PI Chemistry - PI 24 ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING - RADIOLOGICAL EMISSIONS
|
|
|
- Edward Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemistry - PI 24 ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING - RADIOLOGICAL EMISSIONS Objectives: L In your own words define or describe the term "Derived Emission Limit". This description should centre on: ( i ) (ii ) ( iii) Types of releases, eg, controlled or failure. Pathways to man. Basis for limits, ie, dose received by the critical group. 2. State that the monitored radiological emissions fall in the following categories: (a) Airborne - Tritium - Noble Gases - Iodine-I3l - Particulate. ( b) Liquid - Tritium - gross B, y. and that the NGD target is 1% of the DEL in each case. 3. Given access to suitable data (reference #2), prepare a worksheet showing the DEL for each of the items for objective #2 above, for the station to which the trainee has been deployed. Note the target and. performance and briefly discuss any highlights or abnormalities. June
2 Ref.erences: 1. Basis for the Derived Limits for the Release of Radionuelides in Gaseous and Liquid Effluents from Ontario Hydro's Nuclear Stations. K.W. Wong, H.P.D August NCD Annual Environmental Summary, 1980 (or current); Environmental Protection Section, RMEP. 3. Provided as a text for this module is a summary of reference #1 prepared by Health and Safety Division. Here's What To Do: 1. Peruse the references paying particular attention to the station to which you have been deployed. 2. Do the practice exercises on worksheet *1. results with a colleage. Check your 3 Fill in the data plus comments on worksheet #2 for station to which you have been deployed. (If not played to a station, choose Pickering or Bruce). plain this worksheet to the course manager and have initial the sheet. the de Exhim - 2 -
3 DERIVED EMISSION LIMITS 1. Introduction The operation of a nuclear power station may resuit in small amounts of radioactive materials, in the form of activation and fission products, being dispersed to the environment. The Atomic Energy Control Board prescribes, in the operating license of a station, maximum limits for the radioactivity that may be released in the station effluents. In practice, the very small doses from nuclear plants are barely measurable, so the regulations are translated into derived emission limits (DEL's) for specific radionuclides. The quantities of radionuclides released must be monitared to ensure that they remain within these limits. This lesson summarizes the basis for the derived limits for the release of radionuclides in gaseous and liquid effluents. These Derived Emission Limits (DEL 's) apply to the total release resulting from controlled short-term releases; and from short-term releases resulting from failures of process equipment. The emission limits are derived from the maximum radiation doses permitted to members of the public as recommended by the International Commission on Radiological Protection. For gaseous emissions, the limits are such that if the release were continued for the whole year, the dose received by someone spending the full year at the station boundary would not exceed the dose limit. Any circumstances which could concentrate the radioactive material or increase the dose are taken into account. The limits for liquid effluents are based on a person not only drinking the undiluted effluent, but also eating 18 kilograms of fish raised in the effluent. Fish and other edible aquatic life can concentrate radionuclides, so this is taken into account in deriving emission limits. 2. Dose Limits the are The annual dose limits public, comply with the summarized in Table 1. for individual members of regulations of the AECB, - 3 -
4 TABLE 1 Dose Limits for Members of the Public Organ Whole Body Gonads Red-bone marrow Annual Dose Limit 0.5 rem Skin, bone 3.0 rem Thyroid 3.0 rem (Adults) 1.5 rem (Children up to 16 years) Other single organs 1. 5 rem Extremities 7.5 rem The AECB further limits the population dose by stipulating the following population dose limits: 10 4 man-rems per year to whole body man-rems per year to thyroid. The integration area extends over all areas, outside the exclusion area, in which individual dose exceeds 1% of the individual dose at the boundary. The population density around a given site ano local meteorological conditions determine whether the population dose or dose to the individual is limit~ng. If dose to the population is found to be limiting, permissible individual doses at the station boundary will be reduced proportionately to ensure that the AECB population dose limits are not exceeded
5 3. Pathways to Man Radioactivity released into the environment may lead to external exposure of the public or internal exposure via food chains and through direct inhalation. These pathways are summarized in Figure 1. GASEOUS EHLUE~TS LIQUID EfFLUENTS DEPOSITION tmgestion (FOODSI ~~~~~ ~~~~~ 't. '.. -/.'.J:~C..,,--,-, " INGEST'ON Figure 1 Pathways to Man The radionuclides released in the gaseous are tritium, radioiodines, noble gases and lates. The various pathways from the stack to effluent particuman are: Tritium There is no known mechanism whereby tritiated water can be significantly concentrated in the biosphere; the important routes of entry into the human bony for this radionuclide from airborne releases are inhalation and absorption thc')'lcjh the skin. A continuous airborn8 concentration (MPC a ) 10-7 Ci/m3 at the station boundary would give a residing there a \I"hole body dose of 500 mrem per of 3 x person year. - 5 ~
6 A combination of factors makes the Atmosphere -+ Pasture -+ Cow -+ Milk -+ Man chain the most important food chain leading to internal exposure. Milk is the major component of diet for the infant, whose small organ masses cause him to receive doses significantly higher than that to an adult. The most important radionuclides transmitted through food chains from airborne releases are generally considered to be and Sr-90 with being the dominant cause of radiation exposure. These radionuclides are rapidly transmitted to milk, and dairy cattle may graze over large areas of contaminated pasture land. If other food chains are operative, the resulting doses are considerably lower. Maximum permissible radionuclides in air over assuming the pathway to be + Milk + Child. concentrations for these pasture land are derived Atmosphere + Pasture + Cow Radionuclide I-131 Sr-90 MPCICi/m3 ) 6 x x Unidentified Particulate* 1. 5 x *the IOWE?st MPC val ue for "particulates II is used for unidentified particulate. Noble Gases Fission product noble gases consist of isotopes of xenon and krypton. Ar-41 is produced by neutron activation of Ar-40 in air. Noble gases are considered external whole body irradiators (from the gamma). Using the semi-infinite cloud approximation, the dose rate is given by DR = 0.25 EC rem/sec 11 ) where C is the air concentration in Ci/rn3 and E is the effective gamma energy per disintegration. Some of the important noble gas rac'lionuclic'les are summarized on the following Table
