General Medicine 2016/17
|
|
|
- Junior Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ÚSTAV LÉKAŘSKÉ BIOCHEMIE A LABORATORNÍ DIAGNOSTIKY 1. LF UK Buffers, buffer capacity. Oxidoreduction, electrode processes Practical lesson on medical biochemistry General Medicine Martin Vejražka, Tomáš Navrátil 2016/17
2 Contents TASK 1: CALCULATION OF PH OF BUFFERS USING HENDERSON-HASSELBALCH EQUATION AND DETERMINATION OF BUFFER CAPACITY 2 1. PROCEDURE 2 2. RESULTS 3 TASK 2: RELATIONSHIP OF BUFFER CAPACITY ON THE MOLAR CONCENTRATION OF BUFFER 4 1. PROCEDURE 4 2. RESULTS 4 TASK 3: EFFECT OF IONIC STRENGTH ON PH OF BUFFER 5 1. PROCEDURE 5 2. RESULTS 5 TASK 4: ELECTROCHEMICAL CELL 6 1. PROCEDURE 6 2. RESULTS 7 TASK 5: ELECTROLYSIS 8 1. PROCEDURE 8 2. RESULTS 8 TASK 6: ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES OF METALS 9 1. PROCEDURE 9 2. RESULTS 9 Translated and edited by Jan Pláteník 1
3 Task 1: Calculation of ph of buffers using Henderson- Hasselbalch equation and determination of buffer capacity 1. Test tubes, pipettes, beakers 2. ph meter 3. Solution of NaH 2 PO mol l Solution of Na 2 HPO mol l Solution of NaCl 0.1 mol l Solution of HC1 0.1 mol l Solution of NaOH 0.1 mol l Use the plastic containers pre-marked 1-4 and glass pipettes to measure the appropriate volumes of all solutions according to Table 1. Mix. 2. Measure ph of each mixture with ph meter equipped with a glass combined electrode (do not forget to rinse the electrode with distilled water and wipe gently with piece of tissue in between measurements). Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate the theoretical ph of each buffer and compare it with the value determined experimentally. 3. Into each mixture prepared according to Table 1 add either 1 ml of hydrochloric acid (c = 0.1 mol l -1 ) mark the containers with letter A (Table 2a); or 1 ml of sodium hydroxide (c = 0.1 mol l -1 ) mark the containers with letter B (Table 2b). 4. Measure the ph and calculate the theoretical values according to Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Record and compare the results. Note: For dissociation of trihydrogenphosphoric acid the following dissociation constants were found: to the first degree to the second degree to the third degree
4 Table 1 Container No NaH 2 PO 4 c = 0.1 mol l -1 5 ml 1 ml 9 ml - Na 2 HPO 4 c = 0.1 mol l -1 5 ml 9 ml 1 ml - NaCl c = 0.1 mol l ml Ratio NaH 2 PO 4 /Na 2 HPO 4 Table 2a Container No. 1A 2A 3A 4A add HCl c = 0.1 mol l -1 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml ph Buffer capacity β Table 2b Container No. 1B 2B 3B 4B add NaOH c = 0.1 mol l -1 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml ph Buffer capacity β 3
5 Task 2: Relationship of buffer capacity on the molar concentration of buffer 1. Into vessel marked as stock buffer prepare 10 ml of phosphate buffer 1:1, c = 0.1 mol l -1 : Make it in the same way as in Task 1, container No Into container pre-marked with No. 5 prepare 10 ml of phosphate buffer 1:1, c = 0.04 mol l -1 : Measure 4 ml of the stock buffer from the previous step and add 6 ml of distilled water. 3. Measure ph of both mixtures and record the values. 4. Add either 1 ml HCl, c = 0.1 mol l -1 (mark as 5A), or 1 ml of NaOH, c = 0.1 mol l -1 (5B). Measure ph and record the values. 5. Compare the results of 5A with 1A from the previous task, or 5B with 1B, respectively. Explain the differences. Table 3a Phosphate buffer 1: mol l -1 add HCl c = 0.1 mol l -1 ph Buffer capacity β Container No. 5 (A) 10 ml 1 ml Table 3b Phosphate buffer 1: mol l -1 add NaOH c = 0.1 mol l -1 ph Buffer capacity β Container No. 5(B) 10 ml 1 ml 4
6 Task 3: Effect of ionic strength on ph of buffer 1. Into container pre-marked with No. 6 prepare phosphate buffer 1:1, c = 0.01 mol l -1 : Measure 1 ml of the stock buffer from the previous task and add 9 ml of distilled water. 2. Measure ph and record the value. 3. Into container No. 7 prepare phosphate buffer 1:1, c = mol l -1 : Measure 1 ml from the container No. 6 and add 9 ml of distilled water. 4. Measure ph and record the value. 5. Compare the obtained results with phosphate buffer 1:1, c = 0.1 mol l -1 (Cont. No. 1, Task 1) and c = 0.04 mol l -1 (Cont. No. 5, Task 2). Table 4 Container No Buffer concentration [mol l -1 ] Ratio 1 : 1 1 : 1 1 : 1 1 : 1 5
7 Task 4: Electrochemical cell 1. Analog voltmeter HD-075 1V 2. Copper wire and zinc-coated steel wire (each about 15 cm long) 3. Aqueous solution of CuSO 4 1 mol l Aqueous solution of ZnSO 4 1 mol l Saturated solution of NaCl 6. Cables with connectors and crocodile clips, absorbent paper 7. Emery paper 1. Assemble Daniell s electrochemical cell: Zinc-coated wire Absorbent paper soaked to saturated NaCl solution Copper wire Solution of ZnSO 4 1 mol/l Solution of CuSO 4 1 mol/l a. Into adjacent positions of a tube rack place two long glass test tubes, one almost filled with solution of copper sulfate (1 mol/l), the other one with solution of zinc sulfate (1 mol/l). b. Connect the electrolytes in both test tubes with a salt bridge: take a firm and well absorbing paper (such as piece of paper towel), roll it into a rod and wet it thoroughly with saturated solution of sodium chloride. Arrange the paper roll so that one its end reaches into the copper sulfate solution and the other end into the zinc sulfate solution. 6
