SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Allison Nelson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The effect of particle proximity on the oxygen reduction rate of size-selected platinum clusters Markus Nesselberger 1, Melanie Roefzaad 1, R. Fayçal Hamou 2, P. Ulrich Biedermann 2, Florian F. Schweinberger 3, Sebastian Kunz 3, Katrin Schloegl 1, Gustav K.H. Wiberg 1, Sean Ashton 1, Ueli Heiz 3, Karl J.J. Mayrhofer 2, Matthias Arenz 1 * 1 Department of Chemistry, University of Copenhagen, Universitetsparken 5, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø Denmark 2 Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH, Max-Planck-Straße 1, D Düsseldorf, Germany 3 Lehrstuhl für Physikalische Chemie, Zentralinstitut für Katalyseforschung, Technische Universität München, Lichtenbergstr. 4, D Garching, Germany Corresponding author: m.arenz@chem.ku.dk I: Effect of the EDL potential distribution on the ORR In order to demonstrate the effect of the EDL structure and potential distribution on the specific activity (SA) of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), it is important to scrutinize the effect of additional parameters governing the structure of the EDL (in comparison to the EDL overlap effect). Therefore the effect of the electrolyte concentration, which determines the potential drop at the compact and the diffuse layers, is investigated and its influence on the specific activity of a flat platinum surface is analysed. The impact of the ion concentration on the potential drop within the EDL compact layer has been discussed, modelled, and compared to the experimentally determined specific ORR activity of a polycrystalline platinum sample. Furthermore, the NATURE MATERIALS 1
2 existence of a causality between the variation of the potential drop within the compact layer and the enhancement of the ORR specific activity is discussed. The variation of the potential at the electrical double layer (EDL) compact layer due to the EDLs overlap effect was extensively investigated in the last century. Verwey and Overbeek 1 demonstrated the increase of the potential at the compact layer V c with decreasing the distance between identical interacting flat double layers. The authors stated that the increase of V c depends on the Debye length and the specific adsorption potential of counter-ions. Later, Usui 2 has extended the investigation to dissimilar interacting flat EDLs in which he reported similar observations. Only recently the concept of EDL overlap effect has been applied in electrocatalytic investigations. In studies concerning the structural effect of nanoporous electrodes on electrocatalytic reactions, it has been shown that an enhanced electrocatalytic activity observed on nanoporous Pt cannot simply be explained by a mere enhancement of the surface area 3. Other factors must play an additional role. This conclusion was verified by the fact that a significant enhancement in electrocatalytic activity remained even after normalizing the electrochemical redox behaviour of O 2 and H 2 O 2 to the surface area of the nanoporous Pt. In a more recent study, the authors highlighted the overlap of the EDL in the nano-confined space as additional contribution of the electrocatalytic performance 4. The importance of the EDL potential distribution inside the pores was discussed in terms of pore and ions size, volume exclusion effects, ionic concentration and dielectric permittivity inside the pores 4. Furthermore, a strong correlation between the adsorption of hydrogen and oxygen on platinum surface and the potential difference at the EDL was demonstrated by early works of Frumkin 5. Beside the existence of a well-defined connection between the adsorption fraction coverage and the electrode potential, i.e., the Frumkin isotherm, it was found that the adsorption of hydrogen and oxygen atoms contribute to setting up of a potential difference at the platinum/solution interface. This was explained by the fact that adsorbed hydrogen 2 NATURE MATERIALS
3 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION and oxygen atoms form dipoles with the metal surface, thus influencing the potential difference at the compact layer 6. Therefore, due to the existing interrelation between the adsorption coverage and the potential at the reaction plane, we propose that a substantial alteration of the potential at the compact layer has a direct effect on the adsorbate coverage, and thus on the ORR activity. In our present communication, we related the enhancement of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) specific activity to the alteration of the EDL potential distribution due to the overlap effect. The experimental results show a clear enhancement of the ORR activity when the interparticle distance decreases. Considering that each nanoparticle is surrounded by an EDL, it is obvious that the EDLs overlap for separating distances below the EDL Debye length, and thus an alteration of the EDLs potential distribution occurs. The local change of the EDL potential, in the nano-confined region between the NCs, is not limited to the EDL diffuse part but also affects the potential at the compact layer V c, i.e., the EDL reaction plane. Consequently, the potential difference ΔV=E- V c (E: electrode potential) shifts within the EDL compact layer, which defines the EDL capacitance, specific adsorption and favours or hinders faradaic reactions occurring at the reaction plane. In particular, the coverage of adsorbed species and the potential drop ΔV are interrelated, as demonstrated e.g. by Frumkin (see above). As the adsorbate coverage defines the potential at the compact layer we hypothesized that a change of this potential, by means of the EDL overlap effect or by modifying the EDL structure (e.g. ionic strength), would affect the coverage, and thus the ORR activity. As mentioned earlier we investigated the EDL structure and its influence to the compact layer potential to emphasize the validity of the model. In order to compare experimental measurements with results of modelling the potential drop in the compact layer, we determined the ORR activity of polycrystalline Pt as a function of the electrolyte concentration of a perchloric acid electrolyte. These results are then compared with the modelled potential drop in the compact layer of a flat surface. NATURE MATERIALS 3
4 It is a well-known concept that increasing or decreasing the electrolyte concentration leads to a change of the counter-ion concentration at the compact layer, and thus to a shift of ΔV. Equivalently, the decrease of the electrolyte concentration shifts ΔV to lower values, and thus higher ORR activities would be expected. In order to experimentally determine these effects, it is of utmost importance to carefully design and perform the experiments in order to eliminate all disturbing effects, which can occur in low and high concentrated electrolytes. The ORR activity has been determined for polycrystalline platinum sample and all measurements in the different electrolyte concentrations were performed in a row using the same working electrode. The working electrode was a polycrystalline platinum disc (ø5mm, MaTecK) encapsulated in a PTFE cylinder. It was mirror polished prior to the experiments. The measurements were conducted with a careful analog compensation of the solution resistance 7. A saturated Calomel electrode and a platinum wire were used as reference and counter electrodes, respectively. The electrolyte concentrations used in the this study were 0.05M, 0.1M, 0.2M, 0.3M and 0.4M HClO 4. The specific activity of the ORR was measured as described previously 8. The reversible hydrogen potential of each electrolyte was carefully measured for each electrolyte prior to the measurement in order to employ exactly the same upper and lower potential limits in the measurements. To rule out an influence of the electrolyte conductivity on the reduction current, for each measurement the solution resistance was compensated to the same residual value of 2Ω. The results of the measurements were confirmed three times (on different days) in freshly prepared electrolyte solutions using two different perchloric acids (Merck, Suprapure and AnalR, Normapur ). 4 NATURE MATERIALS
5 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1: Polarization curves and Tafel plot. A) Polarization curves recorded in oxygen saturated perchloric acid electrolyte of different concentrations; the scan speed was 100mVs-1, the rotation speed 1600rpm. B) Extracted kinetic currents of A) presented in a Tafel Plot. An increase in ORR activity towards lower concentrations is clearly visible. Figure S1 summarizes the experimental results for a representative measurement series in different perchloric acid solutions ranging from 0.05M to 0.4M in concentration. Figure S1 A) shows the capacitive background corrected anodic sweeps. With increasing electrolyte concentration, the half wave potential clearly shifts to lower values. The corresponding Tafel plots are presented in FigureS1 B). The Tafel plots are parallel to each other, exhibiting an identical shape from the kinetic region towards the beginning of the diffusion limited potential region (U~0.8V vs. RHE). This shows that in all measurements the electrolyte resistance is exactly the same (2Ω) and differences in conductivity could be completely eliminated by the positive feedback scheme of the home build potentiostat; thus demonstrating the high quality of the measurements. NATURE MATERIALS 5