7 TABLE 2 Radionuclide Half-Life E(MeV) Ar-41 Kr-88 (Rb-88) Xe-133 Xe-138 (Cs-138) h 2.8 h (17.8 min) 5.27 d 17.5 min (32.2 min) The external immersion dose delivered by noble gases is determined by the energy released per unit volume, ie, E. The unit Ci-MeV is a measure of the effective gamma energy and hence the maximum permissible air concentrations are quoted in terms of Ci-Mev/m3 body tion The maximum permissible is 0.5 rem/year or 1.6 x ( 1 ) : dose rate for 10-8 rem/sec. the From whole equa- MPC = 1.6 x = 6.4 x 10-8 Ci-MeV m3 ( 2 ) 4. Dispersion of Airborne Activity The dilution of gaseous emissions by the atmosphere is given by the relationship: C = KQ ( 3 ) where Q is the stack release rate (Ci/sec), C is the concentration at the point of interest (Ci/m3 ), and K, the dilution factor (sec/m3 ), is a function of the distance from the stack, the effective height of release, the weather, and the averaging time, ie, the time over which it is Pleasured. 5. Derived Emission Limits for Airborne Activity The permissible continuous emission rate' for a single radionllclide is: Values for MPCa were given earlier, K for various effective stack heights have been established. ( 4 ) - 7 -
8 Maximum permissible daily intakes are calculated directly from the permissible limits and the dosimetric data for the various radionuclides. TABLE 3 Radionuclide MPDI MPCw x x 10-7 H x 10-3 Sr-90 8.B x x 10-7 Maximum permissible concentrations in drinking water (MPC w) are given by: MPCw = MPDI "D-=a-'i'17y~W;Ca"tOCe:Cro-ITn=t7a"k-=e ( 6 ) The daily water intake for the adult and the infant are 2200 IIll and 800 ml respectively. The effects of radionuclide concentration in fish are described by the biological concentration factor, b. b = llci/g fish ljci/ml water (7) The average daily fish consumption for the adult is taken at 50 grams. Radionuclide intake from fish consumption by the adult is equivalent to drinking an additional 50 x b ml of contaminated water a day. The maximum permissible concentrations in fresh water which supports fish life, MPCfw' are given by: MPCfw = MPDI 50 b ( 8 ) - 8 -
9 TABLE 4 Radionuclide H-3 Sr-90 MPCfw 3 x 10-7 * 5.5 x 10-3 * 3 x 10-7 *Critical group for and H-3 is the infant; critical pathway is drinking water. 10. Derived Emission Limits for Liquid Effluents The average radionuclide concentrations in the station effluent must not exceed the MPDfw'so The period of averaging is one month. Since liquid wastes are discharged into the condenser cooling water, permissible ~onthly releases are given by: Total Activity Released into cow in 1 month < MPCfw (9) ccw Flow in 1 Month 11. Releases of Several Radionuclides; MPCfw for Gross-Beta Gamma Activity Constraints similar to equation 5 will be used if necessary to limit the releases of several radionuelides in liquid effluents so that the dose limit for any giv~n organ is not exceeded. In practice, since detailed radiochemical analysis of the liquid effluent is seldom performed, the MPCfw for the most restrictive radionuclide (Sr-90), 3 x 10-/ ~Ci/ml, is used for gross beta-gamma activity 12. Exposure from Combined Gaseous and Liquid Emissions Although permissible emission levels have been set separately for gaseous and for liquid releases, the possibility of combined exposure from these two release routes cannot be excluded. That the dose limit for any organ is not exceeded is generally accomplished if equation (10) is not violated for any group of N radionuclides which irradiate a common critical organ
10 N Lt = 1 Q; QiUM +Li = N 1 (Liquid Effluent Concentration) i (MPCCw) i ~ Actual Emissions The emiss ion limits are derived from dose permitted to a practice, Ontario member of the Hydro works general to less hundredth of this. the maximum public. In than one- Since releases of radioactivity can easily be limi ted to less than 1 % of the DELlsit is reasonable to ask whether the official AECB standards should be tightened. This suggestion is rejected by the AECB on the grounds that it is unnecessary and would undermine the international uniformity of standards. P.O. Dodgson
11 WORKSHEET #l 1. Define or describe IIDerived Emission Limit". 2. List the categories or i terns for which there are radiological DEL's
12 WORKSHEET #2 Station: Reference Year: CATEGORY DEL TARGET PERFORMANCE Airborne Tritium Noble Gases Particulates Liquid Tritium gross B,y Highlights or Abnormalities: Date: Course Manager:
Regulatory Guide Exposure Pathways, Equations, and Input Requirements
 Regulatory Guide 1.109 Exposure Pathways, Equations, and Input Requirements Ken Sejkora Entergy Nuclear Northeast Pilgrim Station Presented at the 23rd Annual RETS-REMP Workshop Training Session Westminster,
Regulatory Guide 1.109 Exposure Pathways, Equations, and Input Requirements Ken Sejkora Entergy Nuclear Northeast Pilgrim Station Presented at the 23rd Annual RETS-REMP Workshop Training Session Westminster,
SOUTHERN NUCLEAR COMPANY VOGTLE ELECTRIC GENERATING PLANT UNITS 1 AND 2 NRC DOCKET NOS AND
 SOUTHERN NUCLEAR COMPANY VOGTLE ELECTRIC GENERATING PLANT UNITS 1 AND 2 NRC DOCKET NOS. 50-424 AND 50-425 FACILITY OPERATING LICENSE NOS. NPF-68 AND NPF-81 ANNUAL RADIOACTIVE EFFLUENT RELEASE REPORT FOR
SOUTHERN NUCLEAR COMPANY VOGTLE ELECTRIC GENERATING PLANT UNITS 1 AND 2 NRC DOCKET NOS. 50-424 AND 50-425 FACILITY OPERATING LICENSE NOS. NPF-68 AND NPF-81 ANNUAL RADIOACTIVE EFFLUENT RELEASE REPORT FOR
O R D E R OF THE HEAD OF THE STATE NUCLEAR POWER SAFETY INSPECTORATE
 O R D E R OF THE HEAD OF THE STATE NUCLEAR POWER SAFETY INSPECTORATE ON THE APPROVAL OF NUCLEAR SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BSR-1.9.1-2011 STANDARDS OF RELEASE OF RADIONUCLIDES FROM NUCLEAR INSTALLATIONS AND REQUIREMENTS
O R D E R OF THE HEAD OF THE STATE NUCLEAR POWER SAFETY INSPECTORATE ON THE APPROVAL OF NUCLEAR SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BSR-1.9.1-2011 STANDARDS OF RELEASE OF RADIONUCLIDES FROM NUCLEAR INSTALLATIONS AND REQUIREMENTS
IAEA-TECDOC Clearance
 IAEA-TECDOC-1000 Clearance The IAEA does The originating Section of this publication in the IAEA was: Waste Safety Section International Atomic Energy Agency Wagramerstrasse FOREWORD It has long been recognized
IAEA-TECDOC-1000 Clearance The IAEA does The originating Section of this publication in the IAEA was: Waste Safety Section International Atomic Energy Agency Wagramerstrasse FOREWORD It has long been recognized
HALF LIFE. NJSP HMRU June 10, Student Handout CBRNE AWARENESS Module 4 1. Objectives. Student will
 June 10, 2004 Radiological/Nuclear Overview 1 Student will demonstrate a knowledge of self protection techniques identify types of radiation and their associated hazards demonstrate a knowledge of terminology
June 10, 2004 Radiological/Nuclear Overview 1 Student will demonstrate a knowledge of self protection techniques identify types of radiation and their associated hazards demonstrate a knowledge of terminology
Estimation of accidental environmental release based on containment measurements
 Estimation of accidental environmental release based on containment measurements Péter Szántó, Sándor Deme, Edit Láng, Istvan Németh, Tamás Pázmándi Hungarian Academy of Sciences Centre for Energy Research,
Estimation of accidental environmental release based on containment measurements Péter Szántó, Sándor Deme, Edit Láng, Istvan Németh, Tamás Pázmándi Hungarian Academy of Sciences Centre for Energy Research,
WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION
 WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION Margarita Saraví National Atomic Energy Commission - Argentina Workshop on Ionizing Radiation SIM Buenos Aires 10 November 2011 What is ionizing radiation? What is ionizing radiation?