8 c. Put a copper electrode (copper wire) into the tube with copper sulfate, and a zinc electrode (zinc-coated steel wire) into the tube with zinc sulfate. The wires must not be in contact with salt bridge. The electrodes must be perfectly clean; they can be cleaned with emery paper if necessary (take care not to damage the zinc layer of the zinc electrode). 2. Use the cables with crocodile clips to attach the voltmeter. Connect the copper electrode to the position +1, zinc to position. A B 1 0 The front (A) and rear (B) view on the voltmeter HD V. The connectors on the rear side are designed for attachment of crocodile clips and offer several ranges of measurement. The one marked as is for the negative electrode, whereas the other contacts are for the positive electrode, range +1 V, +2 V, +3 V and +4 V ). 3. Read the voltage of the assembled electrochemical cell and calculate what would be the voltage, if the cell worked with 100% efficiency. 4. Remove both electrodes from the solutions, wash with distilled water and dry carefully. Then immerse them to the electrolytes in the opposite way, i.e. the copper wire is placed in the solution of zinc sulfate and the zinc electrode in the solution of copper sulfate. Measure the voltage of this assembly. Observe whether the electrodes undergo any changes in this arrangement. Standard redox potentials: Cu 2+ / Cu V Zn 2+ / Zn V Measured voltage of Daniell s cell: Calculated voltage of Daniell s cell: Voltage of the cell with reversed electrodes: Observable changes on the electrodes during experiment: 7
9 Task 5: Electrolysis 1. Glass plate, aluminum foil 2. Indicator paper 3. Saturated solution of sodium chloride 4. Battery 4.5 V Wrap the glass plate with two strips of aluminum foil so that two metallic surfaces are produced with a gap of about 1 cm in between them. Across the gap place about 3 cm long strip of universal indicator paper and wet it with saturated solution of sodium chloride. When the sodium chloride solution has soaked into the indicator paper, remove any eventual excess of the electrolyte with a piece of tissue. Then connect the plate to a 4.5 V battery so that one metallic surface is in contact with the positive pole whereas the other one with the negative pole. Observe the color changes of the indicator paper. BATTERY + Indicator paper soaked with NaCl Aluminum foil Observable changes of the indicator paper during experiment: 8
10 Task 6: Electrochemical series of metals 1. Iron wire (2 7 cm) 2. Copper wire (2 7 cm) 3. Zinc-coated steel wire (2 7 cm) 4. Saturated aqueous solution of Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 5. Aqueous solution of CuSO 4 1 mol l Aqueous solution of ZnSO 4 1 mol l Aqueous solution of AgNO 3 2 mol l Petri dishes Observe what processes take place on the surface of zinc-coated, iron or copper wires after immersion into solutions of metal ions. Proceed according to the table. Use always about 5 cm long piece of wire and immerse it for about 30 s into the appropriate solution in Petri dish. Stir the solution with the wire during the whole period. Record your observations to the table ZnSO 4 Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 CuSO 4 AgNO 3 Zinc-coated wire Iron wire Copper wire 9
Buffers, Electrochemistry. Jan Pláteník & Tomáš Navrátil 2010/2011
 Buffers, Electrochemistry Practical Lesson on Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry General Medicine Jan Pláteník & Tomáš Navrátil 2010/2011 1 BUFFERS AND BUFFER CAPACITY 1.1 Principle of buffering: A buffer
Buffers, Electrochemistry Practical Lesson on Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry General Medicine Jan Pláteník & Tomáš Navrátil 2010/2011 1 BUFFERS AND BUFFER CAPACITY 1.1 Principle of buffering: A buffer
Lab #14: Electrochemical Cells
 Lab #14: Electrochemical Cells Objectives: 1. To understand the nature of electrochemical cells. 2. To construct a table listing the reduction potentials of a series of metal ions, in order of ease of
Lab #14: Electrochemical Cells Objectives: 1. To understand the nature of electrochemical cells. 2. To construct a table listing the reduction potentials of a series of metal ions, in order of ease of
UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
95414101 UNIT 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q. 1. Which solution will allow greater conductance of electricity, 1 M NaCl at 93 K or 1 M NaCl at 33 K and why? Ans. 1 M NaCl at 33 K as the ionic mobilities
#13 Electrochemical Cells
 #13 Electrochemical Cells If a copper strip is placed in a solution of copper ions, one of the following reactions may occur: Cu 2+ + 2e - Cu Cu Cu 2+ + 2e - The electrical potential that would be developed
#13 Electrochemical Cells If a copper strip is placed in a solution of copper ions, one of the following reactions may occur: Cu 2+ + 2e - Cu Cu Cu 2+ + 2e - The electrical potential that would be developed
A601. Milwaukie HS Chemistry Linman. Period Date / / In each of the following chemicals, determine the oxidation states of each element:
 A601 Assigning Oxidation Numbers In each of the following chemicals, determine the oxidation states of each element: Example: sodium nitrate NaNO 3 12) N 2 O 3 +1 +5-2 2) ammonia 13) H 2 SO 4 3) zinc oxide
A601 Assigning Oxidation Numbers In each of the following chemicals, determine the oxidation states of each element: Example: sodium nitrate NaNO 3 12) N 2 O 3 +1 +5-2 2) ammonia 13) H 2 SO 4 3) zinc oxide
Unit 13 Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry Ch. 19 & 20 of your book.
