TEPZZ 878 6_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/23
|
|
|
- Dylan Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ 878 6_A_T (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 1/23 (21) Application number: (1) Int Cl.: B01D 3/94 (06.01) B01J 23/72 (06.01) B01J 29/072 (06.01) B01J 29/76 (06.01) (22) Date of filing: (84) Designated Contracting States: AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR () Priority: GB (62) Document number(s) of the earlier application(s) in accordance with Art. 76 EPC: / (71) Applicant: Johnson Matthey Public Limited Company London EC4A 4AB (GB) (72) Inventors: Chandler, Guy Richard Cambridge, Cambridgeshire CB23 1HB (GB) Collins, Neil Litlington, Hertfordshire SG8 0QL (GB) Foo, Rodney, Kok Shin Reading, Berkshire RG4 9NH (GB) Green, Alexander, Nicholas, Michael Baldock, Hertfordshire SG7 AL (GB) Phillips, Paul Royston, Hertfordshire SG8 YR (GB) Rajaram, Raj Rao Slough, Berkshire SL3 7PH (GB) Reid, Stuart, David Cambourne, Cambridgeshire CB23 JA (GB) (74) Representative: Nunn, Andrew Dominic Johnson Matthey PLC Gate Orchard Road Royston, Hertfordshire SG8 HE (GB) Remarks: This application was filed on as a divisional application to the application mentioned under INID code 62. (4) Transition metal-containing aluminosilicate zeolite (7) A synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal selected from the group consisting of Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Au, In, V, lanthanides and Group VIII transition metals, which aluminosilicate zeolite is a small pore aluminosilicate zeolite having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms, wherein the mean crystallite size of the aluminosilicate zeolite determined by scanning electron microscope is >0.0 micrometre. EP A1 Printed by Jouve, 7001 PARIS (FR)
2 Description [0001] The present invention relates to a synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal. The zeolites can be used for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases, such as exhaust gases from internal combustion engines, using a nitrogenous reductant. [0002] It is known to convert oxides of nitrogen (NO x ) in a gas to nitrogen by contacting the NO x with a nitrogenous reducing agent, e.g. ammonia or an ammonia precursor such as urea, in the presence of a zeolite catalyst containing at least one transition metal, and it has been suggested to adopt this technique for treating NO x emitted from vehicular lean-burn internal combustion engines, see for example DieselNet Technology Guide "Selective Catalytic Reduction" Revision 0.0d, by W. Addy Majewski published on [0003] US patent no. 4,44, 38 discloses a synthetic zeolite having a crystal structure of chabazite (CHA), designated SSZ-13 prepared using a Structure Directing Agent (SDA) such as the N,N,N-trimethyl-1-adamantammonium cation. The SSZ-13 can be ion exchanged with transition metals such as rare earth, Mn, Ca, Mg, Zn, Cd, Pt, Pd, Ni, Co, Ti, Al, Sn, Fe and Co for use e.g. in hydrocarbon conversion reactions. [0004] US patent no. 6,709,644 discloses a synthetic zeolite having a crystal structure of chabazite (CHA) of small crystallite size (on average <0. micrometres) designated SSZ-62. SSZ-62 can also be prepared using the N,N,Ntrimethyl-1-adamantammonium cation SDA. Example 1 of US 6,709,644 compares the average crystal size of SSZ-62 with the average crystal size of SSZ-13. The document suggests that SSZ-62 can be used in a process for converting lower alcohols or the zeolite can be exchanged with copper or cobalt for use in catalysing the reduction of NO x in a lean gas stream e.g. of an internal combustion engine. However, the activity of small and large crystallite size materials are only illustrated by a methanol to olefin reaction. [000] In our International patent application no. PCT/GB08/00141 filed 24th April 08 we explain that transition metal/zeolite catalysts such as Cu/Beta and/or Fe/Beta are being considered for urea and/or NH 3 SCR of NO x from mobile diesel engines to meet new emission standards. These catalysts are required to withstand relatively high temperatures under exhaust conditions, and may also be exposed to relatively high levels of hydrocarbons (HC), which can be adsorbed onto or into the pores of the zeolites. The adsorbed HC may affect the NH 3 SCR activities of these metal zeolites catalysts by blocking the active sites or blocking access to the active sites for the NH 3 -NO x reaction. Furthermore, these adsorbed HC species may be oxidised as the temperature of the catalytic system is raised, generating a significant exotherm, which can thermally or hydrothermally damage the catalyst. It is therefore desirable to minimise HC adsorption on the SCR catalyst, especially during cold start when significant amounts of HC can be emitted from the engine. [0006] In our PCT/GB08/00141 we suggest that both of these disadvantages of larger pore zeolite catalysts can be reduced or overcome by using small pore zeolites, which generally allow the diffusion of NH 3 and NO x to the active sites inside the zeolite pores, but which generally hinder diffusion of hydrocarbon molecules into the pores. Zeolites that have the small pore dimensions to induce this shape selectivity whereby larger hydrocarbons are prevented from accessing the active metal sites within the zeolite cavities include CHA, ERI and LEV. Additionally, small pore zeolitebased SCR catalysts produce less N 2 O as a by-product of the NO x reduction reaction. [0007] We have researched into aluminosilicate zeolite materials and have discovered, very surprisingly, that large crystallite aluminosilicate zeolite materials have higher activity for the SCR process using a nitrogenous reductant than the same aluminosilicate zeolite material of smaller crystallite size. [0008] According to one aspect, the invention provides a synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal selected from the group consisting of Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Au, In, V, lanthanides and Group VIII transition metals, which aluminosilicate zeolite is a small pore aluminosilicate zeolite having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms, wherein the mean crystallite size of the aluminosilicate zeolite determined by scanning electron microscope is >0.0 micrometre. Preferably, the at least one catalytically active transition metal is one of copper and iron. In embodiments, the zeolite can contain both copper and iron. [0009] The Examples show a trend of increasing NO x reduction activity of fresh and aged copper/cha catalysts with increasing crystallite size. [00] Scanning electron microscopy can determine the morphology and crystallite size of zeolites according to the invention. It is desirable that the mean particle size of the aluminosilicate zeolite as measured by SEM is >0.0 micrometre, but preferably greater than 1.00 micrometre, such as >1.0 micrometres. In embodiments, the mean crystallite size is <1.0 micrometres, such as <.0 micrometres or <.0 micrometres. [0011] In embodiments, the aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to the invention is selected from the group consisting of zeolites having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms especially Framework Type Codes CHA, ERI and LEV, most preferably CHA. [0012] Where the Framework Type Code of the aluminosilicate zeolite is CHA, an isotype framework structure of CHA can be selected from the group consisting of, for example, Linde-D, Linde-R, SSZ-13, LZ-218, Phi and ZK-14. [0013] A type material or isotype framework structure of ERI Framework Type Code zeolites can be, for example, erionite, ZSM-34 or Linde Type T. 2
