13-14) 5
80 8. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s) expected from each step in the following reactions. You do not have to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapters 13 and 14) a. 1. NaB 4,C 3 N P 3 3. NaN 3,DMS racemic racemic racemic b. Cl 1. Mg, ether ClMg 1. MgCl C 3 C 3. dil. aq. N 4 Cl racemic racemic c S 4, 2. s 4, 2 2,Na 3. I C racemic d. 1. 2, 2 2. NaN 2,TF 3. NaSC 3,DMF SC 3 Na racemic meso racemic e. 1. LiAl 4, ether 1. AlR dil. aq. N 4 Cl 3. C 3 CCl, pyridine racemic racemic racemic 6
81 Chemistry 3720 Practice Exam 2 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use the attached spectroscopy sheet as needed. Good Luck. Unsaturation number = [#C atoms ½# atoms ½#alogen atoms + ½#N atoms] (10 pts) Give the expected major product(s) from the following nitration reaction, and then give a complete mechanism for the conversion that includes resonance structures for the intermediate(s) formed. Explain why you only get certain isomer(s) as the major product(s) in this reaction. (Klein Chapter 19) 1
82 2. (8 pts) Give the structure of an unknown organic compound with the formula C and the following spectral characteristics, and then match the 1 signals to your structure: 1 NMR (CDCl 3 ): 0.90 (t, 3, J = 7.0 z), 1.14 (d, 6, J = 6.9 z), 1.73 (sextet, 2, J = 7.0 z), 2.67 (septet, 1, J = 6.9 z), 4.13 (t, 2, J = 7.0 z) 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): 10.3 (q), 19.1 (q, double intensity), 21.9 (t), 34.0 (d), 66.5 (t), (s) (Klein Chapter 16) 3. (10 pts) Provide the expected major product(s) from the following reaction, and then give a complete mechanism for the process that includes any important resonance structures. (Klein Chapter 19) C 2 2,Fe 3 2
83 4. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s) expected from each step in the following reaction sequences. You do not have to show any mechanisms here. (Klein Chapters 17-19) a C=CC 2 Et 2. LiAl 4, ether 3. + (quench) b. 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 2. Zn, Cl 3. 2, heat c. 1. (C 3 ) 3 CCl, AlCl ,Fe Li, ether 4. D 2 d. 1. S 3, 2 S 4 2. Cl 2, AlCl 3 3. Na e. 1. (C 3 ) 2 CCl, AlCl ,Fe 3 3. N 3, 2 S 4 4. NaC 3,C 3 3
84 5. (12 pts) Provide syntheses of the compounds below, starting from benzene, that show each product formed along the way. You have access to all of the usual reagents in the lab (e.g. N 3, 2, Na, AlCl 3, etc.), as well as techniques for separating any isomers and byproducts as needed. (Klein Chapter 19) a. C 2 N 2 b. C(C 3 ) 2 6. (12 pts) Give the products from each step of the following synthetic sequence and then, on the NMR axis given below, draw the expected 1 spectrum of the final product. (Klein Chapters 13 and 16) 4
85 7. (12 pts) Consider the following reaction and then answer the questions below related to the mechanism. (Klein Chapter 17) Draw a reaction profile (on the axes given below) that describes energy changes during the reaction. Energy Reaction coordinate In the space below, draw diagrams of all transition states and reactive intermediates (including resonance structures), and indicate where they appear on the graph above. Indicate the rate-determining step, and label that step as unimolecular or bimolecular. Finally, explain why the major product is formed here. 5
86 8. (10 pts) Provide a retrosynthetic plan for the molecule shown that goes back only to the organic compounds provided, and then show how you would build the molecule using chemistry seen in 3719 and (Klein Chapter 19) 9. (6 pts) Indicate which of the following molecules are aromatic and explain your choices based on applying ückels rule. (Klein Chapter 16) 6
87 Chemistry 3720 Practice Exam 2 Key Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use the attached spectroscopy sheet as needed. Good Luck. Unsaturation number = [#C atoms ½# atoms ½#alogen atoms + ½#N atoms] (10 pts) Give the expected major product(s) from the following nitration reaction, and then give a complete mechanism for the conversion that includes resonance structures for the intermediate(s) formed. Explain why you only get certain isomer(s) as the major product(s) in this reaction. (Klein Chapter 19) 1
