Name Date Hour Table. Semester One Review #1-11 Directions: Mark the correct answer on each of the following questions.
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Hodges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Semester One Review #1-11 Directions: Mark the correct answer on each of the following questions. 1. Which of the following are subatomic particles? A. negative electrons, neutral nuclei, negative elements B. positive protons, negative electrons, neutral atoms C. negative electrons, positive protons, positive or negative ions D. positive protons, negative electrons, neutral neutrons 2. Physical changes result in A. changes in total mass B. changes of the shape or state of matter C. changes in the arrangement of atoms D. change in charge 3. The first atmosphere that formed above Earth was most likely due to what process? A. eruption of volcanoes B. movement of water C. development of land plants D. occurrence of violent storms 4. Which of these is not a chemical change A. a bike chain rusting B. an antacid in stomach acid C. two liquids mixing together to form a solid D. melting snow 5. What is the volume of the liquid in the graduated cylinder? A. 40 ml B. 43 ml C. 44mL D. 45 ml 6. Which of the following causes particles to have the highest energy? A. increase in thermal energy (heat) B. decrease in thermal energy (heat) C. condensation D. freezing point 7. The Law of Conservation of Matter states that A. there must be more reactants than products in a reaction B. there will be more products created C. it doesn t matter how many reactants or products you have D. the reactants in a reaction must equal the products in a reaction 8. Which has the highest potential energy? A. a student with two bags of M&Ms B. a student with no candy C. a car with two bags of M&Ms D. an old person on a bench 9. Which of the following is NOT true of terrestrial planets? A. they are larger in volume, but have the same average mass B. they have the same overall chemical compositions as gaseous planets C. they are larger than the gaseous planets D. all of the above. 10. Density is A. a chemical property B. a physical property that is specific to each substance C. a physical property that can be changed D. a chemical property that can be changed 11. When energy is transferred or transformed A. all energy is transferred from one type to another B. some energy is transferred and some is lost as thermal energy to the environment C. most energy is lost as thermal energy to the environment D. energy cannot be changed from one type to another
2 #12-42 Directions: Record the correct letter of the definition that matches each of the terms. 12. physical changes 27. independent variable 13. Law of Conservation of Matter 14. Law of Conservation of Energy 15. noncontact forces 28. theory 29. waxing gibbous 30. atomic number 16. motion 31. element 17. velocity 32. acceleration 18. convection 33. friction 19. balanced forces 34. unbalanced forces 20. Newton 35. energy inefficiency 21. atomic nucleus 36. chemical change 22. displacement volume 37. lunar eclipse 23. weight 38. Erlenmeyer flask 24. heliocentric 39. graduated cylinder 25. gravitational pull 40. gravity 26. substance 41. triple beam balance 42. mixture 43. substance
3 A. a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary chemical changes; consists of atoms of only one type B. a cylindrical container marked with horizontal lines to represent units of measurement and used to precisely measure the volume of liquids C. a combination of two or more substances that can be separated by physical means D. matter with a definite, uniform, chemical composition E. a narrow- mouthed container used to transport, heat, or store substances, often used when a stopper is required F. the variable in an experiment that the INVESTIGATOR or I change G. a positive or negative change in speed H. in all energy transfers, some energy is lost as thermal energy I. the speed and direction of an objects motion J. a scientific hypothesis that has been tested many times with the same outcome K. a type of force that acts upon an object without touching it (ex. magnetism, gravity, electrostatic) L. two forces acting on an object in opposite directions, but no movements seem to happen or movement occurs at a constant speed M. the SI unit of measure of force N. theory that places the Sun at the center of the universe with planets and other objects orbiting around it O. a change that does not alter the identity of substance (pizza is still pizza after it is cut in slices) P. in a chemical reaction, the reactants must equal the products Q. the method of determining the volume of an irregularly shaped object R. the Moon passes directly behind the Earth or through Earth s shadow S. consists of protons and neutrons and is surrounded by the electron cloud T. the transfer of heat by the movement of a liquid or gas U. a contact force that slows or stops sliding motion V. energy cannot be created or destroyed, only changed into different forms W. represents the number of protons in an element, if changed, results in a new element X. the attraction between two objects that have mass Y. a Moon phase that is less than full, but more than half illuminated Z. instrument to measure mass AA. change in composition of a substance that cannot be undone by physical means BB. forces working in opposite directions that result in movement of an object CC. described using a reference point, direction, and displacement DD. the measurement of the amount of gravitational force applied to an object EE. a force affected by the mass of the objects and distance between them
4 43. Which would you most likely be able to separate into its parts by filtering? A. Heterogeneous mixture of two liquids B. Heterogeneous mixture of two solids C. Homogeneous mixture of two liquids D. Homogeneous mixture of two solids # Directions: Use the words in the word bank to answer each question. Not all words are used. atom compound element heterogeneous mixture homogeneous mixture nucleus 44. The parts of a(n) are evenly mixed but not bonded together. 45. A(n), such as table salt, contains two or more substances in a specific combination. 46. In a(n), the individual components are not evenly mixed. 47. Pure gold is an example of a(n). #48-52 Directions: Fill in the missing States of Matter information in the table using this image: State of Matter Gas Liquid Solid Energy of Particles High Movement of Particles 50. Sliding 51. Space between Particles 52. Medium Very little
5 #53-61 Directions: Fill in the missing information, using the word bank below: *revolution *groups *properties *molecule *families *positive *decreases *day *increases *negative *unbalanced *kinetic *periods *compound *chemical *asteroid belt 53. The rows on the periodical table are called, the columns on the periodic table are called or. 54. Elements in families have similar and act similarly in reactions. 55. A(n) is two or more atoms bonded together. A(n) is a type of molecule with two or more different elements bonded together. 56. Objects with mass have gravity. Gravity with an increase in mass. Gravity with an increase in distance between the objects. 57. Two forces are acting on an object. The object is moving forward at an uneven pace. We can say that the two forces are. 58. energy is found in the food we digest. We convert this type of energy to when our bodies move. Some of this energy is lost or unused as heat (thermal energy) in the transformation from one type of energy to the other. 59. A planet makes one around the Sun every year. The planet makes one rotation around its axis every. 60. A(n) separates the terrestrial planets from the gaseous planets. 61. Acceleration can be either positive or negative. acceleration causes an increase in speed, while acceleration will cause an object to slow or even stop.