3 1 2 [0014] LEV Framework Type Code isotype framework structures or type material can be, for example, levynite, Nu- 3, LZ-132 or ZK-. [001] The total at least one transition metal present in the catalyst is from 0.1 to.0 wt% based on the total weight of the zeolite catalyst, such as 0. to.0 wt% based on the total weight of the zeolite catalyst. [0016] According to another aspect, the invention provides a method of converting nitrogen oxides in a gas to nitrogen by contacting the nitrogen oxides with a nitrogenous reducing agent in the presence of an aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to the invention. [0017] The nitrogen oxides can be reduced with the reducing agent at a temperature of at least 0 C, for example from about 10 C to 70 C. [0018] In a particular embodiment, the nitrogen oxides reduction is performed in the presence of oxygen. [0019] The addition of nitrogenous reductant can be controlled so that NH 3 at the zeolite catalyst inlet is controlled to be 60% to 0% of theoretical ammonia calculated at 1:1 NH 3 /NO and 4:3 NH 3 /NO 2. [00] In a particular embodiment, wherein nitrogen monoxide in the gas is oxidised to nitrogen dioxide using an oxidation catalyst located upstream of the zeolite catalyst and the resulting gas is then mixed with nitrogenous reductant before the mixture is fed into the zeolite catalyst, wherein the oxidation catalyst is adapted to yield a gas stream entering the zeolite catalyst having a ratio of NO to NO 1 of from about 4:1 to about 1:3 by volume. [0021] In the method according to the invention, the nitrogenous reductant can be ammonia per se, hydrazine or an ammonia precursor selected from the group consisting of urea ((NH 2 ) 2 CO), ammonium carbonate, ammonium carbamate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and ammonium formate. [0022] The gas containing nitrogen oxides to be treated with the method according to the present invention can be derived from a combustion process, particularly from an internal combustion engine such as a stationary source or preferably a vehicular lean burn internal combustion engine. [0023] According to another aspect, the invention provides an exhaust system for a vehicular lean-burn internal combustion engine, which system comprising a conduit for carrying a flowing exhaust gas, a source of nitrogenous reductant, a synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal selected from the group consisting of Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Au, In, V, lanthanides and Group VIII transition metals, which aluminosilicate zeolite is a small pore aluminosilicate zeolite having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms, disposed in a flow path of the exhaust gas and means for metering nitrogenous reductant into a flowing exhaust gas upstream of the zeolite catalyst, wherein the mean crystallite size of the aluminosilicate zeolite determined by scanning electron microscope is >0.0 micrometre. [0024] The invention may also be defined according to the following definitions: 3 1) A synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal selected from the group consisting of Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Au, In, V, lanthanides and Group VIII transition metals, which aluminosilicate zeolite is a small pore aluminosilicate zeolite having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms, wherein the mean crystallite size of the aluminosilicate zeolite determined by scanning electron microscope is >0.0 micrometre. 2) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 1), wherein the at least one catalytically active transition metal is copper, iron or copper and iron. 3) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 1) or 2), wherein the at least one catalytically active transition metal consists of copper. 4 4) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 1), 2) or 3), wherein the mean crystallite size is >1.00 micrometre. ) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 1), 2), 3) or 4), wherein the mean crystallite size is >1.0 micrometres. 0 6) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any of 1) to ) inclusive, wherein the mean crystallite size is <1.00 micrometres. 7) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any of 1) to 6) inclusive, wherein the aluminosilicate zeolite is selected from the group consisting of Framework Type Codes CHA, ERI and LEV. 8) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any of 1) to 6) inclusive, wherein the aluminosilicate zeolite is from the Framework Type Code CHA. 3
4 9) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 7) or 8) wherein isotype framework structures of CHA are selected from the group consisting of Linde-D, Linde-R, SSZ-13, LZ-218, Phi and ZK-14. ) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 7), wherein a type material or isotype framework structures of ERI are erionite, ZSM-34 or Linde Type T. 11) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 7), wherein a type material or isotype framework structures of LEV are levynite, Nu-3, LZ-132 or ZK-. 12) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any of 1) to 11) inclusive, wherein the total at least one transition metal present in the catalyst is from 0.1 to.0 wt% based on the total weight of the zeolite catalyst. 1 13) An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to 12), wherein the total at least one transition metal present in the catalyst is from 0. to.0 wt% based on the total weight of the zeolite catalyst. 14) A method of converting nitrogen oxides in a gas to nitrogen by contacting the nitrogen oxides with a nitrogenous reducing agent in the presence of an aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any preceding claim. 1) A method according to 14), wherein the nitrogen oxides are reduced with the reducing agent at a temperature of at least 0 C. 16) A method according to 1), wherein the temperature is from about 10 C to 70 C. 2 17) A method according to 14), 1) or 16), wherein the nitrogen oxides reduction is performed in the presence of oxygen. 3 18) A method according to 14), 1), 16) or 17), wherein addition of nitrogenous reductant is controlled so that NH 3 at the zeolite catalyst inlet is controlled to be 60% to 0% of theoretical ammonia calculated at 1:1 NH 3 /NO and 4:3 NH 3 /NO 2. 19) A method according to any of 14) to 18) inclusive, wherein nitrogen monoxide in the gas is oxidised to nitrogen dioxide using an oxidation catalyst located upstream of the zeolite catalyst and the resulting gas is then mixed with nitrogenous reductant before the mixture is fed into the zeolite catalyst, wherein the oxidation catalyst is adapted to yield a gas stream entering the zeolite catalyst having a ratio of NO to NO 2 of from about 4:1 to about 1:3 by volume. ) A method according to any of 14) to 19) inclusive, wherein the nitrogenous reductant is ammonia per se, hydrazine or an ammonia precursor selected from the group consisting of urea ((NH 2 ) 2 CO), ammonium carbonate, ammonium carbamate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and ammonium formate. 