WHAT IS IONIZING RADIATION Margarita Saraví National Atomic Energy Commission - Argentina Workshop on Ionizing Radiation SIM Buenos Aires 10 November 2011 What is ionizing radiation? What is ionizing radiation?
Radionuclides in food and water. Dr. Ljudmila Benedik
 Radionuclides in food and water Dr. Ljudmila Benedik ISO-FOOD WP 3 and WP4 WP 3 Research and education P1 Food authenticity P2 Translation of regional isotopic and elemental signatures from natural environment
Radionuclides in food and water Dr. Ljudmila Benedik ISO-FOOD WP 3 and WP4 WP 3 Research and education P1 Food authenticity P2 Translation of regional isotopic and elemental signatures from natural environment
RADIATION PROTECTION
 DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR TECHNOLOGY, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING CHULALONGKORN UNIVERSITY PHAYATHAI ROAD, BANGKOK 10330, THAILAND TEL: (662) 218-6772, (662) 218-6784. FAX: (662) 218-6770 E-mail: fnegbr@eng.chula.ac.th
DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR TECHNOLOGY, FACULTY OF ENGINEERING CHULALONGKORN UNIVERSITY PHAYATHAI ROAD, BANGKOK 10330, THAILAND TEL: (662) 218-6772, (662) 218-6784. FAX: (662) 218-6770 E-mail: fnegbr@eng.chula.ac.th
Tritium Dose Pathway Comparison Regulatory Guide and Beyond
 Tritium Dose Pathway Comparison Regulatory Guide 1.109 and Beyond Ken Sejkora Entergy Nuclear Northeast Pilgrim Station Presented at the 15 th Annual RETS-REMP Workshop Wilmington, NC / 27-29 June 2005
Tritium Dose Pathway Comparison Regulatory Guide 1.109 and Beyond Ken Sejkora Entergy Nuclear Northeast Pilgrim Station Presented at the 15 th Annual RETS-REMP Workshop Wilmington, NC / 27-29 June 2005
Department of Energy Office of Worker Protection Programs and Hazards Management Radiological Control Technical Position RCTP 99-02
 Issue: Title 10 Code of Federal Regulations, Part 835 (10 CFR 835), Occupational Radiation Protection, specifies occupational radiation protection requirements for Department of Energy (DOE) activities
Issue: Title 10 Code of Federal Regulations, Part 835 (10 CFR 835), Occupational Radiation Protection, specifies occupational radiation protection requirements for Department of Energy (DOE) activities
ESTIMATION OF RADIONUCLIDE RELEASES IN ATMOSPHERE FROM CERNAVODA NPP BASED ON CONTINUOUS GASEOUS EFFLUENT MONITORING
 International Conference Nuclear Energy in Central Europe 2001 Hoteli Bernardin, Portorož, Slovenia, September 10-13, 2001 www: http://www.drustvo-js.si/port2001/ e-mail: PORT2001@ijs.si tel.:+ 386 1 588
International Conference Nuclear Energy in Central Europe 2001 Hoteli Bernardin, Portorož, Slovenia, September 10-13, 2001 www: http://www.drustvo-js.si/port2001/ e-mail: PORT2001@ijs.si tel.:+ 386 1 588
11. Radioactive Waste Management AP1000 Design Control Document
 CHAPTER 11 RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT 11.1 Source Terms This section addresses the sources of radioactivity that are treated by the liquid and gaseous radwaste systems. Radioactive materials are generated
CHAPTER 11 RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT 11.1 Source Terms This section addresses the sources of radioactivity that are treated by the liquid and gaseous radwaste systems. Radioactive materials are generated
User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of
 Version 1.1 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 Florian Gering, Heinz Müller USER
Version 1.1 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 Florian Gering, Heinz Müller USER
2016 No. 410 (W. 128) WATER, ENGLAND AND WALES. The Water Supply (Water Quality) (Amendment) Regulations 2016
 W E L S H S T A T U T O R Y I N S T R U M E N T S 2016 No. 410 (W. 128) WATER, ENGLAND AND WALES The Water Supply (Water Quality) (Amendment) Regulations 2016 Made - - - - 21 March 2016 Laid before Parliament
W E L S H S T A T U T O R Y I N S T R U M E N T S 2016 No. 410 (W. 128) WATER, ENGLAND AND WALES The Water Supply (Water Quality) (Amendment) Regulations 2016 Made - - - - 21 March 2016 Laid before Parliament
AP1000 European 15. Accident Analyses Design Control Document EVALUATION MODELS AND PARAMETERS FOR ANALYSIS OF RADIOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF ACCIDENTS
 APPENDIX 15A EVALUATION MODELS AND PARAMETERS FOR ANALYSIS OF RADIOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF ACCIDENTS This appendix contains the parameters and models that form the basis of the radiological consequences
APPENDIX 15A EVALUATION MODELS AND PARAMETERS FOR ANALYSIS OF RADIOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF ACCIDENTS This appendix contains the parameters and models that form the basis of the radiological consequences
AP1000 European 11. Radioactive Waste Management Design Control Document
 CHAPTER 11 RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT 11.1 Source Terms This section addresses the sources of radioactivity that are treated by the liquid and gaseous radwaste systems. Radioactive materials are generated
CHAPTER 11 RADIOACTIVE WASTE MANAGEMENT 11.1 Source Terms This section addresses the sources of radioactivity that are treated by the liquid and gaseous radwaste systems. Radioactive materials are generated
Active concentration for material not requiring radiological regulation
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB27742-2011 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net Wayne Zheng et al. ICS 17. 240 F 70 GB National Standard of the People s Republic of China Active
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB27742-2011 www.chinesestandard.net Sales@ChineseStandard.net Wayne Zheng et al. ICS 17. 240 F 70 GB National Standard of the People s Republic of China Active
External Dosimetry at NPPs; NVLAP, Noble Gas, and TEDE
 External Dosimetry at NPPs; NVLAP, Noble Gas, and TEDE Joseph L Danek - CHP 2018 Fall Meeting FLORIDA CHAPTER HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY 1 Part 1 National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP)
External Dosimetry at NPPs; NVLAP, Noble Gas, and TEDE Joseph L Danek - CHP 2018 Fall Meeting FLORIDA CHAPTER HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY 1 Part 1 National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP)
Radioactive effluent releases from Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant (1) - Gaseous effluent -
 Radioactive effluent releases from Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant (1) - Gaseous effluent - K.Anzai, S.Keta, M.Kano *, N.Ishihara, T.Moriyama, Y.Okamura K.Ogaki, K.Noda a a Reprocessing Business Division,
Radioactive effluent releases from Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant (1) - Gaseous effluent - K.Anzai, S.Keta, M.Kano *, N.Ishihara, T.Moriyama, Y.Okamura K.Ogaki, K.Noda a a Reprocessing Business Division,
Gy can be used for any type of radiation. Gy does not describe the biological effects of the different radiations.