 Unit 13 Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry Ch. 19 & 20 of your book. Early Booklet E.C.: + 2 Unit 13 Hwk. Pts.: / 32 Unit 13 Lab Pts.: / 32 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Learning Targets
Unit 13 Redox Reactions & Electrochemistry Ch. 19 & 20 of your book. Early Booklet E.C.: + 2 Unit 13 Hwk. Pts.: / 32 Unit 13 Lab Pts.: / 32 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Learning Targets
Voltaic Cells. 100 ml graduated cylinder Emery cloth 150 ml beakers, 3 Salt bridge Voltmeter Wires with alligator clips, 2
 Skills Practice Voltaic Cells DATASHEET FOR IN-TEXT LAB In voltaic cells, oxidation and reduction half-reactions take place in separate halfcells, which can consist of a metal electrode immersed in a solution
Skills Practice Voltaic Cells DATASHEET FOR IN-TEXT LAB In voltaic cells, oxidation and reduction half-reactions take place in separate halfcells, which can consist of a metal electrode immersed in a solution
05 Reduction potentials: Micro-voltaic cells. An electrochemical cell uses an oxidation reduction (redox) reaction to produce electrical energy.
 Chemistry Sensors: Loggers: Voltage Any EASYSENSE Logging time: SnapShot 05 Reduction potentials: Micro-voltaic cells Read An electrochemical cell uses an oxidation reduction (redox) reaction to produce
Chemistry Sensors: Loggers: Voltage Any EASYSENSE Logging time: SnapShot 05 Reduction potentials: Micro-voltaic cells Read An electrochemical cell uses an oxidation reduction (redox) reaction to produce
Electrochemistry. To use principles of electrochemistry to understand the properties of electrochemical cells and electrolysis.
 Electrochemistry Objectives: To use principles of electrochemistry to understand the properties of electrochemical cells and electrolysis. Background: Part I: Galvanic Cells: A Galvanic cell is a device
Electrochemistry Objectives: To use principles of electrochemistry to understand the properties of electrochemical cells and electrolysis. Background: Part I: Galvanic Cells: A Galvanic cell is a device
Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution
 Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution Introduction: Electrical current can be thought of as the movement of electrons or ionic charges from an area of high potential to an area of low potential. Materials
Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution Introduction: Electrical current can be thought of as the movement of electrons or ionic charges from an area of high potential to an area of low potential. Materials
EXPERIMENT 16 Electrochemical Cells: A Discovery Exercise 1. Introduction. Discussion
 EXPERIMENT 16 Electrochemical Cells: A Discovery Exercise 1 Introduction This lab is designed for you to discover the properties of electrochemical cells. It requires little previous knowledge of electrochemical
EXPERIMENT 16 Electrochemical Cells: A Discovery Exercise 1 Introduction This lab is designed for you to discover the properties of electrochemical cells. It requires little previous knowledge of electrochemical
Electrochemistry. Part I: Electrochemical Activity from Chemical Reactions. Part II. Electrochemical activity from cell potentials.
 Electrochemistry Introduction: Redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions will be used to determine the relative electrochemical reactivity of 5 metals. In Part I of the experiment, you will determine the activity
Electrochemistry Introduction: Redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions will be used to determine the relative electrochemical reactivity of 5 metals. In Part I of the experiment, you will determine the activity
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Electrochemistry 1. Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one reactant to another 2. Electric current is a flow of electrons in a circuit Many reduction-oxidation
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Electrochemistry 1. Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one reactant to another 2. Electric current is a flow of electrons in a circuit Many reduction-oxidation
Chemistry 213. Electrochemistry
 Chemistry 213 Electrochemistry Part A: Electrochemical Cells Objective Oxidation/reduction reactions find their most important use in the construction of voltaic cells (chemical batteries). In this experiment,
Chemistry 213 Electrochemistry Part A: Electrochemical Cells Objective Oxidation/reduction reactions find their most important use in the construction of voltaic cells (chemical batteries). In this experiment,
A Study of Electrochemistry Prelab
 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? A Study of Electrochemistry Prelab 2. a. Calculate the standard cell potential of a cell constructed from Mg 2+ /Mg and Ni 2+ /Ni (Table I). Which is the anode
1. What is the purpose of this experiment? A Study of Electrochemistry Prelab 2. a. Calculate the standard cell potential of a cell constructed from Mg 2+ /Mg and Ni 2+ /Ni (Table I). Which is the anode
Experiment 18: Galvanic Cells
 Chem 1B Dr. White 131 Experiment 18: Galvanic Cells Objectives Introduction To construct galvanic cells To learn how reduction potentials can be used to predict the relative reactivity of metals In a redox
Chem 1B Dr. White 131 Experiment 18: Galvanic Cells Objectives Introduction To construct galvanic cells To learn how reduction potentials can be used to predict the relative reactivity of metals In a redox
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 Experiment 11 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a series of electrochemical cells. For
Experiment 11 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a series of electrochemical cells. For
1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number
 General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
Electrochemical Cells
 reactions involve the processes of oxidation and reduction. In this three-part lab, these reactions are studied by with sugars, fats, and proteins that provide energy for life to the corrosion of metals,
reactions involve the processes of oxidation and reduction. In this three-part lab, these reactions are studied by with sugars, fats, and proteins that provide energy for life to the corrosion of metals,
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF COPPER AND PERCENT YIELD
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF COPPER AND PERCENT YIELD Objective To gain familiarity with basic laboratory procedures, some chemistry of a typical transition element, and the concept of percent yield. Apparatus
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF COPPER AND PERCENT YIELD Objective To gain familiarity with basic laboratory procedures, some chemistry of a typical transition element, and the concept of percent yield. Apparatus
