Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Psychrometrics
|
|
|
- Kristopher Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 21) Solutions to Example Problems on Psychrometrics 1. We begin by identifying the conditions of the two streams on the psychrometric chart as follows. For the first stream, the point on the psychrometric chart is obtained by following the constant enthalpy line of 175 kj/kg till we intersect the relative humidity curve of 15 %. For the second stream, the point on the psychrometric chart is obtained by following the constant wet bulb temperature of 25 C till we intersect the humidity ratio line corresponding to kg water / kg dry air. We then join the two points on the psychrometric chart by a straight line. The length of this line was measured and found to be 5.5 cm. We then mark out [2/(2 + )](5.5)] cm (= 2.2 cm) from the point corresponding to the first stream on the line joining the two points, and this point represents the conditions of the mixture of the two streams. The properties of the mixture were determined from the psychrometric chart to be: T db = 59 C, T wb = 5.8 C, W = kg water / kg dry air RH = 2 %, H = 15 kj/kg, V' = 0.98 m /kg dry air 2. We first identify the conditions of the air on the psychrometric chart by following the constant enthalpy line of 190 kj/kg till we intersect the line corresponding to a specific volume of 1.07 m /kg dry air. In order to determine the dew point temperature of this air, we move horizontally from this point to the left till we intersect the 100 % relative humidity line (this corresponds to the dew-point temperature) and we find that the dew-point is 6.5 C.. We perform the following energy balance to determine the enthalpy of the heated air (H 2): m a (H 1) + 1,250 = m a (H 2) where m a = 60 kg/hr, and H 1 = 55 kj/kg dry air Converting to SI units, we get: m a = 1/60 kg/s, and H 1 = 55,000 J/kg dry air This yields, H = 10 kj/kg dry air 2 We identify the conditions of the inlet air on the psychrometric chart by following the constant enthalpy line of 55 kj/kg till we intersect the relative humidity line of 20 %. We then follow the constant humidity ratio line from this point and move to the right till we intersect the constant enthalpy line of 10 kj/kg dry air. This represents the conditions of the heated air. The humidity ratio of air at this point is kg water vapor / kg dry air (= W ) We then perform the following mass balance for water to determine the humidity ratio of the air exiting the spray dryer (= W ): m p (0.95) + m a (W 2) = m a (W ) - In the above equation m p = 15 x 10 /60 kg/s = kg/s and m a = 1/60 kg/s Solving, we get: W = kg water vapor / kg dry air Thus, to identify the conditions of the exit air, we follow the constant enthalpy line from the conditions of the heated air till we intersect the constant humidity ratio of At this point we find that the specific volume is 1.01 m /kg dry air and that the relative humidity is 10 %. 2
2 4. a. We begin by drawing a horizontal line from the 20 C point on the 100 % RH curve and intersecting it with the vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 0 C. This represents the conditions of the air at kg/s. We then follow the constant enthalpy line of 12 kj/kg till we intersect the horizontal line corresponding to a humidity ratio of kg water vapor per kg dry air. This represents the conditions of the air at 12 kg/s. We join the above two points by a straight line. The length of the line happens to 9.5 cm. We mark off {/(+12)}{9.5} cm from the second point (air at 12 kg/s) and this point represents the conditions of the mixture of the two streams of air. This point is 1.9 cm from the point that represents the conditions of air at 12 kg/s. The properties of the mixture at this point (Point A) are: Dry bulb temperature = 78 C Wet bulb temperature = 2.5 C Enthalpy = 11 kj/kg Relative humidity = 4.5 % Humidity ratio = kg water vapor / kg dry air Specific volume = 1.02 m / kg dry air b. From this point, we follow the constant enthalpy line till we intersect a relative humidity line of 40 %. This represents the conditions of the exit air (after drying the product) -- Point B on the chart. The humidity ratio at this point happens to be kg water vapor per kg dry air, the specific volume 0.94 m per kg dry air, and the enthalpy at this point happens to be 11 kj/kg dry air. From this point, we go horizontally till we intersect a relative humidity line of 10 %. This is point C on the chart. The enthalpy of the mixture at this point happens to be 145 kj/kg dry air. Amount of water removed from product = = (2/1.02) ( ) = kg/s Thus, in 0 minutes, amount of water removed = (0) (60) = 45.9 kg Initially, the product had 50 kg water and 150 kg solids. Finally, the product has ( ) kg water, i.e., 04.1 kg water and 150 kg solids. Thus final moisture content = 04.1/( ) = 0.67 = 67 % c. Energy supplied by heater = = (2/0.94) ( ) (10 ) = 70.2 kw 5. a. We begin by horizontal line from the 25 C point on the wet bulb saturation temperature curve till we intersect the constant enthalpy line of 90 kj/kg (this is point A on the chart). Since this air is heated till the dry bulb temperature is 85 C, we move horizontally from point A till we intersect the dry bulb temperature of 85 C (this is point B on the chart). The enthalpy at point B turns out to be 141 kj/kg. The wattage of the heater required to take air from point A to point B is given by:
