Organolithium Compounds *
|
|
|
- Ariel Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OpenStax-CNX module: m Organolithium Compounds * Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 One of the major uses of lithium is in the synthesis of organolithium compounds, RLi. They have great importance and utility in industry and chemical research. Their reactivity resembles that of Grignard reagents, but they are generally more reactive. 1 Synthesis The best general method for RLi synthesis involves the reaction of an alkyl or aryl chloride with lithium metal in benzene or an aliphatic hydrocarbon (e.g., hexane), (1). While it is possible to use diethyl ether (Et 2 O), the solvent slowly attack the resultant alkyl lithium compound, (2). Metal-hydrogen exchange, (3), metal-halogen exchange, (4), and metal-metal exchange can also be used, (5). (1) (2) (3) (4) All organolithium compounds are produced as solutions and are hence used in synthetic protocols by volume of solution. It is therefore important to know the exact concentration of RLi in solution. The simplest approach to quantify the amount of organolithium is to react a known volume with water, (6), and then titrate (with acid) the resultant base that is formed. However, while the concentration of freshly prepared samples of organolithium reagents can the theoretically measured in this way, real samples always contain some amount of LiOH or other bases. A simple titration inevitably results in an over estimation of the organolithium reagent. To overcome this a double titration method is used. * Version 1.2: Jan 26, :27 pm (5) (6)
2 OpenStax-CNX module: m Gillman double titration method The careful addition of a known volume of an organolithium reagent solution (between 0.5 and 1.5 ml) to an excess of water yields a solution of LiOH that can be titrated with a standardized solution of hydrochloric acid, using phenolphthalein as the indicator. The presence of any LiOH in the original organolithium solution will be incorporated into this titration, and thus the result will be a measure of the total base content in the solution, i.e., (7). In order to determine the amount of LiOH present as impurity in the organolithium solution it is necessary to react the RLi without the formation of base, then titrate the resulting solution. To do this, an aliquot (the same amount as used before) of the organolithium is reacted slowly with 1,2-dibromoethane (BrCH 2 CH 2 Br) dissolved in dry diethyl ether (Et 2 O). After 5 min of stirring, the solution is diluted with an excess of water and then titrated with a standardized solution of hydrochloric acid, again using phenolphthalein as the indicator. The dierence of the two titrations gives the exact concentration of the organolithium. Example 1 An aliquot of n BuLi in hexanes (0.50 ml) was added to degassed water (20 ml). After any visible reaction had ceased, a few drops of a phenolphthalein solution in water/methanol are added resulting in a pink color indicative of a basic ph. The resulting mixture is titrated with standardized hydrochloric acid ([HCl] = N) until complete disappearance of the pink color (7.90 ml). A second aliquot of n BuLi in hexanes (0.50 ml) is added to 1,2-dibromoethane (0.20 ml, Et 2 O). After 5 min of stirring, the mixture was diluted with water (20 ml) and after addition of the phenolphthalein indicator titrated (with vigorous stirring due to the biphasic nature of the system) with standardized hydrochloric acid ([HCl] = N) until complete disappearance of the pink color (0.25 ml). The concentration of nbuli is calculated as follows: (7) Step 1. Step 2. Step 3. 2 Properties Alkyl lithium compounds are either low melting solids or liquids, and often with high volatility (depending on the substituent) due to the covalent nature of the bonding. They are soluble in aliphatics, aromatics, and ethers. However, while the reaction with ethers is generally slow, (2), alkyl lithium compounds can polymerize tetrahydrofuran (THF). Organolithium compounds react rapidly with air and water (both vapor and liquid). The reaction with water is the basis of the Gillman double titration method for determining the concentration of organolithium reagents in solution.