Chemistry 213. Electrochemistry I
 1 Chemistry 213 Electrochemistry I Electrochemical Cells Objective Oxidation/reduction reactions find their most important use in the construction of voltaic cells (chemical batteries). In this experiment,
1 Chemistry 213 Electrochemistry I Electrochemical Cells Objective Oxidation/reduction reactions find their most important use in the construction of voltaic cells (chemical batteries). In this experiment,
Santa Monica College Chemistry 11
 Types of Reactions Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To perform several types of simple chemical reactions, To become familiar with some common observable signs of chemical reactions,
Types of Reactions Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To perform several types of simple chemical reactions, To become familiar with some common observable signs of chemical reactions,
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS NAME ROW PD
 4-26-12 NAME ROW PD (1) Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? The diagram below shows the electrolysis of fused KCl. A) It is spontaneous and requires
4-26-12 NAME ROW PD (1) Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? The diagram below shows the electrolysis of fused KCl. A) It is spontaneous and requires
Experiment 7 Buffer Capacity & Buffer Preparation
 Chem 1B Dr. White 57 Experiment 7 Buffer Capacity & Buffer Preparation Objectives To learn how to choose a suitable conjugate acid- base pair for making a buffer of a given ph To gain experience in using
Chem 1B Dr. White 57 Experiment 7 Buffer Capacity & Buffer Preparation Objectives To learn how to choose a suitable conjugate acid- base pair for making a buffer of a given ph To gain experience in using
Based on the work you have completed in S1 to S3, complete Prior Learning 3.1.
 3.2: Metals In this chapter you will learn about the structure of pure metals, alloys and how they react with other substances. You will develop skills in the correct use of the SQA data booklet to create
3.2: Metals In this chapter you will learn about the structure of pure metals, alloys and how they react with other substances. You will develop skills in the correct use of the SQA data booklet to create
Chemistry 212 Lab, Spring Design of the Experiment: Standard and Non-Standard Reduction Potentials For Metal/Metal Ion Half-Cells
 Chemistry 212 Lab, Spring 2009 Electrochemical Cells: Determination of Reduction Potentials for a Series of Metal/Metal Ion Systems, Verification of Nernst Equation, and Determination of Formation Constant
Chemistry 212 Lab, Spring 2009 Electrochemical Cells: Determination of Reduction Potentials for a Series of Metal/Metal Ion Systems, Verification of Nernst Equation, and Determination of Formation Constant
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells of a galvanic cell?
 Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemical Cells PURPOSE To see how changes in concentration and ph affect the potential in an electrochemical cell, and confirm the Nernst equation. GOALS To examine how standard reduction potentials
Electrochemical Cells PURPOSE To see how changes in concentration and ph affect the potential in an electrochemical cell, and confirm the Nernst equation. GOALS To examine how standard reduction potentials
To determine relative oxidizing and reducing strengths of a series of metals and ions.
 Redox Reactions PURPOSE To determine relative oxidizing and reducing strengths of a series of metals and ions. GOALS 1 To explore the relative oxidizing and reducing strengths of different metals. 2 To
Redox Reactions PURPOSE To determine relative oxidizing and reducing strengths of a series of metals and ions. GOALS 1 To explore the relative oxidizing and reducing strengths of different metals. 2 To
Chemistry 12. Resource Exam B. Exam Booklet
 Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
Chemistry 12 Resource Exam B Exam Booklet Contents: 21 pages Examination: 2 hours 50 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes Province of British Columbia PART
AP Chemistry Laboratory #21: Voltaic Cells. Lab day: Monday, April 21, 2014 Lab due: Wednesday, April 23, 2014
 AP Chemistry Laboratory #21: Voltaic Cells Lab day: Monday, April 21, 2014 Lab due: Wednesday, April 23, 2014 Goal (list in your lab book): The goal of this lab is to determine what factors affect the
AP Chemistry Laboratory #21: Voltaic Cells Lab day: Monday, April 21, 2014 Lab due: Wednesday, April 23, 2014 Goal (list in your lab book): The goal of this lab is to determine what factors affect the
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW. C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3. A. Fe B. CO
 CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
In this activity, you will observe and predict products for some simple
 Chemistry Not Chemistry My Type Not My Type Classifying Chemical Reactions In this activity, you will observe and predict products for some simple chemical reactions. You will classify the reactions as
Chemistry Not Chemistry My Type Not My Type Classifying Chemical Reactions In this activity, you will observe and predict products for some simple chemical reactions. You will classify the reactions as
Experiment Eight Acids and Bases
 Name: Lab Section: Experiment Eight Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
Name: Lab Section: Experiment Eight Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
Electrochemical Cells
 Chem 100 Section Experiment 13 Name Partner s Name Electrochemical Cells Introduction This experiment is designed to accompany Chapter 8 in Chemistry in Context 5th Ed. You will construct several simple
Chem 100 Section Experiment 13 Name Partner s Name Electrochemical Cells Introduction This experiment is designed to accompany Chapter 8 in Chemistry in Context 5th Ed. You will construct several simple
Electrochemistry. Galvanic Cell. Page 1. Applications of Redox
 Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Page 1 Name: 2Al 3+ (aq) + 3Mg(s) 3Mg 2+ (aq) + 2Al(s) Fe 2 O 3 + 2Al Al 2 O 3 + 2Fe
 9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
9666-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) What is the oxidation number of chromium in the chromate ion, CrO 2-4? A) +8 B) +3 C) +2 D) +6 2) What is the oxidation number of sulfur in Na 2 S 2 O 3? A) +6 B) +4 C) +2 D) -1
Chemistry 1B Experiment 14 65
 Chemistry 1B Experiment 14 65 14 Electrochemistry Introduction In this experiment you will observe some spontaneous and non-spontaneous oxidation-reduction reactions, and see how the spontaneous reactions
Chemistry 1B Experiment 14 65 14 Electrochemistry Introduction In this experiment you will observe some spontaneous and non-spontaneous oxidation-reduction reactions, and see how the spontaneous reactions
