CONTROL OF H 2 GAS EVOLUTION AT CATHODE DURING ELECTROCHEMICAL MACHINING OF IRON BY USING PALLADIUM BASED MEMBRANES
|
|
|
- Roy Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONTROL OF H 2 GAS EVOLUTION AT CATHODE DURING ELECTROCHEMICAL MACHINING OF IRON BY USING PALLADIUM BASED MEMBRANES R.K Upadhyay 1, Arbind Kumar 2, P.K Srivastava 3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering Birla Institute of Technology, Deoghar Campus (India) 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra- Ranchi (India) 3 Department of Applied Chemistry Birla Institute of Technology, Deoghar Campus (India) ABSTRACT A mathematical equation and experimental procedure have been proposed to determine the permeability of H 2 gas during electrochemical machining of iron at higher current density through palladium based membranes (Pd/Ag) which is placed within the reservoir. The permeability can measure in the low pressure range (1 3 bar absolute). The functionalities of the membranes can also measure in terms of the hydrogen gas transport. A relationship between temperature at which process occurs and corresponding transport of the permeate has been established. The membrane does not expose to high pressure and therefore membranes used for the purpose are less prone to damage. The proposed method will be used to optimize the process parameters. Keywords: Electrochemical Machining, Hydrogen Evolution, Membrane I. INTRODUCTION Over the years ECM principles have been employed for performing a number of machining operations involving machining of hard and tough materials, at atomic level [1-2] with higher surface finish. Many groups of Researchers and Engineers have been engaged in manufacturing sophisticated and precise parts used in various technologically advanced industries like Aerospace, Automotive and Medical. Which require accurately machined components of complex shapes, of materials [3] which are difficult to machine such as super alloys, tungsten carbide and alloys of titanium. The Electrochemical Machining process is best suited for such operations and thus dominants over several non-conventional processes, but the capabilities of this process have not been exploited to its fullest extent mainly because of the inherent problems associated with tool design, electrolyte, heat transfer and gas development [4-6]. In Electrochemical Machining Process, the effect of Hydrogen gas development include their obstructions of electric current and stirring of electrolyte within the cell H 2 gas bubbles decrease the effective conductivity of the electrolyte [7] that leads to the ohmic losses in the cell and therefore it would affect the local anodic dissolution rate. 510 P a g e
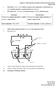
2 In this paper, an attempt has been made to optimize the machining parameters during Electrochemical machining of iron workpiece with respect to transport of hydrogen gas (based on diffusion mechanism) through dense palladium membrane to enhance the local anodic dissolution. Electrochemical and Chemical Reaction Scheme In aqueous solution of NaCl following reaction occurs NaCl Na + + Cl - H 2 O H + + OH - On passing the electric current through the solution, positive ions moves towards cathode and negative ions move towards anode. Each Na + ions gain an electron and are converted to Na. Hence Na ions are reduced at the cathode by means of electrons. Reactions at Cathode Na + + e - Na Na + H 2 O NaOH + H + 2H + + 2e - H 2 It shows that only hydrogen gas will evolve at cathode. Fe Fe e - Fe Cl - FeCl 2 Fe (OH) - Fe(OH) 2 FeCl 2 + 2(OH) - Fe(OH) 2 + 2Cl - 2Cl - Cl 2 + 2e - 2FeCl 2 + Cl 2 2FeCl 3 H + + Cl - HCl 2Fe(OH) 2 + H 2 O +O 2 2Fe(OH) 3 Fe(OH) 3 + 3HCl FeCl 3 + 3H 2 O FeCl 3 + 3NaOH Fe(OH) 3 + 3NaCl Thus, the net effect of hydrogen gas concentrated near the cathode is to decrease the electrolyte s electrical conductivity and hence affects the local anodic dissolution rate also. Fig one shows a schematic of an electrochemical machining system consists mainly of four sub-systems: power source, electrolyte supply system, device and tool-feed system, and work and work-holding system. Low voltage DC (2-50 V) capable of giving high current density can be used as the power source. The material removal rate mainly depends upon the current density employed. The electrolyte supply and cleaning system consists of a pump, filters, pipings, control valves, pressure gauges and a reservoir. Electrolyte supply ports 511 P a g e
3 (connections) are made in the tool. An anti-corrosive materials for tools with high thermal and electrical conductivity like brass can be used as tool. Two sides (Feed side and Permeate side) are separated through a dense palladium membrane which is an inorganic dense membrane having capability to separate hydrogen completely from the gaseous mixture. One pressure gauge and one temperature sensor are also integrated on each side of the rectangular flow chamber in order to measure the pressure and temperature. During electrochemical Machining, the rate of evolution of hydrogen gas bubbles at the cathode surface is governed by current density on its surface. As the current density increases mass concentration of hydrogen also increases and the pressure and temperature on both the sides of the Pd/Ag Membrane will be measured with the help of pressure gauge and temperature sensor which drives the transport phenomena. Fig.1 Schematic of Electrochemical Machining set up II. RESULT AND DISCUSSION The hydrogen molecular transport in the palladium membrane occurs through a solution diffusion mechanism, which follows the following steps [8]: 1. Dissociation of molecular hydrogen at the gas/ metal interface. 512 P a g e