21) A method according to any of 14) to ) inclusive, wherein the gas containing nitrogen oxides is derived from a combustion process ) A method according to 21), wherein the combustion process is the combustion of fuel in a vehicular lean burn internal combustion engine. 23) An exhaust system for a vehicular lean-burn internal combustion engine, which system comprising a conduit for carrying a flowing exhaust gas, a source of nitrogenous reductant, a synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal selected from the group consisting of Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Au, In, V, lanthanides and Group VIII transition metals, which aluminosilicate zeolite is a small pore aluminosilicate zeolite having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms, disposed in a flow path of the exhaust gas and means for metering nitrogenous reductant into a flowing exhaust gas upstream of the zeolite catalyst, wherein the mean crystallite size of the aluminosilicate zeolite determined by scanning electron microscope is >0.0 micrometre. [002] In order that the invention may be more fully understood, the following Examples are provided by way of illustration only. 4
5 Example 1 - Preparation of zeolite samples Zeolite A [0026] Small crystallite CHA was prepared according to Example 1 of US (the entire contents of which is incorporated herein by reference). Zeolite B 1 [0027] Large crystallite CHA was prepared according to a method of making SSZ-13 by S.I. Zones and R A. Van Nordstrand, Zeolites 8 (1988) 166 (the entire contents of which is incorporated herein by reference) also published on International Zeolite Association Synthesis Commission web-site as follows: [0028] The source materials were: sodium hydroxide (1 N), (Baker, reagent grade); N,N,N, trimethyl-1-adamantanammonium hydroxide (RN-OH)(O.72M); deionized water; aluminium hydroxide (Reheis F-00 dried gel, 0% Al 2 O 3 ); and fumed silica (Cab-Q-Sil, M grade, 97% SiO 2 ). [0029] The reaction mixture was prepared as follows: 2 (1) 2.00 g IN NaOH g 0.72 M RN OH g water, add sequentially to a Teflon cup of a Parr 23 ml autoclave; (2) (1) g aluminium hydroxide, mix until solution clears; (3) (2) g fumed silica, mix until uniform. [00] The reaction mixture was crystallised: in a Teflon-lined 23 ml autoclave (Parr model 474) at a temperature of 160 C for 4 days without agitation; After cooling to room temperature the mixture was filtered, washed with de-mineralised water and air-dried overnight. [0031] The resulting product was characterised by powder x-ray diffraction and identified as: 3 CHA zeolite with a SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 ratio of 28 as determined by ICP. [0032] SEM analysis showed: cubes of 2- micrometres. Zeolite C 4 0 [0033] A reaction mixture was prepared of molar composition 60 SiO 2-1. Al 2 O 3-6 Na 2 O - 12 NNNAnOH - 26 H 2 O, where NNNAnOH is the structure directing agent (SDA) or template N,N,N-trimethyladamantanammonium hydroxide [0034] The reaction was prepared using cab-o-sil M (Cabot Corporation) as the source of silica, sodium aluminate (BDH Ltd), sodium hydroxide (Alfa Aesar). The SDA (NNNAnOH) was prepared following the method described in US patent no. 4,44,38 (the entire contents of which is incorporated herein by reference). The required amount of the SDA solution was weighed out and the NaOH added and stirred until it dissolved. The sodium aluminate solid was then added with stirring and stirring was continued until it dissolved. The cab-o-sil was then mixed in and the resulting mixture transferred to a 1L stainless steel autoclave. The autoclave was sealed and the mixture heated to 16C with stirring (0rpm) for 4 days. [003] The resulting product was identified as a CHA type material by powder x-ray diffraction. Visually, the product crystals were approximately 2 microns on edge. The product composition had a silica-alumina ratio (SAR) of 24:1. Example 2 - Preparation of 3wt%Cu/aluminosilicate zeolite [0036] Copper was deposited on zeolites A, B and C prepared according to Example 1 by the standard wet impregnation method using copper acetate as the copper precursor. For g of aluminosilicate zeolite, 0.471g of copper acetate was
6 dissolved in a sufficient amount of water to wet the aluminosilicate zeolite material. The solution was added to the aluminosilicate zeolite material and stirred. The wet powder was dried at C, before being calcined at 00 C for 2 hours. Following calcination, a majority of the copper is understood to be present as copper (II) oxide. [0037] The copper-loaded catalysts prepared according to this Example were designated as Catalysts A, B and C. Catalysts prepared according to Example 2 are referred to as "Fresh Catalysts A-C". Example 3 - Hydrothermal Ageing [0038] Fresh Catalysts A-C prepared according to Example 2 were hydrothermally aged in an atmosphere containing % oxygen, % water, balance nitrogen at 70 C for a period of 24 hours. The hydrothermally aged catalyst is referred to as "Aged Catalysts A-C". 1 2 Table 1: surface area, silica alumina ratio, crystal size and copper loading of the different catalysts (fresh). Chabazite Aluminosilicate code BET surface area Silica to alumina ratio (SAR) Average SEM Crystal Dimension (micrometre)* Cu loading wt% A B C * The samples were dispersed in methanol and subjected to ultrasound for mins and a drop of this liquid was put on a standard carbon padded Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) stub. Counting and sizing was determined by number averaged digital particle size analysis, based on "thresholding" the intensities from each pixel of an image, and exploiting the differences in intensity between particles and the background. The software assumes that each object detected is circular/spherical. Example 4 - Activity Tests 3 4 [0039] The NO x conversion of Catalysts A-C of Examples 2 and 3 at an inlet gas temperature of 0 C or 0 C are given in Table 2. The NO x reduction performance was measured on a powder sample in a laboratory reactor by ramping the catalyst at C per minute in a gas mixture containing 00ppm NO and NH 3, %O 2, %H 2 O and N 2. Table 2: NOx conversion at a catalyst inlet gas temperature of 0 C and 0 C for Fresh and 70 C 24 hour-aged Conditions Catalyst SAR Average SEM Crystal Dimension (micrometre) Cu Loading wt% 00 C Calcined % NOx Conversion 70 C Aged % NOx Conversion 190 C 0 C 0 C 190 C 0 C 0 C A B C See notes on Table 1. 0 [00] It can be seen from Table 2 that the activity of the catalysts generally follows a trend of increasing activity with crystallite size. Hence we conclude that larger crystallite size aluminosilicate zeolite materials are surprisingly more active either fresh or hydrothermally aged than catalysts prepared from smaller crystals of the same aluminosilicate zeolite material. Claims 1. A synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal selected from the group consisting of Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Au, In, V, lanthanides and Group VIII transition metals, which aluminosilicate zeolite is a small pore aluminosilicate zeolite having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms, wherein the 6