6 Figure S2: Experimentally determined, normalized ORR specific activities at 0.9VRHE (red open triangles) and the modelled potential at the compact layer (blue open circles) as function of electrolyte concentration. Figure S2 compares the results from the experiment and computational modelling. It can be clearly seen that the ORR activity and the potential at the compact layer are following the same trend when changing the electrolyte concentration. The calculated potential at the compact layer V c increased by about 35mV when decreasing the electrolyte concentration, corresponding to an increase of the specific activity by a factor of 2. By comparison, the calculated V c in the NCs model shows an increase of about 100mV (at the same potential applied to the electrode), which corresponds to an enhancement of the specific activity by a factor of 5. The different magnitudes of V c follow from the way how the compact layer potential is varied in the experiments. According to our model, in the NCs experiment the potential at the compact layer is varied by the polarization effect due to the EDL overlap at different interparticle distance. On the other hand, for the flat Pt 6 NATURE MATERIALS
7 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION electrode experiment, the potential at the compact layer is changed by variation of the electrolyte concentration. By using different procedures to vary the potential V c, we show in both experiments evidence of an interrelation between the EDL potential distribution and the ORR specific activity. However, other effects can also be involved in the observed enhancement of the ORR specific activity like electronic coupling, non-linearity and unusual structure of the solvent at the interface for small clusters and smaller separating distances. Our numerical simulation is based on a simple continuum approach. Various effects are simplified as the real shape of the NCs, the surface charge distribution and discreetness of charges at the interface, which would have an effect on the EDL structure. Nevertheless, the variation of the potential distribution at the compact layer with interparticle distance would remain even under a more accurate approach. We consider the model as a first step to a more refined model in future, which goes beyond the mean-field approach or electron transfer kinetics theory and would probably need an atomistic modelling that should include the EDL effect. This has never been done appropriately so far due to the complexity of the interface, but our experimental results indicate its implication for understanding electrocatalytic reactions. II: Finite element method The model presented in this study has been simulated using a commercial finite element method software package (COMSOL). The modified Poisson-Boltzmann (MPB) equation was implemented in the electrolyte domain above an electrode consisting of NCs distributed on a flat conducting support. A dense tetrahedral mesh was set at the boundaries of the flat electrode, the distributed NCs and the compact layers where a steeper potential gradient is expected. Moreover, we used the Booth equation, which is based on the Onsager and Kirkwood theories for polar dielectric solvent, to model the dependence of the dielectric permittivity on the electric field strength. This equation was implemented in the entire electrolyte domain including the NATURE MATERIALS 7
8 diffuse and the compact EDL regions. Due to the high non-linearity and the self-consistency of the equations, the solution with constant dielectric permittivity was used as a first guess. The water dipole interaction with the electric field in the EDL affects the potential distribution in the compact layer and hence the EDL potential profile. This effect is more pronounced when the EDLs are overlapping and their electric fields are interacting within a nano-gap separating the NCs. As the distance separating the NCs becomes smaller than the Debye length λ, the EDL electric field and the dielectric permittivity are affected. This dependence can be seen comparing Fig. S3a and b, which show the distribution of the electric field at the NC compact layer and the electric field lines in the nano-gap for two different separating distances. The EDLs overlap effect is reflected by the deviation of the electric field lines in the nano-gap emanating from opposite NCs as the edge to edge distance is decreased. As a consequence of the mutual interaction, the electric field at the compact layer is lowered in regions where the edge to edge is smaller. This leads to a local increase of the potential at the compact layer V c, thus decreasing ΔV. Moreover, the dielectric permittivity is significantly increased in regions at the compact layer edge where the electric field is lowered. Figure S3: Electric field distribution at the compact layer. Field lines are drawn in the region confined between two NCs for separating distance (a) d=2nm and (b) d=0.5nm. Note that for sake of clarity, the field stream lines are plotted only for the foreground NCs. 8 NATURE MATERIALS
9 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION III: Supplementary Experimental information Figure S4: Representative size distribution of Pt + clusters created by the laser ablation cluster source in the mass range of Pt 46 (8810 to 9150 amu). The integrated current during deposition is recorded while performing a slow mass scan with the QMS, thus revealing the current corresponding to a certain mass (black dots). Fitting tangents to the slopes of the peaks (orange), representing one single mass, the areas for absolute mass selectivity (green) can be determined by using the intersection with the x axis. For a selected deposition (here for Pt 46 ), the QMS is set to the mass value of the peak maximum (as indicated at 8970 amu) and consequently clusters with absolute control of size can be deposited. NATURE MATERIALS 9
10 Figure S5: Electrochemical roughness factor calculated from the integrated CO stripping charge vs. geometrical roughness. The geometrical roughness is calculated by adding up surface of clusters per cm² measured during deposition taking into account the contact face to the support. The data clearly show a linear relationship between the deposition measured and the electrochemically measured Pt surface area of the NCs. 10 NATURE MATERIALS
11 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S6: Determination of the number of absorbed hydrogen (H ads ) and carbon monoxide (CO ads ) atoms, respectively, per Pt 20 NC. The H ads is determined from the H upd charge in the CV, CO ads from CO stripping curves. Fitting a linear relation between the total number of adsorbed species and the cluster density we calculated N = 9 ± 1 for the number of adsorbed species per Pt 20 NC. This value corresponds to an ECSA of ~80 m 2 g Pt -1. For the Pt 46 and Pt >46 samples average values of ~110 m 2 g Pt -1 and ~95 m 2 g Pt -1, respectively, were obtained. For the Pt >46 samples the individual ECSA values varied more, as the deposition was done in the RF-only (ion guide) mode of the QMS, which acts as high-pass rather than a band-pass filter. NATURE MATERIALS 11
12 Figure S7: RDE polarization curves (1600 rpm) of the ORR. Different Pt NC samples are shown from which the activities of Figure 1 were calculated. Different diffusion limited currents are detected due to the different (geometric) coverage of the Pt NCs. As reference we included Pt poly. For the establishing the correct normalized activities Tafel plots were established. The ORR activity of the samples is determined with two normalizations. Normalized to surface area, i.e. SA, and normalized to Pt mass, i.e. MA. To obtain the SA the kinetic ORR current obtained in the RDE measurements is divided by the CO oxidation charge determined in CO stripping experiments after the ORR measurements assuming a charge CO oxidation charge of 400 μc cm Pt -2 for Pt. To obtain the MA, first the ECSA is calculated from the CO oxidation charge and the cluster deposition current assuming single charged clusters. Then the MA is calculated by the simple relation MA = SA * ECSA. Alternatively we calculated the MA from the absolute kinetic currents of the RDE measurements and the cluster deposition current, thus avoiding any influence of the surface area determination on the results. Both calculations let to the same (within the experimental error) values. 12 NATURE MATERIALS