4 2. Adsorption of the atomic hydrogen on the membrane surface. 3. Dissolution of atomic hydrogen into the palladium matrix. 4. Diffusion of atomic hydrogen through the membrane. 5. Recombination of atomic hydrogen to form hydrogen molecules at the gas/metal interface. 6. Desorption of hydrogen molecules. Membrane d pore (nm) Diffusion mechanism Macroporous >50 Poiseuille (Viscous flow) Mesoporous 2 50 Knudsen Microporous <2 Activated process Dense Pd Fick Table 1.1 Diffusion mechanisms in porous and dense membranes The hydrogen permeating flux can be expressed as following equation [9]: J H2 = (P n H2, feed - P n H2, perm)..(1) Where, J H2 : Flux or permeation rate of hydrogen (mol/m 2 s) P eh2 :Hydrogen Permiability (mol m/m 2 s Pa) : Membrane Thickness (µm) n: Dependence factor of the hydrogen flux to the hydrogen partial pressure (0.5-1) P H2,feed : Hydrogen partial pressure in the feed side (bar) P H2,perm : Hydrogen partial pressure in the permeate side (bar) 513 P a g e
5 When pressure is relatively low, diffusion is assumed to be rate limiting step and factor n is equal to 0.5 [10]. Hence the equation becomes Sievert s Fick law: J H2 = ( P 0.5 H2, feed - P 0.5 H2, perm ) (2) The relationship between hydrogen permeability and temperature follows an Arrhenius behavior P eh2 = P 0 eh2 exp (-E a /RT) (3) Where P 0 eh2 is the pre-exponential factor, E a the apparent activation energy, R the universal gas constant and T the absolute temperature. Thus by using equation (2) Hydrogen permeating flux can be determine in terms of mol/m 2 s. and once the hydrogen permeating flux for given area is determined, the exact amount of hydrogen transported through the membrane can be obtain for known area of the membrane and time by using the following relation. Number of mole = III. CONCLUSION A theoretical approach concerning palladium based membranes (Pd/Ag), in order to control hydrogen evolution during Electrochemical Machining is presented. The corresponding mathematical equation and experimental procedure to determine the permeability of H 2 through the same has also been proposed. The hydrogen gas evolution at cathode can be minimizing as the maximum fraction of H 2 will be transported through membrane and hence the local anodic dissolution enhances with better accuracy and high surface finish. Based upon the concept of H 2 gas transported through Pd/Ag membrane mathematical equations are proposed. REFERENCES [1] Acharya, B.G., Jain,V.K and Batra, J.L., Multi Objective Optimization of ECM Process", Precision Engineering, Vol. 8, No. 2, 1986, pp , [2] Hocheng, H., Kao, P.S and Lin, S. C., Prediction of the Eroded Profile during Electrochemical Machining of Hole, Proc. JSME/ASME Int. Conf. Materials and Processing, 2002,pp [3] Jain,V.K and Murugan, S., Int. J. Prod. Res , 1986 ; Dayanand S.Biligi, V.K Jain R.Shekhar R, Mehrotra Shaifali J.Material Processing Technology, 2004,149, [4] Mukherjee, S.K., Kumar, S., Srivastava, P.K., Kumar, Arbind.,Effect of valency on metal removal rate in Electrochemical Machining of aluminium. J. Material Processing Technology P a g e
6 [5] Schultze, J.W, and Bressel, A., Principle of Electro chemical Micro and Nano- system Technologies:, Electrochimica Acta, Vol.47; 2001,pp 3-21,. [6] Bhattacharya, B., Doloi, B., and Sridhar, P.J Electrochemical Micromachining: New possibilities for Micro Manufacturing, J. Material. Proc.Tech; Vol.113, 2001, pp [7] Acharya, B. G, Jain, V. K. and Batra, J. L. "Multi Objective Optimization of ECM Process", Precision Engineering, Vol. 8, No. 2, 1986, pp , [8] Koros, W.J., Fleming, G.K Membrane-based gas separation. J Memb Sci 83:1 80 [9] Basile, A Hydrogen production using Pd-based membrane reactors for fuel cells. Top Catal 51: , [10] Dolald, M.D., Dave, N.C., Ilyushechkin, A.Y., Morpeth, L.D., McLennan, K.G. Composition and operation of hydrogen-selective amorphous alloy membranes. J Memb Sci 285:30 55, P a g e
Effect of Over Voltage on Material Removal Rate During Electrochemical Machining
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 8, No 1, pp. 23 28 (2005) 23 Effect of Over Voltage on Material Removal Rate During Electrochemical Machining S. K. Mukherjee 1, S. Kumar 1 and P. K. Srivastava
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 8, No 1, pp. 23 28 (2005) 23 Effect of Over Voltage on Material Removal Rate During Electrochemical Machining S. K. Mukherjee 1, S. Kumar 1 and P. K. Srivastava
High Rate Anodic Dissolution of Stainless Steel 316 (SS316) Using Nano Zero Valent Iron as Reducing Agent
 Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 47 52 (2016) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2016.19.1.06 High Rate Anodic Dissolution of Stainless Steel 316 (SS316) Using Nano Zero Valent Iron as Reducing
Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 47 52 (2016) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2016.19.1.06 High Rate Anodic Dissolution of Stainless Steel 316 (SS316) Using Nano Zero Valent Iron as Reducing
DEVELOPMENT OF AN ELECTRO CHEMICAL MACHINE SET-UP AND EXPERIMENTATIONS
 DEVELOPMENT OF AN ELECTRO CHEMICAL MACHINE SET-UP AND EXPERIMENTATIONS Aniket Jadhav 1, Kishor D. Patil, D. B. Jadhav 3, W. G. Kharche 4 1 M.Tech.Student, Mechanical Engineering Department, B.V.D.U.C.O.E.
DEVELOPMENT OF AN ELECTRO CHEMICAL MACHINE SET-UP AND EXPERIMENTATIONS Aniket Jadhav 1, Kishor D. Patil, D. B. Jadhav 3, W. G. Kharche 4 1 M.Tech.Student, Mechanical Engineering Department, B.V.D.U.C.O.E.