6 #62 Directions: Use the following word bank to complete the missing information. gravitational distance stored 62. There are many types of energy. Potential energy is the energy that is due to the interactions between objects or particles. One type of potential energy is potential energy. This is the form of energy that is due to the mass of an object and it s from another object. 63. Label each of the following with the type of eclipse represented in the diagram. A. B. #64-69 Directions: Circle True or False to identify each of the following statements as TRUE or FALSE. True or False 64. Earth s Moon orbits the Sun. True or False 65. Planets orbit the Moon. True or False 66. A galaxy is larger than a universe. True or False 67. The Milky way is the only galaxy in the universe. True or False 68. The Earth experiences two low and high tides daily due to the gravitational pull between the Earth and the Moon True or False 69. If the tilt of Earth s axis was at zero degrees, Oklahoma would experience only winter. 70. Circle each of the following that reflect the light produced by something else in the solar system stars planets moons comets 71. Circle each of the following that is correct about terrestrial planets has a dense core has rings inner planets outer planets rocky surfaces very large made of gases 72. Circle each of the following that is correct about the gas giants has a dense core has rings inner planets outer planets rocky surfaces very large made of gases
7 73. Identify each of the solar system components shown in the diagram At which position is the Northern Hemisphere experiencing each of the following seasons? Spring- Summer- Winter- Fall/Autumn-
8 75. On the diagram below, color and label each of the Moon phases in the order that they occur, Page 359 in your book may be a help to you. light rays position 1 position 2 position 8 People in Center position 3 position 7 position 4 position 6 position 5
9 76-77 Using the diagrams, fill in the data tables with the requested information. 76. Label Name Description of temperature and moisture level North American Air Masses A Continental Arctic frigid (very cold) and dry B C D E F G H 77. Layer Description-Identifying Characteristic(s) exosphere 6 thermosphere
10 The circle graph represents the composition of dry air. Identify the gases that belong in each section of the circle and list the percentage of the air that each gas represents. # Type of gas or gases % Which diagram best represents the movement of air during the day? 83. Which diagram best represents the movement of air during the night? 84. What is the circular movement of air caused by temperature and pressure differences shown in the diagrams called?
11 Name Date Hour Table
Name Date Hour Table. Semester One Review #1-11 Directions: Mark the correct answer on each of the following questions.
 Semester One Review #1-11 Directions: Mark the correct answer on each of the following questions. 1. Which of the following are subatomic particles? A. negative Electrons, neutral nuclei, negative elements
Semester One Review #1-11 Directions: Mark the correct answer on each of the following questions. 1. Which of the following are subatomic particles? A. negative Electrons, neutral nuclei, negative elements
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SCIENCE 8 SCIENCE GATE/HONORS 8
 CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SCIENCE 8 SCIENCE GATE/HONORS 8 Course number 3042-Science 8 3043-Science GATE/Honors 8 Department Science Length of course One (1) year Grade Level
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE SCIENCE 8 SCIENCE GATE/HONORS 8 Course number 3042-Science 8 3043-Science GATE/Honors 8 Department Science Length of course One (1) year Grade Level
Astronomy Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
Name: ate: 1. In laska, there are fewer hours of daylight in the winter than in the summer. Which statement best explains why this difference occurs?. The Sun burns hotter in the summer.. The Sun moves
SPI Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe.
 SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
SPI 0607.6.1 - Use data to draw conclusions about the major components of the universe. o Stars are huge, hot, brilliant balls of gas trillions of kilometers away. A Galaxy is a collection of billions
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar System Glossary. The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting
 Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
Solar System Glossary Apogee Atmosphere Asteroid Axis Autumn Barred spiral The point in an object s elliptical orbit farthest from the body it is orbiting The air that surrounds Earth and other planets
What is in outer space?
