DIRECT IMAGING OF ZIRCONIA PILLARS IN MONTMORILLONITE BY ANALYTICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
|
|
|
- Scott Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clays and Clay Minerals. Vol. 47, No. 6, , DRECT MAGNG OF ZRCONA PLLARS N MONTMORLLONTE BY ANALYTCAL ELECTRON MCROSCOPY P.A. CROZER, 1 M. PAN, x't C. BATEMAN, 2'r J.J. ALCARAZ, 2 AND J.S. HOLMGREN 2 Center for Solid State Science, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona , USA 2 UOR 50 East Algonquin Rd, Des Plaines, llinois , USA Abstract--Analytical electron microscopy was used to confirm the location of pillars of zirconia in pillared montmorillonite. Data show that the pillared clayo is of "high" quality, with surface areas ranging from 200 to 250 m2/g and (001) spacings in the A range. The zirconia-rich pillars were observed using bright-field imaging, annular dark-field imaging, and energy-filtered imaging. The composition of the pillars was confirmed by performing nano-analysis using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and electron energy-loss spectroscopy. The pillars apparently have an irregular shape <50 A in size. The shape and relatively large size of the pillars suggest that zirconia dispersion is not ideally distributed in this sample. This study is apparently the first report of electron microscopy observation of pillaring material in clays. Key Words~Clays, Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy, Elemental Mapping, Energy-Filtered maging, mage Analysis, Materials Characterization. NTRODUCTON The ability to vary the basal spacing in different clays is important in catalysis and other technological applications (Vaughan et al., 1979, 1980; Mitchell, 1990 and articles therein; Bartley, 1988). Pillared clays are microporous materials that may provide alternatives to zeolite catalysts. Current effort includes understanding the mechanisms for pillaring these materials, creating better control of the formation of the basal spacing, and understanding the active sites for the application of interest. X-ray diffraction (XRD) gives the inteflamellar spacing and the average crystallite size, but little information about the morphology or the pillaring process. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is useful to image small features at, or close to, atomic resolution and to provide important data about defects in the structure. Techniques available in analytical electron microscopy (AEM) can yield information about the morphological and elemental variations on the nanometer scale (Datye and Smith, 1992; Crozier and Pan, 1995). We were able to use AEM to directly image the pillars in zirconia-pillared montmorillonite. By using a combination of TEM techniques, morphological data were correlated with composition to identify the location of the zirconia (ZrO2) pillars. After initial detailed characterization of the pillar morphology, simple bright-field imaging techniques could be used to identify the pillars in clays treated in various ways. A zirconia-pillared clay was chosen over an alumina-pil- '~ Present address: Gatan nc., 6678 Owens Dr., Pleasanton, California 94588, USA. Present address: Northboro R&D Center, Saint-Gobain Norton, Goddard Road, Northboro, Massachusetts , USA. lared material, because tile higher atomic number of the zirconia pillars relative to the Si, A1, and Mg in the clay provides better contrast. MATERALS AND METHODS Reagents were purchased from Aldrich Chemical Company and used as received. Natural montmorillonite clay, trade name HPM-20, was obtained from American Colloid Company and used as received. Montmorillonite is easily swellable and can be readily pillared using standard techniques. Zirconia-pillared montmorillonite was prepared following Bartley (1988). The zirconia pillars were prepared using hydroxyzirconium cations produced by the solvation of zirconyl chloride. A 0.1 M solution of ZrOC12 was prepared by diluting a 1.63 M stock solution. After aging for 2 h, 150 ml of the 0.1 M solution was combined with 1000 g of water. This solution was heated to 60~ while being stirred for h. HPM-20 montmorillonite (15 g) was added with vigorous stirring. The suspension was heated and stirred for an additional 24 h. The clay was recovered using centrifugation, washed with deionized water until C free, dried at 110~ overnight, and then calcined at 550~ in flowing air. XRD was used to determine the d(001)- value of the "as prepared" and calcined clays; in both cases the (001) spacing was 17-18,~. The surface areas of the clays were determined by BET analysis (Brunauer et al., 1938) using N~ and were m2/g for "as prepared" clay and m2/g for calcined material. A JEOL 4000 EX operated at 400 kv was used to perform high-resolution imaging. A VG HB501 dedicated scanning-transmission electron microscope (STEM) operated at 100 kv was used to obtain annular dark-field (ADF) images and energy-dispersive Copyright , The Clay Minerals Society 683