13 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S8: Tafel plots of the ORR SA for the size selected Pt 20 NC series. It is seen that due to the small Pt surface area at low NC coverage an activity determination at 0.9V RHE is less reliable. Therefore for all samples the ORR activity was determined at 0.85V RHE. References for Supplementary Information 1 Verwey, E. J. W. & Overbeek, J. T. G. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids. (Elsevier, Amsterdam,, 1948). 2 Usui, S. VARIATION OF THE POTENTIAL OF THE STERN PLANE WITH INTERACTION OF DISSIMILAR FLAT ELECTRICAL DOUBLE-LAYERS. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 97, , doi: / (84)90290-x (1984). 3 Han, J. H., Lee, E., Park, S., Chang, R. & Chung, T. D. Effect of Nanoporous Structure on Enhanced Electrochemical Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, , doi: /jp909382b (2010). 4 Bae, J. H., Han, J.-H. & Chung, T. D. Electrochemistry at nanoporous interfaces: new opportunity for electrocatalysis. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 14, (2012). 5 Frumkin, A. THE DEPENDENCE OF THE DOUBLE LAYER STRUCTURE ON THE NATURE OF THE METAL SURFACE. J. Res. Inst. Catalysis 15, (1967). 6 Petry, O., Frumkin, A. & Kotlov, Y. THE DEPENDENCE OF THE SURFACE CHARGE OF PLATINUM ELECTRODES ON THE POTENTIAL IN ALKALINE SOLUTIONS. J. Res. Inst. Catalysis 16, (1968). 7 Wiberg, G. K. H. The development of a state-of-the-art experimental setup demonstrated by the investigation of fuel cell reactions in alkaline electrolyte, Technische Universität München, (2010). 8 Nesselberger, M. et al. The Particle Size Effect on the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity of Pt Catalysts: Influence of Electrolyte and Relation to Single Crystal Models. Journal of the American Chemical Society 133, , doi: /ja207016u (2011). NATURE MATERIALS 13
The particle size effect on the oxygen reduction reaction activity of Pt catalysts: Influence of electrolyte and relation to single crystal models
 The particle size effect on the oxygen reduction reaction activity of Pt catalysts: Influence of electrolyte and relation to single crystal models M. Nesselberger, S. Ashton, J.C. Meier, I. Katsounaros,
The particle size effect on the oxygen reduction reaction activity of Pt catalysts: Influence of electrolyte and relation to single crystal models M. Nesselberger, S. Ashton, J.C. Meier, I. Katsounaros,
VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER
 VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER 74 26. EIS Studies of Pb nanospheres Impedance (valid for both DC and AC), a complex resistance occurs when current flows through a circuit (composed of various resistors,
VI. EIS STUDIES LEAD NANOPOWDER 74 26. EIS Studies of Pb nanospheres Impedance (valid for both DC and AC), a complex resistance occurs when current flows through a circuit (composed of various resistors,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/NMAT3668 Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behavior during electrocatalysis Chunhua Cui 1, Lin Gan 1, Marc Heggen 2, Stefan Rudi 1 and Peter Strasser
DOI: 1.138/NMAT3668 Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behavior during electrocatalysis Chunhua Cui 1, Lin Gan 1, Marc Heggen 2, Stefan Rudi 1 and Peter Strasser
Supporting information: Stability limits of tin-based electrocatalyst supports. Max-Planck-Institut für Eisenforschung GmbH, Düsseldorf, Germany
 Supporting information: Stability limits of tin-based electrocatalyst supports Simon Geiger a,*, Olga Kasian a, Andrea M. Mingers a, Karl J. J. Mayrhofer a,b,c, Serhiy Cherevko a,b,* a Department of Interface
Supporting information: Stability limits of tin-based electrocatalyst supports Simon Geiger a,*, Olga Kasian a, Andrea M. Mingers a, Karl J. J. Mayrhofer a,b,c, Serhiy Cherevko a,b,* a Department of Interface
Screening Effects in Probing the Electric Double Layer by Scanning Electrochemical Potential Microscopy (SECPM)
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Screening Effects in Probing the Electric Double Layer by Scanning Electrochemical Potential Microscopy (SECPM) R. Fayçal Hamou MaxPlanckInstitut für Eisenforschung
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Screening Effects in Probing the Electric Double Layer by Scanning Electrochemical Potential Microscopy (SECPM) R. Fayçal Hamou MaxPlanckInstitut für Eisenforschung
Investigation of the oxygen reduction activity on Silver a rotating disk electrode study
 Investigation of the oxygen reduction activity on Silver a rotating disk electrode study Gustav K.H. Wiberg, Karl J.J. Mayrhofer, Matthias Arenz To cite this version: Gustav K.H. Wiberg, Karl J.J. Mayrhofer,
Investigation of the oxygen reduction activity on Silver a rotating disk electrode study Gustav K.H. Wiberg, Karl J.J. Mayrhofer, Matthias Arenz To cite this version: Gustav K.H. Wiberg, Karl J.J. Mayrhofer,
UTC Power, South Windsor, CT United Technologies Research Center, East Hartford, CT
 Supporting Information Electrocatalysis on Platinum Nanoparticles: Particle Size Effect on Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity Minhua Shao,, * Amra Peles,, * Krista Shoemaker UTC Power, South Windsor, CT
Supporting Information Electrocatalysis on Platinum Nanoparticles: Particle Size Effect on Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity Minhua Shao,, * Amra Peles,, * Krista Shoemaker UTC Power, South Windsor, CT
(name) Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant. Final Exam
 10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
10.626 Electrochemical Energy Systems, Spring 2014, M. Z. Bazant Final Exam Instructions. This is a three-hour closed book exam. You are allowed to have five doublesided pages of personal notes during
CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION
 CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 143 CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 6.1 Introduction Based on the previous three experimental chapters dealing
CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 143 CHAPTER 6. ELECTROCHEMICAL OSCILLATIONS IN METHANOL OXIDATION 6.1 Introduction Based on the previous three experimental chapters dealing
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 SUPPOING INFORMATION Unifying theoretical framework for deciphering the oxygen
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 SUPPOING INFORMATION Unifying theoretical framework for deciphering the oxygen
The Effect of the Voltage Scan Rate on the Determination of the Oxygen Reduction Activity of Pt/C Fuel Cell Catalyst
 DOI 10.1007/s12678-015-0255-0 LETTER The Effect of the Voltage Scan Rate on the Determination of the Oxygen Reduction Activity of Pt/C Fuel Cell Catalyst Nejc Hodnik 1 & Claudio Baldizzone 1 & Serhiy Cherevko
DOI 10.1007/s12678-015-0255-0 LETTER The Effect of the Voltage Scan Rate on the Determination of the Oxygen Reduction Activity of Pt/C Fuel Cell Catalyst Nejc Hodnik 1 & Claudio Baldizzone 1 & Serhiy Cherevko
Supporting information. Stability Issues in Pd-based Catalysts: The Role of Surface Pt in Improving the Stability
 Supporting information Stability Issues in Pd-based Catalysts: The Role of Surface Pt in Improving the Stability and Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) Activity R. K. Singh, R. Rahul, M. Neergat 1 Department
Supporting information Stability Issues in Pd-based Catalysts: The Role of Surface Pt in Improving the Stability and Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) Activity R. K. Singh, R. Rahul, M. Neergat 1 Department
In a typical routine, the pristine CNT (purchased from Bill Nanotechnology, Inc.) were
 Supplementary Information Pd induced Pt(Ⅳ) reduction to form Pd@Pt/CNT core-shell catalyst for a more complete oxygen reduction Preparation of SH- functionalized CNT In a typical routine, the pristine
Supplementary Information Pd induced Pt(Ⅳ) reduction to form Pd@Pt/CNT core-shell catalyst for a more complete oxygen reduction Preparation of SH- functionalized CNT In a typical routine, the pristine
Supporting Information. The Study of Multireactional Electrochemical Interfaces Via a Tip Generation/Substrate
 Supporting Information The Study of Multireactional Electrochemical Interfaces Via a Tip Generation/Substrate Collection Mode of Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction for
Supporting Information The Study of Multireactional Electrochemical Interfaces Via a Tip Generation/Substrate Collection Mode of Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction for
Supplementary Information. Unusual High Oxygen Reduction Performance in All-Carbon Electrocatalysts
 Supplementary Information Unusual High Oxygen Reduction Performance in All-Carbon Electrocatalysts Wei Wei 1, 4,, Ying Tao 1, 4,, Wei Lv 2,, Fang-Yuan Su 2, Lei Ke 2, Jia Li 2, Da-Wei Wang 3, *, Baohua
Supplementary Information Unusual High Oxygen Reduction Performance in All-Carbon Electrocatalysts Wei Wei 1, 4,, Ying Tao 1, 4,, Wei Lv 2,, Fang-Yuan Su 2, Lei Ke 2, Jia Li 2, Da-Wei Wang 3, *, Baohua
Electronic supplementary information. Amorphous carbon supported MoS 2 nanosheets as effective catalyst for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information Amorphous carbon supported MoS 2 nanosheets as effective
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic supplementary information Amorphous carbon supported MoS 2 nanosheets as effective
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 217 Supporting Information Catalyst preparation A certain of aqueous NiCl 2 6H 2 O (2 mm), H 2 PtCl
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 217 Supporting Information Catalyst preparation A certain of aqueous NiCl 2 6H 2 O (2 mm), H 2 PtCl
Title: Electrochemical studies for oxygen reduction reaction using Zn 1-x Co x O for fuel cell applications.