 What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
What is in outer space? Celestial Objects are any natural objects that move through space. Star:_a huge sphere of gas in space _Nuclear fusion within stars give off enormous amounts of energy such as light
SPACE REVIEW. 1. The time it takes for the Earth to around the sun is one year. a. rotate b. revolve
 SPACE REVIEW 1. The time it takes for the Earth to around the sun is one year. a. rotate b. revolve 2. Which planet is known as the "Red Planet"? a. Earth b. Mars c. Uranus d. Venus 3. One complete revolution
SPACE REVIEW 1. The time it takes for the Earth to around the sun is one year. a. rotate b. revolve 2. Which planet is known as the "Red Planet"? a. Earth b. Mars c. Uranus d. Venus 3. One complete revolution
Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide
 Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When are tides highest? a. during the moon s first quarter phase
Name Period Chapter 12 &13 Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When are tides highest? a. during the moon s first quarter phase
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Lesson 2 The Inner Planets
 Lesson 2 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 School to Home 32 Key Concept Builders 33 Enrichment
Lesson 2 Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 School to Home 32 Key Concept Builders 33 Enrichment
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
refractors satellite electromagnetic radiation
 Chapter 19 Exploring Space space probe reflectors mirror refractors satellite electromagnetic radiation light lens thrust 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the. 2. Two types of telescopes
Chapter 19 Exploring Space space probe reflectors mirror refractors satellite electromagnetic radiation light lens thrust 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the. 2. Two types of telescopes
Content Standard 1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. National Science Standard
 1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. s 1.a) Position is defined relative to some choice of standard reference point and a set of reference directions. Identifying
1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. s 1.a) Position is defined relative to some choice of standard reference point and a set of reference directions. Identifying
ASTRONOMY. S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c,
 ASTRONOMY S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c, UNIVERSE Age 13.7 billion years old The Big Bang Theory Protons and Neutrons formed hydrogen and helium. This created heat that formed the stars. Other elements
ASTRONOMY S6E1 a, b, c, d, e, f S6E2 a, b, c, UNIVERSE Age 13.7 billion years old The Big Bang Theory Protons and Neutrons formed hydrogen and helium. This created heat that formed the stars. Other elements
EARTH MOON SUN REVIEW
 1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. A student read in a newspaper that the maximum length of the daylight period for the year in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, had just been reached. What was the date of this newspaper? 4. In the diagram below,
1. The diagram below shows Earth, four different positions of the Moon, and the direction of incoming sunlight.
 G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
G8 Semester I MCAS Pre-Test Please answer on Scantron Card; not on this test form Standard: 9 - Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and tides. Relate them to the relative positions
1. Cosmology is the study of. a. The sun is the center of the Universe. b. The Earth is the center of the Universe
 Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe b. The Earth is the center of the Universe 3. The two most abundant gases
Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe b. The Earth is the center of the Universe 3. The two most abundant gases
MIDDLE SCHOOL SCIENCE LABORATORY 1ST SEMESTER
 Name: Date: Teacher: MR. ALBERT HERNANDEZ Grade: 1 A I. Read the text below and answer the questions that follows. A) Phases of the moon. As the moon orbits around Earth, different parts of it appear to
Name: Date: Teacher: MR. ALBERT HERNANDEZ Grade: 1 A I. Read the text below and answer the questions that follows. A) Phases of the moon. As the moon orbits around Earth, different parts of it appear to
Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM)
 Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM) The Milky Way the galaxy that contains our solar system Our solar system is a speck in the Milky Way galaxy Pluto is now considered
Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM) The Milky Way the galaxy that contains our solar system Our solar system is a speck in the Milky Way galaxy Pluto is now considered
Chapter 19 Exploring Space. I. Fill in the blank
 Chapter 19 Exploring Space 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. Two types of telescopes that collect visible light are refractors and reflectors. 3. An uncrewed
Chapter 19 Exploring Space 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. Two types of telescopes that collect visible light are refractors and reflectors. 3. An uncrewed
Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY. 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry.
 Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry. 2. Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter.
Physical Science Final Examination-Review Sheet (14-15) KEY 1. A process used to answer questions or solve problems is called scientific inquiry. 2. Anything that has mass and takes up space is matter.
Investigations in Earth and Space Science Semester Review: Unit 1 and Unit 2
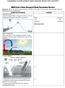 IESS Unit 1: Solar Energy & Fluid Circulation Review Directions: Write the answer to each question in the box to the right of the question. Fold your paper along the line and use this as a review sheet!
IESS Unit 1: Solar Energy & Fluid Circulation Review Directions: Write the answer to each question in the box to the right of the question. Fold your paper along the line and use this as a review sheet!