3 Q = = 80 (142-90) = 4080 kj/hr = 1.16 kw b. To determine the exit conditions of the air (after drying), we follow a constant enthalpy line from point B till we intersect the 70% relative humidity line. From the chart, we see that the moisture contents of the air at points B and C are: W B = 0.02 kg water / kg dry air W = kg water / kg dry air C Thus, amount of water removed from product = = 80 ( ) = 1.64 kg/hr Since 1.64 kg of moisture is removed from milk every hour, and milk contains 90% moisture, the mass flow rate of milk = 1.64/0.9 = 1.82 kg/hr 6. We begin by identifying the conditions of ambient air by intersecting the dry bulb temperature line of 25 C with a relative humidity line of 50%. This is point A on the psychrometric chart. From this point, we draw a horizontal line and intersect it with the vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 90 C (point B on chart). The humidity ratio at point A and B is 0.01 kg water / kg dry air (= W ). In order to identify the condition of the exit air, we perform a water balance as follows (with the assumption that no moisture leaves with the dried milk powder): B 0.9 (2) + 85 (W B) = 85 (W C) Substituting W = 0.01, we get W = 0.01 kg water / kg dry air B C From point B, we follow a constant enthalpy line till we intersect a horizontal line corresponding to a humidity ratio of This represents the conditions of the exit air (point C on the chart). We note that the relative humidity at point C is 65 %. 7. We begin by identifying the state of the two streams of air on the low temperature range psychrometric chart. The point of intersection of the vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 0 C and the curved line corresponding to a relative humidity of 50% yields the conditions of the air of the first stream (point A on the chart). The point of intersection of the vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 45 C and the inclined line corresponding to a wet bulb temperature of 20 C yields the conditions of the air of the seconds stream (point B on the chart). We then join the points A and B by a straight line. The length of this line turns out to be 6.6 cm. The conditions of the mixture of the two streams of air (point C ) are obtained by dividing line AB in the inverse ratio of the mass flow rates of the two streams of air. Accordingly, distance AC = [/( + 2)]*5.5 =. cm Or, distance BC = [2/(2 + )]*5.5 = 2.2 cm Thus, we can locate point C on the chart. We then look at the constant relative humidity lines (curved lines) and note that the relative humidity at point C is ~ 18%.
4 8. We begin by identifying the conditions of ambient air on the psychrometric chart (point A ) as the point of intersection of the vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 25 C and the curved line corresponding to a relative humidity of 50%. The condition of the heated air is obtained by moving horizontally from point A till we intersect the vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 70 C (point B ). The condition of the exit air is obtained by following a constant enthalpy line from point B till we intersect the horizontal line corresponding to a dew point temperature of 25 C (point C ). a. Energy input to ambient air by heater = = (98-51) (2)/(0.86) = 109. kw Cost of operating heater for 2 hrs = (109.)(0.05)(2) = $ 10.9 b. Amount of moisture lost by product = amount of moisture gained by air = = (2/0.86) (20-10) = 2. g/s Thus, in 2 hrs, moisture lost by product = 2.*600*2 = g = kg Thus, final mass of product = ( ) = 82.2 kg Total moisture in product before drying = 0.75(250) = kg Total solids in product before drying = 0.25(250) = 62.5 kg Total moisture in product after drying = = 19.7 kg Total solids in product after drying = 62.5 kg Thus, moisture content of final product = [19.9/( )]*100 = 24 % 9. We begin by identifying the conditions of the first stream on the psychrometric chart (point 1 ) as follows. From the 25 C point on the 100% RH line, we move horizontally till we intersect the RH = 50% curved line. We then identify the conditions of the second stream (point 2') on the chart as follows. We draw a vertical line from the x-axis corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 60 C and intersect it with the horizontal line from the right side y- axis corresponding to humidity ratio of kg water / kg dry air. The mass flow rate of the first stream of air = 0.4/V 1' = 0.4/0.91 = 0.44 kg/s The mass flow rate of the second stream of air = 0.9/V ' = 0.9/0.96 = 0.94 kg/s The conditions of the mixture of the above two streams is determined as follows: We draw a straight line between points 1 and 2. The length of this line is.4 cm. We divide this line in the inverse ratio of the mass flow rates to obtain the conditions of the mixture (point A on the chart). Thus, point A is located [0.44/( )]{.4 cm} = 1.1 cm from point 2. The enthalpy at point A turns out to be 85 kj/kg dry air and the humidity ratio at point A 1
5 turns out to be kg water / kg dry air. Also, the mass flow rate of the mixture is = 1.8 kg/s. We denote the conditions of the heated air by point B on the chart and the conditions of the exit air from the dryer as point C on the chart. Performing an energy balance between points A and B, we get: 1.8 (85000) = 1.8 (H B) Solving, we get: H = J/kg = 12.1 kj/kg B Thus, we identify point B on the chart by going horizontally from point A till we intersect the line corresponding to an enthalpy of 12.1 kj/kg. We then identify point C on the chart by following a constant enthalpy line of 12.1 kj/kg from point B till we intersect the vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 45 C. We note that the humidity ratio at point C is 0.04 kg water / kg dry air. We then perform a water balance during the drying process as follows: 1.8 (0.012) + mass of water from product per second = 1.8 (0.04) Thus, mass of water from product per second = kg/s Thus, in 0 mins, amount of water removed from product = 0.006*0*60 kg = 54.7 kg Thus, moisture content of final product = [(0.85)(100) ]/[ ] = 0.67 Thus, moisture content = 67% 10. a. We begin by looking at the high temperature psychrometrics chart. Here, we identify the conditions of the exit air by drawing a horizontal line from 5 C on the curved wet bulb temperature line and intersecting it with the 50% RH line. This is point C on the chart. We note that at this point, H = 145 kj/kg and W = 0.07 kg water / kg dry air. c c From C, we follow the constant enthalpy line till we intersect the curved line corresponding to a RH of 1%. This represents the condition of the hot air entering the spray dryer and is denoted by point B on the chart. We note that at this point, W = kg water / kg dry air. To identify point A on the chart, we would need to draw a horizontal line from point B and intersect this line with a vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 15 C. Since this point cannot be located on the high temperature chart, we use the low temperature chart and intersect a horizontal line corresponding to a moisture content of kg water / kg dry air with a vertical line corresponding to a dry bulb temperature of 15 C. This is point A on the chart. We note that at this point, H a = 9 kj/kg and W a = kg water / kg dry air. b. The mass flow rate of air = (Vol. flow rate of air at point A )/(sp. volume at point A ) = 0.2/0.8 = 0.24 kg/s = m a b