3 OpenStax-CNX module: m Structure The structure of organolithium compounds is dominated by their highly oligomeric nature as a result of 3-center 2-electron bridging bonds. In all cases the extent of oligomerization is dependant on the identity of the alkyl (or aryl) group. The alkyl-bridged bond is similar to those found for beryllium and aluminum compounds. In the vapor phase any particular organolithium derivative show a range of oligomeric structures. For example, the mass spectrum of EtLi shows ions associated with both tetramers (e.g., [Et 3 Li 4 ] + ) and hexamers (e.g., [Et 5 Li 6 ] + ). The structures of the dierent oligomers have been predicted by molecular orbital calculations (Figure 7). Figure 7: Proposed vapor phase structures for various oligomers of RLi. Solution molecular weight measurements indicate the oligomerization is present (in the absence of a coordinating ligand such as Et 2 O or an amine). The extent of oligomerization depends on the steric bulk of the alkyl group (Table 1). Oligomerization and solution structures have also been investigated by 7 Li and 13 C NMR spectroscopy. R [RLi] n R [RLi] n Me 4 Et 6 n Bu 6 t Bu 4 Table 1: Extent of oligomerization (n) for organolithium compounds [RLi] n in benzene solution. There are a large number of X-ray crystallographically determined structures for organolithium derivatives. The archetypal example is MeLi, which exists as a tetramer in the solid state (Figure 7). The lithium atoms are arranged as a tetrahedron and the carbon atoms are positioned on the center of the facial planes, i.e., the carbon is equidistant from each of the lithium atoms. In contrast, EtLi has a similar tetrahedral structure, but the α-carbon of the ethyl groups are asymmetrically arranged such that it is closer to one lithium atom than the other two.
4 OpenStax-CNX module: m Figure 7: Solid state structure of MeLi. Copyright: Ben Mills (2007). It is possible to prepare monomeric organolithium compounds by the addition of amines, especially chelate ligands such as ethylenediamine (en) and tetramethylethylenediamine (TMED). The reactivity of RLi is increased dramatically by the addition of such Lewis bases. For example, PhCH 2 Li shows an increased reactivity of 10 4 with the addition of TMED. The bonding in organolithium compounds is dicult to describe: Based upon the relative electronegativity of Li (0.98) and C (2.5) it would be expected to have significant ionic character. Organolithium compounds form electron decient oligomers typical of covalent bonding and clearly not as a result of ionic aggregation. The spin-spin coupling, J(C-Li), observed by NMR spectroscopy (10 15 Hz) are consistent with a covalent bond. Organolithium compounds undergo radical reactions. However, the overall description of the bonding in RLi is that of a covalent interaction with signicant polar (ionic) character, i.e., M δ+ -C δ-. 4 The use of organolithium compounds in organic synthesis Organolithium compounds perform many of the reactions commonly observed for Grignard reagents. However, lithium reagents are generally more reactive than their Grignard analogs.
5 OpenStax-CNX module: m Hydrolysis Organolithium compounds react with water to give the hydrocarbon and lithium hydroxide, (8). Lithium alkyls also react with other hydroxylic compounds such as alcohols and carboxylic acids, (9). (8) One important use of the hydrolysis reaction is specically deuteration, (10). (9) (10) 4.2 Reaction with carbonyls Organolithium compounds react with organic carbonyls (aldehydes, ketones, and esters) to yield the alcohol on hydrolysis, (11). This synthetic route is particularly useful since lithium reagents are far more reactive than the analogous Grignard, allowing reactions to be carried out at lower temperatures and minimizing enolization side reactions. The high reactivity of alkyl lithium compounds means that they react with carboxylic acids to yield the ketone rather than the lithium carboxylate. (11) Organolithium compounds generally react with α,β-unsaturated ketones to give the 1,2-addition product, (13). However, lithium dialkylcuprates, which are formed from the alkyl lithium and copper(i) iodide, (14), add exclusively by the 1,4-addition, (15). (12) (13) (14) (15)
6 OpenStax-CNX module: m Transmetallation One of the most useful methods of preparing organometallic compounds is the exchange reaction of one organometallic compound with a salt of a dierent metal, (16). This is an equilibrium process, whose equilibrium constant is dened by the reduction potential of both metals. In general the reaction will proceed so that the more electropositive metal will form the more ionic salt (usually chloride). Lithium reagents may be used to prepare a wide range of organometallic compounds. (16) (17) 5 Bibliography G. Graham, S. Richtsmeier, D. A. Dixon. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1980, 102, E. Weiss, E. A. C. Lucken, J. Organomet. Chem., 1964, 2, 197. H. O. House, Acc. Chem. Res., 1976, 9, 59.
Organometallic Compounds of Magnesium *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m32494 1 Organometallic Compounds of Magnesium * Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 While beryllium
OpenStax-CNX module: m32494 1 Organometallic Compounds of Magnesium * Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 While beryllium
18.8 Oxidation. Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium
 18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation-Reduction and Organometallic Compounds Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION
 CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTION Introduction Several functional groups contain the carbonyl group Carbonyl groups can be converted into alcohols by various reactions Structure of the Carbonyl
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water.
 Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water. Alcohols are usually classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Alcohols with the hydroxyl bound directly
Synthesis and Structure of Alcohols Alcohols can be considered organic analogues of water. Alcohols are usually classified as primary, secondary and tertiary. Alcohols with the hydroxyl bound directly
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Carvone Reduction * Mary McHale. 1 Reduction of Carvone
 OpenStax-CNX module: m15745 1 Carvone Reduction * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Reduction of Carvone 1.1 Objective
OpenStax-CNX module: m15745 1 Carvone Reduction * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Reduction of Carvone 1.1 Objective
Reducing Agents. Linda M. Sweeting 1998
 Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Organomagnesium (Grignard) and organolithium reagents
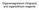 rganomagnesium (Grignard) and organolithium reagents Different polarization of non-metallic and organometallic reagents H CH 3 - I H - CH 3 + I H 3 H 3 C H 3 C H 3 + H 3 C H 3 C H 2 H 3 C H3C H I - CH
rganomagnesium (Grignard) and organolithium reagents Different polarization of non-metallic and organometallic reagents H CH 3 - I H - CH 3 + I H 3 H 3 C H 3 C H 3 + H 3 C H 3 C H 2 H 3 C H3C H I - CH
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
12.5 Organometallic Compounds
 12.5 rganometallic Compounds Compounds that contain carbon-metal bond are called organometallic compounds. C M C δ δ + M C M Primarily ionic Primarily covalent (M = Na + or K + )(M = Mg or Li) (M = Pb,
12.5 rganometallic Compounds Compounds that contain carbon-metal bond are called organometallic compounds. C M C δ δ + M C M Primarily ionic Primarily covalent (M = Na + or K + )(M = Mg or Li) (M = Pb,
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
Chapter 10: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives The back of the white willow tree (Salix alba) is a source of salicylic acid which is used to make aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) The functional group
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Advanced Organic Chemistry
 D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Chem 530A Chemistry 530A Advanced Organic Chemistry Lecture notes part 8 Carbanions Organolithium and Grignard reagents Organocopper reagents 1. Direct metalation 2. From radical
D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Chem 530A Chemistry 530A Advanced Organic Chemistry Lecture notes part 8 Carbanions Organolithium and Grignard reagents Organocopper reagents 1. Direct metalation 2. From radical
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 2 - COVALENT BONDING AND CHEMICAL REACTIVITY
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
Alcohol Synthesis. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy
 By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Carboxylic acids and Their Derivatives 1 Structure of Carboxylic Acids -The functional
By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Carboxylic acids and Their Derivatives 1 Structure of Carboxylic Acids -The functional
Chapter 16. Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group. Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones. Synthesis of Aldehydes
 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer Portraits: h+p://scien1s1c.tumblr.com
 344 rganic hemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 5 Introduction to organometallic chemistry July 29 2013 Portraits: h+p://scien1s1c.tumblr.com What is organometallic chemistry? The chemistry of compounds
344 rganic hemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 5 Introduction to organometallic chemistry July 29 2013 Portraits: h+p://scien1s1c.tumblr.com What is organometallic chemistry? The chemistry of compounds
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
 ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
Aldehydes and Ketones. Dr. Munther A. M. Ali
 Aldehydes and Ketones Dr. Munther A. M. Ali ALDYHYDES AND KETONES Aldehydes are compounds of the general formula RCHO Ketones are compounds of the general formula RR'CO Aldehydes A ketone Both aldehydes
Aldehydes and Ketones Dr. Munther A. M. Ali ALDYHYDES AND KETONES Aldehydes are compounds of the general formula RCHO Ketones are compounds of the general formula RR'CO Aldehydes A ketone Both aldehydes
Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group In Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups In Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group O O - - O - O R Y R C+ Y R Y Nu -Ȳ R N u + Y=goodleavinggroup
Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group In Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups In Chapter 19 Substitutions at the Carbonyl Group O O - - O - O R Y R C+ Y R Y Nu -Ȳ R N u + Y=goodleavinggroup