Experimental Study on Parametric Optimization of Titanium based Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) in Electrochemical Machining Process
 Experimental Study on Parametric Optimization of Titanium based Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) in Electrochemical Machining Process Pravin D.Babar Mechanical Engineering Department, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology
Experimental Study on Parametric Optimization of Titanium based Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) in Electrochemical Machining Process Pravin D.Babar Mechanical Engineering Department, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology
Experimental Investigation of Machining Parameter in Electrochemical Machining
 Experimental Investigation of Machining Parameter in Electrochemical Machining Deepanshu Shrivastava 1, Abhinav Sharma 2, Harsh Pandey 2 1 M.TECH Sholar, DR.C.V. RAMAN UNIVERSITY, KOTA C.G.,INDIA 2 M.TECH
Experimental Investigation of Machining Parameter in Electrochemical Machining Deepanshu Shrivastava 1, Abhinav Sharma 2, Harsh Pandey 2 1 M.TECH Sholar, DR.C.V. RAMAN UNIVERSITY, KOTA C.G.,INDIA 2 M.TECH
Need & Overview of Electrochemical Micro Machining
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-490, ISSN(Online):455-9555 Vol.10 No.10, pp 5-45, 017 Need & Overview of Electrochemical Micro Machining S.Dharmalingam 1, C.Sabarinathan,
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-490, ISSN(Online):455-9555 Vol.10 No.10, pp 5-45, 017 Need & Overview of Electrochemical Micro Machining S.Dharmalingam 1, C.Sabarinathan,
International journal of advanced production and industrial engineering. Bare tool design to overcome overcut problem in ECM process
 Available online at www.ijapie.org International journal of advanced production and industrial engineering IJAPIE-2017-01-112, Vol 2 (1), 07-16 IJAPIE Connecting Science & Technology with Management. A
Available online at www.ijapie.org International journal of advanced production and industrial engineering IJAPIE-2017-01-112, Vol 2 (1), 07-16 IJAPIE Connecting Science & Technology with Management. A
Optimization of Machining Parameters in ECM of Al/B4C Composites Using Taguchi Method
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2014. 12, 2: 87-97 Optimization of Machining Parameters in ECM of Al/B4C Composites Using Taguchi Method S. R. Rao a* and G. Padmanabhan b a Department
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2014. 12, 2: 87-97 Optimization of Machining Parameters in ECM of Al/B4C Composites Using Taguchi Method S. R. Rao a* and G. Padmanabhan b a Department
Aalborg Universitet. Transport phenomena in gas-selective silica membranes Boffa, Vittorio. Creative Commons License Unspecified
 Aalborg Universitet Transport phenomena in gas-selective silica membranes Boffa, Vittorio Creative Commons License Unspecified Publication date: 2016 Link to publication from Aalborg University Citation
Aalborg Universitet Transport phenomena in gas-selective silica membranes Boffa, Vittorio Creative Commons License Unspecified Publication date: 2016 Link to publication from Aalborg University Citation
ECM PROCESS CHARACTERISTICS
 ECM PROCESS CHARACTERISTICS A PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT FOR THE DEGREE OF Bachelor of Technology In Mechanical Engineering Submitted by: ANIL KUMAR MEHER ROLL NO. : 10503046
ECM PROCESS CHARACTERISTICS A PROJECT SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT FOR THE DEGREE OF Bachelor of Technology In Mechanical Engineering Submitted by: ANIL KUMAR MEHER ROLL NO. : 10503046
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Introduction to Mass Transfer
 Introduction to Mass Transfer Introduction Three fundamental transfer processes: i) Momentum transfer ii) iii) Heat transfer Mass transfer Mass transfer may occur in a gas mixture, a liquid solution or
Introduction to Mass Transfer Introduction Three fundamental transfer processes: i) Momentum transfer ii) iii) Heat transfer Mass transfer Mass transfer may occur in a gas mixture, a liquid solution or
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12. Chem 4631
 Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12 Chem 4631 What is a fuel cell? An electro-chemical energy conversion device A factory that takes fuel as input and produces electricity as output. O 2 (g) H 2 (g)
Advanced Analytical Chemistry Lecture 12 Chem 4631 What is a fuel cell? An electro-chemical energy conversion device A factory that takes fuel as input and produces electricity as output. O 2 (g) H 2 (g)
e - Galvanic Cell 1. Voltage Sources 1.1 Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell
 Galvanic cells convert different forms of energy (chemical fuel, sunlight, mechanical pressure, etc.) into electrical energy and heat. In this lecture, we are interested in some examples of galvanic cells.
Galvanic cells convert different forms of energy (chemical fuel, sunlight, mechanical pressure, etc.) into electrical energy and heat. In this lecture, we are interested in some examples of galvanic cells.