Experiment 8 - Double Displacement Reactions
 Experiment 8 - Double Displacement Reactions A double displacement reaction involves two ionic compounds that are dissolved in water. In a double displacement reaction, it appears as though the ions are
Experiment 8 - Double Displacement Reactions A double displacement reaction involves two ionic compounds that are dissolved in water. In a double displacement reaction, it appears as though the ions are
Chapter Objectives. Chapter 13 Electrochemistry. Corrosion. Chapter Objectives. Corrosion. Corrosion
 Chapter Objectives Larry Brown Tom Holme Describe at least three types of corrosion and identify chemical reactions responsible for corrosion. www.cengage.com/chemistry/brown Chapter 13 Electrochemistry
Chapter Objectives Larry Brown Tom Holme Describe at least three types of corrosion and identify chemical reactions responsible for corrosion. www.cengage.com/chemistry/brown Chapter 13 Electrochemistry
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 Experiment 11 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a table of reduction potentials and
Experiment 11 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a table of reduction potentials and
Getting a Charge Out of It
 Getting a Charge Out of It Electrochemical cells (sometimes called batteries) often seem magical to students. Understanding the steps necessary to make electric current flow can be seen by removing components
Getting a Charge Out of It Electrochemical cells (sometimes called batteries) often seem magical to students. Understanding the steps necessary to make electric current flow can be seen by removing components
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Introduction to electrochemistry
 Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Determination of the K a of a Weak Acid and the K b of a Weak Base from ph Measurements
 Experiment 6 Determination of the K a of a Weak Acid and the K b of a Weak Base from ph Measurements Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that
Experiment 6 Determination of the K a of a Weak Acid and the K b of a Weak Base from ph Measurements Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that
# 12 ph-titration of Strong Acids with Strong Bases
 # 12 ph-titration of Strong Acids with Strong Bases Purpose: A strong acid solution is titrated with a strong base solution. A titration curve is then used to determine the endpoint and find the concentration
# 12 ph-titration of Strong Acids with Strong Bases Purpose: A strong acid solution is titrated with a strong base solution. A titration curve is then used to determine the endpoint and find the concentration
Galvanic Cells Spontaneous Electrochemistry. Electrolytic Cells Backwards Electrochemistry
 Today Galvanic Cells Spontaneous Electrochemistry Electrolytic Cells Backwards Electrochemistry Balancing Redox Reactions There is a method (actually several) Learn one (4.10-4.12) Practice (worksheet)
Today Galvanic Cells Spontaneous Electrochemistry Electrolytic Cells Backwards Electrochemistry Balancing Redox Reactions There is a method (actually several) Learn one (4.10-4.12) Practice (worksheet)
Lab #14: Qualitative Analysis of Cations and Anions
 Lab #14: Qualitative Analysis of Cations and Anions Objectives: 1. To understand the rationale and the procedure behind the separation for various cations and anions. 2. To perform qualitative analysis
Lab #14: Qualitative Analysis of Cations and Anions Objectives: 1. To understand the rationale and the procedure behind the separation for various cations and anions. 2. To perform qualitative analysis
Experiment 21. Voltaic Cells
 Experiment 21 Voltaic Cells INTRODUCTION: A voltaic cell is a specially prepared system in which an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs spontaneously. The oxidation and reduction half-reactions are separated
Experiment 21 Voltaic Cells INTRODUCTION: A voltaic cell is a specially prepared system in which an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs spontaneously. The oxidation and reduction half-reactions are separated
Experiment Nine Acids and Bases
 Name: Lab Section: Experiment Nine Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
Name: Lab Section: Experiment Nine Acids and Bases Objective Identifying and understanding the nature of acids and bases is an important part of the laboratory toolbox, the purpose of this lab is to help
Mathematics Education
 Redox reaction, Electrolysis and Electrochemistry group 8 1. Rini Kurniasih K1310069 2. Susi Cahyanti K1310076 3. Wahyu Nugroho K1310082 Mathematics Education Training Teacher and Education Faculty SEBELAS
Redox reaction, Electrolysis and Electrochemistry group 8 1. Rini Kurniasih K1310069 2. Susi Cahyanti K1310076 3. Wahyu Nugroho K1310082 Mathematics Education Training Teacher and Education Faculty SEBELAS
Electrochemistry and Concentration Effects on Electrode Potentials Prelab
 Electrochemistry and Concentration Effects on Electrode Potentials Prelab 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. a. Calculate the standard cell potential of a cell constructed from Mg 2+ /Mg and
Electrochemistry and Concentration Effects on Electrode Potentials Prelab 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. a. Calculate the standard cell potential of a cell constructed from Mg 2+ /Mg and
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful
 What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 Experiment 11 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a table of reduction potentials and
Experiment 11 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Prepared by Ross S. Nord, Masanobu M. Yamauchi, and Stephen E. Schullery, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE You will construct a table of reduction potentials and
Buffer Preparation. Learning Objectives:
 Proteomics Buffer Preparation Buffer Preparation Maintaining the optimum ph during the biological sample processing is to maintain the proper functional and structural aspects of the sample. It is important
Proteomics Buffer Preparation Buffer Preparation Maintaining the optimum ph during the biological sample processing is to maintain the proper functional and structural aspects of the sample. It is important
PRACTICAL 3 ph AND BUFFERS
 PRACTICAL 3 ph AND BUFFERS ph and Buffers Structure 3.1 Introduction 3.2 ph and Buffers: Basic Concept 3.2.1 ph 3.2.2 Buffers and Buffer Solutions 3.3 Methods for Determining ph Experiment 1: Measurement
PRACTICAL 3 ph AND BUFFERS ph and Buffers Structure 3.1 Introduction 3.2 ph and Buffers: Basic Concept 3.2.1 ph 3.2.2 Buffers and Buffer Solutions 3.3 Methods for Determining ph Experiment 1: Measurement
Aim: What are electrochemical cells?