LECTURE #22 Thurs., Nov.15, 2007
 Provide a rxn sequence to make these as the major products Answers: 1. i Pr-Cl, AlCl 3 2. conc. fuming? H 2 S 4 3. Cl 2, FeCl 3 or AlCl 3 4. dilute H 2 S 4 note: normally aqueous workup after step 1, but
Provide a rxn sequence to make these as the major products Answers: 1. i Pr-Cl, AlCl 3 2. conc. fuming? H 2 S 4 3. Cl 2, FeCl 3 or AlCl 3 4. dilute H 2 S 4 note: normally aqueous workup after step 1, but
Allyl radicals are especially stable due to resonance ( and double bond switch places):
 Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
14.11 Alkane Synthesis Using Organocopper Reagents
 14.11 Alkane Synthesis Using Organocopper Reagents Lithium Dialkylcuprates Lithium dialkylcuprates are useful synthetic reagents. They are prepared from alkyllithiums and a copper(i) halide. 2RLi + CuX
14.11 Alkane Synthesis Using Organocopper Reagents Lithium Dialkylcuprates Lithium dialkylcuprates are useful synthetic reagents. They are prepared from alkyllithiums and a copper(i) halide. 2RLi + CuX
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids
 1 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids I. Introduction: Carboxylic acid structure: Classification of carboxylic acids: A carboxylic acid donates protons by the heterocyclic cleavage of the O-H bond, generating
1 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids I. Introduction: Carboxylic acid structure: Classification of carboxylic acids: A carboxylic acid donates protons by the heterocyclic cleavage of the O-H bond, generating
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
N_HW1 N_HW1. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this sequence?
 N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Electronegativity Scale F > O > Cl, N > Br > C, H
 Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium
 Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
The Characteristics of a Soln
 Goal 1 The Characteristics of a Soln Define the term solution, and, given a description of a substance, determine if it is a solution. The Characteristics of a Soln Solution (as used in chemistry) A homogenous
Goal 1 The Characteristics of a Soln Define the term solution, and, given a description of a substance, determine if it is a solution. The Characteristics of a Soln Solution (as used in chemistry) A homogenous
Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes. I. Introduction
 1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons contain six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. The ring is sometimes shown with a circle in the center instead
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
Name Date Class. aryl halides substitution reaction
 23.1 INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Section Review Objectives Explain how organic compounds are classified Identify the IUPAC rules for naming halocarbons Describe how halocarbons can be prepared Vocabulary
23.1 INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Section Review Objectives Explain how organic compounds are classified Identify the IUPAC rules for naming halocarbons Describe how halocarbons can be prepared Vocabulary
NECTA A-Level CHEMISTRY 2 May 2004
 NECTA A-Level CHEMISTRY 2 May 2004 [04/2] SECTION A 1. (a) Draw a sketch of a cell formed by combining Zn 2+ (aq)/zn(s) and Cu 2+ (aq)/cu(s) half-cells. Indicate on the sketch the following: The positive
NECTA A-Level CHEMISTRY 2 May 2004 [04/2] SECTION A 1. (a) Draw a sketch of a cell formed by combining Zn 2+ (aq)/zn(s) and Cu 2+ (aq)/cu(s) half-cells. Indicate on the sketch the following: The positive
Additions to the Carbonyl Groups
 Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
ACETONE. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION CAS NO EINECS NO MOL WT H.S. CODE Oral rat LD50: 5800 mg/kg
 ACETONE www.pawarchemicals.com PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION CAS NO 67-64-1 EINECS NO. 200-662-2 FORMULA (CH3)2C=O MOL WT. 58.08 H.S. CODE 2914.11 TOXICITY SYNONYMS Oral rat LD50: 5800 mg/kg Dimethyl ketone;
ACETONE www.pawarchemicals.com PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION CAS NO 67-64-1 EINECS NO. 200-662-2 FORMULA (CH3)2C=O MOL WT. 58.08 H.S. CODE 2914.11 TOXICITY SYNONYMS Oral rat LD50: 5800 mg/kg Dimethyl ketone;
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem reaction what is added to the C=C what kind of molecule results addition of HX HX only
 I. Addition Reactions of Alkenes Introduction Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem 2310 An addition reaction always involves changing a double bond to a single bond and adding a new bond
I. Addition Reactions of Alkenes Introduction Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 Alkenes (II) Chem 2310 An addition reaction always involves changing a double bond to a single bond and adding a new bond
Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding.
 Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding. Sigma and Pi Bonds: All single bonds are sigma(σ), that
Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding. Sigma and Pi Bonds: All single bonds are sigma(σ), that
PAPER No. : Paper-9, Organic Chemistry-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) MODULE No. : Module-10, Hydroboration Reaction CHEMISTRY
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper-9, Organic Chemistry-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module-10, Hydroboration Reaction CHE_P9_M10 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper-9, Organic Chemistry-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module-10, Hydroboration Reaction CHE_P9_M10 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes
Aryl Halides. Structure
 Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
Lecture 15. More Carbonyl Chemistry. Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first O R'OH, H + OR" 2R"OH R + H 2 O OR" 3/8/16
 Lecture 15 More Carbonyl Chemistry R" R C + R' 2R" R C R" R' + 2 March 8, 2016 Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first R', + R R 1 emiacetal reacts further in acid to yield an acetal
Lecture 15 More Carbonyl Chemistry R" R C + R' 2R" R C R" R' + 2 March 8, 2016 Alcohols React with Aldehydes and Ketones in two steps first R', + R R 1 emiacetal reacts further in acid to yield an acetal
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
Ethers. Synthesis of Ethers. Chemical Properties of Ethers
 Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
The C-X bond gets longerand weakergoing down the periodic table.
 Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
Chapter 10: Organohalides Organic molecules containing halogen atoms (X) bonded to carbon are useful compounds in synthesis and on their own. 10.2 Structure of alkyl halides The C-X bond gets longerand
Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides. Diethyl ether in starting fluid
 Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides Diethyl ether in starting fluid 8.1 Nomenclature of Ethers Ethers are usually named by giving the name of each alkyl or aryl group, in alphabetical order, followed by the
Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides Diethyl ether in starting fluid 8.1 Nomenclature of Ethers Ethers are usually named by giving the name of each alkyl or aryl group, in alphabetical order, followed by the
Carboxylic Acids O R C + H + O - Chemistry 618B
 arboxylic Acids R H R + H + - R - Nomenclature - IUPA IUPA names: drop the -e from the parent alkane and add the suffix -oic acid If the compound contains a carbon-carbon double bond, change the infix
arboxylic Acids R H R + H + - R - Nomenclature - IUPA IUPA names: drop the -e from the parent alkane and add the suffix -oic acid If the compound contains a carbon-carbon double bond, change the infix
Review Experiments Formation of Polymers Reduction of Vanillin
 Review Experiments Formation of Polymers What is a polymer? What is polymerization? What is the difference between an addition polymerization and a condensation polymerization? Which type of polymerization
Review Experiments Formation of Polymers What is a polymer? What is polymerization? What is the difference between an addition polymerization and a condensation polymerization? Which type of polymerization
Paper 9: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-III (Reaction Mechanism-2) Module 16: Reduction by Metal hydrides Part-I
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 9: ORGANIC -III (Reaction Mechanism-2) 16: Reduction by Metal hydrides Part-I CHE_P9_M16 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 9: ORGANIC -III (Reaction Mechanism-2) 16: Reduction by Metal hydrides Part-I CHE_P9_M16 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy
 By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Multi-step Synthesis: Preparation of Organic Dyes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m15877 1 Multi-step Synthesis: Preparation of Organic Dyes * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Multi-step
OpenStax-CNX module: m15877 1 Multi-step Synthesis: Preparation of Organic Dyes * Mary McHale This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1 Multi-step
media), except those of aluminum and calcium
 1- Aspirin occurs as white crystals or as a white crystalline powder. 2- It is slightly soluble in water (1:300), soluble in alcohol (1 :5), chloroform (1:17) & ether (1:15). It dissolves easily in glycerin.
1- Aspirin occurs as white crystals or as a white crystalline powder. 2- It is slightly soluble in water (1:300), soluble in alcohol (1 :5), chloroform (1:17) & ether (1:15). It dissolves easily in glycerin.