6 Performing an energy balance between points A and B, we get: 0.24 (9000) + Q = 0.24 (145000) Solving, we get: Q = W = kw c. We then perform a water balance during the drying process as follows: (m a) (W b) + (mass flow rate of milk) (m.c. of milk) = (m a) (W b) Thus, 0.24 (0.0095) + m milk (0.9) = 0.24 (0.07) Solving, we get: m = kg/s milk
Lecture 3: DESIGN CONSIDERATION OF DRIERS
 Lecture 3: DESIGN CONSIDERATION OF DRIERS 8. DESIGN OF DRYER Design of a rotary dryer only on the basis of fundamental principle is very difficult. Few of correlations that are available for design may
Lecture 3: DESIGN CONSIDERATION OF DRIERS 8. DESIGN OF DRYER Design of a rotary dryer only on the basis of fundamental principle is very difficult. Few of correlations that are available for design may
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Mass Balance
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Mass Balance 1. The mass balance equation for the system is: 2 + 3 = m This yields, m = 5 kg 2. The mass balance
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Mass Balance 1. The mass balance equation for the system is: 2 + 3 = m This yields, m = 5 kg 2. The mass balance
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Problems on Heat Transfer
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
ln P s T and P s T where R 22,105, D A 27, E B 97.
 ASAE D271.2 DEC94 Psychrometric Data Reviewed by ASAE s Structures and Environment Division and the Food Engineering Division Standards Committees; approved by the Electric Power and Processing Division
ASAE D271.2 DEC94 Psychrometric Data Reviewed by ASAE s Structures and Environment Division and the Food Engineering Division Standards Committees; approved by the Electric Power and Processing Division
Non-Reacting Gas Mixtures. Introduction. P-V-T Relationships for Ideal Gas Mixtures. Amagat Model (law of additive volumes)
 Non-Reacting Gas Mixtures Reading Problems 13-1 13-3 13-52, 13-60 14-1 14-7 14-32, 14-35, 14-68, 14-71, 14-75 14-79, 14-103, 14-112 Introduction homogeneous gas mixtures are frequently treated as a single
Non-Reacting Gas Mixtures Reading Problems 13-1 13-3 13-52, 13-60 14-1 14-7 14-32, 14-35, 14-68, 14-71, 14-75 14-79, 14-103, 14-112 Introduction homogeneous gas mixtures are frequently treated as a single
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Section 2 of 6 Applied Psychrometrics
 Section 2 of 6 Applied Psychrometrics Psychrometric chart - your energy map Key psychrometric variables for humidity Predicting building condensation Hot weather Cold weather Predicting moisture sorption
Section 2 of 6 Applied Psychrometrics Psychrometric chart - your energy map Key psychrometric variables for humidity Predicting building condensation Hot weather Cold weather Predicting moisture sorption
Lab 8. Lab-tray dryer
 BAEN/CHEN-474 page 1 of 6 Student s Name: Factors influencing the drying rates in Objectives: 1.) To become familiar with the operation of a tray dryer 2.) To determine the psychrometric properties of
BAEN/CHEN-474 page 1 of 6 Student s Name: Factors influencing the drying rates in Objectives: 1.) To become familiar with the operation of a tray dryer 2.) To determine the psychrometric properties of
Subject: Principles of Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Lecturer: Assistant Professor Dr. Waheed Shaty Mohammed
 Subject: Principles of Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Lecturer: Assistant Professor Dr. Waheed Shaty Mohammed Refrences: 1-A. R. Trott and T. Welch " Refrigeration and Air conditioning ",Third Edition
Subject: Principles of Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Lecturer: Assistant Professor Dr. Waheed Shaty Mohammed Refrences: 1-A. R. Trott and T. Welch " Refrigeration and Air conditioning ",Third Edition
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
Heat Flow Calculations Made Using the Models 8386 and 8386A VELOCICALC Plus Air Velocity Meters Application Note ITI-124
 Ventilation Test Instruments Heat Flow Calculations Made Using the Models 8386 and 8386A VELOCICALC Plus Air Velocity Meters Application Note ITI-124 The Models 8386 and 8386A calculate the heat flow between
Ventilation Test Instruments Heat Flow Calculations Made Using the Models 8386 and 8386A VELOCICALC Plus Air Velocity Meters Application Note ITI-124 The Models 8386 and 8386A calculate the heat flow between
Theory. Humidity h of an air-vapor mixture is defined as the mass ratio of water vapor and dry air,
 Theory Background In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special
Theory Background In a cooling tower with open water circulation, heat is removed from water because of the material and heat exchange between the water and the ambient air. The cooling tower is a special
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2017
 CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2017 October 5, 2017 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com Twitter: @built_envi
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2017 October 5, 2017 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com Twitter: @built_envi
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2015
 CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2015 Week 5: September 24, 2015 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com