 Aim: What are electrochemical cells? Electrochemistry Electrochemistry- involves a redox reaction and a flow of electrons TWO TYPES of ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 1.Voltaic (similar to a battery) 2.Electrolytic
Aim: What are electrochemical cells? Electrochemistry Electrochemistry- involves a redox reaction and a flow of electrons TWO TYPES of ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 1.Voltaic (similar to a battery) 2.Electrolytic
2002 D Required 2001 D Required
 2002 D Required A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, H neut, for the reaction represented above. The student combines equal volumes of 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 M NaOH in an open
2002 D Required A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, H neut, for the reaction represented above. The student combines equal volumes of 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 M NaOH in an open
Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Process. The Galvanic Cell or Voltaic Cell
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
EXPERIMENT 7 Reaction Stoichiometry and Percent Yield
 EXPERIMENT 7 Reaction Stoichiometry and Percent Yield INTRODUCTION Stoichiometry calculations are about calculating the amounts of substances that react and form in a chemical reaction. The word stoichiometry
EXPERIMENT 7 Reaction Stoichiometry and Percent Yield INTRODUCTION Stoichiometry calculations are about calculating the amounts of substances that react and form in a chemical reaction. The word stoichiometry
11.3. Electrolytic Cells. Electrolysis of Molten Salts. 524 MHR Unit 5 Electrochemistry
 11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
Electrochemistry. Pre-Lab Assignment. Purpose. Background. Experiment 12
 Experiment 12 Electrochemistry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. The questions should be answered
Experiment 12 Electrochemistry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. The questions should be answered
Types of Chemical Reactions
 Types of Chemical Reactions Objectives Perform and observe the results of a variety of chemical reactions. Become familiar with the observable signs of chemical reactions. Identify the products formed
Types of Chemical Reactions Objectives Perform and observe the results of a variety of chemical reactions. Become familiar with the observable signs of chemical reactions. Identify the products formed
Redox and Electrochemistry
 Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
Redox and Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry in Action! 2 Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number of any uncombined element is 0. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. Part A: Solutions That Conduct Electricity
 Chemical Dominoes Activity 6 Electrochemical Cells GALS In this activity you will: Determine if a substance will conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Construct a galvanic cell and explain the function
Chemical Dominoes Activity 6 Electrochemical Cells GALS In this activity you will: Determine if a substance will conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Construct a galvanic cell and explain the function
POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATIONS & SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA. Background
 POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATIONS & SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA Background In this experiment, students will familiarize themselves with potentiometric titration, practice using the first derivative to find the equivalence
POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATIONS & SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA Background In this experiment, students will familiarize themselves with potentiometric titration, practice using the first derivative to find the equivalence
Partner: Alisa 1 March Preparation and Properties of Buffer Solutions
 Partner: Alisa 1 March 2012 Preparation and Properties of Buffer Solutions Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to compare the ph effect on buffered and non-buffered solutions as well as making a
Partner: Alisa 1 March 2012 Preparation and Properties of Buffer Solutions Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to compare the ph effect on buffered and non-buffered solutions as well as making a
CHM-201 General Chemistry and Laboratory I Laboratory 4. Introduction to Chemical Reactions (based in part on Small Scale Chemistry methodology as
 CHM-201 General Chemistry and Laboratory I Laboratory 4. Introduction to Chemical Reactions (based in part on Small Scale Chemistry methodology as described in Chemtrek by Stephen Thompson at Colorado
CHM-201 General Chemistry and Laboratory I Laboratory 4. Introduction to Chemical Reactions (based in part on Small Scale Chemistry methodology as described in Chemtrek by Stephen Thompson at Colorado
Aqueous Chemical Reactions
 Aqueous Chemical Reactions Introduction Many chemical reactions occur in water and therefore they are considered aqueous chemical reactions. The reagents are typically dissolved or diluted in water and
Aqueous Chemical Reactions Introduction Many chemical reactions occur in water and therefore they are considered aqueous chemical reactions. The reagents are typically dissolved or diluted in water and
CET Q UESTIONS QUESTIONS
 CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CET QUESTIONS ON ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance differs from 1. Electrolytic and metallic conductance increases with increase of temperature 2. Electrolytic conductance increases
CHM 130LL: Chemical and Physical Changes
 CHM 130LL: Chemical and Physical Changes In this experiment you will observe and record observations of properties of substances and you will cause changes to occur and classify these changes as physical
CHM 130LL: Chemical and Physical Changes In this experiment you will observe and record observations of properties of substances and you will cause changes to occur and classify these changes as physical
Chapter 17. Additional Aspects of Equilibrium