 Title: Electrochemical studies for oxygen reduction reaction using Zn 1-x Co x O for fuel cell applications. Authors: Alonso-Sevilla, Suheily; Martínez-Torres, Dinorah; Estrada-Álvarez, Ana G.; Sánchez-Zalduondo,
Title: Electrochemical studies for oxygen reduction reaction using Zn 1-x Co x O for fuel cell applications. Authors: Alonso-Sevilla, Suheily; Martínez-Torres, Dinorah; Estrada-Álvarez, Ana G.; Sánchez-Zalduondo,
Correlating Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Activity in Alkaline Electrolyte to Hydrogen Binding Energy on Monometallic Surfaces
 Supplemental Materials for Correlating Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Activity in Alkaline Electrolyte to Hydrogen Binding Energy on Monometallic Surfaces Wenchao Sheng, a MyatNoeZin Myint, a Jingguang G.
Supplemental Materials for Correlating Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Activity in Alkaline Electrolyte to Hydrogen Binding Energy on Monometallic Surfaces Wenchao Sheng, a MyatNoeZin Myint, a Jingguang G.
Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous carbon derived from human hair as. highly efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped porous
Effect of ordering of PtCu 3 nanoparticle structure on the activity and stability for the oxygen reduction reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Effect of ordering of PtCu 3 nanoparticle structure on the activity and stability
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2014 Effect of ordering of PtCu 3 nanoparticle structure on the activity and stability
This paper reports a very well executed insitu study of core shell nanoparticles of Pt and Pd that are used for ORR.
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This paper reports a very well executed insitu study of core shell nanoparticles of Pt and Pd that are used for ORR. these experiments are not
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This paper reports a very well executed insitu study of core shell nanoparticles of Pt and Pd that are used for ORR. these experiments are not
High-Flux CO Reduction Enabled by Three-Dimensional Nanostructured. Copper Electrodes
 Supporting Information High-Flux CO Reduction Enabled by Three-Dimensional Nanostructured Copper Electrodes Yuxuan Wang, David Raciti, Chao Wang * Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Johns
Supporting Information High-Flux CO Reduction Enabled by Three-Dimensional Nanostructured Copper Electrodes Yuxuan Wang, David Raciti, Chao Wang * Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Johns
Highly efficient hydrogen evolution of platinum via tuning the interfacial dissolved-gas concentration
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Highly efficient hydrogen evolution of platinum via tuning
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information for Highly efficient hydrogen evolution of platinum via tuning
Electronic Supplementary Material. Methods. Synthesis of reference samples in Figure 1(b) Nano Res.
 Electronic Supplementary Material Shaped Pt Ni nanocrystals with an ultrathin Pt-enriched shell derived from one-pot hydrothermal synthesis as active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction Jun Gu 1,, Guangxu
Electronic Supplementary Material Shaped Pt Ni nanocrystals with an ultrathin Pt-enriched shell derived from one-pot hydrothermal synthesis as active electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction Jun Gu 1,, Guangxu
Nickel Sulfides Freestanding Holey Films as Air-Breathing Electrodes for. Flexible Zn-Air Batteries
 Nickel Sulfides Freestanding Holey Films as Air-Breathing Electrodes for Flexible Zn-Air Batteries Kyle Marcus, 1,# Kun Liang, 1,# Wenhan Niu, 1,# Yang Yang 1,* 1 NanoScience Technology Center, Department
Nickel Sulfides Freestanding Holey Films as Air-Breathing Electrodes for Flexible Zn-Air Batteries Kyle Marcus, 1,# Kun Liang, 1,# Wenhan Niu, 1,# Yang Yang 1,* 1 NanoScience Technology Center, Department
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tuning the Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity and Stability of Shaped-Controlled Pt-Ni Nanoparticles by Thermal Annealing Elucidating the Surface Atomic Structural
Supporting Information Tuning the Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity and Stability of Shaped-Controlled Pt-Ni Nanoparticles by Thermal Annealing Elucidating the Surface Atomic Structural
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Oxygen Reduction on Graphene-Carbon Nanotube Composites Doped Sequentially with Nitrogen and Sulfur Drew C. Higgins, Md Ariful Hoque, Fathy Hassan, Ja-Yeon Choi, Baejung Kim, Zhongwei
Supporting Information Oxygen Reduction on Graphene-Carbon Nanotube Composites Doped Sequentially with Nitrogen and Sulfur Drew C. Higgins, Md Ariful Hoque, Fathy Hassan, Ja-Yeon Choi, Baejung Kim, Zhongwei
Three-dimensionally co-stabilized metal catalysts towards. oxygen reduction reaction
 Three-dimensionally co-stabilized metal catalysts towards oxygen reduction reaction Kun Cheng, Min Jiang, Bei Ye, Ibrahim Saana Amiinu, Xiaobo Liu, Zongkui Kou, Wenqiang Li and Shichun Mu* State Key Laboratory
Three-dimensionally co-stabilized metal catalysts towards oxygen reduction reaction Kun Cheng, Min Jiang, Bei Ye, Ibrahim Saana Amiinu, Xiaobo Liu, Zongkui Kou, Wenqiang Li and Shichun Mu* State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information for Active Pt 3 Ni (111) Surface of Pt 3 Ni Icosahedron for Oxygen Reduction
 Supporting Information for Active Pt 3 Ni (111) Surface of Pt 3 Ni Icosahedron for Oxygen Reduction Jianbing Zhu,, Meiling Xiao,, Kui Li,, Changpeng Liu, Xiao Zhao*,& and Wei Xing*,, State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information for Active Pt 3 Ni (111) Surface of Pt 3 Ni Icosahedron for Oxygen Reduction Jianbing Zhu,, Meiling Xiao,, Kui Li,, Changpeng Liu, Xiao Zhao*,& and Wei Xing*,, State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Adding refractory 5d transition metal W into PtCo
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Adding refractory 5d transition metal W into PtCo
Department of Chemical, Materials and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Connecticut, 191
 High Stability, High Activity Pt/ITO Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts Ying Liu and William E. Mustain* Department of Chemical, Materials and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Connecticut, 191 Auditorium
High Stability, High Activity Pt/ITO Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts Ying Liu and William E. Mustain* Department of Chemical, Materials and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Connecticut, 191 Auditorium
An extraordinarily stable catalyst: Pt NPs supported on two-dimensional Ti 3 C 2 X 2 (X=OH, F) nanosheets for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
 An extraordinarily stable catalyst: Pt NPs supported on two-dimensional Ti 3 X 2 (X=OH, F) nanosheets for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Xiaohong Xie, Siguo Chen*, Wei Ding, Yao Nie, and Zidong Wei* Experimental