CAE 331/513 Building Science Fall 2015 Week 5: September 24, 2015 Psychrometrics (equations) Advancing energy, environmental, and sustainability research within the built environment www.built-envi.com
AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri. Chapter 6 Energy Balances on Chemical Processes
 AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri Chapter 6 Energy Balances on Chemical Processes Thermodynamics system surroundings system boundary Forms of Energy 1. Energy Possessed
AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri Chapter 6 Energy Balances on Chemical Processes Thermodynamics system surroundings system boundary Forms of Energy 1. Energy Possessed
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Psychometric Processes Good afternoon, yesterday we
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Psychometric Processes Good afternoon, yesterday we
Brown Hills College of Engineering & Technology
 UNIT 4 Flow Through Nozzles Velocity and heat drop, Mass discharge through a nozzle, Critical pressure ratio and its significance, Effect of friction, Nozzle efficiency, Supersaturated flow, Design pressure
UNIT 4 Flow Through Nozzles Velocity and heat drop, Mass discharge through a nozzle, Critical pressure ratio and its significance, Effect of friction, Nozzle efficiency, Supersaturated flow, Design pressure
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
1. Nusselt number and Biot number are computed in a similar manner (=hd/k). What are the differences between them? When and why are each of them used?
 1. Nusselt number and Biot number are computed in a similar manner (=hd/k). What are the differences between them? When and why are each of them used?. During unsteady state heat transfer, can the temperature
1. Nusselt number and Biot number are computed in a similar manner (=hd/k). What are the differences between them? When and why are each of them used?. During unsteady state heat transfer, can the temperature
Solid-Liquid Extraction
 Chapter (10) Solid-Liquid Extraction (( Leaching )) Leaching: is the separation of a solute from solid mixture by dissolving it in a liquid phase. Leaching occurs in two steps: 1. Contacting solvent and
Chapter (10) Solid-Liquid Extraction (( Leaching )) Leaching: is the separation of a solute from solid mixture by dissolving it in a liquid phase. Leaching occurs in two steps: 1. Contacting solvent and
Prediction of Evaporation Losses in Wet Cooling Towers
 Heat Transfer Engineering, 27(9):86 92, 2006 Copyright C Taylor and Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0145-7632 print / 1521-0537 online DOI: 10.1080/01457630600846372 Prediction of Evaporation Losses in Wet Cooling
Heat Transfer Engineering, 27(9):86 92, 2006 Copyright C Taylor and Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0145-7632 print / 1521-0537 online DOI: 10.1080/01457630600846372 Prediction of Evaporation Losses in Wet Cooling
8.3 DESIGN OF A SINGLE-EFFECT EVAPORATOR
 554 CHAPTER 8 Evaporation are presented in a general way. Custom-designed modifications of these types can significantly alter the specific duties. 8.3 DESIGN OF A SINGLE-EFFECT EVAPORATOR In a single-effect
554 CHAPTER 8 Evaporation are presented in a general way. Custom-designed modifications of these types can significantly alter the specific duties. 8.3 DESIGN OF A SINGLE-EFFECT EVAPORATOR In a single-effect
2.0 KEY EQUATIONS. Evaporator Net Refrigeration Effect. Compressor Work. Net Condenser Effect
 2.0 KEY EQUATIONS Evaporator Net Refrigeration Effect Q net refrigeration effect [] = (H 1 H 4 ) lb (Refrig Flow Rate) (60) min lb min hr H 1 = leaving evaporator enthalpy lb ; H 4 = entering evaporator
2.0 KEY EQUATIONS Evaporator Net Refrigeration Effect Q net refrigeration effect [] = (H 1 H 4 ) lb (Refrig Flow Rate) (60) min lb min hr H 1 = leaving evaporator enthalpy lb ; H 4 = entering evaporator
Water-Temperature-Dependent Wet Bulb Temperature Calculation
 Water-Temperature-Dependent Wet Bulb Temperature Calculation Oxycom Fresh Air BV December 7th, 2012 Abstract A numerical solution for the exact calculation of the wet bulb temperature of air has been derived,
Water-Temperature-Dependent Wet Bulb Temperature Calculation Oxycom Fresh Air BV December 7th, 2012 Abstract A numerical solution for the exact calculation of the wet bulb temperature of air has been derived,
S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 [4062]-186 S.E. (Chemical) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2011 HEAT TRANSFER (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100 N.B. : (i) Answers
Welcome. Vaisala Industrial Measure Webinar Series - Humidity Theory, Terms & Definitions. Yumi Alanoly Vaisala Application Engineer
 Welcome Vaisala Industrial Measure Webinar Series - Humidity Theory, Terms & Definitions Yumi Alanoly Vaisala Application Engineer Agenda 1. Why do we measure humidity? 2. Dalton s Law 3. Relative humidity
Welcome Vaisala Industrial Measure Webinar Series - Humidity Theory, Terms & Definitions Yumi Alanoly Vaisala Application Engineer Agenda 1. Why do we measure humidity? 2. Dalton s Law 3. Relative humidity
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Exam 2 Part A -- Closed Book (50 points)
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Exam 2 Part A -- Closed Book (50 points) 1. Are the following statements true or false? (20 points) a. Thermal conductivity of a substance is a measure
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Exam 2 Part A -- Closed Book (50 points) 1. Are the following statements true or false? (20 points) a. Thermal conductivity of a substance is a measure
The Numerical Psychrometric Analysis
 he Numerical sychrometric Analysis by Jorge R. López Busó, MSME, E Introduction he sychrometric Analysis is the base of any HVAC system design. Nowadays, the psychrometric analysis is mainly done by means
he Numerical sychrometric Analysis by Jorge R. López Busó, MSME, E Introduction he sychrometric Analysis is the base of any HVAC system design. Nowadays, the psychrometric analysis is mainly done by means
KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a 1.6-cm-diameter pipe.