 Absorbed Dose Dose is a measure of the amount of energy from an ionizing radiation deposited in a mass of some material. SI unit used to measure absorbed dose is the gray (Gy). 1J 1 Gy kg Gy can be used
Absorbed Dose Dose is a measure of the amount of energy from an ionizing radiation deposited in a mass of some material. SI unit used to measure absorbed dose is the gray (Gy). 1J 1 Gy kg Gy can be used
Glossary of Terms* BIOASSAY: Assay and measurement procedures used to determine the amount of radioactive material in a biological system.
 Glossary of Terms* *With permission from the Manual of Policies and Procedures for Radiation Protection, for the University of Minnesota, Department of Environmental Health and Safety, Radiation Protection
Glossary of Terms* *With permission from the Manual of Policies and Procedures for Radiation Protection, for the University of Minnesota, Department of Environmental Health and Safety, Radiation Protection
RADIATION MONITORING NETWORKS and some results from the reactor accident in Fukushima
 RADIATION MONITORING NETWORKS and some results from the reactor accident in Fukushima Sixth Annual Workshop on Radiation Measurement Cross Calibration Project June 13-15, 2011 Middle East Scientific Institute
RADIATION MONITORING NETWORKS and some results from the reactor accident in Fukushima Sixth Annual Workshop on Radiation Measurement Cross Calibration Project June 13-15, 2011 Middle East Scientific Institute
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy
 RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
Nuclear Chemistry. Chapter 23
 Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 23 n/p too large beta decay X Y n/p too small positron decay or electron capture Nuclear Stability Certain numbers of neutrons and protons are extra stable n or p = 2, 8, 20,
Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 23 n/p too large beta decay X Y n/p too small positron decay or electron capture Nuclear Stability Certain numbers of neutrons and protons are extra stable n or p = 2, 8, 20,
Tritium The French situation
 資料 3 (No.3) Tritium The French situation Jean-Luc LACHAUME Deputy Director General ASN 9 April 2014 Tokyo Tritium 1 Content The regulation of the discharges of tritium from nuclear facilities in France
資料 3 (No.3) Tritium The French situation Jean-Luc LACHAUME Deputy Director General ASN 9 April 2014 Tokyo Tritium 1 Content The regulation of the discharges of tritium from nuclear facilities in France
Radiation Safety Basic Terms
 Radiation Safety Basic Terms Radiation Radiation is energy in transit in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves. We encounter electromagnetic waves every day. They make up our visible
Radiation Safety Basic Terms Radiation Radiation is energy in transit in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves. We encounter electromagnetic waves every day. They make up our visible
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm 1 Lightning
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm 1 Lightning
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lightning Review Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lightning Review Lecture 19 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear Reactions Medical Applications Radiation Detectors Chapter 29 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
INTERNAL RADIATION DOSIMETRY
 INTERNAL RADIATION DOSIMETRY Introduction to Internal Dosimetry Importance of External and Internal Exposures by Radiation Type Charged particle radiation (α, p, β) Generally important only for internal
INTERNAL RADIATION DOSIMETRY Introduction to Internal Dosimetry Importance of External and Internal Exposures by Radiation Type Charged particle radiation (α, p, β) Generally important only for internal
BASIC OF RADIATION; ORIGIN AND UNITS
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243 - LECTURE 2 BASIC OF RADIATION; ORIGIN AND UNITS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243 - LECTURE 2 BASIC OF RADIATION; ORIGIN AND UNITS DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam
RADIATION SAFETY. Working Safely with Radiation
 RADIATION SAFETY Working Safely with Radiation 12 NOV 2015 Dr. Raed Felimban Department of Transfusion Medicine King Abdul-Aziz University E-mail: felimbanr@yahoo.com KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY How most
RADIATION SAFETY Working Safely with Radiation 12 NOV 2015 Dr. Raed Felimban Department of Transfusion Medicine King Abdul-Aziz University E-mail: felimbanr@yahoo.com KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY How most
Radiation Fundamentals. Radiation Safety Training Module 1
 Radiation Fundamentals Module 1 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the process of unstable (or radioactive) atoms becoming stable. This is done by emitting radiation. This process over a period of time is
Radiation Fundamentals Module 1 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the process of unstable (or radioactive) atoms becoming stable. This is done by emitting radiation. This process over a period of time is
AP1000 European 15. Accident Analyses Design Control Document
 15.7 Radioactive Release from a Subsystem or Component This group of events includes the following: Gas waste management system leak or failure Liquid waste management system leak or failure (atmospheric
15.7 Radioactive Release from a Subsystem or Component This group of events includes the following: Gas waste management system leak or failure Liquid waste management system leak or failure (atmospheric
12 Moderator And Moderator System
 12 Moderator And Moderator System 12.1 Introduction Nuclear fuel produces heat by fission. In the fission process, fissile atoms split after absorbing slow neutrons. This releases fast neutrons and generates
12 Moderator And Moderator System 12.1 Introduction Nuclear fuel produces heat by fission. In the fission process, fissile atoms split after absorbing slow neutrons. This releases fast neutrons and generates
Number of protons. 2. What is the nuclear symbol for a radioactive isotope of copper with a mass number of 60? A) Cu
 Chapter 5 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Problems 1. Fill in the missing information in the chart: Medical Use Atomic Mass symbol number Heart imaging 201 Tl 81 Number of protons Number of neutrons Abdominal
Chapter 5 Nuclear Chemistry Practice Problems 1. Fill in the missing information in the chart: Medical Use Atomic Mass symbol number Heart imaging 201 Tl 81 Number of protons Number of neutrons Abdominal
