Radiation Glossary. Radioactive material dispersed in the air in the form of dusts, fumes, particulates, mists, vapors, or gases.
|
|
|
- Lucas Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Activity The rate of disintegration (transformation) or decay of radioactive material. The units of activity are Curie (Ci) and the Becquerel (Bq). Agreement State Any state with which the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission has entered into an effective agreement under subsection 274b. of the Atomic Energy Act of 1954, as amended. Under the agreement, the state regulates the use of by-product, source, and small quantities of special nuclear material within said state. Airborne Radioactive Material Radioactive material dispersed in the air in the form of dusts, fumes, particulates, mists, vapors, or gases. ALARA Acronym for "As Low As Reasonably Achievable". Making every reasonable effort to maintain exposures to ionizing radiation as far below the dose limits as practical, consistent with the purpose for which the licensed activity is undertaken. It takes into account the state of technology, the economics of improvements in relation to state of technology, the economics of improvements in relation to benefits to the public health and safety, societal and socioeconomic considerations, and in relation to utilization of radioactive materials and licensed materials in the public interest. Alpha Particle A positively charged particle ejected spontaneously from the nuclei of some radioactive elements. It is identical to a helium nucleus, with a mass number of 4 and a charge of +2. Annual Limit on Intake (ALI) Annual intake of a given radionuclide by "Reference Man" which would result in either a committed effective dose equivalent of 5 rems or a committed dose equivalent of 50 rems to an organ or tissue. Attenuation The process by which radiation is reduced in intensity when passing through some material. It is the combination of absorption and scattering processes. Background Radiation Radiation from cosmic sources; naturally occurring radioactive materials, including radon and fallout from nuclear weapons tests. Laboratory Safety 46 Blackstone Street, Cambridge, MA T: F: lab_safety@harvard.edu
2 Beta (particle) High speed electrons, which are emitted from the nuclei of radioactive atoms during radioactive decay, as a result of the transformation of a neutron into a proton. They can be stopped by a thin (thickness varies for different radionuclides) sheet of plastic or glass. Becquerel A unit, in the International System of Units (SI), of measurement of activity equal to one decay per second. Bioassay The determination of kinds, quantities, or concentrations, and, in some cases, the locations of radioactive material in the human body, whether by direct counting (in vivo) or by analysis and evaluation of materials excreted or removed from the body. Biological Half Life The time that is required by an organism to eliminate half the amount of a substance that has entered it. Bremstrahlung X-rays produced when a charged particle loses energy in interactions with heavy nuclei when moving through matter. Calibration The check or correction of the accuracy of a measuring instrument to assure proper operational characteristics. Charged Particle An elementary particle or ion which carries a positive or negative electric charge. Committed Effective Dose Equivalent The dose equivalent to organs or tissues of reference that will be received from an intake of radioactive material by an individual during the 50-year period following intake. Contamination The deposition of unwanted radioactive material on the surfaces of structures, areas, objects, or personnel. Can either be fixed or removable. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 2 of 10
3 Counter A general term used for a radiation detection instrument, survey meter, or a liquid scintillation counter (LSC) that detects and measures radiation. The signals (needle blip and audio beep) show ionization events called counts. CPM (Counts Per Minute) A commonly used measure of radioactivity from particle emitters; since a detection instrument cannot operate at 100% efficiency, the CPM found will be less than the actual DPM Critical Organ The organ receiving the highest dose or highest amount of a particular nuclide that results in the greatest damage to the body as a result of an intake. Cumulative Dose The total dose resulting from repeated exposures of radiation to the same region, or to the whole body, over a period of time. Curie (Ci) The basic unit used to describe the intensity of radioactivity in a sample of material. The curie is equal to 37 billion disintegrations per second, which is approximately the rate of decay of 1 gram of radium. Named for Marie and Pierre Curie, who discovered radium in Decay, Radioactive The decrease in the amount of any radioactive material with the passage of time, due to the spontaneous emission from the atomic nuclei of either alpha, beta particles, or gamma rays. Declared Pregnant Worker A woman who has voluntarily informed her employer, in writing, of her pregnancy and the estimated date of conception. Decontamination The reduction or removal of contaminating radioactive material from a structure, area, object, or person. Deep Dose Equivalent A term that applies to external whole-body exposure, and is the dose equivalent at a tissue depth of 1 cm. Detector A material or device that is sensitive to radiation and can produce a signal suitable for measurement or analysis. A radiation detection instrument. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 3 of 10
4 Disintegration See decay, radioactive. Dose A generic term referring to the amount of radiation received by a biological organism. Dose Equivalent The product of the absorbed dose in tissue, quality factor, and other modifying factors at the location of interest. The units are mrem. Dose Rate The ionizing radiation dose delivered per unit time, such as mrem/hour. Dosimeter A portable instrument for measuring the total accumulated exposure to ionizing radiation. DPM (Disintegrations per Minute) The number of radioactive disintegrations per unit time; there are 2.2E6 disintegrations per minute in a microcurie. Effective Dose Equivalent The sum of the products of the dose equivalent to the organ or tissue and the weighting factors applicable to each of the body organs or tissues that are irradiated. Effective Half-Life The time required for the amount of a radioactive element deposited in a living organism to be reduced by 50% from the combined removal mechanisms of radioactive decay and biological elimination. Embryo/Fetus The developing human organism from conception until the time of birth. More specifically; embryo: 2 weeks (implantation) - 8 weeks; fetus : 8 weeks - term. Exposure 1) A measure of the ionization produced in air by X or gamma radiation. The unit of exposure is the Roentgen (R). 2) Being exposed to ionizing radiation or to radioactive material. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 4 of 10