2 684 Crozier et al. Clays and Clay Minerals Figure 1. High resolution image of pillared clay showing microstructural layering along the basal plane. X-ray spectra (EDX) from the pillared montmorillonire. We used a LEO 912 microscope to perform energy-filtered analysis of the clay. RESULTS AND DSCUSSON nitial attempts were made to view pillared samples prepared for TEM by microtomy. Figure 1 shows a high-resolution image from a typical region of the pillared clay using low-dose conditions (Pan and Crozier, 1993) to avoid electron-beam damage to the clay structure. n this orientation, individual (001) layers of the clay can be seen clearly (the dark and light lines are lattices fringes). The insert, obtained by taking the Fourier transform of the image, shows the presence of spacings of 15 and 18.5 A in this region of the clay. The 18.5-A spacing is in good agreement with XRD measurements. The spacing of 15 A is probably evidence for partial collapse of some of the layers in this region. Microtoming is useful to determine the degree of crystallinity and disordering in the clays. However, we were unable to unambiguously identify the zirconia pillars because the sample was too thick (microtomed sections are typically A thick). The easiest way of imaging the pillars is to obtain small platelets only a few layers in thickness and to view these crystallites along the [001] or "basal plane projection". A successful approach for preparing such TEM samples is to grind the clay and to suspend in it water by dispersing with an ultrasonic probe. Then, a drop of the mixture is placed on a holey carbon film. Very small ultrathin platelets lying on the basal plane were then imaged. Figure 2 shows bright-field images from the LEO microscope obtained from thin regions of a pillared Figure 2. Bright-field images of platelet of (a) unpillared clay and (b) pillared montmorillonite. The images were recorded using a small objective aperture (4.3 mrad) to enhance the contrast (scale bar applies to both images). and unpillared montmorillonite in the [001] projection. A small objective aperture (collection semi-angle = 4.3 mrad) was used for imaging to reduce phase contrast and to enhance sensitivity for regions of nighermass density. (Underfocusing the objective lens was also found to enhance the contrast from dark features). The image from the pillared clay (Figure 2b) shows the presence of dark patches which are not present in the tmpillared sample (Figure 2a). These patches are
3 Vol. 47, No. 6, 1999 Direct imaging of Zr pillars ::uk~ a, = e- -i o Si Cu~ ZrKa 4:8 9,' X-ray energy (key) Figure 3. An ADF STEM image recorded from the pillared materials showing bright regions (which indicate higher atomic number). between 10-50,~ in size and irregular in shape. solated patches are only visible in the thinnest regions of the sample, presumably because in thicker areas, overlap between the patches degrades visibility. To confirm that the patches present in Figure 2b were indeed zirconia pillars, a number of analytical techniques were applied. An ADF STEM image from a similar region is shown in Figure 3. The ADF image is formed by collecting electrons scattered through large angles as the electron probe is rastered over the sample. For sufficiently high angles, the electron scattering has a strong dependence on the average atomic number of the sample (Treacy et al., 1980; Treacy and Rice, 1989). n an ADF image, bright contrast corresponds to regions of high atomic number. The presence of light patches indicates higher atomic-number regions <50 A in size with a morphology similar to the dark regions in Figure 2b. EDX was used to determine the local chemical composition of different parts of the clay. Spectra were taken from small light patches and regions between patches using a STEM probe of --10 A in diameter. Figure 4a and 4b shows spectra obtained from both the light patches and surrounding darker regions (Figure 3), respectively. Figure 4a clearly shows an enhancement of the L and K lines of Zr at 2.04 and kev, respectively. This enhancement proves that the patches observed in Figures 1 and 2 are Zr-rich. Some Zr also shows in the spectra recorded between the patches. This Zr signal is probably a spurious effect caused by the extended tails on the electron probe that produce a non-local contribution to the X-ray spectrum. However, the important point is the factor of 2-3 increase in the Zr/Si ratio that is consistently obtained from the light regions. Chemical analysis of the clay was also obtained by applying energy-filtered imaging to generate an elemental map from the electron energy-loss spectrum O 200 o N Zr ' cuka ZrK~ ZrKa o ~, v - L.,~,,..~,,,~ ~/L..... _ ~.. ~ 4.~ 9.~ X-ray energy (kev) Figure 4. High-spatial resolution EDX spectra recorded from 20-,~ regions from the platelet shown in Figure 2. Spectrum (a) is recorded from one of the light patches and shows an enhanced Zr signal and (b) is recorded from a darker region and shows a much weaker Zr signal. (EELS). The energy-loss spectrum contains ionization edges characteristic of elements in the sample. The LEO 912 energy-filtering microscope is equipped with an in-colunm spectrometer and an energy-selecting slit, both of which can be used to select a particular energy loss for imaging. By appropriate choice of the energy-loss, electron images can be generated from spectroscopic information about an element. See Crozier (1995) for a detailed description of this technique. The energy-filtering experiments were performed on the sample region shown in Figure 2b, and Figure 5 shows a typical energy-loss spectrum from the clay platelet. The spectrum shows a main low-loss peak at -25 ev that corresponds to plasmon excitation and a second peak with an onset close to 40 ev that corresponds to the Zr N-edge. Figure 6a and 6b shows the energy-filtered images recorded from the clay using the Zr pre-edge region at 36 ev and the post-edge region at 43 ev energy loss, which corresponds to the maximum of the Zr peak. A slit width of --5 ev was used. Figure 6 shows structure similar to that of Figure 2, except the contrast is reversed because energy-filtered images are dark-field images, Evidence exists for etching the thin-clay layer because of the high electron doses needed to perform energy-filtered imaging. The