Electrophoretic Deposition. - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode
 Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
Simulation of the concrete chloride NT build-492 migration test
 Simulation of the concrete chloride NT build-492 migration test Aix-en-Provence, France May 29-June 1, 2012 J. Lizarazo-Marriaga 1, J. Gonzalez 1, P. Claisse 2, 1 Universidad Nacional de Colombia 2 Coventry
Simulation of the concrete chloride NT build-492 migration test Aix-en-Provence, France May 29-June 1, 2012 J. Lizarazo-Marriaga 1, J. Gonzalez 1, P. Claisse 2, 1 Universidad Nacional de Colombia 2 Coventry
Molecular Sieve Silica Membranes For H 2 /CO Separation
 Molecular Sieve Silica Membranes For H 2 /CO Separation M. C. Duke a, J. C. Diniz da Costa a, P. G. Gray b, G. Q. (Max) Lu a* a Department of Chemical Engineering, The University of Queensland Brisbane,
Molecular Sieve Silica Membranes For H 2 /CO Separation M. C. Duke a, J. C. Diniz da Costa a, P. G. Gray b, G. Q. (Max) Lu a* a Department of Chemical Engineering, The University of Queensland Brisbane,
Technical Data Sheet
 Technical Data Sheet Product Description: A photoelectrochemical (PEC) device capable of splitting water into storable hydrogen fuel directly using solar energy is becoming a very attractive technology
Technical Data Sheet Product Description: A photoelectrochemical (PEC) device capable of splitting water into storable hydrogen fuel directly using solar energy is becoming a very attractive technology
Design and Modelling of ECM Rifling Tool
 Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Simulation, Modelling and Optimization, Beijing, China, September 5-7, 7 369 Design and Modelling of ECM Rifling Tool R.A.MAHDAVINEJAD School of
Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Simulation, Modelling and Optimization, Beijing, China, September 5-7, 7 369 Design and Modelling of ECM Rifling Tool R.A.MAHDAVINEJAD School of
Membrane processes selective hydromechanical diffusion-based porous nonporous
 Membrane processes Separation of liquid or gaseous mixtures by mass transport through membrane (= permeation). Membrane is selective, i.e. it has different permeability for different components. Conditions
Membrane processes Separation of liquid or gaseous mixtures by mass transport through membrane (= permeation). Membrane is selective, i.e. it has different permeability for different components. Conditions
Influence of Input Parameters on Characteristics of Electro Chemical Machining Process
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 23., : 3-24 Influence of Input Parameters on Characteristics of Electro Chemical Machining Process C. Senthilkumara,*, G. Ganesana, and R. Karthikeyanb
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 23., : 3-24 Influence of Input Parameters on Characteristics of Electro Chemical Machining Process C. Senthilkumara,*, G. Ganesana, and R. Karthikeyanb
Chapter 17 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 17 Electrochemistry 17.1 Galvanic Cells A. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Rxns) 1. Oxidation = loss of electrons a. the substance oxidized is the reducing agent 2. Reduction = gain of electrons
Chapter 17 Electrochemistry 17.1 Galvanic Cells A. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Rxns) 1. Oxidation = loss of electrons a. the substance oxidized is the reducing agent 2. Reduction = gain of electrons
Electrochemical reaction
 Electrochemical reaction electrochemistry electrochem. reaction mechanism electrode potential Faradays law electrode reaction kinetics 1 Electrochemistry in industry Chlor-Alkali galvano industry production
Electrochemical reaction electrochemistry electrochem. reaction mechanism electrode potential Faradays law electrode reaction kinetics 1 Electrochemistry in industry Chlor-Alkali galvano industry production
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells of a galvanic cell?
 Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number
 General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
K n. III. Gas flow. 1. The nature of the gas : Knudsen s number. 2. Relative flow : Reynold s number R = ( dimensionless )
 III. Gas flow. The nature of the gas : Knudsen s number K n λ d 2. Relative flow : U ρ d η U : stream velocity ρ : mass density Reynold s number R ( dimensionless ) 3. Flow regions - turbulent : R > 2200
III. Gas flow. The nature of the gas : Knudsen s number K n λ d 2. Relative flow : U ρ d η U : stream velocity ρ : mass density Reynold s number R ( dimensionless ) 3. Flow regions - turbulent : R > 2200
Design of arrow-head electrode in electropolishing of cylindrical part
 312 Int. J. Materials and Product Technology, Vol. 20, No. 4, 2004 Design of arrow-head electrode in electropolishing of cylindrical part H. Hocheng* Department of Power Mechanical Engineering, National
312 Int. J. Materials and Product Technology, Vol. 20, No. 4, 2004 Design of arrow-head electrode in electropolishing of cylindrical part H. Hocheng* Department of Power Mechanical Engineering, National
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: Solutions In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Agitation prevents settling
Assessment Chapter Test A Chapter: Solutions In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Agitation prevents settling
Fernando O. Raineri. Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby).
 Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
Fernando O. Raineri Office Hours: MWF 9:30-10:30 AM Room 519 Tue. 3:00-5:00 CLC (lobby). P1) What is the reduction potential of the hydrogen electrode g bar H O aq Pt(s) H,1 2 3 when the aqueous solution
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
Dr. Anand Gupta
 By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
Chapter 18. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
CHAPTER 6 Modern Theory Principles LECTURER SAHEB M. MAHDI
 CHAPTER 6 Modern Theory Principles LECTURER SAHEB M. MAHDI Modern Theory principles in Corrosion and their applications :- Corrosion studies can be carried-out by two methods 1 Thermodynamics. or 2 By
CHAPTER 6 Modern Theory Principles LECTURER SAHEB M. MAHDI Modern Theory principles in Corrosion and their applications :- Corrosion studies can be carried-out by two methods 1 Thermodynamics. or 2 By
Performance Simulation of Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
 International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 50-334 Volume 8, Number 1 (018), pp. 05-1 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Performance Simulation of Passive Direct
International Journal of Advanced Mechanical Engineering. ISSN 50-334 Volume 8, Number 1 (018), pp. 05-1 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Performance Simulation of Passive Direct
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
Fuel Cells Activation polarization
 Fuel Cells The principle of fuel cells Oxygen and hydrogen, when mixed together in the presence of enough activation energy have a natural tendency to react and form water, because the Gibbs free energy
Fuel Cells The principle of fuel cells Oxygen and hydrogen, when mixed together in the presence of enough activation energy have a natural tendency to react and form water, because the Gibbs free energy
REACTION KINETICS OF CORROSION OF MILD STEEL IN PHOSPHORIC ACID
 Journal of the University Aprael of S. Chemical Yaro, Rafal Technology K. Wael, Anees and Metallurgy, A. Khadom45, 4, 010, 443-448 REACTION KINETICS OF CORROSION OF MILD STEEL IN PHOSPHORIC ACID Aprael
Journal of the University Aprael of S. Chemical Yaro, Rafal Technology K. Wael, Anees and Metallurgy, A. Khadom45, 4, 010, 443-448 REACTION KINETICS OF CORROSION OF MILD STEEL IN PHOSPHORIC ACID Aprael
Name: Regents Chemistry Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
D DAVID PUBLISHING. 1. Introduction. Akira Nishimura 1, Masashi Baba 1, Kotaro Osada 1, Takenori Fukuoka 1, Masafumi Hirota 1 and Eric Hu 2
 Journal of Energy and Power Engineering () - doi:./-/.. D DAVID PUBLISHING Temperature Distributions in Single Cell of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Simulated by an D Multi-plate Heat-Transfer Model and
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering () - doi:./-/.. D DAVID PUBLISHING Temperature Distributions in Single Cell of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Simulated by an D Multi-plate Heat-Transfer Model and
State-Space Modeling of Electrochemical Processes. Michel Prestat
 State-Space Modeling of Electrochemical Processes Who uses up my battery power? Michel Prestat ETH-Zürich Institute for Nonmetallic Materials Head: Prof. L.J. Gauckler Outline Electrochemistry Electrochemical
State-Space Modeling of Electrochemical Processes Who uses up my battery power? Michel Prestat ETH-Zürich Institute for Nonmetallic Materials Head: Prof. L.J. Gauckler Outline Electrochemistry Electrochemical
Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous
 Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electric energy to bring
Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electric energy to bring
Supplementary Figure 1 Nano-beam electron diffraction Nano-beam electron diffraction
 Supplementary Figure 1 Nano-beam electron diffraction Nano-beam electron diffraction (NBED) patterns of different Pd-W nanoparticles on OMCs (Pd-W/OMCs), all exhibiting a body-centered cubic (bcc) microstructure.