5 Exposure Rate The amount of ionization in air caused by x-ray or gamma ray radiation per unit time; unit of measurement is the Roentgen per unit time (R/hr) External Dose The portion of the dose equivalent received from radiation sources outside the body. Extremity Arm below the elbow and the leg below the knee. Eye Dose Equivalent Applies to the external exposure of the lens of the eye and is taken as the dose equivalent at a tissue depth of 0.3 cm. Gamma Ray Relatively short wavelength electromagnetic radiation released from the nucleus of an atom. Geiger-Mueller Counter (GM) A radiation detection instrument that can detect alpha, beta and gamma radiation; response is not energy dependent. Half-life The time in which half the atoms of a particular radioactive substance disintegrate to another nuclear form. Measured half lives vary from millionths of a second to billions of years. Also referred to as the physical half-life. Half Value Layer The thickness of any given absorber (shield) that will reduce the intensity of incident radiation to one half of its initial value. Health Physics The science concerned with recognition, evaluation, and control of health hazards from non-ionizing and ionizing radiation. High Radiation Area An area, accessible to individuals, in which radiation levels could result in an individual receiving a dose equivalent in excess of 0.1 mrem in 1 hour at 30 cm from the radiation source or from any surface that the radiation penetrates. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 5 of 10
6 Intake Quantity of material introduced into the body by inhalation, ingestion, or through the skin. Internal Dose That portion of the dose equivalent received from radioactive material taken into the body. Ionization The process of adding or removing one or more electrons from atoms or molecules. High temperatures, electrical discharges, or radiation can cause ionization. Ionization Chamber An instrument that detects and measures ionizing radiation by measuring the electrical current that flows when radiation ionizes gas in a chamber, making the gas a conductor of electricity. Ionizing Radiation Any radiation capable of displacing electrons from atoms or molecules, producing ions. Examples: alpha, beta, gamma, X-rays, neutrons, and ultraviolet light. High doses may produce severe skin or tissue damage. Irradiation Exposure to radiation. Isotope One of two or more atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons, in their nuclei. Example: 12 C, 13 C, and 14 C are isotopes of the same element. Isotopes have very nearly the same chemical properties, but often different physical properties ( 12 C and 13 C are stable, while 14 C is radioactive). Limits The permissible upper bounds of radiation doses. Liquid Scintillation Counting A method of determining activity of a radioactive sample using a liquid Fluor and a means of detecting the scintillation resulting from the interaction of radiation with the Fluor. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 6 of 10
7 NaI (Sodium Iodide) Detector A detector which combines a scintillation crystal (produces light when struck by ionizing radiation), a photomultiplier tube, and associated electronic circuits for counting light emissions produced in the crystal (NaI) by ionizing radiation. A NaI scintillation probe with a ratemeter can be used for detection of gamma and x-rays. Nuclide A general term referring to all known isotopes, both stable (~279) and unstable (~5000), of the chemical elements. Occupational Dose The dose received by an individual in a restricted area or in the course of employment in which the individual's assigned duties involve exposure to radiation and to radioactive material. This does not include dose received from background radiation, as a patient from medical procedures, from voluntary participation in medical research programs, or as a member of the general public. Personnel Monitoring The determination of the degree of radioactive contamination on individuals using survey meters, or the determination of radiation dosage received by means of dosimetry devices. Physical Half Life The time required for a radioisotope to reduce activity by half. Pig A container (usually lead) used to ship or store radioactive materials. The thick walls protect the person handling the container from radiation. Large containers are usually called casks. Proportional Counter A radiation detection instrument in which an electronic system receives pulses that are proportional to the number of ions formed in a gas-filled tube/probe by ionizing radiation. Quality Factor The modifying factor that is used to derive dose equivalent from the absorbed dose. They vary for different radiation types and reflect the degree of biological effect. Quarter A period of time equal to one-fourth of the year observed by the licensee (approx. 13 consecutive weeks). Providing that the beginning of the first quarter in a year coincides with the starting date of the year and that no day is omitted or duplicated in consecutive quarters. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 7 of 10
8 Rad The special unit of absorbed dose. One rad is equivalent to 100 ergs/gram or 0.01 J/kg. Radiation Alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, x-rays, neutrons, high speed electrons, high speed protons, and other charged particles capable of producing ions. Radiation, as used in this context, does not include non-ionizing radiation, such as radio waves, microwaves, or visible, infrared, or ultraviolet light. Radiation Area An area, accessible to individuals, in which radiation levels could result in an individual receiving a dose equivalent in excess of 5 mrem in 1 hour at 30 cm from the radiation source or from any surface that the radiation penetrates. Radiation Detection Instrument A device that detects and records the characteristics of ionizing radiation. Radiation Machine Any device capable of producing radiation except those which produce radiation only from radioactive material. Radiation Shielding Reduction of radiation by placing a shield of absorbing material between any radioactive source and a person, work area, or radiation sensitive device. Radiation Source Usually a manmade sealed source of radiation used in teletherapy, radiography, as a power source for batteries, calibration, or in various industrial gauges. Machines such as accelerators, radioisotope generators, and natural radionuclides may be considered sources. Radiation Standards Exposure standards, permissible concentrations, rules for safe handling, regulations for transportation, regulations for industrial control of radiation and control of radioactive material by legislative means. Radiation Warning Symbol An officially prescribed symbol (a magenta trefoil) on a yellow background that must be displayed where certain quantities of radioactive materials are present or where certain doses of radiation could be received. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 8 of 10