88 2. (8 pts) Give the structure of an unknown organic compound with the formula C and the following spectral characteristics, and then match the 1 signals to your structure: (Klein Chapter 16) 1 NMR (CDCl 3 ): 0.90 (t, 3, J = 7.0 z), 1.14 (d, 6, J = 6.9 z), 1.73 (sextet, 2, J = 7.0 z), 2.67 (septet, 1, J = 6.9 z), 4.13 (t, 2, J = 7.0 z) 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): 10.3 (q), 19.1 (q, double intensity), 21.9 (t), 34.0 (d), 66.5 (t), (s) a = 0.90 (t, 3, J = 7.0 z) b = 1.73 (sextet, 2, J = 7.0 z) c = 4.13 (t, 2, J = 7.0 z) d = 1.14 (d, 6, J = 6.9 z) e = 2.67 (septet, 1, J = 6.9 z) 3. (10 pts) Provide the expected major product(s) from the following reaction, and then give a complete mechanism for the process that includes any important resonance structures. (Klein Chapter 19) C 2 C 2 Fe 3 Fe 3 Fe 3 C 2 C 2 C 2 Fe 3 2
89 4. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s) expected from each step in the following reaction sequences. You do not have to show any mechanisms here. (Klein Chapters 17-19) a C=CC 2 Et 2. LiAl 4, ether 3. + (quench) Et 2 C LiC 2 C 2 b. C 3 C 3 C 3 1. C 3 CCl, AlCl 3 2. Zn, Cl 3. 2, heat c. C(C 3 ) 3 C(C 3 ) 3 C(C 3 ) 3 C(C 3 ) 3 1. (C 3 ) 3 CCl, AlCl ,Fe Li, ether 4. D Li 4. D d. 1. S 3, 2 S 4 S 3 S 3 S 3 Na 2. Cl 2, AlCl 3 3. Na Cl 3. Cl e. 1. (C 3 ) 2 CCl, AlCl ,Fe 3 1. C(C 3 ) 2 2. C(C 3 ) 2 3. C(C 3 ) 2 4. C(C 3 ) 2 3. N 3, 2 S 4 4. NaC 3,C 3 N 2 C 3 N 2 3
90 5. (12 pts) Provide syntheses of the compounds below, starting from benzene, that show each product formed along the way. You have access to all of the usual reagents in the lab (e.g. N 3, 2, Na, AlCl 3, etc.), as well as techniques for separating any isomers and byproducts as needed. (Klein Chapter 19) 6. (12 pts) Give the products from each step of the following synthetic sequence and then, on the NMR axis given below, draw the expected 1 spectrum of the final product. (Klein Chapters 13 and 16) 4
91 7. (12 pts) Consider the following reaction and then answer the questions below related to the mechanism. (Klein Chapter 17) Draw a reaction profile (on the axes given below) that describes energy changes during the reaction. In the space below, draw diagrams of all transition states and reactive intermediates (including resonance structures), and indicate where they appear on the graph above. Indicate the rate-determining step, and label that step as unimolecular or bimolecular. Finally, explain why the major product is formed here first step T.S. intermediate second step T.S. - First step is R.D.S. and it is bimolecular (diene and are involved); major product is the thermodynamic outcome since reaction is reversible at higher temperatures and more substituted alkene is favoured. 5
92 8. (8 pts) Provide a retrosynthetic plan for the molecule shown that goes back only to the organic compounds provided, and then show how you would build the molecule using chemistry seen in 3719 and (Klein Chapter 19)? and Retrosynthesis Li Synthesis Li 2Li C Li N 4 Cl ether ether 9. (6 pts) Indicate which of the following molecules are aromatic and explain your choices based on applying ückels rule. (Klein Chapter 16) N 1=No 2=Yes 3=Yes For 1 : 8 pi electrons so 4n+2 = 8 ; n = 3/2 ; not lat, not aromatic For 2 : 6 pi electrons so 4n+2 = 8 ; n = 1 ; flat and aromatic For 3 : 6 pi electrons so 4n+2 = 8 ; n = 1 ; flat and aromatic 6
93 Chemistry 3720 Practice Exam 3 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam. Good Luck. 1. (8 pts) Provide a complete mechanism, including all important resonance structures, for the following: (Klein Chapter 22) 1
94 2. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s), including any stereochemical issues, expected from each step in the following reactions. You do not have to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapters 20-22) a. 1. xs C 3,cat Sn, Cl N 2 b. 1. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 2. xs Na, xs I 2 c. 1. SCl 2,pyridine 2. NEt 2, pyridine d P=C 2,TF 2. 2,Pd e. 1. LDA, TF 2. C 3 C 2 C 2 2