 4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in the Corrugated Packing of the Counter Flow Cooling Tower
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 59-577 (2008) Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in the Corrugated Packing of the Counter Flow Cooling Tower Montri Pirunkaset* and Santi Laksitanonta BSTRCT This paper
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 59-577 (2008) Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in the Corrugated Packing of the Counter Flow Cooling Tower Montri Pirunkaset* and Santi Laksitanonta BSTRCT This paper
Content. Climate Parameters used for the measurement and recording of weather phenomena The Psychrometric Chart
 Climate Content Climate Parameters used for the measurement and recording of weather phenomena The Psychrometric Chart Climate Climate is a measure of the average pattern of variation in temperature, humidity,
Climate Content Climate Parameters used for the measurement and recording of weather phenomena The Psychrometric Chart Climate Climate is a measure of the average pattern of variation in temperature, humidity,
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002
 10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
Humidification requirements in economizer-type HVAC systems
 Humidification requirements in economizer-type HVAC systems Viktor T. Toth January 2, 2012 Abstract We develop a formulation to compute the maximum humidification load for economizer-type HVAC systems.
Humidification requirements in economizer-type HVAC systems Viktor T. Toth January 2, 2012 Abstract We develop a formulation to compute the maximum humidification load for economizer-type HVAC systems.
Simultaneous heat and mass transfer studies in drying ammonium chloride in a batch-fluidized bed dryer
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 13, September 006, pp. 440-447 Simultaneous heat and mass transfer studies in drying ammonium chloride in a batch-fluidized bed dryer R Kumaresan a & T Viruthagiri
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 13, September 006, pp. 440-447 Simultaneous heat and mass transfer studies in drying ammonium chloride in a batch-fluidized bed dryer R Kumaresan a & T Viruthagiri
Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables
 Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Name Notes: Topic 1 The Atmosphere Regents Earth Science Topic 1 The Atmosphere and Atmospheric Variables What is the atmosphere? Meteorology is the study of A. Structure of the Atmosphere: What two gases
Pyschrometric Sample Problem Pharmaceutical Engineering Graduate Program New Jersey Institute of Technology
 Background A pharmaceutical company wishes to construct a manufacturing space which will require an HVAC system that functions within the following parameters: Space drybulb temperature = 70 F Space relative
Background A pharmaceutical company wishes to construct a manufacturing space which will require an HVAC system that functions within the following parameters: Space drybulb temperature = 70 F Space relative
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Lecture Ch. 6. Condensed (Liquid) Water. Cloud in a Jar Demonstration. How does saturation occur? Saturation of Moist Air. Saturation of Moist Air
 Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
Lecture Ch. 6 Saturation of moist air Relationship between humidity and dewpoint Clausius-Clapeyron equation Dewpoint Temperature Depression Isobaric cooling Moist adiabatic ascent of air Equivalent temperature
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
1. Water Vapor in Air
 1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
1. Water Vapor in Air Water appears in all three phases in the earth s atmosphere - solid, liquid and vapor - and it is one of the most important components, not only because it is essential to life, but
Review for Exam #3. Refrigeration. Refrigerants/Coolants
 Review for Exam #3 Refrigeration 2 Refrigerants/Coolants Cold water (at say, 0 C) Heat extracted from product is used as sensible heat and increases water temperature Ice (at 0 C) Heat extracted from product
Review for Exam #3 Refrigeration 2 Refrigerants/Coolants Cold water (at say, 0 C) Heat extracted from product is used as sensible heat and increases water temperature Ice (at 0 C) Heat extracted from product
Review of Mathematics
 Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics 2 Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material 2 is P 2 If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x 2 amount of
Review for Exam #1 Review of Mathematics 2 Weighted Mean A certain property of material 1 is P 1 and that of material 2 is P 2 If x 1 amount (weight or volume) of material 1 is mixed with x 2 amount of
Contents. 1 Introduction 4. 2 Methods Results and Discussion 15
 Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Methods 11 3 Results and Discussion 15 4 Appendices 21 4.1 Variable Definitions................................ 21 4.2 Sample Calculations............................... 22
Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Methods 11 3 Results and Discussion 15 4 Appendices 21 4.1 Variable Definitions................................ 21 4.2 Sample Calculations............................... 22
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 1 LIQUIDS VAPOURS - GASES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 1 LIQUIDS VAPOURS - GASES SAE
 Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia- Water Pair Nagendra M CBM Engineer, Hindusthan Zink.Ltd The specific objectives of this lesson are to: 1. Introduce ammonia-water based vapour
Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Systems Based On Ammonia- Water Pair Nagendra M CBM Engineer, Hindusthan Zink.Ltd The specific objectives of this lesson are to: 1. Introduce ammonia-water based vapour
1. (25 points) C 6 H O 2 6CO 2 + 7H 2 O C 6 H O 2 6CO + 7H 2 O
 MEEBAL Exam 2 November 2013 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
MEEBAL Exam 2 November 2013 Show all work in your blue book. Points will be deducted if steps leading to answers are not shown. No work outside blue books (such as writing on the flow sheets) will be considered.