9 Radioactive waste A solid, liquid, or gaseous material from experiment/research operations that is radioactive and for which there is no further use. Radioactivity The spontaneous emission of radiation, generally alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays from the nucleus of an unstable isotope. Radioisotope An unstable isotope of an element that decays or disintegrates spontaneously, emitting radiation. Rem The special unit for dose equivalent. The dose equivalent in rem is equal to the absorbed dose in rads, multiplied by the quality factor. Roentgen (R) A unit of exposure to ionizing radiation. It is that amount of gamma or x-rays required to produce ions carrying 1 electrostatic unit of electrical charge in 1 cubic centimeter of dry air under standard conditions. Named after Wilhelm Roentgen, German scientist who discovered x-rays in Restricted Area An area, access to which is limited by the licensee for the purpose of protecting individuals against undue risks from exposure to radiation or radioactive materials. Restricted area does not include areas used as residential quarters, offices, etc. Scintillation Detector A radiation detection instrument comprised of a phosphor, photomultiplier tube(s), and associated electronic circuits for counting light emissions produced in the phosphor by ionizing radiation. Sealed Source Radioactive material that is permanently bonded or fixed in a capsule or matrix designed to prevent release and dispersal under the most severe conditions which are likely to be encountered in normal use and handling. Secondary Radiation Radiation originating as the result of absorption of other radiation in matter. It may be either electromagnetic (e.g. Bremsstrahlung from 32P betas passing through lead) or particulate in nature. Shallow Dose Equivalent Applies to the external exposure of the skin or an extremity. This is the dose equivalent at a tissue depth cm averaged over an area of 1 square centimeter. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 9 of 10
10 Shielding Any material or obstruction that absorbs radiation and thus tends to protect personnel or materials from the effects of ionizing radiation. Survey Meter Any portable radiation detection instrument especially adapted for inspecting an area to establish the existence and amount of radioactive material or contamination present. TLD (ThermoLuminescent Dosimeter) A crystalline material which emits light when heated after radiation exposure; used in dosimetry. Whole Body Refers to the head, trunk (including gonads), arms above the elbow, and legs above the knee. Wipe Sample Wiping of 100 square centimeters of a surface with a filter paper or a cotton swab for the purpose of determining if removable contamination is present. The wipe is then analyzed with a radiation detection instrument, such as a survey meter or a LSC). X-rays Penetrating electromagnetic radiation (photon) having a wavelength that is much shorter than that of visible light. They can be produced by excitation of the electrons around certain nuclei (characteristic x-rays) or by the interaction of high speed electrons with the electric fields around nuclei. radiation_protection@harvard.edu to send comments and suggestions to the Radiation Protection Office. Revision Date: 10/10/2012 Page 10 of 10
GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY
 GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY ABSORBED DOSE: The amount of energy absorbed, as a result of radiation passing through a material, per unit mass of material. Measured in rads (1 rad
GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY ABSORBED DOSE: The amount of energy absorbed, as a result of radiation passing through a material, per unit mass of material. Measured in rads (1 rad
Glossary of Terms* BIOASSAY: Assay and measurement procedures used to determine the amount of radioactive material in a biological system.
 Glossary of Terms* *With permission from the Manual of Policies and Procedures for Radiation Protection, for the University of Minnesota, Department of Environmental Health and Safety, Radiation Protection
Glossary of Terms* *With permission from the Manual of Policies and Procedures for Radiation Protection, for the University of Minnesota, Department of Environmental Health and Safety, Radiation Protection
"Accelerator-produced material" means any material made radioactive by a particle accelerator.
 : Glossary "Absorbed dose" means the energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The units of absorbed dose are the gray (Gy) and the rad. "Accelerator" (particle accelerator)
: Glossary "Absorbed dose" means the energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The units of absorbed dose are the gray (Gy) and the rad. "Accelerator" (particle accelerator)
Appendix A. Glossary. Absorbed Dose
 Appendix A Glossary Absorbed Dose Accelerator Activate Activity, A ALARA Alpha Particle, α Alpha Emitter Amendment Annual Limit of Intake (ALI) Atom Auger Electron Authorized User Background Radiation
Appendix A Glossary Absorbed Dose Accelerator Activate Activity, A ALARA Alpha Particle, α Alpha Emitter Amendment Annual Limit of Intake (ALI) Atom Auger Electron Authorized User Background Radiation
APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
 Former NAVWPNSTA Concord, Inland Area APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 This page intentionally left blank. Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
Former NAVWPNSTA Concord, Inland Area APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 This page intentionally left blank. Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
RADIATION SAFETY. Working Safely with Radiation
 RADIATION SAFETY Working Safely with Radiation 12 NOV 2015 Dr. Raed Felimban Department of Transfusion Medicine King Abdul-Aziz University E-mail: felimbanr@yahoo.com KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY How most
RADIATION SAFETY Working Safely with Radiation 12 NOV 2015 Dr. Raed Felimban Department of Transfusion Medicine King Abdul-Aziz University E-mail: felimbanr@yahoo.com KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY How most
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment
 Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
BASIC OF RADIATION; ORIGIN AND UNITS
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243 - LECTURE 2 BASIC OF RADIATION; ORIGIN AND UNITS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243 - LECTURE 2 BASIC OF RADIATION; ORIGIN AND UNITS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam
WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION
 WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION Margarita Saraví National Atomic Energy Commission - Argentina Workshop on Ionizing Radiation SIM Buenos Aires 10 November 2011 What is ionizing radiation? What is ionizing radiation?
WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION Margarita Saraví National Atomic Energy Commission - Argentina Workshop on Ionizing Radiation SIM Buenos Aires 10 November 2011 What is ionizing radiation? What is ionizing radiation?
NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal
 NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal Ionizing Radiation and Hazard Potential John R. Frazier, Ph.D. Certified Health Physicist May 12, 2014 Radiation Radiation is a word that
NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal Ionizing Radiation and Hazard Potential John R. Frazier, Ph.D. Certified Health Physicist May 12, 2014 Radiation Radiation is a word that
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Radiation: It is defined as the process by which energy is emitted from a source and propagated through the surrounding
Radiation Safety Glossary
 This glossary contains all the terms that you should know when working with radioisotopes. Absorbed dose The energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The units of absorbed
This glossary contains all the terms that you should know when working with radioisotopes. Absorbed dose The energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The units of absorbed
RADIATION SAFETY GLOSSARY
 Introduction This glossary contains all the terms that you should know when working with radioisotopes. Absorbed dose The energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The
Introduction This glossary contains all the terms that you should know when working with radioisotopes. Absorbed dose The energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 1 RADIATION PHYSICS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam 16-02-2015
Radiation Terminology
 Radiation Terminology This section discusses the terms and concepts which are necessary for a meaningful discussion of radiation, its sources, and its risks. USNRC Technical Training Center 5-1 0703 Energy
Radiation Terminology This section discusses the terms and concepts which are necessary for a meaningful discussion of radiation, its sources, and its risks. USNRC Technical Training Center 5-1 0703 Energy
Radiation Safety Basic Terms
 Radiation Safety Basic Terms Radiation Radiation is energy in transit in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves. We encounter electromagnetic waves every day. They make up our visible
Radiation Safety Basic Terms Radiation Radiation is energy in transit in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves. We encounter electromagnetic waves every day. They make up our visible
Alpha decay usually occurs in heavy nuclei such as uranium or plutonium, and therefore is a major part of the radioactive fallout from a nuclear
 Radioactive Decay Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei. This phenomenon was first reported in 1896 by the French physicist Henri Becquerel. Marie Curie and her husband Pierre
Radioactive Decay Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei. This phenomenon was first reported in 1896 by the French physicist Henri Becquerel. Marie Curie and her husband Pierre
Radiation Fundamentals. Radiation Safety Training Module 1
 Radiation Fundamentals Module 1 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the process of unstable (or radioactive) atoms becoming stable. This is done by emitting radiation. This process over a period of time is
Radiation Fundamentals Module 1 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the process of unstable (or radioactive) atoms becoming stable. This is done by emitting radiation. This process over a period of time is
Radiation Safety Glossary
 Radiation Safety Glossary Absorbed dose Activity Airborne radioactive material Airborne radioactivity area ALARA The energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The units
Radiation Safety Glossary Absorbed dose Activity Airborne radioactive material Airborne radioactivity area ALARA The energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The units
Name Date Class. alpha particle radioactivity gamma ray radioisotope beta particles radiation X-ray radioactive decay
 Name Date _ Class _ Nuclear Chemistry Section.1 Nuclear Radiation In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe nuclear changes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Name Date _ Class _ Nuclear Chemistry Section.1 Nuclear Radiation In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe nuclear changes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects
 Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects Reading Assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610) Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual
Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects Reading Assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610) Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual
Radiation Protection & Radiation Therapy
 Radiation Protection & Radiation Therapy For Medical Students Professor of Medical Physics Radiation Units Activity Number disintegrations per second (Curie, Becquerel) Exposure (Roentgen, C/kg) Absorbed
Radiation Protection & Radiation Therapy For Medical Students Professor of Medical Physics Radiation Units Activity Number disintegrations per second (Curie, Becquerel) Exposure (Roentgen, C/kg) Absorbed
Radiation Protection Training Manual & Study Guide. Jump to the Table of Contents
 Radiation Protection Training Manual & Study Guide Jump to the Table of Contents December 1986 Revised 1994 Radiation Safety Office Radiation Protection Training Course Course Outline Time Lecture Topic
Radiation Protection Training Manual & Study Guide Jump to the Table of Contents December 1986 Revised 1994 Radiation Safety Office Radiation Protection Training Course Course Outline Time Lecture Topic
Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects: Session 1
 Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects: Session 1 Reading assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610): Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual and Resource Book: Parts
Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects: Session 1 Reading assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610): Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual and Resource Book: Parts
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES. Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision
 Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
Radiation and Radioactivity. PHYS 0219 Radiation and Radioactivity
 Radiation and Radioactivity 1 Radiation and Radioactivity This experiment has four parts: 1. Counting Statistics 2. Gamma (g) Ray Absorption Half-length and shielding 3. 137 Ba Decay Half-life 4. Dosimetry
Radiation and Radioactivity 1 Radiation and Radioactivity This experiment has four parts: 1. Counting Statistics 2. Gamma (g) Ray Absorption Half-length and shielding 3. 137 Ba Decay Half-life 4. Dosimetry
PS-21 First Spring Institute say : Teaching Physical Science. Radioactivity
 PS-21 First Spring Institute say 2012-2013: Teaching Physical Science Radioactivity What Is Radioactivity? Radioactivity is the release of tiny, highenergy particles or gamma rays from the nucleus of an
PS-21 First Spring Institute say 2012-2013: Teaching Physical Science Radioactivity What Is Radioactivity? Radioactivity is the release of tiny, highenergy particles or gamma rays from the nucleus of an
sample What happens when we are exposed to radiation? 1.1 Natural radiation Cosmic radiation
 1.1 Natural radiation 3 1 What happens when we are exposed to radiation? 1.1 Natural radiation For as long as humans have walked the earth, we have continually been exposed to naturally-occurring radiation.
1.1 Natural radiation 3 1 What happens when we are exposed to radiation? 1.1 Natural radiation For as long as humans have walked the earth, we have continually been exposed to naturally-occurring radiation.
Radiation Basics. Candace C. Davison, M.Engr. Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, Ph.D.
 Radiation Basics Candace C. Davison, M.Engr. Research & Education Specialist Pennsylvania State University Radiation Science and Engineering Center Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, Ph.D. Assistant Prof of Nuclear
Radiation Basics Candace C. Davison, M.Engr. Research & Education Specialist Pennsylvania State University Radiation Science and Engineering Center Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, Ph.D. Assistant Prof of Nuclear
Radioactivity. General Physics II PHYS 111. King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences
 King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Radioactivity General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa Outline Radioactive Decay
King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Radioactivity General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa Outline Radioactive Decay
Radiation Safety Talk. UC Santa Cruz Physics 133 Winter 2018
 Radiation Safety Talk UC Santa Cruz Physics 133 Winter 2018 Outline Types of radiation Sources of radiation Dose limits and risks ALARA principle Safety procedures Types of radiation Radiation is energy
Radiation Safety Talk UC Santa Cruz Physics 133 Winter 2018 Outline Types of radiation Sources of radiation Dose limits and risks ALARA principle Safety procedures Types of radiation Radiation is energy
U (superscript is mass number, subscript atomic number) - radionuclides nuclei that are radioactive - radioisotopes atoms containing radionuclides
 Chapter : Nuclear Chemistry. Radioactivity nucleons neutron and proton all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, atomic number isotopes atoms with the same atomic number but different
Chapter : Nuclear Chemistry. Radioactivity nucleons neutron and proton all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, atomic number isotopes atoms with the same atomic number but different
10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY
 10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before.
10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before.