95 3. (14 pts) Provide the major organic product from each step of the following synthetic sequence (in the boxes provided). The spectroscopic clues along the way might help. (Klein Chapters 13-22) (C 3 ) 2 CuLi 3 + TF (quench) IR : 1700 cm -1 C 3 Mg TF Na 2 Cr S (quench) IR : 1700 cm -1 IR : 3200 cm -1 Mg TF 3 + (quench) Final product: Molecular formula = C IR : 1700 cm (6 pts) Number the following compounds in order of their decreasing reactivity with nucleophiles; 1 = most reactive, 3 = least reactive. Then explain your reasoning. (Klein Chapter 21) 3
96 5. (8 pts) Provide a complete mechanism that describes the following conversion. Include all resonance structures for any intermediates that are formed. (Klein Chapter 21) 6. (8 pts) Provide a complete mechanism for the following annulation that includes any important resonance structures along the way. (Klein Chapter 22) 4
97 7. (8 pts) Provide a retrosynthetic analysis for the following molecule that leads back only to 1-propanol as the source of carbon. Then show an actual synthesis in the forward direction. (Klein Chapters 13-22) 8. (8 pts) Provide a complete mechanism for the following ester saponification sequence: (Klein Chapter 21) i. K, Et, ii. dilute aq. Cl + 5
98 9. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s) expected from each step in the following reactions. You do not have to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapters 20-22) a in 2 2. NaCN in DMF b. 1. Mg, TF 2. dilute Cl (quench) c C 3 Mg, TF 2. dilute Cl (quench) d. 1. N 2 N 2,cat K, heat e. 1. excess NaD/D 2 2. NaBD 4,C 3 D 6
99 Chemistry 3720 Practice Exam 3 - Key Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam. Good Luck. 1. (8 pts) Provide a complete mechanism, including all important resonance structures, for the following: (Klein Chapter 22) Et Et 1. NaEt, Et 2. + (quench) Et Et Et Et Et Et + Et Et Et Et Et Et Et Dieckmann Cyclization 1
100 2. (20 pts) Give the major organic product(s), including any stereochemical issues, expected from each step in the following reactions. You do not have to show any mechanisms. (Klein Chapters 20-22) a. 1. xs C 3,cat C 3 C 3 2. Sn, Cl N 2 N 2 N 2 b. 1. PCC, C 2 Cl 2 2. xs Na, xs I Na + CI 3 c. 1. SCl 2, pyridine 2. NEt 2, pyridine Cl NEt 2 d P=C 2,TF C C 2 C ,Pd e. 1. LDA, TF Li C 3 C 2 C 2 N 2 N 2 2
Chemistry 3720, Spring 2004 Exam 3 Name:
 Chemistry 3720, Spring 2004 Exam 3 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use the spectroscopy data
Chemistry 3720, Spring 2004 Exam 3 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3720/3720L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use the spectroscopy data
Chemistry 3720 Old Exams. Practice Exams & Keys
 Chemistry 3720 ld Exams Practice Exams & Keys 2015-17 Spring 2017 Page File 3 Spring 2017 Exam 1 10 Spring 2017 Exam 1 Key 16 Spring 2017 Exam 2 23 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Key 29 Spring 2017 Exam 3 36 Spring
Chemistry 3720 ld Exams Practice Exams & Keys 2015-17 Spring 2017 Page File 3 Spring 2017 Exam 1 10 Spring 2017 Exam 1 Key 16 Spring 2017 Exam 2 23 Spring 2017 Exam 2 Key 29 Spring 2017 Exam 3 36 Spring
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
THE UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 350
 Page 1 of 16 TE UNIVERSITY F CALGARY FACULTY F SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATIN CEMISTRY 350 April, 1997 Time: 3 ours PLEASE WRITE YUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER AND SECTIN NUMBER (01 for MWF lectures and 02 for
Page 1 of 16 TE UNIVERSITY F CALGARY FACULTY F SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATIN CEMISTRY 350 April, 1997 Time: 3 ours PLEASE WRITE YUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER AND SECTIN NUMBER (01 for MWF lectures and 02 for
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
A. B. C. D. 2. Which compound does not give a stable Grignard reagent when reacting with Mg metal?
 Practice Test, Chemistry 2220 Final Exam 1. Which structure has the MST signals for its proton NMR? 2. Which compound does not give a stable Grignard reagent when reacting with Mg metal? 3. Which of these
Practice Test, Chemistry 2220 Final Exam 1. Which structure has the MST signals for its proton NMR? 2. Which compound does not give a stable Grignard reagent when reacting with Mg metal? 3. Which of these
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM # 2 November 02, The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck!