10 CFR 50 Appendix I Time for a Change?
 10 CFR 50 Appendix I Time for a Change? RETS-REMP Workshop Savannah, GA 25-Jun-2014 By Richard Conatser, NRC Background NRC regulations use: ICRP-2 Recommendations, 1959 (Appendix I) ICRP-26 Recommendations,
10 CFR 50 Appendix I Time for a Change? RETS-REMP Workshop Savannah, GA 25-Jun-2014 By Richard Conatser, NRC Background NRC regulations use: ICRP-2 Recommendations, 1959 (Appendix I) ICRP-26 Recommendations,
Tritium Environmental Assessment for Fusion Reactor Using TAS3.0
 Tritium Environmental Assessment for Fusion Reactor Using TAS3.0 Baojie Nie, Muyi Ni, Minghuang Wang, Jing Song Contributed by FDS Team Key laboratory of Neutronics and Radiation Safety Institute of Nuclear
Tritium Environmental Assessment for Fusion Reactor Using TAS3.0 Baojie Nie, Muyi Ni, Minghuang Wang, Jing Song Contributed by FDS Team Key laboratory of Neutronics and Radiation Safety Institute of Nuclear
Fission is the process by which energy is released in the nuclear reactor. Figure 1. Figure 2
 Q1.Electricity is generated in a nuclear power station. Fission is the process by which energy is released in the nuclear reactor. (a) Figure 1 shows the first part of the nuclear fission reaction. Complete
Q1.Electricity is generated in a nuclear power station. Fission is the process by which energy is released in the nuclear reactor. (a) Figure 1 shows the first part of the nuclear fission reaction. Complete
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy
 RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
COURSE NAME: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES FOR ALL COURSES PAPER TITLE: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES
 COURSE NAME: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES FOR ALL COURSES PAPER TITLE: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES UNIT: 5 ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION TOPIC : CAUSES, EFFECTS AND CONTROL MEASURES
COURSE NAME: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES FOR ALL COURSES PAPER TITLE: ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES FOR UNDERGRADUATES UNIT: 5 ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION TOPIC : CAUSES, EFFECTS AND CONTROL MEASURES
(2) (1) Describe how beta radiation is produced by a radioactive isotope (1) (Total 4 marks)
 1 (a) (i) Describe the structure of alpha particles. (ii) What are beta particles? (b) Describe how beta radiation is produced by a radioactive isotope....... (Total 4 marks) Page 1 of 25 2 Atoms are very
1 (a) (i) Describe the structure of alpha particles. (ii) What are beta particles? (b) Describe how beta radiation is produced by a radioactive isotope....... (Total 4 marks) Page 1 of 25 2 Atoms are very
STUDIES ON THE AEROSOL RADIOACTIVITY LEVEL AND AIR QUALITY AROUND NUCLEAR RESEARCH INSTITUTE AREA
 STUDIES ON THE AEROSOL RADIOACTIVITY LEVEL AND AIR QUALITY AROUND NUCLEAR RESEARCH INSTITUTE AREA A. STOCHIOIU 1, F. MIHAI 1, C. STOCHIOIU 2 1 Horia Hulubei National Institute for Physics and Nuclear Engineering,
STUDIES ON THE AEROSOL RADIOACTIVITY LEVEL AND AIR QUALITY AROUND NUCLEAR RESEARCH INSTITUTE AREA A. STOCHIOIU 1, F. MIHAI 1, C. STOCHIOIU 2 1 Horia Hulubei National Institute for Physics and Nuclear Engineering,
Storing, using and disposing of unsealed radioactive substances in a Type C Laboratory: Extract of regulatory requirements
 Storing, using disposing of unsealed radioactive substances in a Type C Laboratory: Extract of regulatory requirements Radiation Protection Control (Ionising Radiation) Regulations 2000 Requirements for
Storing, using disposing of unsealed radioactive substances in a Type C Laboratory: Extract of regulatory requirements Radiation Protection Control (Ionising Radiation) Regulations 2000 Requirements for
Radiation Emergencies -Preparing for Response-
 Radiation Emergencies -Preparing for Response- Tribal Lands Forum San Diego, CA August 25, 2010 Tom Clawson US Department of Energy Transportation Emergency Preparedness Program 1 Radiological Training
Radiation Emergencies -Preparing for Response- Tribal Lands Forum San Diego, CA August 25, 2010 Tom Clawson US Department of Energy Transportation Emergency Preparedness Program 1 Radiological Training
APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
 Former NAVWPNSTA Concord, Inland Area APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 This page intentionally left blank. Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
Former NAVWPNSTA Concord, Inland Area APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 This page intentionally left blank. Draft ECSD-3211-0005-0004 08/2009 APPENDIX A RADIATION OVERVIEW
Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e -
 Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. radiation a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e - This can destroy the delicate balance of chemical reactions in living cells. The
Interaction of the radiation with a molecule knocks an electron from the molecule. radiation a. Molecule ¾ ¾ ¾ ion + e - This can destroy the delicate balance of chemical reactions in living cells. The
11/23/2014 RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS. Units of Radioactivity
 CHAPTER 4 RADIATION UNITS RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS 1 Units of Radioactivity 2 1 Radiation Units There are specific units for the amount of radiation you receive in a given time and for the total
CHAPTER 4 RADIATION UNITS RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS 1 Units of Radioactivity 2 1 Radiation Units There are specific units for the amount of radiation you receive in a given time and for the total
A Nuclear Power Plant
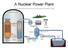 A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
UNCORRECTED PROOF. Table of Contents
 00-Stabin-Prelims SNY001-Stabin (Typeset by spi publisher services, Delhi) vii of xvi June 1, 2007 17:15 Preface xiii Acknowledgments xv Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of Health
00-Stabin-Prelims SNY001-Stabin (Typeset by spi publisher services, Delhi) vii of xvi June 1, 2007 17:15 Preface xiii Acknowledgments xv Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of Health
Six decades of environmental radioactivity measurements. Sven P. Nielsen
 Six decades of environmental radioactivity measurements Sven P. Nielsen Research Establishment Risø Established by Government in 1950 s to keep Denmark in line with development of nuclear technology including
Six decades of environmental radioactivity measurements Sven P. Nielsen Research Establishment Risø Established by Government in 1950 s to keep Denmark in line with development of nuclear technology including
Tritium in Drinking Water: Science, Regulation and Society
 Tritium in Drinking Water: Science, Regulation and Society TAM-E: Environmental Section Special Session: Tritium in the Environment Presented To: 57th Annual Meeting of the Health Physics Society Sacramento
Tritium in Drinking Water: Science, Regulation and Society TAM-E: Environmental Section Special Session: Tritium in the Environment Presented To: 57th Annual Meeting of the Health Physics Society Sacramento
Review A Z. a particle. proton. neutron. electron e -1. positron. e +1. Mass Number Atomic Number. Element Symbol
 Nuclear Chemistry 1 Review Atomic number (Z) = number of protons in nucleus Mass number (A) = number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic number (Z) + number of neutrons Mass Number Atomic Number A
Nuclear Chemistry 1 Review Atomic number (Z) = number of protons in nucleus Mass number (A) = number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic number (Z) + number of neutrons Mass Number Atomic Number A
Meteorological Data Collection, X/Q and D/Q, Critical Receptors
 Meteorological Data Collection, X/Q and D/Q, Critical Receptors Ken Sejkora Entergy Nuclear Northeast Pilgrim Station Presented at the 23rd Annual RETS-REMP Workshop Training Session Westminster, CO /
Meteorological Data Collection, X/Q and D/Q, Critical Receptors Ken Sejkora Entergy Nuclear Northeast Pilgrim Station Presented at the 23rd Annual RETS-REMP Workshop Training Session Westminster, CO /
sample What happens when we are exposed to radiation? 1.1 Natural radiation Cosmic radiation
 1.1 Natural radiation 3 1 What happens when we are exposed to radiation? 1.1 Natural radiation For as long as humans have walked the earth, we have continually been exposed to naturally-occurring radiation.