Radiation Basics. Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, PhD Idaho State University/Idaho National Laboratory. ANS Teachers Workshop Anaheim, CA November 2014
 Radiation Basics Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, PhD Idaho State University/Idaho National Laboratory ANS Teachers Workshop Anaheim, CA November 2014 Medicine/Health Voyager Soda Can Bugs What we ll cover... Atomic
Radiation Basics Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, PhD Idaho State University/Idaho National Laboratory ANS Teachers Workshop Anaheim, CA November 2014 Medicine/Health Voyager Soda Can Bugs What we ll cover... Atomic
Atomic Structure Summary
 Atomic Structure Summary All atoms have: a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons around it Atomic nucleus consists of: positively charged protons and neutrons that have no electric
Atomic Structure Summary All atoms have: a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons around it Atomic nucleus consists of: positively charged protons and neutrons that have no electric
Radiation Response and Removals: Getting Down to the Nitty Gritty. 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program
 Radiation Response and Removals: Getting Down to the Nitty Gritty 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 0 Radiation Fundamentals Tony Honnellio Health Physicist U.S. EPA, Region
Radiation Response and Removals: Getting Down to the Nitty Gritty 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 0 Radiation Fundamentals Tony Honnellio Health Physicist U.S. EPA, Region
SECTION 8 Part I Typical Questions
 SECTION 8 Part I Typical Questions 1. For a narrow beam of photons, the relaxation length is that thickness of absorber that will result in a reduction of in the initial beam intensity. 1. 1/10. 2. 1/2.
SECTION 8 Part I Typical Questions 1. For a narrow beam of photons, the relaxation length is that thickness of absorber that will result in a reduction of in the initial beam intensity. 1. 1/10. 2. 1/2.
Dosimetry. Sanja Dolanski Babić May, 2018.
 Dosimetry Sanja Dolanski Babić May, 2018. What s the difference between radiation and radioactivity? Radiation - the process of emitting energy as waves or particles, and the radiated energy Radioactivity
Dosimetry Sanja Dolanski Babić May, 2018. What s the difference between radiation and radioactivity? Radiation - the process of emitting energy as waves or particles, and the radiated energy Radioactivity
The basic structure of an atom is a positively charged nucleus composed of both protons and neutrons surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
 4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science
 Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
notes Radiological Basics Transportation Emergency Preparedness Program
 INTRODUCTION The reliance upon, and use of, radioactive material in agriculture, industry, and medicine continues to increase. As the manufacture, use, and disposal of radioactive material has increased,
INTRODUCTION The reliance upon, and use of, radioactive material in agriculture, industry, and medicine continues to increase. As the manufacture, use, and disposal of radioactive material has increased,
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 21. Nuclear Chemistry. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 21, Inc. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Energy: Chemical vs. Chemical energy is associated with making and breaking chemical bonds. energy is enormous in comparison.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 21, Inc. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Energy: Chemical vs. Chemical energy is associated with making and breaking chemical bonds. energy is enormous in comparison.
Radioactivity. General Physics II PHYS 111. King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences
 King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Radioactivity General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa Outline Radioactive Decay
King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Radioactivity General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa Outline Radioactive Decay
Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors
 King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa
King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa
Michael G. Stabin. Radiation Protection and Dosimetry. An Introduction to Health Physics. 4) Springer
 Michael G. Stabin Radiation Protection and Dosimetry An Introduction to Health Physics 4) Springer Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgments Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of
Michael G. Stabin Radiation Protection and Dosimetry An Introduction to Health Physics 4) Springer Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgments Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of
What happens during nuclear decay? During nuclear decay, atoms of one element can change into atoms of a different element altogether.
 When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
RADIATION PROTECTION
 DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR TECHNOLOGY, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING CHULALONGKORN UNIVERSITY PHAYATHAI ROAD, BANGKOK 10330, THAILAND TEL: (662) 218-6772, (662) 218-6784. FAX: (662) 218-6770 E-mail: fnegbr@eng.chula.ac.th
DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR TECHNOLOGY, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING CHULALONGKORN UNIVERSITY PHAYATHAI ROAD, BANGKOK 10330, THAILAND TEL: (662) 218-6772, (662) 218-6784. FAX: (662) 218-6770 E-mail: fnegbr@eng.chula.ac.th
Lecture 1 Bioradiation
 1 1 Radiation definition: Radiation, when broadly defined, includes the entire spectrum of electromagnetic waves : radiowaves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and x-rays and particles.
1 1 Radiation definition: Radiation, when broadly defined, includes the entire spectrum of electromagnetic waves : radiowaves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and x-rays and particles.
Chapter 18. Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
4.4.1 Atoms and isotopes The structure of an atom Mass number, atomic number and isotopes. Content
 4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
Radiological Preparedness & Emergency Response. Session II. Objectives. Basic Radiation Physics
 Radiological Preparedness & Emergency Response Session II Basic Radiation Physics Objectives Discuss the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Describe radioactive decay. Discuss the
Radiological Preparedness & Emergency Response Session II Basic Radiation Physics Objectives Discuss the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Describe radioactive decay. Discuss the
Introduction. Principle of Operation
 Introduction Ionizing radiation that is associated with radioactivity cannot be directly detected by our senses. Ionization is the process whereby the radiation has sufficient energy to strip electrons
Introduction Ionizing radiation that is associated with radioactivity cannot be directly detected by our senses. Ionization is the process whereby the radiation has sufficient energy to strip electrons
A Nuclear Power Plant
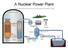 A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e -
 Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. radiation a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e - This can destroy the delicate balance of chemical reactions in living cells. The
Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. radiation a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e - This can destroy the delicate balance of chemical reactions in living cells. The
UNCORRECTED PROOF. Table of Contents
 00-Stabin-Prelims SNY001-Stabin (Typeset by spi publisher services, Delhi) vii of xvi June 1, 2007 17:15 Preface xiii Acknowledgments xv Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of Health
00-Stabin-Prelims SNY001-Stabin (Typeset by spi publisher services, Delhi) vii of xvi June 1, 2007 17:15 Preface xiii Acknowledgments xv Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of Health
HALF LIFE. NJSP HMRU June 10, Student Handout CBRNE AWARENESS Module 4 1. Objectives. Student will
 June 10, 2004 Radiological/Nuclear Overview 1 Student will demonstrate a knowledge of self protection techniques identify types of radiation and their associated hazards demonstrate a knowledge of terminology
June 10, 2004 Radiological/Nuclear Overview 1 Student will demonstrate a knowledge of self protection techniques identify types of radiation and their associated hazards demonstrate a knowledge of terminology
RADIATION SAFETY TRAINING SEALED SOURCES
 RADIATION SAFETY TRAINING SEALED SOURCES PLEASE REFER TO THE RADIATION SAFETY HANDBOOK, PARTICULARLY THE SEALED SOURCES CHAPTER, AS A SUPPLEMENT TO THIS PACKET. Sealed source use at CU State and federal
RADIATION SAFETY TRAINING SEALED SOURCES PLEASE REFER TO THE RADIATION SAFETY HANDBOOK, PARTICULARLY THE SEALED SOURCES CHAPTER, AS A SUPPLEMENT TO THIS PACKET. Sealed source use at CU State and federal
Nuclear Spectroscopy: Radioactivity and Half Life
 Particle and Spectroscopy: and Half Life 02/08/2018 My Office Hours: Thursday 1:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Some nuclei are unstable and decay spontaneously into two or more particles.