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
Chem Final Examination August 7, 2004
 Chem 281 2004-2 Final Examination August 7, 2004 Name: Student Number: Note: You are allowed to use models for this exam. Notes, textbooks and calculators are strictly prohibited. Write your final answers
Chem 281 2004-2 Final Examination August 7, 2004 Name: Student Number: Note: You are allowed to use models for this exam. Notes, textbooks and calculators are strictly prohibited. Write your final answers
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
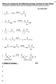 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Score: Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320N Due Monday, April 17. NAME (Print): Chemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 9th Homework April 10, 2017
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Name: Student Number:
 Page 1 of 5 Name: Student Number: l University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CEM 2220 - Introductory rganic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 14, 2008 This is a 2-hour test, marked
Page 1 of 5 Name: Student Number: l University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CEM 2220 - Introductory rganic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 14, 2008 This is a 2-hour test, marked
THE UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353
 TE UNIVERSITY F CALGARY FACULTY F SCIENCE FINAL EAMINATIN CEMISTRY 353 April 25 th, 2000 Time: 3 ours PLEASE WRITE YUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER AND SECTIN NUMBER (01 for MWF lectures and 02 for TR lectures)
TE UNIVERSITY F CALGARY FACULTY F SCIENCE FINAL EAMINATIN CEMISTRY 353 April 25 th, 2000 Time: 3 ours PLEASE WRITE YUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER AND SECTIN NUMBER (01 for MWF lectures and 02 for TR lectures)
Chemistry Organic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis FINAL EXAM Winter 2003
 Name: Student No: Page 1 of 13 Chemistry 2.222 rganic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis FINAL EXAM Winter 2003 Paper Number 546 Thursday April 24, 2003 6:00 9:00 pm Frank Kennedy own Gym Students
Name: Student No: Page 1 of 13 Chemistry 2.222 rganic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis FINAL EXAM Winter 2003 Paper Number 546 Thursday April 24, 2003 6:00 9:00 pm Frank Kennedy own Gym Students
I pledge my honor that I have neither given nor received aid on this examination
 Chemistry 220b, Section 1 Exam 1 (100 pts) Tuesday, February 3, 2015 Chapters 13, 15, 16 Name Write and sign the VU onor Pledge: I pledge my honor that I have neither given nor received aid on this examination
Chemistry 220b, Section 1 Exam 1 (100 pts) Tuesday, February 3, 2015 Chapters 13, 15, 16 Name Write and sign the VU onor Pledge: I pledge my honor that I have neither given nor received aid on this examination
(2) After dissolving a solid in a solvent at high temperature, the solution is not filtered.
 Name Key 216 W13-Exam No. 1 Page 2 I. (10 points) The goal of recrystallization is to obtain purified material with a maximized recovery. For each of the following cases, indicate as to which of the two
Name Key 216 W13-Exam No. 1 Page 2 I. (10 points) The goal of recrystallization is to obtain purified material with a maximized recovery. For each of the following cases, indicate as to which of the two
Carbonyl Chemistry. aldehydes ketones. carboxylic acid and derivatives. Wednesday, April 29, 2009
 Carbonyl Chemistry X aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid and derivatives Electrophiles (eg. + ) Nucleophiles (eg. C 3 MgBr) an enolate Base β β β α α α 1 2 3 4 Nuc- 1 2 Nuc 3 4 1,2-addition 1 2 3 4 Nuc-
Carbonyl Chemistry X aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid and derivatives Electrophiles (eg. + ) Nucleophiles (eg. C 3 MgBr) an enolate Base β β β α α α 1 2 3 4 Nuc- 1 2 Nuc 3 4 1,2-addition 1 2 3 4 Nuc-
Luckily this intermediate has three saturated carbons between the carbonyls, which again points to a Michael reaction:
 Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
Answers to Hour Examination #3, Chemistry 302X, 2006
 Answers to our Examination #, Chemistry 02X, 2006 1. (a). That SN2 shown just can t happen with the required inversion. The back of that methyl group is not reachable by the putative nucleophile, the pi
Answers to our Examination #, Chemistry 02X, 2006 1. (a). That SN2 shown just can t happen with the required inversion. The back of that methyl group is not reachable by the putative nucleophile, the pi
Organic Chemistry II (CHE ) Final Examination April 30, Name (Print legibly):
 rganic hemistry II (E 232-002) Final Examination April 30, 2007 Name (Print legibly): (last) (first) PLEASE observe the following: You are allowed to have scratch paper (provided by me), and a simple model
rganic hemistry II (E 232-002) Final Examination April 30, 2007 Name (Print legibly): (last) (first) PLEASE observe the following: You are allowed to have scratch paper (provided by me), and a simple model
1. (6 points) Provide IUPAC accepted names for the following compounds. 2. (6 points) Provide a structure for the following compounds.
 Chem52 omework Set 1 This homework set is similar to a Chem 51 final exam. Please provide answers in the spaces provided or, preferably, on attached sheets. Point values are listed only to give you the
Chem52 omework Set 1 This homework set is similar to a Chem 51 final exam. Please provide answers in the spaces provided or, preferably, on attached sheets. Point values are listed only to give you the
NH 2 O O O O OCH (6 pts) Provide an acceptable name for each of the following compounds: NH 2 COOH HOOC COOH. piperidine
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 1, 2003 Statistics: Average: 87 pts (72%); ighest: 116 pts (97%); Lowest: 49 pts (41%) umber of students performing at or above average: 13 (62%) 1. (9 pts) Mark as true
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 1, 2003 Statistics: Average: 87 pts (72%); ighest: 116 pts (97%); Lowest: 49 pts (41%) umber of students performing at or above average: 13 (62%) 1. (9 pts) Mark as true
c. Oxidizing agent shown here oxidizes 2º alcohols to ketones and 1º alcohols to carboxylic acids. 3º alcohols DO NOT REACT.