An extraordinarily stable catalyst: Pt NPs supported on two-dimensional Ti 3 X 2 (X=OH, F) nanosheets for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Xiaohong Xie, Siguo Chen*, Wei Ding, Yao Nie, and Zidong Wei* Experimental
Supplementary Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 014 Supplementary Information for High Resolution Mapping of Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 014 Supplementary Information for High Resolution Mapping of Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Supplementary Figure S1: Particle size distributions of the Pt ML /Pd 9 Au 1 /C
 a 2 15 before cycle test mean particle size: 3.8 ± 1.2 nm b 2 15 after.6v - 1.V 1k cycle test mean particle size: 4.1 ± 1.5 nm Number 1 total number: 558 Number 1 total number: 554 5 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
a 2 15 before cycle test mean particle size: 3.8 ± 1.2 nm b 2 15 after.6v - 1.V 1k cycle test mean particle size: 4.1 ± 1.5 nm Number 1 total number: 558 Number 1 total number: 554 5 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Electrochemical Water Splitting by Layered and 3D Cross-linked Manganese Oxides: Correlating Structural Motifs and Catalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Information Electrochemical Water Splitting by Layered and 3D Cross-linked Manganese Oxides: Correlating Structural Motifs and Catalytic Activity Arno Bergmann,* a Ivelina Zaharieva,*
Electronic Supplementary Information Electrochemical Water Splitting by Layered and 3D Cross-linked Manganese Oxides: Correlating Structural Motifs and Catalytic Activity Arno Bergmann,* a Ivelina Zaharieva,*
Formic acid electro-synthesis from carbon dioxide in a room temperature ionic liquid
 Supporting Information: Formic acid electro-synthesis from carbon dioxide in a room temperature ionic liquid Benjamin C. M. Martindale and Richard G. Compton a * Department of Chemistry, Physical and Theoretical
Supporting Information: Formic acid electro-synthesis from carbon dioxide in a room temperature ionic liquid Benjamin C. M. Martindale and Richard G. Compton a * Department of Chemistry, Physical and Theoretical
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Thiocyanate Anchors for Salt-like Iron(II) Complexes on Au(111): Promises and Caveats Philipp Stock, a,b Andreas Erbe, b Gerald Hörner, a Manfred Buck, c Hervé Ménard, d and Andreas
Supporting Information Thiocyanate Anchors for Salt-like Iron(II) Complexes on Au(111): Promises and Caveats Philipp Stock, a,b Andreas Erbe, b Gerald Hörner, a Manfred Buck, c Hervé Ménard, d and Andreas
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Nano-engineered Ir core /Pt shell Nanoparticles with Controlled Pt Shell Coverages for Direct Methanol Electro-oxidation Ehab N. El Sawy a,b and Viola I. Birss a,* a Department of
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Nano-engineered Ir core /Pt shell Nanoparticles with Controlled Pt Shell Coverages for Direct Methanol Electro-oxidation Ehab N. El Sawy a,b and Viola I. Birss a,* a Department of
Principles and Applications of Electrochemistry
 Principles and Applications of Electrochemistry Fourth edition D. R. CROW Professor of Electrochemistry and Dean of Research University of Wolverhampton BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman
Principles and Applications of Electrochemistry Fourth edition D. R. CROW Professor of Electrochemistry and Dean of Research University of Wolverhampton BLACKIE ACADEMIC & PROFESSIONAL An Imprint of Chapman
Electronic Supplementary Information:
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information: Platinum-Nickel Nanowire Catalysts
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information: Platinum-Nickel Nanowire Catalysts
The Effect of Platinum Loading and Surface Morphology on Oxygen Reduction Activity
 Electrocatalysis (2016) 7:287 296 DOI 10.1007/s12678-016-0304-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Effect of Platinum Loading and Surface Morphology on Oxygen Reduction Activity S. Taylor 1 & E. Fabbri 2 & P. Levecque
Electrocatalysis (2016) 7:287 296 DOI 10.1007/s12678-016-0304-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Effect of Platinum Loading and Surface Morphology on Oxygen Reduction Activity S. Taylor 1 & E. Fabbri 2 & P. Levecque
Supporting Information. Oxygen reduction and methanol oxidation behaviour of SiC based Pt. nanocatalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
 Supporting Information Oxygen reduction and methanol oxidation behaviour of SiC based Pt nanocatalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells Rajnish Dhiman a *, Serban N. Stamatin a, Shuang M. Andersen
Supporting Information Oxygen reduction and methanol oxidation behaviour of SiC based Pt nanocatalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells Rajnish Dhiman a *, Serban N. Stamatin a, Shuang M. Andersen
Supplementary Figure 1. HRTEM images of PtNi / Ni-B composite exposed to electron beam. The. scale bars are 5 nm.
 Supplementary Figure 1. HRTEM images of PtNi / Ni-B composite exposed to electron beam. The scale bars are 5 nm. S1 Supplementary Figure 2. TEM image of PtNi/Ni-B composite obtained under N 2 protection.
Supplementary Figure 1. HRTEM images of PtNi / Ni-B composite exposed to electron beam. The scale bars are 5 nm. S1 Supplementary Figure 2. TEM image of PtNi/Ni-B composite obtained under N 2 protection.
Time (s)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Ozone: an effective tool for simultaneous activation and dealloying
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Ozone: an effective tool for simultaneous activation and dealloying
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Electrocatalytic Performance for Oxygen Reduction via Active Interfaces of Layer-By-Layered Titanium Nitride / Titanium Carbonitride Structures Zhaoyu Jin, 1 Panpan Li,
Supporting Information Enhanced Electrocatalytic Performance for Oxygen Reduction via Active Interfaces of Layer-By-Layered Titanium Nitride / Titanium Carbonitride Structures Zhaoyu Jin, 1 Panpan Li,
Computational Materials Design and Discovery Energy and Electronic Applications Synthesis Structure Properties
 Computational Materials Design and Discovery Energy and Electronic Applications Synthesis Structure Properties Supercapacitors Rechargeable batteries Supercomputer Photocatalysts Fuel cell catalysts First
Computational Materials Design and Discovery Energy and Electronic Applications Synthesis Structure Properties Supercapacitors Rechargeable batteries Supercomputer Photocatalysts Fuel cell catalysts First
V. Electrostatics. MIT Student
 V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
V. Electrostatics Lecture 26: Compact Part of the Double Layer MIT Student 1 Double-layer Capacitance 1.1 Stern Layer As was discussed in the previous lecture, the Gouy-Chapman model predicts unphysically
Supporting Information for. Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen. reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with.