Supplementary Figure 1 Nano-beam electron diffraction Nano-beam electron diffraction (NBED) patterns of different Pd-W nanoparticles on OMCs (Pd-W/OMCs), all exhibiting a body-centered cubic (bcc) microstructure.
7.1 Electrolyte and electrolytic solution
 Out-class reading: Levine, pp. 294-310 Section 10.6 solutions of electrolytes Section 10.9 ionic association pp. 512-515 Section 16.6 electrical conductivity of electrolyte solutions. Contents of solution
Out-class reading: Levine, pp. 294-310 Section 10.6 solutions of electrolytes Section 10.9 ionic association pp. 512-515 Section 16.6 electrical conductivity of electrolyte solutions. Contents of solution
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Basic Concepts of Electrochemistry
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electricity-driven Chemistry or Chemistry-driven Electricity Electricity: Chemistry (redox): charge flow (electrons, holes, ions) reduction = electron uptake oxidation = electron loss
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electricity-driven Chemistry or Chemistry-driven Electricity Electricity: Chemistry (redox): charge flow (electrons, holes, ions) reduction = electron uptake oxidation = electron loss
Chapter 2 Transport Mechanism of Carbon Membranes 2.1 Transport of Gas Through CMSMs
 Chapter 2 Transport Mechanism of Carbon Membranes 2.1 Transport of Gas Through CMSMs Mass transfer of gas through a porous membrane can involve several processes depending on the pore structure and the
Chapter 2 Transport Mechanism of Carbon Membranes 2.1 Transport of Gas Through CMSMs Mass transfer of gas through a porous membrane can involve several processes depending on the pore structure and the
CHAPTER 12. Practice exercises
 CHAPTER 12 Practice exercises 12.1 2Al(s) + 3Cl 2 (g) 2AlCl 3 (aq) Aluminium is oxidised and is therefore the reducing agent. Chlorine is reduced and is therefore the oxidising agent. 12.3 First the oxidation
CHAPTER 12 Practice exercises 12.1 2Al(s) + 3Cl 2 (g) 2AlCl 3 (aq) Aluminium is oxidised and is therefore the reducing agent. Chlorine is reduced and is therefore the oxidising agent. 12.3 First the oxidation
balancing equations notes website 2018.notebook November 12, 2018
 1 Particle model and Balancing Equations Used to show chemical reactions have occured. Matter is made up of atoms and molecules and is subject to change. Counting atoms in a molecule NaCl 3 NaCl Na 2 SO
1 Particle model and Balancing Equations Used to show chemical reactions have occured. Matter is made up of atoms and molecules and is subject to change. Counting atoms in a molecule NaCl 3 NaCl Na 2 SO
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Modeling Hydrogen Permeation through a TiO 2 Film and Palladium
 Modeling Hydrogen Permeation through a TiO 2 Film and Palladium Zack Qin, Y. Zeng, P.R. Norton, and D.W. Shoesmith Department of Chemistry and Surface Science Western Western University London, Ontario,
Modeling Hydrogen Permeation through a TiO 2 Film and Palladium Zack Qin, Y. Zeng, P.R. Norton, and D.W. Shoesmith Department of Chemistry and Surface Science Western Western University London, Ontario,
Electrodes are normally made out of inert (unreactive) materials. Graphite and platinum are common electrode materials.
 Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
INDIVIDUAL EXAM INDIVIDUAL WUCT 2018
 INDIVIDUAL EXAM WUCT 2018 60 minutes are allotted for the individual round. Questions on the individual exam will consist of multiple parts that must each be answered with numerical results or short answers.
INDIVIDUAL EXAM WUCT 2018 60 minutes are allotted for the individual round. Questions on the individual exam will consist of multiple parts that must each be answered with numerical results or short answers.