Particle and Spectroscopy: and Half Life 02/08/2018 My Office Hours: Thursday 1:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Some nuclei are unstable and decay spontaneously into two or more particles.
Isotopes of an element have the same symbol and same atomic number - Mass number refers to the protons plus neutrons in an isotope
 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. This radiation consists of high energy particles or waves being emitted from a variety of materials Radioactivity
7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. This radiation consists of high energy particles or waves being emitted from a variety of materials Radioactivity
NATO HANDBOOK ON THE MEDICAL ASPECTS OF NBC DEFENSIVE OPERATIONS AMedP-6(B) PART I - NUCLEAR ANNEX A RADIATION DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT
 NATO HANDBOOK ON THE MEDICAL ASPECTS OF NBC DEFENSIVE OPERATIONS AMedP-6(B) PART I - NUCLEAR RADIATION DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT 1 FEBRUARY 1996 NATO UNCLASSIFIED A ORIGINAL (Reverse Blank) TABLE OF CONTENTS
NATO HANDBOOK ON THE MEDICAL ASPECTS OF NBC DEFENSIVE OPERATIONS AMedP-6(B) PART I - NUCLEAR RADIATION DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT 1 FEBRUARY 1996 NATO UNCLASSIFIED A ORIGINAL (Reverse Blank) TABLE OF CONTENTS
Working Correctly & Safely with Radiation. Talia Tzahor Radiation safety officer Tel:
 Working Correctly & Safely with Radiation Talia Tzahor Radiation safety officer Tel: 5196 Email: talia.tzahor@weizmann.ac.il Environmental Exposure The typical human body contains: Potassium-40 ( 40 K)
Working Correctly & Safely with Radiation Talia Tzahor Radiation safety officer Tel: 5196 Email: talia.tzahor@weizmann.ac.il Environmental Exposure The typical human body contains: Potassium-40 ( 40 K)
Refresher Radiation Safety Training Scott Jaqua, RSO
 Refresher Radiation Safety Training Scott Jaqua, RSO 1 Section 1 Introduction 2 RSO Contact Information www.pdx.edu/environmental-health-safety Look for Research Safety Scott Jaqua, RSO 503-725-5269 phone
Refresher Radiation Safety Training Scott Jaqua, RSO 1 Section 1 Introduction 2 RSO Contact Information www.pdx.edu/environmental-health-safety Look for Research Safety Scott Jaqua, RSO 503-725-5269 phone
Chapter. Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 01 Chapter 22 Slide 2 Chapter 22 Slide 3 Alpha Decay: Loss of an α-particle (a helium nucleus) 4 2 He 238 92 U 234 4 U He 90 + 2 Chapter 22 Slide 4 Beta Decay:
Chapter Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 01 Chapter 22 Slide 2 Chapter 22 Slide 3 Alpha Decay: Loss of an α-particle (a helium nucleus) 4 2 He 238 92 U 234 4 U He 90 + 2 Chapter 22 Slide 4 Beta Decay:
UALR Radiation Safety Office
 UALR Radiation Safety Office ETAS-329 501-569 8210 Graduate Institute of Technology University of Arkansas at Little Rock Regulatory Authority Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) EPA, DoE, DoT, OSHA Agreement
UALR Radiation Safety Office ETAS-329 501-569 8210 Graduate Institute of Technology University of Arkansas at Little Rock Regulatory Authority Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) EPA, DoE, DoT, OSHA Agreement
Ch05. Radiation. Energy and matter that comes from the nucleus of an atom. version 1.6
 Ch05 Radiation Energy and matter that comes from the nucleus of an atom. version 1.6 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Ch05 Radiation The Discovery of Radioactivity Phosphorescence Radioactive history Antoine
Ch05 Radiation Energy and matter that comes from the nucleus of an atom. version 1.6 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Ch05 Radiation The Discovery of Radioactivity Phosphorescence Radioactive history Antoine
Number of protons. 2. What is the nuclear symbol for a radioactive isotope of copper with a mass number of 60? A) Cu
 Chapter 5 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Problems 1. Fill in the missing information in the chart: Medical Use Atomic Mass symbol number Heart imaging 201 Tl 81 Number of protons Number of neutrons Abdominal
Chapter 5 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Problems 1. Fill in the missing information in the chart: Medical Use Atomic Mass symbol number Heart imaging 201 Tl 81 Number of protons Number of neutrons Abdominal
Portable Radiation Survey Instruments
 Published on UC Davis Safety Services (https://safetyservices.ucdavis.edu) Portable Radiation Survey Instruments GUIDELINES FOR BASIC INSTRUMENT CARE Portable radiation survey instruments, often called
Published on UC Davis Safety Services (https://safetyservices.ucdavis.edu) Portable Radiation Survey Instruments GUIDELINES FOR BASIC INSTRUMENT CARE Portable radiation survey instruments, often called
Nuclear forces and Radioactivity. Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom
 Nuclear forces and Radioactivity Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom Forces act in opposing directions Electrostatic repulsion: pushes protons apart Strong nuclear force: pulls protons
Nuclear forces and Radioactivity Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom Forces act in opposing directions Electrostatic repulsion: pushes protons apart Strong nuclear force: pulls protons
11/23/2014 RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS. Units of Radioactivity
 CHAPTER 4 RADIATION UNITS RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS 1 Units of Radioactivity 2 1 Radiation Units There are specific units for the amount of radiation you receive in a given time and for the total
CHAPTER 4 RADIATION UNITS RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS 1 Units of Radioactivity 2 1 Radiation Units There are specific units for the amount of radiation you receive in a given time and for the total
Chapter 29. Nuclear Physics
 Chapter 29 Nuclear Physics Ernest Rutherford 1871 1937 Discovery that atoms could be broken apart Studied radioactivity Nobel prize in 1908 Some Properties of Nuclei All nuclei are composed of protons
Chapter 29 Nuclear Physics Ernest Rutherford 1871 1937 Discovery that atoms could be broken apart Studied radioactivity Nobel prize in 1908 Some Properties of Nuclei All nuclei are composed of protons
Chapter 21. Preview. Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear Reactions
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear Reactions Section 1 The Nucleus Lesson Starter Nuclear reactions result in much larger energy
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear Reactions Section 1 The Nucleus Lesson Starter Nuclear reactions result in much larger energy
TEXAS STATE UNIVERSITY SAN MARCOS RADIATION SAFETY RAD MAT HANDLER TRAINING
 TEXAS STATE UNIVERSITY SAN MARCOS RADIATION SAFETY Table of Contents RADIATION SAFETY I. INTRODUCTION... 1 A. Non-ionizing radiation...1 B. Ionizing Radiation...1 II. OBJECTIVES... 3 III. SOURCES OF RADIATION...