7 mean crystallite size of the aluminosilicate zeolite determined by scanning electron microscope is >0.0 micrometre. 2. An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to claim 1, wherein the at least one catalytically active transition metal is copper, iron or copper and iron. 3. An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the at least one catalytically active transition metal consists of copper. 4. An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any preceding claim, wherein the mean crystallite size is <1.00 micrometres.. An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any preceding claim, wherein the aluminosilicate zeolite is selected from the group consisting of Framework Type Codes ERI and LEV An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to claim, wherein a type material or isotype framework structures of ERI are erionite, ZSM-34 or Linde Type T. 7. An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to claim, wherein a type material or isotype framework structures of LEV are levynite, Nu-3, LZ-132 or ZK-. 8. An aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any preceding claim, wherein the total at least one transition metal present in the catalyst is from 0.1 to.0 wt% based on the total weight of the zeolite catalyst A method of converting nitrogen oxides in a gas to nitrogen by contacting the nitrogen oxides with a nitrogenous reducing agent in the presence of an aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst according to any preceding claim.. A method according to claim 9, wherein the nitrogen oxides are reduced with the reducing agent at a temperature of from 10 C to 70 C. 11. A method according to claim 9 or, wherein addition of nitrogenous reductant is controlled so that NH 3 at the zeolite catalyst inlet is controlled to be 60% to 0% of theoretical ammonia calculated at 1:1 NH 3 /NO and 4:3 NH 3 /NO A method according to any of claims 9 to 11, wherein nitrogen monoxide in the gas is oxidised to nitrogen dioxide using an oxidation catalyst located upstream of the zeolite catalyst and the resulting gas is then mixed with nitrogenous reductant before the mixture is fed into the zeolite catalyst, wherein the oxidation catalyst is adapted to yield a gas stream entering the zeolite catalyst having a ratio of NO to NO 2 of from about 4:1 to about 1:3 by volume. 13. A method according to any of claims 9 to 12, wherein the nitrogenous reductant is ammonia per se, hydrazine or an ammonia precursor selected from the group consisting of urea ((NH 2 ) 2 CO), ammonium carbonate, ammonium carbamate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and ammonium formate A method according to any of claims 9 to 13, wherein the gas containing nitrogen oxides is derived from the combustion of fuel in a vehicular lean burn internal combustion engine. 1. An exhaust system for a vehicular lean-burn internal combustion engine, which system comprising a conduit for carrying a flowing exhaust gas, a source of nitrogenous reductant, a synthetic aluminosilicate zeolite catalyst containing at least one catalytically active transition metal selected from the group consisting of Cu, Fe, Hf, La, Au, In, V, lanthanides and Group VIII transition metals, which aluminosilicate zeolite is a small pore aluminosilicate zeolite having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms, disposed in a flow path of the exhaust gas and means for metering nitrogenous reductant into a flowing exhaust gas upstream of the zeolite catalyst, wherein the mean crystallite size of the aluminosilicate zeolite determined by scanning electron microscope is >0.0 micrometre. 7
8
9
10
11
12
13 REFERENCES CITED IN THE DESCRIPTION This list of references cited by the applicant is for the reader s convenience only. It does not form part of the European patent document. Even though great care has been taken in compiling the references, errors or omissions cannot be excluded and the EPO disclaims all liability in this regard. Patent documents cited in the description US A [0003] [0034] US B [0004] [0026] GB W [000] [0006] Non-patent literature cited in the description W. ADDY MAJEWSKI. Selective Catalytic Reduction. DieselNet Technology Guide, May 0, [0002] S.I. ZONES ; R A. VAN NORDSTRAND. Zeolites, 1988, vol. 8, 166 [0027] International Zeolite Association Synthesis Commission, [0027] 13
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6 6697A_T (11) EP 2 626 697 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 30/32 (2006.01) G01N 30/20 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6 6697A_T (11) EP 2 626 697 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 30/32 (2006.01) G01N 30/20 (2006.01) (21) Application
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B01D 9/00 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 505 243 A1 (43) Date of publication: 03.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/40 (51) Int Cl.: B01D 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12162017.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 505 243 A1 (43) Date of publication: 03.10.2012 Bulletin 2012/40 (51) Int Cl.: B01D 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 12162017.3 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 89955_A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/06
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 281 809 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.02.2011 Bulletin 2011/06 (21) Application number: 09178846.3 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 231/24 (2006.01) C07C 237/46 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 281 809 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.02.2011 Bulletin 2011/06 (21) Application number: 09178846.3 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 231/24 (2006.01) C07C 237/46 (2006.01)
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
TEPZZ 6_Z6_ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6_Z6_ A_T (11) EP 2 6 612 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/27 (51) Int Cl.: G01N 27/333 (2006.01) G01N 27/416 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6_Z6_ A_T (11) EP 2 6 612 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/27 (51) Int Cl.: G01N 27/333 (2006.01) G01N 27/416 (2006.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01J 5/62 ( ) G01J 3/28 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
(19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Efficient synthesis of the Cu-SSZ-39 catalyst for DeNOx
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001610121A1* (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158(3) EPC (43) Date of publication:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001610121A1* (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158(3) EPC (43) Date of publication:
Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Atom-Economical Synthesis of High Silica CHA Zeolite from
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
TEPZZ 6 Z487A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/31
 (19) TEPZZ 6 Z487A_T (11) EP 2 620 487 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/31 (21) Application number: 1313366.3 (1) Int Cl.: C11D 1/37 (2006.01) C11D
(19) TEPZZ 6 Z487A_T (11) EP 2 620 487 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.07.2013 Bulletin 2013/31 (21) Application number: 1313366.3 (1) Int Cl.: C11D 1/37 (2006.01) C11D
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2004/22
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP0014222A1* (11) EP 1 422 2 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.0.04 Bulletin 04/22 (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP0014222A1* (11) EP 1 422 2 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.0.04 Bulletin 04/22 (1) Int