 Chapter 17. Additional Aspects of Equilibrium 17.1 The Common Ion Effect The dissociation of a weak electrolyte is decreased by the addition of a strong electrolyte that has an ion in common with the weak
Chapter 17. Additional Aspects of Equilibrium 17.1 The Common Ion Effect The dissociation of a weak electrolyte is decreased by the addition of a strong electrolyte that has an ion in common with the weak
ph Titration of H 3 PO 4 Mixtures Calculation of K 1, K 2, and K 3
 ph Titration of H 3 PO 4 Mixtures Calculation of K 1, K 2, and K 3 Purpose In this experiment the titration of pure H 3 PO 4 and H 3 PO 4 with HCl or NaH 2 PO 4 is followed by measuring the ph of the solution
ph Titration of H 3 PO 4 Mixtures Calculation of K 1, K 2, and K 3 Purpose In this experiment the titration of pure H 3 PO 4 and H 3 PO 4 with HCl or NaH 2 PO 4 is followed by measuring the ph of the solution
Types of Chemical Reactions and Predicting Products
 Types of Chemical Reactions and Predicting Products Pre-Lab Discussion There are many kinds of chemical reactions and several ways to classify them. One useful method classifies reactions into four major
Types of Chemical Reactions and Predicting Products Pre-Lab Discussion There are many kinds of chemical reactions and several ways to classify them. One useful method classifies reactions into four major
Electrochemical cells. Section 21.1
 Electrochemical cells Section 21.1 Electrochemical processes Chemical process either release energy or absorb energy This does not have to be solely heat or light - sometimes it can be in the form of electricity
Electrochemical cells Section 21.1 Electrochemical processes Chemical process either release energy or absorb energy This does not have to be solely heat or light - sometimes it can be in the form of electricity
UNIT 6 REDOX REACTIONS Answers
 UNIT 6 REDOX REACTIONS Answers Lesson 1 What is oxidation, what is reduction and what are oxidation numbers? Thinkabout Activity 1.1: What is oxidation and what is reduction? 2Mg + O 2 2MgO Mg loses its
UNIT 6 REDOX REACTIONS Answers Lesson 1 What is oxidation, what is reduction and what are oxidation numbers? Thinkabout Activity 1.1: What is oxidation and what is reduction? 2Mg + O 2 2MgO Mg loses its
Determination of an Electrochemical Series
 In electrochemistry, a voltaic cell is a specially prepared system in which an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs spontaneously. This spontaneous reaction produces an easily measured electrical potential
In electrochemistry, a voltaic cell is a specially prepared system in which an oxidation-reduction reaction occurs spontaneously. This spontaneous reaction produces an easily measured electrical potential
EXPERIMENT 6. Properties of Buffers INTRODUCTION
 EXPERIMENT 6 Properties of Buffers INTRODUCTION A chemical buffer is any substance in a solution that tends to stabilize the hydronium ion concentration by neutralizing any added acid or base. Buffers
EXPERIMENT 6 Properties of Buffers INTRODUCTION A chemical buffer is any substance in a solution that tends to stabilize the hydronium ion concentration by neutralizing any added acid or base. Buffers
Section I: Synthesis reactions Synthesis reactions occur when two or more substances come together to form a single new substance.
 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS A Laboratory Investigation Purpose: Observe the five major types of reactions. Record observations for these reactions. Complete balanced equations for these reactions. Introduction:
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS A Laboratory Investigation Purpose: Observe the five major types of reactions. Record observations for these reactions. Complete balanced equations for these reactions. Introduction:
CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY
 Advanced Chemistry Name Hour Advanced Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY Day Plans
Advanced Chemistry Name Hour Advanced Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 4 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS & SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY Day Plans
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
 9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
Prince George s Community College PL 2: CHARACTERIZATION OF A MONOPROTIC WEAK ACID BY POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATION
 Prince George s Community College Name Section Partner(s) Date PL 2: CHARACTERIZATION OF A MONOPROTIC WEAK ACID BY POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATION PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. Complete the neutralization reactions given
Prince George s Community College Name Section Partner(s) Date PL 2: CHARACTERIZATION OF A MONOPROTIC WEAK ACID BY POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATION PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. Complete the neutralization reactions given
AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers
 AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers 14. Questions 14-17 The spontaneous reaction that occurs when the cell in the picture operates is as follows: 2Ag + + Cd (s) à 2 Ag (s) + Cd 2+ (A)
AP Chemistry: Electrochemistry Multiple Choice Answers 14. Questions 14-17 The spontaneous reaction that occurs when the cell in the picture operates is as follows: 2Ag + + Cd (s) à 2 Ag (s) + Cd 2+ (A)
Review. Chapter 17 Electrochemistry. Outline. Voltaic Cells. Electrochemistry. Mnemonic
 Review William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. Neth cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Oxidation Loss of electrons Occurs at electrode called the anode Reduction Gain of
Review William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. Neth cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Oxidation Loss of electrons Occurs at electrode called the anode Reduction Gain of
Electrochemistry C020. Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy
 Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
ElectroChemistry * Section I: Reactivity of Metals and Metal Ions PRELAB
 ElectroChemistry * Name Section Instructions: You and your partner(s) will be working with a computer simulation that covers electrochemistry, please discuss each question with your partner(s) and write