4 686 Crozier et al. Clays and Clay Minerals ~ r t,-- = i i, 80 Energy Loss (ev) Figure 5. Electron energy-loss spectrum from pillared clay showing the Zr N23 edge used to form the Zr elemental map. To perform elemental mapping, images are recorded from the pre-edge and post-edge region. image recorded with the Zr edge shows greater contrast at the pillar structures. However, to obtain a more accurate representation of Zr distribution, the background below the Zr edge must be removed to obtain an image that represents only the Zr distribution. Several ways to accomplish this are discussed in the literature. We used a simple method that involves scaling the post- and pre-edge images to give the same value in regions that have no pillars (Johnson, 1979). The scaled background image is then subtracted from the post-edge image. The error involved in this background correction should be small in the thinnest region of the crystal. The result of this operation is shown in Figure 6c. The image is more noisy but gives a better representation of the distribution of zirconia pillars in the clay. The elemental identification from energy-filtered mapping confirms the results obtained from X-ray mapping and ADF imaging. CONCLUSON The three analytical techniques demonstrate conclusively that zirconia pillars in montmorillonite can be directly imaged in very thin samples in the [001] orientation. The pillars can be imaged using three different signals: amplitude contrast in conventional brightfield TEM, ADF imaging in a dedicated STEM, and elemental mapping in an energy-filtering microscope. The energy-filtering technique is useful for confirming the composition of the pillars but requires a large electron dose which may result in damage to the clay. However, the damage does not appear to substantially alter the morphology of the pillars (compare the damaged region of Figure 6 with the same undamaged region of Figure 2). However, future studies on this material can use the more straightforward bright-field ira- Figure 6. Energy-filtered images from (a) Zr pre-edge region at 36 ev and (b) the post-edge region at 43 ev. (c) Zr elemental map derived from (a) and (b) [scale bar applies to (a), (b), and (c)]. aging approach to rapidly characterize the pillar structure in different zirconia-pillared systems. For the zirconia-pillared clay studied, the pillar structure appears to consist mainly of irregularly
5 Vol. 47, No. 6, 1999 Direct imaging of Zr pillars 687 shaped regions <50,~ in size. Some curved elongated structures, 10-20/k wide and <200,~ in length, can be observed. n principle, the same approach may be useful to image pillars composed of other elements. However, when pillars are composed of the same elements as the clay matrix, energy-filtered imaging and annular dark-field imaging may be less useful. On the other hand, bright-field amplitude contrast with a small objective aperture may be fruitful for extremely thin crystals in the correct orientation. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Funding for this project was provided by UOP and the ndustrial Associates Program of Arizona State University. REFERENCES Bartley, G.J. (1988) Zirconium pillared clays. Catalysis Today, 2, Brunauer, S., Emmett, RH., and Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gasses in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60, Crozier, RA. (1995) Quantitative elemental mapping of materials by energy-filtered imaging. Ultramicroscopy, 58, Crozier, RA. and Pan, M. (1995) Quantitative nano-characterization of heterogeneous catalysts. n Microscopy and Microanalysis Proceedings, G.W. Bailey, M.H. Ellisman, R.A. Hennigar, and N.J. Zaluzec, eds., Jones and Begell Publishing, Boston, Datye, A.K. and Smith D.J. (1992) The study of heterogeneous catalysts by high resolution transmission electron microscopy. Catalysis Reviews in Science and Engineering, 34, Johnson, D.E. (1979) Energy Loss Spectrometry for Biological Research. ntroduction to Analytical Electron Microscopy. Plenum Press, New York. Mitchell,.V. (1990) Pillared Layered Structures: Current Trends and Applications. Elsevier Applied Science, New York, Pan, M. and Crozier, EA. (1993) Low-dose high-resolution electron microscopy of zeolite materials with a slow scan CCD camera. Uttramicroscopy, 48, Treacy, M.M.J. and Rice S.B. (1989) Catalyst particle sizes from Rutherford scattered intensities. Journal of Microscopy, 156, Treacy, M.M.L, Howie, A., and Pennycook, S.J. (1980) Z contrast of supported catalysts particles on the STEM. nstitute of Physics Conference Series, 52, Vaughan, D.E.W., Lussier, R., and Magee, J. (1979) U.S. Patent 4,175,090. Vaughan, D.E.W., Lussier, R., and Magee, J. (1980) U.S. Patent 4,248,739. of corresponding author: Crozier@asu.edu (Received 6 June 1997; accepted 25 October 1998; Ms )
Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation
 Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation Zhigang Xiong, Li Li Zhang, Jizhen Ma, X. S. Zhao* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene-gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation Zhigang Xiong, Li Li Zhang, Jizhen Ma, X. S. Zhao* Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,
Electronic Supplementary Information. Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave Hexagon and Nanorod like Polyoxometalates
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave
Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO 3 Layered Double Hydroxide
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles Nathan E. Motl, James F. Bondi, and Raymond E. Schaak* Department of
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Synthesis of Colloidal Au-Cu 2 S Heterodimers via Chemically Triggered Phase Segregation of AuCu Nanoparticles Nathan E. Motl, James F. Bondi, and Raymond E. Schaak* Department of