 Supporting Information for Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with silica Sakae Takenaka 1 *, Naoto Susuki 1, Hiroaki Miyamoto 1, Eishi
Supporting Information for Highly durable Pd metal catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells; Coverage of Pd metal with silica Sakae Takenaka 1 *, Naoto Susuki 1, Hiroaki Miyamoto 1, Eishi
Scanning Flow Cell SFC SFC-OLEMS Summary CO2 reduction on Cu-Co thin films Summary
 Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Product Distribution Screening on Cu-Co Thin Film Composition Spread Samples by Coupling of a Scanning Flow Cell to OLEMS Department of Interface Chemistry and Surface Engineering
Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Product Distribution Screening on Cu-Co Thin Film Composition Spread Samples by Coupling of a Scanning Flow Cell to OLEMS Department of Interface Chemistry and Surface Engineering
Simple synthesis of urchin-like Pt-Ni bimetallic nanostructures as enhanced electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Simple synthesis of urchin-like Pt- bimetallic nanostructures
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Simple synthesis of urchin-like Pt- bimetallic nanostructures
Tunable nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels as sustainable electrocatalysts in the oxygen. reduction reaction Electronic Supplementary information (ESI)
 Tunable nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels as sustainable electrocatalysts in the oxygen reduction reaction Electronic Supplementary information (ESI) Stephanie-Angelika Wohlgemuth,* a Tim-Patrick Fellinger
Tunable nitrogen-doped carbon aerogels as sustainable electrocatalysts in the oxygen reduction reaction Electronic Supplementary information (ESI) Stephanie-Angelika Wohlgemuth,* a Tim-Patrick Fellinger
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Poly(ionic liquid) Binders as Ion conductors and Polymer
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Sustainable Energy & Fuels. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Poly(ionic liquid) Binders as Ion conductors and Polymer
Potential Modulated Spectroscopy in Electrochemical Systems
 Potential Modulated Spectroscopy in Electrochemical Systems David J. Fermín Action D36 www.chm.bris.ac.uk/pt/electrochemistry Overview Combining potential modulation and spectroscopy? Electroreflectance
Potential Modulated Spectroscopy in Electrochemical Systems David J. Fermín Action D36 www.chm.bris.ac.uk/pt/electrochemistry Overview Combining potential modulation and spectroscopy? Electroreflectance
Electrophoretic Deposition. - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode
 Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
Electrophoretic Deposition - process in which particles, suspended in a liquid medium, migrate in an electric field and deposit on an electrode no redox differs from electrolytic in several ways deposit
Cation-Hydroxide-Water Co-Adsorption Inhibits the. Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction
 Supporting Information Cation-Hydroxide-Water Co-Adsorption Inhibits the Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction Hoon Taek Chung [a], Ulises Martinez [a], Ivana Matanovic [b,c] and Yu Seung Kim* [a]. [a]
Supporting Information Cation-Hydroxide-Water Co-Adsorption Inhibits the Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction Hoon Taek Chung [a], Ulises Martinez [a], Ivana Matanovic [b,c] and Yu Seung Kim* [a]. [a]
Effect of Chloride Anions on the Synthesis and. Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanocoral
 Supporting Information Effect of Chloride Anions on the Synthesis and Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanocoral Electrodes for CO 2 Electroreduction Polyansky* Yu-Chi Hsieh, Sanjaya D. Senanayake,
Supporting Information Effect of Chloride Anions on the Synthesis and Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Silver Nanocoral Electrodes for CO 2 Electroreduction Polyansky* Yu-Chi Hsieh, Sanjaya D. Senanayake,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Nanoporous Metal/Ionic Liquid Composite Electrocatalysts Supplemental Information 1. Materials and Methods NiPt alloys were made by co-melting Ni
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Nanoporous Metal/Ionic Liquid Composite Electrocatalysts Supplemental Information 1. Materials and Methods NiPt alloys were made by co-melting Ni
A doping of phosphorus and/or sulfur into nitrogen-doped carbon for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in acid media
 Supporting Information A doping of phosphorus and/or sulfur into nitrogen-doped carbon for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in acid media Chang Hyuck Choi, a Min Wook Chung, b Sung Hyeon Park, a and
Supporting Information A doping of phosphorus and/or sulfur into nitrogen-doped carbon for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in acid media Chang Hyuck Choi, a Min Wook Chung, b Sung Hyeon Park, a and
Supplementary Figure 1 Morpholigical properties of TiO 2-x SCs. The statistical particle size distribution (a) of the defective {001}-TiO 2-x SCs and
 Supplementary Figure 1 Morpholigical properties of TiO 2-x s. The statistical particle size distribution (a) of the defective {1}-TiO 2-x s and their typical TEM images (b, c). Quantity Adsorbed (cm 3
Supplementary Figure 1 Morpholigical properties of TiO 2-x s. The statistical particle size distribution (a) of the defective {1}-TiO 2-x s and their typical TEM images (b, c). Quantity Adsorbed (cm 3
Supplementary Figure 1. TEM analysis of Co0.5 showing (a) a SAED pattern, and (b-f) bright-field images of the microstructure. Only two broad rings
 Supplementary Figure 1. TEM analysis of Co0.5 showing (a) a SAED pattern, and (bf) brightfield images of the microstructure. Only two broad rings were observed in the SAED pattern, as expected for amorphous
Supplementary Figure 1. TEM analysis of Co0.5 showing (a) a SAED pattern, and (bf) brightfield images of the microstructure. Only two broad rings were observed in the SAED pattern, as expected for amorphous
e - Galvanic Cell 1. Voltage Sources 1.1 Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell
 Galvanic cells convert different forms of energy (chemical fuel, sunlight, mechanical pressure, etc.) into electrical energy and heat. In this lecture, we are interested in some examples of galvanic cells.
Galvanic cells convert different forms of energy (chemical fuel, sunlight, mechanical pressure, etc.) into electrical energy and heat. In this lecture, we are interested in some examples of galvanic cells.
Monolithic Cells for Solar Fuels
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Society Reviews. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Monolithic Cells for Solar Fuels Jan Rongé, Tom Bosserez, David Martel, Carlo Nervi,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Society Reviews. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Monolithic Cells for Solar Fuels Jan Rongé, Tom Bosserez, David Martel, Carlo Nervi,
Effect of Ball Milling on Electrocatalytic Activity of Ba 0.5 Sr 0.5 Co 0.8 Fe 0.2 O 3 toward Oxygen Evolution Reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Scientific Report. Concerning the implementation of the project: January December 2014
 E / V (Ag/AgCl) Scientific Report Concerning the implementation of the project: January December 2014 During this period the research work was mainly directed towards two distinct objectives: evidencing
E / V (Ag/AgCl) Scientific Report Concerning the implementation of the project: January December 2014 During this period the research work was mainly directed towards two distinct objectives: evidencing
Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY. Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization.
 Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY T.Y.B.Sc Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization. Ans. The phenomenon of reverse e.m.f. brought about by the presence of product of electrolysis
Topic: APPLIED ELECTROCHEMISTRY T.Y.B.Sc Q.1 What is polarization? Explain the various type of polarization. Ans. The phenomenon of reverse e.m.f. brought about by the presence of product of electrolysis
Supporting Information. Electropolymerization of aniline on nickel-based electrocatalysts substantially
 Supporting Information Electropolymerization of aniline on nickel-based electrocatalysts substantially enhances their performance for hydrogen evolution Fuzhan Song, Wei Li, Guanqun Han, and Yujie Sun*
Supporting Information Electropolymerization of aniline on nickel-based electrocatalysts substantially enhances their performance for hydrogen evolution Fuzhan Song, Wei Li, Guanqun Han, and Yujie Sun*
Catalytic Pt-on-Au Nanostructures: Why Pt Becomes More Active on Smaller Au Particles
 Supporting Information Catalytic Pt-on-Au Nanostructures: Why Pt Becomes More Active on Smaller Au Particles Gui-Rong Zhang, Dan Zhao, Yuan-Yuan Feng, Bingsen Zhang, Dang Sheng Su, Gang Liu, Bo-Qing Xu
Supporting Information Catalytic Pt-on-Au Nanostructures: Why Pt Becomes More Active on Smaller Au Particles Gui-Rong Zhang, Dan Zhao, Yuan-Yuan Feng, Bingsen Zhang, Dang Sheng Su, Gang Liu, Bo-Qing Xu
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces
 Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Lecture 3 Charged interfaces rigin of Surface Charge Immersion of some materials in an electrolyte solution. Two mechanisms can operate. (1) Dissociation of surface sites. H H H H H M M M +H () Adsorption
Supplementary Figure 1 SEM image for the bulk LCO.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEM image for the bulk LCO. S1 Supplementary Figure 2 TEM and HRTEM images of LCO nanoparticles. (a)-(c) TEM, HRTEM images, and SAED pattern for the 60 nm LCO, respectively. (d)-(f)
Supplementary Figure 1 SEM image for the bulk LCO. S1 Supplementary Figure 2 TEM and HRTEM images of LCO nanoparticles. (a)-(c) TEM, HRTEM images, and SAED pattern for the 60 nm LCO, respectively. (d)-(f)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Efficient hydrogen evolution catalysis using ternary pyrite-type cobalt phosphosulphide Miguel Cabán-Acevedo 1, Michael L. Stone 1, J. R. Schmidt 1, Joseph G. Thomas 1, Qi Ding 1, Hung- Chih Chang 2, Meng-Lin
Efficient hydrogen evolution catalysis using ternary pyrite-type cobalt phosphosulphide Miguel Cabán-Acevedo 1, Michael L. Stone 1, J. R. Schmidt 1, Joseph G. Thomas 1, Qi Ding 1, Hung- Chih Chang 2, Meng-Lin
Jaemin Kim, Xi Yin, Kai-Chieh Tsao, Shaohua Fang and Hong Yang *
 Jaemin Kim, Xi Yin, Kai-Chieh Tsao, Shaohua Fang and Hong Yang * Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 114 Roger Adams Laboratory, MC-712, 600
Jaemin Kim, Xi Yin, Kai-Chieh Tsao, Shaohua Fang and Hong Yang * Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 114 Roger Adams Laboratory, MC-712, 600
Supplementary Figure 1 Morphology and composition of the original carbon nanotube (CNT) sample. (a, b) TEM images of CNT; (c) EDS of CNT.
 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Morphology and composition of the original carbon nanotube (CNT sample. (a, b TEM images of CNT; (c EDS of CNT. Cobalt is not detected in the original CNT sample (Note: The accidentally
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Morphology and composition of the original carbon nanotube (CNT sample. (a, b TEM images of CNT; (c EDS of CNT. Cobalt is not detected in the original CNT sample (Note: The accidentally
Simulating the Electrical Double Layer Guigen Zhang, Ph.D.
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference Boston Simulating the Electrical Double Layer Guigen Zhang, Ph.D. Dept. of Bioengineering, Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Institute for Biological Interfaces
Presented at the COMSOL Conference Boston Simulating the Electrical Double Layer Guigen Zhang, Ph.D. Dept. of Bioengineering, Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Institute for Biological Interfaces
Supplementary Figure 1 XPS, Raman and TGA characterizations on GO and freeze-dried HGF and GF. (a) XPS survey spectra and (b) C1s spectra.
 Supplementary Figure 1 XPS, Raman and TGA characterizations on GO and freeze-dried HGF and GF. (a) XPS survey spectra and (b) C1s spectra. (c) Raman spectra. (d) TGA curves. All results confirm efficient
Supplementary Figure 1 XPS, Raman and TGA characterizations on GO and freeze-dried HGF and GF. (a) XPS survey spectra and (b) C1s spectra. (c) Raman spectra. (d) TGA curves. All results confirm efficient
Electronic supplementary information for Chemical Communications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information for Chemical Communications Synthesis of hierarchical Pd 4
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information for Chemical Communications Synthesis of hierarchical Pd 4
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information What do Laser Induced Transient Techniques Reveal for Batteries? Na- and K-Intercalation from Aqueous Electrolytes as an Example Daniel Scieszka a,b,(1), Jeongsik Yun a,b,(1), Aliaksandr
Supporting Information What do Laser Induced Transient Techniques Reveal for Batteries? Na- and K-Intercalation from Aqueous Electrolytes as an Example Daniel Scieszka a,b,(1), Jeongsik Yun a,b,(1), Aliaksandr
Bistriazole-p-benzoquinone and its alkali salts: electrochemical behaviour in aqueous alkaline solutions
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Bistriazole-p-benzoquinone and its alkali salts: electrochemical behaviour in aqueous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Bistriazole-p-benzoquinone and its alkali salts: electrochemical behaviour in aqueous
Bruno Bastos Sales, Joost Helsen and Arne Verliefde
 FEM modeling of capacitive deionization for complex streams Dennis Cardoen Bruno Bastos Sales, Joost Helsen and Arne Verliefde International Conference on Numerical and Mathematical ing of Flow and Transport
FEM modeling of capacitive deionization for complex streams Dennis Cardoen Bruno Bastos Sales, Joost Helsen and Arne Verliefde International Conference on Numerical and Mathematical ing of Flow and Transport
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION An Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalyst Based on Carbon Nanotube- Nanographene Complexes Yanguang Li, Wu Zhou, Hailiang Wang, Liming Xie, Yongye Liang, Fei Wei, Juan-Carlos Idrobo,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION An Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalyst Based on Carbon Nanotube- Nanographene Complexes Yanguang Li, Wu Zhou, Hailiang Wang, Liming Xie, Yongye Liang, Fei Wei, Juan-Carlos Idrobo,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Phosphorus-Doped CoS 2 Nanosheet Arrays as
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Phosphorus-Doped CoS 2 Nanosheet Arrays as
Water dissociation on well-defined platinum surfaces: the electrochemical perspective
 I didn t fail the test, I just found 100 ways to do it wrong. 11 Benjamin Franklin (1706 1790) Water dissociation on well-defined platinum surfaces: the electrochemical perspective Abstract We discuss
I didn t fail the test, I just found 100 ways to do it wrong. 11 Benjamin Franklin (1706 1790) Water dissociation on well-defined platinum surfaces: the electrochemical perspective Abstract We discuss
Goals. The laboratory instructor has already purged the solutions of dissolved. Purging the from these solutions prevents spurious
 Goals 41 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
Goals 41 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
Control of nanoparticle aggregation in PEMFCs using surfactants