Carbonyl Chemistry V + C O C. Chemistry /30/02
 arbonyl hemistry V Ō - + Keto-enol enol Tautomerism H 3 H 3 Ketone H H R 2 H R' H H 3 H 2 H Enol H Acid atalyzed α Halogenation R 2 R' + X 2 H + R 2 R' + HX H X X 2 can be l 2, Br 2, or I 2. Substitution
arbonyl hemistry V Ō - + Keto-enol enol Tautomerism H 3 H 3 Ketone H H R 2 H R' H H 3 H 2 H Enol H Acid atalyzed α Halogenation R 2 R' + X 2 H + R 2 R' + HX H X X 2 can be l 2, Br 2, or I 2. Substitution
Organic Chemistry. Introduction to Organic Molecules and Functional Groups
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Introduction to Organic Molecules and Functional Groups by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Introduction to Organic Molecules and Functional Groups by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
Alkyl phenyl ketones are usually named by adding the acyl group as prefix to phenone.
 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Aldehydes: Often called by their common names instead of IUPAC names. Ketones: Derived by naming two alkyl or aryl groups bonded
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones Aldehydes: Often called by their common names instead of IUPAC names. Ketones: Derived by naming two alkyl or aryl groups bonded
21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids. Acids Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids.
 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are abundant in nature and in pharmaceuticals. 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids The US produces over 2.5 million tons of acetic acid per year, which
21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids are abundant in nature and in pharmaceuticals. 21.1 Introduction Carboxylic Acids The US produces over 2.5 million tons of acetic acid per year, which
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar. Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry
 A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
Chapter 22 Amines. Nomenclature Amines are classified according to the degree of substitution at nitrogen.
 CH. 22 Chapter 22 Amines Amines are very important in biological chemistry. Most of the bases in biological acid-base reactions are amines. They are also very important nucleophiles in biochemical reactions.
CH. 22 Chapter 22 Amines Amines are very important in biological chemistry. Most of the bases in biological acid-base reactions are amines. They are also very important nucleophiles in biochemical reactions.
Amines and Heterocycles. McMurry: Chapter 24
 Amines and Heterocycles McMurry: Chapter 24 Introduction to Amines and Heterocycles Amines and heterocycles (cyclic amines) are ammonia derivatives, many of whichare found widely in livingorganisms: 2
Amines and Heterocycles McMurry: Chapter 24 Introduction to Amines and Heterocycles Amines and heterocycles (cyclic amines) are ammonia derivatives, many of whichare found widely in livingorganisms: 2
AMINES. 3. Secondary When two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two alkyl or aryl groups.
 AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
Lecture 18. Oxidation and Reduction. Oxidation. Reduction O CH 4 CH 3 OH H C H. Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 18 xidation and Reduction C 4 C 3 C C C xidation Reduction March 27, 2018 Suppose you want to make this compound????? C + BrC 2 C 2 C?? CC 2 C 2 C 4-ydroxy-4-phenylbutanal It s an alcohol. Use
Lecture 18 xidation and Reduction C 4 C 3 C C C xidation Reduction March 27, 2018 Suppose you want to make this compound????? C + BrC 2 C 2 C?? CC 2 C 2 C 4-ydroxy-4-phenylbutanal It s an alcohol. Use
PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS
 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS OBJECTIVES: Gaining insight into property and reactivity trends within families and across periods for the chemical elements through experimental observation. SKILLS: Observations,
PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS OBJECTIVES: Gaining insight into property and reactivity trends within families and across periods for the chemical elements through experimental observation. SKILLS: Observations,
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry
 UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections:
 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Chemistry Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers
 Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Chemistry 235 - Final Examinations Summer 2006 answers A GEERAL CEMISTRY answers are given from 1-20: no reaction C 3 CC 3 Ph C C C C C 3 Et 2 2 2 B. REACTIS AD REAGETS [32 MARKS] 2. A single substance
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
H H O C C O H Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives C CH 2 C. N Goalby chemrevise.org. Strength of carboxylic acids.
 19 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending -oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
19 arboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming arboxylic acids These have the ending -oic acid but no number is necessary for the acid group as it must always be at the end of the chain. The numbering always
Derived copy of Bis2A 02.2 Appendix I Working with functional groups: Aldehydes, Ketones Carboxylic Acids and Esters *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56835 1 Derived copy of Bis2A 02.2 Appendix I Working with functional groups: Aldehydes, Ketones Carboxylic Acids and Esters * Erin Easlon Based on Bis2A 02.2 Appendix I Working with
OpenStax-CNX module: m56835 1 Derived copy of Bis2A 02.2 Appendix I Working with functional groups: Aldehydes, Ketones Carboxylic Acids and Esters * Erin Easlon Based on Bis2A 02.2 Appendix I Working with
Alcohols. Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
 Alcohols Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group Uses: synthetic intermediate, cleanser, cosmetics, fuel, alcoholic beverages, etc. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
Alcohols Alcohol any organic compound containing a hydroxyl (R-OH) group Uses: synthetic intermediate, cleanser, cosmetics, fuel, alcoholic beverages, etc. Alcohols are an extremely important organic source
REALLY, REALLY STRONG BASES. DO NOT FORGET THIS!!!!!