1.1 Natural radiation 3 1 What happens when we are exposed to radiation? 1.1 Natural radiation For as long as humans have walked the earth, we have continually been exposed to naturally-occurring radiation.
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment
 Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
Industrial Hygiene: Assessment and Control of the Occupational Environment Main Topics Air Pollution Control Analytical Methods Ergonomics Gas and Vapour Sampling General Practice Heat and Cold Stress
Michael G. Stabin. Radiation Protection and Dosimetry. An Introduction to Health Physics. 4) Springer
 Michael G. Stabin Radiation Protection and Dosimetry An Introduction to Health Physics 4) Springer Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgments Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of
Michael G. Stabin Radiation Protection and Dosimetry An Introduction to Health Physics 4) Springer Table of Contents Preface Acknowledgments Chapter 1. Introduction to Health Physics 1 1.1 Definition of
The sources include Am-241 which emits alpha radiation, Sr-90 which emits beta radiation and Co-60 which emits gamma radiation.
 1 The physics department in a college has a number of radioactive sources which are used to demonstrate the properties of ionising radiations. The sources include Am-241 which emits alpha radiation, Sr-90
1 The physics department in a college has a number of radioactive sources which are used to demonstrate the properties of ionising radiations. The sources include Am-241 which emits alpha radiation, Sr-90
U (superscript is mass number, subscript atomic number) - radionuclides nuclei that are radioactive - radioisotopes atoms containing radionuclides
 Chapter : Nuclear Chemistry. Radioactivity nucleons neutron and proton all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, atomic number isotopes atoms with the same atomic number but different
Chapter : Nuclear Chemistry. Radioactivity nucleons neutron and proton all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, atomic number isotopes atoms with the same atomic number but different
SLOVENIAN ALARM AND MONITORING NETWORKS
 SLOVENIAN ALARM AND MONITORING NETWORKS Jasmina Kožar Logar, Denis Glavič-Cindro "Jožef Stefan" Institute,, Slovenia CHERNOBYL 25 YEARS LATER: STUDIES, REMARKS AND RECENT FINDINGS June 21-22-23, 2011 UDINE
SLOVENIAN ALARM AND MONITORING NETWORKS Jasmina Kožar Logar, Denis Glavič-Cindro "Jožef Stefan" Institute,, Slovenia CHERNOBYL 25 YEARS LATER: STUDIES, REMARKS AND RECENT FINDINGS June 21-22-23, 2011 UDINE
European Fallout from Chernobyl
 European Fallout from Chernobyl Fukushima Reactors: before & after earthquake and tsunami Fukushima reactors 3 & 4 (picture released by Tokyo Electric Power Company) Fukushima Reactor 1 A view inside one
European Fallout from Chernobyl Fukushima Reactors: before & after earthquake and tsunami Fukushima reactors 3 & 4 (picture released by Tokyo Electric Power Company) Fukushima Reactor 1 A view inside one
Radiation Response and Removals: Getting Down to the Nitty Gritty. 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program
 Radiation Response and Removals: Getting Down to the Nitty Gritty 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 0 Radiation Fundamentals Tony Honnellio Health Physicist U.S. EPA, Region
Radiation Response and Removals: Getting Down to the Nitty Gritty 15 th Annual OSC Readiness Training Program www.oscreadiness.org 0 Radiation Fundamentals Tony Honnellio Health Physicist U.S. EPA, Region
ICONE DRAFT - EVALUATION OF THE CONSERVATISM OF NPP SAFETY ANALYSIS DOSE CALCULATIONS AS TYPICAL FOR LICENSING PURPOSES
 Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering ICONE18 May 17-21, 21, Xi'an, China ICONE18-29465 DRAFT - EVALUATION OF THE CONSERVATISM OF NPP SAFETY ANALYSIS DOSE CALCULATIONS
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering ICONE18 May 17-21, 21, Xi'an, China ICONE18-29465 DRAFT - EVALUATION OF THE CONSERVATISM OF NPP SAFETY ANALYSIS DOSE CALCULATIONS
Safety Standards. of the Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (KTA) Monitoring the Discharge of Radioactive Substances from Research Reactors
 Safety Standards of the Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (KTA) KTA 1507 (2017-11) Monitoring the Discharge of Radioactive Substances from Research Reactors (Überwachung der Ableitungen radioaktiver
Safety Standards of the Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (KTA) KTA 1507 (2017-11) Monitoring the Discharge of Radioactive Substances from Research Reactors (Überwachung der Ableitungen radioaktiver
Chapter. Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 01 Chapter 22 Slide 2 Chapter 22 Slide 3 Alpha Decay: Loss of an α-particle (a helium nucleus) 4 2 He 238 92 U 234 4 U He 90 + 2 Chapter 22 Slide 4 Beta Decay:
Chapter Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 01 Chapter 22 Slide 2 Chapter 22 Slide 3 Alpha Decay: Loss of an α-particle (a helium nucleus) 4 2 He 238 92 U 234 4 U He 90 + 2 Chapter 22 Slide 4 Beta Decay:
Safety Information and Specific Handling Precautions for Radionuclides H-3, C-14, S-35, P-32 and I-125
 Yale Environmental Health & Safety 135 College Street, Suite 100 New Haven, CT 06510-2483 T 203 785-3550 F 203 785-7588 www.yale.edu/ehs Safety Information and Specific Handling Precautions for Radionuclides
Yale Environmental Health & Safety 135 College Street, Suite 100 New Haven, CT 06510-2483 T 203 785-3550 F 203 785-7588 www.yale.edu/ehs Safety Information and Specific Handling Precautions for Radionuclides
Radiation Glossary. Radioactive material dispersed in the air in the form of dusts, fumes, particulates, mists, vapors, or gases.