POLITECNICO DI MILANO
 POLITECNICO DI MILANO Facoltà di Ingegneria Industriale POLITECNICO DI MILANO Department Corso di Laurea of Energy in Doctoral Ingegneria Program in Energy and Nuclear Science and Technology DMFC MODELING:
POLITECNICO DI MILANO Facoltà di Ingegneria Industriale POLITECNICO DI MILANO Department Corso di Laurea of Energy in Doctoral Ingegneria Program in Energy and Nuclear Science and Technology DMFC MODELING:
Technologies and Approaches of CO 2 Capture
 Southwest Regional Partnership Project Technologies and Approaches of CO 2 Capture Liangxiong Li, Brian McPherson, Robert Lee Petroleum Recovery Research Center New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology,
Southwest Regional Partnership Project Technologies and Approaches of CO 2 Capture Liangxiong Li, Brian McPherson, Robert Lee Petroleum Recovery Research Center New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology,
On Continuum Models for Heat Transfer in Small Scale Porous Materials Professor Jinliang Yuan
 On Continuum Models for Heat Transfer in Small Scale Porous Materials Professor Jinliang Yuan August 30, 2013 Department of Energy Sciences Lund University, Sweden Jinliang.yuan@energy.lth.se Why porous
On Continuum Models for Heat Transfer in Small Scale Porous Materials Professor Jinliang Yuan August 30, 2013 Department of Energy Sciences Lund University, Sweden Jinliang.yuan@energy.lth.se Why porous
MEMBRANE CAPACITIVE DEIONIZATION
 MEMBRANE CAPACITIVE DEIONIZATION Albert van der Wal and Hank Reinhoudt Voltea b.v., Wassenaarseweg 72, 2333 AL, Leiden, the Netherlands Presenter Hank Reinhoudt Corresponding author: Hank.Reinhoudt@voltea.com
MEMBRANE CAPACITIVE DEIONIZATION Albert van der Wal and Hank Reinhoudt Voltea b.v., Wassenaarseweg 72, 2333 AL, Leiden, the Netherlands Presenter Hank Reinhoudt Corresponding author: Hank.Reinhoudt@voltea.com
CHEMISTRY 15 EXAM II-Version A (White)
 CHEMISTRY 15 EXAM II-Version A (White) Dr. M. Richards-Babb June 8, 2001 An optical scoring machine will grade this examination. The machine is not programmed to accept the correct one of two sensed answers
CHEMISTRY 15 EXAM II-Version A (White) Dr. M. Richards-Babb June 8, 2001 An optical scoring machine will grade this examination. The machine is not programmed to accept the correct one of two sensed answers
AUTOMOTIVE EXHAUST AFTERTREATMENT
 AUTOMOTIVE EXHAUST AFTERTREATMENT CATALYST FUNDAMENTLS Catalyst in its simplest term is a material that increase the rate (molecules converted by unit time) of a chemical reaction while itself not undergoing
AUTOMOTIVE EXHAUST AFTERTREATMENT CATALYST FUNDAMENTLS Catalyst in its simplest term is a material that increase the rate (molecules converted by unit time) of a chemical reaction while itself not undergoing
3.014 MATERIALS LABORATORY MODULE- β3 November 16 21, 2005 GEETHA P. BERERA. Visualizing Gibbs Free Energy Anodic Corrosion and the EMF Series
 3.014 MATERIALS LABORATORY MODULE- β3 November 16 21, 2005 GEETHA P. BERERA Visualizing Gibbs Free Energy Anodic Corrosion and the EMF Series OBJECTIVES: Understand what is galvanic (anodic) corrosion
3.014 MATERIALS LABORATORY MODULE- β3 November 16 21, 2005 GEETHA P. BERERA Visualizing Gibbs Free Energy Anodic Corrosion and the EMF Series OBJECTIVES: Understand what is galvanic (anodic) corrosion
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful
 What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
Experimental Study of Effect of Parameter variations on output parameters for Electrochemical Machining of SS AISI 202
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684 Volume 5, Issue 5 (Mar. - Apr. 2013), PP 65-71 Experimental Study of Effect of Parameter variations on output parameters for
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684 Volume 5, Issue 5 (Mar. - Apr. 2013), PP 65-71 Experimental Study of Effect of Parameter variations on output parameters for
Chemical Reactions. Burlingame High School Chemistry 1
 Chemical Reactions 1 Chemical Equations Chemical equations are use to describe: the substances that react, the reactants the substances that are formed, the products the relative amounts of all substances
Chemical Reactions 1 Chemical Equations Chemical equations are use to describe: the substances that react, the reactants the substances that are formed, the products the relative amounts of all substances
Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis
 Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis Electrolysis is defined as the passage of an electric current through an electrolyte with subsequent migration of positively and negatively charged ions
Electrolysis and Faraday's laws of Electrolysis Electrolysis is defined as the passage of an electric current through an electrolyte with subsequent migration of positively and negatively charged ions
i i ne. (1) i The potential difference, which is always defined to be the potential of the electrode minus the potential of the electrolyte, is ln( a
 We re going to calculate the open circuit voltage of two types of electrochemical system: polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells and lead-acid batteries. To do this, we re going to make use of two
We re going to calculate the open circuit voltage of two types of electrochemical system: polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells and lead-acid batteries. To do this, we re going to make use of two
GATUNDU SUB COUNTY FORM FOUR 2014 EVALUATION EXAM
 NAME.. IDEX NO. 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (THEORY) TIME; 2HRS Instructions; Candidates signature.. Date GATUNDU SUB COUNTY FORM FOUR 2014 EVALUATION EXAM Answer all the questions in the space provided Mathematical
NAME.. IDEX NO. 233/1 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 (THEORY) TIME; 2HRS Instructions; Candidates signature.. Date GATUNDU SUB COUNTY FORM FOUR 2014 EVALUATION EXAM Answer all the questions in the space provided Mathematical
ELECTROCHEMISTRY (SUMMER VACATION WORKSHEET)
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY (SUMMER VACATION WORKSHEET) QUESTION CARRYING 1 MARK 1. What is the effect of temperature on molar conductivity? 2. Why is it not possible to measure single electrode potential? 3. Name
ELECTROCHEMISTRY (SUMMER VACATION WORKSHEET) QUESTION CARRYING 1 MARK 1. What is the effect of temperature on molar conductivity? 2. Why is it not possible to measure single electrode potential? 3. Name
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry
 Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
Paper I PHYSICS TEST CODE Paper II CHEMISTRY TEST CODE 1371
 Physics by Shiv R Goel, (B.Tech, IIT Delhi) WAVES Chemistry by Dr. Sangeeta Khanna, Ph.D. (CCC) MOCK TEST - NAME: ROLL NO. Time: 3 Hr. Date 04.08.03 Max. Marks:98 BOOKLET A Paper I PHYSICS TEST CODE 370
Physics by Shiv R Goel, (B.Tech, IIT Delhi) WAVES Chemistry by Dr. Sangeeta Khanna, Ph.D. (CCC) MOCK TEST - NAME: ROLL NO. Time: 3 Hr. Date 04.08.03 Max. Marks:98 BOOKLET A Paper I PHYSICS TEST CODE 370
18.3 Electrolysis. Dr. Fred Omega Garces. Chemistry 201. Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction. Miramar College.