 Exam 1 (Ch 17 and Review of CEM 331) Answer Key: 1. ne-step Questions: You need to know reagents for reagent arrows and to be able to draw products. I know a lot of them seem to look alike its your job
Exam 1 (Ch 17 and Review of CEM 331) Answer Key: 1. ne-step Questions: You need to know reagents for reagent arrows and to be able to draw products. I know a lot of them seem to look alike its your job
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
CHEM 2220 Organic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis Prof. P.G. Hultin. FINAL EXAM Winter Session 2017R
 CHEM 2220 Organic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis Prof. P.G. Hultin FINAL EXAM Winter Session 2017R Tuesday April 25, 2017 8:00 am 11:00 am Frank Kennedy Gold Gym PRINT LEGIBLY PLEASE Name: Student
CHEM 2220 Organic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis Prof. P.G. Hultin FINAL EXAM Winter Session 2017R Tuesday April 25, 2017 8:00 am 11:00 am Frank Kennedy Gold Gym PRINT LEGIBLY PLEASE Name: Student
Chemistry Organic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis ANSWERS FOR FINAL EXAM Winter 2004
 ASWER KEY Page 1 of 18 Chemistry 2.222 rganic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis ASWERS FR FIAL EXAM Winter 2004 Paper umber 631 Thursday April 22, 2004 1:30 4:30 pm University Centre Rm 210-224 Students
ASWER KEY Page 1 of 18 Chemistry 2.222 rganic Chemistry II: Reactivity and Synthesis ASWERS FR FIAL EXAM Winter 2004 Paper umber 631 Thursday April 22, 2004 1:30 4:30 pm University Centre Rm 210-224 Students
CHAPTER 22 HW: CO 2 H DERIVATIVES
 APTER 22 W: 2 DERIVATIVES MELATURE 1. Give the name for each compound (IUPA or common name). Use R/S naming where needed. Structure 2 3 1 3 ame 2,2-dimethylpropanoyl chloride (R)-3-methylpentanoyl bromide
APTER 22 W: 2 DERIVATIVES MELATURE 1. Give the name for each compound (IUPA or common name). Use R/S naming where needed. Structure 2 3 1 3 ame 2,2-dimethylpropanoyl chloride (R)-3-methylpentanoyl bromide
CHEM 303 Organic Chemistry II Exam II 11-April-2006 Answers
 CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Exam II 11-April-2006 Answers 1) Compound D, C 8 14, is converted by C 2 =PPh 3 into E, C 9 16. Treatment of D with LiAl 4 yields two isomeric products, F and G, both of formula
CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Exam II 11-April-2006 Answers 1) Compound D, C 8 14, is converted by C 2 =PPh 3 into E, C 9 16. Treatment of D with LiAl 4 yields two isomeric products, F and G, both of formula
CHEMISTRY Topic #8: Oxidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #8: xidation and Reduction Reactions Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay xidation States of Carbon Carbon can have any oxidation state from -4 (C 4 ) to +4 (C 2 ). As a general rule, increasing
235 Organic II. Final Exam Review REACTIONS OF CONJUGATED DIENES 1,2 VS 1,4 ADDITION REACTIONS OF CONJUGATED DIENES
 b. the ompound 7 i 1 Spectral Data: singlet, 196.5 ppm singlet, 14.1 ppm singlet, 14.4 ppm doublet, 19.1 ppm doublet, 18.5 ppm 1 MR Mass Spectrum Absorbance Intensity Infrared Spectrum 65 91 9. Structure:
b. the ompound 7 i 1 Spectral Data: singlet, 196.5 ppm singlet, 14.1 ppm singlet, 14.4 ppm doublet, 19.1 ppm doublet, 18.5 ppm 1 MR Mass Spectrum Absorbance Intensity Infrared Spectrum 65 91 9. Structure:
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
2.222 Introductory Organic Chemistry II Midterm Exam
 NAME: STUDENT NUMBE: Page 1 of 7 University of Manitoba Department of hemistry 2.222 Introductory rganic hemistry II Midterm Exam Wednesday February 20, 2002 Put all answers in the spaces provided. If
NAME: STUDENT NUMBE: Page 1 of 7 University of Manitoba Department of hemistry 2.222 Introductory rganic hemistry II Midterm Exam Wednesday February 20, 2002 Put all answers in the spaces provided. If
Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386)
 Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
Chemistry 242 Organic Chemistry II Spring Term 2012 Dr. Williams (309 Zurn, ex 2386) Web Page: http://math.mercyhurst.edu/~jwilliams/ jwilliams@mercyhurst.edu (or just visit Department web site and look
Organic Chemistry CHM 224
 rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
CHEMISTRY 341. Final Exam Tuesday, December 16, Problem 1 15 pts Problem 9 8 pts. Problem 2 5 pts Problem pts
 CEMISTRY 341 Final Exam Tuesday, December 16, 1997 Name NAID Problem 1 15 pts Problem 9 8 pts Problem 2 5 pts Problem 10 21 pts Problem 3 26 pts Problem 11 15 pts Problem 4 10 pts Problem 12 6 pts Problem
CEMISTRY 341 Final Exam Tuesday, December 16, 1997 Name NAID Problem 1 15 pts Problem 9 8 pts Problem 2 5 pts Problem 10 21 pts Problem 3 26 pts Problem 11 15 pts Problem 4 10 pts Problem 12 6 pts Problem
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Chem 3719 Example Exams. Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams
 Chem 3719 Example Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2018 Chemistry 3719, Fall 2017 Exam 1 Student Name: Y Number: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 700 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L.