Supplementary Information. Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information of Fluoride-free synthesis of Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
(19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/19
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 40 336 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/19 (21) Application number: 19081.8 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 41/6 (2006.01) C07C 43/30 (2006.01) C07C
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 40 336 A1 (43) Date of publication: 09.0.2012 Bulletin 2012/19 (21) Application number: 19081.8 (1) Int Cl.: C07C 41/6 (2006.01) C07C 43/30 (2006.01) C07C
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous α-al 2 O 3 Supports
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Template-Free Synthesis of Beta Zeolite Membranes on Porous
TEPZZ ZZ Z_ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ Z_ A_T (11) EP 3 002 013 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.16 Bulletin 16/14 (21) Application number: 14382379.7 (1) Int Cl.: A61L 9/ (06.01) A61L 9/22 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ ZZ Z_ A_T (11) EP 3 002 013 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.16 Bulletin 16/14 (21) Application number: 14382379.7 (1) Int Cl.: A61L 9/ (06.01) A61L 9/22 (06.01)
Supporting Information. CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information CdS/mesoporous ZnS core/shell particles for efficient
Application Challenges for Nanostructured Porous Materials
 Application Challenges for Nanostructured Porous Materials Dr Liz Rowsell Director, Johnson Matthey Technology Centre 1 Paradigm Shift in Automotive NOx Control Catalysts A paradigm shift describes a fundamental
Application Challenges for Nanostructured Porous Materials Dr Liz Rowsell Director, Johnson Matthey Technology Centre 1 Paradigm Shift in Automotive NOx Control Catalysts A paradigm shift describes a fundamental
Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry
 Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry A. The chemical equation B. Types of chemical reactions A. Activity series of metals B. Solubility rules C. Rules for writing and balancing equations D. Calculations
Unit IV: Chemical Equations & Stoichiometry A. The chemical equation B. Types of chemical reactions A. Activity series of metals B. Solubility rules C. Rules for writing and balancing equations D. Calculations
Controlling the Isolation and Pairing of Aluminum in Chabazite Zeolites Using Mixtures of Organic and Inorganic Structure-Directing Agents
 Controlling the Isolation and Pairing of Aluminum in Chabazite Zeolites Using Mixtures of Organic and Inorganic Structure-Directing Agents John R. Di Iorio, Rajamani Gounder * SUPPORTING INFORMATION Section
Controlling the Isolation and Pairing of Aluminum in Chabazite Zeolites Using Mixtures of Organic and Inorganic Structure-Directing Agents John R. Di Iorio, Rajamani Gounder * SUPPORTING INFORMATION Section
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
TEPZZ 95785_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
 (Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
(Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation
 Supporting Information for Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min, Wei Zhu, Hao-Shuai Wu, Ya-Wen Zhang* and Chun-Hua
Supporting Information for Multiply twinned Pt Pd nanoicosahedrons as highly active electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min, Wei Zhu, Hao-Shuai Wu, Ya-Wen Zhang* and Chun-Hua
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Supporting Information Tetraethylammonium hydroxide (35 wt.%) (TEAOH), aluminum powder, fumed silica, zinc acetate dehydrate, Ludox HS-40, pure silica MCM-41, and tetraethylammonium fluoride were purchased
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts
 Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information 1. Thermodynamic data The isomerization of glucose into fructose using can be represented as: The equilibrium constant K eq and equilibrium conversion were calculated as follows:
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing. twin crystal growth during the secondary growth
 Supplementary Information Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing twin crystal growth during the secondary growth Xianming Li, a Yong Peng, a Zhengbao Wang,* a and Yushan Yan a,
Supplementary Information Synthesis of highly b-oriented zeolite MFI films by suppressing twin crystal growth during the secondary growth Xianming Li, a Yong Peng, a Zhengbao Wang,* a and Yushan Yan a,
DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 5 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
 DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 5 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Charles Kappenstein, Professor Emeritus, University of Poitiers, France Preparation of catalysts
DICP Course - Dalian, 2012 Preparation of solid catalysts Part 5 Supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Charles Kappenstein, Professor Emeritus, University of Poitiers, France Preparation of catalysts
UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD UMICORE AG & CO. KG, Petitioner
 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD UMICORE AG & CO. KG, Petitioner Patent No. 8,404,203 Issue Date: March 16, 2013 Title: PROCESS FOR REDUCING NITROGEN OXIDES
UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD UMICORE AG & CO. KG, Petitioner Patent No. 8,404,203 Issue Date: March 16, 2013 Title: PROCESS FOR REDUCING NITROGEN OXIDES
Sintering-resistant Ni-based Reforming Catalysts via. the Nanoconfinement Effect
 Supporting Information Sintering-resistant Ni-based Reforming Catalysts via the Nanoconfinement Effect Chengxi Zhang a,b, Wancheng Zhu c, Shuirong Li a,b, Gaowei Wu a,b, Xinbin Ma a,b, Xun Wang c, and
Supporting Information Sintering-resistant Ni-based Reforming Catalysts via the Nanoconfinement Effect Chengxi Zhang a,b, Wancheng Zhu c, Shuirong Li a,b, Gaowei Wu a,b, Xinbin Ma a,b, Xun Wang c, and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry
 Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Chem 6A Michael J. Sailor, UC San Diego 1 Announcements: Thursday (Sep 29) quiz: Bring student ID or we cannot accept your quiz! No notes, no calculators Covers chapters 1 and
Chapter 3: Stoichiometry Chem 6A Michael J. Sailor, UC San Diego 1 Announcements: Thursday (Sep 29) quiz: Bring student ID or we cannot accept your quiz! No notes, no calculators Covers chapters 1 and
IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry
 IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry Principles of Chemistry Chemical Formulae, Equations and Calculations NOTES 1.25: Write word equations and balanced chemical equations (including state symbols): For reactions
IGCSE (9-1) Edexcel - Chemistry Principles of Chemistry Chemical Formulae, Equations and Calculations NOTES 1.25: Write word equations and balanced chemical equations (including state symbols): For reactions
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Bonus Final Exam 3. 1 Calculate the heat of reaction,δh 0 rxn, for the following reaction as written at 298 K: g 2H 2 CH 4. g CF 4.