 Activity The rate of disintegration (transformation) or decay of radioactive material. The units of activity are Curie (Ci) and the Becquerel (Bq). Agreement State Any state with which the U.S. Nuclear
Activity The rate of disintegration (transformation) or decay of radioactive material. The units of activity are Curie (Ci) and the Becquerel (Bq). Agreement State Any state with which the U.S. Nuclear
IEC Tritium Standard
 detect and identify IEC 62303 Tritium Standard Dr. Alfred Klett Berthold Technologies, Bad Wildbad, Germany 21 st Annual Air Monitoring Users Group (AMUG) Meeting Palace Station Hotel, Las Vegas, Nevada,
detect and identify IEC 62303 Tritium Standard Dr. Alfred Klett Berthold Technologies, Bad Wildbad, Germany 21 st Annual Air Monitoring Users Group (AMUG) Meeting Palace Station Hotel, Las Vegas, Nevada,
Ch. 18 Problems, Selected solutions. Sections 18.1
 Sections 8. 8. (I) How many ion pairs are created in a Geiger counter by a 5.4-MeV alpha particle if 80% of its energy goes to create ion pairs and 30 ev (average in gases) is required per ion pair? Notice
Sections 8. 8. (I) How many ion pairs are created in a Geiger counter by a 5.4-MeV alpha particle if 80% of its energy goes to create ion pairs and 30 ev (average in gases) is required per ion pair? Notice
Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain
 Version 1.0 Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Florian Gering, Stephan
Version 1.0 Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Florian Gering, Stephan
Chapter 18. Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
METHOD TEST METHODS FOR MEASURING RADIONUCLIDE EMISSION FROM STATIONARY SOURCES
 METHOD 114 - TEST METHODS FOR MEASURING RADIONUCLIDE EMISSION FROM STATIONARY SOURCES 1. Purpose and Background. This method provides the requirements for: (1) Stack monitoring and sample collection methods
METHOD 114 - TEST METHODS FOR MEASURING RADIONUCLIDE EMISSION FROM STATIONARY SOURCES 1. Purpose and Background. This method provides the requirements for: (1) Stack monitoring and sample collection methods
Unit 08 Nuclear Structure. Unit 08 Nuclear Structure Slide 1
 Unit 08 Nuclear Structure Unit 08 Nuclear Structure Slide 1 The Plan Nuclear Structure Nuclear Decays Measuring Radiation Nuclear Power Plants Major Nuclear Power Accidents New Possibilities for Nuclear
Unit 08 Nuclear Structure Unit 08 Nuclear Structure Slide 1 The Plan Nuclear Structure Nuclear Decays Measuring Radiation Nuclear Power Plants Major Nuclear Power Accidents New Possibilities for Nuclear
Modeling the Physical Processes that Impact the Fate and Fallout of Radioactive Materials
 Modeling the Physical Processes that Impact the Fate and Fallout of Radioactive Materials J.V. Ramsdell, Jr. Radiological Science and Engineering Group Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington
Modeling the Physical Processes that Impact the Fate and Fallout of Radioactive Materials J.V. Ramsdell, Jr. Radiological Science and Engineering Group Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Richland, Washington
Understanding Radiation
 APPENDIX B Understanding Radiation This section introduces the general reader to some basic concepts of radioactivity and an understanding of the radiation emitted as radioactive materials decay to a stable
APPENDIX B Understanding Radiation This section introduces the general reader to some basic concepts of radioactivity and an understanding of the radiation emitted as radioactive materials decay to a stable
Radiation Basics. Rad Training for Clinical Laboratories. Key Points. What are 3 types of Ionizing particles/waves we are concerned with???
 1 Rad Training for Clinical Laboratories Jesse Fillmore Minnesota Department of Health PHLD, nvironmental Health RSO/RP Coordinator May 23, 2011 Key Points Radiation protection Laboratory Safety Purpose
1 Rad Training for Clinical Laboratories Jesse Fillmore Minnesota Department of Health PHLD, nvironmental Health RSO/RP Coordinator May 23, 2011 Key Points Radiation protection Laboratory Safety Purpose
Fundamentals of radiation protection
 Fundamentals of radiation protection Kamel ABBAS European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute for Transuranium Elements, Nuclear Security Unit Via E. Fermi, 2749, I-21027 Ispra, Italy tel. +39-0332-785673,
Fundamentals of radiation protection Kamel ABBAS European Commission, Joint Research Centre Institute for Transuranium Elements, Nuclear Security Unit Via E. Fermi, 2749, I-21027 Ispra, Italy tel. +39-0332-785673,
Karlsruhe Chart of the Nuclides Nuclear Data. Zsolt Sóti Institute for Transuranium Elements - Karlsruhe Joint Research Centre
 Karlsruhe Chart of the Nuclides Nuclear Data Zsolt Sóti Institute for Transuranium Elements - Karlsruhe Joint Research Centre Overview Nuclide Charts Karlsruhe Chart of Nuclides Electronic Nuclide Charts
Karlsruhe Chart of the Nuclides Nuclear Data Zsolt Sóti Institute for Transuranium Elements - Karlsruhe Joint Research Centre Overview Nuclide Charts Karlsruhe Chart of Nuclides Electronic Nuclide Charts
College Physics B - PHY2054C
 College - PHY2054C Physics - Radioactivity 11/24/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Review Question 1 Isotopes of an element A have the same number of protons and electrons,
College - PHY2054C Physics - Radioactivity 11/24/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Review Question 1 Isotopes of an element A have the same number of protons and electrons,
Douglas Millican Chief Executive Scottish Water Castle House 6 Castle Drive DUNFERMLINE KY11 8GG Our Reference: 9 January 2014
 Drinking Water Quality Regulator for Scotland T: 0131 244 0224 F: 0131 244 0743 E: regulator@dwqr.org.uk www.dwqr.org.uk Douglas Millican Chief Executive Scottish Water Castle House 6 Castle Drive DUNFERMLINE
Drinking Water Quality Regulator for Scotland T: 0131 244 0224 F: 0131 244 0743 E: regulator@dwqr.org.uk www.dwqr.org.uk Douglas Millican Chief Executive Scottish Water Castle House 6 Castle Drive DUNFERMLINE
Organ and effective dose rate coefficients for submersion exposure in occupational settings
 Radiat Environ Biophys (2017) 56:453 462 DOI 10.1007/s00411-017-0705-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Organ and effective dose rate coefficients for submersion exposure in occupational settings K. G. Veinot 1,2 S. A.
Radiat Environ Biophys (2017) 56:453 462 DOI 10.1007/s00411-017-0705-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Organ and effective dose rate coefficients for submersion exposure in occupational settings K. G. Veinot 1,2 S. A.
Tritium Releases and Dose Consequences in Canada in 2006
 Canada s Nuclear Regulator Tritium Releases and Dose Consequences in Canada in 2006 Part of the Tritium Studies Project INFO-0793 December 2009 Tritium Releases and Dose Consequences in Canada in 2006
Canada s Nuclear Regulator Tritium Releases and Dose Consequences in Canada in 2006 Part of the Tritium Studies Project INFO-0793 December 2009 Tritium Releases and Dose Consequences in Canada in 2006
Radiation Dose Limits. Radiation Safety Training Module 3
 Module 3 This module will address Western Kentucky University radiation dose limits. Basis for WKU limits Kentucky Administrative Regulations, specifically 902 KAR 100:019 Overview Module 3, Page 2 Annual
Module 3 This module will address Western Kentucky University radiation dose limits. Basis for WKU limits Kentucky Administrative Regulations, specifically 902 KAR 100:019 Overview Module 3, Page 2 Annual
DISMANTLEMENT OF AN UNIT OF METABOLIC TREATMENTS WITH IODINE 131
 DISMANTLEMENT OF AN UNIT OF METABOLIC TREATMENTS WITH IODINE 131 Autores: J.M. Jiménez 1, A.R. Cortés 2, P.Alcorta 2 E-mail: jmjimenez@hsan.osakidetza.net 1 Unidad de Radiofísica. Hospital Santiago Apóstol,
DISMANTLEMENT OF AN UNIT OF METABOLIC TREATMENTS WITH IODINE 131 Autores: J.M. Jiménez 1, A.R. Cortés 2, P.Alcorta 2 E-mail: jmjimenez@hsan.osakidetza.net 1 Unidad de Radiofísica. Hospital Santiago Apóstol,
Study of ratio of tritium concentration in plants water to tritium concentration in air moisture for chronic atmospheric release of tritium
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 5 (2011) 2421 2425 IACEED2010 Study of ratio of tritium concentration in plants water to tritium concentration in air moisture for chronic atmospheric
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 5 (2011) 2421 2425 IACEED2010 Study of ratio of tritium concentration in plants water to tritium concentration in air moisture for chronic atmospheric
IONIZING RADIATION: SOURCES AND BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS
 IONIZING RADIATION: SOURCES AND BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation 1982 Report to the General Assembly, with annexes UNITED NATIONS New York, 1982
IONIZING RADIATION: SOURCES AND BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation 1982 Report to the General Assembly, with annexes UNITED NATIONS New York, 1982
There are no stable isotopes of elements above atomic number 83.