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer
 9210-221 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book non programmable calculator pen, pencil, drawing instruments
9210-221 Level 7 Post Graduate Diploma in Engineering Heat and mass transfer 0 You should have the following for this examination one answer book non programmable calculator pen, pencil, drawing instruments
Class IX Chapter 11 Work and Energy Science
 Class IX Chapter 11 Work and Energy Science Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on
Class IX Chapter 11 Work and Energy Science Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
Chemical Engineering 3. Lecture 9: Spray drying
 Chemical Engineering 3 Lecture 9: Spray drying Outline Principles of spray drying Macroscopic view: mass and enthalpy balance Microscopic view: single droplet evaporaaon Control of paracle properaes Spray
Chemical Engineering 3 Lecture 9: Spray drying Outline Principles of spray drying Macroscopic view: mass and enthalpy balance Microscopic view: single droplet evaporaaon Control of paracle properaes Spray
Modeling the Process of Drying Stationary Objects inside a Tumble Dryer Using COMSOL Multiphysics
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Modeling the Process of Drying Stationary Objects inside a Tumble Dryer Using COMSOL Multiphysics Tarek H.M. Zeineldin Outline Introduction - Drying processes
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2008 Hannover Modeling the Process of Drying Stationary Objects inside a Tumble Dryer Using COMSOL Multiphysics Tarek H.M. Zeineldin Outline Introduction - Drying processes
NEBB Fundamental Formulas
 Approved NEBB - May 1, 17 Page 1 of 8 Version 1.3 A = Area (ft²) IP, (m²) SI M = Mass (lb) IP, (kg) SI ACH = Air Changes per Hour ma = Mixed Air Ak = Effective Area m = meter (metre) AV = Average m³/s
Approved NEBB - May 1, 17 Page 1 of 8 Version 1.3 A = Area (ft²) IP, (m²) SI M = Mass (lb) IP, (kg) SI ACH = Air Changes per Hour ma = Mixed Air Ak = Effective Area m = meter (metre) AV = Average m³/s
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 17 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good morning to all of you. We were discussing
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 17 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good morning to all of you. We were discussing
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Relative Humidity and Dew Point Lab
 Name: Relative Humidity and Dew Point Lab Weather is the present state of the atmosphere. Factors that determine the type of weather the world will have are: air pressure, wind, temperature and the air
Name: Relative Humidity and Dew Point Lab Weather is the present state of the atmosphere. Factors that determine the type of weather the world will have are: air pressure, wind, temperature and the air
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 16 Merry X mas! Happy New Year 2019! Final Exam When? Thursday, January 10th What time? 3:10-5 pm Where? 91203 What? Lecture materials from Week 1 to 16 (before
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 16 Merry X mas! Happy New Year 2019! Final Exam When? Thursday, January 10th What time? 3:10-5 pm Where? 91203 What? Lecture materials from Week 1 to 16 (before
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I PART-B 1. During a flow process 5kw paddle wheel work is supplied while the internal energy of the system increase in one minute is 200kJ.Find the heat transfer
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I PART-B 1. During a flow process 5kw paddle wheel work is supplied while the internal energy of the system increase in one minute is 200kJ.Find the heat transfer
LECTURE 5 THE CONTENTS OF THIS LECTURE ARE AS FOLLOWS: 1.0 SOME OF THE THEORETICAL CONCEPTS INVOLVED IN HEAT FLOW. 1.1 Sensible Heat Flow
 LECTURE 5 THE CONTENTS OF THIS LECTURE ARE AS FOLLOWS: 1.0 SOME OF THE THEORETICAL CONCEPTS INVOLVED IN HEAT FLOW 1.1 Sensible Heat Flow 1.2 Latent heat Flow 1.3 Humidity 1.4 Thermostat Condition in the
LECTURE 5 THE CONTENTS OF THIS LECTURE ARE AS FOLLOWS: 1.0 SOME OF THE THEORETICAL CONCEPTS INVOLVED IN HEAT FLOW 1.1 Sensible Heat Flow 1.2 Latent heat Flow 1.3 Humidity 1.4 Thermostat Condition in the
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : THERMODYNAMICS Course Code : AME00 Regulation : IARE - R1 Year
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : THERMODYNAMICS Course Code : AME00 Regulation : IARE - R1 Year
COOLING TOWER MODEL IN MNR
 COOLING TOWER MODEL IN MNR 1 COOLING TOWER MODEL The cooling tower model used in Liu s study [2] was adapted from the model developed by Eric Weber (1988). One modification is the use of a counterflow
COOLING TOWER MODEL IN MNR 1 COOLING TOWER MODEL The cooling tower model used in Liu s study [2] was adapted from the model developed by Eric Weber (1988). One modification is the use of a counterflow
NCERT solution for Work and energy
 1 NCERT solution for Work and energy Question 1 A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (See below figure). Let us take it that the force acts on the
1 NCERT solution for Work and energy Question 1 A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (See below figure). Let us take it that the force acts on the
Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model
 Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model The energy balance for the greenhouse was obtained by applying energy conservation to the greenhouse system as a control volume and identifying the energy terms.