Chem 3719 Example Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2018 Chemistry 3719, Fall 2017 Exam 1 Student Name: Y Number: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 700 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L.
Chem 342 Organic Chemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009
 hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
Final Exam Professor R. Hoenigman
 I pledge to uphold the CU onor Code: CEM 3311-200 Fall 2006 Final Exam Professor. oenigman Average Score = 145 igh Score = 235 Low Score = 27 Signature Name (printed) Last four digits of your student ID
I pledge to uphold the CU onor Code: CEM 3311-200 Fall 2006 Final Exam Professor. oenigman Average Score = 145 igh Score = 235 Low Score = 27 Signature Name (printed) Last four digits of your student ID
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 12, 2015; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Chem 2320 Final 210 points Dr. Luther Giddings
 Chem 2320 Final 210 points Dr. Luther Giddings Name Phone or E-Mail Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notebook test. You may not discuss this exam with anyone, either during or after the exam,
Chem 2320 Final 210 points Dr. Luther Giddings Name Phone or E-Mail Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notebook test. You may not discuss this exam with anyone, either during or after the exam,
(5) a. b. (6) N H CH 3 N H O H O (7) CH 3 O (8) OCH 3 2. explanation:
 ame Key 15 W1-Exam o. Page I. (16 points) For each of the following pairs of compounds, predict which compound is more acidic. Compare the two underlined s for each pair and circle the compound that is
ame Key 15 W1-Exam o. Page I. (16 points) For each of the following pairs of compounds, predict which compound is more acidic. Compare the two underlined s for each pair and circle the compound that is
SYSTEMWIDE CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM. Department Of Physical Sciences
 SYSTEMWIDE CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM Department f Physical Sciences Morphine NAME: RGANIC CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM DIRECTINS- A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions in
SYSTEMWIDE CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM Department f Physical Sciences Morphine NAME: RGANIC CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM DIRECTINS- A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions in
Practice Synthetic Problems: CHEM 235 Page 2
 Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
ANSWER KEY Page 1 of 11
 ANWER KEY Page 1 of 11 Chemistry 002.222 rganic Chemistry II: Reactivity and ynthesis FINAL EXAM Winter ession 06R Paper 325 Frank Kennedy own Gym aturday April 15, 2006 1:30 pm 4:30 pm tudents are permitted
ANWER KEY Page 1 of 11 Chemistry 002.222 rganic Chemistry II: Reactivity and ynthesis FINAL EXAM Winter ession 06R Paper 325 Frank Kennedy own Gym aturday April 15, 2006 1:30 pm 4:30 pm tudents are permitted
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
CHE 325 ALDEHYDES AND KETONES I CHAP 18 ASSIGN OCH 3 HCN C 4 H 7 NO. would be: CH 3 B. CH 3CH 2COOCH 3
 CE 325 ALDEYDES AND KETNES I CAP 18 ASSIGN 1. What is the correct IUPAC name for the following compound A. 2-Methyl-5-heptanone B. 7-Methyl-4-octanone C. 6-Isopropyl-4-octanone D. Isobutyl propyl ketone
CE 325 ALDEYDES AND KETNES I CAP 18 ASSIGN 1. What is the correct IUPAC name for the following compound A. 2-Methyl-5-heptanone B. 7-Methyl-4-octanone C. 6-Isopropyl-4-octanone D. Isobutyl propyl ketone
Chem 2320 Exam 1. January 30, (Please print)
 Chem 2320 Exam 1 January 30, 2006 Name: (first) (last) (Please print) Last 4 digits of I.D. I. Multiple Choice ( /20) Score /60 II /15 III /25 Total score /100 I. Multiple choice questions. (3 points each).
Chem 2320 Exam 1 January 30, 2006 Name: (first) (last) (Please print) Last 4 digits of I.D. I. Multiple Choice ( /20) Score /60 II /15 III /25 Total score /100 I. Multiple choice questions. (3 points each).