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Transmission Electron Microscopy
 L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
A novel Ag 3 AsO 4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information A novel Ag 3 AsO 4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information A novel Ag 3 AsO 4 visible-light-responsive photocatalyst: facile synthesis and exceptional photocatalytic performance
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Chemical Analysis in TEM: XEDS, EELS and EFTEM. HRTEM PhD course Lecture 5
 Chemical Analysis in TEM: XEDS, EELS and EFTEM HRTEM PhD course Lecture 5 1 Part IV Subject Chapter Prio x-ray spectrometry 32 1 Spectra and mapping 33 2 Qualitative XEDS 34 1 Quantitative XEDS 35.1-35.4
Chemical Analysis in TEM: XEDS, EELS and EFTEM HRTEM PhD course Lecture 5 1 Part IV Subject Chapter Prio x-ray spectrometry 32 1 Spectra and mapping 33 2 Qualitative XEDS 34 1 Quantitative XEDS 35.1-35.4
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Remarkable performance of Ir 1 /FeO x single-atom catalyst in water gas shift reaction Jian Lin, Aiqin Wang, Botao Qiao, Xiaoyan Liu, Xiaofeng Yang, Xiaodong Wang, Jinxia Liang,
Supporting Information Remarkable performance of Ir 1 /FeO x single-atom catalyst in water gas shift reaction Jian Lin, Aiqin Wang, Botao Qiao, Xiaoyan Liu, Xiaofeng Yang, Xiaodong Wang, Jinxia Liang,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers
 Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/321/5894/1331/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Identification of Active Gold Nanoclusters on Iron Oxide Supports for CO Oxidation Andrew A. Herzing, Christopher J.
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/321/5894/1331/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Identification of Active Gold Nanoclusters on Iron Oxide Supports for CO Oxidation Andrew A. Herzing, Christopher J.
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2014. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201404493 Micro/Macroporous System: MFI-Type Zeolite Crystals with Embedded
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2014. Supporting Information for Adv. Mater., DOI: 10.1002/adma.201404493 Micro/Macroporous System: MFI-Type Zeolite Crystals with Embedded
Supporting Information. Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
Supporting Information Synthesis and Upconversion Luminescence of BaY 2 F 8 :Yb 3+ /Er 3+ Nanobelts 5 Guofeng Wang, Qing Peng, and Yadong Li* Department of Chemistry and State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite
 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
Leveraging Commercial Silver Inks as Oxidation Reduction Reaction Catalysts in Alkaline Medium
 Supporting Information Leveraging Commercial Silver Inks as Oxidation Reduction Reaction Catalysts in Alkaline Medium Shlomi Polani, Naftali Kanovsky and David Zitoun, *, Bar Ilan University, Department
Supporting Information Leveraging Commercial Silver Inks as Oxidation Reduction Reaction Catalysts in Alkaline Medium Shlomi Polani, Naftali Kanovsky and David Zitoun, *, Bar Ilan University, Department
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Direct observation of crystal defects in an organic molecular crystals of copper hexachlorophthalocyanine by STEM-EELS Mitsutaka Haruta*, Hiroki Kurata Institute for hemical Research,
Supplementary Information Direct observation of crystal defects in an organic molecular crystals of copper hexachlorophthalocyanine by STEM-EELS Mitsutaka Haruta*, Hiroki Kurata Institute for hemical Research,
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Exfoliated semiconducting pure 2H-MoS 2 and 2H-WS 2 assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Exfoliated semiconducting pure 2H-MoS 2 and 2H-WS 2 assisted
Supporting Information. For. Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver
 Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4 Nor Aida
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4 Nor Aida
Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
Energy-Filtering. Transmission. Electron Microscopy
 Part 3 Energy-Filtering Transmission Electron Microscopy 92 Energy-Filtering TEM Principle of EFTEM expose specimen to mono-energetic electron radiation inelastic scattering in the specimen poly-energetic
Part 3 Energy-Filtering Transmission Electron Microscopy 92 Energy-Filtering TEM Principle of EFTEM expose specimen to mono-energetic electron radiation inelastic scattering in the specimen poly-energetic
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic
 Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Lei Liu, ab Yijie Xia, b Jie Zhang* b a) China Center for Modernization
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Lei Liu, ab Yijie Xia, b Jie Zhang* b a) China Center for Modernization
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Pd-P nanoalloys supported on porous carbon frame as efficient catalyst for benzyl alcohol oxidation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information Pd-P nanoalloys supported on porous carbon frame as
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information Pd-P nanoalloys supported on porous carbon frame as
Pt-Ni alloyed nanocrystals with controlled archtectures for enhanced. methanol oxidation
 Supplementary Information Pt-Ni alloyed nanocrystals with controlled archtectures for enhanced methanol oxidation Xiao-Jing Liu, Chun-Hua Cui, Ming Gong, Hui-Hui Li, Yun Xue, Feng-Jia Fan and Shu-Hong
Supplementary Information Pt-Ni alloyed nanocrystals with controlled archtectures for enhanced methanol oxidation Xiao-Jing Liu, Chun-Hua Cui, Ming Gong, Hui-Hui Li, Yun Xue, Feng-Jia Fan and Shu-Hong