TEXAS STATE UNIVERSITY SAN MARCOS RADIATION SAFETY Table of Contents RADIATION SAFETY I. INTRODUCTION... 1 A. Non-ionizing radiation...1 B. Ionizing Radiation...1 II. OBJECTIVES... 3 III. SOURCES OF RADIATION...
Radiation Detection. 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program.
 Radiation Detection 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org GM Detectors 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 1 A closer look 15 th Annual OSC Readiness
Radiation Detection 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org GM Detectors 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 1 A closer look 15 th Annual OSC Readiness
Become Aware: Preparation for a Radiological Terrorism Event Ionizing Radiation and Its Biological and Human Health Effects
 Become Aware: Preparation for a Radiological Terrorism Event Ionizing Radiation and Its Biological and Human Health Effects The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio November 12, 2002
Become Aware: Preparation for a Radiological Terrorism Event Ionizing Radiation and Its Biological and Human Health Effects The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio November 12, 2002
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity
 Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain why the evidence from the scattering experiment
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain why the evidence from the scattering experiment
Radiation Safety Training for General Radiation Workers
 Radiation Safety Training for General Radiation Workers Walter Shmayda LLE Radiation Safety Officer University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 1 Summary The sources and effects of radiation
Radiation Safety Training for General Radiation Workers Walter Shmayda LLE Radiation Safety Officer University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 1 Summary The sources and effects of radiation
Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure
 Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure No. Question Answer 1 What did scientists think about atoms before the discovery of the They were tiny spheres that could not be broken up electron? 2 Which
Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure No. Question Answer 1 What did scientists think about atoms before the discovery of the They were tiny spheres that could not be broken up electron? 2 Which
Radiation Safety Training
 Radiation Safety Training Radioactivity is the property of certain nuclides to spontaneously emit particles and/or waves (photons) These nuclides are called radionuclides, radioisotopes, or just isotopes
Radiation Safety Training Radioactivity is the property of certain nuclides to spontaneously emit particles and/or waves (photons) These nuclides are called radionuclides, radioisotopes, or just isotopes
6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics Chapter 6.2 Radioactivity From IB OCC, prepared by J. Domingues based on Tsokos Physics book Warm Up Define: nucleon atomic number mass number isotope. Radioactivity In 1896,
6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics Chapter 6.2 Radioactivity From IB OCC, prepared by J. Domingues based on Tsokos Physics book Warm Up Define: nucleon atomic number mass number isotope. Radioactivity In 1896,
Radiation: What it is and what it does
 Radiation: What it is and what it does Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, Ph.D. Associate Chair of Nuclear Engineering at Idaho State University with joint appointment at Idaho National Laboratory Candace C. Davison,
Radiation: What it is and what it does Mary Lou Dunzik-Gougar, Ph.D. Associate Chair of Nuclear Engineering at Idaho State University with joint appointment at Idaho National Laboratory Candace C. Davison,
((Radiation )) أيهمدغيم. Ionizing RadiationNon-ionizing radiation. This is the last sheet for Dr. Madi s lectures & its number is ((22)).
 ((Radiation )) This is the last sheet for Dr. Madi s lectures & its number is ((22)). This sheet contains (Slides and recording).. So I did my best to let you not refer to slides. First of all, there is
((Radiation )) This is the last sheet for Dr. Madi s lectures & its number is ((22)). This sheet contains (Slides and recording).. So I did my best to let you not refer to slides. First of all, there is
Radiation Awareness Training. Stephen Price Office of Research Safety
 Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
University of Victoria Radiation Safety Refresher Course
 University of Victoria Radiation Safety Refresher Course Catherine Franz Radiation Safety Officer Occupational Health, Safety & Environment Telephone: 721-8876 cfranz@uvic.ca Overview Welcome to the online
University of Victoria Radiation Safety Refresher Course Catherine Franz Radiation Safety Officer Occupational Health, Safety & Environment Telephone: 721-8876 cfranz@uvic.ca Overview Welcome to the online
11 Gamma Ray Energy and Absorption
 11 Gamma Ray Energy and Absorption Before starting this laboratory, we must review the physiological effects and the proper use of the radioactive samples you will be using during the experiment. Physiological
11 Gamma Ray Energy and Absorption Before starting this laboratory, we must review the physiological effects and the proper use of the radioactive samples you will be using during the experiment. Physiological
3 Radioactivity - Spontaneous Nuclear Processes
 3 Radioactivity - Spontaneous Nuclear Processes Becquerel was the first to detect radioactivity. In 1896 he was carrying out experiments with fluorescent salts (which contained uranium) and found that
3 Radioactivity - Spontaneous Nuclear Processes Becquerel was the first to detect radioactivity. In 1896 he was carrying out experiments with fluorescent salts (which contained uranium) and found that
Ch 17 Radioactivity & Nuc. Chemistry Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON
 Ch 17 Radioactivity & Nuc. Chemistry Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name No-Calculators Allowed /65 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Ch 17 Radioactivity & Nuc. Chemistry Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name No-Calculators Allowed /65 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Introduction to Ionizing Radiation
 Introduction to Ionizing Radiation Bob Curtis OSHA Salt Lake Technical Center Supplement to Lecture Outline V. 10.02 Basic Model of a Neutral Atom Electrons(-) orbiting nucleus of protons(+) and neutrons.