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Introduction & Definitions Catalytic Hydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of H- and H+ Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of
 CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
Chemistry Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers
 Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
CHAPTER 21 HW: ALDEHYDES + KETONES
 CAPTER 21 W: ALDEYDES + KETES MECLATURE 1. Give the name for each compound (IUPAC or common name). Structure 6 5 4 1 C 2 ame 3,3-dimethyl-2-pentanone (or 1,1-dimethylpropyl methyl ketone) 5-hydroxy-4-methylhexanal
CAPTER 21 W: ALDEYDES + KETES MECLATURE 1. Give the name for each compound (IUPAC or common name). Structure 6 5 4 1 C 2 ame 3,3-dimethyl-2-pentanone (or 1,1-dimethylpropyl methyl ketone) 5-hydroxy-4-methylhexanal
Chem 14D Spring 2010 Garg Midterm 1 Review / Practice Problems
 Some Topics to Study (very broad): Chem 14D Spring 2010 Garg Midterm 1 Review / Practice Problems Reactivity stuff Classify atoms as electrophilic or nucleophilic Definitions of nucleophiles/electrophiles
Some Topics to Study (very broad): Chem 14D Spring 2010 Garg Midterm 1 Review / Practice Problems Reactivity stuff Classify atoms as electrophilic or nucleophilic Definitions of nucleophiles/electrophiles
Chem 312 SS05 Page 1 of 6 Kantorowski. 17 August 2005 Name:
 Chem 32 SS05 Page of 6 Kantorowski Exam III Key 7 August 2005 Name: This exam contains 5 pages of questions confirm this once you begin. You will have 50 minutes An abbreviated Periodic Table can be found
Chem 32 SS05 Page of 6 Kantorowski Exam III Key 7 August 2005 Name: This exam contains 5 pages of questions confirm this once you begin. You will have 50 minutes An abbreviated Periodic Table can be found
Solution problem 22: Non-Benzoid Aromatic Sytems
 Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry
 Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Cyclooctatetraene (2R)-2-phenylbutane benzyl chloride cycloocta-1,3,5,7-tetraene
 CM238-02 S05 Practice Material for xam 1 This is a compilation from relevant problems from last spring s exam 1&2. This is too long! 1. (4 pts) Draw 2 of the following 3: Cross one out or graded in order.
CM238-02 S05 Practice Material for xam 1 This is a compilation from relevant problems from last spring s exam 1&2. This is too long! 1. (4 pts) Draw 2 of the following 3: Cross one out or graded in order.
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
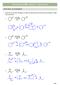 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
THE UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353
 TE UNIVERSITY F CALGARY FACULTY F SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATIN CEMISTRY 353 April 29 th, 2002 Time: 3 ours PLEASE WRITE YUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER AND SECTIN NUMBER (01 for MWF lectures and 02 for TR lectures)
TE UNIVERSITY F CALGARY FACULTY F SCIENCE FINAL EXAMINATIN CEMISTRY 353 April 29 th, 2002 Time: 3 ours PLEASE WRITE YUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER AND SECTIN NUMBER (01 for MWF lectures and 02 for TR lectures)
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II)
 Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
Suggested solutions for Chapter 27
 uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY
 4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
B. (3 pts) The following values are independent of the operating frequency of the NMR: a. Coupling constant; c. Chemical shift; b. Gyromagnetic ratio;
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 1 answer key September 29, 2009 Statistics: Average: 70 pts (70%); ighest: 96 pts (96%); Lowest: 37 pts (37%) Number of students performing at or above average: 16 (57%) Number
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 1 answer key September 29, 2009 Statistics: Average: 70 pts (70%); ighest: 96 pts (96%); Lowest: 37 pts (37%) Number of students performing at or above average: 16 (57%) Number
Homework - Review of Chem 2310
 omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
INTRODUCTORY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II --- PROBLEM SET #2
 CHEM 222 Section 01 Fall 2007 Dr. C. Rogers Page 1 of 5 INTRDUCTRY RGANIC CHEMISTRY II --- PRBLEM SET #2 DISTRIBUTED: Thurs.Nov.15 th. CMPLETIN DEADLINE: Thurs.Nov.29 th @ 10:15am. INSTRUCTINS: Work through
CHEM 222 Section 01 Fall 2007 Dr. C. Rogers Page 1 of 5 INTRDUCTRY RGANIC CHEMISTRY II --- PRBLEM SET #2 DISTRIBUTED: Thurs.Nov.15 th. CMPLETIN DEADLINE: Thurs.Nov.29 th @ 10:15am. INSTRUCTINS: Work through
CHE 232 Organic Chemistry II Exam 4 Name: KEY
 CE 232 rganic Chemistry II Exam 4 ame: KEY Student number: Before you begin this exam: First: You are allowed to have a simple model set at your seat. Please put away all other materials. Second: Place
CE 232 rganic Chemistry II Exam 4 ame: KEY Student number: Before you begin this exam: First: You are allowed to have a simple model set at your seat. Please put away all other materials. Second: Place
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 1 Thursday, February 11, 2016; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES. 3. Predict the relative acidity and basicity of compounds and ions. Important criteria include:
 CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND TEIR DERIVATIVES A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Give the IUPAC name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name, of carboxylic acids and their metal salts, acyl chlorides,
CARBXYLIC ACIDS AND TEIR DERIVATIVES A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. Give the IUPAC name given the structure, and draw the structure given the name, of carboxylic acids and their metal salts, acyl chlorides,
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Answers to Assignment #5
 Answers to Assignment #5 A. 9 8 l 2 5 DBE (benzene + 1 DBE) ( 9 2(9)+2-9 8+1+1 = 10 ˆ 5 DBE) nmr pattern of two doublets of equal integration at δ7.4 and 7.9 ppm means the group (the δ7.9 shift) IR band
Answers to Assignment #5 A. 9 8 l 2 5 DBE (benzene + 1 DBE) ( 9 2(9)+2-9 8+1+1 = 10 ˆ 5 DBE) nmr pattern of two doublets of equal integration at δ7.4 and 7.9 ppm means the group (the δ7.9 shift) IR band
Important Note: We will NOT accept papers written in pencil back for re-marking after they have been returned to you. Please do not ask!
 Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 15, 2012; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
Name: Student Number: University of Manitoba - Department of Chemistry CHEM 2220 - Introductory Organic Chemistry II - Term Test 2 Thursday, March 15, 2012; 7-9 PM This is a 2-hour test, marked out of
COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION. Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University. Type of the course unit
 Course unit title Organic Chemistry II Lecturer(s) Rimantas Vaitkus COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION Department Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University Cycle First Type of the course unit Mode of delivery Period
Course unit title Organic Chemistry II Lecturer(s) Rimantas Vaitkus COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION Department Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University Cycle First Type of the course unit Mode of delivery Period
12. Aldehydes & Ketones (text )
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 12.1 12. Aldehydes & Ketones (text 13.1 13.11) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 12.1 12. Aldehydes & Ketones (text 13.1 13.11) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Note: You must have your answers written in pen if you want a regrade!!!!
 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 310N Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 27, 2008 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long,
NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 310N Dr. Brent Iverson 2nd Midterm March 27, 2008 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long,
CHEM Chapter 13. Nuclear Magnetic Spectroscopy (Homework) W
 CHEM 2423. Chapter 13. Nuclear Magnetic Spectroscopy (Homework) W Short Answer 1. For a nucleus to exhibit the nuclear magnetic resonance phenomenon, it must be magnetic. Magnetic nuclei include: a. all
CHEM 2423. Chapter 13. Nuclear Magnetic Spectroscopy (Homework) W Short Answer 1. For a nucleus to exhibit the nuclear magnetic resonance phenomenon, it must be magnetic. Magnetic nuclei include: a. all
Answers To Chapter 7 Problems.
 Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Chapter 11 Reaction of Alcohols
 Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chem 2061 Final Exam. Fall Andy Aspaas, Instructor. Thursday, December 15, Instructions: Please print: Last name: First name:
 Please print: Last name: First name: hem 2061 Final Exam Fall 2005 Andy Aspaas, Instructor Thursday, December 15, 2005 Instructions: You may start as soon as you arrive. The exam was designed to be finished
Please print: Last name: First name: hem 2061 Final Exam Fall 2005 Andy Aspaas, Instructor Thursday, December 15, 2005 Instructions: You may start as soon as you arrive. The exam was designed to be finished
(please print and circle your last name) CHEMISTRY 332 FINAL EXAM. December 11, 2006
 Seat No. Name (please print and circle your last name) CEMISTRY 332 FINAL EXAM December 11, 2006 I. (18 points) II. III. IV. (48 points) (50 points) (40 points) V. (26 points) VI. (18 points) TTAL (200
Seat No. Name (please print and circle your last name) CEMISTRY 332 FINAL EXAM December 11, 2006 I. (18 points) II. III. IV. (48 points) (50 points) (40 points) V. (26 points) VI. (18 points) TTAL (200
Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones
 Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
Chemistry 2213a Fall 2012 Western University Topic 9. Aldehydes & Ketones A. Structure and Nomenclature The carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones and is the most important group in bio-organic
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Product obtained by reaction with resorcinol
 33 rd International hemistry lympiad Preparatory Problems 3 ( Z ) 3-( 4-methoxyphenyl )-2-pentenedioic acid d. Two products are possible when compound A reacts with bromine. 2 2 3 3 [1] [2] Structures
33 rd International hemistry lympiad Preparatory Problems 3 ( Z ) 3-( 4-methoxyphenyl )-2-pentenedioic acid d. Two products are possible when compound A reacts with bromine. 2 2 3 3 [1] [2] Structures
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 12, This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models. This test contains 11 pages
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 12, 2012 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 11 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 24 3. / 26 4. / 30
CEM 203 Final Exam December 12, 2012 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 11 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 24 3. / 26 4. / 30
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry
 UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
Exam III 17 August 2005 Name:
 Chem 312 SS05 Page 1 of 6 Kantorowski Exam III 17 August 2005 Name: This exam contains 5 pages of questions confirm this once you begin. You will have 50 minutes An abbreviated Periodic Table can be found
Chem 312 SS05 Page 1 of 6 Kantorowski Exam III 17 August 2005 Name: This exam contains 5 pages of questions confirm this once you begin. You will have 50 minutes An abbreviated Periodic Table can be found