 Nuclear Chemistry Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. All
Nuclear Chemistry Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. All
The Nature of Radioactivity. Chapter 19 Nuclear Chemistry. The Nature of Radioactivity. Nuclear Reactions. Radioactive Series
 John W. Moore Conrad L. Stanitsi Peter C. Jurs http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/moore Chapter 9 Nuclear Chemistry Stephen C. Foster Mississippi State University The Nature of Radioactivity Henri Becquerel
John W. Moore Conrad L. Stanitsi Peter C. Jurs http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/moore Chapter 9 Nuclear Chemistry Stephen C. Foster Mississippi State University The Nature of Radioactivity Henri Becquerel
Nuclear Chemistry. Background Radiation. Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation.
 Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry Background Radiation Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation. Most of the remaining one-fourth comes from medical irradiation such as X-rays.
Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry Background Radiation Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation. Most of the remaining one-fourth comes from medical irradiation such as X-rays.
Measurements and Dispersion Calculations by the Deutscher Wetterdienst Regarding the Release of Radionuclides at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant
 Measurements and Dispersion Calculations by the Deutscher Wetterdienst Regarding the Release of Radionuclides at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant T. Steinkopff, J. Barth, A. Dalheimer, A. Ehlers,
Measurements and Dispersion Calculations by the Deutscher Wetterdienst Regarding the Release of Radionuclides at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant T. Steinkopff, J. Barth, A. Dalheimer, A. Ehlers,
THE ENVIRONMENTAL RADIATION ANALYSIS ON THE RESIDENTIAL AREA AROUND NUCLEAR POWER PLANTS
 Proceedings of the 2013 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering ICONE21 July 29 - August 2, 2013, Chengdu, China ICONE21-16111 THE ENVIRONMENTAL RADIATION ANALYSIS ON THE RESIDENTIAL AREA
Proceedings of the 2013 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering ICONE21 July 29 - August 2, 2013, Chengdu, China ICONE21-16111 THE ENVIRONMENTAL RADIATION ANALYSIS ON THE RESIDENTIAL AREA
WM 00 Conference, February 27 - March 2, 2000, Tucson, AZ EFFECTS OF SPENT FUEL TYPES ON OFFSITE CONSEQUENCES OF HYPOTHETICAL ACCIDENTS 1
 ABSTRACT EFFECTS OF SPENT FUEL TYPES ON OFFSITE CONSEQUENCES OF HYPOTHETICAL ACCIDENTS 1 J.C. Courtney, C.C. Dwight, and M.A. Lehto Argonne National Laboratory P.O. Box 2528 Idaho Falls, ID 83403-2528
ABSTRACT EFFECTS OF SPENT FUEL TYPES ON OFFSITE CONSEQUENCES OF HYPOTHETICAL ACCIDENTS 1 J.C. Courtney, C.C. Dwight, and M.A. Lehto Argonne National Laboratory P.O. Box 2528 Idaho Falls, ID 83403-2528
OVERVIEW OF THE TRITIUM-IN-AIR MONITORING SYSTEM OF CERNAVODA NPP U1 ROMANIA MODERNIZATION AND IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
 International Conference Nuclear Energy in Central Europe 2001 Hoteli Bernardin, Portorož, Slovenia, September 10-13, 2001 www: http://www.drustvo-js.si/port2001/ e-mail: PORT2001@ijs.si tel.:+ 386 1 588
International Conference Nuclear Energy in Central Europe 2001 Hoteli Bernardin, Portorož, Slovenia, September 10-13, 2001 www: http://www.drustvo-js.si/port2001/ e-mail: PORT2001@ijs.si tel.:+ 386 1 588
RADIOACTIVITY & HALF-LIFE Part 2
 RADIOACTIVITY & HALF-LIFE Part 2 Radioactivity Radioactivity: Results from radioactive decay, which is the process whereby unstable atomic nuclei transform and emit radiation. Has existed longer than the
RADIOACTIVITY & HALF-LIFE Part 2 Radioactivity Radioactivity: Results from radioactive decay, which is the process whereby unstable atomic nuclei transform and emit radiation. Has existed longer than the
SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY
 Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Dosimetry. Sanja Dolanski Babić May, 2018.
 Dosimetry Sanja Dolanski Babić May, 2018. What s the difference between radiation and radioactivity? Radiation - the process of emitting energy as waves or particles, and the radiated energy Radioactivity
Dosimetry Sanja Dolanski Babić May, 2018. What s the difference between radiation and radioactivity? Radiation - the process of emitting energy as waves or particles, and the radiated energy Radioactivity
Radiation Terminology
 Radiation Terminology This section discusses the terms and concepts which are necessary for a meaningful discussion of radiation, its sources, and its risks. USNRC Technical Training Center 5-1 0703 Energy
Radiation Terminology This section discusses the terms and concepts which are necessary for a meaningful discussion of radiation, its sources, and its risks. USNRC Technical Training Center 5-1 0703 Energy
Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects
 Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects Reading Assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610) Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual
Radiation Safety Training Session 1: Radiation Protection Fundamentals and Biological Effects Reading Assignment: LLE Radiological Controls Manual (LLEINST 6610) Part 1 UR Radiation Safety Training Manual
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY teacher version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY teacher version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
Sensitivity Analysis of a Dynamic Food Chain Model DYNACON Considering Korean Agricultural Conditions
 Sensitivity Analysis of a Dynamic Food Chain Model DYNACON Considering Korean Agricultural Conditions W. T. Hwang 1, G. C. Lee 1, K. S. Suh 1, E. H. Kim 1, Y. G. Choi 1, M. H. Han 1 and G.S. Cho 2 1 Korea
Sensitivity Analysis of a Dynamic Food Chain Model DYNACON Considering Korean Agricultural Conditions W. T. Hwang 1, G. C. Lee 1, K. S. Suh 1, E. H. Kim 1, Y. G. Choi 1, M. H. Han 1 and G.S. Cho 2 1 Korea