Greenhouse Steady State Energy Balance Model The energy balance for the greenhouse was obtained by applying energy conservation to the greenhouse system as a control volume and identifying the energy terms.
Work and Energy. Intext Exercise 2
 Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement.
Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (Fig. 11.3). Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement.
4.1. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 4 - Heat GCKL UNDERSTANDING THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM. What is thermal equilibrium?
 4.1 4 UNDERSTANDING THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM What is thermal equilibrium? 1. ( Heat, Temperature ) is a form of energy that flows from a hot body to a cold body. 2. The SI unit for ( heat, temperature) is Joule,
4.1 4 UNDERSTANDING THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM What is thermal equilibrium? 1. ( Heat, Temperature ) is a form of energy that flows from a hot body to a cold body. 2. The SI unit for ( heat, temperature) is Joule,
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 3 Content: Weather Instruments Notes
 Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
Introduction In order for meteorologists to accurately predict the weather, they take thousands of different weather measurements each day. Meteorologists need to use many tools in order to draw an accurate
The Choice of Supply Design Conditions
 6 The Choice of Supply Design Conditions 6.1 Sensible heat removal If there is a continuous source of heat having an output of Q in a hermetically sealed room the temperature within the room, tr, will
6 The Choice of Supply Design Conditions 6.1 Sensible heat removal If there is a continuous source of heat having an output of Q in a hermetically sealed room the temperature within the room, tr, will
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Evaporation
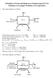 Princiles of Food and Biorocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Examle Problems on Eaoration 1. The system diagram is as follows: Solids balance equation: 0.1 (m f) = 0.5 (1,000) Thus, m f = 5,000 kg/hr
Princiles of Food and Biorocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Examle Problems on Eaoration 1. The system diagram is as follows: Solids balance equation: 0.1 (m f) = 0.5 (1,000) Thus, m f = 5,000 kg/hr
Thermal Effects. IGCSE Physics
 Thermal Effects IGCSE Physics Starter What is the difference between heat and temperature? What unit is thermal energy measured in? And what does it depend on? In which direction does heat flow? Heat (Thermal
Thermal Effects IGCSE Physics Starter What is the difference between heat and temperature? What unit is thermal energy measured in? And what does it depend on? In which direction does heat flow? Heat (Thermal
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
Thermal Properties, Moisture Diffusivity Chpt 8
 Processing and Storage of Ag Products Heating Cooling Combination of heating and cooling Grain dried for storage Noodles dried Fruits/Vegetables rapidly cooled Vegetables are blanched, maybe cooked and
Processing and Storage of Ag Products Heating Cooling Combination of heating and cooling Grain dried for storage Noodles dried Fruits/Vegetables rapidly cooled Vegetables are blanched, maybe cooked and
Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology
 S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
S c i e n c e s Weather, Atmosphere and Meteorology Key words: Atmosphere, Ozone, Water vapor, solar radiation, Condensation, Evaporation, Humidity, Dew-Point Temperature, Cirrus Clouds, Stratus Clouds,
Cryogenic Engineering Prof. M. D. Atrey Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture No. #23 Gas Separation
 Cryogenic Engineering Prof. M. D. Atrey Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. #23 Gas Separation So, welcome to the 23rd lecture, on Cryogenic Engineering,
Cryogenic Engineering Prof. M. D. Atrey Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. #23 Gas Separation So, welcome to the 23rd lecture, on Cryogenic Engineering,
Dew Point and Cloud Formation
 Name: Date: ES: 1 2 3 4 Dew Point and Cloud Formation Part A: Run some water over your hands. After shaking off the excess, wave them back and forth until they are dry. 1. Describe the change in temperature
Name: Date: ES: 1 2 3 4 Dew Point and Cloud Formation Part A: Run some water over your hands. After shaking off the excess, wave them back and forth until they are dry. 1. Describe the change in temperature
Business. Final Exam Review. Competencies. Schedule Today. Most missed on Exam 3. Review Exam #3
 Business Final Exam Review Online course evaluation (19/32 = 59%) Counts as a homework assignment (by Thurs) Professional program application Past due! Case study due today by 5 pm Leadership evaluation
Business Final Exam Review Online course evaluation (19/32 = 59%) Counts as a homework assignment (by Thurs) Professional program application Past due! Case study due today by 5 pm Leadership evaluation