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI )
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI ) Hollow nitrogen-doped carbon spheres as an efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI ) Hollow nitrogen-doped carbon spheres as an efficient
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Supplementary Information for Facile transformation of low cost thiourea into nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride nanocatalyst with high visible light photocatalytic performance Fan Dong *a, Yanjuan
Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor
 Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Electronic Supplementary Information. Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite Nanowires
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Low-temperature Benchtop-synthesis of All-inorganic Perovskite
KMÜ 396 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECH. I PRESENTATION ELECTRON ENERGY LOSS SPECTROSCOPY (EELS) TUĞÇE SEZGİN
 KMÜ 396 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECH. I PRESENTATION ELECTRON ENERGY LOSS SPECTROSCOPY (EELS) TUĞÇE SEZGİN 20970725 HACETTEPE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING, SPRING 2011,APRIL,ANKARA CONTENTS
KMÜ 396 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND TECH. I PRESENTATION ELECTRON ENERGY LOSS SPECTROSCOPY (EELS) TUĞÇE SEZGİN 20970725 HACETTEPE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING, SPRING 2011,APRIL,ANKARA CONTENTS
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Information. Enhanced Photocatalytic/photoelectrocatalytic Activities
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Electrospun BiVO 4 Nanobelts with Tailored Structures
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Electrospun BiVO 4 Nanobelts with Tailored Structures
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Nucleation of FAU and LTA Zeolites from Heterogeneous Aluminosilicate Precursors Matthew D. Oleksiak 1, Jennifer A. Soltis 2,4, Marlon T. Conato, 1,3 R. Lee Penn 2, Jeffrey D. Rimer 1* 1 University of
Nucleation of FAU and LTA Zeolites from Heterogeneous Aluminosilicate Precursors Matthew D. Oleksiak 1, Jennifer A. Soltis 2,4, Marlon T. Conato, 1,3 R. Lee Penn 2, Jeffrey D. Rimer 1* 1 University of
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
A novel AgIO 4 semiconductor with ultrahigh activity in photodegradation of organic dyes: insights into the photosensitization mechanism
 Supporting Information for: A novel AgIO 4 semiconductor with ultrahigh activity in photodegradation of organic dyes: insights into the photosensitization mechanism Jianting Tang*, Datang Li*, Zhaoxia
Supporting Information for: A novel AgIO 4 semiconductor with ultrahigh activity in photodegradation of organic dyes: insights into the photosensitization mechanism Jianting Tang*, Datang Li*, Zhaoxia
Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag Nanoclusters
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting information for Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Morphology-dependent Luminescent Ag
B k k. Fig. 1: Energy-loss spectrum of BN, showing the how K-loss intensities I K (β, ) for boron and nitrogen are defined and measured.
 The accuracy of EELS elemental analysis The procedure of EELS elemental analysis can be divided into three parts, each of which involves some approximation, with associated systematic or statistical errors.
The accuracy of EELS elemental analysis The procedure of EELS elemental analysis can be divided into three parts, each of which involves some approximation, with associated systematic or statistical errors.
Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals
 Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Supporting Information Pioneering In Situ Recrystallization during Bead Milling: A Top-down Approach to Prepare Zeolite A Nanocrystals Chokkalingam Anand 1, Yudai Yamaguchi 1, Zhendong Liu 1, Sayoko Ibe
Instantaneous reduction of graphene oxide at room temperature
 Instantaneous reduction of graphene oxide at room temperature Barun Kuma Burman, Pitamber Mahanandia and Karuna Kar Nanda Materials Research Centre, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore-560012, India
Instantaneous reduction of graphene oxide at room temperature Barun Kuma Burman, Pitamber Mahanandia and Karuna Kar Nanda Materials Research Centre, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore-560012, India
In a typical routine, the pristine CNT (purchased from Bill Nanotechnology, Inc.) were
 Supplementary Information Pd induced Pt(Ⅳ) reduction to form Pd@Pt/CNT core-shell catalyst for a more complete oxygen reduction Preparation of SH- functionalized CNT In a typical routine, the pristine
Supplementary Information Pd induced Pt(Ⅳ) reduction to form Pd@Pt/CNT core-shell catalyst for a more complete oxygen reduction Preparation of SH- functionalized CNT In a typical routine, the pristine
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Techniques EDX, EELS et HAADF en TEM: possibilités d analyse et applications
 Techniques EDX, EELS et HAADF en TEM: possibilités d analyse et applications Thomas Neisius Université Paul Cézanne Plan Imaging modes HAADF Example: supported Pt nanoparticles Electron sample interaction
Techniques EDX, EELS et HAADF en TEM: possibilités d analyse et applications Thomas Neisius Université Paul Cézanne Plan Imaging modes HAADF Example: supported Pt nanoparticles Electron sample interaction
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
Supplementary Information. Large Scale Graphene Production by RF-cCVD Method