 Control of nanoparticle aggregation in PEMFCs using surfactants... Jill E. Newton *, Jon A. Preece and Bruno G. Pollet Centre for Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Research, School of Chemical Engineering, University
Control of nanoparticle aggregation in PEMFCs using surfactants... Jill E. Newton *, Jon A. Preece and Bruno G. Pollet Centre for Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Research, School of Chemical Engineering, University
Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells
 Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Supplementary Information Facile and Gram-scale Synthesis of Metal-free Catalysts: Toward Realistic Applications for Fuel Cells Ok-Hee Kim 1, Yong-Hun Cho 2, Dong Young Chung 3,4, Minjeong Kim 3,4, Ji
Electrochemical Modification of Pt/C Catalyst by Silicomolybdic Acid
 ACTA PHYSICO-CHIMICA SINICA Volume 22, Issue 4, April 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2006, 22(4), 419 423. RESEARCH PAPER Electrochemical
ACTA PHYSICO-CHIMICA SINICA Volume 22, Issue 4, April 2006 Online English edition of the Chinese language journal Cite this article as: Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2006, 22(4), 419 423. RESEARCH PAPER Electrochemical
Sieving Behaviour of Nanoscopic Pores by. Hydrated Ions
 Sieving Behaviour of Nanoscopic Pores by Hydrated Ions Joohan Lee a and Juhyoun Kwak* a Department of Chemistry, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), 373-1 Guseong-dong, Yuseong-gu,
Sieving Behaviour of Nanoscopic Pores by Hydrated Ions Joohan Lee a and Juhyoun Kwak* a Department of Chemistry, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), 373-1 Guseong-dong, Yuseong-gu,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of immobilized cobalt protoporphyrin electrode. The cyclic voltammogram of: (a) pyrolytic graphite
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of immobilized cobalt protoporphyrin electrode. The cyclic voltammogram of: (a) pyrolytic graphite electrode; (b) pyrolytic graphite electrode with 100 µl 0.5 mm
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of immobilized cobalt protoporphyrin electrode. The cyclic voltammogram of: (a) pyrolytic graphite electrode; (b) pyrolytic graphite electrode with 100 µl 0.5 mm
Division of Physics and Semiconductor Science, Dongguk University, Seoul 04620, South Korea
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary information for Self-assembled Two-dimensional Copper Oxide
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary information for Self-assembled Two-dimensional Copper Oxide
Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts
 Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts Raja Swaidan The Cooper Union Advisor: Dr. Branko N. Popov Electrochemical Engineering 26 July 2007 Overview of Research Studied
Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide In ORR Over Low Loadings of Pt/C Catalysts Raja Swaidan The Cooper Union Advisor: Dr. Branko N. Popov Electrochemical Engineering 26 July 2007 Overview of Research Studied
Basic Concepts in Electrochemistry
 Basic Concepts in Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemical Cell Electrons Current + - Voltage Source ANODE Current CATHODE 2 Fuel Cell Electrons (2 e) Current - + Electrical Load ANODE Current CATHODE H 2 2H
Basic Concepts in Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemical Cell Electrons Current + - Voltage Source ANODE Current CATHODE 2 Fuel Cell Electrons (2 e) Current - + Electrical Load ANODE Current CATHODE H 2 2H
Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example)
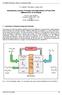 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil -4 December 00 3 rd LAMNET Workshop Brazil 00 Introductory Lecture: Principle and Applications of Fuel Cells (Methanol/Air as Example) Prof. Dr. Wolf Vielstich University of
Carbon Quantum Dots/NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide. Composite as High Efficient Electrocatalyst for Water
 Supplementary Information Carbon Quantum Dots/NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Composite as High Efficient Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation Di Tang, Juan Liu, Xuanyu Wu, Ruihua Liu, Xiao Han, Yuzhi Han,
Supplementary Information Carbon Quantum Dots/NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Composite as High Efficient Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation Di Tang, Juan Liu, Xuanyu Wu, Ruihua Liu, Xiao Han, Yuzhi Han,
Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of Ultrathin Platinum Nanoplates for Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of Ultrathin Platinum Nanoplates for Enhanced
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of Ultrathin Platinum Nanoplates for Enhanced
Solution Purging. Goals. 1. Purge both solutions with an inert gas (preferably N 2
 Goals 43 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
Goals 43 Cyclic Voltammetry XXGoals The goals of this experiment are to: Learn how to set up a screen-printed electrode Learn how to operate the Gamry potentiostat Determine the redox potential of potassium
Determination of Electron Transfer Number for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: from Theory to Experiment
 Supporting Information Determination of Electron Transfer Number for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: from Theory to Experiment Ruifeng Zhou 1, 2, Yao Zheng 1, Mietek Jaroniec 3 and Shi-Zhang Qiao 1, * 1 School
Supporting Information Determination of Electron Transfer Number for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: from Theory to Experiment Ruifeng Zhou 1, 2, Yao Zheng 1, Mietek Jaroniec 3 and Shi-Zhang Qiao 1, * 1 School
and constant current operations in capacitive deionization
 Energy consumption analysis of constant voltage and constant current operations in capacitive deionization Supporting information Yatian Qu, a,b Patrick G. Campbell, b Lei Gu, c Jennifer M. Knipe, b Ella
Energy consumption analysis of constant voltage and constant current operations in capacitive deionization Supporting information Yatian Qu, a,b Patrick G. Campbell, b Lei Gu, c Jennifer M. Knipe, b Ella
Oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyzed on a Fenton-treated gold surface. P. Esakki Karthik, C. Jeyabharathi and K. L. N.
 Oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyzed on a Fenton-treated gold surface P. Esakki Karthik, C. Jeyabharathi and K. L. N. Phani* Nanoscale Electrocatalysis & Sensor Research Group Electrodics & Electrocatalysis
Oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyzed on a Fenton-treated gold surface P. Esakki Karthik, C. Jeyabharathi and K. L. N. Phani* Nanoscale Electrocatalysis & Sensor Research Group Electrodics & Electrocatalysis
Supplementary Materials
 Atomic layer-deposited tunnel oxide stabilizes silicon photoanodes for water oxidation Yi Wei Chen 1, Jonathan D. Prange 2, Simon Dühnen 2, Yohan Park 1, Marika Gunji 1, Christopher E. D. Chidsey 2, and
Atomic layer-deposited tunnel oxide stabilizes silicon photoanodes for water oxidation Yi Wei Chen 1, Jonathan D. Prange 2, Simon Dühnen 2, Yohan Park 1, Marika Gunji 1, Christopher E. D. Chidsey 2, and
Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Kinetics for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction of Hangman Porphyrins
 Electronic Supplementary Information Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Kinetics for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction of Hangman Porphyrins Manolis M. Roubelakis, D. Kwabena Bediako, Dilek K. Dogutan and
Electronic Supplementary Information Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Kinetics for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction of Hangman Porphyrins Manolis M. Roubelakis, D. Kwabena Bediako, Dilek K. Dogutan and