REALIZATION OF HUMIDITY STANDARD FACILITY USING TWO-PRESSURE HUMIDITY GENERATOR AND HUMIDITY CHAMBER
 METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Index 3393, ISSN 86-8229 www.metrology.pg.gda.pl REALIZATION OF HUMIDITY STANDARD FACILITY USING TWO-PRESSURE HUMIDITY GENERATOR AND HUMIDITY CHAMBER Essam El-Din, Mostafa
METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS Index 3393, ISSN 86-8229 www.metrology.pg.gda.pl REALIZATION OF HUMIDITY STANDARD FACILITY USING TWO-PRESSURE HUMIDITY GENERATOR AND HUMIDITY CHAMBER Essam El-Din, Mostafa
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Evapotranspiration. Rabi H. Mohtar ABE 325
 Evapotranspiration Rabi H. Mohtar ABE 325 Introduction What is it? Factors affecting it? Why we need to estimate it? Latent heat of vaporization: Liquid gas o Energy needed o Cooling process Saturation
Evapotranspiration Rabi H. Mohtar ABE 325 Introduction What is it? Factors affecting it? Why we need to estimate it? Latent heat of vaporization: Liquid gas o Energy needed o Cooling process Saturation
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6301-ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
Business. Professional application due Nov 17
 Business Professional application due Nov 17 Need to estiate what elective courses you will take Mark how you fulfilled Math & Cheistry Major and Total GPA Fill out fors and spreadsheet Then eet with your
Business Professional application due Nov 17 Need to estiate what elective courses you will take Mark how you fulfilled Math & Cheistry Major and Total GPA Fill out fors and spreadsheet Then eet with your
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
V i = component volume of component i. T282. c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Gas Mixture ME 203 (2017) 6 / 22. Moist Air T284
 Ideal Gas ixtures Properties of Homogeeous ixtures & Pyschrometry Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Departmet of echaical Egieerig Bagladesh Uiversity of Egieerig & Techology (BUET) Dhaka-000, Bagladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Ideal Gas ixtures Properties of Homogeeous ixtures & Pyschrometry Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Departmet of echaical Egieerig Bagladesh Uiversity of Egieerig & Techology (BUET) Dhaka-000, Bagladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
FORCED-CIRCULATION AIR-COOLING AND AIR-HEATING COILS
 Certification Program for FORCED-CIRCULATION AIR-COOLING AND AIR-HEATING OPERATIONAL MANUAL APRIL 1981 ADDENDUM Administered by AIR-CONDITIONING AND REFRIGERATION INSTITUTE 4100 North Fairfax Dr. Suite
Certification Program for FORCED-CIRCULATION AIR-COOLING AND AIR-HEATING OPERATIONAL MANUAL APRIL 1981 ADDENDUM Administered by AIR-CONDITIONING AND REFRIGERATION INSTITUTE 4100 North Fairfax Dr. Suite
At a certain moment the following temperatures are measured with a psychrometer: 25 C and 17,5 C
 ANSWERS Practical Day 1 Exercise Humidity Saturated vapour pressure e s (kpa) γ Temperature t ( C) In the figure above you see (an example of) the relation between vapour pressure and temperature. The
ANSWERS Practical Day 1 Exercise Humidity Saturated vapour pressure e s (kpa) γ Temperature t ( C) In the figure above you see (an example of) the relation between vapour pressure and temperature. The
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
Chapter 4 Water Vapor
 Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Chapter 4 Water Vapor Chapter overview: Phases of water Vapor pressure at saturation Moisture variables o Mixing ratio, specific humidity, relative humidity, dew point temperature o Absolute vs. relative
Topic 19b. Thermal Properties of Matter
 Topic 19b The infra-red image of a head shows the distribution of heat. Different colours indicate different temperatures. Which do you think are the warmest regions? Thermal Properties of Matter contents
Topic 19b The infra-red image of a head shows the distribution of heat. Different colours indicate different temperatures. Which do you think are the warmest regions? Thermal Properties of Matter contents
ERT 313 BIOSEPARATION ENGINEERING EXTRACTION. Prepared by: Miss Hairul Nazirah Abdul Halim
 ERT 313 BIOSEPARATION ENGINEERING EXTRACTION Prepared by: Miss Hairul Nazirah Abdul Halim Definition of Extraction Liquid-Liquid extraction is a mass transfer operation in which a liquid solution (the
ERT 313 BIOSEPARATION ENGINEERING EXTRACTION Prepared by: Miss Hairul Nazirah Abdul Halim Definition of Extraction Liquid-Liquid extraction is a mass transfer operation in which a liquid solution (the
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Comprehend and execute the 10 elements of effective problem
 Lecture 8, 3/9/2012 Chapter 7: A GENERAL Strategy for Solving Material Balance Problems Objectives: Comprehend and execute the 10 elements of effective problem Drive a flow chart and Place labels on the
Lecture 8, 3/9/2012 Chapter 7: A GENERAL Strategy for Solving Material Balance Problems Objectives: Comprehend and execute the 10 elements of effective problem Drive a flow chart and Place labels on the