 Supplementary Information Large Scale Graphene Production by RF-cCVD Method Enkeleda Dervishi, *a,b Zhongrui Li, b Fumiya Watanabe, b Abhijit Biswas, c Yang Xu, b Alexandru R. Biris, d Viney Saini, a,b
Supplementary Information Large Scale Graphene Production by RF-cCVD Method Enkeleda Dervishi, *a,b Zhongrui Li, b Fumiya Watanabe, b Abhijit Biswas, c Yang Xu, b Alexandru R. Biris, d Viney Saini, a,b
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany 3D Honeycomb-Like Structured Graphene and Its High Efficiency as a Counter-Electrode Catalyst for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells** Hui Wang, Kai
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany 3D Honeycomb-Like Structured Graphene and Its High Efficiency as a Counter-Electrode Catalyst for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells** Hui Wang, Kai
photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation
 Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
Electronic Supplementary Information for WO 3 modified titanate network film: highly efficient photo-mineralization of 2-propanol under visible light irradiation Experimental Preparation of STN, and WO
IMAGING DIFFRACTION SPECTROSCOPY
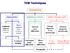 TEM Techniques TEM/STEM IMAGING DIFFRACTION SPECTROSCOPY Amplitude contrast (diffracion contrast) Phase contrast (highresolution imaging) Selected area diffraction Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
TEM Techniques TEM/STEM IMAGING DIFFRACTION SPECTROSCOPY Amplitude contrast (diffracion contrast) Phase contrast (highresolution imaging) Selected area diffraction Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Single-crystalline Pd square nanoplates enclosed by {100}
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information Single-crystalline Pd square nanoplates enclosed by {100}
A doping of phosphorus and/or sulfur into nitrogen-doped carbon for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in acid media
 Supporting Information A doping of phosphorus and/or sulfur into nitrogen-doped carbon for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in acid media Chang Hyuck Choi, a Min Wook Chung, b Sung Hyeon Park, a and
Supporting Information A doping of phosphorus and/or sulfur into nitrogen-doped carbon for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in acid media Chang Hyuck Choi, a Min Wook Chung, b Sung Hyeon Park, a and
Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
 (Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
(Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation. and Elimination of Bacteria
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
Controlling Interfacial Contact and Exposed Facets for. Enhancing Photocatalysis via 2D-2D Heterostructure
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Controlling Interfacial Contact and Exposed
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Controlling Interfacial Contact and Exposed
Characterisation of Catalysts Using Secondary and Backscattered Electron In-lens Detectors
 Platinum Metals Rev., 2014, 58, (2), 106 110 FINAL ANALYSIS Characterisation of Catalysts Using Secondary and Backscattered Electron In-lens Detectors Heterogeneous catalysis often involves the use of
Platinum Metals Rev., 2014, 58, (2), 106 110 FINAL ANALYSIS Characterisation of Catalysts Using Secondary and Backscattered Electron In-lens Detectors Heterogeneous catalysis often involves the use of
Imaging of built-in electric field at a p-n junction by scanning transmission electron microscopy
 Imaging of built-in electric field at a p-n junction by scanning transmission electron microscopy N. Shibata, S.D. Findlay, H. Sasaki, T. Matsumoto, H. Sawada, Y. Kohno, S. Otomo, R. Minato and Y. Ikuhara
Imaging of built-in electric field at a p-n junction by scanning transmission electron microscopy N. Shibata, S.D. Findlay, H. Sasaki, T. Matsumoto, H. Sawada, Y. Kohno, S. Otomo, R. Minato and Y. Ikuhara
Supplementary information for:
 Supplementary information for: Solvent dispersible nanoplatinum-carbon nanotube hybrids for application in homogeneous catalysis Yuhong Chen, Xueyan Zhang and Somenath Mitra* Department of Chemistry and
Supplementary information for: Solvent dispersible nanoplatinum-carbon nanotube hybrids for application in homogeneous catalysis Yuhong Chen, Xueyan Zhang and Somenath Mitra* Department of Chemistry and
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Supporting Information. Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive Photocatalyst for the Suzuki Coupling Reaction**
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Graphene Oxide-Palladium Modified Ag-AgBr: A Novel Visible-Light- Responsive
Chapter 9. Electron mean free path Microscopy principles of SEM, TEM, LEEM
 Chapter 9 Electron mean free path Microscopy principles of SEM, TEM, LEEM 9.1 Electron Mean Free Path 9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) -SEM design; Secondary electron imaging; Backscattered electron
Chapter 9 Electron mean free path Microscopy principles of SEM, TEM, LEEM 9.1 Electron Mean Free Path 9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) -SEM design; Secondary electron imaging; Backscattered electron
Energy-Filtered High-Resolution Electron Microscopy for Quantitative Solid State Structure Determination
 [J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 102, 1 (1997)] Energy-Filtered High-Resolution Electron Microscopy for Quantitative Solid State Structure Determination Volume 102 Number 1 January February 1997 Z.
[J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 102, 1 (1997)] Energy-Filtered High-Resolution Electron Microscopy for Quantitative Solid State Structure Determination Volume 102 Number 1 January February 1997 Z.