 Bonus Final Exam 3 1 Calculate the heat of reaction,δh rxn, for the following reaction as written at 298 K: CH 4 2F 2 CF 4 2H 2 substance CH 4 CF 4 ΔH f kj/mol 75 68 (A) ΔH rxn 23 kj (B) ΔH rxn 914 kj
Bonus Final Exam 3 1 Calculate the heat of reaction,δh rxn, for the following reaction as written at 298 K: CH 4 2F 2 CF 4 2H 2 substance CH 4 CF 4 ΔH f kj/mol 75 68 (A) ΔH rxn 23 kj (B) ΔH rxn 914 kj
Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes
 Supporting Information Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min,
Supporting Information Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min,
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information MgFeCe ternary layered double hydroxide as highly efficient and recyclable heterogeneous base catalyst for synthesis of dimethyl carbonate by transesterification Nayana T. Nivangune
Supporting Information MgFeCe ternary layered double hydroxide as highly efficient and recyclable heterogeneous base catalyst for synthesis of dimethyl carbonate by transesterification Nayana T. Nivangune
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with. High Oxidation-Resistant Property as Efficient and Durable
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with High
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Sub-10-nm Au-Pt-Pd Alloy Trimetallic Nanoparticles with High
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Supporting Information High Performance Electrocatalyst: Pt-Cu Hollow Nanocrystals Xiaofei Yu, a Dingsheng, a Qing Peng a and Yadong Li* a a Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal
 Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Dr. Mya Mya Oo 2, Dr. Su Su Hlaing 3 Abstract-- To overcome arsenic toxicity; which has become
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Dr. Mya Mya Oo 2, Dr. Su Su Hlaing 3 Abstract-- To overcome arsenic toxicity; which has become
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/49
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 128 133 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.12.09 Bulletin 09/49 (1) Int Cl.: C07D /08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 08689.8 (22) Date of filing: 26.0.08
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 128 133 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.12.09 Bulletin 09/49 (1) Int Cl.: C07D /08 (06.01) (21) Application number: 08689.8 (22) Date of filing: 26.0.08
Shape Assisted Fabrication of Fluorescent Cages of Squarate based Metal-Organic Coordination Frameworks
 Supporting Information Shape Assisted Fabrication of Fluorescent Cages of Squarate based Metal-Organic Coordination Frameworks Kolleboyina Jayaramulu, a Katla Sai Krishna, a Subi J. George, b Muthuswamy
Supporting Information Shape Assisted Fabrication of Fluorescent Cages of Squarate based Metal-Organic Coordination Frameworks Kolleboyina Jayaramulu, a Katla Sai Krishna, a Subi J. George, b Muthuswamy
M10/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ CHEMISTRY. Wednesday 12 May 2010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M10/4/EMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 22106110 EMISTRY standard level Paper 1 Wednesday 12 May 2010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUTIONS TO ANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
M10/4/EMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 22106110 EMISTRY standard level Paper 1 Wednesday 12 May 2010 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUTIONS TO ANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Answer
Precious Metal-free Electrode Catalyst for Methanol Oxidations
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information SnO 2 Nanocrystals Decorated-Mesoporous ZSM-5 Spheroidicity
Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations
 Calculating moles Moles and elements Moles and compounds Moles and gases Moles and solutions Calculating formulae Finding the formula Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations Moles and chemical equations Checklist
Calculating moles Moles and elements Moles and compounds Moles and gases Moles and solutions Calculating formulae Finding the formula Chapter 5 Chemical Calculations Moles and chemical equations Checklist
ICSE Board Class IX Chemistry Paper 5 Solution
 ICSE Board Class IX Chemistry Paper 5 Solution SECTION I Answer 1 i. Dalton used the symbol for oxygen and the symbol for hydrogen. Symbol represents gram atom(s) of an element. i Symbolic expression for
ICSE Board Class IX Chemistry Paper 5 Solution SECTION I Answer 1 i. Dalton used the symbol for oxygen and the symbol for hydrogen. Symbol represents gram atom(s) of an element. i Symbolic expression for
Half Yearly Exam 2015
 GOZO COLLEGE Secondary School KULLEĠĠ TA GĦAWDEX Skola Sekondarja Half Yearly Exam 015 Year 9 Track 3 CHEMISTRY Time: 1½ hours Name: Class: Useful Data: Atomic numbers and relative atomic masses are given
GOZO COLLEGE Secondary School KULLEĠĠ TA GĦAWDEX Skola Sekondarja Half Yearly Exam 015 Year 9 Track 3 CHEMISTRY Time: 1½ hours Name: Class: Useful Data: Atomic numbers and relative atomic masses are given
02/05/09 Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Dr. Jessica Parr
 Chemistry 05 B First Letter of PLEASE PRINT YOUR NAME IN BLOCK LETTERS Exam last Name Name: 02/05/09 Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Dr. Jessica Parr Lab TA s Name: Question Points Score Grader 2 2 9 3 9 4 2
Chemistry 05 B First Letter of PLEASE PRINT YOUR NAME IN BLOCK LETTERS Exam last Name Name: 02/05/09 Last 4 Digits of USC ID: Dr. Jessica Parr Lab TA s Name: Question Points Score Grader 2 2 9 3 9 4 2
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 5, No. 1, March 1983, pp. i3-19 @ Printed in India. Growth and characterization of hydrothermally-grown zeolite crystals M S JOSHI and B T BHOSKAR* Department of Physics, Sardar