 18.3 Electrolysis Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Electrolysis Voltaic Vs. Electrolytic Cells Voltaic Cell Energy is released
18.3 Electrolysis Driving a non-spontaneous Oxidation-Reduction Reaction Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College 1 Electrolysis Voltaic Vs. Electrolytic Cells Voltaic Cell Energy is released
UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Studies on bi-directional hydrogen isotopes permeation through the first wall of a magnetic fusion power reactor
 Studies on bi-directional hydrogen isotopes permeation through the first wall of a magnetic fusion power reactor IAEA-CRP Plasma-Wall Interaction with Reduced Activation Steel Surfaces in Fusion Devices
Studies on bi-directional hydrogen isotopes permeation through the first wall of a magnetic fusion power reactor IAEA-CRP Plasma-Wall Interaction with Reduced Activation Steel Surfaces in Fusion Devices
Measurement and modelling of hydrogen uptake and transport. Alan Turnbull
 Measurement and modelling of hydrogen uptake and transport Alan Turnbull Hydrogen gas (+ H 2 O vapour, H 2 S) dissociation General and localised corrosion, cathodic protection, galvanic coupling; electroplating
Measurement and modelling of hydrogen uptake and transport Alan Turnbull Hydrogen gas (+ H 2 O vapour, H 2 S) dissociation General and localised corrosion, cathodic protection, galvanic coupling; electroplating
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials. Compiled by. Dr. A.O. Oladebeye
 CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
Gas Permeation Study Using Porous Ceramic Membranes
 Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 4, No. 3; 2014 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Gas Permeation Study Using Porous Ceramic Membranes Mohammed N.
Energy and Environment Research; Vol. 4, No. 3; 2014 ISSN 1927-0569 E-ISSN 1927-0577 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Gas Permeation Study Using Porous Ceramic Membranes Mohammed N.
CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 3
 CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 3 April 4, 2012 (50 minutes) Name (please print) Please box your answers, and remember that significant figures, phases (for chemical equations), and units do count! 1. (18 points)
CHEM 10123/10125, Exam 3 April 4, 2012 (50 minutes) Name (please print) Please box your answers, and remember that significant figures, phases (for chemical equations), and units do count! 1. (18 points)
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Learning goals and key skills: Identify oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent in a chemical equation Complete and balance redox equations using the method
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Learning goals and key skills: Identify oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent in a chemical equation Complete and balance redox equations using the method
Optimization of process parameter in electrochemical machining. Of Inconel 718 by Taguchi analysis
 International Journal of Engineering Research and General Science Volume, Issue, January-February, 05 ISSN 09-70 Optimization of process parameter in electrochemical machining Of Inconel 78 by Taguchi
International Journal of Engineering Research and General Science Volume, Issue, January-February, 05 ISSN 09-70 Optimization of process parameter in electrochemical machining Of Inconel 78 by Taguchi
Review. Chapter 17 Electrochemistry. Outline. Voltaic Cells. Electrochemistry. Mnemonic
 Review William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. Neth cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Oxidation Loss of electrons Occurs at electrode called the anode Reduction Gain of
Review William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. Neth cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Oxidation Loss of electrons Occurs at electrode called the anode Reduction Gain of
Multi-Objective Optimization of Electrochemical machining of EN31 steel by Grey Relational Analysis
 International Journal of Modeling and Optimization, Vol. 1, No., June 011 Multi-Objective Optimization of Electrochemical machining of EN1 steel by Grey Relational Analysis D. Chakradhar, A. Venu Gopal
International Journal of Modeling and Optimization, Vol. 1, No., June 011 Multi-Objective Optimization of Electrochemical machining of EN1 steel by Grey Relational Analysis D. Chakradhar, A. Venu Gopal
ph = pk a + log 10 {[base]/[acid]}
![ph = pk a + log 10 {[base]/[acid]} ph = pk a + log 10 {[base]/[acid]}](/thumbs/80/80846619.jpg) FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
FORMULA SHEET (tear off) N A = 6.022 x 10 23 C = ( 5 / 9 ) ( F - 32) F = ( 9 / 5 )( C) + 32 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-27 kg C = K - 273.15 K = C + 273.15 1 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg 1 atm = 1.013 bar pv = nrt
SURFACE SMOOTHING USING ULTRASONICALLY ASSISTED PULSE ELECTROCHEMICAL MACHINING
 Proceedings of the 4 nd International Conference on Machining and Measurements of Sculptured Surfaces Kraków, 7 9 September 006 SURFACE SMOOTHING USING ULTRASONICALLY ASSISTED PULSE ELECTROCHEMICAL MACHINING
Proceedings of the 4 nd International Conference on Machining and Measurements of Sculptured Surfaces Kraków, 7 9 September 006 SURFACE SMOOTHING USING ULTRASONICALLY ASSISTED PULSE ELECTROCHEMICAL MACHINING
CHAPTER 1 QUANTITATIVE CHEMISTRY
 Page 4 Ex 4 (a) element; (b) mixture; (c) compound; (d) element; (e) compound 5. (a) mixture; (b) compound; (c) mixture; (d) element; (e) compound. Page 5 Ex 1.1 3. C 4. D 5. C 6. D 7. a) 0.20 b) 1.2 10
Page 4 Ex 4 (a) element; (b) mixture; (c) compound; (d) element; (e) compound 5. (a) mixture; (b) compound; (c) mixture; (d) element; (e) compound. Page 5 Ex 1.1 3. C 4. D 5. C 6. D 7. a) 0.20 b) 1.2 10
Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry
 Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Oxidation-Reduction Review. Electrochemistry. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Sample Problem.