Concepts and Challenges Physical Science. New York Intermediate Level Science Core Curriculum
 Concepts and Challenges Physical Science correlated to New York Intermediate Level Science Core Curriculum TE/PE: Teacher s Edition/Pupil s Edition TRB: Teacher s Resource Book LP: Laboratory Program RW:
Concepts and Challenges Physical Science correlated to New York Intermediate Level Science Core Curriculum TE/PE: Teacher s Edition/Pupil s Edition TRB: Teacher s Resource Book LP: Laboratory Program RW:
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS
 MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
MIDTERM PRACTICE EXAM ANSWERS 1. (2) Location B shows that the altitude of the noon Sun increases between Dec 21. and June 21. Location B also shows that the Dec. 21 noon Sun is at an altitude of approximately
8TH GRADE SCIENCE CONTENT STANDARDS
 8TH GRADE SCIENCE CONTENT STANDARDS (simplified from CA State Science Standards) DAVID GREENMYER COMPUTECH MIDDLE SCHOOL 1. MOTION a) In order to describe your position, you must use another position (reference
8TH GRADE SCIENCE CONTENT STANDARDS (simplified from CA State Science Standards) DAVID GREENMYER COMPUTECH MIDDLE SCHOOL 1. MOTION a) In order to describe your position, you must use another position (reference
Chapter 17 Solar System
 Chapter 17 Solar System Rotation Earth spinning on its axis (like a top) "TOP" imaginary rod running through the center of the Earth from North pole to South pole The Earth is tilted on its axis at an
Chapter 17 Solar System Rotation Earth spinning on its axis (like a top) "TOP" imaginary rod running through the center of the Earth from North pole to South pole The Earth is tilted on its axis at an
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2013 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy, Universe
 Dr. V s Study Guide : Astronomy Unit 1) Place the following in order of increasing size: The Galaxy, the Solar System, a Star, the Universe,a Moon and a Planet. Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy,
Dr. V s Study Guide : Astronomy Unit 1) Place the following in order of increasing size: The Galaxy, the Solar System, a Star, the Universe,a Moon and a Planet. Moon, Planet, Star, Solar System, Galaxy,
Chapter 8 notes. 8.1 Matter. 8.1 objectives. Earth Chemistry
 Chapter 8 notes Earth Chemistry 8.1 Matter 8.1 objectives Compare chemical properties and physical properties of matter. Describe the basic structure of an atom. Compare atomic number, mass number, and
Chapter 8 notes Earth Chemistry 8.1 Matter 8.1 objectives Compare chemical properties and physical properties of matter. Describe the basic structure of an atom. Compare atomic number, mass number, and
Effective August 2007 All indicators in Standard / 14
 8-4.1 Summarize the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Taxonomy level: 2.4-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Previous/Future
8-4.1 Summarize the characteristics and movements of objects in the solar system (including planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteors). Taxonomy level: 2.4-B Understand Conceptual Knowledge Previous/Future
Chapter 23. Our Solar System
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Planets Inner vs. outer Composition inner planets are rocky/outer are gas Size inner are smaller/outer are much larger Distance from sun inner are
 Planets Inner vs. outer Composition inner planets are rocky/outer are gas Size inner are smaller/outer are much larger Distance from sun inner are close/outer are farther. Earth is 1 AU from the sun Life
Planets Inner vs. outer Composition inner planets are rocky/outer are gas Size inner are smaller/outer are much larger Distance from sun inner are close/outer are farther. Earth is 1 AU from the sun Life
Academic Year Second Term. Science Revision Sheet. Grade
 Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
Academic Year 2017-2018 Second Term Science Revision Sheet Grade 6 Name: Grade Date: Section: Part A. Science Practice. Circle the letter of your answer. 1. When the moon is waxing, its lighted part appears
GRADE EIGHT CURRICULUM. Unit 1: The Makeup and Interactions of Matter
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GRADE EIGHT CURRICULUM Unit 1: The Makeup and Interactions of Matter OVERVIEW Summary The performance expectations for this unit help
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 GRADE EIGHT CURRICULUM Unit 1: The Makeup and Interactions of Matter OVERVIEW Summary The performance expectations for this unit help
Astronomy Regents Review
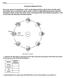 Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
Name Astronomy Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows s orbit around the un as viewed from space. is shown at eight different positions labeled A through
*These items are to be integrated throughout the content. However, you will find new resources for student practice with these concepts here.