 CHEM 345 Problem Set 4 Key Grignard (RMgX) Problem Set You will be using Grignard reagents throughout this course to make carbon-carbon bonds. To use them effectively, it will require some knowledge from
CHEM 345 Problem Set 4 Key Grignard (RMgX) Problem Set You will be using Grignard reagents throughout this course to make carbon-carbon bonds. To use them effectively, it will require some knowledge from
Experiment 1: Preparation of Vanillyl Alcohol
 Experiment 1: Preparation of Vanillyl Alcohol INTRDUCTIN A common method for preparing alcohols is the reduction of aldehydes to form primary alcohols [equation (1)] or of ketones to produce secondary
Experiment 1: Preparation of Vanillyl Alcohol INTRDUCTIN A common method for preparing alcohols is the reduction of aldehydes to form primary alcohols [equation (1)] or of ketones to produce secondary
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018
 CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids
 Carboxylic acids have the formula RCO2H. Nomenclature Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids For the parent alkane, drop the terminal e and add the suffix oic acid. The parent alkane is the longest continuous chain
Carboxylic acids have the formula RCO2H. Nomenclature Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids For the parent alkane, drop the terminal e and add the suffix oic acid. The parent alkane is the longest continuous chain
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
Lecture 2. The framework to build materials and understand properties
 Lecture 2 The framework to build materials and understand properties 1 Trees are made into a solid materials/structures in an environment that consists of small molecules: CO 2, N 2, H 2 0, CH 4 O C 2.58Ǻ
Lecture 2 The framework to build materials and understand properties 1 Trees are made into a solid materials/structures in an environment that consists of small molecules: CO 2, N 2, H 2 0, CH 4 O C 2.58Ǻ
Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol
 1 Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol Reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds are among the most useful to the synthetic organic chemist. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel
1 Experiment 12: Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol Reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds are among the most useful to the synthetic organic chemist. In 1912, Victor Grignard received the Nobel
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Metal Ligand Complexes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m34660 1 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Metal Ligand Complexes * Jiebo Li Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m34660 1 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Metal Ligand Complexes * Jiebo Li Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Name/CG: 2012 Term 2 Organic Chemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question
 Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Name/G: 2012 Term 2 rganic hemistry Revision (Session II) Deductive Question 1(a) A yellow liquid A, 7 7 N 2, reacts with alkaline potassium manganate (VII) and on acidification gives a yellow solid B,
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
The Synthesis of Triphenylmethano. will synthesize Triphenylmethanol, a white crystalline aromatic
 HEM 333L rganic hemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of Triphenylmethano ol In this laboratory exercise we will synthesize Triphenylmethanol, a white crystalline aromatic compound. Triphenylmethanol
HEM 333L rganic hemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 The Synthesis of Triphenylmethano ol In this laboratory exercise we will synthesize Triphenylmethanol, a white crystalline aromatic compound. Triphenylmethanol
Aromatic Compounds II
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
About the GRE Chemistry Subject Test p. 1 About the GRE Chemistry Subject Test GRE Chemistry Topics Test Dates Testing Fee Test Format Testing Time
 About the GRE Chemistry Subject Test p. 1 About the GRE Chemistry Subject Test GRE Chemistry Topics Test Dates Testing Fee Test Format Testing Time Scoring To Guess or Not to Guess On the Day of the Test
About the GRE Chemistry Subject Test p. 1 About the GRE Chemistry Subject Test GRE Chemistry Topics Test Dates Testing Fee Test Format Testing Time Scoring To Guess or Not to Guess On the Day of the Test
Ammonia * Andrew R. Barron. 1 Synthesis. 2 Structure
 OpenStax-CNX module: m32956 1 Ammonia * Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Ammonia (NH 3 ) is a colorless, pungent gas
OpenStax-CNX module: m32956 1 Ammonia * Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Ammonia (NH 3 ) is a colorless, pungent gas