Supporting Information. Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic Compound Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer Drug Delivery
 Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Stoichiometry ( ) ( )
 Stoichiometry Outline 1. Molar Calculations 2. Limiting Reactants 3. Empirical and Molecular Formula Calculations Review 1. Molar Calculations ( ) ( ) ( ) 6.02 x 10 23 particles (atoms or molecules) /
Stoichiometry Outline 1. Molar Calculations 2. Limiting Reactants 3. Empirical and Molecular Formula Calculations Review 1. Molar Calculations ( ) ( ) ( ) 6.02 x 10 23 particles (atoms or molecules) /
Ionic liquid-supported Pt nanoparticles as catalysts for enantioselective hydrogenation
 Supporting information Ionic liquid-supported Pt nanoparticles as catalysts for enantioselective hydrogenation Matthias Josef Beier, Jean-Michel Andanson, Tamas Mallat, Frank Krumeich and Alfons Baiker*
Supporting information Ionic liquid-supported Pt nanoparticles as catalysts for enantioselective hydrogenation Matthias Josef Beier, Jean-Michel Andanson, Tamas Mallat, Frank Krumeich and Alfons Baiker*
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 15 Exam II John II. Gelder March 4, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table, a solubility
CHEM 15 Exam II John II. Gelder March 4, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table, a solubility
3.2.1 Energetics. Enthalpy Change. 263 minutes. 259 marks. Page 1 of 41
 ..1 Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 41 Q1. (a) Define the term standard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔH f. (b) State Hess s law. (c) Propanone, CO, burns in oxygen as shown by the
..1 Energetics Enthalpy Change 6 minutes 59 marks Page 1 of 41 Q1. (a) Define the term standard molar enthalpy of formation, ΔH f. (b) State Hess s law. (c) Propanone, CO, burns in oxygen as shown by the
Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor
 Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
Supporting Information Synthesis of nano-sized anatase TiO 2 with reactive {001} facets using lamellar protonated titanate as precursor Liuan Gu, Jingyu Wang *, Hao Cheng, Yunchen Du and Xijiang Han* Department
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1215 Exam III John III. Gelder November 11, 1998 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and
CHEM 1215 Exam III John III. Gelder November 11, 1998 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last page includes a periodic table and
TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T (11) EP 2 618 130 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.07.13 Bulletin 13/30 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/ (06.01) G01N 21/77 (06.01) G01N 33/43 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6_8_ ZA_T (11) EP 2 618 130 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.07.13 Bulletin 13/30 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 21/ (06.01) G01N 21/77 (06.01) G01N 33/43 (06.01) (21) Application
The impacts of Pdin BEA zeolite on decreasing cold start HC emission of an E85 vehicle
 CLEERS presentation October, 2017 The impacts of Pdin BEA zeolite on decreasing cold start HC emission of an E85 vehicle Lifeng Xu*, Jason Lupescu, Jeffery Hepburn, Giovanni Cavataio, Kevin Guo, Paul Laing,
CLEERS presentation October, 2017 The impacts of Pdin BEA zeolite on decreasing cold start HC emission of an E85 vehicle Lifeng Xu*, Jason Lupescu, Jeffery Hepburn, Giovanni Cavataio, Kevin Guo, Paul Laing,
and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment
 Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials Sodium
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials Sodium
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry)
 Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Balancing chemical reaction equations (stoichiometry) This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit
Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR
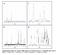 a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
a c b d Supplementary Figure S1: Solution NMR spectra for D-glucose with a 4:1 sugar:sb molar ratio in H 2 O. a) 13 C NMR of D-(1-13 C)glucose, b) 13 C NMR of D-glucose, c) 11 B NMR, d) 1 H NMR a c b d
Study on the Selective Hydrogenation of Nitroaromatics to N-aryl hydroxylamines using a Supported Pt nanoparticle Catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 204 Supporting Information Study on the Selective Hydrogenation of Nitroaromatics
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 204 Supporting Information Study on the Selective Hydrogenation of Nitroaromatics
How many hydrogen atoms are there in the empirical formula of propene, C 3 H 6? How many neutrons are there in one atom of 24 Mg?
 1 A 2 B 3 C The atomic number of Na is 11. How many electrons are there in a sodium ion, Na +? How many hydrogen atoms are there in the empirical formula of propene, C 3 H 6? What is the mass in grams
1 A 2 B 3 C The atomic number of Na is 11. How many electrons are there in a sodium ion, Na +? How many hydrogen atoms are there in the empirical formula of propene, C 3 H 6? What is the mass in grams
Marks for each question are as indicated in [] brackets.
![Marks for each question are as indicated in [] brackets. Marks for each question are as indicated in [] brackets.](/thumbs/77/75878580.jpg) Name Student Number CHEMISTRY 140 FINAL EXAM December 10, 2002 Numerical answers must be given with appropriate units and significant figures. Please place all answers in the space provided for the question.
Name Student Number CHEMISTRY 140 FINAL EXAM December 10, 2002 Numerical answers must be given with appropriate units and significant figures. Please place all answers in the space provided for the question.