 6 th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 1 st Quarter 2017-2018 Sequence of Concepts Rationale for Sequence Prior Knowledge Scientific Method and Engineering Design *These items are to be integrated throughout
6 th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 1 st Quarter 2017-2018 Sequence of Concepts Rationale for Sequence Prior Knowledge Scientific Method and Engineering Design *These items are to be integrated throughout
Topic 1: Earth s Motion Topic 2: The Moon Earth s Satellite Topic 3: Solar System Topic 4: The Planets Topic 5: Stars & Galaxies
 Topic 1: Earth s Motion Topic 2: The Moon Earth s Satellite Topic 3: Solar System Topic 4: The Planets Topic 5: Stars & Galaxies Topic 1: Earth s Motion Essential Question: What causes the cycle of seasons
Topic 1: Earth s Motion Topic 2: The Moon Earth s Satellite Topic 3: Solar System Topic 4: The Planets Topic 5: Stars & Galaxies Topic 1: Earth s Motion Essential Question: What causes the cycle of seasons
Astronomy 3. Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets
 Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Milford Public Schools Curriculum
 Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: SCIENCE Course Name: Grade 8 Course Description Physical Science UNIT 1 - Motion LEARNING GOALS Enduring Understanding(s): Motion is relative to a reference
Milford Public Schools Curriculum Department: SCIENCE Course Name: Grade 8 Course Description Physical Science UNIT 1 - Motion LEARNING GOALS Enduring Understanding(s): Motion is relative to a reference
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide. Assessment Date : Term Rotation Revolution
 Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
Name: Earth and Space Assessment Study Guide Assessment Date : Earth s Rotation and Revolution Term Rotation Revolution Brief Definition Earth s Time to Complete One complete spin on an axis 24 hours (or
8 th Grade Earth, Moon and Sun Systems Review
 8 th Grade Earth, Moon and Sun Systems Review #1 Click on the link to learn What causes Seasons? A #2 H G B D C What is season A in this diagram? E F A: Summer B: Fall C: Winter D: Spring D. Spring A #3
8 th Grade Earth, Moon and Sun Systems Review #1 Click on the link to learn What causes Seasons? A #2 H G B D C What is season A in this diagram? E F A: Summer B: Fall C: Winter D: Spring D. Spring A #3
Semester One Test Review
 Semester One Test Review Net Forces a. 5N 2N b. 5N 3N c. 3N 3N d. 2N 4N 2N 1. Which forces diagrams above show a Net Force of zero? a. All of them b. None of them c. c only d. c and d 2. Which force diagrams
Semester One Test Review Net Forces a. 5N 2N b. 5N 3N c. 3N 3N d. 2N 4N 2N 1. Which forces diagrams above show a Net Force of zero? a. All of them b. None of them c. c only d. c and d 2. Which force diagrams
Astronomy, PART 2. Vocabulary. A. Universe - Our Milky Way Galaxy is one of of galaxies in an expanding universe.
 Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
Astronomy, PART 2 Vocabulary Aphelion Asteroid Astronomical Unit Comet Constellation Crater Eccentricity Eclipse Equinox Geocentric model Gravitation Heliocentric model Inertia Jovian Perihelion Revolution
Earth Science Curriculum Seventh Grade
 Earth Science Curriculum Seventh Grade The Seventh Grade earth science curriculum encompasses the study of the earth s composition, structure, processes, and history. Emphasis is placed on the interpretation
Earth Science Curriculum Seventh Grade The Seventh Grade earth science curriculum encompasses the study of the earth s composition, structure, processes, and history. Emphasis is placed on the interpretation
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up. Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earth s Motion Lesson 2 Earth s Moon Lesson 3 Eclipses and Tides Chapter Wrap-Up Jason Reed/Photodisc/Getty Images What natural phenomena do the motions of Earth and the Moon
Science Period. Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7
 Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
Name: Date: Science Period Astronomy Unit PracticeTest 2014 Sci 7 Directions: Write the letter of the BEST answer on the appropriate space on the answer sheet. 2 points each 1.The model in which SUN is
Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test
 is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
is really cool! 1. The diagram below shows one model of a portion of the universe. Astronomy Section 2 Solar System Test 4. Which arrangement of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth results in the highest high
Name: Date: Class: 2. Which animal listed below would complete this food chain? (6.L.2.1)
 Name: Date: Class: 6 th Grade Science MSL Practice 1. The diagram below represents the Earth in space. (6.E.1.1) Which date is most likely represented by the diagram? A. May 4 B. September 2 C. June 6
Name: Date: Class: 6 th Grade Science MSL Practice 1. The diagram below represents the Earth in space. (6.E.1.1) Which date is most likely represented by the diagram? A. May 4 B. September 2 C. June 6
Explain the Big Bang Theory and give two pieces of evidence which support it.
 Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
Name: OBJECTIVES Correctly define: asteroid, celestial object, comet, constellation, Doppler effect, eccentricity, eclipse, ellipse, focus, Foucault Pendulum, galaxy, geocentric model, heliocentric model,
Grade 8 Science and IPC TEKS Comparison
 Color Coding: Readiness Supporting Not tested Not addressed Partially addressed Addressed Knowledge & Skills C Grade 8HEMISTRY Notes correlating Grade 8 to IPC IPC (5) Matter and Energy. The student knows
Color Coding: Readiness Supporting Not tested Not addressed Partially addressed Addressed Knowledge & Skills C Grade 8HEMISTRY Notes correlating Grade 8 to IPC IPC (5) Matter and Energy. The student knows
AST101IN Final Exam. 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points)
 Name: Possibly useful formulae: AST101IN Final Exam F g = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 p 2 =a 3 F=ma E=mc 2 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points) The sun The Earth The universe The Milky
Name: Possibly useful formulae: AST101IN Final Exam F g = Gm 1 m 2 /r 2 p 2 =a 3 F=ma E=mc 2 1.) Arrange the objects below from smallest to largest. (3 points) The sun The Earth The universe The Milky
8P7:What information about elements can you get from the Periodic Table? 8P7
 The Nature of Matter Essential Question by Framework Begin with a review of the scientific method and discuss the science fair to be held later in the year. Grade( 2, 5, 8) - Type(L, E, P, T) - Number
The Nature of Matter Essential Question by Framework Begin with a review of the scientific method and discuss the science fair to be held later in the year. Grade( 2, 5, 8) - Type(L, E, P, T) - Number
2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky
 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What are constellations? How do we locate objects in the sky? Why do stars rise and set? Why don t we see the same constellations throughout the year?