Introduction to Ionizing Radiation Bob Curtis OSHA Salt Lake Technical Center Supplement to Lecture Outline V. 10.02 Basic Model of a Neutral Atom Electrons(-) orbiting nucleus of protons(+) and neutrons.
Radiation Safety For Laboratory Workers
 Radiation Safety For Laboratory Workers Radiation Safety Program University Safety and Assurances University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee P.O. Box 413 Milwaukee, WI 53201 414-229-6339 January 2017 Table of Contents
Radiation Safety For Laboratory Workers Radiation Safety Program University Safety and Assurances University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee P.O. Box 413 Milwaukee, WI 53201 414-229-6339 January 2017 Table of Contents
College Physics B - PHY2054C
 College - PHY2054C Physics - Radioactivity 11/24/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Review Question 1 Isotopes of an element A have the same number of protons and electrons,
College - PHY2054C Physics - Radioactivity 11/24/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Review Question 1 Isotopes of an element A have the same number of protons and electrons,
Radiation Safety. PIXE PAN 2008 Ed Stech University of Notre Dame
 Radiation Safety PIXE PAN 2008 Ed Stech University of Notre Dame Outline Radiation Overview Radiation Safety in during PIXE PAN Other Safety Issues Ionizing Radiation 4 Types Alpha Beta Photon (Gamma and
Radiation Safety PIXE PAN 2008 Ed Stech University of Notre Dame Outline Radiation Overview Radiation Safety in during PIXE PAN Other Safety Issues Ionizing Radiation 4 Types Alpha Beta Photon (Gamma and
Module 1. An Introduction to Radiation
 Module 1 An Introduction to Radiation General Definition of Radiation Ionizing radiation, for example, X-rays, gamma-rays, α particles Ionizing radiation is capable of removing an electron from the atom
Module 1 An Introduction to Radiation General Definition of Radiation Ionizing radiation, for example, X-rays, gamma-rays, α particles Ionizing radiation is capable of removing an electron from the atom
The sources include Am-241 which emits alpha radiation, Sr-90 which emits beta radiation and Co-60 which emits gamma radiation.
 1 The physics department in a college has a number of radioactive sources which are used to demonstrate the properties of ionising radiations. The sources include Am-241 which emits alpha radiation, Sr-90
1 The physics department in a college has a number of radioactive sources which are used to demonstrate the properties of ionising radiations. The sources include Am-241 which emits alpha radiation, Sr-90
Gy can be used for any type of radiation. Gy does not describe the biological effects of the different radiations.
 Absorbed Dose Dose is a measure of the amount of energy from an ionizing radiation deposited in a mass of some material. SI unit used to measure absorbed dose is the gray (Gy). 1J 1 Gy kg Gy can be used
Absorbed Dose Dose is a measure of the amount of energy from an ionizing radiation deposited in a mass of some material. SI unit used to measure absorbed dose is the gray (Gy). 1J 1 Gy kg Gy can be used
VAMC BASIC RADIATION SAFETY TRAINING. Non-Medical Use of Radioactive Materials in Basic Sciences March 2011
 VAMC BASIC RADIATION SAFETY TRAINING Non-Medical Use of Radioactive Materials in Basic Sciences March 2011 The University of Iowa Radiation Safety Program 1 Course Credit To Obtain Credit for This Course:
VAMC BASIC RADIATION SAFETY TRAINING Non-Medical Use of Radioactive Materials in Basic Sciences March 2011 The University of Iowa Radiation Safety Program 1 Course Credit To Obtain Credit for This Course:
R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N a n d t h e N R C
 R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N and the NRC Radiation is all around us. It is naturally present in our environment and has been since before the birth of this planet. Radiation occurs in nature,
R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N and the NRC Radiation is all around us. It is naturally present in our environment and has been since before the birth of this planet. Radiation occurs in nature,
da u g ht er + radiation
 RADIOACTIVITY The discovery of radioactivity can be attributed to several scientists. Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895 and shortly after that Henri Becquerel observed radioactive behavior while
RADIOACTIVITY The discovery of radioactivity can be attributed to several scientists. Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895 and shortly after that Henri Becquerel observed radioactive behavior while
Waves & Radiation exam questions
 National 5 Physics Waves & Radiation exam questions these questions have been collated from previous Standard Grade (Credit) and Intermediate 2 exams Thurso High School 1. A mountain climber carries a
National 5 Physics Waves & Radiation exam questions these questions have been collated from previous Standard Grade (Credit) and Intermediate 2 exams Thurso High School 1. A mountain climber carries a
Section 3: Nuclear Radiation Today
 : Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
: Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
Radioactivity. Ernest Rutherford, A New Zealand physicist proved in the early 1900s a new model of the atom.
 Radioactivity In 1896 Henri Becquerel on developing some photographic plates he found that the uranium emitted radiation. Becquerel had discovered radioactivity. Models of the Atom Ernest Rutherford, A
Radioactivity In 1896 Henri Becquerel on developing some photographic plates he found that the uranium emitted radiation. Becquerel had discovered radioactivity. Models of the Atom Ernest Rutherford, A
Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions o-o-o- 3.6 Radiation
 Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions 2000-2010 -o-o-o- 3.6 Radiation 2000 Q29 Radium (Ra) decays to radon (Rn) by the emission of an alpha particle. Some energy is also released by this decay. The decay
Higher -o-o-o- Past Paper questions 2000-2010 -o-o-o- 3.6 Radiation 2000 Q29 Radium (Ra) decays to radon (Rn) by the emission of an alpha particle. Some energy is also released by this decay. The decay