ElectroChemistry * Name Section Instructions: You and your partner(s) will be working with a computer simulation that covers electrochemistry, please discuss each question with your partner(s) and write
Experiment 5E BOTTLES WITHOUT LABELS: STUDIES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 Experiment 5E BOTTLES WITHOUT LABELS: STUDIES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS FV 1-21-16 MATERIALS: Eight 50 ml beakers, distilled water bottle, two 250 ml beakers, conductivity meter, ph paper (A/B/N), stirring
Experiment 5E BOTTLES WITHOUT LABELS: STUDIES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS FV 1-21-16 MATERIALS: Eight 50 ml beakers, distilled water bottle, two 250 ml beakers, conductivity meter, ph paper (A/B/N), stirring
Aqueous Chemical Reactions
 Aqueous Chemical Reactions Introduction Many chemical reactions occur in water and therefore they are considered aqueous chemical reactions. The reagents are typically dissolved or diluted in water and
Aqueous Chemical Reactions Introduction Many chemical reactions occur in water and therefore they are considered aqueous chemical reactions. The reagents are typically dissolved or diluted in water and
Chem 2115 Experiment #10. Acids, Bases, Salts, and Buffers
 Chem 2115 Experiment #10 Acids, Bases, Salts, and Buffers OBJECTIVE: The goal of this series of experiments is to investigate the characteristics of acidic and basic solutions. We will explore the neutralization
Chem 2115 Experiment #10 Acids, Bases, Salts, and Buffers OBJECTIVE: The goal of this series of experiments is to investigate the characteristics of acidic and basic solutions. We will explore the neutralization
S4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES
 S4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES 1. The Mole One mole of a substance = GRAM FORMULA MASS e.g. H 2 SO 4 RAM from databook pg.7 2H 2 x 1 = 2 1S 1 x 32 = 32 4O 4 x 16 = 64 98g Mass = number of moles x Mass of 1
S4 CHEMISTRY SUMMARY NOTES 1. The Mole One mole of a substance = GRAM FORMULA MASS e.g. H 2 SO 4 RAM from databook pg.7 2H 2 x 1 = 2 1S 1 x 32 = 32 4O 4 x 16 = 64 98g Mass = number of moles x Mass of 1
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Scientific Observations and Reaction Stoichiometry: The Qualitative Analysis and Chemical Reactivity of Five White Powders
 Scientific Observations and Reaction Stoichiometry: The Qualitative Analysis and Chemical Reactivity of Five White Powders Objectives Part 1: To determine the limiting reagent and percent yield of CuCO
Scientific Observations and Reaction Stoichiometry: The Qualitative Analysis and Chemical Reactivity of Five White Powders Objectives Part 1: To determine the limiting reagent and percent yield of CuCO
Aqueous Chemical Reactions
 Aqueous Chemical Reactions Introduction Many chemical reactions occur in water and therefore they are considered aqueous chemical reactions. The reagents are typically dissolved or diluted in water and
Aqueous Chemical Reactions Introduction Many chemical reactions occur in water and therefore they are considered aqueous chemical reactions. The reagents are typically dissolved or diluted in water and
To measure ph s in a variety of solutions and mixtures and to account for the results obtained.
 Acid-Base Studies PURPOSE To measure ph s in a variety of solutions and mixtures and to account for the results obtained. GOALS 1 To learn to use ph paper and a ph meter to measure the ph of a given solution.
Acid-Base Studies PURPOSE To measure ph s in a variety of solutions and mixtures and to account for the results obtained. GOALS 1 To learn to use ph paper and a ph meter to measure the ph of a given solution.
5.7 Galvanic Cells. Electrochemical Gizmos
 5.7 Galvanic Cells Have you ever accidentally bitten into a piece of aluminum foil? If you have silver amalgam fillings, you may have experienced a bit of a jolt (Figure 1). The aluminium, in contact with
5.7 Galvanic Cells Have you ever accidentally bitten into a piece of aluminum foil? If you have silver amalgam fillings, you may have experienced a bit of a jolt (Figure 1). The aluminium, in contact with
Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation
 Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation LEARNING OBJECTIVES The objectives of this experiment are to... construct galvanic cells and develop an electrochemical series based on potential differences between
Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation LEARNING OBJECTIVES The objectives of this experiment are to... construct galvanic cells and develop an electrochemical series based on potential differences between
Physical Changes and Chemical Reactions
 Physical Changes and Chemical Reactions Gezahegn Chaka, Ph.D., and Sudha Madhugiri, Ph.D., Collin College Department of Chemistry Objectives Introduction To observe physical and chemical changes. To identify
Physical Changes and Chemical Reactions Gezahegn Chaka, Ph.D., and Sudha Madhugiri, Ph.D., Collin College Department of Chemistry Objectives Introduction To observe physical and chemical changes. To identify
CHEMISTRY CORE PRACTICALS
 CHEMISTRY CORE PRACTICALS Science (9-1) Combined Science / Chemistry Core Practicals www.chemistryinfo.co.uk Modified 23/03/2018 (MJB) Core Practical INDEX Paper 1 Paper 2 CP1a: Topic: 2.11 Investigate
CHEMISTRY CORE PRACTICALS Science (9-1) Combined Science / Chemistry Core Practicals www.chemistryinfo.co.uk Modified 23/03/2018 (MJB) Core Practical INDEX Paper 1 Paper 2 CP1a: Topic: 2.11 Investigate
Electrochemical Cells PreLab Worksheet
 header.jpg Electrochemical Cells PreLab Worksheet 1. There are several hazards associated with the chemicals in the electrochemical cells experiment. For each chemical, determine which hazards it possesses.
header.jpg Electrochemical Cells PreLab Worksheet 1. There are several hazards associated with the chemicals in the electrochemical cells experiment. For each chemical, determine which hazards it possesses.
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
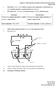 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