2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What are constellations? How do we locate objects in the sky? Why do stars rise and set? Why don t we see the same constellations throughout the year?
What is the maximum mass, in grams, that could be measured by this balance?
 1. A student examined a rock sample and described it as having particles of various colors that were 1 millimeter to 12 millimeters in size. The student was making (1) an inference (3) a prediction (2)
1. A student examined a rock sample and described it as having particles of various colors that were 1 millimeter to 12 millimeters in size. The student was making (1) an inference (3) a prediction (2)
Grade 9 End semester exam Revision sheet Answer key. Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Education Ahlia School -ABCD
 Grade 9 End semester exam Revision sheet Answer key Question 1: Directions: Put a check mark in the column that each type of matter describes. 1. Oxygen Substances Element Compound Mixtures 2. Granite
Grade 9 End semester exam Revision sheet Answer key Question 1: Directions: Put a check mark in the column that each type of matter describes. 1. Oxygen Substances Element Compound Mixtures 2. Granite
Correlation to Missouri Science Expectations, Grade 9-11 Foundations of Physical Science Student Text and Investigation Manual
 1.1.A.a Changes in properties and states of matter provide evidence of the atomic theory of matter Objects, and the materials they are made of, have properties that can be used to describe and classify
1.1.A.a Changes in properties and states of matter provide evidence of the atomic theory of matter Objects, and the materials they are made of, have properties that can be used to describe and classify
Grade 8: Physical Sciences, Life Sciences Earth Sciences, Investigation and Experimentation. California State Science Content Standards
 Grade 8: Physical Sciences, Life Sciences Earth Sciences, Investigation and Experimentation California State Science Content Standards Covered in: Hands-on science labs, demonstrations, & activities. Investigation
Grade 8: Physical Sciences, Life Sciences Earth Sciences, Investigation and Experimentation California State Science Content Standards Covered in: Hands-on science labs, demonstrations, & activities. Investigation
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
6 th Grade Introduction to Chemistry
 Lesson 1 (Describing Matter) 6 th Grade Introduction to Chemistry Matter anything that has mass and takes up space All the stuff in the natural world is matter. Chapter 1: Introduction to Matter Chemistry
Lesson 1 (Describing Matter) 6 th Grade Introduction to Chemistry Matter anything that has mass and takes up space All the stuff in the natural world is matter. Chapter 1: Introduction to Matter Chemistry
The Earth in the Universe Geology
 The Earth in the Univers e The Earth in the Universe Geology The origin of the Universe The position of the Earth in the Universe Distances in the Universe Galaxies The Milky Way Stars: The Sun The Solar
The Earth in the Univers e The Earth in the Universe Geology The origin of the Universe The position of the Earth in the Universe Distances in the Universe Galaxies The Milky Way Stars: The Sun The Solar
Name Period Date Physical Science 2nd Semester Final Exam Study Guide ( )
 Name Period Date Physical Science 2nd Semester Final Exam Study Guide (2012-2013) 1. Physical Science Basics a. What tool(s) would you want to use to find the: i. Mass of an object? Basic SI Unit? ii.
Name Period Date Physical Science 2nd Semester Final Exam Study Guide (2012-2013) 1. Physical Science Basics a. What tool(s) would you want to use to find the: i. Mass of an object? Basic SI Unit? ii.
LESSON 2. Speeding in Space. Literacy Article 2A. Name. Date
 Literacy Article 2A Name Date LESSON 2 Speeding in Space The solar system is composed of many things. It includes our star, the Sun, the planets and their moons, comets, and asteroids. All of these objects
Literacy Article 2A Name Date LESSON 2 Speeding in Space The solar system is composed of many things. It includes our star, the Sun, the planets and their moons, comets, and asteroids. All of these objects
Objective3: Earth and Space Systems
 Name Objective3: Earth and Space Systems 1. The diagram above shows the orbit of the moon around Earth. At which point in the moon s orbit will a person standing on Earth see a waxing crescent moon? (8.7B)
Name Objective3: Earth and Space Systems 1. The diagram above shows the orbit of the moon around Earth. At which point in the moon s orbit will a person standing on Earth see a waxing crescent moon? (8.7B)
composition of matter, and the changes that matter undergoes. Examples of Uses of Chemistry in Everyday Life
 Name Matter and Change: Unit Objective Study Guide Date Due Directions: Write your answers to the following questions in the space provided. For problem solving, all of the work leading up to the final
Name Matter and Change: Unit Objective Study Guide Date Due Directions: Write your answers to the following questions in the space provided. For problem solving, all of the work leading up to the final
Atom - the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element From the Greek word for indivisible
 Matter Atom - the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element From the Greek word for indivisible 3 subatomic particles Proton - positively charged particle in the nucleus of an
Matter Atom - the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element From the Greek word for indivisible 3 subatomic particles Proton - positively charged particle in the nucleus of an
Our Material World 1 Write On Booklet. 1. Earth and the Solar System
 Our Material World 1 Write On Booklet 1. Earth and the Solar System Know the names of all the planets and their order from the sun Know what the nearest star is called Know that Earth is a planet with
Our Material World 1 Write On Booklet 1. Earth and the Solar System Know the names of all the planets and their order from the sun Know what the nearest star is called Know that Earth is a planet with
10-20 billion years old
 Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Defining and Describing Position
 Defining and Describing Position 8.1.a, page 2 1. Choice D is correct. The person s location is compared to Los Angeles. Choices A, B, and C are incorrect. Although distances and directions help describe
Defining and Describing Position 8.1.a, page 2 1. Choice D is correct. The person s location is compared to Los Angeles. Choices A, B, and C are incorrect. Although distances and directions help describe
ANSWER KEY. Introduction to Matter
 Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. The object to be massed is placed on one side of the balance. Objects with known masses are placed on the other side of the arm until the balance arm is level. 2. Sample
Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. The object to be massed is placed on one side of the balance. Objects with known masses are placed on the other side of the arm until the balance arm is level. 2. Sample
UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM.
 UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM. 1) A BRIEF HISTORY Theories of the Universe In the second century BC, the astronomer Ptolemy proposed that the Earth was the centre of the Universe, and that the Sun,
UNIT 1: EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM. 1) A BRIEF HISTORY Theories of the Universe In the second century BC, the astronomer Ptolemy proposed that the Earth was the centre of the Universe, and that the Sun,
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES SAMPLE. Earth and Space. Secondary Science 7C. Years 7 9. Written by Valerie Marett. CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544
 AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Earth and Space Secondary Science 7C Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544 Secondary Science Earth and Space Contents The Earth. 2 Movements
AUSTRALIAN HOMESCHOOLING SERIES Earth and Space Secondary Science 7C Years 7 9 Written by Valerie Marett CORONEOS PUBLICATIONS Item No 544 Secondary Science Earth and Space Contents The Earth. 2 Movements
Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars.
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Name Date Class. Earth in Space
 Chapter Review Earth in Space Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Select the term from the following list that matches each description. axis orbit rotation revolution equinox solstice lunar eclipse
Chapter Review Earth in Space Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Select the term from the following list that matches each description. axis orbit rotation revolution equinox solstice lunar eclipse
Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n)
 When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
3rd Grade: Thriving, threatened, endangered, and extinct organisms. 6th Grade: Food webs and ecosystems
 8 th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 1 st Quarter 2016 2017 Biodiversity Definition Importance: maintaining relationships (food web, symbiotic) Human Impacts Classification Levels of Classification Dichotomous
8 th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 1 st Quarter 2016 2017 Biodiversity Definition Importance: maintaining relationships (food web, symbiotic) Human Impacts Classification Levels of Classification Dichotomous
Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System
 Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Chapter 7 Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section 1: Earth in Space Section 2: Time and Seasons Section 3: Earth s Moon 1 Earth in Space Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements
Astronomy Review. Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4.
 Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Astronomy Review Use the following four pictures to answer questions 1-4. 1. Put an X through the pictures that are NOT possible. 2. Circle the picture that could be a lunar eclipse. 3. Triangle the picture
Lesson 2 Changes in State
 Lesson 2 Changes in State Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 Language Arts Support 32 School to
Lesson 2 Changes in State Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 Language Arts Support 32 School to
1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture.
 Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Test 2 1. The pictures below show the Sun at midday. Write winter, spring or summer under the correct picture. 2. Look carefully at the phases of the Moon. Number them (1 to 4) in the order that you would
Intro to Astronomy. Looking at Our Space Neighborhood
 Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
Intro to Astronomy Looking at Our Space Neighborhood Astronomy: The Original Science Ancient cultures used the movement of stars, planets and the moon to mark time Astronomy: the study of the universe
Earth s Motion. Lesson Outline LESSON 1. A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than
 Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Lesson Outline Earth s Motion LESSON 1 A. Earth and the Sun 1. The diameter is more than 100 times greater than Earth s diameter. a. In the Sun, atoms combine during, producing huge amounts of energy.