3D and Atomic-resolution Imaging with Coherent Electron Nanobeams - Opportunities and Challenges for X-rays
 3D and Atomic-resolution Imaging with Coherent Electron Nanobeams - Opportunities and Challenges for X-rays David A. Muller Lena Fitting Kourkoutis, Megan Holtz, Robert Hovden, Qingyun Mao, Julia Mundy,
3D and Atomic-resolution Imaging with Coherent Electron Nanobeams - Opportunities and Challenges for X-rays David A. Muller Lena Fitting Kourkoutis, Megan Holtz, Robert Hovden, Qingyun Mao, Julia Mundy,
Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene oxide) templated nickel oxide nanofibers for dye degradation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Supporting Information for: Emulsion-assisted synthesis of monodisperse binary metal nanoparticles
 Supporting Information for: Emulsion-assisted synthesis of monodisperse binary metal nanoparticles Zhen Yin, Ding Ma* and Xinhe Bao* Synthesis of the PdCu nanoparticles: All synthesis was carried out under
Supporting Information for: Emulsion-assisted synthesis of monodisperse binary metal nanoparticles Zhen Yin, Ding Ma* and Xinhe Bao* Synthesis of the PdCu nanoparticles: All synthesis was carried out under
Supporting Information. for. Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Alumina as a Catalyst for Surface Plasmon-Enhanced Selective Reductions of Nitrobenzene
 Supporting Information for Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Alumina as a Catalyst for Surface Plasmon-Enhanced Selective Reductions of Nitrobenzene Kittichai Chaiseeda, Shun Nishimura, and Kohki Ebitani
Supporting Information for Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Alumina as a Catalyst for Surface Plasmon-Enhanced Selective Reductions of Nitrobenzene Kittichai Chaiseeda, Shun Nishimura, and Kohki Ebitani
Core-shell 2 mesoporous nanocarriers for metal-enhanced fluorescence
 Core-shell Ag@SiO 2 @msio 2 mesoporous nanocarriers for metal-enhanced fluorescence Jianping Yang a, Fan Zhang a *, Yiran Chen a, Sheng Qian a, Pan Hu a, Wei Li a, Yonghui Deng a, Yin Fang a, Lu Han a,
Core-shell Ag@SiO 2 @msio 2 mesoporous nanocarriers for metal-enhanced fluorescence Jianping Yang a, Fan Zhang a *, Yiran Chen a, Sheng Qian a, Pan Hu a, Wei Li a, Yonghui Deng a, Yin Fang a, Lu Han a,
Electron Microscopy I
 Characterization of Catalysts and Surfaces Characterization Techniques in Heterogeneous Catalysis Electron Microscopy I Introduction Properties of electrons Electron-matter interactions and their applications
Characterization of Catalysts and Surfaces Characterization Techniques in Heterogeneous Catalysis Electron Microscopy I Introduction Properties of electrons Electron-matter interactions and their applications
Imaging the structure of activated carbon using aberration corrected TEM
 Imaging the structure of activated carbon using aberration corrected TEM Article Accepted Version Harris, P. J. F., Liu, Z. and Suenaga, K. (2010) Imaging the structure of activated carbon using aberration
Imaging the structure of activated carbon using aberration corrected TEM Article Accepted Version Harris, P. J. F., Liu, Z. and Suenaga, K. (2010) Imaging the structure of activated carbon using aberration
Scientific report 2016 January September. Designing composite nanoarchitectures for hydrogen production and environmental depollution
 Scientific report 2016 January September Designing composite nanoarchitectures for hydrogen production and environmental depollution Synthesis of the spherical Pt nanoparticles We have chosen to synthesize
Scientific report 2016 January September Designing composite nanoarchitectures for hydrogen production and environmental depollution Synthesis of the spherical Pt nanoparticles We have chosen to synthesize
Engineering electronic structure of Two-Dimensional Subnanopore. nanosheet by Molecular Titanium-oxide Incorporation for Enhanced
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information for Engineering electronic structure of Two-Dimensional
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information for Engineering electronic structure of Two-Dimensional
Supporting Information
 1 Supporting Information Photoluminescent Carbogenic Dots A. B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Zboril, V. Georgakilas, E. P. Giannelis *, Institute of Materials Science, NCSR Demokritos, Ag.
1 Supporting Information Photoluminescent Carbogenic Dots A. B. Bourlinos, A. Stassinopoulos, D. Anglos, R. Zboril, V. Georgakilas, E. P. Giannelis *, Institute of Materials Science, NCSR Demokritos, Ag.
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. CO 2 light off curve obtained from the 5 wt% Pt/Al 2 O 3 catalyst obtained through heating the catalyst under a 50 ml.min -1 flow
Supplementary information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. CO 2 light off curve obtained from the 5 wt% Pt/Al 2 O 3 catalyst obtained through heating the catalyst under a 50 ml.min -1 flow
Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification.
 Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification. Synthesis of the Steep Rhombohedra MnCO 3 : In a typical synthesis,
Supporting Information Detailed Experiments Materials: All the reagents were analytical grate and used without further purification. Synthesis of the Steep Rhombohedra MnCO 3 : In a typical synthesis,
Supporting Information. Solution-Phase Synthesis of Highly Conductive Tungsten Diselenide Nanosheets
 Supporting Information Solution-Phase Synthesis of Highly Conductive Tungsten Diselenide Nanosheets Priscilla D. Antunez, David H. Webber, and Richard L. Brutchey* Department of Chemistry and the Center
Supporting Information Solution-Phase Synthesis of Highly Conductive Tungsten Diselenide Nanosheets Priscilla D. Antunez, David H. Webber, and Richard L. Brutchey* Department of Chemistry and the Center
Supporting Information for. Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin
 Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
Supporting Information for Size-Dependent Oxidation State and CO Oxidation Activity of Tin Oxide Clusters Yusuke Inomata, Ken Albrecht,, Kimihisa Yamamoto *,, Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Supporting Information. Rh-doped Pt-Ni octahedral nanoparticles: understanding the correlation between elemental distribution, ORR and shape stability
 Supporting Information Rh-doped Pt-Ni octahedral nanoparticles: understanding the correlation between elemental distribution, ORR and shape stability Experimental part Chemicals and materials Platinum(II)acetylacetonate
Supporting Information Rh-doped Pt-Ni octahedral nanoparticles: understanding the correlation between elemental distribution, ORR and shape stability Experimental part Chemicals and materials Platinum(II)acetylacetonate
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Experimental Materials: For the gold nanocuboids, the chemicals gold (ш) chloride trihydrate, sodium borohydride, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, copper sulfate, L-ascorbic acid
Supporting Information Experimental Materials: For the gold nanocuboids, the chemicals gold (ш) chloride trihydrate, sodium borohydride, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, copper sulfate, L-ascorbic acid
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh
 Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Supplementary Information for Self-assembled, monodispersed, flowerlike γ-alooh hierarchical superstructures for greatly fast removal of heavy metal ions with high efficiency Yong-Xing Zhang, a,b Yong
Unraveling Surface Plasmon Decay in Core Shell Nanostructures towards Broadband Light-Driven Catalytic Organic Synthesis
 Supporting Information Unraveling Surface Plasmon Decay in Core Shell Nanostructures towards Broadband Light-Driven Catalytic Organic Synthesis Hao Huang,, Lei Zhang,, Zhiheng Lv, Ran Long, Chao Zhang,
Supporting Information Unraveling Surface Plasmon Decay in Core Shell Nanostructures towards Broadband Light-Driven Catalytic Organic Synthesis Hao Huang,, Lei Zhang,, Zhiheng Lv, Ran Long, Chao Zhang,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Hydrothermal synthesis of - alloy nanooctahedra and their enhanced electrocatalytic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Hydrothermal synthesis of - alloy nanooctahedra and their enhanced electrocatalytic
Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance. absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive ions from.
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
Nanoelectronics 09. Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics. Quick Review over the Last Lecture
 Nanoelectronics 09 Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics 13:00 Monday, 12/February/2018 (P/T 006) Quick Review over the Last Lecture ( Field effect transistor (FET) ): ( Drain ) current increases
Nanoelectronics 09 Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics 13:00 Monday, 12/February/2018 (P/T 006) Quick Review over the Last Lecture ( Field effect transistor (FET) ): ( Drain ) current increases
In Situ Nanoscale Characterization of Redox Processes in Ceria Zirconia. Introduction
 In Situ Nanoscale Characterization of Redox Processes in Ceria Zirconia Ruigang Wang, *, ** Peter A. Crozier, *, ** Renu Sharma, *, ** and James B. Adams * * School of Materials, Arizona State University,
In Situ Nanoscale Characterization of Redox Processes in Ceria Zirconia Ruigang Wang, *, ** Peter A. Crozier, *, ** Renu Sharma, *, ** and James B. Adams * * School of Materials, Arizona State University,
Nanoporous Organosilica Membrane for Water Desalination
 Electronic Supplementary Information Nanoporous Organosilica Membrane for Water Desalination Yen Thien Chua a, Chun Xiang Cynthia Lin a, Freddy Kleitz b, Xiu Song Zhao a, Simon Smart a* a The University
Electronic Supplementary Information Nanoporous Organosilica Membrane for Water Desalination Yen Thien Chua a, Chun Xiang Cynthia Lin a, Freddy Kleitz b, Xiu Song Zhao a, Simon Smart a* a The University
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Supplementary Information. ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni(0) Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane
 Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Min Bum Park, Sang Hyun Ahn, Nak Ho Ahn and Suk Bong Hong*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 S1 Supplementary Information for Charge density mismatch synthesis of MEI- and BPH-type zeolites
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Anisotropic and Multi-Component Nanostructures by Controlled Symmetry Breaking of Metal Halide Intermediates Alexander E. Kossak,,^ Benjamin O. Stephens,,^ Yuan Tian,, Pan Liu, Mingwei
Supporting Information Anisotropic and Multi-Component Nanostructures by Controlled Symmetry Breaking of Metal Halide Intermediates Alexander E. Kossak,,^ Benjamin O. Stephens,,^ Yuan Tian,, Pan Liu, Mingwei