4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table. GCSE Chemistry
 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table GCSE Chemistry All substances are made of atoms this is cannot be chemically broken down it is the smallest part of an element. Elements are made of only one
4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table GCSE Chemistry All substances are made of atoms this is cannot be chemically broken down it is the smallest part of an element. Elements are made of only one
TEPZZ 84 9Z8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 84 9Z8A_T (11) EP 2 842 908 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.03.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 131879.7 (1) Int Cl.: C01B 2/4 (06.01) H01M /02 (.01) H01M
(19) TEPZZ 84 9Z8A_T (11) EP 2 842 908 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.03.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 131879.7 (1) Int Cl.: C01B 2/4 (06.01) H01M /02 (.01) H01M
TEPZZ 8 768A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 8 768A_T (11) EP 2 832 768 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 04.02.1 Bulletin 1/06 (21) Application number: 1287238.2
(19) TEPZZ 8 768A_T (11) EP 2 832 768 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 04.02.1 Bulletin 1/06 (21) Application number: 1287238.2
CHAPTER 4. SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL
 93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
93 CHAPTER 4 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION OF TiO 2 NANOTUBES AND THEIR APPLICATION IN DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL 4.1 INTRODUCTION TiO 2 -derived nanotubes are expected to be applicable for several applications,
EFFECTS OF ADDITIONAL GASES ON THE CATALYTIC DECOMPOSITION OF N20 OVER Cu-ZSM-5
 Jointly published by Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam and Akad~miai Kiad6, Budapest RKCL3296 Reaet.Kinet. Catal.Lett. Vol. 64, No. 2, 215-220 (1998) EFFECTS OF ADDITIONAL GASES ON THE CATALYTIC DECOMPOSITION
Jointly published by Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam and Akad~miai Kiad6, Budapest RKCL3296 Reaet.Kinet. Catal.Lett. Vol. 64, No. 2, 215-220 (1998) EFFECTS OF ADDITIONAL GASES ON THE CATALYTIC DECOMPOSITION
Chemical Reactions Chapter 12 Study Guide (Unit 9)
 Name: Hr: Understand and be able to explain all of the key concepts. Define and understand all of the survival words Memorize the names and symbols for these elements: (Ag, Al, Ar, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Br,
Name: Hr: Understand and be able to explain all of the key concepts. Define and understand all of the survival words Memorize the names and symbols for these elements: (Ag, Al, Ar, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Br,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ucleophilic addition of amines, alcohols, and thiophenol with epoxide/olefin using highly efficient
DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES
 1 Exam 9 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709. Answer all question in part I and six
1 Exam 9 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709. Answer all question in part I and six
Selective aerobic oxidation of biomass-derived HMF to 2,5- diformylfuran using a MOF-derived magnetic hollow Fe-Co
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Selective aerobic oxidation of biomass-derived HMF to 2,5- diformylfuran using a MOF-derived
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Selective aerobic oxidation of biomass-derived HMF to 2,5- diformylfuran using a MOF-derived
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction
 Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Method and process for combustion synthesized supported cobalt catalysts for fixed bed Fischer Tropsch reaction Center for Sustainable Technologies Indian Institute of Science Bangalore IDF presentation
Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins
 Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
Supporting Information Facile fabrication of ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst with high durability to coke formation during catalytic cracking of paraffins Satoshi Inagaki, a, Shoma Shinoda, a Yoshihiro Kaneko,
CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL
 *P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
*P15* PRE-LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 CHEMISTRY HIGHER LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS 400 MARKS Answer eight questions in all These must include at least two questions from Section A All questions carry
Section 1 Chemical Changes
 Chemical Reactions Section 1 Chemical Changes What You ll Learn: How to identify the reactants & products in a chemical reaction How a chemical reaction follows the law of conservation of mass How chemists
Chemical Reactions Section 1 Chemical Changes What You ll Learn: How to identify the reactants & products in a chemical reaction How a chemical reaction follows the law of conservation of mass How chemists
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
Supporting Information Collapsed (Kippah) Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Kun-Che Kao, Chieh-Jui Tsou and Chung-Yuan Mou* Experimental Section Materials: Reagents: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, 99%+),
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp , 2016
 KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No. 4, pp. 255 259, 216 Research Article Effect of Strong Metal Support Interactions of Supported Ni and Ni-Co Catalyst on Metal Dispersion and Catalytic Activity
M09/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ CHEMISTRY. Monday 18 May 2009 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M09/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 22096110 CHEMISTRY standard level Paper 1 Monday 18 May 2009 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so.
M09/4/CHEMI/SPM/ENG/TZ1/XX+ 22096110 CHEMISTRY standard level Paper 1 Monday 18 May 2009 (afternoon) 45 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so.
(02) WMP/Jun10/CHEM2
 Energetics 2 Section A Answer all the questions in the spaces provided. 1 An equation for the equilibrium reaction between hydrogen, iodine and hydrogen iodide is shown below. H 2 (g) + I 2 (g) 2HI(g)
Energetics 2 Section A Answer all the questions in the spaces provided. 1 An equation for the equilibrium reaction between hydrogen, iodine and hydrogen iodide is shown below. H 2 (g) + I 2 (g) 2HI(g)
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131,
 Palladium Nanoparticles on Graphite Oxide and Its Functionalized Graphene Derivatives as Highly Active Catalysts for the Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling Reaction J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8262 8270 Rolf Műlhaupt
Palladium Nanoparticles on Graphite Oxide and Its Functionalized Graphene Derivatives as Highly Active Catalysts for the Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling Reaction J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8262 8270 Rolf Műlhaupt
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
As. J. Energy Env. 2006, 7(01), 241-245 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Hydrogen Production from Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane
PCT PCT/GB2008/ kind of national protection available): AE, AG, AL, AM, PCT/GB2007/ AO, AT,AU, AZ, BA, BB, BG, BH, BR, BW, BY, BZ, CA,
 (12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (43) International Publication Date (10) International
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (43) International Publication Date (10) International