 1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation
 Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
Synthesis of Zeolite Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation April. 10. 2003 Sang Hoon Hyun, Dong Wook Shin, Young Eun Lee, Moon Hee Han*, and Churl Hee Cho* School of Materials Science & Engineering Yonsei
electrodeposition is a special case of electrolysis where the result is deposition of solid material on an electrode surface.
 Electrochemical Methods Electrochemical Deposition is known as electrodeposition - see CHEM* 1050 - electrolysis electrodeposition is a special case of electrolysis where the result is deposition of solid
Electrochemical Methods Electrochemical Deposition is known as electrodeposition - see CHEM* 1050 - electrolysis electrodeposition is a special case of electrolysis where the result is deposition of solid
EVALUATION OF Ag/AgCl SENSORS FOR IN-SITU MONITORING OF FREE CHLORIDE CONCENTRATION IN REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURES
 EVALUATION OF Ag/AgCl SENSORS FOR IN-SITU MONITORING OF FREE CHLORIDE CONCENTRATION IN REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURES Farhad Pargar, Dessi Koleva, Oguzhan Copuroglu, Eduard Koenders, Klaas vab Breugel
EVALUATION OF Ag/AgCl SENSORS FOR IN-SITU MONITORING OF FREE CHLORIDE CONCENTRATION IN REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURES Farhad Pargar, Dessi Koleva, Oguzhan Copuroglu, Eduard Koenders, Klaas vab Breugel
SEPARATION BY BARRIER
 SEPARATION BY BARRIER SEPARATION BY BARRIER Phase 1 Feed Barrier Phase 2 Separation by barrier uses a barrier which restricts and/or enhances the movement of certain chemical species with respect to other
SEPARATION BY BARRIER SEPARATION BY BARRIER Phase 1 Feed Barrier Phase 2 Separation by barrier uses a barrier which restricts and/or enhances the movement of certain chemical species with respect to other
Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at
 Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Chapter 7 What is steady state diffusion? Steady-state diffusion is diffusion in which the concentration of the diffusing atoms at any point, x, and hence the concentration gradient at x, in the solid,
Sulfur Poisoning of Pd and PdCu Alloy Hydrogen Separation Membranes. the degree of. Doctor of Philosophy. Chemical Engineering. Casey P.
 Sulfur Poisoning of Pd and PdCu Alloy Hydrogen Separation Membranes Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Chemical Engineering Casey P. O Brien
Sulfur Poisoning of Pd and PdCu Alloy Hydrogen Separation Membranes Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Chemical Engineering Casey P. O Brien
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 008, 8, 1475-1487 Full Research Paper sensors ISSN 144-80 008 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Three-Dimensional Transport Modeling for Proton Exchange Membrane(PEM) Fuel Cell with Micro Parallel Flow
Sensors 008, 8, 1475-1487 Full Research Paper sensors ISSN 144-80 008 by MDPI www.mdpi.org/sensors Three-Dimensional Transport Modeling for Proton Exchange Membrane(PEM) Fuel Cell with Micro Parallel Flow
Chemistry 102 Chapter 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS
 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. Electrons are transferred from Al to Cu 2+. We can re write this equation as two separate half reactions:
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY A. INTRODUCTION 1. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which is concerned with the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, and vice versa. Electrochemical reactions
ELECTROCHEMISTRY A. INTRODUCTION 1. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which is concerned with the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, and vice versa. Electrochemical reactions
Kentaro INOUE. Introduction. Measurement principle (membrane polarographic method)
 FFeature Article Article Performance of the Dissolved Oxygen Monitor Used in the Semiconductor Wet Process; Low Concentration Monitoring, High Temperature, Small Amount of Sampling Volume, Chemical Resistance
FFeature Article Article Performance of the Dissolved Oxygen Monitor Used in the Semiconductor Wet Process; Low Concentration Monitoring, High Temperature, Small Amount of Sampling Volume, Chemical Resistance
Isotope Effects on Tritium Mass Transfer in Li 17 Pb 83 Liquid Blanket
 CJWS-3 Kunming, China, Jun 0-3, 010 Isotope Effects on Tritium Mass Transfer in Li 17 Pb 83 Liquid Blanket S. Fukada, *Y. Edao, H. Okitsu and M. Okada Department Of Advanced Energy Engineering Science
CJWS-3 Kunming, China, Jun 0-3, 010 Isotope Effects on Tritium Mass Transfer in Li 17 Pb 83 Liquid Blanket S. Fukada, *Y. Edao, H. Okitsu and M. Okada Department Of Advanced Energy Engineering Science
Effects of Complexing Agent on Electrochemical Micro Machining of Stainless Steel
 American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (1): 7-12, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications Effects of Complexing Agent on Electrochemical Micro Machining of Stainless Steel 1,2 Chen Hui, 2 Wang Yu-Kui,
American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (1): 7-12, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications Effects of Complexing Agent on Electrochemical Micro Machining of Stainless Steel 1,2 Chen Hui, 2 Wang Yu-Kui,
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells
 Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
Direct Energy Conversion: Fuel Cells References and Sources: Direct Energy Conversion by Stanley W. Angrist, Allyn and Beacon, 1982. Fuel Cell Systems, Explained by James Larminie and Andrew Dicks, Wiley,
Chapter 12 & 13 Test Review. Bond, Ionic Bond
 Chapter 12 & 13 Test Review A solid solute dissolved in a solid solvent is an Alloy What is happening in a solution at equilibrium? The Ionic rate of Bond dissolving is equal to the rate of crystallization.
Chapter 12 & 13 Test Review A solid solute dissolved in a solid solvent is an Alloy What is happening in a solution at equilibrium? The Ionic rate of Bond dissolving is equal to the rate of crystallization.