Belle Vernon Area School District Curriculum. Timeframe: 20 days
 Biology and Life Science: Characteristics of Life, Cells, Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis Biological Sciences 3.1.A.1 3.1.A2,3.1.A.3,3.1.A4,3.1.A. 5,3.1.A.6,3.1.A.7,3.1.A. 8,3.1.A.9,3.1.B.1, 3.1.A.2, 3.1.A.3,
Biology and Life Science: Characteristics of Life, Cells, Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis Biological Sciences 3.1.A.1 3.1.A2,3.1.A.3,3.1.A4,3.1.A. 5,3.1.A.6,3.1.A.7,3.1.A. 8,3.1.A.9,3.1.B.1, 3.1.A.2, 3.1.A.3,
1/3/12. Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System. Ancient Measurements. Earth s Size and Shape. Ancient Measurements. Ancient Measurements
 // Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
// Table of Contents Chapter: The Earth-Moon-Sun System Section : Chapter 7 Section : Section : Earth s Size and Shape Ancient Measurements First, no matter where you are on Earth, objects fall straight
Name ANSWER KEY Class Table Seat Date
 Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. EARTH S MOTIONS: 1. Describe how Earth moves
Directions: Answer the following open ended review questions. Utilize a diagram where appropriate and do make sure that you label and describe the drawing. EARTH S MOTIONS: 1. Describe how Earth moves
Meteorology Study Guide
 Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
McKinley Presidential Library & Museum Planetarium Show Ohio Science Standards Fifth Grade
 Fifth Grade-Interconnections Within Systems: Cycles on, such as those occurring in ecosystems, in the solar system, and in the movement of light and sound result in describable patterns. Speed is a measurement
Fifth Grade-Interconnections Within Systems: Cycles on, such as those occurring in ecosystems, in the solar system, and in the movement of light and sound result in describable patterns. Speed is a measurement
6 th Grade GLEs (Draft Alignment 4/22/08) EARL 1 Systems
 6 th Grade GLEs (Draft Alignment 4/22/08) EARL 1 Systems Energy, Machines and Motion (EMM) Motion of Objects 1.1.2 Understand the positions, relative speeds, and changes in speed of objects. W Describe
6 th Grade GLEs (Draft Alignment 4/22/08) EARL 1 Systems Energy, Machines and Motion (EMM) Motion of Objects 1.1.2 Understand the positions, relative speeds, and changes in speed of objects. W Describe
Key Science Vocabulary Scientific Inquiry
 Scientific Inquiry 1. science-- the systematic study of everything 2. scientific method--a system for solving problems or questions 3. P.H.E.O.C.S--problem hypothesis experiment observe conclusion share
Scientific Inquiry 1. science-- the systematic study of everything 2. scientific method--a system for solving problems or questions 3. P.H.E.O.C.S--problem hypothesis experiment observe conclusion share
8 th Grade Science. Reporting Category 3 STAAR
 8 th Grade Science Reporting Category 3 STAAR Which letter on the model illustrates rotation on an axis? This length of time takes one day. Which letter on the model illustrates a revolution around the
8 th Grade Science Reporting Category 3 STAAR Which letter on the model illustrates rotation on an axis? This length of time takes one day. Which letter on the model illustrates a revolution around the
Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key
 Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of how the universe is arranged. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe Heliocentric
Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of how the universe is arranged. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe Heliocentric
Kindergarten through 7 th grade: Inquiry and Engineering Design has been embedded
 Scientific Method and Engineering Design Biodiversity Definition Importance: maintaining relationships (food web, symbiotic) Human Impacts *These items are to be integrated throughout the content. However,
Scientific Method and Engineering Design Biodiversity Definition Importance: maintaining relationships (food web, symbiotic) Human Impacts *These items are to be integrated throughout the content. However,
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)
 MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
MIDTERM REVIEW QUESTIONS - PACKET #2 (75 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) 1. Which graph best represents the effect that heating has on air density in the atmosphere? 2. An empty 250-milliliter beaker has a
Physical Science Study Guide Semester
 Physical Science Study Guide Semester 1 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The prefix kilo- means. a. 1,000 c. 0.01 b. 100 d. 0.001 2.
Physical Science Study Guide Semester 1 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The prefix kilo- means. a. 1,000 c. 0.01 b. 100 d. 0.001 2.
Date Class Block. Science SOL Review 6 th grade material
 Name Science SOL Review 6 th grade material Date Class Block Interrelationship of Earth and Space Systems Vocabulary: gravity, comet, meteorite, meteor, asteroid, meteoroid, rotation, revolution, year,
Name Science SOL Review 6 th grade material Date Class Block Interrelationship of Earth and Space Systems Vocabulary: gravity, comet, meteorite, meteor, asteroid, meteoroid, rotation, revolution, year,
Solar System Test - Grade 5
 Solar System Test - Grade 5 Multiple Choice Directions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write this answer on your answer document. 1. The tilt of Earth s
Solar System Test - Grade 5 Multiple Choice Directions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Write this answer on your answer document. 1. The tilt of Earth s
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System
 CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
CHAPTER 2 Strand 1: Structure and Motion within the Solar System Chapter Outline 2.1 EARTH, MOON, AND SUN SYSTEM (6.1.1) 2.2 GRAVITY AND INERTIA (6.1.2) 2.3 SCALE OF SOLAR SYSTEM (6.1.3) 2.4 REFERENCES
Neshoba Central Elementary School 5 th Grade Science Pacing Guide 1 st Nine Weeks
 Neshoba Central Elementary School 5 th Grade Science Pacing Guide 1 st Nine Weeks (Brief Description) LIFE SCIENCE Plants - Communicate the process of photosynthesis explain using application of photosynthesis.
Neshoba Central Elementary School 5 th Grade Science Pacing Guide 1 st Nine Weeks (Brief Description) LIFE SCIENCE Plants - Communicate the process of photosynthesis explain using application of photosynthesis.
THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM
 Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Date Period Name THE SUN-EARTH-MOON SYSTEM SECTION 27.1 Tools of Astronomy In your textbook, read about electromagnetic radiation and telescopes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
1UNIT. The Universe. What do you remember? Key language. Content objectives
 1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
